
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (6): 1255-1268.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0226
• Genetic & Breeding·Germplasm Resources·Molecular Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
HE Weizhi1,2, LEI Weiqi1, GUO Xiangxin1, LI Ruilian1,3, CHEN Guanqun1,*( )
)
Received:2022-12-29
Revised:2023-05-05
Online:2023-06-25
Published:2023-06-27
Contact:
* (E-mail:CLC Number:
HE Weizhi, LEI Weiqi, GUO Xiangxin, LI Ruilian, CHEN Guanqun. Identification of the MYB Gene Family and Functional Analysis of Key Genes Related to Blue Flower Coloration in Agapanthus praecox[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(6): 1255-1268.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0226
| 基因名称 Gene name | 正向引物序列(5′-3′) Forward primer sequence | 反向引物序列(5′-3′) Reverse primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| ApActin | AACACCACCAGACTTATGT | GCCGTTGAACTTGATGAG |
| ApMYB4 | CTACTGGAACACGCACATCAA | CTCTCGTCGGTAGAATCCTCAT |
| ApMYB6 | AGTTGTCGGCTTCGTTGGA | TGTCTGTTCTTCCTGGTAGTCTT |
| ApMYB7 | GACCTATCCATTAGCCTTCCTTATC | CTGTTGTTCTTGTCGCTGTCA |
| ApMYB12 | GACCTCGACCAAGACTTGTTAC | ATCTAGCACCTTCTCCTCAACTT |
| ApMYB111 | GGCACGGTATCAGCGGTAT | TTCTCATGCTCGTCTCTTGTTG |
| ApMYB123 | CCTTATCATCCGACTCCACTCT | TTGCTGAGGTGACTGTTCCA |
| pHB-ApMYB4 | CTCTCTCTCAAGCTTGGATCCATGGGTAGGTCTCCATGTTG | CATACTAGTGAGCTCCTGCAGAGCATTATACCCATCCTGTA |
| pHB-ApMYB6 | CTCTCTCTCAAGCTTGGATCCATGGGTAGATCTCCTTGTTG | CATACTAGTGAGCTCCTGCAGCTTCATCTGAAAACTTCTAT |
| pHB-ApMYB7 | CTCTCTCTCAAGCTTGGATCCATGGGAAGGTCCCCATGTTG | CATACTAGTGAGCTCCTGCAGTATCCATCCTTCCTCCAACG |
