
园艺学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (7): 1518-1534.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0564
王晓芳1, 夏群2, 栾日昇3, 许莉4, 尹承苗5, 王艳芳6, 陈学森5, 毛志泉5,*( ), 相昆1,*(
), 相昆1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-11-21
修回日期:2023-05-15
出版日期:2023-07-25
发布日期:2023-07-26
通讯作者:
基金资助:
WANG Xiaofang1, XIA Qun2, LUAN Risheng3, XU Li4, YIN Chengmiao5, WANG Yanfang6, CHEN Xuesen5, MAO Zhiquan5,*( ), XIANG Kun1,*(
), XIANG Kun1,*( )
)
Received:2022-11-21
Revised:2023-05-15
Published:2023-07-25
Online:2023-07-26
摘要:
为探讨万寿菊秸秆粉末处理对苹果连作障碍相关病原镰孢菌的抑制作用及田间防治效果,在室内条件下研究了万寿菊秸秆粉末对4种镰孢属真菌(尖孢、腐皮、层出和串珠镰孢菌)的抑制效果;在田间条件下,以2年生苹果幼树(‘烟富3号’/M9T337)为试材,设置连作土对照、溴甲烷熏蒸、万寿菊混栽、0.5%和1%万寿菊秸秆粉末、0.5%和1%玉米芯粉末7个处理,研究其对苹果幼树生长及土壤微生态环境的影响。结果表明,万寿菊挥发性成分对4种镰孢菌菌丝生长具有较强的抑制作用,1.67 ~ 33.30 g · L-1万寿菊秸秆粉末用量对菌丝生长的抑制率为20% ~ 100%,抑制率随用量增加而升高。万寿菊秸秆粉末处理的腐皮镰孢菌菌丝变细,分支增多,短小且杂乱,表面破损,逐渐皱缩塌陷,呈枯死状。凤毛寨试验地壤土条件下以0.5%万寿菊秸秆粉末处理的效果最好,湾头村试验地粘壤土条件下以1%万寿菊秸秆粉末处理的效果最好,苹果幼树的株高、地径和枝条年生长量等指标显著高于连作对照。经万寿菊处理的土壤酶活性均明显升高,土壤可培养细菌数量增加、真菌数量减少,细菌/真菌增加。在凤毛寨试验点,0.5%万寿菊秸秆粉末处理的青霉菌属相对丰度增加幅度最大,是连作对照的59倍。在湾头村试验点,万寿菊处理后土壤被孢霉属、毛壳菌属、青霉菌属的相对丰度均增加,其中青霉菌属增加幅度最大,1%万寿菊秸秆粉末处理的青霉菌属是连作对照的125倍。主坐标(PCoA)分析发现,凤毛寨和湾头村不同处理间土壤真菌群落结构差异显著。综上,万寿菊秸秆粉碎物可显著改善苹果连作土壤的微生物群落结构及土壤环境,减轻连作障碍对苹果幼树造成的危害,促进树体生长。
王晓芳, 夏群, 栾日昇, 许莉, 尹承苗, 王艳芳, 陈学森, 毛志泉, 相昆. 万寿菊秸秆粉末处理对镰孢菌的抑制及苹果连作土壤施用效果[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(7): 1518-1534.
WANG Xiaofang, XIA Qun, LUAN Risheng, XU Li, YIN Chengmiao, WANG Yanfang, CHEN Xuesen, MAO Zhiquan, XIANG Kun. Inhibition of Tagetes erecta Straw Powder on the Main Pathogens of Apple Continuous Cropping Obstacle and Its Field Application Effect[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(7): 1518-1534.
| 试验地 Test site | 容重/(g · cm-3) Bulk density | 总孔隙度/% Total porosity | pH | 有机质/(g · kg-1) Organic matter | NO3-N/(mg · kg-1) | NH4+-N / (mg · kg-1) | 速效磷/ (mg · kg-1) Available P | 速效钾/ (mg · kg-1) Available K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 凤毛寨Fengmaozhai | 1.21 | 50.10 | 4.75 | 5.12 | 33.96 | 22.23 | 9.84 | 21.74 |
| 湾头村Wantoucun | 1.15 | 53.03 | 6.49 | 7.88 | 34.59 | 14.13 | 7.15 | 40.26 |
表1 供试土壤的基本特性
Table 1 The basic characteristics of the test soil
| 试验地 Test site | 容重/(g · cm-3) Bulk density | 总孔隙度/% Total porosity | pH | 有机质/(g · kg-1) Organic matter | NO3-N/(mg · kg-1) | NH4+-N / (mg · kg-1) | 速效磷/ (mg · kg-1) Available P | 速效钾/ (mg · kg-1) Available K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 凤毛寨Fengmaozhai | 1.21 | 50.10 | 4.75 | 5.12 | 33.96 | 22.23 | 9.84 | 21.74 |
| 湾头村Wantoucun | 1.15 | 53.03 | 6.49 | 7.88 | 34.59 | 14.13 | 7.15 | 40.26 |
| 万寿菊秸秆粉末用量/(g · L-1) T. erecta powder | 尖孢镰孢菌 F. oxysporum | 腐皮镰孢菌 F. solani | 层出镰孢菌 F. proliferatum | 串珠镰孢菌 F. verticillioides |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.67 | 25.48 | 30.44 | 20.51 | 28.92 |
| 3.30 | 40.13 | 43.48 | 37.82 | 45.18 |
| 6.70 | 54.14 | 58.39 | 55.13 | 57.23 |
| 13.30 | 69.43 | 72.05 | 72.44 | 75.90 |
| 26.70 | 88.54 | 89.44 | 88.46 | 92.17 |
| 33.30 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
表2 万寿菊秸秆粉末挥发性成分对4种镰孢菌菌丝生长的抑制率
Table 2 Inhibitory effects of volatile substances from Tagetes erecta straw powder on four Fusariums species %
| 万寿菊秸秆粉末用量/(g · L-1) T. erecta powder | 尖孢镰孢菌 F. oxysporum | 腐皮镰孢菌 F. solani | 层出镰孢菌 F. proliferatum | 串珠镰孢菌 F. verticillioides |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.67 | 25.48 | 30.44 | 20.51 | 28.92 |
| 3.30 | 40.13 | 43.48 | 37.82 | 45.18 |
| 6.70 | 54.14 | 58.39 | 55.13 | 57.23 |
| 13.30 | 69.43 | 72.05 | 72.44 | 75.90 |
| 26.70 | 88.54 | 89.44 | 88.46 | 92.17 |
| 33.30 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| 菌种 Strain | 毒力回归方程 Regression equation of virulence | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| 尖孢镰孢菌F. oxysporum | y = 0.4435x-13.76 | 0.938 |
| 腐皮镰孢菌F. solani | y = 0.4719x-16.81 | 0.931 |
| 层出镰孢菌F. proliferatum | y = 0.4087x-11.34 | 0.901 |
| 串珠镰孢菌F. verticillioides | y = 0.4513x-15.88 | 0.912 |
表3 万寿菊秸秆粉末挥发性成分对4种镰孢菌菌丝生长抑制的毒力回归方程
Table 3 Toxicity regression equation of volatile substances from Tagetes erecta straw powder on mycelial growth
| 菌种 Strain | 毒力回归方程 Regression equation of virulence | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| 尖孢镰孢菌F. oxysporum | y = 0.4435x-13.76 | 0.938 |
| 腐皮镰孢菌F. solani | y = 0.4719x-16.81 | 0.931 |
| 层出镰孢菌F. proliferatum | y = 0.4087x-11.34 | 0.901 |
| 串珠镰孢菌F. verticillioides | y = 0.4513x-15.88 | 0.912 |
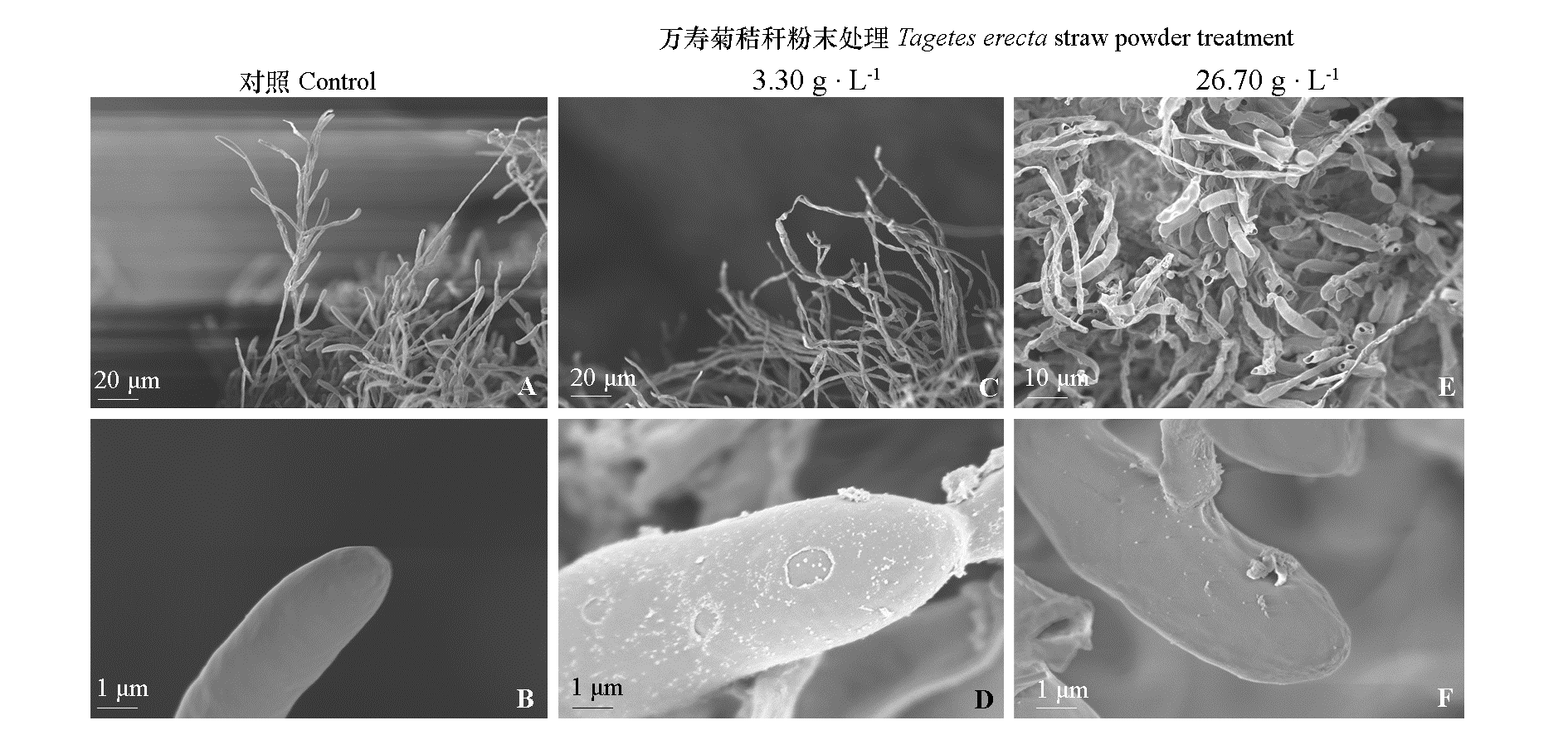
图2 万寿菊秸秆粉末处理1 d的腐皮镰孢菌菌丝形态扫描电镜观察
Fig. 2 Mycelium morphology of Fusarium solani treated one day with Tagetes erecta straw powder under scanning electron microscope
| 取样时间 (Y-M) Sampling time | 取样地点 Sampling area | 处理 Treatment | 株高/cm Plant height | 地径/mm Ground diameter | 新梢生长量/cm Shoot length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017-08 | 凤毛寨 Fengmaozhai | 溴甲烷Methyl bromide | 1.99 ± 0.14 a | 45.65 ± 1.08 a | 80.33 ± 4.25 a |
| 连作土(对照)Replanted soil(Control) | 1.71 ± 0.16 b | 24.81 ± 1.95 e | 55.89 ± 5.00 c | ||
| 万寿菊混栽Tagetes erecta mixed planting | 1.87 ± 0.09 ab | 30.54 ± 0.90 cd | 59.78 ± 6.11 c | ||
| 0.5%万寿菊秸秆粉末 0.5% Tagetes erecta straw powder | 1.98 ± 0.06 a | 36.44 ± 1.35 b | 68.89 ± 0.51 b | ||
| 0.5%玉米芯粉末 0.5% Corncob powder | 1.83 ± 0.12 ab | 31.76 ± 1.36 cd | 55.33 ± 2.34 c | ||
| 1%万寿菊秸秆粉末1% Tagetes erecta straw powder | 1.92 ± 0.11 ab | 32.46 ± 2.17 c | 62.00 ± 3.51 c | ||
| 1%玉米芯粉末1% Corncob powder | 1.91 ± 0.07 ab | 28.98 ± 1.66 d | 57.33 ± 2.34 c | ||
| 湾头村 Wantoucun | 溴甲烷Methyl bromide | 2.18 ± 0.15 a | 49.56 ± 2.46 a | 80.11 ± 3.02 ab | |
| 连作土(对照)Replanted soil(Control) | 1.84 ± 0.06 c | 39.85 ± 1.70 de | 58.44 ± 4.00 e | ||
| 万寿菊混栽Tagetes erecta mixed planting | 2.06 ± 0.18 abc | 37.09 ± 1.04 e | 73.78 ± 1.07 c | ||
| 0.5%万寿菊秸秆粉末0.5%Tagetes erecta straw powder | 2.09 ± 0.17 abc | 44.45 ± 0.96 bc | 74.56 ± 2.22 bc | ||
| 0.5%玉米芯粉末0.5% Corncob powder | 1.85 ± 0.10 c | 41.57 ± 0.62 cd | 67.11 ± 6.17 d | ||
| 1%万寿菊秸秆粉末1% Tagetes erecta straw powder | 2.14 ± 0.19 ab | 46.71 ± 1.99 ab | 82.33 ± 2.33 a | ||
| 1%玉米芯粉末1% Corncob powder | 1.89 ± 0.04 bc | 40.71 ± 3.03 d | 70.22 ± 2.51 cd | ||
| 2018-08 | 凤毛寨 Fengmaozhai | 溴甲烷Methyl bromide | 2.54 ± 0.15 a | 47.09 ± 0.60 a | 96.00 ± 1.17 a |
| 连作土(对照)Replanted soil(Control) | 1.92 ± 0.06 c | 26.17 ± 1.23 e | 57.22 ± 3.86 c | ||
| 万寿菊混栽Tagetes erecta mixed planting | 2.03 ± 0.02 bc | 32.68 ± 0.56 cd | 58.44 ± 3.35 c | ||
| 0.5%万寿菊秸秆粉末0.5% Tagetes erecta straw powder | 2.23 ± 0.02 b | 37.25 ± 1.10 b | 75.00 ± 1.92 b | ||
| 0.5%玉米芯粉末0.5% Corncob powder | 2.05 ± 0.03 bc | 33.31 ± 0.49 cd | 55.22 ± 2.78 c | ||
| 1%万寿菊秸秆粉末1% Tagetes erecta straw powder | 2.11 ± 0.03 bc | 35.22 ± 1.34 bc | 60.56 ± 2.78 c | ||
| 1%玉米芯粉末1% Corncob powder | 2.11 ± 0.05 bc | 30.58 ± 1.00 d | 57.22 ± 3.55 c | ||
| 湾头村 Wantoucun | 溴甲烷Methyl bromide | 2.93 ± 0.04 a | 50.28 ± 0.96 a | 97.11 ± 3.02 a | |
| 连作土(对照)Replanted soil(Control) | 2.55 ± 0.08 b | 41.59 ± 0.96 bc | 64.33 ± 4.22 d | ||
| 万寿菊混栽Tagetes erecta mixed planting | 2.72 ± 0.09 ab | 38.16 ± 1.78 c | 82.22 ± 1.78 bc | ||
| 0.5%万寿菊秸秆粉末0.5% Tagetes erecta straw powder | 2.75 ± 0.10 ab | 46.40 ± 1.37 ab | 91.44 ± 1.31 ab | ||
| 0.5%玉米芯粉末0.5% Corncob powder | 2.74 ± 0.16 ab | 45.95 ± 1.96 ab | 75.44 ± 9.10 cd | ||
| 1%万寿菊秸秆粉末1% Tagetes erecta straw powder | 2.90 ± 0.08 ab | 49.25 ± 3.19 a | 93.00 ± 4.44 ab | ||
| 1%玉米芯粉末 1% Corncob powder | 2.72 ± 0.15 ab | 42.28 ± 1.68 bc | 86.00 ± 1.71 abc |
表4 万寿菊秸秆粉末处理对大田连作苹果树体生长的影响
Table 4 Effects of Tagetes erecta straw powder on the growth of apple saplings in field continuous cropping
| 取样时间 (Y-M) Sampling time | 取样地点 Sampling area | 处理 Treatment | 株高/cm Plant height | 地径/mm Ground diameter | 新梢生长量/cm Shoot length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017-08 | 凤毛寨 Fengmaozhai | 溴甲烷Methyl bromide | 1.99 ± 0.14 a | 45.65 ± 1.08 a | 80.33 ± 4.25 a |
| 连作土(对照)Replanted soil(Control) | 1.71 ± 0.16 b | 24.81 ± 1.95 e | 55.89 ± 5.00 c | ||
| 万寿菊混栽Tagetes erecta mixed planting | 1.87 ± 0.09 ab | 30.54 ± 0.90 cd | 59.78 ± 6.11 c | ||
| 0.5%万寿菊秸秆粉末 0.5% Tagetes erecta straw powder | 1.98 ± 0.06 a | 36.44 ± 1.35 b | 68.89 ± 0.51 b | ||
| 0.5%玉米芯粉末 0.5% Corncob powder | 1.83 ± 0.12 ab | 31.76 ± 1.36 cd | 55.33 ± 2.34 c | ||
| 1%万寿菊秸秆粉末1% Tagetes erecta straw powder | 1.92 ± 0.11 ab | 32.46 ± 2.17 c | 62.00 ± 3.51 c | ||
| 1%玉米芯粉末1% Corncob powder | 1.91 ± 0.07 ab | 28.98 ± 1.66 d | 57.33 ± 2.34 c | ||
| 湾头村 Wantoucun | 溴甲烷Methyl bromide | 2.18 ± 0.15 a | 49.56 ± 2.46 a | 80.11 ± 3.02 ab | |
| 连作土(对照)Replanted soil(Control) | 1.84 ± 0.06 c | 39.85 ± 1.70 de | 58.44 ± 4.00 e | ||
| 万寿菊混栽Tagetes erecta mixed planting | 2.06 ± 0.18 abc | 37.09 ± 1.04 e | 73.78 ± 1.07 c | ||
| 0.5%万寿菊秸秆粉末0.5%Tagetes erecta straw powder | 2.09 ± 0.17 abc | 44.45 ± 0.96 bc | 74.56 ± 2.22 bc | ||
| 0.5%玉米芯粉末0.5% Corncob powder | 1.85 ± 0.10 c | 41.57 ± 0.62 cd | 67.11 ± 6.17 d | ||
| 1%万寿菊秸秆粉末1% Tagetes erecta straw powder | 2.14 ± 0.19 ab | 46.71 ± 1.99 ab | 82.33 ± 2.33 a | ||
| 1%玉米芯粉末1% Corncob powder | 1.89 ± 0.04 bc | 40.71 ± 3.03 d | 70.22 ± 2.51 cd | ||
| 2018-08 | 凤毛寨 Fengmaozhai | 溴甲烷Methyl bromide | 2.54 ± 0.15 a | 47.09 ± 0.60 a | 96.00 ± 1.17 a |
| 连作土(对照)Replanted soil(Control) | 1.92 ± 0.06 c | 26.17 ± 1.23 e | 57.22 ± 3.86 c | ||
| 万寿菊混栽Tagetes erecta mixed planting | 2.03 ± 0.02 bc | 32.68 ± 0.56 cd | 58.44 ± 3.35 c | ||
| 0.5%万寿菊秸秆粉末0.5% Tagetes erecta straw powder | 2.23 ± 0.02 b | 37.25 ± 1.10 b | 75.00 ± 1.92 b | ||
| 0.5%玉米芯粉末0.5% Corncob powder | 2.05 ± 0.03 bc | 33.31 ± 0.49 cd | 55.22 ± 2.78 c | ||
| 1%万寿菊秸秆粉末1% Tagetes erecta straw powder | 2.11 ± 0.03 bc | 35.22 ± 1.34 bc | 60.56 ± 2.78 c | ||
| 1%玉米芯粉末1% Corncob powder | 2.11 ± 0.05 bc | 30.58 ± 1.00 d | 57.22 ± 3.55 c | ||
| 湾头村 Wantoucun | 溴甲烷Methyl bromide | 2.93 ± 0.04 a | 50.28 ± 0.96 a | 97.11 ± 3.02 a | |
| 连作土(对照)Replanted soil(Control) | 2.55 ± 0.08 b | 41.59 ± 0.96 bc | 64.33 ± 4.22 d | ||
| 万寿菊混栽Tagetes erecta mixed planting | 2.72 ± 0.09 ab | 38.16 ± 1.78 c | 82.22 ± 1.78 bc | ||
| 0.5%万寿菊秸秆粉末0.5% Tagetes erecta straw powder | 2.75 ± 0.10 ab | 46.40 ± 1.37 ab | 91.44 ± 1.31 ab | ||
| 0.5%玉米芯粉末0.5% Corncob powder | 2.74 ± 0.16 ab | 45.95 ± 1.96 ab | 75.44 ± 9.10 cd | ||
| 1%万寿菊秸秆粉末1% Tagetes erecta straw powder | 2.90 ± 0.08 ab | 49.25 ± 3.19 a | 93.00 ± 4.44 ab | ||
| 1%玉米芯粉末 1% Corncob powder | 2.72 ± 0.15 ab | 42.28 ± 1.68 bc | 86.00 ± 1.71 abc |
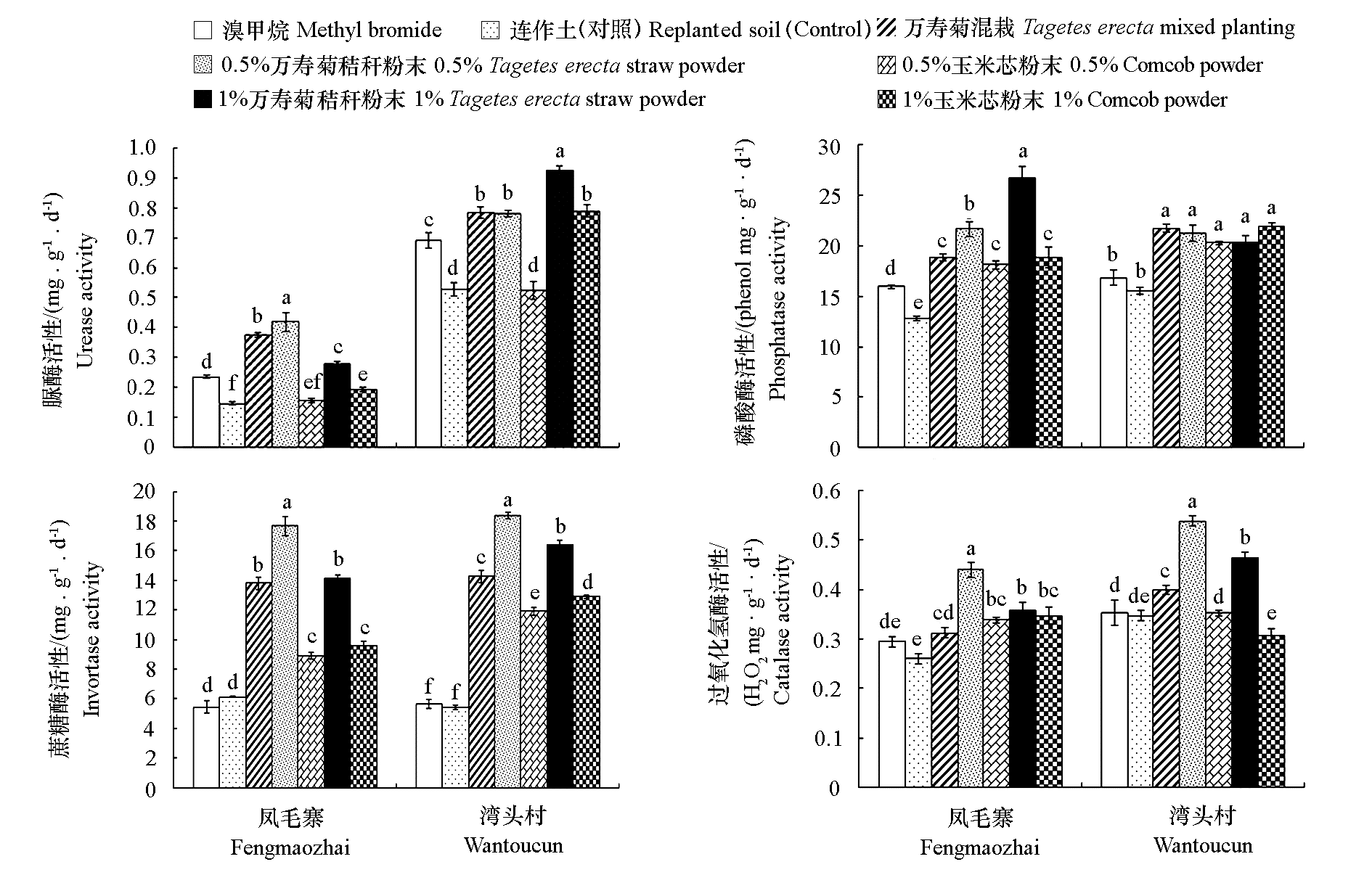
图3 万寿菊秸秆粉末处理大田连作土壤对其脲酶、磷酸酶、蔗糖酶和过氧化氢酶活性的影响
Fig. 3 Effects of Tagetes erecta straw powder on soil enzyme(urease,phosphatase,invertase,and catalase)activities in soils under field continuous cropping
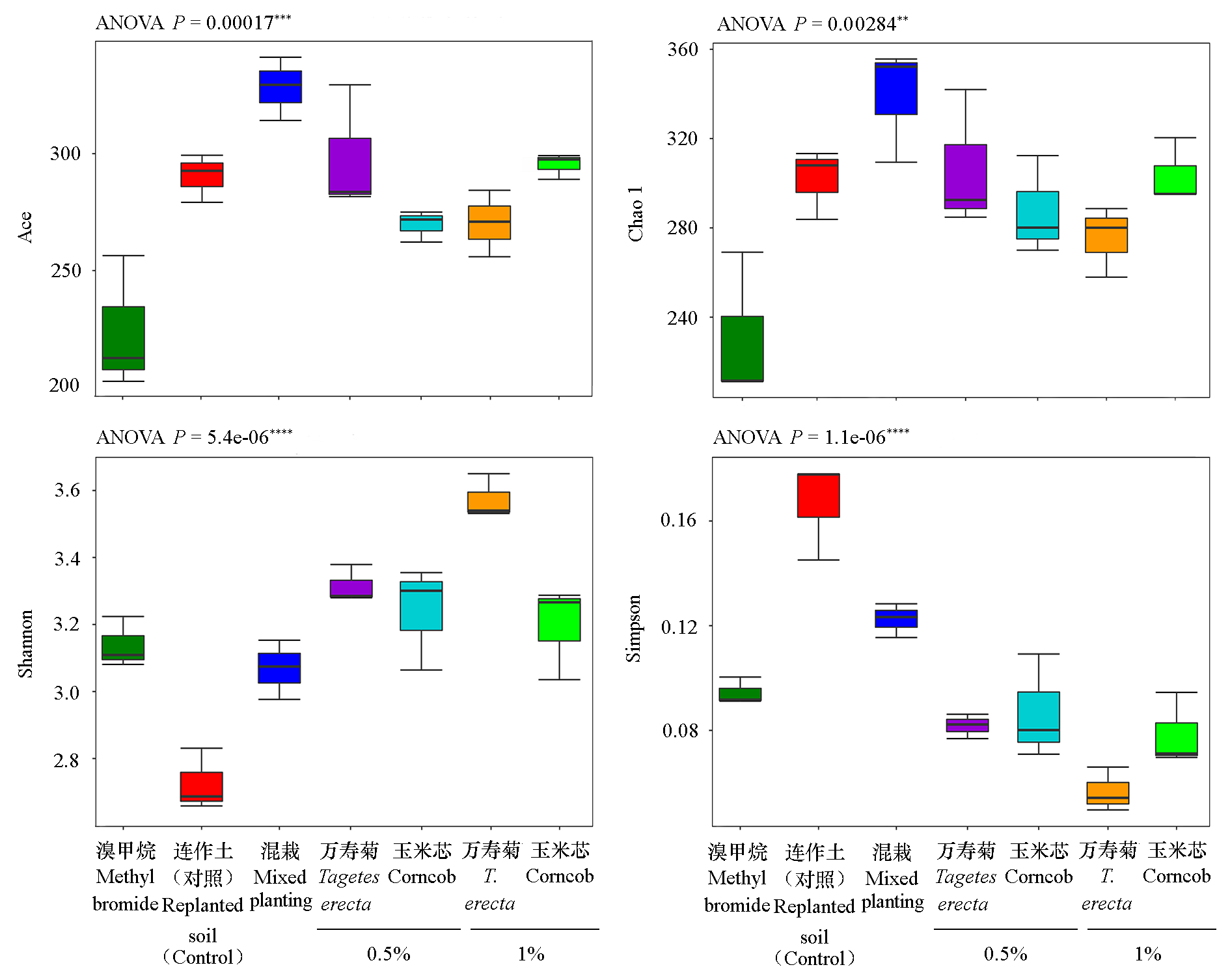
图5 凤毛寨试验点万寿菊秸秆粉末处理对土壤真菌α多样性的影响 选择P < 0.05的物种绘制柱形图,每个柱子为差异物种的相对丰度,误差线为标准误, **代表0.001 < P < 0.01,***代表0.0001 < P < 0.001,****代表P < 0.0001。下同。
Fig. 5 Effects of Tagetes erecta straw powder on the soil fungal α diversity in Fengmaozhai test site Select the species with P < 0.05 to draw the column chart. Each column is the relative abundance of different species,and the error line is the standard error,where ** represents 0.001 < P < 0.01,*** represents 0.0001 < P < 0.001,and **** represents P < 0.0001. The same below.
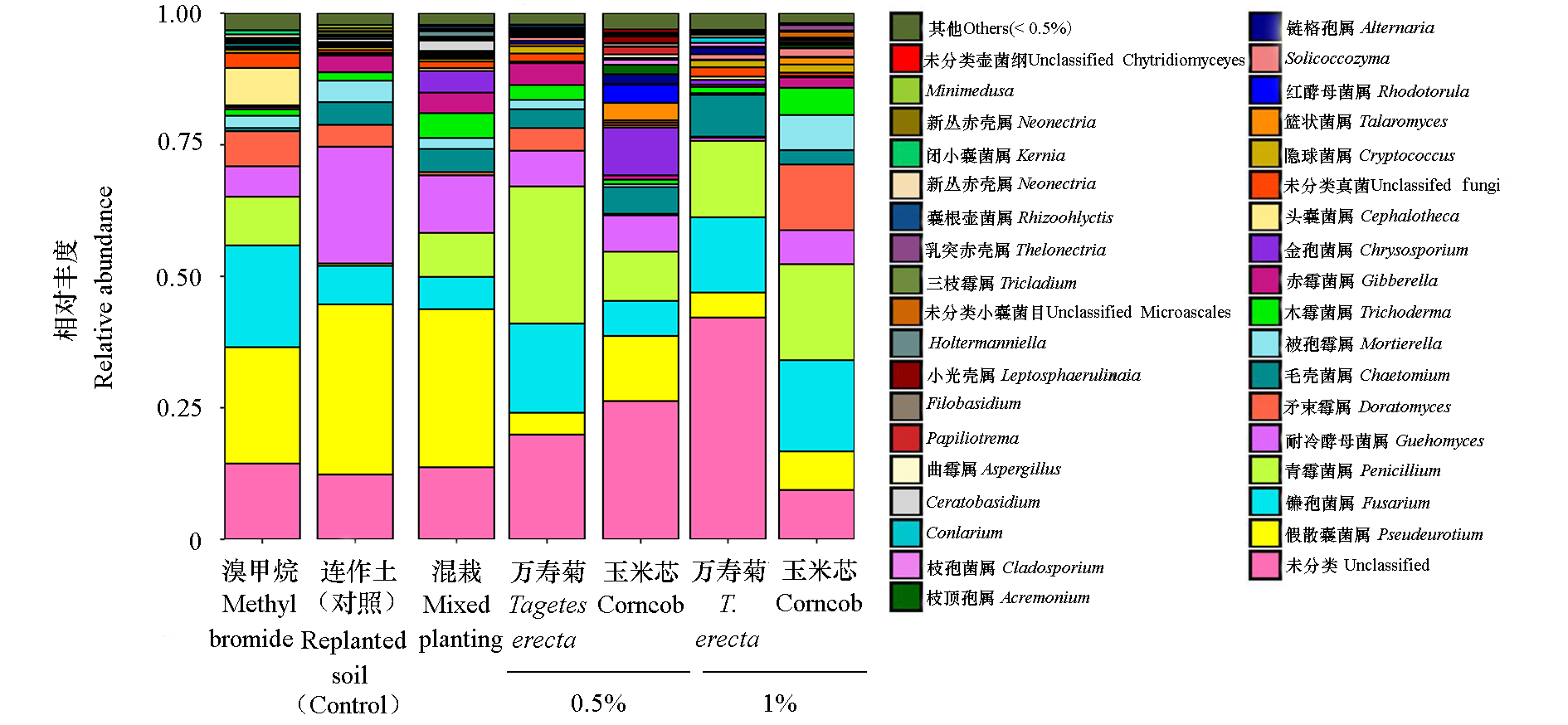
图7 凤毛寨试验点万寿菊秸秆粉末处理土壤样品真菌属水平的相对丰度变化
Fig. 7 Changes in relative abundance of soil fungi at phylum level in soil samples of Tagetes erecta straw powder in Fengmaozhai text site
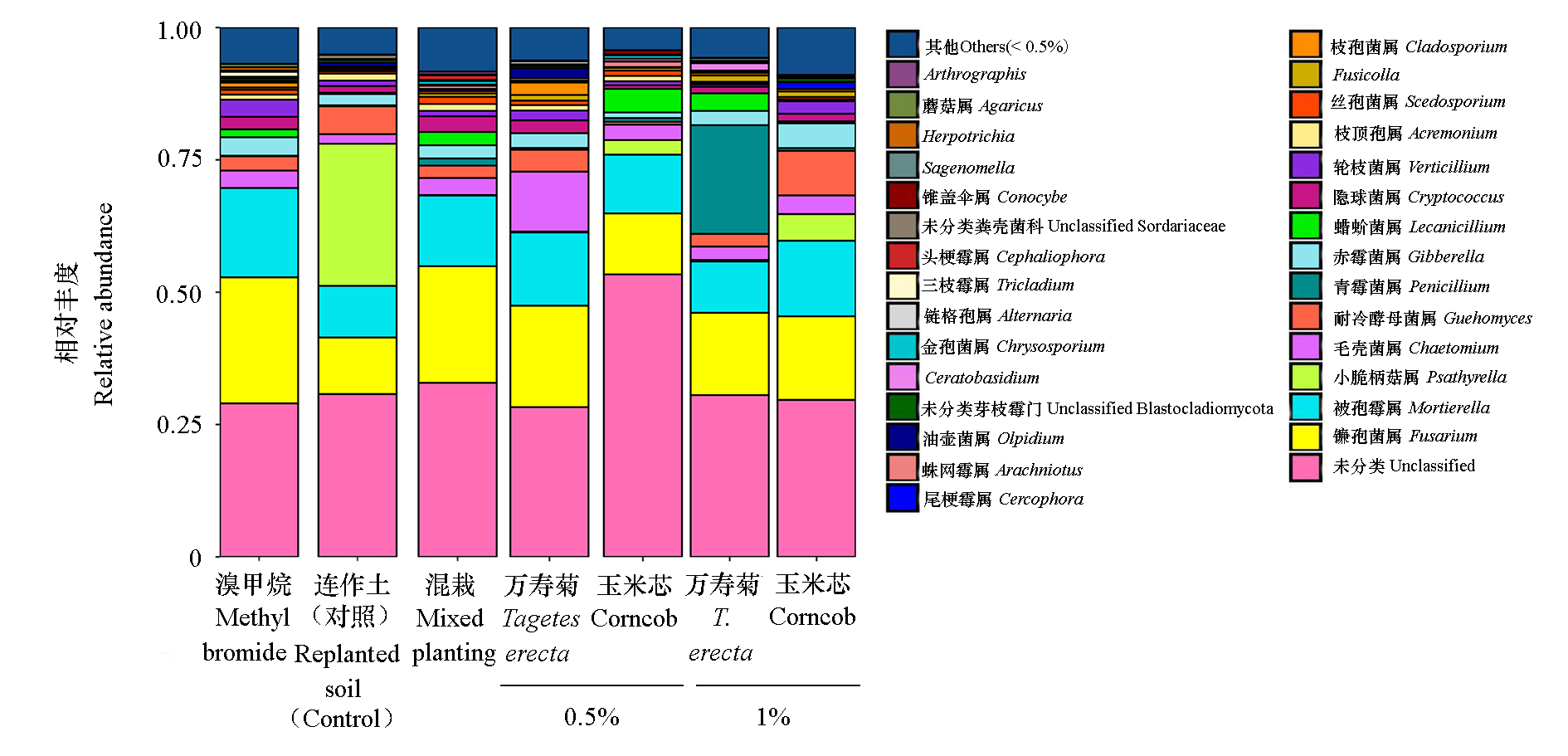
图8 湾头村试验点万寿菊秸秆粉末处理土壤样品真菌属水平的相对丰度变化
Fig. 8 Changes in relative abundance of soil fungi at phylum level in soil samples of Tagetes erecta straw powder in Wantoucun test site
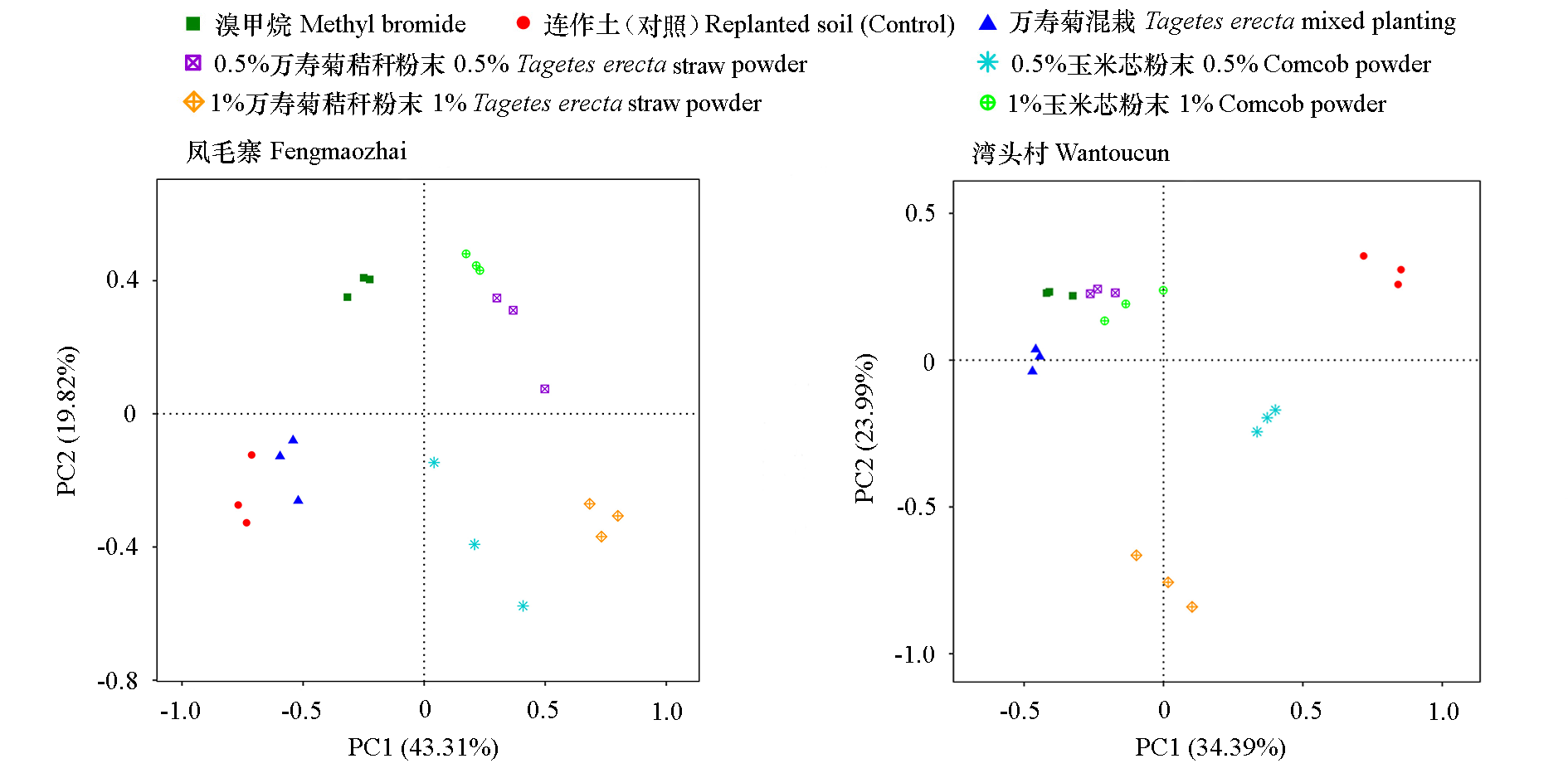
图9 凤毛寨和湾头村不同处理的土壤真菌群落结构的PCoA分析
Fig. 9 PCoA plots based on OTUs for the structures of soil fungi in soil samples of different treatments in Fengmaozhai and Wantoucun test sites
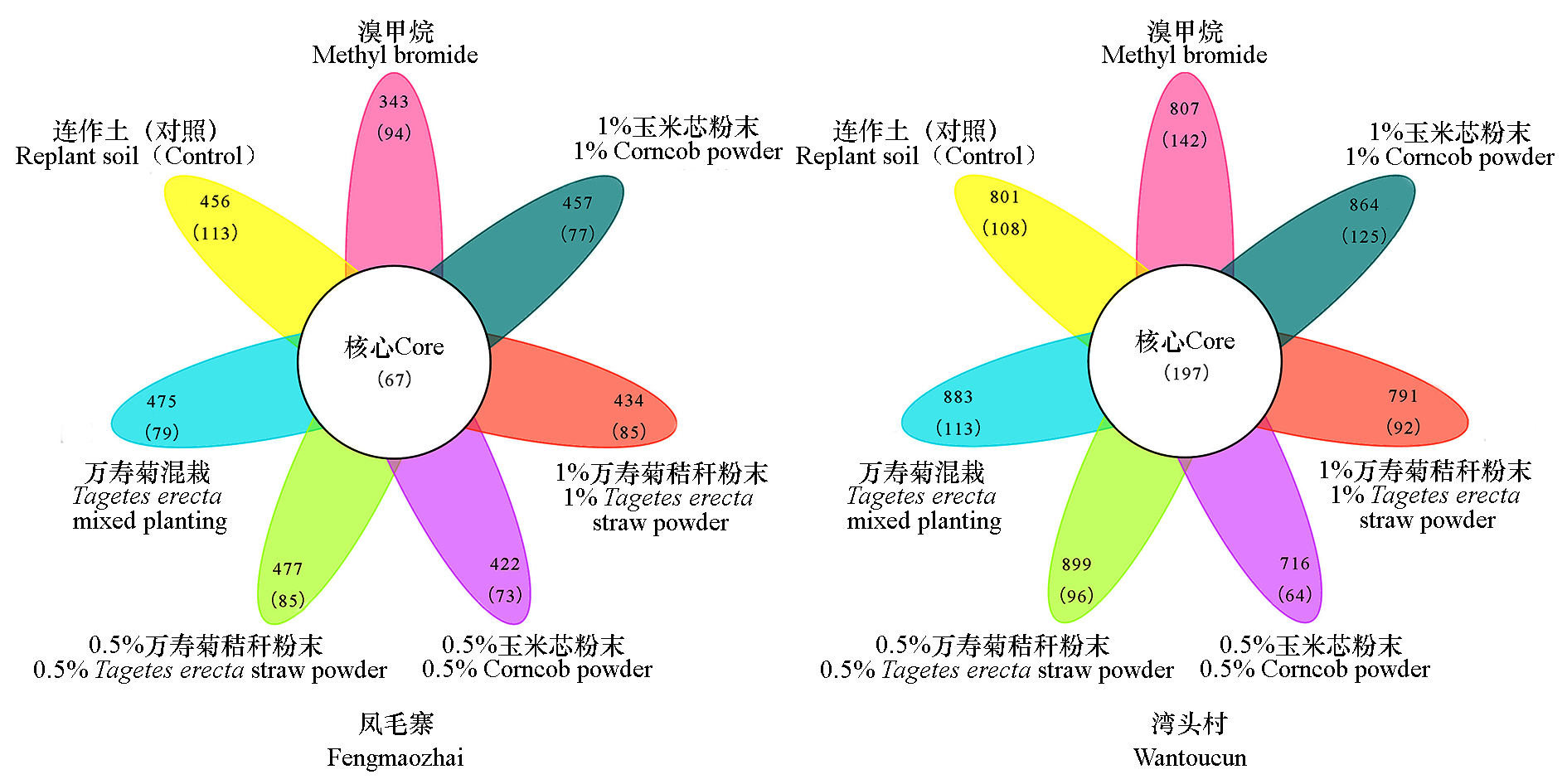
图10 凤毛寨和湾头村不同处理的独有和共有OTU数目 花瓣中包括两行数字,上面为每个样本包含的所有OTU数量,下面括号中为每个样本独有(Unique)的OTU数量。
Fig. 10 Number of unique and shared OTUs for different treatments in Fengmaozhai and Wantoucun test sites The petals contain two lines of numbers. Above is the number of all OTUs contained in each sample,and below is the number of unique OTUs of each sample.
| [1] |
|
|
曹云, 宋修超, 郭德杰, 王秋君, 马艳, 沈其荣. 2018. 棉隆熏蒸与微生物有机肥联用对西瓜枯萎病的防控研究. 土壤, 50 (1):93-100.
|
|
| [2] |
doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2019.07.1472 |
|
陈昱, 张福建, 范淑英, 王丰, 王强, 吴才君. 2019. 秸秆腐解物对豇豆连作土壤性质及幼苗生理指标的影响. 核农学报, 33 (7):1472-1479.
doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2019.07.1472 |
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.3390/agronomy7020037 URL |
| [4] |
|
|
方中达. 1998. 植病研究方法(第三版). 北京: 中国农业出版社.
|
|
| [5] |
|
|
高晶霞, 高昱, 牛勇琴, 吴雪梅, 谢华. 2021. 不同作物秸秆腐解对连作辣椒生长及根际环境的影响. 西北农业学报, 30 (8):1220-1226.
|
|
| [6] |
|
|
关松荫. 1986. 土壤酶及其研究法. 北京: 农业出版社.
|
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.3390/agronomy10030425 URL |
| [8] |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-95741-w pmid: 34381095 |
| [9] |
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1099-1026 URL |
| [10] |
doi: 10.1007/s11104-010-0522-z URL |
| [11] |
|
|
黎妍妍, 李锡宏, 王林, 冯吉, 张英, 尹忠春. 2021. 万寿菊秸秆熏蒸对烟株根际土壤原核微生物群落的影响. 烟草科技, 54 (4):15-22.
|
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2013.07.011 URL |
| [13] |
|
|
毛志泉, 尹承苗, 陈学森, 沈向, 姜远茂. 2017. 我国苹果产业节本增效关键技术Ⅴ: 苹果连作障碍防控技术. 中国果树,(5):1-4,14.
|
|
| [14] |
doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-081211-173005 pmid: 22559069 |
| [15] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0066 |
|
潘凤兵, 陈冉, 姜伟涛, 王海燕, 吕毅, 沈向, 陈学森, 尹承苗, 毛志泉. 2022. 不同蛋白发酵物对连作土壤微生物环境和平邑甜茶幼苗生长的影响. 园艺学报, 49 (2):395-406.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0066 |
|
| [16] |
|
|
秦冲. 2015. 万寿菊秸秆制备活性炭及其应用的初步研究[硕士论文]. 北京: 北京林业大学.
|
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
|
沈萍, 陈向东. 2007. 微生物学实验. 北京: 高等教育出版社.
|
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.1007/s10658-011-9747-9 URL |
| [20] |
|
|
万红娟. 2012. 旋覆花活性分子对辣椒疫霉菌作用机理初步研究[硕士论文]. 郑州: 河南农业大学.
|
|
| [21] |
|
|
王芳, 李静, 张欢. 2013. 青霉菌、放线菌株和石灰水对尖孢镰刀菌抑制作用的研究. 中国农学通报, 29 (12):185-189.
|
|
| [22] |
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2021.04.010 URL |
| [23] |
|
|
王功帅. 2018. 环渤海连作土壤真菌群落结构分析及混作葱减轻苹果连作障碍的研究[博士论文]. 泰安: 山东农业大学.
|
|
| [24] |
|
|
王晓芳, 相昆, 王艳芳, 李前进, 姜伟涛, 盛月凡, 王海燕, 陈学森, 尹承苗, 毛志泉. 2019. 万寿菊植株粉末熏蒸对苹果连作土壤环境及平邑甜茶生理特性的影响. 园艺学报, 46 (12):2383-2396.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0851 |
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2019-0941 |
|
王晓琪, 姜伟涛, 姚媛媛, 尹承苗, 陈学森, 毛志泉. 2020. 苹果连作障碍土壤微生物的研究进展. 园艺学报, 47 (11):2223-2237.
|
|
| [26] |
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2020.12.005 URL |
| [27] |
doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2007.09.024 URL |
| [28] |
|
|
谢占芳. 2016. 八种菊花挥发性成分及其抑菌活性研究[硕士论文]. 开封: 河南大学.
|
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.2095-4050.2011-xb0889 |
|
杨滨娟, 钱海燕, 黄国勤, 樊哲文, 方豫. 2012. 秸秆还田及其研究进展. 农学学报, 2 (5):1-4,28.
|
|
| [30] |
|
|
杨永, 张学军, 李寐华, 王登明, 王广智, 张永兵, 伊鸿平. 2018. 微生物肥料对设施长期连作哈密瓜根际土壤真菌群落结构的影响. 应用与环境生物学报, 24 (1):68-74.
|
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
|
张大琪, 颜冬冬, 方文生, 黄斌, 王献礼, 王晓宁, 李雄亚, 王倩, 靳茜, 李园, 欧阳灿彬, 王秋霞, 曹坳程. 2020. 生物熏蒸——环境友好型土壤熏蒸技术. 农药学学报, 22 (1):11-18.
|
|
| [33] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2015-0735 |
|
张先富, 相立, 王艳芳, 王功帅, 刘会香, 孙庚午, 沈向, 陈学森, 周慧, 尹承苗, 毛志泉. 2016. 草酸青霉A1菌株的鉴定及对苹果4种镰孢病菌的拮抗作用. 园艺学报, 43 (5):841-852.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2015-0735 |
|
| [34] |
|
|
张燕. 2017. 不同作物秸秆对连作番茄幼苗及土壤微生物的影响[硕士论文]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学.
|
| [1] | 李少旋, 王芝云, 胡大刚, 朱 波, 韩明三, . 晚熟苹果新品种‘琴富 1 号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 1-2. |
| [2] | 孙燕霞, 唐 岩, 刘大亮, 赵玲玲, 张学勇, 刘学卿, Dorota Ewa Kruczynska, 程志娟, Sylwia Keller-Przybylkowicz, 宋来庆, . 早熟苹果新品种‘烟青玉’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 3-4. |
| [3] | 赵国栋, 贾林光, 陈东玫, 赵同生, 张新生, 张朝红, 李春敏, 付 友. 苹果新品种‘映红’ [J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 5-6. |
| [4] | 蔚 露, 牛自勉, 郭文龙, 林 琭, 李 全, 李志强, 王红宁, 李鸿雁 . 早熟苹果新品种‘夏露’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 7-8. |
| [5] | 孙志娟, 刘文杰, 郑晓东, 袭祥利, 马长青, 刘晓丽, 王彩虹, 田义轲, . 褪黑素对盐碱胁迫下平邑甜茶幼苗生长的影响及其机制[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1697-1710. |
| [6] | 王金鑫, 黄晶淼, 郝婕, 李学营, 冯建忠, 索相敏, 鄢新民. 晚熟苹果新品种‘冀苹5号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(7): 1601-1602. |
| [7] | 秦嗣军, 张阔, 齐边斌, 于波, 吕德国. 外源碳对苹果根区土壤活性有机碳及植株生长的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(6): 1295-1304. |
| [8] | 坎智勇, 张德辉, 李中兴, 余思思, 钱谦, 樊天乐, 李雪薇, 马锋旺, 管清美. 90个苹果品种耐寒性评价和全基因组关联分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(5): 921-932. |
| [9] | 张琨, 思彬彬, 周军, 任玉锋, 张欣, 徐文娣, 王佳伟, 乔帅, 王惠冉. 苹果砧木‘青砧1号’叶片cDNA文库构建及MdMLO上游调控因子的筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(5): 933-946. |
| [10] | 高美娜, 孙明飞, 朱杰, 井俊丽, 李佳, 周莎莎, 梁博文, 徐继忠, 李中勇. 苹果砧木‘冀砧2号’绞缢、环割压条生根效果及过程中IAA含量的变化[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(5): 1063-1072. |
| [11] | 刘柚藓, 李国防, 檀鸣, 杨志昌, 周世伟, 霍文静, 张鹤, 孙建设, 邵建柱. 苹果MdTOPP13/28在腋芽萌发中的表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(4): 697-712. |
| [12] | 宁源生, 李欢, 宋建飞, 于婷婷, 韩梦圆, 彭璐琳, 贾竣淇, 张玮玮, 杨洪强. 苹果NCL家族基因与根系细胞钙离子浓度变化的关系[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(3): 475-484. |
| [13] | 于婷婷, 李欢, 宁源生, 宋建飞, 彭璐琳, 贾竣淇, 张玮玮, 杨洪强. 苹果GRAS全基因组鉴定及其对生长素的响应分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 397-409. |
| [14] | 韩晓蕾, 张彩霞, 刘 锴, 杨 安, 严家帝, 李武兴, 康立群, 丛佩华. 中熟苹果新品种‘中苹优蕾’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 1-2. |
| [15] | 韩晓蕾, 张彩霞, 刘 锴, 严家帝, 李武兴, 康立群, 丛佩华. 中熟苹果新品种‘苹优2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 1-2. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司