
园艺学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (2): 378-394.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0946
杨妮1, 万绮雯1, 李逸民1, 韩妙华1, 滕瑞敏1, 刘洁霞2, 庄静1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-05-17
修回日期:2021-10-23
出版日期:2022-02-25
发布日期:2022-02-28
通讯作者:
庄静
E-mail:zhuangjing@njau.edu.cn
基金资助:
YANG Ni1, WAN Qiwen1, LI Yimin1, HAN Miaohua1, TENG Ruimin1, LIU Jiexia2, ZHUANG Jing1,*( )
)
Received:2021-05-17
Revised:2021-10-23
Online:2022-02-25
Published:2022-02-28
Contact:
ZHUANG Jing
E-mail:zhuangjing@njau.edu.cn
摘要:
为了探讨外源亚精胺(Spd)对盐胁迫下茶树光合特性的调控机理,以茶树品种‘中茶108’为试验材料,通过Spd不同浓度(0、0.5、1.0、1.5 mmol · L-1)的喷施处理,研究盐胁迫(200 mmol · L-1 NaCl)下外源Spd对茶树的光合参数、叶绿素含量、气孔开度及关键酶基因表达的影响。结果显示:盐胁迫处理显著降低了茶树叶片的净光合速率(Pn)、蒸腾速率(Tr)及叶绿素含量等,提高了叶片的胞间CO2浓度(Ci),处理初期(1、3 d)促进气孔开度,后期(5、9 d)逐渐抑制气孔开度;盐胁迫下,外源Spd显著提高了茶树的Pn、Tr、气孔导度(Gs)、叶绿素a、b及总含量;外源Spd可以不同程度地诱导CsRbcL、CsTK、CsFBPase、CsPRK等光合碳同化基因的表达,并且缓解了盐胁迫对大多叶绿素合成基因抑制的影响。研究表明叶面喷施外源Spd可以有效缓解叶绿素的降解,促进茶树的光合作用,提高茶树的耐盐性,其中以喷施0.5 mmol · L-1亚精胺的缓解效应最为显著。
中图分类号:
杨妮, 万绮雯, 李逸民, 韩妙华, 滕瑞敏, 刘洁霞, 庄静. 外源亚精胺对盐胁迫下茶树光合特性及关键酶基因表达的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(2): 378-394.
YANG Ni, WAN Qiwen, LI Yimin, HAN Miaohua, TENG Ruimin, LIU Jiexia, ZHUANG Jing. Effects of Exogenous Spermidine on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Gene Expression of Key Enzymes Under Salt Stress in Tea Plant[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(2): 378-394.
| 基因 Gene | 名称 Name | 正向引物(5′-3′) Forward primer sequence | 反向引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| CsACT7 | 肌动蛋白 Actin | TTGGATTCTGGGGATGGTGTTAGC | AGCAAGTTTCTCTTTCACATCACGG |
| CsADC | 精氨酸脱酸酶 Arginine decarboxylase | TCAAGGAAGGGTCTTTGGGTA | GGTATGTGCGAATGGGGTCT |
| CsCHLM | Mg-原卟啉 Ⅸ 甲基转移酶 Magnesium protoporphyrin Ⅸ methyltransferase | CTCTATTGCCTCATTCCTC | ATTTAGTGTTTGGGTTGGT |
| CsCRD1 | Mg-原卟啉 Ⅸ 单甲基酯环化酶 Magnesium protoporphyrin Ⅸ monomethyl ester cyclase | CAATGACTGGAAGGCTAA | ATTCTTTGGTGTTGAGGC |
| CsFBPase | 果糖-1,6-二磷酸酶 Furetose-1,6-bisphosphate phosphatase | GCAGATTGCTTCGTTGGTTC | TGCTATTATCCCTGTCCTCCC |
| CsHEMA1 | 谷氨酸-tRNA还原酶 Glutamyl-tRNA reductase | ATTCGTTGCGAGATTGTT | GCTGCTCCTTTCCTTTGT |
| CsHEMC | 胆色素原脱氨酶 Porphobilinogen deaminase | TGACCGCCATTCTTTCTA | GCTAATCTTGTTTCCTCGT |
| CsHEMD | 尿卟啉原 Ⅲ 合成酶 Uroporphyrinogen Ⅲ synthase | TGTCTGGGCTGTCTTCGA | CAAATCAGGCAACCGTGT |
| CsHEME2 | 尿卟啉原 Ⅲ 脱羧酶 Uroporphyrinogen Ⅲ decarboxylase | ACATTCGCTTCTGTTCCC | TTTCTACTTCCAGCCCTC |
| CsHEMG2 | 原卟啉原氧化酶 Protoporphyrinogen oxidase | TCTGTGGAAGAAACGGAACT | CCGCAACGAAAGGGTCAA |
| CsODC | 鸟氨酸脱羧酶 Ornithine decarboxylase | TTCCAAACATGGGTGCGTAT | TGTGAGGTGGGTCGTAATCG |
| CsPRK | 核酮糖-5-磷酸激酶 Ribulose5-phosphate kinase | AGTATTGGAGCCCGAAAGCC | CAAACAGGTAAACTGGGGTGAA |
| CsPPOX | 原卟啉原氧化酶 Protoporphyrinogen oxidase | GAAGCAGTTGACCGTGAC | AAAGCCCTCTGAACCCAC |
| CsRbcL | 核酮糖-1,5-二磷酸羧化/加氧酶大亚基 Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase large subunit | TGGCTGGAGATGGGACGA | CCTCTGGTAATCAGAACAGGGTT |
| CsSAMDC | S-腺苷甲硫氨酸脱羧酶 S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase | TACTCTGCTTCTGCTGAATCGA | GCCTTCTTCCTGTCCAAACC |
| CsSPDS | 亚精胺合成酶 Spermidine synthases | AACCCAATAGACGCCGATGA | CGCAAAAGATGGCAAACAGA |
| CsSAMS | S-腺苷甲硫氨酸合成酶 S-adenosylmethionine synthases | CGATGAGACCGTGACAAATGA | AGGGTTGAGGTGGAAGATGG |
| CsTK | 转酮醇酶 Transketolase | TGCCCAATGTTTTGATGCTACG | ATCCACCCTTTTCCACTCCCTC |
表1 荧光定量引物序列
Table 1 Quantitative RT-PCR primer sequence
| 基因 Gene | 名称 Name | 正向引物(5′-3′) Forward primer sequence | 反向引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| CsACT7 | 肌动蛋白 Actin | TTGGATTCTGGGGATGGTGTTAGC | AGCAAGTTTCTCTTTCACATCACGG |
| CsADC | 精氨酸脱酸酶 Arginine decarboxylase | TCAAGGAAGGGTCTTTGGGTA | GGTATGTGCGAATGGGGTCT |
| CsCHLM | Mg-原卟啉 Ⅸ 甲基转移酶 Magnesium protoporphyrin Ⅸ methyltransferase | CTCTATTGCCTCATTCCTC | ATTTAGTGTTTGGGTTGGT |
| CsCRD1 | Mg-原卟啉 Ⅸ 单甲基酯环化酶 Magnesium protoporphyrin Ⅸ monomethyl ester cyclase | CAATGACTGGAAGGCTAA | ATTCTTTGGTGTTGAGGC |
| CsFBPase | 果糖-1,6-二磷酸酶 Furetose-1,6-bisphosphate phosphatase | GCAGATTGCTTCGTTGGTTC | TGCTATTATCCCTGTCCTCCC |
| CsHEMA1 | 谷氨酸-tRNA还原酶 Glutamyl-tRNA reductase | ATTCGTTGCGAGATTGTT | GCTGCTCCTTTCCTTTGT |
| CsHEMC | 胆色素原脱氨酶 Porphobilinogen deaminase | TGACCGCCATTCTTTCTA | GCTAATCTTGTTTCCTCGT |
| CsHEMD | 尿卟啉原 Ⅲ 合成酶 Uroporphyrinogen Ⅲ synthase | TGTCTGGGCTGTCTTCGA | CAAATCAGGCAACCGTGT |
| CsHEME2 | 尿卟啉原 Ⅲ 脱羧酶 Uroporphyrinogen Ⅲ decarboxylase | ACATTCGCTTCTGTTCCC | TTTCTACTTCCAGCCCTC |
| CsHEMG2 | 原卟啉原氧化酶 Protoporphyrinogen oxidase | TCTGTGGAAGAAACGGAACT | CCGCAACGAAAGGGTCAA |
| CsODC | 鸟氨酸脱羧酶 Ornithine decarboxylase | TTCCAAACATGGGTGCGTAT | TGTGAGGTGGGTCGTAATCG |
| CsPRK | 核酮糖-5-磷酸激酶 Ribulose5-phosphate kinase | AGTATTGGAGCCCGAAAGCC | CAAACAGGTAAACTGGGGTGAA |
| CsPPOX | 原卟啉原氧化酶 Protoporphyrinogen oxidase | GAAGCAGTTGACCGTGAC | AAAGCCCTCTGAACCCAC |
| CsRbcL | 核酮糖-1,5-二磷酸羧化/加氧酶大亚基 Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase large subunit | TGGCTGGAGATGGGACGA | CCTCTGGTAATCAGAACAGGGTT |
| CsSAMDC | S-腺苷甲硫氨酸脱羧酶 S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase | TACTCTGCTTCTGCTGAATCGA | GCCTTCTTCCTGTCCAAACC |
| CsSPDS | 亚精胺合成酶 Spermidine synthases | AACCCAATAGACGCCGATGA | CGCAAAAGATGGCAAACAGA |
| CsSAMS | S-腺苷甲硫氨酸合成酶 S-adenosylmethionine synthases | CGATGAGACCGTGACAAATGA | AGGGTTGAGGTGGAAGATGG |
| CsTK | 转酮醇酶 Transketolase | TGCCCAATGTTTTGATGCTACG | ATCCACCCTTTTCCACTCCCTC |
| 处理后天数/d Days after treatment | 处理/(mmol · L-1) Treatment | 气孔横径/μm Stomatal transverse diameter | 气孔纵径/μm Stomatal longitudinal diameter | 气孔开度/μm2 Stomatal aperture | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NaCl | Spd | ||||
| 1 | 0(对照Control) | 0 | 8.75 ± 0.13 lm | 17.81 ± 0.71 def | 122.54 ± 6.67 jk |
| 0 | 0.5 | 11.88 ± 0.16 abcde | 20.21 ± 0.41 abcd | 188.49 ± 6.36 b | |
| 0 | 1.0 | 9.60 ± 0.29 ijklm | 18.24 ± 0.73 bcdef | 137.16 ± 2.38 hi | |
| 0 | 1.5 | 12.51 ± 0.22 a | 18.79 ± 0.20 abcde | 184.48 ± 1.27 bc | |
| 200 | 0 | 10.44 ± 0.31 efghijk | 18.83 ± 0.46 abcde | 154.03 ± 1.55 fg | |
| 200 | 0.5 | 8.69 ± 0.19 lm | 17.15 ± 0.29 ef | 116.85 ± 1.28 k | |
| 200 | 1.0 | 10.87 ± 0.32 cdefghi | 16.11 ± 0.21 f | 137.47 ± 4.17 hi | |
| 200 | 1.5 | 9.88 ± 0.29 hijkl | 18.85 ± 0.74 abcde | 145.80 ± 2.59 gh | |
| 3 | 0(对照Control) | 0 | 10.39 ± 0.01 efghijk | 17.61 ± 0.38 def | 143.64 ± 3.33 gh |
| 0 | 0.5 | 10.05 ± 0.09 ghijkl | 19.25 ± 0.45 abcde | 151.90 ± 2.27 g | |
| 0 | 1.0 | 11.10 ± 0.27 abcdefgh | 19.64 ± 0.85 abcde | 171.00 ± 3.29 de | |
| 0 | 1.5 | 12.32 ± 0.62 abc | 19.54 ± 0.60 abcde | 188.59 ± 6.56 b | |
| 200 | 0 | 11.74 ± 0.55 abcde | 19.16 ± 0.99 abcde | 175.68 ± 1.93 bcde | |
| 200 | 0.5 | 9.11 ± 0.35 klm | 21.08 ± 0.48 a | 150.63 ± 2.34 g | |
| 200 | 1.0 | 9.09 ± 0.15 klm | 17.53 ± 0.48 def | 125.04 ± 1.40 ijk | |
| 200 | 1.5 | 9.81 ± 0.66 hijkl | 17.91 ± 1.08 cdef | 136.88 ± 1.09 hi | |
| 5 | 0(对照Control) | 0 | 10.92 ± 0.41 bcdefghi | 20.09 ± 1.14 abcd | 171.96 ± 8.84 cde |
| 0 | 0.5 | 11.16 ± 0.68 abcdefgh | 20.54 ± 0.47 abc | 179.77 ± 6.74 bcd | |
| 0 | 1.0 | 10.64 ± 0.53 defghij | 20.17 ± 0.70 abcd | 167.52 ± 2.31 de | |
| 0 | 1.5 | 12.39 ± 0.25 ab | 21.29 ± 0.35 a | 206.93 ± 1.20 a | |
| 200 | 0 | 10.98 ± 0.32 bcdefghi | 19.89 ± 0.59 abcd | 171.24 ± 0.81 de | |
| 200 | 0.5 | 10.72 ± 0.56 defghij | 20.99 ± 1.62 a | 175.85 ± 4.47 bcde | |
| 200 | 1.0 | 11.55 ± 0.16 abcdef | 19.15 ± 0.17 abcde | 173.63 ± 4.02 cde | |
| 200 | 1.5 | 11.53 ± 0.63 abcdefg | 19.09 ± 1.07 abcde | 171.28 ± 3.86 de | |
| 9 | 0(对照Control) | 0 | 11.50 ± 0.21 abcdefg | 18.25 ± 0.34 bcdef | 164.74 ± 3.18 ef |
| 0 | 0.5 | 9.27 ± 0.47 jklm | 17.69 ± 1.03 def | 128.15 ± 5.21 ijk | |
| 0 | 1.0 | 12.27 ± 0.33 abc | 19.54 ± 0.74 abcde | 187.86 ± 2.88 b | |
| 0 | 1.5 | 11.79 ± 0.08 abcde | 18.78 ± 0.51 abcde | 173.70 ± 3.57 cde | |
| 200 | 0 | 8.28 ± 0.41 m | 20.08 ± 0.73 abcd | 129.99 ± 1.68 ij | |
| 200 | 0.5 | 11.56 ± 0.34 abcdef | 20.72 ± 0.45 ab | 187.98 ± 1.47 b | |
| 200 | 1.0 | 11.97 ± 0.39 abcd | 19.10 ± 0.59 abcde | 178.85 ± 2.61 bcd | |
| 200 | 1.5 | 10.13 ± 0.22 fghjkl | 18.94 ± 0.82 abcde | 150.29 ± 3.32 g | |
表2 外源亚精胺对盐胁迫下茶树叶片气孔开度的影响
Table 2 Effects of exogenous Spd on stomatal aperture of tea plant leaves under salt stress
| 处理后天数/d Days after treatment | 处理/(mmol · L-1) Treatment | 气孔横径/μm Stomatal transverse diameter | 气孔纵径/μm Stomatal longitudinal diameter | 气孔开度/μm2 Stomatal aperture | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NaCl | Spd | ||||
| 1 | 0(对照Control) | 0 | 8.75 ± 0.13 lm | 17.81 ± 0.71 def | 122.54 ± 6.67 jk |
| 0 | 0.5 | 11.88 ± 0.16 abcde | 20.21 ± 0.41 abcd | 188.49 ± 6.36 b | |
| 0 | 1.0 | 9.60 ± 0.29 ijklm | 18.24 ± 0.73 bcdef | 137.16 ± 2.38 hi | |
| 0 | 1.5 | 12.51 ± 0.22 a | 18.79 ± 0.20 abcde | 184.48 ± 1.27 bc | |
| 200 | 0 | 10.44 ± 0.31 efghijk | 18.83 ± 0.46 abcde | 154.03 ± 1.55 fg | |
| 200 | 0.5 | 8.69 ± 0.19 lm | 17.15 ± 0.29 ef | 116.85 ± 1.28 k | |
| 200 | 1.0 | 10.87 ± 0.32 cdefghi | 16.11 ± 0.21 f | 137.47 ± 4.17 hi | |
| 200 | 1.5 | 9.88 ± 0.29 hijkl | 18.85 ± 0.74 abcde | 145.80 ± 2.59 gh | |
| 3 | 0(对照Control) | 0 | 10.39 ± 0.01 efghijk | 17.61 ± 0.38 def | 143.64 ± 3.33 gh |
| 0 | 0.5 | 10.05 ± 0.09 ghijkl | 19.25 ± 0.45 abcde | 151.90 ± 2.27 g | |
| 0 | 1.0 | 11.10 ± 0.27 abcdefgh | 19.64 ± 0.85 abcde | 171.00 ± 3.29 de | |
| 0 | 1.5 | 12.32 ± 0.62 abc | 19.54 ± 0.60 abcde | 188.59 ± 6.56 b | |
| 200 | 0 | 11.74 ± 0.55 abcde | 19.16 ± 0.99 abcde | 175.68 ± 1.93 bcde | |
| 200 | 0.5 | 9.11 ± 0.35 klm | 21.08 ± 0.48 a | 150.63 ± 2.34 g | |
| 200 | 1.0 | 9.09 ± 0.15 klm | 17.53 ± 0.48 def | 125.04 ± 1.40 ijk | |
| 200 | 1.5 | 9.81 ± 0.66 hijkl | 17.91 ± 1.08 cdef | 136.88 ± 1.09 hi | |
| 5 | 0(对照Control) | 0 | 10.92 ± 0.41 bcdefghi | 20.09 ± 1.14 abcd | 171.96 ± 8.84 cde |
| 0 | 0.5 | 11.16 ± 0.68 abcdefgh | 20.54 ± 0.47 abc | 179.77 ± 6.74 bcd | |
| 0 | 1.0 | 10.64 ± 0.53 defghij | 20.17 ± 0.70 abcd | 167.52 ± 2.31 de | |
| 0 | 1.5 | 12.39 ± 0.25 ab | 21.29 ± 0.35 a | 206.93 ± 1.20 a | |
| 200 | 0 | 10.98 ± 0.32 bcdefghi | 19.89 ± 0.59 abcd | 171.24 ± 0.81 de | |
| 200 | 0.5 | 10.72 ± 0.56 defghij | 20.99 ± 1.62 a | 175.85 ± 4.47 bcde | |
| 200 | 1.0 | 11.55 ± 0.16 abcdef | 19.15 ± 0.17 abcde | 173.63 ± 4.02 cde | |
| 200 | 1.5 | 11.53 ± 0.63 abcdefg | 19.09 ± 1.07 abcde | 171.28 ± 3.86 de | |
| 9 | 0(对照Control) | 0 | 11.50 ± 0.21 abcdefg | 18.25 ± 0.34 bcdef | 164.74 ± 3.18 ef |
| 0 | 0.5 | 9.27 ± 0.47 jklm | 17.69 ± 1.03 def | 128.15 ± 5.21 ijk | |
| 0 | 1.0 | 12.27 ± 0.33 abc | 19.54 ± 0.74 abcde | 187.86 ± 2.88 b | |
| 0 | 1.5 | 11.79 ± 0.08 abcde | 18.78 ± 0.51 abcde | 173.70 ± 3.57 cde | |
| 200 | 0 | 8.28 ± 0.41 m | 20.08 ± 0.73 abcd | 129.99 ± 1.68 ij | |
| 200 | 0.5 | 11.56 ± 0.34 abcdef | 20.72 ± 0.45 ab | 187.98 ± 1.47 b | |
| 200 | 1.0 | 11.97 ± 0.39 abcd | 19.10 ± 0.59 abcde | 178.85 ± 2.61 bcd | |
| 200 | 1.5 | 10.13 ± 0.22 fghjkl | 18.94 ± 0.82 abcde | 150.29 ± 3.32 g | |
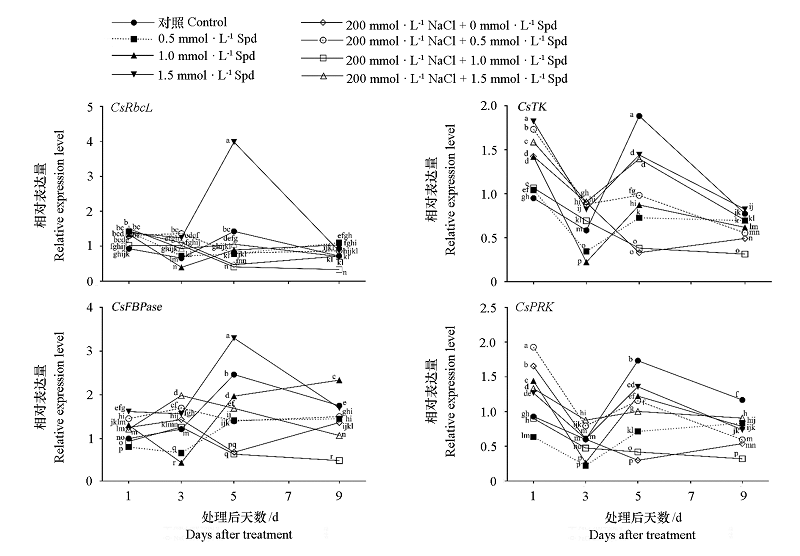
图5 外源亚精胺对盐胁迫下茶树叶片光合碳同化关键酶基因表达的影响
Fig. 5 Effects of exogenous Spd on gene expression of key enzymes of photosynthetic carbon assimilation in tea plant leaves under salt stress
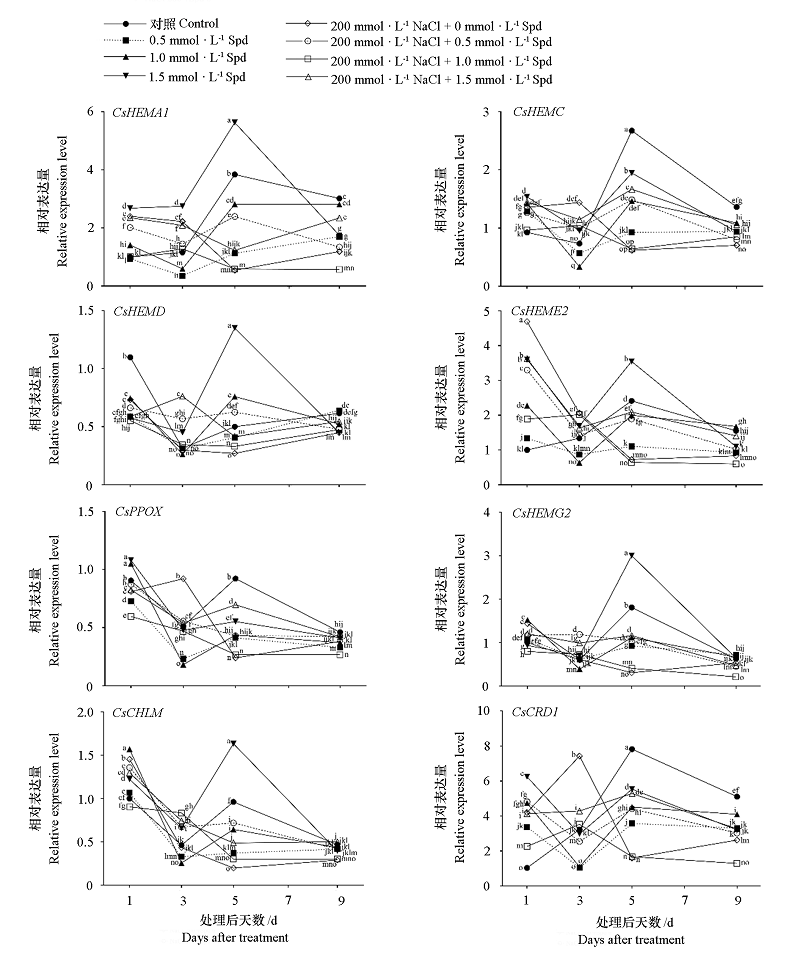
图6 外源亚精胺对盐胁迫下茶树叶片叶绿素合成途径相关基因表达的影响
Fig. 6 Effects of exogenous Spd on gene expression related to chlorophyll synthesis pathway in tea plant leaves under salt stress
| [1] |
Ashraf M, Harris P J C. 2013. Photosynthesis under stressful environments:an overview. Photosynthetica, 51 (2):163-190.
doi: 10.1007/s11099-013-0021-6 URL |
| [2] |
Chaves M M, Flexas J, Pinheiro C. 2009. Photosynthesis under drought and salt stress:regulation mechanisms from whole plant to cell. ANN BOT, 103 (4):551-560.
doi: 10.1093/aob/mcn125 URL |
| [3] | Chen Li-fang. 2011. Effects of exogenous spermidine on CO2 assimilation and metabolism of salt-stressed cucumber seedlings[M. D. Dissertation]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 陈丽芳. 2011. 外源亚精胺对盐胁迫下黄瓜幼苗CO2同化代谢的影响[硕士论文]. 南京: 南京农业大学. | |
| [4] | Chen Xiong-wei, Ma Yan-ping, Xu Cheng-xiang, Xu Xi-zeng. 2012. Effects of exogenous polyamines and polyamine metabolism inhibitors on and chloroplastsionic homeostasis and thylakoid membrane conjugated H+-ATPase activity of Ziziphus jujuba Mill. under salt stress. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 32 (10):1-8. (in Chinese) |
| 陈雄伟, 马艳萍, 徐呈祥, 徐锡增. 2012. 多胺及其代谢抑制剂对盐胁迫下枣树叶绿体离子稳态和类囊体膜H+-ATP酶活性的影响. 中南林业科技大学学报, 32 (10):1-8. | |
| [5] |
Duan J J, Li J, Guo S R, Kang Y. 2008. Exogenous spermidine affects polyamine metabolism in salinity-stressed Cucumis sativus roots and enhances short-term salinity tolerance. Journal of Plant Physiology, 165 (15):1620-1635.
doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2007.11.006 URL |
| [6] | Duan Jiu-ju, Guo Shi-rong. 2005. Effects of exogenous spermidine on salt tolerance of cucumber seedlings under NaCl stress. China Vegetables, 1 (12):8-10. (in Chinese) |
| 段九菊, 郭世荣. 2005. 外源亚精胺对NaCl胁迫下黄瓜幼苗耐盐性的影响. 中国蔬菜, 1 (12):8-10. | |
| [7] | Hasanuzzaman M, Hossain M A, Silva J A T D, Fujita M. 2012. Plant response and tolerance to abiotic oxidative stress:antioxidant defense is a key factor. Crop Stress and its Management:Perspectives and Strategies. Springer Netherlands,261-315 |
| [8] |
Hu L P, Xiang L X, Zhang L, Zhou X T, Zou Z R, Hu X H. 2014. The photoprotective role of spermidine in tomato seedlings under salinity-alkalinity stress. PLoS ONE, 9 (10):e110855.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110855 URL |
| [9] | Hu Li-pan. 2016. Photoprotective mechanism of exogenous Spd in tomato leaves under salnity-alkalinity stress[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University. (in Chinese) |
| 胡立盼. 2016. 盐碱胁迫下外源亚精胺对番茄叶片光抑制保护机理[博士论文]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学. | |
| [10] | Hu X H, Zhang Y, Shi Y, Zhang Z, Zou Z R, Zhang H, Zhao J Z. 2012. Effect of exogenous spermidine on polyamine content and metabolism in tomato exposed to salinity-alkalinity mixed stress. Plant Physiology & Biochemistry, 57:200-209. |
| [11] | Hua Chun, Zhou Feng, Ding Chun-xia, Chen Quan-zhan, Wang Ren-lei, Li Ping. 2012. Effects of exogenous spermidine on photosynthetic parameters and chloroplast ultrastructure of Salicornia bigelovii under NaCl stress. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 21 (2):89-95. (in Chinese) |
| 华春, 周峰, 丁春霞, 陈全战, 王仁雷, 李萍. 2012. 外源亚精胺对NaCl胁迫下毕氏海蓬子光合参数和叶绿体超微结构的影响. 植物资源与环境学报, 21 (2):89-95. | |
| [12] | Jin Xiao-qing. 2019. Exogenous γ-aminobutyric acid regulates reactive oxygen species and chlorophyll metabolism to enhance salinity-alkalinity stress tolerance in muskmelon seedlings. Yangling: Northwest A & F University. (in Chinese) |
| 靳晓青. 2019. 外源γ-氨基丁酸调控活性氧和叶绿素代谢增强甜瓜幼苗盐碱胁迫耐性[硕士论文]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学. | |
| [13] |
Lawson T, Blatt M R. 2014. Stomatal size,speed,and responsiveness impact on photosynthesis and water use efficiency. Plant Physiology, 164 (4):1556-1570.
doi: 10.1104/pp.114.237107 pmid: 24578506 |
| [14] | Li Hai-yun, Wang Xiu-feng, Wei Min, Song Chun-feng. 2003. Effects of different anions on photosynthetic characteristics and yield of cucumber. China Vegetables,(4):12-14. (in Chinese) |
| 李海云, 王秀峰, 魏珉, 宋春凤. 2003. 不同阴离子对黄瓜光合特性及产量的影响. 中国蔬菜,(4):12-14. | |
| [15] |
Li J M, Hu L P, Zhang L, Pan X B, Hu X H. 2015. Exogenous spermidine is enhancing tomato tolerance to salinity-alkalinity stress by regulating chloroplast antioxidant system and chlorophyll metabolism. Bmc Plant Biology, 15 (1):303-320.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-015-0699-7 URL |
| [16] |
Li X G, Meng Q W, Jiang G Q, Zou Q. 2003. The susceptibility of cucumber and sweet pepper to chilling under low irradiance is related to energy dissipation and water-water cycle. Photosynthetica, 41 (2):259-265.
doi: 10.1023/B:PHOT.0000011959.30746.c0 URL |
| [17] | Li Xiang, Sang Qin-qin, Shu Sheng, Sun Jin, Guo Shi-rong. 2016. Effects of epibrassinolide on the activities and gene expression of photosynthetic enzymes in tomato seedlings under low light. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 43 (10):2012-2020. (in Chinese) |
| 李翔, 桑勤勤, 束胜, 孙锦, 郭世荣. 2016. 外源油菜素内酯对弱光下番茄幼苗光合碳同化关键酶及其基因的影响. 园艺学报, 43 (10):2012-2020. | |
| [18] | Li Xiu, Gong Biao, Xu Kun. 2015. Effect of exogenous spermidine on levels of endogenous hormones and chloroplast ultrastructure of ginger leaves under heat stress. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 48 (1):120-129. (in Chinese) |
| 李秀, 巩彪, 徐坤. 2015. 外源亚精胺对高温胁迫下生姜叶片内源激素及叶绿体超微结构的影响. 中国农业科学, 48 (1):120-129. | |
| [19] |
Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCTMethod. Methods, 25 (4):402-408.
doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262 pmid: 11846609 |
| [20] | Lu Wen-yun, Fang Ke, Bian Hong-wu, Zhu Mu-yuan. 2016. Advances in stomatal development and its regulation factors. Plant Physiology Journal, 52 (6):782-788. (in Chinese) |
| 陆雯芸, 房克, 边红武, 朱睦元. 2016. 气孔发育及其调控因素的研究进展. 植物生理学报, 52 (6):782-788. | |
| [21] |
Parida A K, Das A B. 2005. Salt tolerance and salinity effects on plants: a review. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 60 (3):324-349.
pmid: 15590011 |
| [22] | Ren Yan-fang, He Jun-yu. 2008. Effects of NaCl stress on growth and photosynthetic characteristics of lettuce(Lactuca sativa L.)seedlings. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica,(4):149-153. (in Chinese) |
| 任艳芳, 何俊瑜. 2008. NaCl胁迫对莴苣幼苗生长和光合性能的影响. 华北农学报,(4):149-153. | |
| [23] |
Roychoudhury A, Basu S, Sengupta D N. 2011. Amelioration of salinity stress by exogenously applied spermidine or spermine in three varieties of indica rice differing in their level of salt tolerance. Journal of Plant Physiology, 168 (4):317-328.
doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2010.07.009 pmid: 20728960 |
| [24] |
Sairam R K, Srivastava G C. 2002. Changes in antioxidant activity in sub-cellular fractions of tolerant and susceptible wheat genotypes in response to long term salt stress. Plant Science, 162 (6):897-904.
doi: 10.1016/S0168-9452(02)00037-7 URL |
| [25] |
Salvucci M E, Loo F J V D, Stecher D. 2003. Two isoforms of Rubisco activase in cotton, the products of separate genes not alternative splicing. Planta, 216 (5):736-744.
pmid: 12624760 |
| [26] | Shen Wei-qi. 1988. Extraction of mixed solution for determination of chlorophyll content in rice leaf blade. Plant Physiology Journal,(3):64-66. (in Chinese) |
| 沈伟其. 1988. 测定水稻叶片叶绿素含量的混合液提取法. 植物生理学通讯,(3):64-66. | |
| [27] |
Stpień P, Kbus G. 2006. Water relations and photosynthesis in Cucumis sativus L. leaves under salt stress. Biologia Plantarum, 50 (4):610-616.
doi: 10.1007/s10535-006-0096-z URL |
| [28] | Sun Yong-mei, Liu Li-jie, Feng Ming-fang, Wang Jun-hong, Cang Jing, Li Su, Bao Yu-zhuo, Wang Xiu-tian. 2015. Research progress of sugar metabolism of plants under cold stress. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 46 (7):95-102. (in Chinese) |
| 孙永梅, 刘丽杰, 冯明芳, 王军虹, 苍晶, 李速, 包雨卓, 王秀田. 2015. 植物在低温胁迫下的糖代谢研究进展. 东北农业大学学报, 46 (7):95-102. | |
| [29] |
Tanaka A, Tanaka R. 2006. Chlorophyll metabolism. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 9 (3):248-255.
pmid: 16603411 |
| [30] | Tanou G, Ziogas V, Belghazi M, Christou A, Filippou P, Job D, Fotopoulos V, Molassiotis A. 2014. Polyamines reprogram oxidative and nitrosative status and the proteome of citrus plants exposed to salinity stress. Plant Cell & Environment, 37 (4):864-885. |
| [31] |
Tian Li-li, Huang Jian-an, Liu Zhong-hua. 2017. Research progress on resistance saline and alkaline of tea plant. Plant Physiology Journal, 53 (2):167-173. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.1104/pp.53.2.167 URL |
| 田丽丽, 黄建安, 刘仲华. 2017. 茶树抗盐碱研究进展. 植物生理学报, 53 (2):167-173. | |
| [32] | Wang Feng, Yan Jiarong, Chen Xueyu, Jiang Chenghao, Meng Sida, Liu Yufeng, Xu Tao, Qi Mingfang, Li Tianlai. 2019. Light regulation of chlorophyll biosynthesis in plants. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 46 (5):975-994. (in Chinese) |
| 王峰, 闫家榕, 陈雪玉, 姜程浩, 孟思达, 刘玉凤, 许涛, 齐明芳, 李天来. 2019. 光调控植物叶绿素生物合成的研究进展. 园艺学报, 46 (5):975-994. | |
| [33] | Wang Li-min, Huang Dan-feng, Zhang Yi-dong. 2011. Effects of exogenous Ca2+ on stomatal morphological character of melon leaf and regulation under salt stress. Journal of Changjiang Vegetables,(2):36-39. (in Chinese) |
| 王黎敏, 黄丹枫, 张屹东. 2011. 外源Ca2+对盐胁迫下甜瓜叶片气孔开度的调节. 长江蔬菜,(2):36-39. | |
| [34] |
Wang P T, Song C P. 2008. Guard-cell signalling for hydrogen peroxide and abscisic acid. The New phytologist, 178 (4):703-18.
doi: 10.1111/nph.2008.178.issue-4 URL |
| [35] | Wang S P, Guo S R, Hu X H, Li J, Jiao Y S. 2006. Effects of NaCl stress on the content of photosynthetic pigments in the leaves of cucumbe(Cucumis sativus L.)seedlings. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 47 (16):1044-1053. |
| [36] | Wang Zhi-wei, Yun Wen-jun, Xie Jian-ming, Li Ying. 2009. Mitigative effect of exogenous spermidine on growth inhibition in pepper seedlings under NaCl stress. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 44 (4):67-72. (in Chinese) |
| 汪志伟, 贠文俊, 颉建明, 李盈. 2009. 外源亚精胺对盐胁迫下辣椒幼苗生长抑制的缓解效应. 甘肃农业大学学报, 44 (4):67-72. | |
| [37] | Wolz K J, Wertin T M, Abordo M, Dan W, Leakey A D B. 2017. Diversity in stomatal function is integral to modelling plant carbon and water fluxes. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 1 (9):1292-1298. |
| [38] |
Wu Z J, Tian C, Jiang Q, Li X H, Zhuang J. 2016. Selection of suitable reference genes for qRT-PCR normalization during leaf development and hormonal stimuli in tea plant(Camellia sinensis). Scientific Reports, 6:19748.
doi: 10.1038/srep19748 URL |
| [39] | Wu Zhi-jun, Lu Li, Li Xing-hui, Fang Wan-Ping, Zhou Lin, Tan Guo-fei, Zhuang Jing. 2014. Isolation and expression profiles analysis of AP2/ERF-B 3 group transcription factor from Camellia sinensis. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 37 (4):67-75. (in Chinese) |
| 吴致君, 卢莉, 黎星辉, 房婉萍, 周琳, 谭国飞, 庄静. 2014. 茶树AP2/ERF-B3类转录因子基因的克隆与表达特性分析. 南京农业大学学报, 37 (4):67-75. | |
| [40] |
Xiong Hui, Ma Cheng-en, Li Le, Zeng Hui, Guo Da-li. 2014. Stomatal characteristics of ferns and angiosperms and their responses to changing light intensity at different habitats. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 38 (8):868-877. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1258.2014.00081 URL |
|
熊慧, 马承恩, 李乐, 曾辉, 郭大立. 2014. 不同生境条件下蕨类和被子植物的气孔形态特征及其对光强变化的响应. 植物生态学报, 38 (8):868-877.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1258.2014.00081 |
|
| [41] |
Yang X H, Lu C M. 2010. Photosynthesis is improved by exogenous glycinebetaine in salt-stressed maize plants. Physiologia Plantarum, 124 (3):343-352.
doi: 10.1111/ppl.2005.124.issue-3 URL |
| [42] | Yu Bing-jun, Li Suo-na, Liu You-liang. 2002. Comparison of ion effects of salt injury in soybean seedlings. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University,(1):5-9. (in Chinese) |
| 於丙军, 李锁娜, 刘友良. 2002. 大豆苗期盐害离子效应的比较. 南京农业大学学报,(1):5-9. | |
| [43] |
Yu M, Hu C X, Wang Y H. 2006. Effects of molybdenum on the intermediates of chlorophyll biosynthesis in winter wheat cultivars under low temperature. Agricultural Sciences in China, 5 (9):670-677.
doi: 10.1016/S1671-2927(06)60109-0 URL |
| [44] |
Yu X L, Hu S, He C, Zhou J T, Qu F F, Ai Z, Chen Y Q, Ni D J. 2019. Chlorophyll metabolism in postharvest tea(Camellia sinensis L.)leaves:variations in color values, chlorophyll derivatives, and gene expression levels under different withering treatments. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 67 (38):10624-10636.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b03477 URL |
| [45] | Yuan R N, Shu S, Guo S R, Sun J, Wu J Q. 2018. The positive roles of exogenous putrescine on chlorophyll metabolism and xanthophyll cycle in salt-stressed cucumber seedlings. Photosynthetica:International Journal for Photosynthesis Research, 56 (2):557-566. |
| [46] | Zhang Chun-mei, Zou Zhi-rong, Huang Zhi, Zhang Zhi-xin. 2010. Effects of exogenous spermidine on photosynthesis of tomato seedlings under drought stress. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 28 (3):182-187. (in Chinese) |
| 张春梅, 邹志荣, 黄志, 张志新. 2010. 外源亚精胺对干旱胁迫下不同品种番茄幼苗光合作用的影响. 干旱地区农业研究, 28 (3):182-187. | |
| [47] |
Zhang Y, Zhang L, Hu X H. 2014. Exogenous spermidine-induced changes at physiological and biochemical parameters levels in tomato seedling grown in saline-alkaline condition. Botanical Studies, 55 (1):58-65.
doi: 10.1186/s40529-014-0058-2 pmid: 28510977 |
| [48] | Zhang Yi, Shi Yu, Hu Xiao-hui. 2016. Effects of exogenous spermidine on photosynthetic characteristics of tomato seedlings under salinity-alkalinity stress. Journal of Northwest A & F University(Natural Science Edition), 44 (2):144-150. (in Chinese) |
| 张毅, 石玉, 胡晓辉. 2016. 外源亚精胺对盐碱胁迫下番茄幼苗光合特性的影响. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 44 (2):144-150. | |
| [49] | Zhu J K. 2001. Plant salt tolerance. Trends in Plant ence, 6 (2):66-71. |
| [50] | Zhu Jin, Bie Zhi-long. 2007. Effects of NaCl stress on photosynthetic characteristics of three cucumber rootstock seedlings. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 34 (6):1418-1424. (in Chinese) |
| 朱进, 别之龙. 2007. 盐胁迫对3种黄瓜砧木幼苗光合特性的影响. 园艺学报, 34 (6):1418-1424. | |
| [51] | Zhu Yu, Huang Lei, Zheng Yun-pu, Hao Li-hua, Jiang Guo-bin, Wang He-xin, Li Gen-zhu, Zhang Zi-chuan, Gong Xiao-jie. 2016. Effects of high temperatures on leaf stomatal traits and gas exchanges of highbush blueberries. Journal of Fruit Science, 33 (4):444-456. (in Chinese) |
| 朱玉, 黄磊, 郑云普, 郝立华, 姜国斌, 王贺新, 李根柱, 张自川, 弓晓杰. 2016. 高温对高丛越橘叶片气孔特征和气体交换参数的影响. 果树学报, 33 (4):444-456. |
| [1] | 程庆华, 张志鹏, 吴艳萍, 万宇鹤, 陈应娟. 苦参碱对茶树炭疽菌的抑菌作用研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 432-440. |
| [2] | 岳翠男, 王治会, 杨普香, 李文金, 彭 华, 陈罗军, 周汉中. 茶树新品种‘宁州早1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 281-282. |
| [3] | 李兰英, 胥亚琼, 刘东娜, 尧 渝, 龚雪蛟, 罗 晟, 罗 凡, . 茶树新品种‘金凤2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 283-284. |
| [4] | 李兰英, 王 强, 龚雪蛟, 刘东娜, 尧 渝, 王迎春, 胥亚琼, 罗 凡, . 茶树新品种‘甘露1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 285-286. |
| [5] | 任志红, 吴焕焕, 肖文敏, 张 虹, 杨圣祥, 孙海伟, 王 健, 高文星. 抗寒茶树新品种‘岱鼎御丰’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 287-288. |
| [6] | 王治会, 杨普香, 彭 华, 李文金, 王胜利, 鲍润元, 江新凤. 茶树新品种‘浮梁槠叶1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 191-192. |
| [7] | 彭 华, 李文金, 杨普香, 王治会, 岳翠男, 李延升, 谢小群, 李 琛. 早生持嫩性强茶树新品种‘婺绿1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 193-194. |
| [8] | 王治会, 彭 华, 岳翠男, 李文金, 杨普香, 陈年生, 李延升, 蔡海兰, 江新凤. 茶树新品种‘赣茶4号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 195-196. |
| [9] | 马伟伟, 王 云, 李春华, 刘 晓, 唐晓波, 张 厅, 甘 勇, 王小萍, . 茶树新品种‘彝黄1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 197-198. |
| [10] | 马伟伟, 王 云, 李春华, 熊元元, 刘 晓, 王小萍, 李 鑫. 茶树新品种‘天府5号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 199-200. |
| [11] | 郭丽娜, 王璐, 郝心愿, 祁蒙, 李晓嫚, 王新超, 曾建明. 茶树根系吸收硒的生理特性研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(9): 1967-1976. |
| [12] | 闫文渊, 秦军红, 段绍光, 徐建飞, 简银巧, 金黎平, 李广存. 水氮耦合对马铃薯光合特性、块茎形成和品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(7): 1491-1504. |
| [13] | 刘众杰, 郑婷, 赵方贵, 傅伟红, 诸葛雅贤, 张志昌, 房经贵. 葡萄砧木对渗透胁迫的抗性差异及生理响应机理[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(5): 984-994. |
| [14] | 贡长怡, 刘姣姣, 邓强, 张立新. 茶树炭疽病病原菌鉴定及其致病性分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(5): 1092-1101. |
| [15] | 刘筱玮, 夏斌, 李子葳, 杨宇佳, 陈斌, 周蕴薇, 何淼. 拟南芥中过表达野菊miR396a基因增强其耐盐性[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(4): 816-826. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司