| pHB-ApMYB12 | CTCTCTCTCAAGCTTGGATCCATGGGAAGGGCTCCATGTTG | CATACTAGTGAGCTCCTGCAGCAACACATCTGAAAGAAGCC |
| pHB-ApMYB111 | CTCTCTCTCAAGCTTGGATCCATGGGGAGAGTTCCATGTTG | CATACTAGTGAGCTCCTGCAGTAATTTGCACCCACTCTCCC |
| pHB-ApMYB123 | CTCTCTCTCAAGCTTGGATCCATGGGGAGAGCTCCATGCTG | CATACTAGTGAGCTCCTGCAGAATCAACAGAGGCTCTGCAG |
| NtPAL | ATTGAGGTCATCCGTTCTGC | ACCGTGTAACGCCTTGTTTC |
| Nt4CL | TCATTGACGAGGATGACGAG | TGGGATGGTTGAGAAGAAGG |
| NtCHS | TTGTTCGAGCTTGTCTCTGC | AGCCCAGGAACATCTTTGAG |
| NtCHI | GTCAGGCCATTGAAAAGCTC | CTAATCGTCAATGCCCCAAC |
| NtFLS | TTTGGCACTTGGTGTTGTGG | ACTTGACATCATACCAATGG |
| NtDFR | AACCAACAGTCAGGGGAATG | TTGGACATCGACAGTTCCAG |
| NtUFGT | ATGTTGAAGGGCTAAAAGAAAGAGC | CAAGTCCCAGCTGATACATATTCCC |
| NtGAPDH | GGTGTCCACAGACTTCGTGG | GACTCCTCACAGCAGCACCA |
Table 1 Primer list for PCR
| 基因名称 Gene name | 正向引物序列(5′-3′) Forward primer sequence | 反向引物序列(5′-3′) Reverse primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| ApActin | AACACCACCAGACTTATGT | GCCGTTGAACTTGATGAG |
| ApMYB4 | CTACTGGAACACGCACATCAA | CTCTCGTCGGTAGAATCCTCAT |
| ApMYB6 | AGTTGTCGGCTTCGTTGGA | TGTCTGTTCTTCCTGGTAGTCTT |
| ApMYB7 | GACCTATCCATTAGCCTTCCTTATC | CTGTTGTTCTTGTCGCTGTCA |
| ApMYB12 | GACCTCGACCAAGACTTGTTAC | ATCTAGCACCTTCTCCTCAACTT |
| ApMYB111 | GGCACGGTATCAGCGGTAT | TTCTCATGCTCGTCTCTTGTTG |
| ApMYB123 | CCTTATCATCCGACTCCACTCT | TTGCTGAGGTGACTGTTCCA |
| pHB-ApMYB4 | CTCTCTCTCAAGCTTGGATCCATGGGTAGGTCTCCATGTTG | CATACTAGTGAGCTCCTGCAGAGCATTATACCCATCCTGTA |
| pHB-ApMYB6 | CTCTCTCTCAAGCTTGGATCCATGGGTAGATCTCCTTGTTG | CATACTAGTGAGCTCCTGCAGCTTCATCTGAAAACTTCTAT |
