
园艺学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (11): 2453-2465.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0965
潘纪源1,*, 董庆龙2,*, 温海彬1, 刘亚南1, 王晓洁1, 张雪梅2, 刘文菊3, 陆秀君1,**( )
)
收稿日期:2023-05-16
修回日期:2023-08-22
出版日期:2023-11-25
发布日期:2023-11-28
通讯作者:
作者简介:* 共同第一作者
基金资助:
PAN Jiyuan1,*, DONG Qinglong2,*, WEN Haibin1, LIU Yanan1, WANG Xiaojie1, ZHANG Xuemei2, LIU Wenju3, LU Xiujun1,**( )
)
Received:2023-05-16
Revised:2023-08-22
Published:2023-11-25
Online:2023-11-28
Contact:
摘要:
以树龄16年‘红富士’苹果(Malus × domestica)为试材,研究巨大芽孢杆菌(Bacillus megaterium)菌剂处理对新梢生长、果实产量和品质以及土壤微生物数量、微生物群落结构和土壤养分的影响。结果表明,与对照相比,2021、2022连续两年苹果树春季施用巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂,30 d内新梢增长率分别提高了3.45%和17.01%,60 d内新梢增长率分别提高了2.58%和6.71%;产量分别增长了7.17%和7.01%;而对果形指数、硬度、可溶性糖含量、可溶性固形物和维生素C含量等指标均无显著影响。2021年处理组单株果实数量增加4.95%。2022年处理组的果实着色相关指标红绿色度a*低于对照,色度角h高于对照,而2021年无显著差异。施用菌剂后0 ~ 20 cm、20 ~ 40 cm土层真菌数量减少,细菌增加,但随着时间延长,菌剂效果逐渐减弱;真菌和细菌群落的α多样性无显著变化;土壤真菌中短梗蠕孢属(Trichocladium)、产油菌属(Solicoccozyma)、担子菌酵母属(Naganishia)和土赤壳属(Ilyonectria)相对丰度分别是对照的1.87倍、1.92倍、2.91和3.38倍;陶氏菌属(Tausonia)和头束菌属(Cephalotrichum)相对丰度分别是对照的76.44%和67.96%;土壤细菌中链霉菌属(Streptomyces)和芽单胞菌属(Gemmatimonas)相对丰度分别是对照的2.65倍和1.33倍;而朱氏杆菌属(Chujaibacter)的相对丰度是对照的48.88%;处理苹果根际土壤中细菌和真菌OTU数量与对照相比发生显著变化;苹果根系土壤的速效磷、速效钾含量分别比对照高21.87%和20.81%、5.14%和5.31%。综上,春季施用巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂能够抑制土壤有害真菌,改善土壤微生物群落结构和数量,活化土壤磷、钾,促进苹果生长,提高苹果产量。
潘纪源, 董庆龙, 温海彬, 刘亚南, 王晓洁, 张雪梅, 刘文菊, 陆秀君. 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂对苹果产量、品质及土壤微生物的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(11): 2453-2465.
PAN Jiyuan, DONG Qinglong, WEN Haibin, LIU Yanan, WANG Xiaojie, ZHANG Xuemei, LIU Wenju, LU Xiujun. Effects of Bacillus megaterium on Yield,Quality and Soil Microorganism of Apple[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(11): 2453-2465.
