
园艺学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (8): 1697-1710.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0642
孙志娟2,*, 刘文杰1,*, 郑晓东1, 袭祥利1, 马长青1, 刘晓丽1, 王彩虹1, 田义轲1,**( )
)
收稿日期:2023-05-29
修回日期:2023-07-10
出版日期:2023-08-25
发布日期:2023-08-23
通讯作者:
作者简介:* 为共同第一作者
基金资助:
SUN Zhijuan2, LIU Wenjie1, ZHENG Xiaodong1, XI Xiangli1, MA Changqing1, LIU Xiaoli1, WANG Caihong1, TIAN Yike1,**( )
)
Received:2023-05-29
Revised:2023-07-10
Published:2023-08-25
Online:2023-08-23
摘要:
为探究外源褪黑素(melatonin)对盐碱胁迫下平邑甜茶(Malus hupehensis)幼苗生长的影响及其作用机制,以无融合生殖率达到94%的平邑甜茶幼苗为试材,设置3个处理:对照(Hoagland营养液)、盐碱胁迫[100 mmol · L-1 NaHCO3︰NaCl = 1︰1(摩尔比)的Hoagland营养液]、盐碱胁迫 + 褪黑素(0.1 mmol · L-1),15 d后测定幼苗鲜质量、干质量、叶绿素含量、光合速率、矿质元素含量、抗氧化酶活性、渗透物质含量、有机酸含量、内源激素含量以及相关基因的表达量。结果表明,外源褪黑素可以显著降低盐碱胁迫下平邑甜茶幼苗的萎蔫率,并有效提高了盐碱胁迫下植株的生物量和光合效率,同时提高了幼苗中可溶性糖、可溶性蛋白及脯氨酸的含量来缓解渗透胁迫。另外,褪黑素通过增加细胞内有机酸含量和提高AHA家族基因表达量,增强了植株的耐盐碱性;通过调节钠离子转运基因(MhCHX15和MhSOS1)和钾离子转运基因(MhSKOR、MhNHX1、MhNHX2和MhNHX4)的表达,提高细胞质中的钾钠比值以维持离子稳态;并通过提高过氧化物酶(POD)和过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性和调节抗氧化酶基因(MhGPX6、MhpoxN1和MhPER65)的表达,减少盐碱胁迫产生的氧化损伤。此外,外源褪黑素还可通过与赤霉素、生长素、细胞分裂素和茉莉酸甲酯协同作用共同应答盐碱胁迫。综上,盐碱胁迫 + 0.1 mmol · L-1褪黑素处理通过调节离子平衡、渗透物质、抗氧化酶活性并协同其他内源激素来缓解盐碱胁迫对平邑甜茶幼苗造成的损伤。
孙志娟, 刘文杰, 郑晓东, 袭祥利, 马长青, 刘晓丽, 王彩虹, 田义轲. 褪黑素对盐碱胁迫下平邑甜茶幼苗生长的影响及其机制[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1697-1710.
SUN Zhijuan, LIU Wenjie, ZHENG Xiaodong, XI Xiangli, MA Changqing, LIU Xiaoli, WANG Caihong, TIAN Yike. Effects and Functional Mechanism of Melatonin on the Growth of Malus hupehensis Seedlings Under Saline-Alkali Stress[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(8): 1697-1710.
| 基因名称 Gene name | 上游引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 下游引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| MhSKOR | CATCCTGACAACTGGTGGTATCG | AATGCCATTTGCCAATAACCT |
| MhNHX1 | TTCTGCGTGAACTTTAGACCCT | AAGACTGAGATTTCCTTTCAAGC |
| MhNHX2 | CCACATTGATTCCAGTATTGCTT | CTCTTGAACTCTCCGTCACATTG |
| MhNHX4 | ACGAAACTCCTTTACTATACAGCCT | TGATACCACAGATAAGTGAGCATAG |
| MhCHX15 | AGATTATCCGTATCCTCTAAGTCTGG | TGGTTCGGCCTATCGTGAAA |
| MhSOS1 | TACACTGTCGCTCTGCTCATCC | CCAGTCGTAAGGGAAAGTGAGC |
| MhGPX6 | TTCCGAGAGTAAATCAATCCACG | AGGCAAACTCTACAATCTCGTCA |
| MhpoxN1 | GCTCCTCCAAATCATTGTTACTG | AAGAAGGACAGAAGCATCACAA C |
| MhPER65 | GGCATTCTATTCCCATTCCCTT | GAGTTGGAAGCGATGAGGAGG |
| MhAHA1 | CCAGAGAAAACAAAAGAGAGTC | TTCACATTCACACCGAGATTG |
| MhAHA2 | AAAGTGTGAAGAAAGAGAAAATGC | AGTTCATTTGCTTGACATTCTTT |
| MhAHA8 | GGTCAAAAGTGTGTTGGTAAGCA | AAACCAAAATCCTCCAACAGC |
| MhActin | CTTCAATGTGCCTGCCATGTAT | AATTTCCCGTTCAGCAGTAGTG |
表1 qRT-PCR所用的引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences for qRT-PCR
| 基因名称 Gene name | 上游引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 下游引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| MhSKOR | CATCCTGACAACTGGTGGTATCG | AATGCCATTTGCCAATAACCT |
| MhNHX1 | TTCTGCGTGAACTTTAGACCCT | AAGACTGAGATTTCCTTTCAAGC |
| MhNHX2 | CCACATTGATTCCAGTATTGCTT | CTCTTGAACTCTCCGTCACATTG |
| MhNHX4 | ACGAAACTCCTTTACTATACAGCCT | TGATACCACAGATAAGTGAGCATAG |
| MhCHX15 | AGATTATCCGTATCCTCTAAGTCTGG | TGGTTCGGCCTATCGTGAAA |
| MhSOS1 | TACACTGTCGCTCTGCTCATCC | CCAGTCGTAAGGGAAAGTGAGC |
| MhGPX6 | TTCCGAGAGTAAATCAATCCACG | AGGCAAACTCTACAATCTCGTCA |
| MhpoxN1 | GCTCCTCCAAATCATTGTTACTG | AAGAAGGACAGAAGCATCACAA C |
| MhPER65 | GGCATTCTATTCCCATTCCCTT | GAGTTGGAAGCGATGAGGAGG |
| MhAHA1 | CCAGAGAAAACAAAAGAGAGTC | TTCACATTCACACCGAGATTG |
| MhAHA2 | AAAGTGTGAAGAAAGAGAAAATGC | AGTTCATTTGCTTGACATTCTTT |
| MhAHA8 | GGTCAAAAGTGTGTTGGTAAGCA | AAACCAAAATCCTCCAACAGC |
| MhActin | CTTCAATGTGCCTGCCATGTAT | AATTTCCCGTTCAGCAGTAGTG |

图1 外源褪黑素(MT)对盐碱(NaCl + NaHCO3)胁迫下平邑甜茶植株表型的影响
Fig. 1 Effects of exogenous melatonin(MT)on phenotypes of Malus hupehensis plants under(NaCl + NaHCO3)stress
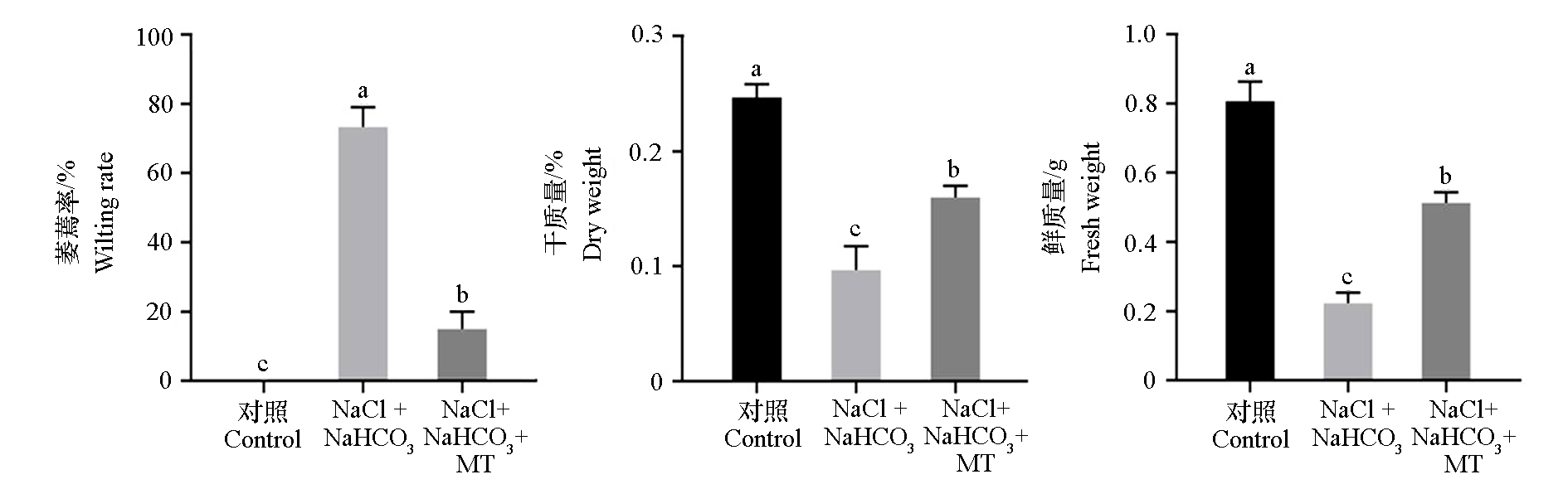
图2 外源褪黑素(MT)对盐碱(NaCl + NaHCO3)胁迫下平邑甜茶植株萎蔫率及生物量的影响 不同小写字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同。
Fig. 2 Effects of exogenous melatonin(MT)on wilting rate and biomass of Malus hupehensis plants under saline-alkali(NaCl + NaHCO3)stress Different lowercase letters represent significant differcences(P < 0.05). The same below.
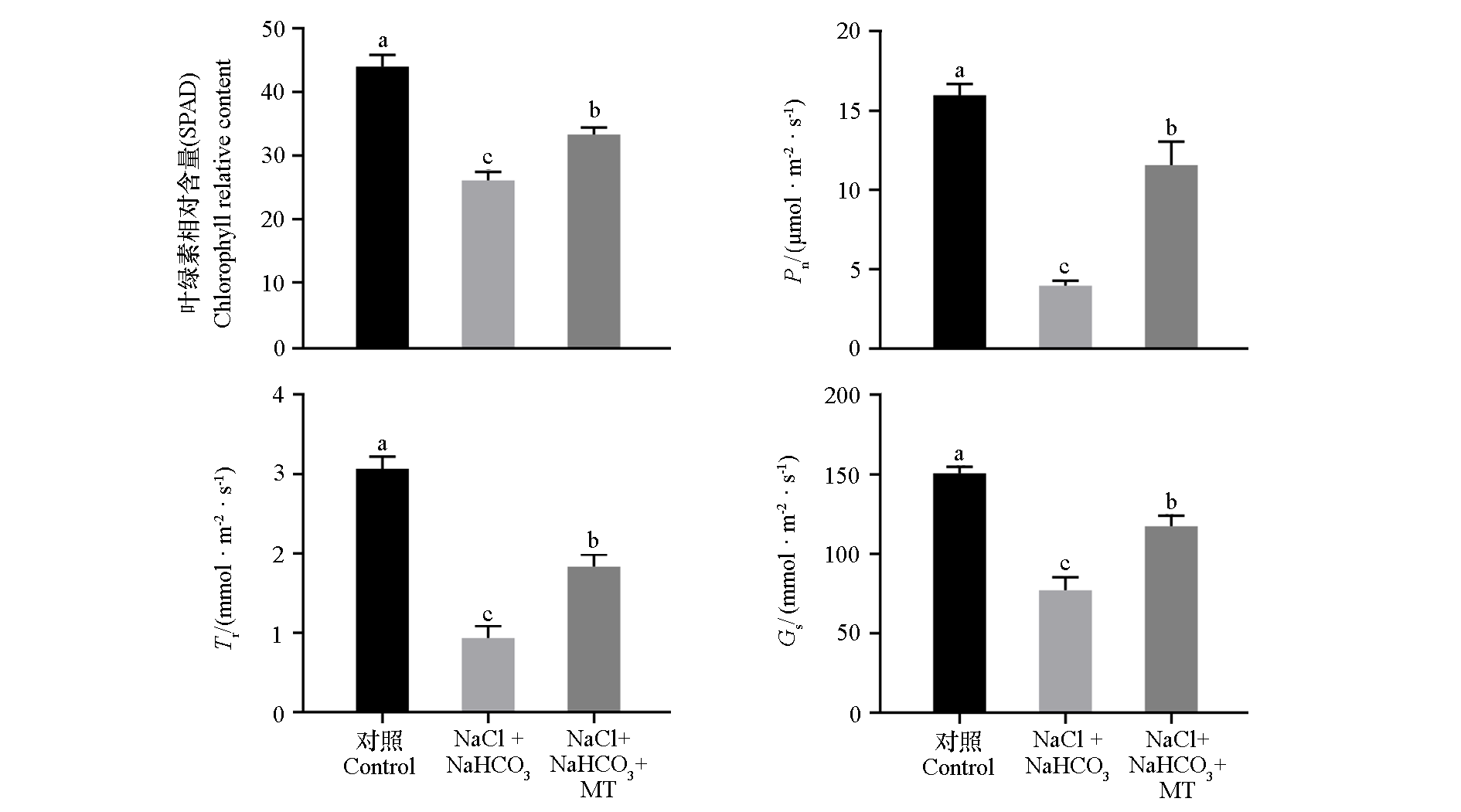
图3 外源褪黑素(MT)对盐碱(NaCl + NaHCO3)胁迫下平邑甜茶植株叶片叶绿素含量及光合指标的影响
Fig. 3 Effects of exogenous melatonin(MT)on chlorophyll content and photosynthetic indexes of Malus hupehensis leaves under saline-alkali(NaCl + NaHCO3)stress

图4 外源褪黑素(MT)对盐碱(NaCl + NaHCO3)胁迫下平邑甜茶植株体内矿质元素含量的影响
Fig. 4 Effects of exogenous melatonin(MT)on the content of mineral elements in Malus hupehensis plants under saline-alkali(NaCl + NaHCO3)stress

图5 外源褪黑素(MT)对盐碱(NaCl + NaHCO3)胁迫下平邑甜茶植株活性氧含量及抗氧化酶活性的影响
Fig. 5 Effects of exogenous melatonin(MT)on reactive oxygen content and antioxidant enzyme activities of Malus hupehensis plants under saline-alkali(NaCl + NaHCO3)stress
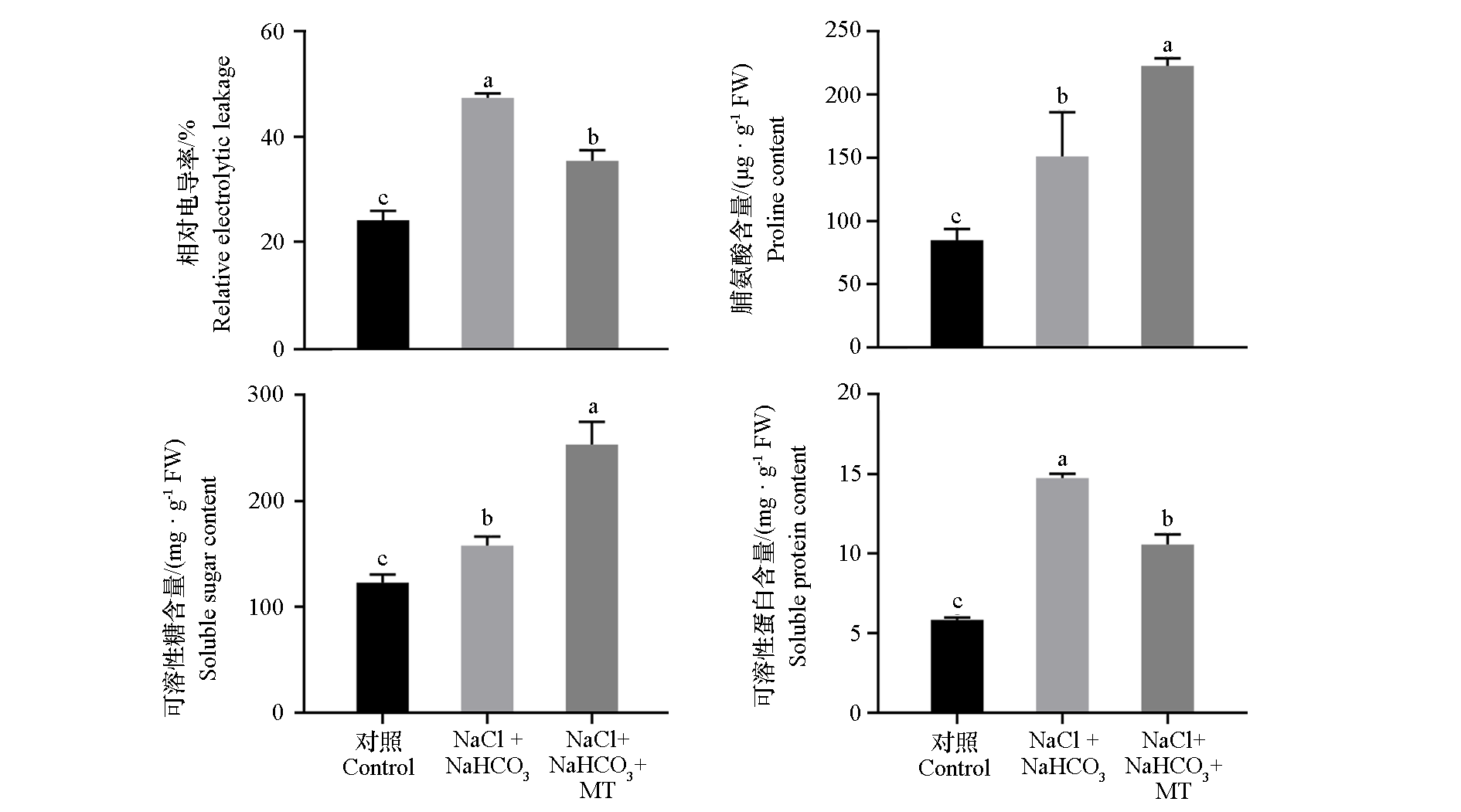
图6 外源褪黑素(MT)对盐碱(NaCl + NaHCO3)胁迫下平邑甜茶植株渗透物质含量的影响
Fig. 6 Effects of exogenous melatonin(MT)on osmotic substance content of Malus hupehensis plants under saline-alkali(NaCl + NaHCO3)stress
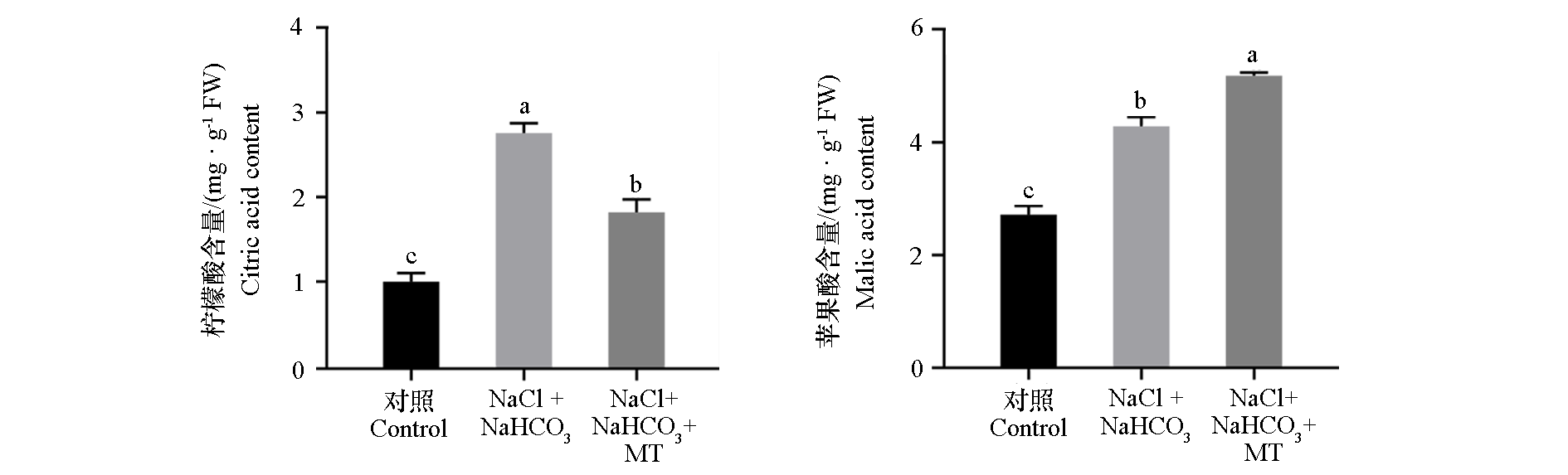
图7 外源褪黑素(MT)对盐碱(NaCl + NaHCO3)胁迫下平邑甜茶植株有机酸含量的影响
Fig. 7 Effects of exogenous melatonin(MT)on organic acid content of Malus hupehensis plants under saline-alkali(NaCl + NaHCO3)stress
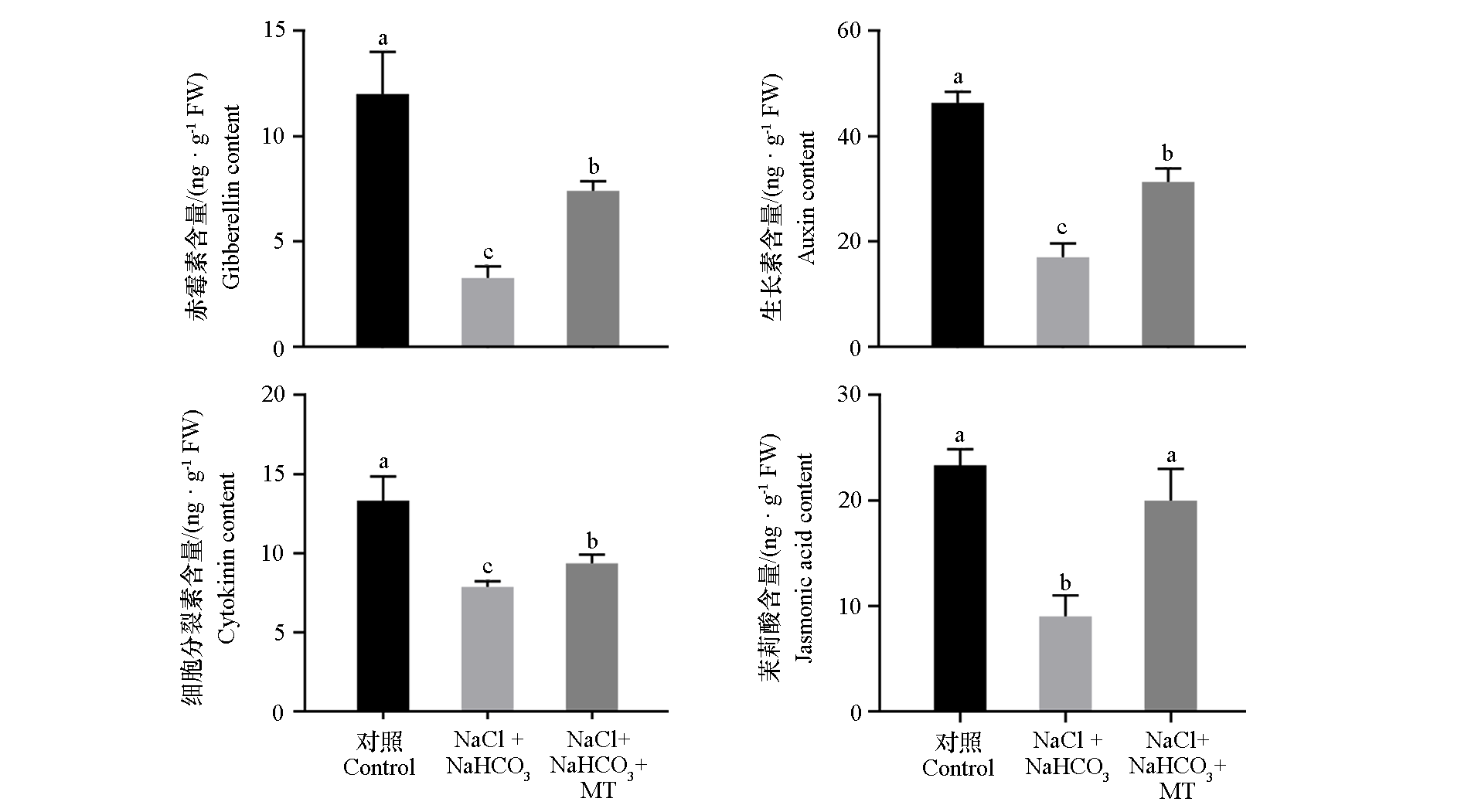
图8 外源褪黑素(MT)对盐碱(NaCl + NaHCO3)胁迫下平邑甜茶植株体内激素含量的影响
Fig. 8 Effects of exogenous melatonin(MT)on hormone content in Malus hupehensis plants under saline-alkali(NaCl + NaHCO3)stress
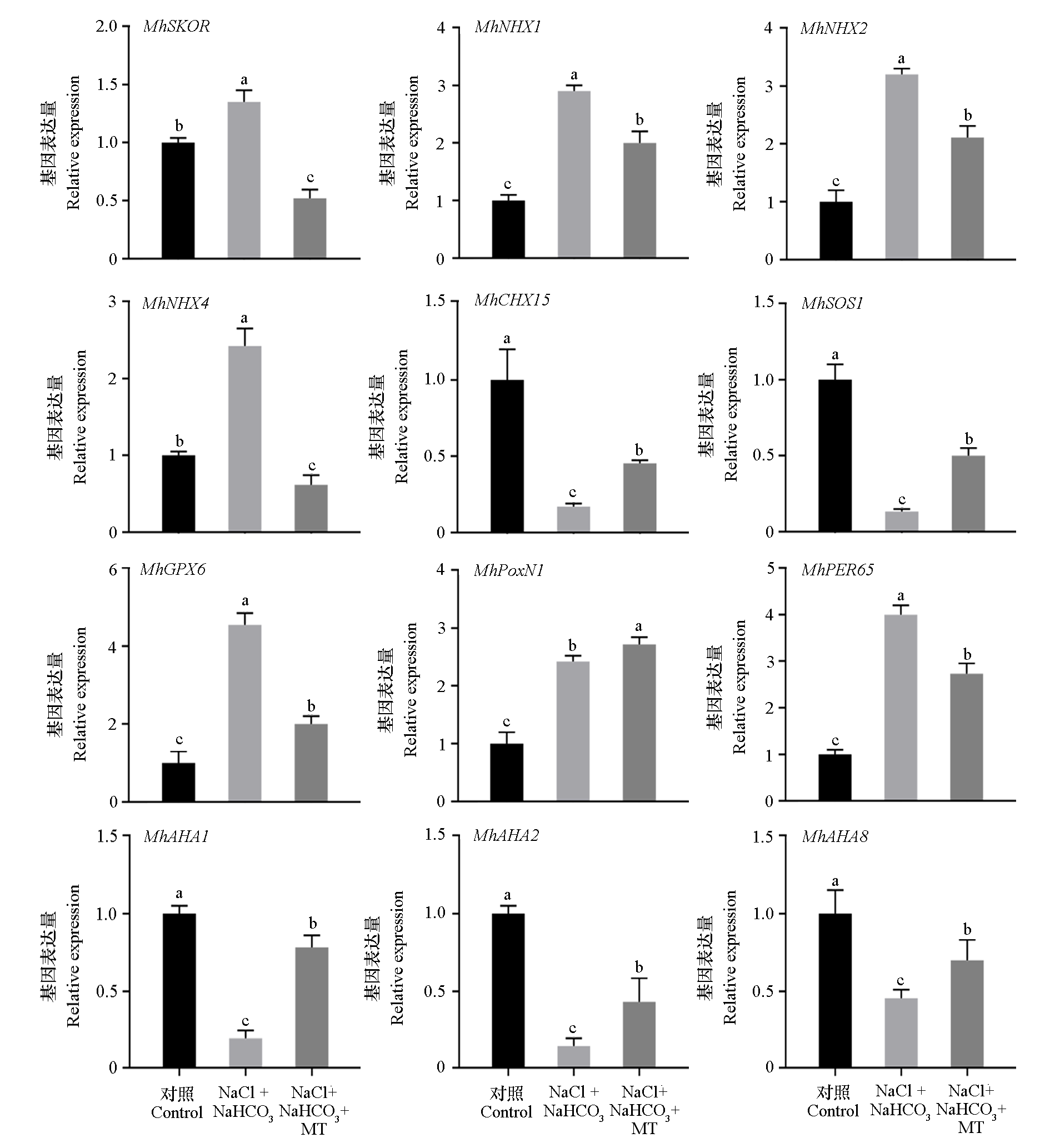
图9 外源褪黑素(MT)对平邑甜茶植株盐碱(NaCl + NaHCO3)胁迫应答基因表达的影响
Fig. 9 Effects of exogenous melatonin(MT)on gene expression of salt-alkali(NaCl + NaHCO3)stress response in Malus hupehensis plants
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
|
陈如男, 任春元, 李贺, 王华美, 张严文, 于高波. 2021. 外源褪黑素通过诱导SIRR基因表达调控番茄盐碱胁迫响应. 北方园艺,(10):7-14.
|
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.1111/ppl.2018.164.issue-3 URL |
| [4] |
|
|
段文静, 孟妍君, 江丹, 刘连涛, 张科, 张永江, 孙红春, 白志英, 李存东. 2022. 外源褪黑素对盐胁迫下棉花幼苗形态及抗氧化系统的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 30 (1):92-104.
|
|
| [5] |
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.667458 URL |
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2016.03.006 URL |
| [8] |
|
|
高倩, 卢楠. 2021. 盐碱地综合治理开发研究现状及展望. 南方农机, 52 (16):153-155.
|
|
| [9] |
|
|
霍宏亮, 王超, 杨祥, 曹玉芬, 田路明, 董星光, 张莹, 齐丹, 徐家玉, 刘超. 2021. 杜梨对盐碱胁迫的生理响应及耐盐碱性评价. 植物遗传资源学报, 23 (2):480-492.
|
|
| [10] |
|
|
焦德志, 赵泽龙. 2019. 盐碱胁迫对植物形态和生理生化影响及植物响应的研究进展. 江苏农业科学, 47 (20):1-4.
|
|
| [11] |
|
|
康益晨. 2021. 马铃薯响应碱性盐胁迫的生理及分子机制研究[博士论文]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学.
|
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2019.03.015 URL |
| [14] |
|
|
刘奕媺, 于洋, 方军. 2018. 盐碱胁迫及植物耐盐碱分子机制研究. 土壤与作物, 7 (2):201-211.
|
|
| [15] |
|
|
刘玉莲, 车飞, 王海, 陈佰鸿, 陈年来. 2016. 苹果果实中糖、酸和花青苷的组分及含量特征分析. 西北林学院学报, 31 (6):236-242.
|
|
| [16] |
|
|
毛恋, 芦建国, 江海燕. 2020. 植物响应盐碱迫的机制. 分子植物育种, 18 (10):3441-3448.
|
|
| [17] |
|
|
毛庆莲, 王胜. 2020. 国内盐碱地治理趋势探究浅析. 湖北农业科学, 59 (S1):302-306.
|
|
| [18] |
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2021.10.23 |
|
毛爽, 周万里, 杨帆, 狄小琳, 蔺吉祥, 杨青杰. 2021. 植物根系应答盐碱胁迫机理研究进展. 浙江农业学报, 33 (10):1991-2000.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2021.10.23 |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
|
沙广利, 郝玉金, 万述伟, 束怀瑞. 2015. 苹果砧木种类及应用进展. 落叶果树, 47 (3):2-6.
|
|
| [22] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110026 URL |
| [23] |
|
|
王佺珍, 刘倩, 高娅妮, 柳旭. 2017. 植物对盐碱胁迫的响应机制研究进展. 生态学报, 37 (16):5565-5577.
|
|
| [24] |
|
|
王晚霞, 高立杨, 张瑞, 赵婷, 张仲兴, 王双成, 王延秀. 2021. 2, 4-表油菜素内酯对盐碱胁迫下垂丝海棠光合及生理特性的影响. 果树学报, 38 (9):1479-1490.
|
|
| [25] |
|
|
王娟, 黄荣峰. 2015. 乙烯调控植物耐盐性的研究进展. 植物生理学报, 51 (10):1567-1572.
|
|
| [26] |
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2020.12.006 URL |
| [27] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0159 |
|
向妙莲, 吴帆, 李树成, 马巧利, 王印宝, 肖刘华, 陈金印, 陈明. 2022. 外源褪黑素调控活性氧代谢诱导梨果实抗采后黑斑病. 园艺学报, 49 (5):1102-1110
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0159 |
|
| [28] |
|
|
许盼云, 李春兰, 宋金迪, 王鑫, 程嘉宝, 吴玉霞, 何天明. 2017. 不同苹果砧木实生苗对盐碱复合胁迫的生理响应. 新疆农业科学, 58 (9):1694-1703.
|
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.07.015 URL |
| [30] |
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2022.04.003 URL |
| [31] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.18.00568 URL |
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
|
赵德英, 程存刚, 仇贵生, 董雅凤, 张彩霞, 李壮, 张怀江, 胡国君, 厉恩茂. 2021. 苹果高质量发展技术创新途径. 中国果树,(8):1-5.
|
|
| [34] |
|
|
赵海亮, 左璐, 马长恩, 白龙强, 胡晓辉, 侯雷平. 2021. 果实膨大期叶面喷施褪黑素对番茄品质的影响. 北方园艺,(17):15-21.
|
|
| [35] |
|
|
赵怀玉, 林鸿宣. 2020. 植物响应盐碱胁迫的分子机制. 土壤与作物, 9 (2):103-113.
|
|
| [36] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0496 |
|
赵雨晴, 陈涛, 袁明. 2021. 褪黑素在果实发育和采后保鲜中的应用. 园艺学报, 48 (6):1233-1249.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0496 |
|
| [37] |
|
|
赵占周. 2020. 土壤盐碱化对植物的影响及改良预防措施. 西北园艺(果树),(6):40-42.
|
|
| [38] |
doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03215-y |
| [39] |
doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.12.015 URL |
| [40] |
|
|
郑晓东, 袭祥利, 李玉琪, 孙志娟, 马长青, 韩明三, 李少旋, 田义轲, 王彩虹. 2022. 油菜素内酯对盐碱胁迫下平邑甜茶幼苗生长的影响及调控机理研究. 园艺学报, 49 (7):1401-1414.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0499 |
|
| [41] |
|
|
朱建峰, 崔振荣, 吴春红, 邓丞, 陈军华, 张华新. 2018. 我国盐碱地绿化研究进展与展望. 世界林业研究, 31 (4):70-75.
|
|
| [42] |
|
| [1] | 李少旋, 王芝云, 胡大刚, 朱 波, 韩明三, . 晚熟苹果新品种‘琴富 1 号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 1-2. |
| [2] | 孙燕霞, 唐 岩, 刘大亮, 赵玲玲, 张学勇, 刘学卿, Dorota Ewa Kruczynska, 程志娟, Sylwia Keller-Przybylkowicz, 宋来庆, . 早熟苹果新品种‘烟青玉’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 3-4. |
| [3] | 赵国栋, 贾林光, 陈东玫, 赵同生, 张新生, 张朝红, 李春敏, 付 友. 苹果新品种‘映红’ [J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 5-6. |
| [4] | 蔚 露, 牛自勉, 郭文龙, 林 琭, 李 全, 李志强, 王红宁, 李鸿雁 . 早熟苹果新品种‘夏露’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 7-8. |
| [5] | 王晓芳, 夏群, 栾日昇, 许莉, 尹承苗, 王艳芳, 陈学森, 毛志泉, 相昆. 万寿菊秸秆粉末处理对镰孢菌的抑制及苹果连作土壤施用效果[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(7): 1518-1534. |
| [6] | 王金鑫, 黄晶淼, 郝婕, 李学营, 冯建忠, 索相敏, 鄢新民. 晚熟苹果新品种‘冀苹5号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(7): 1601-1602. |
| [7] | 秦嗣军, 张阔, 齐边斌, 于波, 吕德国. 外源碳对苹果根区土壤活性有机碳及植株生长的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(6): 1295-1304. |
| [8] | 坎智勇, 张德辉, 李中兴, 余思思, 钱谦, 樊天乐, 李雪薇, 马锋旺, 管清美. 90个苹果品种耐寒性评价和全基因组关联分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(5): 921-932. |
| [9] | 张琨, 思彬彬, 周军, 任玉锋, 张欣, 徐文娣, 王佳伟, 乔帅, 王惠冉. 苹果砧木‘青砧1号’叶片cDNA文库构建及MdMLO上游调控因子的筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(5): 933-946. |
| [10] | 高美娜, 孙明飞, 朱杰, 井俊丽, 李佳, 周莎莎, 梁博文, 徐继忠, 李中勇. 苹果砧木‘冀砧2号’绞缢、环割压条生根效果及过程中IAA含量的变化[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(5): 1063-1072. |
| [11] | 刘柚藓, 李国防, 檀鸣, 杨志昌, 周世伟, 霍文静, 张鹤, 孙建设, 邵建柱. 苹果MdTOPP13/28在腋芽萌发中的表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(4): 697-712. |
| [12] | 宁源生, 李欢, 宋建飞, 于婷婷, 韩梦圆, 彭璐琳, 贾竣淇, 张玮玮, 杨洪强. 苹果NCL家族基因与根系细胞钙离子浓度变化的关系[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(3): 475-484. |
| [13] | 于婷婷, 李欢, 宁源生, 宋建飞, 彭璐琳, 贾竣淇, 张玮玮, 杨洪强. 苹果GRAS全基因组鉴定及其对生长素的响应分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 397-409. |
| [14] | 韩晓蕾, 张彩霞, 刘 锴, 杨 安, 严家帝, 李武兴, 康立群, 丛佩华. 中熟苹果新品种‘中苹优蕾’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 1-2. |
| [15] | 韩晓蕾, 张彩霞, 刘 锴, 严家帝, 李武兴, 康立群, 丛佩华. 中熟苹果新品种‘苹优2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 1-2. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司