
园艺学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (2): 395-406.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0066
潘凤兵1, 陈冉1, 姜伟涛1, 王海燕1, 吕毅2, 沈向1, 陈学森1, 尹承苗1,*( ), 毛志泉1,*(
), 毛志泉1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-02-14
修回日期:2021-05-13
出版日期:2022-02-25
发布日期:2022-02-28
通讯作者:
尹承苗,毛志泉
E-mail:yinchengmiao@163.com;mzhiquan@sdau.edu.cn
基金资助:
PAN Fengbing1, CHEN Ran1, JIANG Weitao1, WANG Haiyan1, LÜ Yi2, SHEN Xiang1, CHEN Xuesen1, YIN Chengmiao1,*( ), MAO Zhiquan1,*(
), MAO Zhiquan1,*( )
)
Received:2021-02-14
Revised:2021-05-13
Online:2022-02-25
Published:2022-02-28
Contact:
YIN Chengmiao,MAO Zhiquan
E-mail:yinchengmiao@163.com;mzhiquan@sdau.edu.cn
摘要:
为探讨不同物料蛋白发酵物防控苹果连作障碍的可行性,以盆栽平邑甜茶为试材,设连作土(对照)、灭菌土(高标对照)和分别在连作土中添加蚯蚓发酵物、大豆粕发酵物、杂鱼发酵物等5个处理,测定土壤微生物总量、有害真菌数量、土壤酶活性、土壤酚酸类物质含量、平邑甜茶生物量和植株根系相关指标。结果表明添加3种不同蛋白发酵物均能有效提高连作土壤细菌数量,降低真菌数量,改变了连作土壤中的真菌群落结构,其中添加蚯蚓发酵物降低有害真菌效果最好,尖孢镰孢菌、层出镰孢菌、腐皮镰孢菌和串珠镰孢菌分别比连作土(对照)降低了59.2%、52.0%、64.9%和67.1%。3种发酵物也不同程度地提高了连作土壤中的土壤酶活性,降低了土壤酚酸类物质含量。蚯蚓发酵物处理的平邑甜茶幼苗生物量明显高于连作土(对照),植株干质量比对照提高了90.22%。发酵物也促进了植株根系的生长、根抗氧化酶活性和呼吸速率的提高,效果最为显著的蚯蚓发酵物,根系的总根长、表面积、根体积和根尖数分别比连作土(对照)提高了147.21%、225.87%、299.85%和291.03%,SOD、POD、CAT和根系呼吸速率分别比连作土(对照)提高了46.90%、133.94%、197.69%和113.23%。综上,不同物料蛋白的发酵物均能通过调节微生物群落结构、改善连作土壤环境、促进植株生长等途径不同程度地缓解苹果连作障碍对幼树造成的危害,综合各项指标来看,蚯蚓发酵的效果最为显著。
中图分类号:
潘凤兵, 陈冉, 姜伟涛, 王海燕, 吕毅, 沈向, 陈学森, 尹承苗, 毛志泉. 不同蛋白发酵物对连作土壤微生物环境和平邑甜茶幼苗生长的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(2): 395-406.
PAN Fengbing, CHEN Ran, JIANG Weitao, WANG Haiyan, LÜ Yi, SHEN Xiang, CHEN Xuesen, YIN Chengmiao, MAO Zhiquan. Effects of Different Material Protein Fermentation Products on Apple Replanted Soil Microbial Environment and the Growth of Malus hupehensis Seedlings[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(2): 395-406.
| 处理 Treatment | 基因拷贝数Gene copies | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 尖孢镰孢菌/ (× 108 copies · g-1) Fusarium oxysporum | 层出镰孢菌/ (× 103 copies · g-1) F. proliferatum | 腐皮镰孢菌/ (× 108 copies · g-1) F. solani | 串珠镰孢菌/ (× 103 copies · g-1) F. moniliforme | |
| 连作土(对照)Control | 9.33 ± 0.50 a | 6.69 ± 0.38 a | 11.39 ± 0.68 a | 11.81 ± 0.71 a |
| 灭菌土 Sterile soil | 3.04 ± 0.24 c | 1.98 ± 0.26 d | 2.86 ± 0.38 c | 2.69 ± 0.17 c |
| 蚯蚓发酵物 Earthworm fermentation products | 3.81 ± 0.25 c | 3.21 ± 0.31 c | 4.00 ± 0.15 c | 3.89 ± 0.31 c |
| 大豆粕发酵物Soybean meal fermentation products | 7.16 ± 0.18 b | 4.57 ± 0.28 b | 7.76 ± 0.35 b | 6.79 ± 0.27 b |
| 杂鱼发酵物 Waste fish fermentation products | 6.58 ± 0.24 b | 4.10 ± 0.09 b | 6.59 ± 0.24 b | 7.47 ± 0.33 b |
表1 苹果连作土壤中添加不同蛋白发酵物对其有害真菌数量的影响
Table 1 Effect of different material protein fermentation products on harmful fungi in replanted soil
| 处理 Treatment | 基因拷贝数Gene copies | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 尖孢镰孢菌/ (× 108 copies · g-1) Fusarium oxysporum | 层出镰孢菌/ (× 103 copies · g-1) F. proliferatum | 腐皮镰孢菌/ (× 108 copies · g-1) F. solani | 串珠镰孢菌/ (× 103 copies · g-1) F. moniliforme | |
| 连作土(对照)Control | 9.33 ± 0.50 a | 6.69 ± 0.38 a | 11.39 ± 0.68 a | 11.81 ± 0.71 a |
| 灭菌土 Sterile soil | 3.04 ± 0.24 c | 1.98 ± 0.26 d | 2.86 ± 0.38 c | 2.69 ± 0.17 c |
| 蚯蚓发酵物 Earthworm fermentation products | 3.81 ± 0.25 c | 3.21 ± 0.31 c | 4.00 ± 0.15 c | 3.89 ± 0.31 c |
| 大豆粕发酵物Soybean meal fermentation products | 7.16 ± 0.18 b | 4.57 ± 0.28 b | 7.76 ± 0.35 b | 6.79 ± 0.27 b |
| 杂鱼发酵物 Waste fish fermentation products | 6.58 ± 0.24 b | 4.10 ± 0.09 b | 6.59 ± 0.24 b | 7.47 ± 0.33 b |
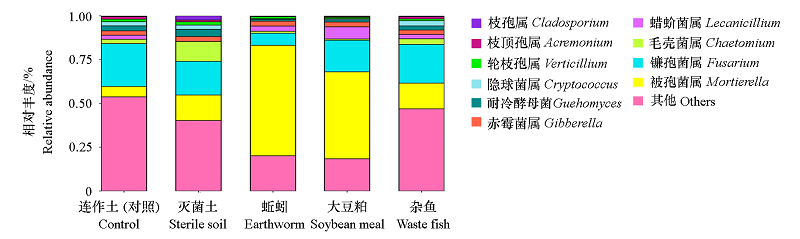
图2 苹果连作土壤中添加不同蛋白发酵物对其真菌群落属水平相对丰度的影响
Fig. 2 Effect of different material protein fermentation products on relative abundances of fungi at the genus level in replanted soil
| 处理 Treatment | ACE指数 ACE index | Chao指数 Chao index | 辛普森指数 Simpson index | 香浓指数 Shannon index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 连作土(对照)Control | 563.55 ± 14.76 a | 563.54 ± 14.65 a | 0.04 ± 0.002 b | 4.05 ± 0.06 a |
| 灭菌土 Sterile soil | 428.15 ± 25.97 b | 434.14 ± 28.88 b | 0.21 ± 0.079 a | 2.66 ± 0.31 b |
| 蚯蚓发酵物Earthworm fermentation products | 570.63 ± 8.95 a | 579.66 ± 8.98 a | 0.04 ± 0.001 b | 4.17 ± 0.03 a |
| 大豆粕发酵物Soybean meal fermentation products | 530.05 ± 6.92 a | 534.59 ± 7.87 a | 0.04 ± 0.003 b | 4.10 ± 0.04 a |
| 杂鱼发酵物Waste fish fermentation products | 463.91 ± 13.21 b | 460.43 ± 13.69 b | 0.13 ± 0.014 ab | 3.61 ± 0.16 b |
表2 苹果连作土壤中添加不同蛋白发酵物对其真菌群落α多样性的影响
Table 2 Effect of different material protein fermentation products on alpha diversity of soil fungi in replanted soil
| 处理 Treatment | ACE指数 ACE index | Chao指数 Chao index | 辛普森指数 Simpson index | 香浓指数 Shannon index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 连作土(对照)Control | 563.55 ± 14.76 a | 563.54 ± 14.65 a | 0.04 ± 0.002 b | 4.05 ± 0.06 a |
| 灭菌土 Sterile soil | 428.15 ± 25.97 b | 434.14 ± 28.88 b | 0.21 ± 0.079 a | 2.66 ± 0.31 b |
| 蚯蚓发酵物Earthworm fermentation products | 570.63 ± 8.95 a | 579.66 ± 8.98 a | 0.04 ± 0.001 b | 4.17 ± 0.03 a |
| 大豆粕发酵物Soybean meal fermentation products | 530.05 ± 6.92 a | 534.59 ± 7.87 a | 0.04 ± 0.003 b | 4.10 ± 0.04 a |
| 杂鱼发酵物Waste fish fermentation products | 463.91 ± 13.21 b | 460.43 ± 13.69 b | 0.13 ± 0.014 ab | 3.61 ± 0.16 b |
| 处理 Treatment | 酚酸类物质含量/(mg · kg-1 dry soil) Phenolic compounds | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 根皮苷 Phlorizin | 根皮素Phloretin | 阿魏酸 Ferulic Acid | 苯甲酸Benzoic acid | |
| 连作土(对照)Control | 3.47 ± 0.06 a | 2.21 ± 0.10 a | 2.16 ± 0.25 a | 3.77 ± 0.02 a |
| 灭菌土 Sterile soil | 1.64 ± 0.06 d | 0.43 ± 0.02 c | 1.68 ± 0.08 b | 0.54 ± 0.01 d |
| 蚯蚓发酵物 Earthworm fermentation products | 1.37 ± 0.08 e | 0.48 ± 0.03 c | 1.07 ± 0.20 c | 0.85 ± 0.03 cd |
| 大豆粕发酵物 Soybean meal fermentation products | 2.23 ± 0.03 c | 0.75 ± 0.08 b | 0.93 ± 0.15 c | 1.16 ± 0.04 c |
| 杂鱼发酵物 Waste fish fermentation products | 2.54 ± 0.02 b | 0.57 ± 0.07 c | 1.35 ± 0.27 bc | 1.60 ± 0.23 b |
表3 苹果连作土壤中添加不同蛋白发酵物对其土壤酚酸含量的影响
Table 3 Effects of different material protein fermentation products on the concentration of phenolic compounds in replant soil
| 处理 Treatment | 酚酸类物质含量/(mg · kg-1 dry soil) Phenolic compounds | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 根皮苷 Phlorizin | 根皮素Phloretin | 阿魏酸 Ferulic Acid | 苯甲酸Benzoic acid | |
| 连作土(对照)Control | 3.47 ± 0.06 a | 2.21 ± 0.10 a | 2.16 ± 0.25 a | 3.77 ± 0.02 a |
| 灭菌土 Sterile soil | 1.64 ± 0.06 d | 0.43 ± 0.02 c | 1.68 ± 0.08 b | 0.54 ± 0.01 d |
| 蚯蚓发酵物 Earthworm fermentation products | 1.37 ± 0.08 e | 0.48 ± 0.03 c | 1.07 ± 0.20 c | 0.85 ± 0.03 cd |
| 大豆粕发酵物 Soybean meal fermentation products | 2.23 ± 0.03 c | 0.75 ± 0.08 b | 0.93 ± 0.15 c | 1.16 ± 0.04 c |
| 杂鱼发酵物 Waste fish fermentation products | 2.54 ± 0.02 b | 0.57 ± 0.07 c | 1.35 ± 0.27 bc | 1.60 ± 0.23 b |
| 时间 Time | 处理 Treatment | 株高/cm Plant height | 地径/cm Ground diameter | 鲜质量/g Fresh weight | 干质量/g Dry weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 连作土(对照)Control | 37.47 ± 2.58 c | 5.39 ± 0.18 d | 21.43 ± 1.25 c | 10.22 ± 0.87 c |
| 灭菌土Sterile soil | 65.53 ± 7.57 a | 8.85 ± 0.41 a | 75.50 ± 4.90 a | 32.99 ± 2.40 a | |
| 蚯蚓发酵物 Earthworm fermentation products | 51.37 ± 0.95 b | 7.13 ± 0.24 b | 45.40 ± 3.12 b | 19.44 ± 2.22 b | |
| 大豆粕发酵物 Soybean meal fermentation products | 42.43 ± 7.16 bc | 6.88 ± 0.27 bc | 32.53 ± 3.82 c | 14.62 ± 2.23 bc | |
| 杂鱼发酵物 Waste fish fermentation products | 41.37 ± 3.25 c | 6.18 ± 0.14 cd | 27.10 ± 3.21 c | 10.85 ± 0.98 c | |
| 2020 | 连作土(对照)Control | 50.10 ± 1.37 d | 6.37 ± 0.12 d | 46.90 ± 1.69 c | 20.54 ± 1.08 cd |
| 灭菌土Sterile soil | 89.57 ± 0.54 a | 10.07 ± 0.05 a | 102.81 ± 5.79 a | 43.19 ± 3.41 a | |
| 蚯蚓发酵物 Earthworm fermentation products | 82.50 ± 1.80 b | 9.11 ± 0.24 b | 78.47 ± 1.64 b | 33.00 ± 0.52 b | |
| 大豆粕发酵物 Soybean meal fermentation products | 71.20 ± 2.27 c | 8.23 ± 0.28 c | 74.43 ± 2.76 b | 28.08 ± 0.79 bc | |
| 杂鱼发酵物 Waste fish fermentation products | 67.67 ± 2.07 c | 7.76 ± 0.11 c | 68.39 ± 2.25 b | 25.68 ± 0.29 c |
表4 苹果连作土壤中添加不同蛋白发酵物对平邑甜茶生物量的影响
Table 4 Effects of different material protein fermentation products on plant biomass of M. hupehensis Rehd. seedlings
| 时间 Time | 处理 Treatment | 株高/cm Plant height | 地径/cm Ground diameter | 鲜质量/g Fresh weight | 干质量/g Dry weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 连作土(对照)Control | 37.47 ± 2.58 c | 5.39 ± 0.18 d | 21.43 ± 1.25 c | 10.22 ± 0.87 c |
| 灭菌土Sterile soil | 65.53 ± 7.57 a | 8.85 ± 0.41 a | 75.50 ± 4.90 a | 32.99 ± 2.40 a | |
| 蚯蚓发酵物 Earthworm fermentation products | 51.37 ± 0.95 b | 7.13 ± 0.24 b | 45.40 ± 3.12 b | 19.44 ± 2.22 b | |
| 大豆粕发酵物 Soybean meal fermentation products | 42.43 ± 7.16 bc | 6.88 ± 0.27 bc | 32.53 ± 3.82 c | 14.62 ± 2.23 bc | |
| 杂鱼发酵物 Waste fish fermentation products | 41.37 ± 3.25 c | 6.18 ± 0.14 cd | 27.10 ± 3.21 c | 10.85 ± 0.98 c | |
| 2020 | 连作土(对照)Control | 50.10 ± 1.37 d | 6.37 ± 0.12 d | 46.90 ± 1.69 c | 20.54 ± 1.08 cd |
| 灭菌土Sterile soil | 89.57 ± 0.54 a | 10.07 ± 0.05 a | 102.81 ± 5.79 a | 43.19 ± 3.41 a | |
| 蚯蚓发酵物 Earthworm fermentation products | 82.50 ± 1.80 b | 9.11 ± 0.24 b | 78.47 ± 1.64 b | 33.00 ± 0.52 b | |
| 大豆粕发酵物 Soybean meal fermentation products | 71.20 ± 2.27 c | 8.23 ± 0.28 c | 74.43 ± 2.76 b | 28.08 ± 0.79 bc | |
| 杂鱼发酵物 Waste fish fermentation products | 67.67 ± 2.07 c | 7.76 ± 0.11 c | 68.39 ± 2.25 b | 25.68 ± 0.29 c |
| 处理 Treatment | 总根长/cm Total fine root length | 表面积/cm2 Total fine root surface area | 根体积/cm3 Total fine root volume | 根尖数 Fine root tip number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 连作土(对照)Control | 1 227.13 ± 27.58 d | 323.59 ± 29.38 d | 6.47 ± 0.85 d | 2 901.30 ± 336.16 d |
| 灭菌土 Sterile soil | 3 928.21 ± 159.49 a | 1 377.04 ± 133.17 a | 34.12 ± 3.08 a | 16 175.67 ± 2 118.52 a |
| 蚯蚓发酵物 Earthworm fermentation products | 3 033.54 ± 476.96 b | 1 054.47 ± 46.23 b | 25.87 ± 2.10 b | 11 345.00 ± 1 144.84 b |
| 大豆粕发酵物 Soybean meal fermentation products | 2 157.90 ± 138.20 c | 518.18 ± 19.39 d | 13.45 ± 1.56 c | 7 038.67 ± 1 038.84 c |
| 杂鱼发酵物 Waste fish fermentation products | 2 292.67 ± 77.50 bc | 821.10 ± 21.54 c | 25.67 ± 1.21 b | 8 114.33 ± 799.70 bc |
表5 苹果连作土壤中添加不同蛋白发酵物对平邑甜茶根系形态的影响
Table 5 Effects of different material protein fermentation products on the root morphology of M. hupehensis Rehd. seedlings
| 处理 Treatment | 总根长/cm Total fine root length | 表面积/cm2 Total fine root surface area | 根体积/cm3 Total fine root volume | 根尖数 Fine root tip number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 连作土(对照)Control | 1 227.13 ± 27.58 d | 323.59 ± 29.38 d | 6.47 ± 0.85 d | 2 901.30 ± 336.16 d |
| 灭菌土 Sterile soil | 3 928.21 ± 159.49 a | 1 377.04 ± 133.17 a | 34.12 ± 3.08 a | 16 175.67 ± 2 118.52 a |
| 蚯蚓发酵物 Earthworm fermentation products | 3 033.54 ± 476.96 b | 1 054.47 ± 46.23 b | 25.87 ± 2.10 b | 11 345.00 ± 1 144.84 b |
| 大豆粕发酵物 Soybean meal fermentation products | 2 157.90 ± 138.20 c | 518.18 ± 19.39 d | 13.45 ± 1.56 c | 7 038.67 ± 1 038.84 c |
| 杂鱼发酵物 Waste fish fermentation products | 2 292.67 ± 77.50 bc | 821.10 ± 21.54 c | 25.67 ± 1.21 b | 8 114.33 ± 799.70 bc |
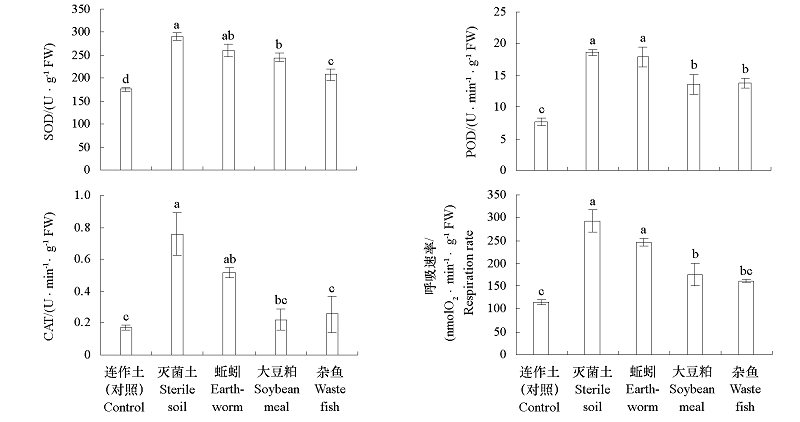
图4 苹果连作土壤中添加不同蛋白发酵物对平邑甜茶根系呼吸速率和抗氧化酶活性的影响
Fig. 4 Effect of different material protein fermentation products on root respiration rate and antioxidant enzymes activity of M. hupehensis Rehd.
| [1] | Chai T T, Tan Y N, Ee K Y, Xiao J B, Wong F C. 2019. Seeds,fermented foods,and agricultural by-products as sources of plant-derived antibacterial peptides. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 59:162-177. |
| [2] | Chen Liang, Qin Su-ya, Heng Jun-ying, Wang Jin-shui, Bian Ke. 2018. Research and application advances of antimicrobial peptides in food industry. Journal of Henan University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 39 (5):119-126. (in Chinese) |
| 陈亮, 秦素雅, 衡军影, 王金水, 卞科. 2018. 微生物抗菌肽在食品工业中的应用研究进展. 河南工业大学学报(自然科学版), 39 (5):119-126. | |
| [3] | Chen Xue-sen, Han Ming-yu, Su Gui-lin, Liu Feng-zhi, Guo Guo-nan, Jiang Yuan-mao, Mao Zhi-quan, Peng Fu-tian, Shu Huai-rui. 2010. Discussion on today’s world apple industry trends and the suggestions on sustainable and efficient development of apple industry in China. Journal of Fruit Science,(4):598-604. (in Chinese) |
| 陈学森, 韩明玉, 苏桂林, 刘凤之, 过国南, 姜远茂, 毛志泉, 彭福田, 束怀瑞. 2010. 当今世界苹果产业发展趋势及我国苹果产业优质高效发展意见. 果树学报,(4):598-604. | |
| [4] | Dong Xiao-qing, Zhang Dong-ming, Qu Gui-juan, Chen Yu-ke, Wang Qing-bin, Guo Wei, Wang Qiu-ju, Yang Yi-yu. 2014. Extraction and antibacterial activity of antibacterial peptides from diferent tissues of microptorus salmonoides. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Drug, 48 (6):8-11. (in Chinese) |
| 董晓庆, 张东鸣, 曲桂娟, 陈玉珂, 王清滨, 郭玮, 王秋举, 杨翼羽. 2014. 大口黑鲈不同组织中抗菌肽粗提及抑菌活性测定. 中国兽药杂志, 48 (6):8-11. | |
| [5] |
Gil-Sotres F, Trasar-Cepeda C, Leirós M C, Seoane S. 2005. Different approaches to evaluating soil quality using biochemical properties. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 37 (5):877-887.
doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.10.003 URL |
| [6] |
Gressent Frédéric, Da Silva P, Eyraud V, Karaki L Royer C. 2011. Pea Albumin 1 Subunit b(PA1b),a promising bioinsecticide of plant origin. Toxins, 3 (12):1502-1517.
doi: 10.3390/toxins3121502 pmid: 22295174 |
| [7] | Guan Songyin. 1986. Soil enzymes and research methods. Beijing: China Agriculture Press. (in Chinese) |
| 关松荫. 1986. 土壤酶及其研究法. 北京: 农业出版社. | |
| [8] |
Kelderer M, Manici L M, Caputo F, Thalheimer M. 2012. Planting in the‘inter-row’to overcome replant disease in apple orchards:a study on the effectiveness of the practice based on microbial indicators. Plant and Soil, 357:381-393.
doi: 10.1007/s11104-012-1172-0 URL |
| [9] |
Klose S, Acosta-Martínez V, Ajwa A H. 2006. Microbial community composition and enzyme activities in a sandy loam soil after fumigation with methyl bromide or alternative biocides. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 38 (6):1243-1254.
doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.09.025 URL |
| [10] |
Li Qing-kai, Liu Ping, Tang Zhao-hui, Zhao Hai-jun, Wang Jiang-tao, Song Xiao-zong, Yang Li, Wan Shu-bo. 2016. Effects of two phenolic acids on root zone soil nutrients,soil enzyme activities and pod yield of peanut. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 27 (4):1189-1195. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.201604.039 pmid: 29732775 |
|
李庆凯, 刘苹, 唐朝辉, 赵海军, 王江涛, 宋效宗, 杨力, 万书波. 2016. 两种酚酸类物质对花生根部土壤养分、酶活性和产量的影响. 应用生态学报, 27 (4):1189-1195.
pmid: 29732775 |
|
| [11] |
Li W, Li S, Zhong J, Wang W. 2011. A novel antimicrobial peptide from skin secretions of the earthworm, Pheretima guillelmi(Michaelsen). Peptides, 32 (6):1146-1150.
doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2011.04.015 URL |
| [12] | Li Yu-nong. 2001. Researches of germplasm resources of Malus Mill. Beijing: China Agriculture Press:208-213. (in Chinese) |
| 李育农. 2001. 苹果属植物种质资源研究. 北京: 中国农业出版社:208-213. | |
| [13] | Li Zheng-zhi. 1984. Dwarf density planting of fruit tree[M. D. Dissertation]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technique Publishing Company:1-8. (in Chinese) |
| 李正之. 1984, 果树矮化密植[硕士论文]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社:1-8. | |
| [14] | Liu Lun-lun, Liu Yan, Li Xun. 2015. Extraction of grass carp intestine antimicrobial substances. China Brewing, 34 (9):49-53. (in Chinese) |
| 刘伦伦, 刘焱, 黎迅. 2015. 草鱼鱼肠抗菌活性物质的提取. 中国酿造, 34 (9):49-53. | |
| [15] | Ma Bao-kun, Xu Ji-zhong, Sun Jian-she. 2010. Consideration for high density planting with dwarf rootstocks in apple in China. Journal of Fruit Science, 27 (1):105-109. (in Chinese) |
| 马宝焜, 徐继忠, 孙建设. 2010. 关于我国苹果矮砧密植栽培的思考. 果树学报, 27 (1):105-109. | |
| [16] |
Manici L M, Kelderer M, Caputo F, Saccà M L, Nicoletti F, Topp A R, Mazzola M. 2018. Involvement of Dactylonectria and Ilyonectria spp. in tree decline affecting multi-generation apple orchards. Plant and Soil, 425:217-230.
doi: 10.1007/s11104-018-3571-3 URL |
| [17] |
Mazzola M, Manici L M. 2012. Apple replant disease:role of microbial ecology in cause and control. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 50:45-65.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-081211-173005 pmid: 22559069 |
| [18] |
Moein S, Mazzola M, Ntushelo N S, McLeod A. 2019. Apple nursery trees and irrigation water as potential external inoculum sources of apple replant disease in South Africa. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 153 (4):1131-1147.
doi: 10.1007/s10658-018-01631-9 |
| [19] |
Ndiaye F, Vuong T, Duarte J, Aluko R E, Matar C. 2012. Anti-oxidant,anti-inflammatory and immunomodulating properties of an enzymatic protein hydrolysate from yellow field pea seeds. European Journal of Nutrition, 51 (1):29-37.
doi: 10.1007/s00394-011-0186-3 pmid: 21442413 |
| [20] |
Omran R G. 1980. Peroxide levels and the activities of catalase,peroxidase,and indoleacetic acid oxidase during and after chilling cucumber seedlings. Plant Physiology, 65 (2):407-408.
doi: 10.1104/pp.65.2.407 pmid: 16661201 |
| [21] |
Pan Feng-bing, Xiang Li, Wang Sen, Li Jia-jia, Shen Xiang, Chen Xue-sen, Yin Cheng-miao, Mao Zhi-quan. 2017. Effects of short-term rotation and Trichoderma application on the soil environment and physiological characteristics of Malus hupehensis Rehd. seedlings under replant conditions. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37 (5):315-321.
doi: 10.1016/j.chnaes.2017.09.003 URL |
| [22] | Pan Feng-bing, Wang Hai-yan, Wang Xiao-fang, Chen Xue-sen, Shen Xiang, Yin Cheng-miao, Mao Zhi-quan. 2019. Biological mechanism of vermicompost reducing the replant disease of Malus hupehensis Rehd. seedlings. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 25 (6):925-932. (in Chinese) |
| 潘凤兵, 王海燕, 王晓芳, 陈学森, 沈向, 尹承苗, 毛志泉. 2019. 蚓粪减轻苹果砧木平邑甜茶幼苗连作障碍的土壤生物学机制. 植物营养与肥料学报, 25 (6):925-932. | |
| [23] |
Piovesana S, Capriotti A L, Cavaliere C, La Barbera G, Montone C M, Zenezini Chiozzi R, Laganà A. 2018. Recent trends and analytical challenges in plant bioactive peptide separation,identification and validation. Anal Bioanal Chem, 410 (15):3425-3444.
doi: 10.1007/s00216-018-0852-x pmid: 29353433 |
| [24] |
Plavšin I, Velki M, Ečimović S, Vrandečić K, Ćosić J. 2017. Inhibitory effect of earthworm coelomic fluid on growth of the plant parasitic fungus Fusarium oxysporum. European Journal of Soil Biology, 78:1-6.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejsobi.2016.11.004 URL |
| [25] | Shen Ping, Chen Xiang-dong. 2007. Experiment of microbiology. Beijing: Higher Education Press. (in Chinese) |
| 沈萍, 陈向东. 2007. 微生物学实验. 北京: 高等教育出版社. | |
| [26] |
Singh B K, Sharma S R, Singh B. 2010. Antioxidant enzymes in cabbage:variability and inheritance of superoxide dismutase,peroxidase and catalase. Scientia Horticulturae, 124 (1):9-13.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2009.12.011 URL |
| [27] |
Spath M, Insam H, Peintner U, Kelderer M, Kuhnert R, Franke-Whittle I H. 2015. Linking soil biotic and abiotic factors to apple replant disease:a greenhouse approach. Journal of Phytopathology, 163 (4):287-299.
doi: 10.1111/jph.12318 URL |
| [28] |
Srivastava R K, Pandey P, Rajpoot R, Rani A, Dubey R S. 2014. Cadmium and lead interactive effects on oxidative stress and antioxidative responses in rice seedlings. Protoplasma, 251 (5):1047-1065.
doi: 10.1007/s00709-014-0614-3 pmid: 24482190 |
| [29] |
Sun J, Zhang Q, Li X, Zhou B, Wei Q. 2017. Apple replant disorder of pingyitiancha rootstock is closely associated with rhizosphere fungal community development. Journal of Phytopathology, 165 (3):162-173.
doi: 10.1111/jph.2017.165.issue-3 URL |
| [30] |
Tessera V, Guida F, Juretic D, Tossi A. 2012. Identification of antimicrobial peptides from teleosts and anurans in expressed sequence tag databases using conserved signal sequences. FEBS Journal, 279 (5):724-736.
doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08463.x URL |
| [31] |
Tewoldemedhin Y T, Mazzola M, Labuschagne I, Mcleod A. 2011. A multi-phasic approach reveals that apple replant disease is caused by multiple biological agents,with some agents acting synergistically. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 43 (9):1917-1927.
doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.05.014 URL |
| [32] |
Wang G S, Yin C M, Pan F B, Wang X B, Xiang L, Wang Y F, Wang J Z, Tian C P, Chen J, Mao Z Q. 2018. Analysis of the fungal community in apple replanted soil around bohai gulf. Horticultural Plant Journal, 4 (5):175-181.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2018.05.003 URL |
| [33] | Wang Gong-shuai. 2018. Studies on fungal community in replanted soil around Bohai gulf and alleviation apple replanted disease by mixed cropping with Allium fistulosum L. [Ph. D. Dissertation]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 王功帅. 2018. 环渤海连作土壤真菌群落结构分析及混作葱减轻苹果连作障碍的研究[博士论文]. 泰安: 山东农业大学. | |
| [34] |
Wang Y F, Pan F B, Wang G S, Zhang G D, Wang Y L, Chen X S, Mao Z Q. 2014. Effects of biochar on photosynthesis and antioxidative system of Malus hupehensis Rehd. seedlings under replant conditions. Scientia Horticulturae, 175:9-15.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2014.05.029 URL |
| [35] | Wang Xiaobao, Wang Gongshuai, Liu Yusong, Chen Xuesen, Shen Xiang, Yin Chengmiao, Mao Zhiquan. 2018. Correlation analysis of apple replant disease and soil fungal community structure in the Northwest Loess Plateau area. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 45 (5):855-864. (in Chinese) |
| 王晓宝, 王功帅, 刘宇松, 陈学森, 沈向, 尹承苗, 毛志泉. 2018. 西北黄土高原地区苹果连作障碍与土壤真菌群落结构的相关性分析. 园艺学报, 45 (5):855-864. | |
| [36] | Wang Xiao qi, Jiang Wei tao, Yao Yuan yuan, Yin Cheng miao, Chen Xue sen, Mao Zhi quan. 2020. Research advance of apple replant disease based on soil microorganism. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47 (11):2223-2237. (in Chinese) |
| 王晓琪, 姜伟涛, 姚媛媛, 尹承苗, 陈学森, 毛志泉. 2020. 苹果连作障碍土壤微生物的研究进展. 园艺学报, 47 (11):2223-2237. | |
| [37] | Xiao Hong, Mao Zhi-quan, Yu Ming-ge, Wang Li-qin, Su Huai-rui. 2005. Effects of successive cropping soil and successive cropping soil pasteurized on the growth and development of Malus hupehensis seedlings. Journal of Fruit Science, 21 (4):370-372. (in Chinese) |
| 肖宏, 毛志泉, 于明革, 王丽琴, 束怀瑞. 2005. 连作土与灭菌土对平邑甜茶幼苗生长发育的影响. 果树学报, 21 (4):370-372. | |
| [38] | Xu Wen-feng. 2011. Diversity analysis of soil fungi from Bohai Bay apple replanted orchard and the screening of the antagonistic fungi[M. D. Dissertation]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 徐文凤. 2011. 环渤海湾地区重茬苹果园土壤真菌群落多样性及生防真菌的筛选[博士论文]. 泰安: 山东农业大学. | |
| [39] |
Yim B, Smalla K, Winkelmann T. 2013. Evaluation of apple replant problems based on different soil disinfection treatments:links to soil microbial community structure? Plant and Soil, 366:617-631.
doi: 10.1007/s11104-012-1454-6 URL |
| [40] | Yin Cheng-miao, Hu Yan-li, Wang Gong-shuai, Zhang Xian-fu, Zhou Hui, Shen Xiang, Chen Xue-sen, Mao Zhi-quan. 2016. Effect of main phenolic acids of the apple replanted soil on the roots of Malus hupehensis Rehd. seedlings. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 49 (5):961-969. (in Chinese) |
| 尹承苗, 胡艳丽, 王功帅, 张先富, 周慧, 沈向, 陈学森, 毛志泉. 2016. 苹果连作土壤中主要酚酸类物质对平邑甜茶幼苗根系的影响. 中国农业科学, 49 (5):961-969. | |
| [41] | Yin Cheng-miao, Wang Gong-shuai, Li Yuan-yuan, Che Jin-shui, Shen Xiang, Chen Xue-sen, Mao Zhi-quan, Wu Shu-jing. 2013. A new method for analysis of phenolic acids in the soil--soil from replantedapple orchards was investigated. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 46 (21):4612-4619. (in Chinese) |
| 尹承苗, 王功帅, 李园园, 车金水, 沈向, 陈学森, 毛志泉, 吴树敬. 2013. 一种分析土壤中酚酸类物质含量的新方法--以连作苹果园土壤为试材. 中国农业科学, 46 (21):4612-4619. | |
| [42] | Yin Cheng-miao, Wang Gong-shuai, Li Yuan-yuan, Chen Xue-sen, Wu Shu-jing, Mao Zhi-quan. 2014. Assessment of fungal diversity in apple replanted orchard soils by T-RFLP analysis. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34 (4):837-846. (in Chinese) |
| 尹承苗, 王功帅, 李园园, 陈学森, 吴树敬, 毛志泉. 2014. 连作苹果园土壤真菌的T-RFLP分析. 生态学报, 34 (4):837-846. | |
| [43] | Yin Cheng-miao, Wang Mei, Wang Jia-yan, Chen Xue-sen, Shen Xiang, Zhang Min, Mao Zhi-quan. 2017. The research advance on apple replant disease. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 44 (11):2215-2230. (in Chinese) |
| 尹承苗, 王玫, 王嘉艳, 陈学森, 沈向, 张民, 毛志泉. 2017. 苹果连作障碍研究进展. 园艺学报, 44 (11):2215-2230. | |
| [44] | Zhao Shi-jie, Shi Guo-an, Dong Xin-chun. 2002. Experimental guidance of plant physiology. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press:98-99. (in Chinese) |
| 赵世杰, 史国安, 董新纯. 2002. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社:98-99. |
| [1] | 于婷婷, 李 欢, 宁源生, 宋建飞, 彭璐琳, 贾竣淇, 张玮玮, 杨洪强. 苹果GRAS全基因组鉴定及其对生长素的响应分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 397-409. |
| [2] | 韩晓蕾, 张彩霞, 刘 锴, 杨 安, 严家帝, 李武兴, 康立群, 丛佩华. 中熟苹果新品种‘中苹优蕾’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 1-2. |
| [3] | 韩晓蕾, 张彩霞, 刘 锴, 严家帝, 李武兴, 康立群, 丛佩华. 中熟苹果新品种‘苹优2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 1-2. |
| [4] | 王 强, 丛佩华, 刘肖烽. 晚熟苹果新品种‘华优甜娃’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 3-4. |
| [5] | 王 强, 丛佩华, 刘肖烽. 中熟苹果新品种‘华优宝蜜’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 5-6. |
| [6] | 杨 玲, 丛佩华, 王 强, 李武兴, 康立群. 中熟鲜食苹果新品种‘华丰’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 7-8. |
| [7] | 丁志杰, 包金波, 柔鲜古丽, 朱甜甜, 李雪丽, 苗浩宇, 田新民. 新疆野苹果与‘元帅’‘金冠’的叶绿体基因组比对研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(9): 1977-1990. |
| [8] | 高彦龙, 吴玉霞, 张仲兴, 王双成, 张瑞, 张德, 王延秀. 苹果ELO家族基因鉴定及其在低温胁迫下的表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(8): 1621-1636. |
| [9] | 郑晓东, 袭祥利, 李玉琪, 孙志娟, 马长青, 韩明三, 李少旋, 田义轲, 王彩虹. 油菜素内酯对盐碱胁迫下平邑甜茶幼苗生长的影响及调控机理研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(7): 1401-1414. |
| [10] | 夏炎, 黄松, 武雪莉, 刘一琪, 王苗苗, 宋春晖, 白团辉, 宋尚伟, 庞宏光, 焦健, 郑先波. 基于宏病毒组测序技术的苹果病毒病鉴定与分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(7): 1415-1428. |
| [11] | 刘照霞, 张鑫, 王璐, 马玉婷, 陈倩, 朱占玲, 葛顺峰, 姜远茂. 肥料穴施位点对苹果细根生长、15N吸收利用及产量品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(7): 1545-1556. |
| [12] | 马维峰, 李艳梅, 马宗桓, 陈佰鸿, 毛娟. 苹果POD家族基因的鉴定与MdPOD15的功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(6): 1181-1199. |
| [13] | 冯琛, 黄学旺, 李兴亮, 周佳, 李天红. 不同苹果矮化砧穗组合的抗旱性比较研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(5): 945-957. |
| [14] | 张晓云, 唐玉薇, 王凯, 张东, 杨伟伟. 苹果冠层枝梢类型对光能截获效率和光合生产力影响的模拟分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(4): 709-722. |
| [15] | 于波, 秦嗣军, 吕德国. 适量稳定供锌促进平邑甜茶幼苗生长和氮的吸收利用[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(3): 473-481. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司