| 测序区域 Sequencing region | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 16S V3-V4 | 338F | 5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3′ |
| 806R | 5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′ | |
| ITs1-5F | ITS1F | 5′-CTTGGTCATTTAGAGGAAGTAA-3′ |
| ITS2R | 5′-GCTGCGTTCTTCATCGATGC-3′ |
表1 微生物测序区域与引物
Table 1 Sequencing region and primers of microorganism
| 测序区域 Sequencing region | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 16S V3-V4 | 338F | 5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3′ |
| 806R | 5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′ | |
| ITs1-5F | ITS1F | 5′-CTTGGTCATTTAGAGGAAGTAA-3′ |
| ITS2R | 5′-GCTGCGTTCTTCATCGATGC-3′ |
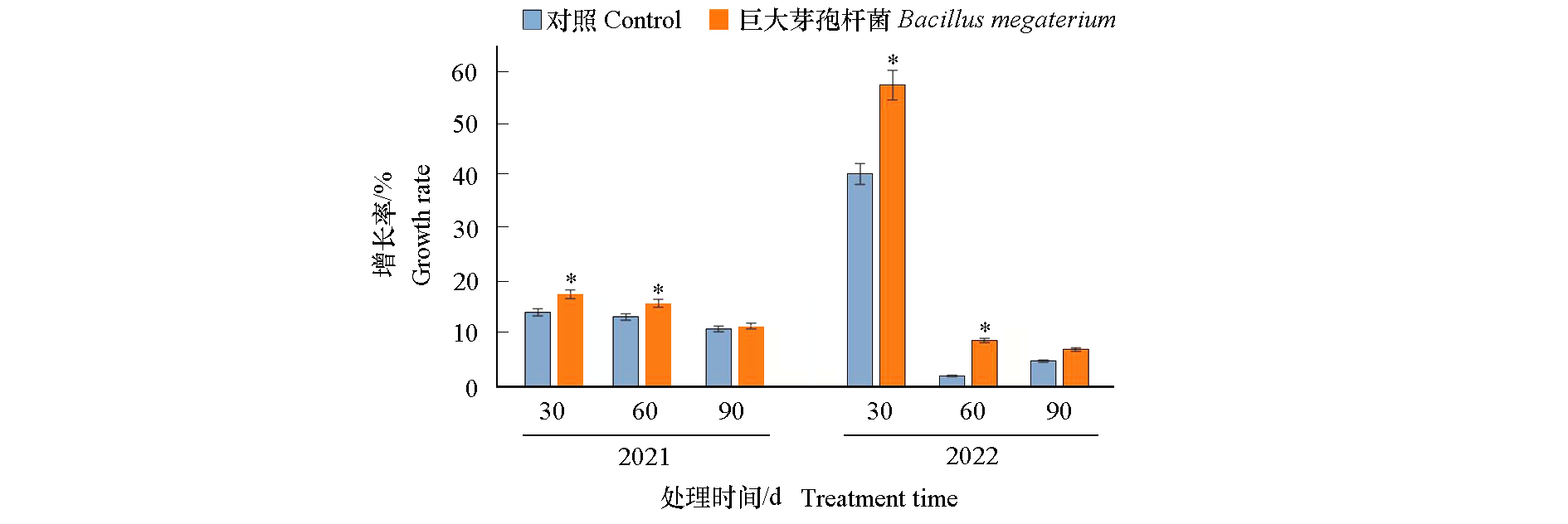
图1 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂对苹果新梢生长的影响 独立样本t检验,*表示在α = 0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 1 Effect of Bacillus megaterium on the growth of new apple shoots t test for independent samples,* correlation is significant at α = 0.05 respectively.
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 单果质量/g Average mass | 单株果实数 Average No. of fruits/piece | 产量/(t · hm-2) Yield | 不同横径果实比例/% Fruiting ratio of different cross-diameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 75 mm | 75 ~ 85 mm | > 85 mm | |||||
| 2021 | 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂 B. megaterium | 222.11 ± 5.58 | 261.67 ± 5.14* | 57.54 ± 2.07* | 23.70 ± 8.40 | 47.78 ± 11.26 | 28.52 ± 12.38 |
| 水Water (对照Control) | 217.52 ± 3.11 | 249.33 ± 3.06 | 53.69 ± 1.14 | 24.15 ± 5.43 | 55.36 ± 11.45 | 20.48 ± 6.11 | |
| 2022 | 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂 B. megaterium | 213.08 ± 5.68 | 300.22 ± 19.68 | 63.33 ± 8.57* | 25.66 ± 8.00* | 67.00 ± 14.00 | 7.34 ± 4.00 |
| 水Water (对照Control) | 210.42 ± 4.04 | 284.11 ± 13.23 | 59.18 ± 6.04 | 43.20 ± 4.63 | 52.19 ± 10.88 | 4.61 ± 4.00 | |
表2 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂对苹果产量的影响
Table 2 Effects of Bacillus megaterium on apple yield
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 单果质量/g Average mass | 单株果实数 Average No. of fruits/piece | 产量/(t · hm-2) Yield | 不同横径果实比例/% Fruiting ratio of different cross-diameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 75 mm | 75 ~ 85 mm | > 85 mm | |||||
| 2021 | 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂 B. megaterium | 222.11 ± 5.58 | 261.67 ± 5.14* | 57.54 ± 2.07* | 23.70 ± 8.40 | 47.78 ± 11.26 | 28.52 ± 12.38 |
| 水Water (对照Control) | 217.52 ± 3.11 | 249.33 ± 3.06 | 53.69 ± 1.14 | 24.15 ± 5.43 | 55.36 ± 11.45 | 20.48 ± 6.11 | |
| 2022 | 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂 B. megaterium | 213.08 ± 5.68 | 300.22 ± 19.68 | 63.33 ± 8.57* | 25.66 ± 8.00* | 67.00 ± 14.00 | 7.34 ± 4.00 |
| 水Water (对照Control) | 210.42 ± 4.04 | 284.11 ± 13.23 | 59.18 ± 6.04 | 43.20 ± 4.63 | 52.19 ± 10.88 | 4.61 ± 4.00 | |
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 果形指数 Fruit shape index | 硬度/(kg · cm-2) Firmness | 可溶性糖/% Soluble sugar | 可溶性固形物/% Soluble solids | 维生素C/(mg · kg-1) Vitamin C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂 B. megaterium | 0.85 ± 0.03 | 7.54 ± 0.53 | 9.85 ± 0.23 | 12.57 ± 0.04 | 2.09 ± 0.10 |
| 水Water (对照Control) | 0.84 ± 0.02 | 7.62 ± 0.77 | 9.35 ± 0.40 | 12.98 ± 0.59 | 2.08 ± 0.17 | |
| 2022 | 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂 B. megaterium | 0.90 ± 0.01 | 7.74 ± 0.44 | 9.56 ± 0.11 | 13.02 ± 0.45 | 2.08 ± 0.09 |
| 水Water (对照Control) | 0.91 ± 0.04 | 7.74 ± 0.16 | 9.28 ± 0.26 | 13.13 ± 0.74 | 2.08 ± 0.10 |
表3 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂对果实品质的影响
Table 3 Effect of Bacillus megaterium on fruit quality of apple
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 果形指数 Fruit shape index | 硬度/(kg · cm-2) Firmness | 可溶性糖/% Soluble sugar | 可溶性固形物/% Soluble solids | 维生素C/(mg · kg-1) Vitamin C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂 B. megaterium | 0.85 ± 0.03 | 7.54 ± 0.53 | 9.85 ± 0.23 | 12.57 ± 0.04 | 2.09 ± 0.10 |
| 水Water (对照Control) | 0.84 ± 0.02 | 7.62 ± 0.77 | 9.35 ± 0.40 | 12.98 ± 0.59 | 2.08 ± 0.17 | |
| 2022 | 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂 B. megaterium | 0.90 ± 0.01 | 7.74 ± 0.44 | 9.56 ± 0.11 | 13.02 ± 0.45 | 2.08 ± 0.09 |
| 水Water (对照Control) | 0.91 ± 0.04 | 7.74 ± 0.16 | 9.28 ± 0.26 | 13.13 ± 0.74 | 2.08 ± 0.10 |
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 明亮度L* Brightness L* | 红绿色度a* Red-green index a* | 黄蓝色度b* Yellow-blue index b* | 色度角h Chroma angle h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂 B. megaterium | 56.44 ± 1.21 | 28.65 ± 0.94 | 25.55 ± 2.05 | 41.46 ± 6.05 |
| 水Water (对照Control) | 56.33 ± 2.34 | 29.59 ± 4.91 | 25.56 ± 1.96 | 39.37 ± 2.94 | |
| 2022 | 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂 B. megaterium | 63.03 ± 5.84 | 26.65 ± 6.20* | 22.05 ± 2.52 | 41.28 ± 9.78* |
| 水Water (对照Control) | 60.38 ± 5.29 | 33.42 ± 7.76 | 20.51 ± 2.59 | 31.87 ± 6.74 |
表4 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂对果实着色的影响
Table 4 Effects of Bacillus megaterium on the coloration of apple fruit
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 明亮度L* Brightness L* | 红绿色度a* Red-green index a* | 黄蓝色度b* Yellow-blue index b* | 色度角h Chroma angle h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂 B. megaterium | 56.44 ± 1.21 | 28.65 ± 0.94 | 25.55 ± 2.05 | 41.46 ± 6.05 |
| 水Water (对照Control) | 56.33 ± 2.34 | 29.59 ± 4.91 | 25.56 ± 1.96 | 39.37 ± 2.94 | |
| 2022 | 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂 B. megaterium | 63.03 ± 5.84 | 26.65 ± 6.20* | 22.05 ± 2.52 | 41.28 ± 9.78* |
| 水Water (对照Control) | 60.38 ± 5.29 | 33.42 ± 7.76 | 20.51 ± 2.59 | 31.87 ± 6.74 |
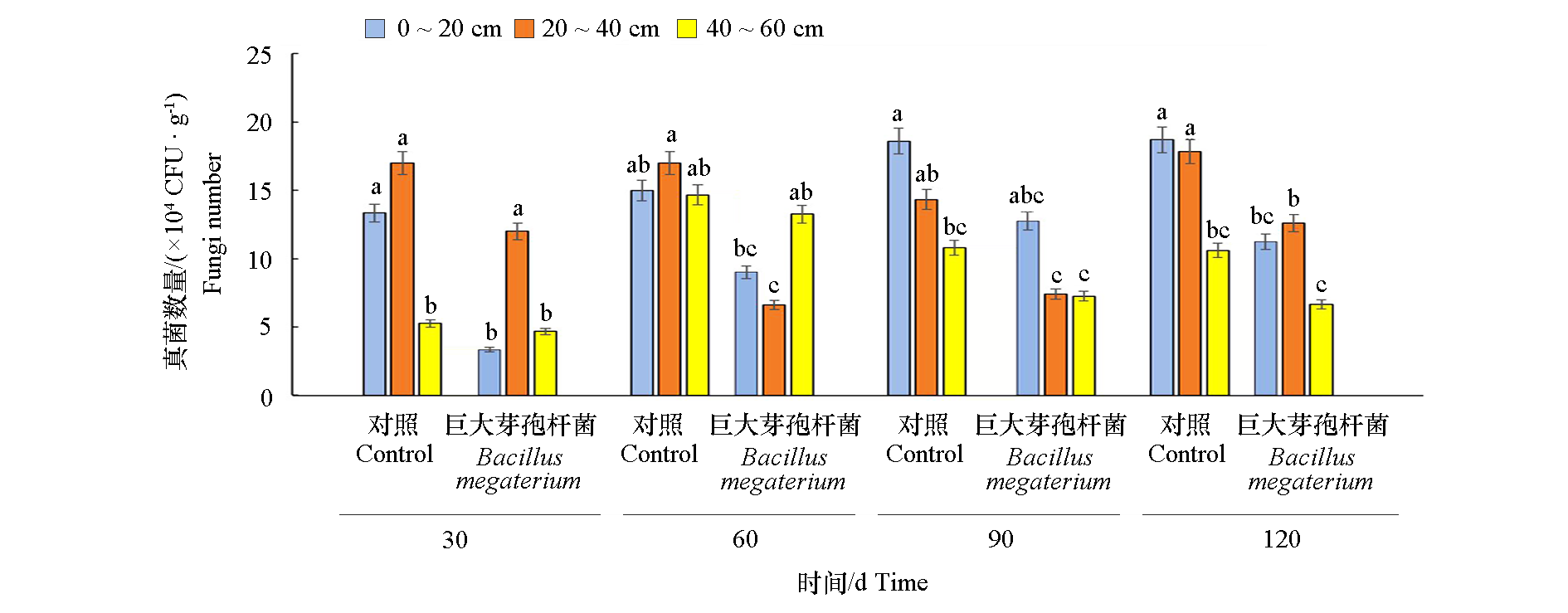
图2 巨大芽孢杆菌(Bacillus megaterium)菌剂对苹果根际20、40和60 cm土层真菌数量的影响 不同小写字母表示0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 2 Effects of Bacillus megaterium on the number of fungi in different soil layers of apple rhizosphere Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference at 0.05 level.
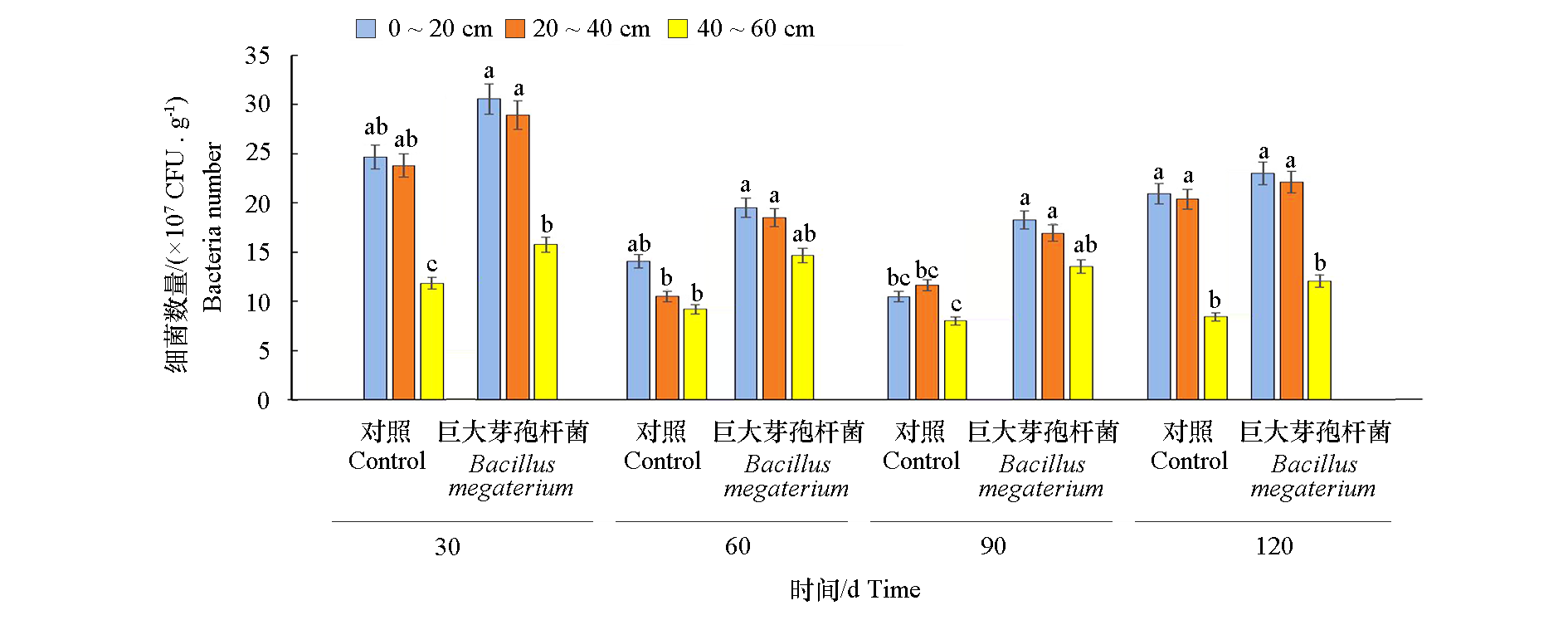
图3 巨大芽孢杆菌(Bacillus megaterium)菌剂对苹果根际20、40和60 cm土层细菌数量的影响 不同小写字母表示0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 3 Effect of Bacillus megaterium on the number of bacteria in different soil layers of apple rhizosphere Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference at 0.05 level.
| 处理 Treatment | ACE指数 ACE index | Chao1指数 Chao1 index | 香农指数 Shannon index | 辛普森指数 Simpson index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂 B. megaterium | 381.69 ± 12.98 | 373.56 ± 6.82 | 3.15 ± 0.10 | 0.08 ± 0.00 |
| 水Water (对照Control) | 359.96 ± 12.63 | 385.43 ± 16.09 | 3.11 ± 0.04 | 0.09 ± 0.00 |
表5 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂对苹果土壤真菌α多样性的影响
Table 5 Effect of Bacillus megaterium on the α-diversity of fungi in apple rhizosphere soil
| 处理 Treatment | ACE指数 ACE index | Chao1指数 Chao1 index | 香农指数 Shannon index | 辛普森指数 Simpson index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂 B. megaterium | 381.69 ± 12.98 | 373.56 ± 6.82 | 3.15 ± 0.10 | 0.08 ± 0.00 |
| 水Water (对照Control) | 359.96 ± 12.63 | 385.43 ± 16.09 | 3.11 ± 0.04 | 0.09 ± 0.00 |
| 处理 Treatment | 陶氏菌属 Tausonia | 短梗蠕孢属 Trichocladium | 产油菌属 Cephalotrichum | 头束菌属 Solicoccozyma | 担子菌酵母菌属 Naganishia | 土赤壳属 Ilyonectria |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂 B. megaterium | 28.26 ± 1.36** | 9.93 ± 1.03** | 4.04 ± 0.65* | 2.63 ± 0.14* | 1.54 ± 0.04** | 0.27 ± 0.02* |
| 水Water (对照Control) | 36.97 ± 1.73 | 5.30 ± 0.70 | 2.10 ± 0.59 | 3.87 ± 0.48 | 0.53 ± 0.13 | 0.08 ± 0.07 |
表6 巨大芽孢杆菌对苹果土壤真菌相对丰度的影响(属水平)
Table 6 Effects of Bacillus megaterium on the relative abundance of fungi in apple soil(genus level)
| 处理 Treatment | 陶氏菌属 Tausonia | 短梗蠕孢属 Trichocladium | 产油菌属 Cephalotrichum | 头束菌属 Solicoccozyma | 担子菌酵母菌属 Naganishia | 土赤壳属 Ilyonectria |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂 B. megaterium | 28.26 ± 1.36** | 9.93 ± 1.03** | 4.04 ± 0.65* | 2.63 ± 0.14* | 1.54 ± 0.04** | 0.27 ± 0.02* |
| 水Water (对照Control) | 36.97 ± 1.73 | 5.30 ± 0.70 | 2.10 ± 0.59 | 3.87 ± 0.48 | 0.53 ± 0.13 | 0.08 ± 0.07 |
| 处理 Treatment | ACE指数 ACE index | Chao1指数 Chao1 index | 香农指数 Shannon index | 辛普森指数 Simpson index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂 B. megaterium | 2 824.52 ± 66.23 | 2 839.26 ± 79.52 | 6.23 ± 0.06 | 0.01 ± 0.00 |
| 水Water (对照Control) | 2 810.25 ± 111.48 | 2 788.77 ± 179.73 | 5.91 ± 0.24 | 0.01 ± 0.00 |
表7 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂对苹果土壤细菌α多样性的影响
Table 7 Effect of Bacillus megaterium on the α-diversity of bacteria in apple rhizosphere soil
| 处理 Treatment | ACE指数 ACE index | Chao1指数 Chao1 index | 香农指数 Shannon index | 辛普森指数 Simpson index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂 B. megaterium | 2 824.52 ± 66.23 | 2 839.26 ± 79.52 | 6.23 ± 0.06 | 0.01 ± 0.00 |
| 水Water (对照Control) | 2 810.25 ± 111.48 | 2 788.77 ± 179.73 | 5.91 ± 0.24 | 0.01 ± 0.00 |
| 处理 Treatment | 类诺卡氏菌属 Nocardioides | 链霉菌属 Streptomyces | 芽单胞菌属 Gemmatimonas | 朱氏杆菌属 Chujaibacter | 德沃斯氏菌属 Devosia |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 巨大芽孢杆菌处理 B. megaterium | 3.73 ± 0.68 | 0.69 ± 0.09** | 0.67 ± 0.08* | 1.97 ± 0.31** | 1.11 ± 0.16 |
| 水Water (对照Control) | 3.34 ± 1.68 | 0.26 ± 0.03 | 0.50 ± 0.03 | 4.03 ± 0.24 | 1.39 ± 0.65 |
表8 巨大芽孢杆菌对苹果土壤细菌相对丰度的影响(属水平)
Table 8 Effects of Bacillus megaterium on the relative abundance of bacteria in apple soil(genus level)
| 处理 Treatment | 类诺卡氏菌属 Nocardioides | 链霉菌属 Streptomyces | 芽单胞菌属 Gemmatimonas | 朱氏杆菌属 Chujaibacter | 德沃斯氏菌属 Devosia |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 巨大芽孢杆菌处理 B. megaterium | 3.73 ± 0.68 | 0.69 ± 0.09** | 0.67 ± 0.08* | 1.97 ± 0.31** | 1.11 ± 0.16 |
| 水Water (对照Control) | 3.34 ± 1.68 | 0.26 ± 0.03 | 0.50 ± 0.03 | 4.03 ± 0.24 | 1.39 ± 0.65 |
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 全磷/(g · kg-1) Total phosphorus | 全钾/(g · kg-1) Total potassium | 速效磷/(mg · kg-1) Available phosphorus | 速效钾/(mg · kg-1) Available potassium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂 B. megaterium | 1.21 ± 0.14* | 9.76 ± 0.24* | 31.93 ± 1.68* | 126.52 ± 2.04* |
| 水Water (对照Control) | 1.88 ± 0.12 | 12.52 ± 0.65 | 26.20 ± 0.98 | 120.34 ± 3.12 | |
| 2022 | 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂 B. megaterium | 1.36 ± 0.51* | 8.26 ± 0.14* | 34.77 ± 1.90* | 128.09 ± 2.96* |
| 水Water (对照Control) | 1.98 ± 0.09 | 12.34 ± 0.21 | 28.78 ± 1.38 | 121.63 ± 4.63 |
表9 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂处理对苹果根际土壤磷钾含量的影响
Table 9 Effects of Bacillus megaterium on phosphorus and potassium contents in rhizosphere soil of apple
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 全磷/(g · kg-1) Total phosphorus | 全钾/(g · kg-1) Total potassium | 速效磷/(mg · kg-1) Available phosphorus | 速效钾/(mg · kg-1) Available potassium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂 B. megaterium | 1.21 ± 0.14* | 9.76 ± 0.24* | 31.93 ± 1.68* | 126.52 ± 2.04* |
| 水Water (对照Control) | 1.88 ± 0.12 | 12.52 ± 0.65 | 26.20 ± 0.98 | 120.34 ± 3.12 | |
| 2022 | 巨大芽孢杆菌菌剂 B. megaterium | 1.36 ± 0.51* | 8.26 ± 0.14* | 34.77 ± 1.90* | 128.09 ± 2.96* |
| 水Water (对照Control) | 1.98 ± 0.09 | 12.34 ± 0.21 | 28.78 ± 1.38 | 121.63 ± 4.63 |
| [1] |
doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2019.02.001 URL |
| [2] |
|
|
鲍士旦. 2000. 土壤农化分析. 北京: 中国农业出版社:56-188.
|
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2021.126733 URL |
| [4] |
doi: S0168-1656(18)30584-4 pmid: 30172784 |
| [5] |
|
|
冯敬涛, 于天武, 吴晓娴, 李秉毓, 葛顺峰, 姜远茂. 2021. 微生物菌肥对苹果土壤理化特性及养分吸收的影响. 北方园艺,(2):97-102.
|
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.1007/s11104-015-2562-x URL |
| [7] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2015-0965 URL |
|
付风云, 相立, 徐少卓, 刘训理, 沈向, 陈学森, 尹承苗, 毛志泉. 2016. 多菌灵与微生物有机肥复合对连作平邑甜茶幼苗及土壤的影响. 园艺学报, 43 (8):1452-1462.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2015-0965 URL |
|
| [8] |
|
|
耿丽平, 范俊, 王婧瑶, 赵全利, 薛培英, 刘文菊. 2020. 解磷、钾功能性微生物耐盐效应研究. 水土保持学报, 34 (4):370-375.
|
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2018.12.024 URL |
| [12] |
doi: 10.1080/03650340.2012.756977 URL |
| [13] |
|
|
李娜. 2020. 巨大芽孢杆菌TA-4的分离鉴定及其生物有机肥对番茄生长和土壤微生物群落的影响[博士论文]. 泰安: 山东农业大学.
|
|
| [14] |
|
|
路晓月, 王子夜, 韩建玮, 许露, 张晓飞, 韩杰, 王志刚, 刘越, 索相敏, 阎爱华. 2022. 木醋液对八棱海棠生长及再植病土壤主要特性的影响. 华北农学报, 37 (3):175-185.
doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.20192879 |
|
| [15] |
|
|
马慧媛, 黄媛媛, 刘胜尧, 徐炳雪, 黄亚丽, 范凤翠, 贾振华, 宋水山. 2020. 微生物菌剂施用对设施茄子根际土壤养分和细菌群落多样性的影响. 微生物学通报, 47 (1):140-150.
|
|
| [16] |
|
|
潘凤兵, 陈冉, 姜伟涛, 王海燕, 吕毅, 沈向, 陈学森, 尹承苗, 毛志泉. 2022. 不同蛋白发酵物对连作土壤微生物环境和平邑甜茶幼苗生长的影响. 园艺学报, 49 (2):396-406.
|
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1016/j.rhisph.2018.04.002 URL |
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
|
孙杨, 王璐, 赵璐, 孟祥龙, 王亚南, 胡同乐, 曹克强, 王树桐. 2022. 复合微生物菌肥对苹果再植病害调控及对根围土壤真菌群落结构的影响. 植物病理学报, 52 (2):256-268.
|
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.1128/AEM.66.8.3134-3141.2000 pmid: 10919761 |
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
|
王叶青, 刘芳, 潘纪源, 陆秀君, 刘文菊, 李博文. 2022. 巨大芽孢杆菌与噁霉灵联用对甜瓜连作障碍的缓解效果. 农药学学报, 24 (4):1-15.
|
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202010.023 |
|
王志康, 徐子恒, 陈紫云, 洑香香. 2020. 有机肥和解磷固氮菌配施对缺碳黄棕壤养分特性的协同效应. 应用生态学报, 31 (10):3413-3423.
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202010.023 |
|
| [24] |
|
|
韦坤逢, 王丽, 李灿灿, 黄剑. 2018. 辣椒根际链霉菌WKFF34的分离鉴定及拮抗作用. 江西农业大学学报, 40 (1):78-88.
|
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0476 URL |
|
闫助冰, 王玫, 明常军, 姜远茂, 沈向, 陈学森, 尹承苗, 毛志泉. 2021. 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌XC1的筛选、鉴定及其对苹果连作障碍的影响. 园艺学报, 48 (3):409-420.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0476 URL |
|
| [27] |
|
|
杨莉莉, 王永合, 韩稳社, 马林英, 杨乖成, 韩艳云, 同延安. 2021. 氮肥减量配施有机肥对苹果产量品质及土壤生物学特性的影响. 农业环境科学学报, 40 (3):631-639.
|
|
| [28] |
|
|
张江周, 李奕赞, 李颖, 张俊伶, 张福锁. 2022. 土壤健康指标体系与评价方法研究进展. 土壤学报, 59 (3):603-616.
|
|
| [29] |
|
|
张敏硕, 赵英男, 杨威, 刘文菊, 李博文. 2019. 微生物菌剂对张北冷凉坝上地区马铃薯产量、品质及活化土壤磷钾的效果. 水土保持学报, 33 (3):235-239.
|
|
| [30] |
doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2020.107236 URL |
| [31] |
doi: 10.1007/s11368-019-02319-1 |
| [32] |
|
|
周晓丽, 包丽君, 柳旭, 熊艺, 褚海燕, 贾仲君. 2022. 干湿交替水分胁迫对水稻土细菌群落影响的研究. 微生物学报, 62 (3):1004-1019.
|
| [1] | 李少旋, 王芝云, 胡大刚, 朱 波, 韩明三, . 晚熟苹果新品种‘琴富 1 号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 1-2. |
| [2] | 孙燕霞, 唐 岩, 刘大亮, 赵玲玲, 张学勇, 刘学卿, Dorota Ewa Kruczynska, 程志娟, Sylwia Keller-Przybylkowicz, 宋来庆, . 早熟苹果新品种‘烟青玉’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 3-4. |
| [3] | 赵国栋, 贾林光, 陈东玫, 赵同生, 张新生, 张朝红, 李春敏, 付 友. 苹果新品种‘映红’ [J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 5-6. |
| [4] | 蔚 露, 牛自勉, 郭文龙, 林 琭, 李 全, 李志强, 王红宁, 李鸿雁 . 早熟苹果新品种‘夏露’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 7-8. |
| [5] | 樊 娟, 沈松真, 苗青青, 张乐辉, 姚恩鹏, 裴卓强. 番茄新品种‘卫红 16 号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 65-66. |
| [6] | 丁捷, 刘春燕, 黄彭, 李红莹, 陈黎维, 蒲小燕, 刘耀文, 秦文. 蓝莓保鲜技术研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(9): 1944-1958. |
| [7] | 刘金莹, 孔令喜, 王威浩, 秦国政, 王豫颖. 草莓果实香气物质生物合成研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(9): 1959-1970. |
| [8] | 孙志娟, 刘文杰, 郑晓东, 袭祥利, 马长青, 刘晓丽, 王彩虹, 田义轲. 褪黑素对盐碱胁迫下平邑甜茶幼苗生长的影响及其机制[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1697-1710. |
| [9] | 代红军, 魏强, 贺琰, 汪月宁, 王振平. 油菜素内酯对高温胁迫下葡萄花色苷合成及果实品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1711-1722. |
| [10] | 王文, 张柯楠, 方莫扉, 丁思悦, 王雪飞, 惠竹梅. 果袋颜色对‘赤霞珠’葡萄果皮花色苷积累的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1723-1738. |
| [11] | 曹雄军, 韩佳宇, 成果, 王博, 马广仁, 林玲, 谭宗琨, 黄秋秘, 陈潇, 陈孚仪, 时晓芳, 盘丰平, 白先进. 光照时数及强度对‘阳光玫瑰’葡萄产量形成的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1739-1746. |
| [12] | 周洁, 李甜竹, 刘汝懿, 李陈浩, 袁泽南, 李建明. 空气湿度与土壤含水量耦合对番茄灰霉病的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1779-1792. |
| [13] | 王晓芳, 夏群, 栾日昇, 许莉, 尹承苗, 王艳芳, 陈学森, 毛志泉, 相昆. 万寿菊秸秆粉末处理对镰孢菌的抑制及苹果连作土壤施用效果[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(7): 1518-1534. |
| [14] | 汪红秀, 周上铃, 何绍国, 田再泽, 马静华, 彭良志, 淳长品. 尤力克柠檬叶片营养元素标准的研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(7): 1535-1546. |
| [15] | 陈敏, 吴天利, 吕远达, 姜波, 闫化学, 李娟, 钟云. 不同砧木红江橙容器栽培生长和果实品质分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(7): 1547-1562. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司