| pHB-ApMYB7 | CTCTCTCTCAAGCTTGGATCCATGGGAAGGTCCCCATGTTG | CATACTAGTGAGCTCCTGCAGTATCCATCCTTCCTCCAACG |
| pHB-ApMYB12 | CTCTCTCTCAAGCTTGGATCCATGGGAAGGGCTCCATGTTG | CATACTAGTGAGCTCCTGCAGCAACACATCTGAAAGAAGCC |
| pHB-ApMYB111 | CTCTCTCTCAAGCTTGGATCCATGGGGAGAGTTCCATGTTG | CATACTAGTGAGCTCCTGCAGTAATTTGCACCCACTCTCCC |
| pHB-ApMYB123 | CTCTCTCTCAAGCTTGGATCCATGGGGAGAGCTCCATGCTG | CATACTAGTGAGCTCCTGCAGAATCAACAGAGGCTCTGCAG |
| NtPAL | ATTGAGGTCATCCGTTCTGC | ACCGTGTAACGCCTTGTTTC |
| Nt4CL | TCATTGACGAGGATGACGAG | TGGGATGGTTGAGAAGAAGG |
| NtCHS | TTGTTCGAGCTTGTCTCTGC | AGCCCAGGAACATCTTTGAG |
| NtCHI | GTCAGGCCATTGAAAAGCTC | CTAATCGTCAATGCCCCAAC |
| NtFLS | TTTGGCACTTGGTGTTGTGG | ACTTGACATCATACCAATGG |
| NtDFR | AACCAACAGTCAGGGGAATG | TTGGACATCGACAGTTCCAG |
| NtUFGT | ATGTTGAAGGGCTAAAAGAAAGAGC | CAAGTCCCAGCTGATACATATTCCC |
| NtGAPDH | GGTGTCCACAGACTTCGTGG | GACTCCTCACAGCAGCACCA |
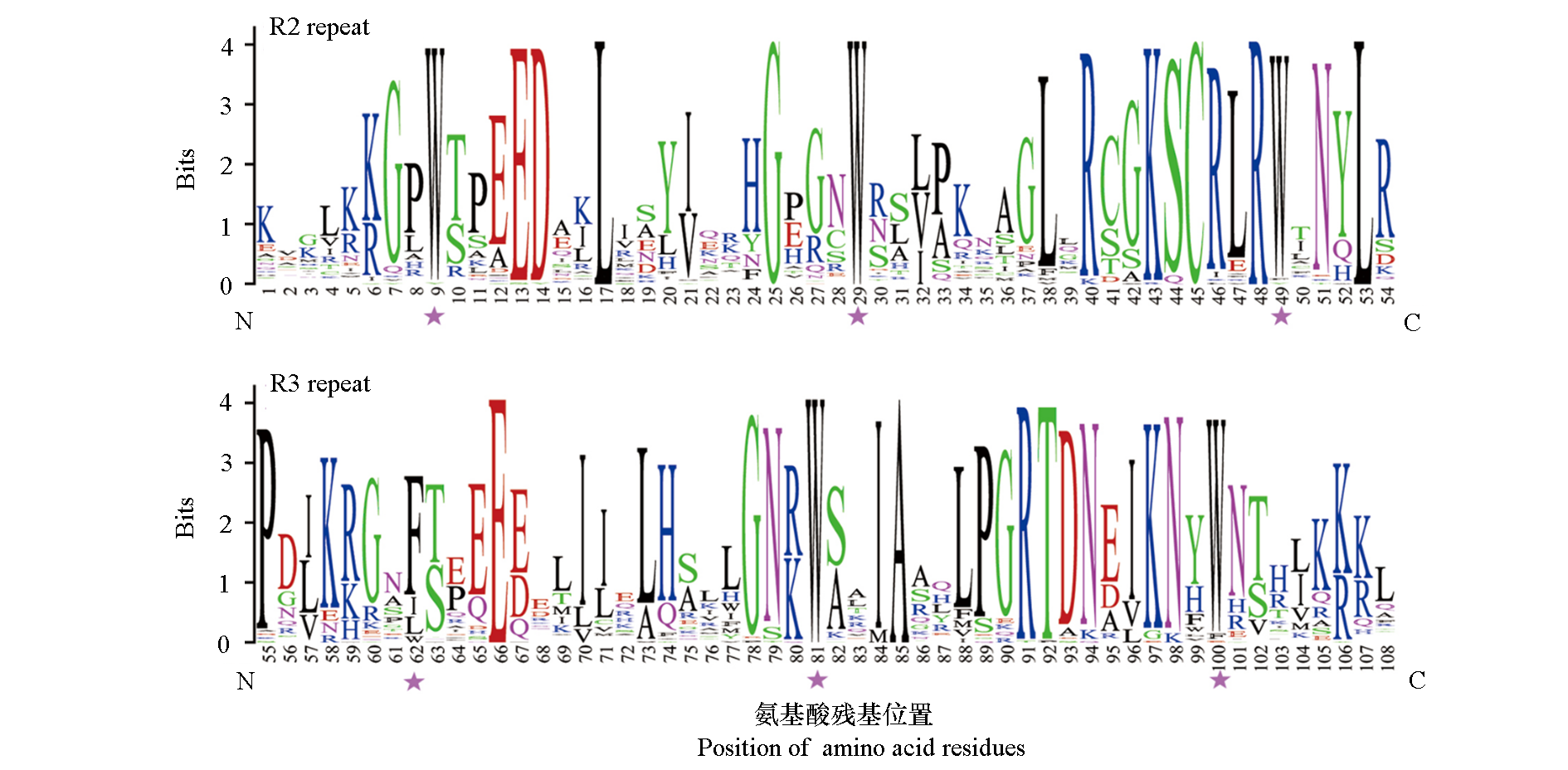
Fig. 2 Consensus sequence of R2R3-MYB domains in Agapanthus praecox The bit score of Y-axis indicated the conservation rate for each X-axis amino acid position in the sequence. Asterisks indicate the conserved residues Trp(W)in the MYB domain.
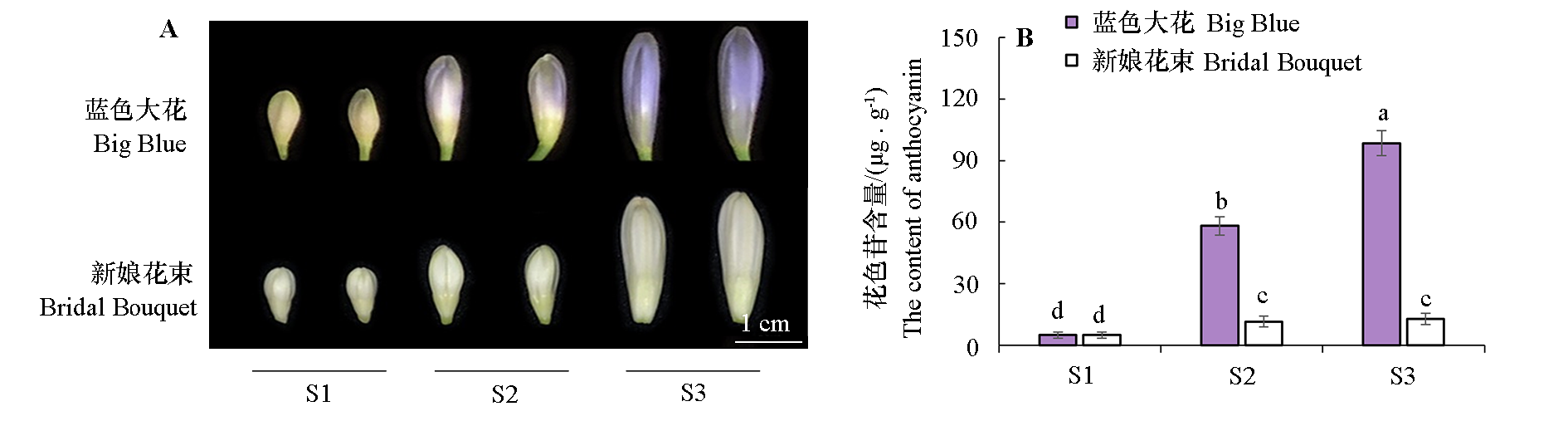
Fig. 3 The anthocyanin contents during flower development in blue-flowered‘Big Blue’and white-flowered‘Bridal Bouquet’ S1:Bud emergence period;S2:Bud elongation period;S3:Pre-opening period. The different lowercase letters respectively indicate the significant difference in the anthocyanin content(P < 0.05).

Fig. 4 Heat map of expression(A)and protein conserved motifs(B)of MYB genes related to flavonoid biosynthesis during flower coloration in blue-flowered‘Big Blue’and white-flowered‘Bridal Bouquet’ S1:Bud emergence period;S2:Bud elongation period;S3:Pre-opening period.

Fig. 6 Flower color phenotypes, flavonol and anthocyanin content in petal and leaf of ApMYB12-transgenic tobacco lines(7#,8#)and wild type ** represents the significant difference between wild-type and transgenic lines(P < 0.01).
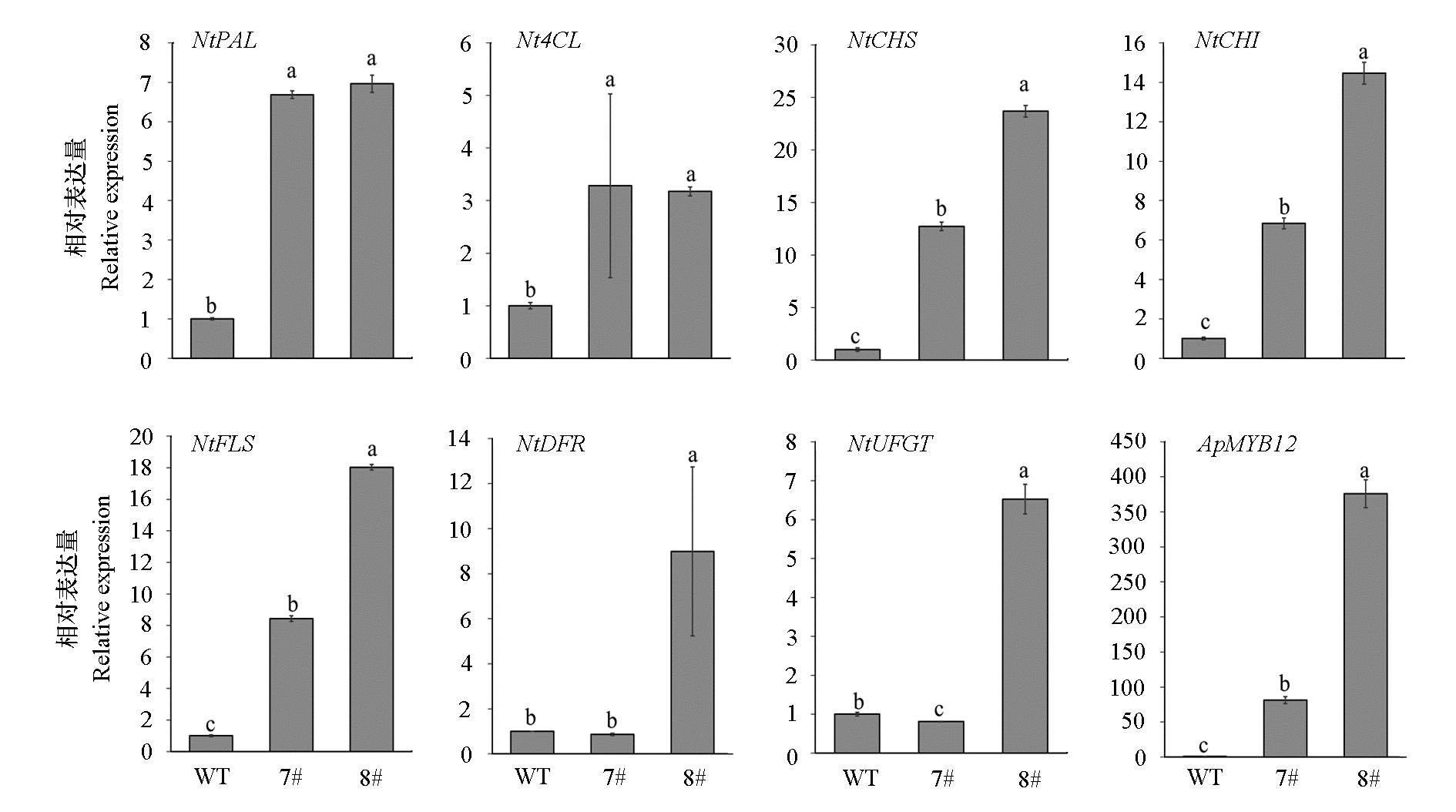
Fig. 8 The expression of key genes in the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway of of ApMYB12-transgenic tobacco lines(7#,8#)and wild type Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between wild-type and transgenic lines(P < 0.05).
| [1] |
Abe H, Urao T, Ito T, Seki M, Shinozaki K. 2003. Arabidopsis AtMYC2 (bHLH) and AtMYB2 (MYB) function as transcriptional activators in abscisic acid signaling. Plant Cell, 15 (1):63-78.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.006130 URL |
| [2] |
Bendahmane M, Dubois A, Raymond O, Bris M L. 2013. Genetics and genomics of flower initiation and development in roses. Journal of Experimental Botany, 64 (4):847-857.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/ers387 pmid: 23364936 |
| [3] |
Bloor S J, Falshaw R. 2000. Covalently linked anthocyanin-flavonol pigments from blue Agapanthus flowers. Phytochemistry, 53 (5):575-579.
pmid: 10724183 |
| [4] | Cao Y, Han Y, Li D, Lin Y, Cai Y. 2016. MYB transcription factors in Chinese pear(Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.):Genome-wide identification, classification, and expression profiling during fruit development. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7:577. |
| [5] |
Cao Y, Xie L, Ma Y, Ren C, Xing M, Fu Z, Wu X, Yin X, Xu C, Li X. 2019. PpMYB15 and PpMYBF 1 transcription factors are involved in regulating flavonol biosynthesis in peach fruit. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 67 (2):644-652.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b04810 URL |
| [6] |
Cba B, Srg A, Ap C, Pkta B. 2020. COP1 mediates light-dependent regulation of flavonol biosynthesis through HY5 in Arabidopsis. Plant Science, 303:110760.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2020.110760 URL |
| [7] |
Chen C J, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas H R, Frank M H, He Y H, Xia R. 2020a. TBtools:an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Molecular Plant, 13 (8):1194-1202.
doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009 URL |
| [8] |
Chen G, He W, Guo X, Pan J. 2021. Genome-wide identification, classification and expression analysis of the MYB transcription factor family in Petunia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22 (9):4838.
doi: 10.3390/ijms22094838 URL |
| [9] |
Chen G, Xu P, Pan J, Li Y, Zhou J, Kuang H, Lian H. 2020b. Inhibition of FvMYB 10 transcriptional activity promotes color loss in strawberry fruit. Plant Science, 298:110578.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2020.110578 URL |
| [10] |
Du H, Yang S S, Liang Z, Feng B R, Liu L, Huang Y B, Tang Y X. 2012. Genome-wide analysis of the MYB transcription factor superfamily in soybean. BMC Plant Biology, 12:106.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-12-106 pmid: 22776508 |
| [11] |
Dubos C, Stracke R, Grotewold E, Weisshaar B, Martin C, Lepiniec L. 2010. MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends in Plant Science, 15 (10):573-581.
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2010.06.005 URL |
| [12] |
Fan H, Cui M, Li N, Li X, Lin Y. 2020. Genome-wide identification and expression analyses of R2R3-MYB transcription factor genes from two orchid species. PeerJ, 8:e9781.
doi: 10.7717/peerj.9781 URL |
| [13] | Fornalé S, Lopez E, Salazar-Henao J E, Fernández-Nohales P, Rigau J, Caparros-Ruiz D. 2014. AtMYB7,a new player in the regulation of UV-sunscreens in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant & Cell Physiology, 55 (3):507-516. |
| [14] |
Gatica-Arias A, Farag M A, Stanke M, Matoušek J, Wessjohann L, Weber G. 2012. Flavonoid production in transgenic hop(Humulus lupulus L.) altered by PAP1/MYB75 from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Reports, 31 (1):111-119.
doi: 10.1007/s00299-011-1144-5 pmid: 21912858 |
| [15] |
Golz J F, Allen P J, Li S F, Parish R W, Jayawardana N U, Bacic A, Doblin M S. 2018. Layers of regulation - Insights into the role of transcription factors controlling mucilage production in the Arabidopsis seed coat. Plant Science, 272:179-192.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2018.04.021 URL |
| [16] |
Han Y, Yu J, Zhao T, Cheng T, Wang J, Yang W, Pan H, Zhang Q. 2019. Dissecting the genome-wide evolution and function of R2R3-MYB transcription factor family in Rosa chinensis. Genes, 10 (10):823.
doi: 10.3390/genes10100823 URL |
| [17] |
He Z, Zhang H, Gao S, Lercher M J, Chen W H, Hu S. 2016. Evolview v2:an online visualization and management tool for customized and annotated phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Research, 44 (W1):W236-W241.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw370 URL |
| [18] |
Hegvold A B, Gabrielsen O S. 1996. The importance of the linker connecting the repeats of the c-Myb oncoprotein may be due to a positioning function. Nucleic Acids Research, 24 (20):3990-3995.
pmid: 8918802 |
| [19] |
Jeff V, Cahid C, Eunseog Y, Chen J, Cazzonelli C I, Georg S. 2012. Transgene silencing and transgene-derived siRNA production in tobacco plants homozygous for an introduced AtMYB90 construct. PLoS ONE, 7 (2):e30141.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030141 URL |
| [20] |
Jiang C, Gu J, Chopra S, Gu X, Peterson T. 2004. Ordered origin of the typical two- and three-repeat Myb genes. Gene, 326:13-22.
pmid: 14729259 |
| [21] | Leighton F M. 1965. The genus Agapanthus L'Héritier. South African Journal of Botany, 4:1-50. |
| [22] |
Li H Y, Yue Y Z, Ding W J, Chen G W, Li L, Li Y L, Shi T T, Yang X L, Wang L G. 2020. Genome-wide identification, classification, and expression profiling reveals R2R3-MYB transcription factors related to monoterpenoid biosynthesis in Osmanthus fragrans. Genes, 11 (4):353.
doi: 10.3390/genes11040353 URL |
| [23] |
Li J, Liu H, Yang C, Wang J, Xu L. 2019. Genome-wide identification of MYB genes and expression analysis under different biotic and abiotic stresses in Helianthus annuus L. Industrial Crops and Products, 143:111924.
doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.111924 URL |
| [24] |
Li Maofu, Yang Yuan, Wang Hua, Fan Youwei, Sun Pei, Jin Wanmei. 2022. Analysis the function of R2R3 MYB transcription factor RhMYB113c on regulating anthocyanin synthesis in Rosa hybrida. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 49 (9):1957-1966. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0630 URL |
|
李茂福, 杨媛, 王华, 范又维, 孙佩, 金万梅. 2022. 月季中R2R3-MYB基因RhMYB113c调控花青素苷合成. 园艺学报, 49 (9):1957-1966.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0630 URL |
|
| [25] | Li Qing-yun, Tang Qian-wen, Chen Guan-qun, Shen Xiao-hui. 2023. Extraction, identification and physical-chemical stability of anthocyanins from two hydrangea varieties. Guihaia, 43 (4):765-776. (in Chinese) |
| 李清韵, 唐倩雯, 陈冠群, 申晓辉. 2023. 两个八仙花品种花色苷的提取、鉴定和理化稳定性. 广西植物, 43 (4):765-776. | |
| [26] | Li Xiang, Duan Jing-jing, Luo Xiao-ning, Zhang Yan-long, Niu Li-xin, Shi Qian-qian. 2019. Formation mechanism of different tree peony flower colors by anatomy and biochemistry. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 47 (3):38-43. (in Chinese) |
| 李想, 段晶晶, 罗小宁, 张延龙, 牛立新, 史倩倩. 2019. 依据理化性质分析牡丹花色形成的影响因素. 东北林业大学学报, 47 (3):38-43. | |
| [27] |
Li Z, Peng R, Tian Y, Han H, Xu J, Yao Q. 2016. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the MYB transcription factor superfamily in Solanum lycopersicum. Plant Cell Physiology, 57 (8):1657-1677.
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcw091 URL |
| [28] |
Mori S, Otani M, Kobayashi H, Nakano M. 2014. Isolation and characterization of the dihydroflavonol 4-reductase gene in the monocotyledonous ornamental Agapanthus praecox ssp. orientalis(Leighton)Leighton. Scientia Horticulturae, 166:24-30.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2013.12.009 URL |
| [29] |
Nemie-Feyissa D, Heidari B, Blaise M, Lillo C. 2015. Analysis of interactions between heterologously produced bHLH and MYB proteins that regulate anthocyanin biosynthesis:quantitative interaction kinetics by Microscale Thermophoresis. Phytochemistry, 111:21-26.
doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2015.01.004 pmid: 25659750 |
| [30] | Nozawa M, Kawahara Y, Nei M. 2007. Genomic drift and copy number variation of sensory receptor genes in humans. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104 (51):20421-20426. |
| [31] |
Ogata K, Morikawa S, Nakamura H, Sekikawa A, Inoue T, Kanai H, Sarai A, Ishii S, Nishimura Y. 1994. Solution structure of a specific DNA complex of the Myb DNA-binding domain with cooperative recognition helices. Cell, 79 (4):639-648.
doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90549-5 pmid: 7954830 |
| [32] |
Paz-Ares J, Ghosal D, Wienand U, Peterson P A, Saedler H. 1987. The regulatory c1 locus of Zea mays encodes a protein with homology to MYB proto-oncogene products and with structural similarities to transcriptional activators. The EMBO Journal, 6 (12):3553-3558.
doi: 10.1002/embj.1987.6.issue-12 URL |
| [33] |
Rosinski J A, Atchley W R. 1998. Molecular evolution of the Myb family of transcription factors:evidence for polyphyletic origin. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 46 (1):74-83.
doi: 10.1007/pl00006285 pmid: 9419227 |
| [34] |
Stracke R, Ishihara H, Huep G, Barsch A, Mehrtens F, Niehaus K, Weisshaar B. 2007. Differential regulation of closely related R2R3-MYB transcription factors controls flavonol accumulation in different parts of the Arabidopsis thaliana seedling. Plant Journal, 50 (4):660-677.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03078.x pmid: 17419845 |
| [35] |
Stracke R, Werber M, Weisshaar B. 2001. The R2R3-MYB gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 4 (5):447-456.
doi: 10.1016/s1369-5266(00)00199-0 pmid: 11597504 |
| [36] |
Wang L, Albert N W, Zhang H, Arathoon S, Boase M R, Ngo H, Schwinn K E, Davies K M, Lewis D H. 2014. Temporal and spatial regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis provide diverse flower colour intensities and patterning in Cymbidium orchid. Planta, 240 (5):983-1002.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-014-2152-9 pmid: 25183255 |
| [37] |
Wang X, Niu Y, Zheng Y. 2021. Multiple functions of MYB transcription factors in abiotic stress responses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22 (11):6125.
doi: 10.3390/ijms22116125 URL |
| [38] |
Wang X C, Wu J, Guan M L, Zhao C H, Geng P, Zhao Q. 2020. Arabidopsis MYB 4 plays dual roles in flavonoid biosynthesis. The Plant Journal, 101 (3):637-652.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.v101.3 URL |
| [39] |
Xu Q, He J, Dong J, Hou X, Zhang X. 2018. Genomic survey and expression profiling of the MYB gene family in watermelon. Horticultural Plant Journal, 4 (1):1-15.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2017.12.001 URL |
| [40] |
Yabuya T, Nakamura M, Iwashina T, Yamaguchi M, Takehara T. 1997. Anthocyanin-flavone copigmentation in bluish purple flowers of Japanese garden iris(Iris ensata Thunb.). Euphytica, 98:163-167.
doi: 10.1023/A:1003152813333 URL |
| [41] |
Ye Zimao, Shen Wanxia, Liu Mengyu, Wang Tong, Zhang Xiaonan, Yu Xin, Liu Xiaofeng, Zhao Xiaochun. 2023. Effect of R2R3-MYB transcription factor CitMYB 21 on flavonoids biosynthesis in citrus. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 50 (2):250-264. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-1188 |
|
叶子茂, 申晚霞, 刘梦雨, 王彤, 张晓楠, 余歆, 刘小丰, 赵晓春. 2023. R2R3-MYB转录因子CitMYB21对柑橘类黄酮生物合成的影响. 园艺学报, 50 (2):250-264.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-1188 URL |
|
| [42] | Zhang Bao-zhi. 2013. Study on the composition of anthocyanins and physiological characteristics of flowering process in Jiangnan Peony[M. D. Dissertation]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University. (in Chinese) |
| 张宝智. 2013. 江南牡丹花色素组成与开花过程生理特征研究[硕士论文]. 上海: 上海交通大学. | |
| [43] | Zhang Ning, Wang Di. 2004. Study on the efficient genetic transformation system of tobacco mediated by Agrobacterium. Gansu Agricultural Science and Technology,(9):11-13. (in Chinese) |
| 张宁, 王蒂. 2004. 农杆菌介导的烟草高效遗传转化体系研究. 甘肃农业科技,(9):11-13. | |
| [44] |
Zhou M, Zhang K, Sun Z, Yan M, Wu Y. 2017. LNK1 and LNK 2 corepressors interact with the MYB3 transcription factor in phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. Plant Physiology, 174 (3):1348-1358.
doi: 10.1104/pp.17.00160 URL |
| [1] | WANG Tonghuan, WU Yuxin, WU Yiyuan, LI Xinxin, LIU Mengyang, YANG Lianlian, LI Jiapeng, ZHANG Zhongshan, CAO Fang, ZHONG Xueting, WANG Zhanqi. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the GRAS Gene Family in Response to Cold Stress in Chrysanthemum nankingense [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(4): 815-830. |
| [2] | ZHENG Jiarui, YANG Xiaoyan, YE Jiabao, LIAO Yongling, XU Feng. Advances in the Functional Studies of MYC2 Transcription Factor in Plants [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(4): 896-908. |
| [3] | LIU Yunuo, CAO Ya, WANG Shuai, DU Meixia, ZHENG Lin, CHEN Shanchun, ZOU Xiuping. Expression Analysis of CsMYB41 and CsMYB63 Genes in Response to Citrus Canker [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(3): 495-507. |
| [4] | YE Zimao, SHEN Wanxia, LIU Mengyu, WANG Tong, ZHANG Xiaonan, YU Xin, LIU Xiaofeng, ZHAO Xiaochun. Effect of R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor CitMYB21 on Flavonoids Biosynthesis in Citrus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 250-264. |
| [5] | SONG Yanhong, CHEN Yaduo, ZHANG Xiaoyu, SONG Pan, LIU Lifeng, LI Gang, ZHAO Xia, ZHOU Houcheng. The Transcription Factor FvbHLH130 Activates Flowering in Fragaria vesca [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 295-306. |
| [6] | HAN Rui, ZHONG Xionghui, CHEN Denghui, CUI Jian, YUE Xiangqing, XIE Jianming, KANG Jungen. Cloning and Functional Analysis of BobHLH34 Gene in Cabbage that Interacts with XopR from Xanthomonas [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 319-330. |
| [7] | TIAN Mingkang, XU Zhixiang, LIU Xiuqun, SUI Shunzhao, LI Mingyang, LI Zhineng. Identification of the AP2 Subfamily Transcription Factors in Chimonanthus praecox and the Functional Study of CpAP2-L11 [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 382-396. |
| [8] | LIN Haijiao, LIANG Yuchen, LI Ling, MA Jun, ZHANG Lu, LAN Zhenying, YUAN Zening. Exploration and Regulation Network Analysis of CBF Pathway Related Cold Tolerance Genes in Lavandula angustifolia [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(1): 131-144. |
| [9] | JIA Xin, ZENG Zhen, CHEN Yue, FENG Hui, LÜ Yingmin, ZHAO Shiwei. Cloning and Expression Analysis of RcDREB2A Gene in Rosa chinensis‘Old Blush’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(9): 1945-1956. |
| [10] | XU Haifeng, WANG Zhongtang, CHEN Xin, LIU Zhiguo, WANG Lihu, LIU Ping, LIU Mengjun, ZHANG Qiong. The Analyses of Target Metabolomics in Flavonoid and Its Potential MYB Regulation Factors During Coloring Period of Winter Jujube [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1761-1771. |
| [11] | QIAN Jieyu, JIANG Lingli, ZHENG Gang, CHEN Jiahong, LAI Wuhao, XU Menghan, FU Jianxin, ZHANG Chao. Identification and Expression Analysis of MYB Transcription Factors Regulating the Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Zinnia elegans and Function Research of ZeMYB9 [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1505-1518. |
| [12] | CHEN Daozong, LIU Yi, SHEN Wenjie, ZHU Bo, TAN Chen. Identification and Analysis of PAP1/2 Homologous Genes in Brassica rapa,B. oleracea and B. napus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1301-1312. |
| [13] | WANG Yan, SUN Zheng, FENG Shan, YUAN Xinyi, ZHONG Linlin, ZENG Yunliu, FU Xiaopeng, CHENG Yunjiang, Bao Manzhu, ZHANG Fan. The Negative Regulation of DcERF-1 on Senescence of Cut Carnation [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1313-1326. |
| [14] | LI Chunhong, WANG Kaituo, LEI Changyi, XU Feng, JI Nana, JIANG Yongbo. Identification of TGA Gene Family in Peach and Analysis of Expression Mode Involved in a BABA-Induced Disease Resistance [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(2): 265-280. |
| [15] | CHEN Sijia, WANG Huan, LI Ruirui, WANG Zhuoyi, LUO Jing, WANG Caiyun. Characterization of CmMYC2 in Formation of Green Color in Ray Florets of Chrysanthemum [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(11): 2377-2387. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd