
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (2): 382-396.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-1114
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
TIAN Mingkang1, XU Zhixiang1, LIU Xiuqun2, SUI Shunzhao1, LI Mingyang1, LI Zhineng1,*( )
)
Received:2022-05-19
Revised:2022-11-05
Online:2023-02-25
Published:2023-03-06
Contact:
*(E-mail:znli@swu.edu.cn)
CLC Number:
TIAN Mingkang, XU Zhixiang, LIU Xiuqun, SUI Shunzhao, LI Mingyang, LI Zhineng. Identification of the AP2 Subfamily Transcription Factors in Chimonanthus praecox and the Functional Study of CpAP2-L11 [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 382-396.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-1114
| 用途 Usage | 引物名称 Primer name | 序列(5′-3′) Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| CpAP2-L11基因克隆引物 CpAP2-L11 gene cloning primer | CpAP2-L11-F | AACAAATCGGACGGTTCAAACCACT |
| CpAP2-L11-R | GAAAATCAAAAACCGATCTCAGCCGG | |
| 表达载体构建引物 Expression vector construction primer | eCpAP2-L11-F | CGGGGTACCATGGGGAAACCATCACAGAAG |
| eCpAP2-L11-R | ACGCGTCGACTTACTGTCCATCCCAGTCGGC | |
| 实时荧光定量PCR qRT-PCR primer | qCpAP2-L11-F | TCCCGACCTTAACGTCTCGTCAGAG |
| qCpAP2-L11-R | GCAGCGGGGAGTTTTGTCGGATTCT | |
| 蜡梅内参基因实时荧光定量PCR qRT-PCR primer of reference gene in | CpActin-F | GTTATGGTTGGGATGGGACAGAAAG |
| CpActin-R | GGGCTTCAGTAAGGAAACAGGA | |
| Chimonanthus praecox | CpTublin-F | TAGTGACAAGACAGTAGGTGGAGGT |
| CpTublin-R | GTAGGTTCCAGTCCTCACTTCATC | |
| 拟南芥内参基因及内源基因实时荧光定量PCR qRT-PCR primer of reference and endogenous genes in Arabidopsis thaliana | AtActin-F | CTTCGTCTTCCACTTCAG |
| AtActin-R | ATCATACCAGTCTCAACAC | |
| AtLFY-F | AGACGGCTGCTTTTGGGATG | |
| AtLFY-R | TATTCCCCGCCGCATCAGTC | |
| AtFT -F | GATTGGTGGAGAAGACCTCAGGAAC | |
| AtFT -R | GCAGCCACTCTCCCTCTGACAAT | |
| AtAP1 -F | TAGGGCTCAACAGGAGCAGT | |
| AtAP1 -R | CAGCCAAGGTTGCAGTTGTA | |
| AtSOC1-F | AATTCGCCAGCTCCAATATG | |
| AtSOC1-R | CCTCGATTGAGCATGTTCCT |
Table 1 Primers used in this study
| 用途 Usage | 引物名称 Primer name | 序列(5′-3′) Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| CpAP2-L11基因克隆引物 CpAP2-L11 gene cloning primer | CpAP2-L11-F | AACAAATCGGACGGTTCAAACCACT |
| CpAP2-L11-R | GAAAATCAAAAACCGATCTCAGCCGG | |
| 表达载体构建引物 Expression vector construction primer | eCpAP2-L11-F | CGGGGTACCATGGGGAAACCATCACAGAAG |
| eCpAP2-L11-R | ACGCGTCGACTTACTGTCCATCCCAGTCGGC | |
| 实时荧光定量PCR qRT-PCR primer | qCpAP2-L11-F | TCCCGACCTTAACGTCTCGTCAGAG |
| qCpAP2-L11-R | GCAGCGGGGAGTTTTGTCGGATTCT | |
| 蜡梅内参基因实时荧光定量PCR qRT-PCR primer of reference gene in | CpActin-F | GTTATGGTTGGGATGGGACAGAAAG |
| CpActin-R | GGGCTTCAGTAAGGAAACAGGA | |
| Chimonanthus praecox | CpTublin-F | TAGTGACAAGACAGTAGGTGGAGGT |
| CpTublin-R | GTAGGTTCCAGTCCTCACTTCATC | |
| 拟南芥内参基因及内源基因实时荧光定量PCR qRT-PCR primer of reference and endogenous genes in Arabidopsis thaliana | AtActin-F | CTTCGTCTTCCACTTCAG |
| AtActin-R | ATCATACCAGTCTCAACAC | |
| AtLFY-F | AGACGGCTGCTTTTGGGATG | |
| AtLFY-R | TATTCCCCGCCGCATCAGTC | |
| AtFT -F | GATTGGTGGAGAAGACCTCAGGAAC | |
| AtFT -R | GCAGCCACTCTCCCTCTGACAAT | |
| AtAP1 -F | TAGGGCTCAACAGGAGCAGT | |
| AtAP1 -R | CAGCCAAGGTTGCAGTTGTA | |
| AtSOC1-F | AATTCGCCAGCTCCAATATG | |
| AtSOC1-R | CCTCGATTGAGCATGTTCCT |
| 名称Name | 框Scaffold | 位置Position | 氨基酸数Amino acids | 分子质量/kD Molecular weigh | 理论等电点pI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CpAP2-L1 | 8 | 633 532 ~ 638 961 | 593 | 65.68 | 6.27 |
| CpAP2-L2 | 12 | 6 666 416 ~ 6 670 043 | 501 | 55.82 | 6.29 |
| CpAP2-L3 | 18 | 2 386 489 ~ 2 389 495 | 516 | 57.15 | 6.06 |
| CpAP2-L4 | 18 | 4 068 635 ~ 4 073 270 | 650 | 71.47 | 7.14 |
| CpAP2-L5 | 22 | 197 714 ~ 200 051 | 389 | 43.87 | 7.12 |
| CpAP2-L6 | 26 | 6 547 145 ~ 6 551 504 | 447 | 49.63 | 5.88 |
| CpAP2-L7 | 32 | 2 029 444 ~ 2 034 037 | 643 | 71.22 | 6.22 |
| CpAP2-L8 | 70 | 2 623 638 ~ 2 627 212 | 479 | 54.38 | 6.17 |
| CpAP2-L9 | 72 | 5 070 756 ~ 5 074 288 | 460 | 50.50 | 7.63 |
| CpAP2-L10 | 86 | 4 575 244 ~ 4 577 540 | 394 | 44.47 | 6.62 |
| CpAP2-L11 | 92 | 926 637 ~ 932 737 | 345 | 38.67 | 6.11 |
| CpAP2-L12 | 120 | 4 203 257 ~ 4 209 225 | 650 | 71.21 | 6.32 |
| CpAP2-L13 | 122 | 2 412 620 ~ 2 417 460 | 721 | 78.19 | 6.06 |
| CpAP2-L14 | 140 | 668 231 ~ 673 284 | 403 | 45.23 | 8.38 |
| CpAP2-L15 | 153 | 849 837 ~ 855 009 | 686 | 75.31 | 6.02 |
| CpAP2-L16 | 156 | 1 808 018 ~ 1 817 462 | 472 | 52.60 | 6.61 |
| CpAP2-L17 | 243 | 654 864 ~ 688 642 | 356 | 40.11 | 7.67 |
| CpAP2-L18 | 463 | 3 517 149 ~ 3 524 013 | 496 | 54.80 | 6.03 |
| CpAP2-L19 | 742 | 586 727 ~ 591 191 | 396 | 43.87 | 5.51 |
| CpAP2-L20 | 752 | 2 116 052 ~ 2 120 180 | 477 | 51.37 | 8.07 |
Table 2 Basic information of the AP2 subfamily members in Chimonanthus praecox
| 名称Name | 框Scaffold | 位置Position | 氨基酸数Amino acids | 分子质量/kD Molecular weigh | 理论等电点pI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CpAP2-L1 | 8 | 633 532 ~ 638 961 | 593 | 65.68 | 6.27 |
| CpAP2-L2 | 12 | 6 666 416 ~ 6 670 043 | 501 | 55.82 | 6.29 |
| CpAP2-L3 | 18 | 2 386 489 ~ 2 389 495 | 516 | 57.15 | 6.06 |
| CpAP2-L4 | 18 | 4 068 635 ~ 4 073 270 | 650 | 71.47 | 7.14 |
| CpAP2-L5 | 22 | 197 714 ~ 200 051 | 389 | 43.87 | 7.12 |
| CpAP2-L6 | 26 | 6 547 145 ~ 6 551 504 | 447 | 49.63 | 5.88 |
| CpAP2-L7 | 32 | 2 029 444 ~ 2 034 037 | 643 | 71.22 | 6.22 |
| CpAP2-L8 | 70 | 2 623 638 ~ 2 627 212 | 479 | 54.38 | 6.17 |
| CpAP2-L9 | 72 | 5 070 756 ~ 5 074 288 | 460 | 50.50 | 7.63 |
| CpAP2-L10 | 86 | 4 575 244 ~ 4 577 540 | 394 | 44.47 | 6.62 |
| CpAP2-L11 | 92 | 926 637 ~ 932 737 | 345 | 38.67 | 6.11 |
| CpAP2-L12 | 120 | 4 203 257 ~ 4 209 225 | 650 | 71.21 | 6.32 |
| CpAP2-L13 | 122 | 2 412 620 ~ 2 417 460 | 721 | 78.19 | 6.06 |
| CpAP2-L14 | 140 | 668 231 ~ 673 284 | 403 | 45.23 | 8.38 |
| CpAP2-L15 | 153 | 849 837 ~ 855 009 | 686 | 75.31 | 6.02 |
| CpAP2-L16 | 156 | 1 808 018 ~ 1 817 462 | 472 | 52.60 | 6.61 |
| CpAP2-L17 | 243 | 654 864 ~ 688 642 | 356 | 40.11 | 7.67 |
| CpAP2-L18 | 463 | 3 517 149 ~ 3 524 013 | 496 | 54.80 | 6.03 |
| CpAP2-L19 | 742 | 586 727 ~ 591 191 | 396 | 43.87 | 5.51 |
| CpAP2-L20 | 752 | 2 116 052 ~ 2 120 180 | 477 | 51.37 | 8.07 |
| 基因1 Gene 1 | 基因2 Gene 2 | 非同义 替换率Ka | 同义 替换率Ks | Ka/Ks | 选择类型 Selection type | 复制类型 Duplication type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CpAP2-L1 | CpAP2-L11 | 0.59 | NaN | NaN | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L3 | CpAP2-L4 | 0.78 | NaN | NaN | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L3 | CpAP2-L8 | 0.20 | 0.66 | 0.30 | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L3 | CpAP2-L11 | 0.66 | NaN | NaN | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L4 | CpAP2-L7 | 0.19 | 0.82 | 0.24 | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L4 | CpAP2-L1 | 0.18 | 1.02 | 0.17 | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L6 | CpAP2-L11 | 0.67 | NaN | NaN | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L8 | CpAP2-L11 | 0.66 | NaN | NaN | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L12 | CpAP2-L3 | 0.72 | NaN | NaN | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L12 | CpAP2-L4 | 0.51 | 2.37 | 0.22 | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L12 | CpAP2-L8 | 0.66 | NaN | NaN | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L12 | CpAP2-L11 | 0.51 | NaN | NaN | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L14 | CpAP2-L10 | 0.16 | 0.73 | 0.22 | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L14 | CpAP2-L11 | 0.49 | NaN | NaN | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L15 | CpAP2-L11 | 0.55 | 2.48 | 0.22 | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L16 | CpAP2-L10 | 0.58 | NaN | NaN | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
Table 3 Evolutionary selection types and duplication types of the AP2 subfamily members in Chimonanthus praecox
| 基因1 Gene 1 | 基因2 Gene 2 | 非同义 替换率Ka | 同义 替换率Ks | Ka/Ks | 选择类型 Selection type | 复制类型 Duplication type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CpAP2-L1 | CpAP2-L11 | 0.59 | NaN | NaN | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L3 | CpAP2-L4 | 0.78 | NaN | NaN | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L3 | CpAP2-L8 | 0.20 | 0.66 | 0.30 | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L3 | CpAP2-L11 | 0.66 | NaN | NaN | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L4 | CpAP2-L7 | 0.19 | 0.82 | 0.24 | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L4 | CpAP2-L1 | 0.18 | 1.02 | 0.17 | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L6 | CpAP2-L11 | 0.67 | NaN | NaN | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L8 | CpAP2-L11 | 0.66 | NaN | NaN | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L12 | CpAP2-L3 | 0.72 | NaN | NaN | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L12 | CpAP2-L4 | 0.51 | 2.37 | 0.22 | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L12 | CpAP2-L8 | 0.66 | NaN | NaN | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L12 | CpAP2-L11 | 0.51 | NaN | NaN | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L14 | CpAP2-L10 | 0.16 | 0.73 | 0.22 | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L14 | CpAP2-L11 | 0.49 | NaN | NaN | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L15 | CpAP2-L11 | 0.55 | 2.48 | 0.22 | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
| CpAP2-L16 | CpAP2-L10 | 0.58 | NaN | NaN | 纯化选择Purify selection | 全基因组复制或片段复制WGD or SD |
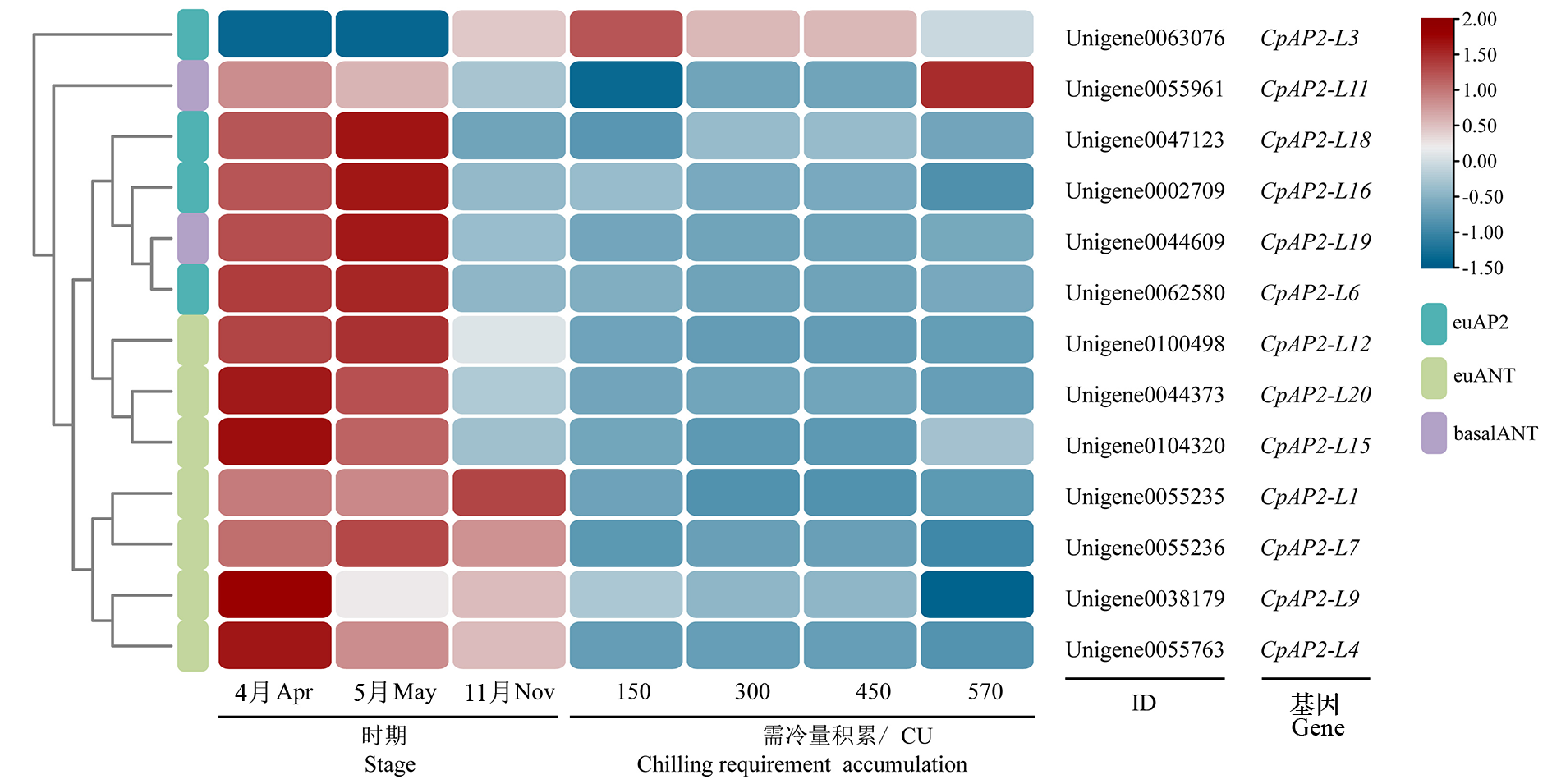
Fig. 4 Heatmap of the expression of members of the AP2 subfamily in Chimonanthus praecox at different stages of flower development and different chilling requirements 570 indicates the flower bud at beginning of initiating blooming stage.
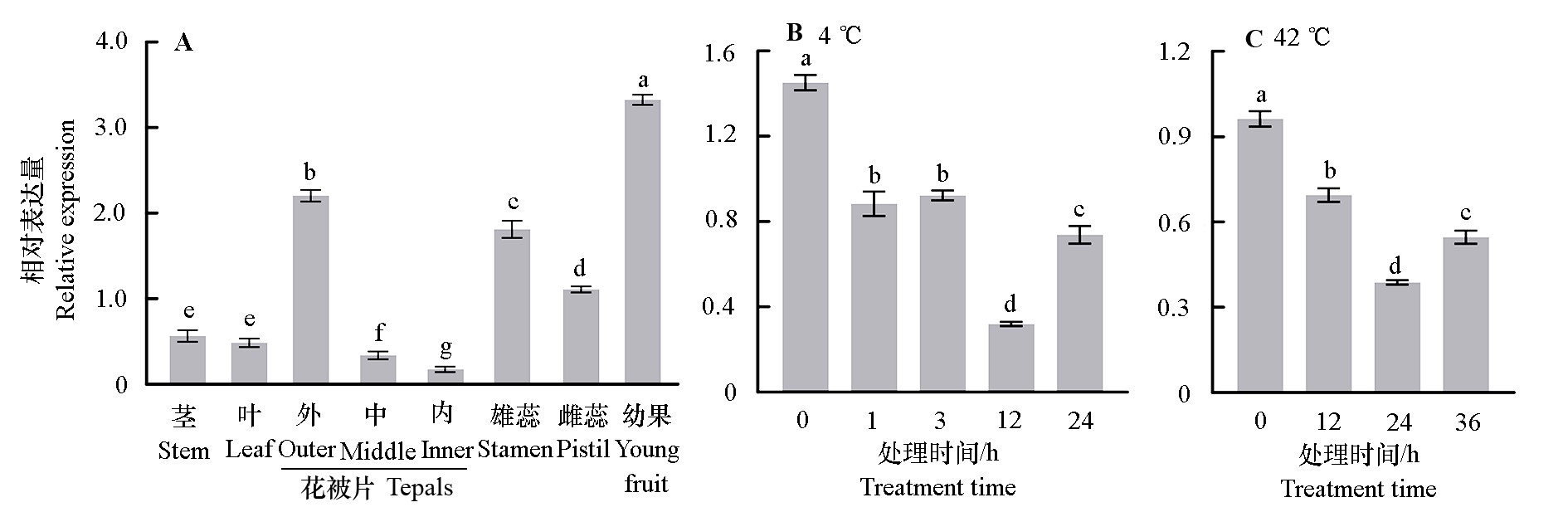
Fig. 5 Relative expression of CpAP2-L11 in different tissues,organs(A),and temperature conditions(B,C)in Chimonanthus praecox Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences(P < 0.05). The same below.
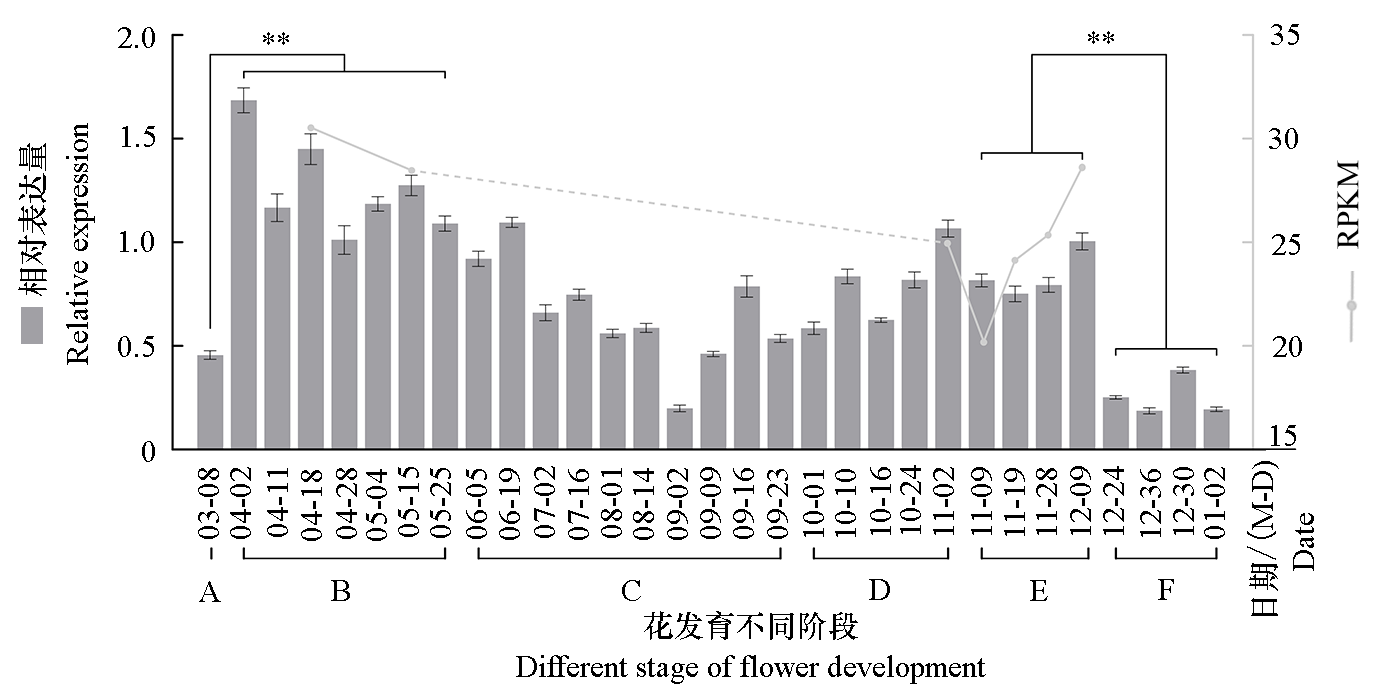
Fig. 6 Relative expression of CpAP2-L11 in different stages of the flower development in Chimonanthus praecox(histogram)and transcriptome database(line graph) A:Branch bud;B:Flower primordium formation and stamen/pistil differentiation;C:Flower bud primordium dormancy;D:Ovary development;E:Chilling requirements accumulation;F:Flower buds opening. ** indicate significant differences(P < 0.05).
| 株系Line | 莲座叶数 Number of rosette leaves | 时间/d Time | 株高/cm Plant height | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 抽薹1 cm Bolting 1 cm | 第1朵花开放 The first flower oping | 第1个果荚形成 The first pod formation | |||
| 野生型Wild type | 10.3 ± 0.9 a | 27.4 ± 0.9 a | 30.6 ± 1.2 a | 33.8 ± 1.1 a | 25.04 ± 0.81 a |
| OE10-12 | 8.3 ± 0.9 b | 25.5 ± 1.2 b | 28.4 ± 1.4 b | 30.9 ± 1.6 b | 18.88 ± 0.88 b |
| OE9-5 | 7.9 ± 0.7 bc | 25.0 ± 1.0 b | 27.8 ± 1.0 b | 30.3 ± 0.9 b | 18.48 ± 0.47 b |
| OE7-6 | 7.4 ± 0.6 c | 22.6 ± 1.1 c | 25.6 ± 1.2 c | 28.3 ± 1.4 c | 17.06 ± 0.55 c |
Table 4 Phenotype of over expression lines in 35S::CpAP2-L11 Arabidopsis
| 株系Line | 莲座叶数 Number of rosette leaves | 时间/d Time | 株高/cm Plant height | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 抽薹1 cm Bolting 1 cm | 第1朵花开放 The first flower oping | 第1个果荚形成 The first pod formation | |||
| 野生型Wild type | 10.3 ± 0.9 a | 27.4 ± 0.9 a | 30.6 ± 1.2 a | 33.8 ± 1.1 a | 25.04 ± 0.81 a |
| OE10-12 | 8.3 ± 0.9 b | 25.5 ± 1.2 b | 28.4 ± 1.4 b | 30.9 ± 1.6 b | 18.88 ± 0.88 b |
| OE9-5 | 7.9 ± 0.7 bc | 25.0 ± 1.0 b | 27.8 ± 1.0 b | 30.3 ± 0.9 b | 18.48 ± 0.47 b |
| OE7-6 | 7.4 ± 0.6 c | 22.6 ± 1.1 c | 25.6 ± 1.2 c | 28.3 ± 1.4 c | 17.06 ± 0.55 c |
| [1] | Ahmed S, Rashid M A R, Zafar S A, Azhar M T, Waqas M, Uzair M, Rana I A, Azeem F, Chung G, Ali Z, Atif R M. 2021. Genome-wide investigation and expression analysis of APETALA-2 transcription factor subfamily reveals its evolution,expansion and regulatory role in abiotic stress responses in Indica rice(Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica). Genomics, 113 (1 Pt 2):10291043. |
| [2] |
Aukerman M J, Sakai H. 2003. Regulation of flowering time and floral organ identity by a microRNA and its APETALA2-Like target genes. The Plant Cell, 15 (11):2730-2741.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.016238 URL |
| [3] | Bennetzen J L. 2005. Transposable elements,gene creation and genome rearrangement in flowering plants. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development, 15 (6):621-627. |
| [4] |
Boutilier K, Offringa R, Sharma V K, Kieft H, Ouellet T, Zhang L, Hattori J, Liu C M, van Lammeren A A M, Miki B L A, Custers J B M, van Lookeren Campagne M M. 2002. Ectopic expression of BABY BOOM triggers a conversion from vegetative to embryonic growth. The Plant Cell, 14 (8):1737-1749.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.001941 URL |
| [5] |
Cannon S B, Mitra A, Baumgarten A, Young N D, May G. 2004. The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biology, 4 (1):10.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-4-10 URL |
| [6] |
Chen C J, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas H R, Frank M H, He Y, Xia R. 2020. Tbtools:an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Molecular Plant, 13 (8):1194-1202.
doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009 URL |
| [7] |
Clough S J, Bent A F. 1998. Floral dip:a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Journal, 16 (6):735-743.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1998.00343.x pmid: 10069079 |
| [8] | Cui bo, Hao Ping’an, Liang Fang, Zhang Yan, Wang Ximeng, Li Junlin, Jiang Suhua, Xu Shenping. 2020. Cloning and expression analysis of AP2/ERF family gene from Phalaenopsis under low temperature. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47 (1):85-97. (in Chinese) |
|
崔波, 郝平安, 梁芳, 张燕, 王喜蒙, 李俊霖, 蒋素华, 许申平. 2020. 蝴蝶兰AP2/ERF家族基因的克隆及在低温下表达特性分析. 园艺学报, 47 (1):85-97.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2019-0091 |
|
| [9] |
Dong C, Xi Y, Chen X, Cheng Z M. 2021. Genome-wide identification of AP2/EREBP in Fragaria vesca and expression pattern analysis of the FvDREB subfamily under drought stress. BMC Plant Biology, 21 (1):295.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03095-2 |
| [10] |
Faraji S, Filiz E, Kazemitabar S K, Vannozzi A, Palumbo F, Barcaccia G, Heidari P. 2020. The AP2/ERF gene family in Triticum durum:genome-wide identification and expression analysis under drought and salinity stresses. Genes, 11 (12):1464.
doi: 10.3390/genes11121464 URL |
| [11] |
Feng K, Hou X L, Xing G M, Liu J X, Duan A Q, Xu Z S, Li M Y, Zhuang J, Xiong A S. 2020. Advances in AP2/ERF super-family transcription factors in plant. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 40 (6):750-776.
doi: 10.1080/07388551.2020.1768509 pmid: 32522044 |
| [12] | Green M R, Sambrook J. 2001. Molecular cloning:a laboratory manual. Analytical Biochemistry, 186 (1):182-183. |
| [13] |
Gutterson N, Reuber T L. 2004. Regulation of disease resistance pathways by AP2/ERF transcription factors. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 7 (4):465-471.
doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2004.04.007 pmid: 15231271 |
| [14] |
Jiang F, Guo M, Yang F, Duncan K, Jackson D, Rafalski A, Wang S, Li B. 2012. Mutations in an AP2 transcription factor-like gene affect internode length and leaf shape in maize. PLoS ONE, 7 (5):e37040.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037040 URL |
| [15] |
Jin J H, Wang M, Zhang H X, Khan A, Wei A M, Luo D X, Gong Z H, Tar’an B. 2018. Genome-wide identification of the AP2/ERF transcription factor family in pepper(Capsicum annuum L.). Genome, 61 (9):663-674.
doi: 10.1139/gen-2018-0036 URL |
| [16] |
Jose L R, Elliot M M. 1998. The AP2/EREBP family of plant transcription factors. Biological Chemistry, 379 (6):633-654.
doi: 10.1515/bchm.1998.379.6.633 pmid: 9687012 |
| [17] | Jung J H, Lee S, Yun J, Lee M, Park C M. 2014. The miR172 target TOE3 represses AGAMOUS expression during Arabidopsis floral patterning. Plant Science, 215:29-38. |
| [18] |
Kim S, Soltis P S, Wall K, Soltis D E. 2006. Phylogeny and domain evolution in the APETALA2-like gene family. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 23 (1):107-120.
pmid: 16151182 |
| [19] | Kondrashov F A, Rogozin I B, Wolf Y I, Koonin E V. 2002. Selection in the evolution of gene duplications. Genome Biology, 3 (2):research0008.0001. |
| [20] |
Krizek B A. 2011. Aintegumenta and Aintegumenta-Like6 regulate auxin-mediated flower development in Arabidopsis. BMC Research Notes, 4 (1):176.
doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-4-176 |
| [21] |
Krizek B A, Eaddy M. 2012. AINTEGUMENTA-LIKE6 regulates cellular differentiation in flowers. Plant Molecular Biology, 78 (3):199-209.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-011-9844-3 pmid: 22076630 |
| [22] |
Lecharny A, Boudet N, Gy I, Aubourg S, Kreis M. 2003. Introns in,introns out in plant gene families:a genomic approach of the dynamics of gene structure. J Struct Funct Genomics, 3 (1-4):111-116.
doi: 10.1023/A:1022614001371 URL |
| [23] |
Lei M, Li Z Y, Wang J B, Fu Y L, Xu L. 2019. Ectopic expression of the Aechmea fasciata APETALA2 gene AfAP2-2 reduces seed size and delays flowering in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 139:642-650.
doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2019.03.034 URL |
| [24] |
Li A, Yu X, Cao B B, Peng L X, Gao Y, Feng T, Li H, Ren Z Y. 2017. LkAP2L2,an AP2/ERF transcription factor gene of Larix kaempferi,with pleiotropic roles in plant branch and seed development. Russian Journal of Genetics, 53 (12):1335-1342.
doi: 10.1134/S1022795417120079 URL |
| [25] |
Li J, Chen F, Li Y, Li P, Wang Y, Mi G, Yuan L. 2019. ZmRAP2.7,an AP 2 transcription factor, is involved in Maize brace roots development. Frontiers in Plant Science, 10 (1):820.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00820 URL |
| [26] |
Li Ying, Meng Xianwei, Ma Zhihang, Liu Mengjun, Zhao Jin. 2022. Identification and expression analysis of microRNA families associated with phase transition in Chinese jujube. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 49 (1):23-40. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0969 |
|
李莹, 孟宪巍, 马志航, 刘孟军, 赵锦. 2022. 枣树阶段转变相关microRNA家族的鉴定及其表达分析. 园艺学报, 49 (1):23-40.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0969 |
|
| [27] |
Li Z N, Liu N, Zhang W, Wu C, Jiang Y, Ma J, Li M, Sui S. 2020. Integrated transcriptome and proteome analysis provides insight into chilling-induced dormancy breaking in Chimonanthus praecox. Horticulture Research, 7 (1):198.
doi: 10.1038/s41438-020-00421-x |
| [28] |
Licausi F, Giorgi F M, Zenoni S, Osti F, Pezzotti M, Perata P. 2010. Genomic and transcriptomic analysis of the AP2/ERF superfamily in Vitis vinifera. BMC Genomics, 11 (1):719.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-719 URL |
| [29] |
Licausi F, Ohme-Takagi M, Perata P. 2013. APETALA2/ethylene responsive factor(AP2/ERF)transcription factors:mediators of stress responses and developmental programs. New Phytologist, 199 (3):639-649.
doi: 10.1111/nph.12291 URL |
| [30] |
Liu M, Sun W, Ma Z, Zheng T, Huang L, Wu Q, Zhao G, Tang Z, Bu T, Li C, Chen H. 2019. Genome-wide investigation of the AP2/ERF gene family in tartary buckwheat(Fagopyum tataricum). BMC Plant Biology, 19:84.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-1681-6 |
| [31] |
Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-∆∆CT method. Methods, 25 (4):402-408.
doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262 pmid: 11846609 |
| [32] |
Ma Xinrui, Li Liang, Liu Jinhang, Yang Mengjie, Chen Jie, Liang Qin, Wu Shaohua, Li Yongyu. 2018. Identification and differentially expressed analysis of microRNA associated with dormancy of pear flower buds. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 45 (11):2089-2105. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0012 |
|
马鑫瑞, 李亮, 刘瑾航, 杨梦洁, 陈洁, 梁沁, 吴少华, 李永裕. 2018. 梨花芽休眠相关miRNA的鉴定和差异表达分析. 园艺学报, 45 (11):2089-2105.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0012 |
|
| [33] |
Maes T, van de Steene N, Zethof J, Karimi M, D'Hauw M, Mares G, van Montagu M, Gerats T. 2001. Petunia AP2-like genes and their role in flower and seed development. The Plant Cell, 13 (2):229-244.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.13.2.229 URL |
| [34] |
Najafi S, Sorkheh K, Nasernakhaei F. 2018. Characterization of the APETALA2/ethylene-responsive factor(AP2/ERF)transcription factor family in sunflower. Scientific Reports, 8:11576.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29526-z |
| [35] |
Nakano T, Suzuki K, Fujimura T, Shinshi H. 2006. Genome-wide analysis of the ERF gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiology, 140 (2):411-432.
doi: 10.1104/pp.105.073783 URL |
| [36] |
Nilsson L, Carlsbecker A, Sundås-Larsson A, Vahala T. 2007. APETALA2 like genes from Picea abies show functional similarities to their Arabidopsis homologues. Planta, 225 (3):589-602.
pmid: 16953432 |
| [37] |
O'Maoileidigh D S, van Driel A D, Singh A, Sang Q,le Bec N, Vincent C, de Olalla E B G, Vayssieres A, Romera Branchat M, Severing E, Martinez Gallegos R, Coupland G. 2021. Systematic analyses of the MIR172 family members of Arabidopsis define their distinct roles in regulation of APETALA2 during floral transition. PLoS Biology, 19 (2):e3001043.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001043 URL |
| [38] |
Park W, Li J, Song R, Messing J, Chen X. 2002. CARPEL FACTORY,a dicer homolog,and HEN1,a novel protein,zct in microRNA metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana. Current Biology, 12 (17):1484-1495.
doi: 10.1016/S0960-9822(02)01017-5 URL |
| [39] | Riaz M W, Lu J, Shah L, Yang L, Chen C, Mei X D, Xue L, Manzoor M A, Abdullah M, Rehman S, Si H, Ma C. 2021. Expansion and molecular characterization of AP2/ERF gene family in wheat(Triticum aestivum L.). Frontiers in Genetics, 12:Article 632155. |
| [40] |
Riechmann J L, Heard J, Martin G, Reuber L, Jiang C, Keddie J, Adam L, Pineda O, Ratcliffe O J, Samaha R R, Creelman R, Pilgrim M, Broun P, Zhang J Z, Ghandehari D, Sherman B K, Yu G. 2000. Arabidopsis transcription factors:genome-wide comparative analysis among eukaryotes. Science, 290 (5499):2105-2115.
doi: 10.1126/science.290.5499.2105 pmid: 11118137 |
| [41] |
Roy S W, Gilbert W. 2005. Rates of intron loss and gain:implications for early eukaryotic evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 102 (16):5773.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0500383102 URL |
| [42] |
Shang J, Tian J, Cheng H, Yan Q, Li L, Jamal A, Xu Z, Xiang L, Saski C A, Jin S, Zhao K, Liu X, Chen L. 2020. The chromosome-level wintersweet(Chimonanthus praecox)genome provides insights into floral scent biosynthesis and flowering in winter. Genome Biology, 21 (1):200.
doi: 10.1186/s13059-020-02088-y |
| [43] |
Wang R, Cheng Y, Ke X, Zhang X, Zhang H, Huang J. 2020. Comparative analysis of salt responsive gene regulatory networks in rice and Arabidopsis. Computational Biology and Chemistry, 85 (1):107188.
doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2019.107188 URL |
| [44] |
Wang Y, Tang H, Debarry J D, Tan X, Li J, Wang X, Lee T H, Jin H, Marler B, Guo H, Kissinger J C, Paterson A H. 2012. MCScanX:a toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Research, 40 (7):e49.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1293 URL |
| [45] |
Wollmann H, Mica E, Todesco M, Long J A, Weigel D. 2010. On reconciling the interactions between APETALA2,miR172 and AGAMOUS with the ABC model of flower development. Development, 137 (21):3633-3642.
doi: 10.1242/dev.036673 pmid: 20876650 |
| [46] |
Xie Y, Yu X, Jiang S, Xiao K, Wang Y, Li L, Wang F, He W, Cai Q, Xie H, Zhang J. 2020. OsGL6,a conserved AP 2 domain protein,promotes leaf trichome initiation in rice. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 522 (2):448-455.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.11.125 URL |
| [47] |
Xie Z, Nolan T M, Jiang H, Yin Y. 2019. AP2/ERF transcription factor regulatory networks in hormone and abiotic stress responses in Arabidopsis. Frontiers in Plant Science, 10:228.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00228 URL |
| [48] |
Zhang B, Wang L, Zeng L, Zhang C, Ma H. 2015. Arabidopsis TOE proteins convey a photoperiodic signal to antagonize CONSTANS and regulate flowering time. Genes & Development, 29 (9):975-987.
doi: 10.1101/gad.251520.114 URL |
| [49] |
Xu Hongxia, Zhou Huifen, Li Xiaoying, Jiang Luhua, Chen Junwei. 2021. Comparative transcriptome analysis of different developmental stages of flowers and fruits in loquat under low temperature stress. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 48 (9):1680-1694. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021- 0219 |
|
徐红霞, 周慧芬, 李晓颖, 姜路花, 陈俊伟. 2021. 低温胁迫下枇杷不同发育阶段的花果转录组比较分析. 园艺学报, 48 (9):1680-1694.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021- 0219 |
|
| [50] |
Zhang J, Shi S Z, Jiang Y, Zhong F, Liu G, Yu C, Lian B, Chen Y. 2021. Genome-wide investigation of the AP2/ERF superfamily and their expression under salt stress in Chinese willow(Salix matsudana). Peerj, 9 (1):e11076.
doi: 10.7717/peerj.11076 URL |
| [51] |
Zhang S T, Zhu C, Lyu Y M, Chen Y, Zhang Z H, Lai Z X, Lin Y L. 2020. Genome-wide identification,molecular evolution,and expression analysis provide new insights into the APETALA2/ethylene responsive factor(AP2/ERF)superfamily in Dimocarpus longan Lour. BMC Genomics, 21 (1):62.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-6469-4 |
| [52] |
Zhou L, Yarra R. 2021. Genome-wide identification and characterization of AP2/ERF transcription factor family genes in oil palm under abiotic stress conditions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22 (6):2821.
doi: 10.3390/ijms22062821 URL |
| [53] | Zhu P, Chen Y, Zhang J, Wu F, Wang X, Pan T, Wei Q, Hao Y, Chen X, Jiang C, Ji K. 2021. Identification,classification,and characterization of AP2/ERF superfamily genes in Masson pine(Pinus massoniana Lamb.). Scientific Report, 11 (1):5441. |
| [54] |
Zhuang J, Xiong A S, Peng R H, Gao F, Zhu B, Zhang J, Fu X Y, Jin X F, Chen J M, Zhang Z, Qiao Y S, Yao Q H. 2010. Analysis of Brassica rapa ESTs:gene discovery and expression patterns of AP2/ERF family genes. Molecular Biology Reports, 37 (5):2485-2492.
doi: 10.1007/s11033-009-9763-4 pmid: 19701799 |
| [1] | LIU Yunuo, CAO Ya, WANG Shuai, DU Meixia, ZHENG Lin, CHEN Shanchun, ZOU Xiuping. Expression Analysis of CsMYB41 and CsMYB63 Genes in Response to Citrus Canker [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(3): 495-507. |
| [2] | YE Zimao, SHEN Wanxia, LIU Mengyu, WANG Tong, ZHANG Xiaonan, YU Xin, LIU Xiaofeng, ZHAO Xiaochun. Effect of R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor CitMYB21 on Flavonoids Biosynthesis in Citrus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 250-264. |
| [3] | SONG Yanhong, CHEN Yaduo, ZHANG Xiaoyu, SONG Pan, LIU Lifeng, LI Gang, ZHAO Xia, ZHOU Houcheng. The Transcription Factor FvbHLH130 Activates Flowering in Fragaria vesca [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 295-306. |
| [4] | HAN Rui, ZHONG Xionghui, CHEN Denghui, CUI Jian, YUE Xiangqing, XIE Jianming, KANG Jungen. Cloning and Functional Analysis of BobHLH34 Gene in Cabbage that Interacts with XopR from Xanthomonas [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 319-330. |
| [5] | REN Fei, LU Miaomiao, LIU Jixiang, CHEN Xinli, LIU Daofeng, SUI Shunzhao, MA Jing. Expression and Adversity Resistance Analysis of a Late Embryogenesis Abundant Protein Gene CpLEA from Chimonanthus praecox [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 359-370. |
| [6] | LIN Haijiao, LIANG Yuchen, LI Ling, MA Jun, ZHANG Lu, LAN Zhenying, YUAN Zening. Exploration and Regulation Network Analysis of CBF Pathway Related Cold Tolerance Genes in Lavandula angustifolia [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(1): 131-144. |
| [7] | JIA Xin, ZENG Zhen, CHEN Yue, FENG Hui, LÜ Yingmin, ZHAO Shiwei. Cloning and Expression Analysis of RcDREB2A Gene in Rosa chinensis‘Old Blush’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(9): 1945-1956. |
| [8] | SONG Xingrong, YUAN Puying, HE Xiangda. A New Chimonanthus praecox Cultivar‘Bianzaosu’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(9): 2059-2060. |
| [9] | XU Haifeng, WANG Zhongtang, CHEN Xin, LIU Zhiguo, WANG Lihu, LIU Ping, LIU Mengjun, ZHANG Qiong. The Analyses of Target Metabolomics in Flavonoid and Its Potential MYB Regulation Factors During Coloring Period of Winter Jujube [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1761-1771. |
| [10] | QIAN Jieyu, JIANG Lingli, ZHENG Gang, CHEN Jiahong, LAI Wuhao, XU Menghan, FU Jianxin, ZHANG Chao. Identification and Expression Analysis of MYB Transcription Factors Regulating the Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Zinnia elegans and Function Research of ZeMYB9 [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1505-1518. |
| [11] | CHEN Daozong, LIU Yi, SHEN Wenjie, ZHU Bo, TAN Chen. Identification and Analysis of PAP1/2 Homologous Genes in Brassica rapa,B. oleracea and B. napus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1301-1312. |
| [12] | WANG Yan, SUN Zheng, FENG Shan, YUAN Xinyi, ZHONG Linlin, ZENG Yunliu, FU Xiaopeng, CHENG Yunjiang, Bao Manzhu, ZHANG Fan. The Negative Regulation of DcERF-1 on Senescence of Cut Carnation [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1313-1326. |
| [13] | LI Chunhong, WANG Kaituo, LEI Changyi, XU Feng, JI Nana, JIANG Yongbo. Identification of TGA Gene Family in Peach and Analysis of Expression Mode Involved in a BABA-Induced Disease Resistance [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(2): 265-280. |
| [14] | CHEN Sijia, WANG Huan, LI Ruirui, WANG Zhuoyi, LUO Jing, WANG Caiyun. Characterization of CmMYC2 in Formation of Green Color in Ray Florets of Chrysanthemum [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(11): 2377-2387. |
| [15] | XIE Siyi, ZHOU Chengzhe, ZHU Chen, ZHAN Dongmei, CHEN Lan, WU Zuchun, LAI Zhongxiong, GUO Yuqiong. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of CsTIFY Transcription Factor Family Under Abiotic Stress and Hormone Treatments in Camellia sinensis [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(1): 100-116. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd