
园艺学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (5): 873-882.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-1829
杨锋, 杨钦淞, 高雨豪, 马云晶, 许英, 滕元文, 白松龄*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-10-10
修回日期:2021-01-26
出版日期:2021-05-25
发布日期:2021-06-07
通讯作者:
白松龄
E-mail:songlingbai@zju.edu.cn
基金资助:
YANG Feng, YANG Qinsong, GAO Yuhao, MA Yunjing, XU Ying, TENG Yuanwen, BAI Songling*( )
)
Received:2020-10-10
Revised:2021-01-26
Online:2021-05-25
Published:2021-06-07
Contact:
BAI Songling
E-mail:songlingbai@zju.edu.cn
摘要:
为了在梨愈伤组织中建立CRISPR/Cas9基因编辑体系,将proDAM3:GUS转入‘茄梨’愈伤组织,通过构建双靶点的CRISPR/Cas9基因编辑载体,利用农杆菌介导的遗传转化法侵染proDAM3:GUS转基因梨愈伤组织,通过测序及GUS染色的方法检验敲除效果,分析靶基因突变类型。结果表明,共有4个转基因株系在靶位点处发生了基因突变,编辑效率为66.7%。对所有基因编辑株系的有效克隆进行分析,结果显示sgRNA1在靶位点GUST1的突变频率达到71.4%,高于sgRNA2在靶位点GUST2突变频率的46.4%,说明sgRNA1可以更有效地与靶位点结合。测序结果表明,4个基因编辑株系中GUS基因均被敲除,基因突变的类型包含碱基缺失、插入及两个靶点之间大片段的缺失,不存在碱基替换。GUS染色结果显示,基因敲除后的GUS转基因愈伤完全呈白色,说明利用CRISPR/Cas9多靶点基因编辑系统可以在梨愈伤组织中实现高效的基因敲除。
中图分类号:
杨锋, 杨钦淞, 高雨豪, 马云晶, 许英, 滕元文, 白松龄. 梨愈伤组织双靶点CRISPR/Cas9基因编辑系统的建立[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(5): 873-882.
YANG Feng, YANG Qinsong, GAO Yuhao, MA Yunjing, XU Ying, TENG Yuanwen, BAI Songling. Establishment of Dual-cut CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing System in Pear Calli[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(5): 873-882.

图1 GUS基因中CRISPR/Cas9靶位点的位置示意图及序列信息 蓝色方框为外显子,灰色方框为内含子,绿色和橙色方框分别代表两个靶位点,方框下方的数字为位置信息,不同颜色的方框宽度按照序列长度比例绘制。下方的序列为靶位点信息,方向均为5′-3′。红色字体代表PAM序列,括号中的+/-号表示核酸酶识别的DNA链。
Fig. 1 Illustration of the target sites and sequences of CRISPR/Cas9 in GUS gene The blue bars represent the exons,the gray bar represents the intron,the green and orange bars represent two target sites,the numbers below the bar are position information,and the width of the bars are drawn in proportion to the sequence length. The sequences below the bars are the sequences of the target sites,which are shown in the direction of 5′-3′. The red font represents the PAM sequences,and the“+/-”in parentheses represent the DNA strand recognized by the nuclease.
| 用途 Usage | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 靶点接头正反向引物 The sense and reverse primers for the target with the adapters | GUSAtU3dT1-F | GTCATTGAGGTCGAAGACGCCAC |
| GUSAtU3dT1-R | AAACGTGGCGTCTTCGACCTCAA | |
| GUSAtU3bT2-F | GTCACGATAGCACCCTCCCGGTG | |
| GUSAtU3bT2-R | AAACCACCGGGAGGGTGCTATCG | |
| 第1轮PCR 1st PCR | U-F | CTCCGTTTTACCTGTGGAATCG |
| gR-R | CGGAGGAAAATTCCATCCAC | |
| 第2轮PCR 2nd PCR | Pps-R | TTCAGAGGTCTCTACCGACTAGTATGGAATCGGCAGCAAAGG |
| Pgs-2 | AGCGTGGGTCTCGTCAGGGTCCATCCACTCCAAGCTC | |
| Pps-2 | TTCAGAGGTCTCTCTGACACTGGAATCGGCAGCAAAGG | |
| Pgs-L | AGCGTGGGTCTCGCTCGACGCGTATCCATCCACTCCAAGCTC | |
| 载体测序引物 The sequencing primers for the vector | SP-R | TGCAATAACTTCGTATAGGCT |
| SP-L2 | GTCGTGCTCCACATGTTGACCG | |
| 阳性转化体筛选引物 The screening primers for positive transformants | Cas9-F | CTGACGCTAACCTCGACAAG |
| Cas9-R | CCGATCTAGTAACATAGATGACACC | |
| 基因编辑鉴定引物 The primers for identifying the gene editing events | GUS-F | ATGGTAGATCTGAGGGTAAATTTCTAGT |
| GUS-R | GTTCTTGTAGCCGAAATCTGGAATG |
表1 本研究中所用的引物
Table 1 All primers used in this study
| 用途 Usage | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 靶点接头正反向引物 The sense and reverse primers for the target with the adapters | GUSAtU3dT1-F | GTCATTGAGGTCGAAGACGCCAC |
| GUSAtU3dT1-R | AAACGTGGCGTCTTCGACCTCAA | |
| GUSAtU3bT2-F | GTCACGATAGCACCCTCCCGGTG | |
| GUSAtU3bT2-R | AAACCACCGGGAGGGTGCTATCG | |
| 第1轮PCR 1st PCR | U-F | CTCCGTTTTACCTGTGGAATCG |
| gR-R | CGGAGGAAAATTCCATCCAC | |
| 第2轮PCR 2nd PCR | Pps-R | TTCAGAGGTCTCTACCGACTAGTATGGAATCGGCAGCAAAGG |
| Pgs-2 | AGCGTGGGTCTCGTCAGGGTCCATCCACTCCAAGCTC | |
| Pps-2 | TTCAGAGGTCTCTCTGACACTGGAATCGGCAGCAAAGG | |
| Pgs-L | AGCGTGGGTCTCGCTCGACGCGTATCCATCCACTCCAAGCTC | |
| 载体测序引物 The sequencing primers for the vector | SP-R | TGCAATAACTTCGTATAGGCT |
| SP-L2 | GTCGTGCTCCACATGTTGACCG | |
| 阳性转化体筛选引物 The screening primers for positive transformants | Cas9-F | CTGACGCTAACCTCGACAAG |
| Cas9-R | CCGATCTAGTAACATAGATGACACC | |
| 基因编辑鉴定引物 The primers for identifying the gene editing events | GUS-F | ATGGTAGATCTGAGGGTAAATTTCTAGT |
| GUS-R | GTTCTTGTAGCCGAAATCTGGAATG |
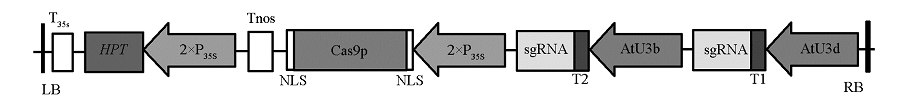
图2 GUS -pYLCRISPR/Cas9载体结构图 LB:左边界;RB:右边界;T35s:35S终止子;Tnos:nos终止子;HPT:潮霉素磷酸转移酶基因;35S:花椰菜花叶病毒 CaMV35S启动子;Cas9p:SpCas9基因;NLS:核定位信号;AtU3d、AtU3b:拟南芥U3d、U3b启动子;T1、T2:GUS突变靶位点序列。
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of GUS -pYLCRISPR/Cas9 vector LB:Left border;RB:Right border;T35s:35S terminator;Tnos:nos terminator;HPT:hygromycin B phosphotransferase;35S:Cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter;Cas9p:SpCas9 gene;NLS:Nuclear localization signal;AtU3d,AtU3b:U3d,U3b promoter fromArabidopsis;T1,T2:GUS Target sequence.
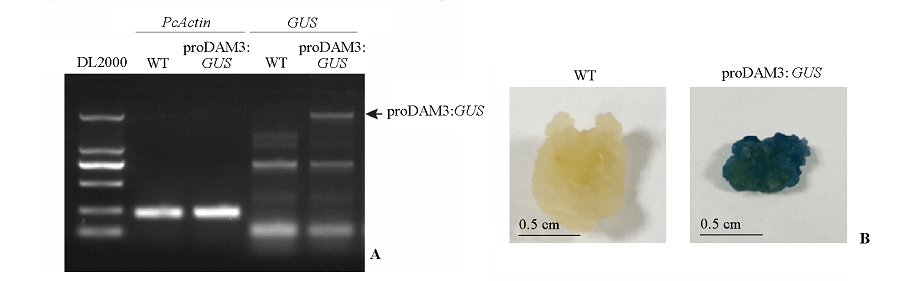
图3 proDAM3:GUS转基因株系的DNA鉴定(A)与GUS染色鉴定(B)
Fig. 3 The PCR(A)and GUS staining(B)confirmations of the fragment insertion of the proDAM3:GUS transgenic line
| 突变类型InDel types | 碱基数/bp Number of base | GUST1 sites(%) | GUST2 sites(%) | 对应株系Line# |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 碱基插入Insertion | 1 ~ 2 | 12(30%) | 2(7.7%) | #1、#2、#3 |
| 单碱基缺失Single base deletion | 1 | 5(12.5%) | 8(30.8%) | #1、#2、#3 |
| 小片段缺失Small fragment deletion | 2 ~ 15 | 7(17.5%) | 0 | #1、#2 |
| 大片段缺失Long fragment deletion | 625 | 16(40.0%) | 16(61.5%) | #5 |
表2 基因编辑株系的突变类型分析
Table 2 Indel types in GUS mutant lines
| 突变类型InDel types | 碱基数/bp Number of base | GUST1 sites(%) | GUST2 sites(%) | 对应株系Line# |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 碱基插入Insertion | 1 ~ 2 | 12(30%) | 2(7.7%) | #1、#2、#3 |
| 单碱基缺失Single base deletion | 1 | 5(12.5%) | 8(30.8%) | #1、#2、#3 |
| 小片段缺失Small fragment deletion | 2 ~ 15 | 7(17.5%) | 0 | #1、#2 |
| 大片段缺失Long fragment deletion | 625 | 16(40.0%) | 16(61.5%) | #5 |
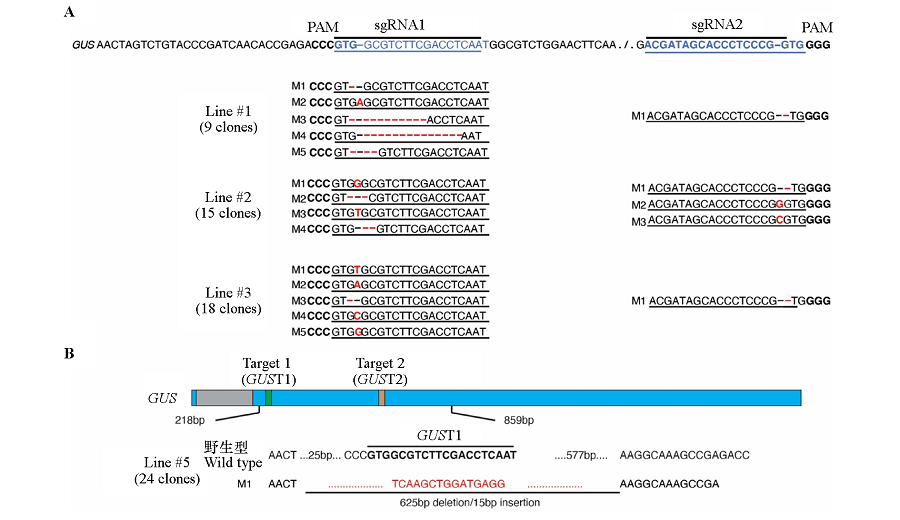
图4 基因编辑株系#1、#2、#3(A)和#5(B)靶位点的突变类型 蓝色方框为外显子,灰色方框为内含子,绿色和橙色方框分别代表两个靶位点,方框下方的数字为位置信息,不同颜色的方框宽度按照序列长度比例绘制。A:黑字体为PAM序列;蓝色字体为靶位点序列;红色字体代表基因编辑突变位点;B:靶位点用加粗字体表示,删除部分和插入序列用红色字体表示。
Fig. 4 The mutation types of #1,#2,#3(A)and #5(B)gene editing lines The blue bars represent the exons,the gray bar represents the intron,the green and orange bars represent two target sites,the numbers below the bar are position information,and the width of the bars are drawn in proportion to the sequence length. A:PAM sequence is shown in bold font;the target sites are shown in blue color;the mutations are represented in red color;B:The target sites are indicated by bold font,and the deletion and insertion are indicated by red color.
| [1] |
Bai S L, Tao R Y, Tang Y X, Yin L, Ma Y J, Ni J B, Yan X H, Yang Q S, Wu Z Y, Zeng Y L, Teng Y W. 2019. BBX16,a B-box protein,positively regulates light-induced anthocyanin accumulation by activating MYB10 in red pear. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 17(10):1985-1997.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.v17.10 URL |
| [2] |
Chen Y T, Mao W W, Liu T, Feng Q Q, Li L, Li B B. 2020. Genome editing as a versatile tool to improve horticultural crop qualities. Horticultural Plant Journal, 6(6):372-384.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2020.11.004 URL |
| [3] | Cui Xia, Zhang Shuaibin. 2017. Gene editing technology and its application and prospect in horticultural crops. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 44(9):1787-1795. (in Chinese) |
| 崔霞, 张率斌. 2017. 基因编辑技术及其在园艺作物中的应用和展望. 园艺学报, 44(9):1787-1795. | |
| [4] |
Du H Y, Zeng X R, Zhao M, Cui X P, Wang Q, Yang H, Cheng H, Yu D Y. 2016. Efficient targeted mutagenesis in soybean by TALENs and CRISPR/Cas9. Journal of Biotechnology, 217:90-97.
doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2015.11.005 URL |
| [5] |
Graf R, Li X, Chu V T, Rajewsky K. 2019. sgRNA sequence motifs blocking efficient CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene editing. Cell Reports, 26(5):1098-1103.
doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.01.024 URL |
| [6] | Guo Ye, Wan Dongyan, Chai Zhuangzhuang, Wang Yuejin, Wen Yingqiang. 2019. Knock-out analysis of VviPDS1gene using CRISPR/Cas9 in grapevine . Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 46(4):623-634. (in Chinese) |
| 郭晔, 万东艳, 柴壮壮, 王跃进, 文颖强. 2019. 利用CRISPR/Cas9敲除葡萄VviPDS1基因的研究. 园艺学报, 46(4):623-634. | |
| [7] |
Jia H, Orbovic V, Jones J B, Wang N. 2016. Modification of the PthA4 effector binding elements in Type I CsLOB1 promoter using Cas9/sgRNA to produce transgenic Duncan grapefruit alleviating XccpthA4:dCsLOB1.3 infection. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 14(5):1291-1301.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.2016.14.issue-5 URL |
| [8] |
Jia H, Wang N. 2014. Targeted genome editing of sweet orange using Cas9/sgRNA. PLoS ONE, 9(4):e93806.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093806 URL |
| [9] |
Jia H, Zhang Y, Orbovic V, Xu J, White F F, Jones J B, Wang N. 2017. Genome editing of the disease susceptibility gene CsLOB1 in citrus confers resistance to citrus canker. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 15(7):817-823.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.12677 URL |
| [10] |
Li C, Unver T, Zhang B H. 2017. A high-efficiency CRISPR/Cas9 system for targeted mutagenesis in cotton(Gossypium hirsutumL.). Scientific Reports, 7:43902.
doi: 10.1038/srep43902 URL |
| [11] |
Li J, Li Y, Ma L G. 2019. CRISPR/Cas9-based genome editing and its applications for functional genomic analyses in plants. Small Methods, 3(3):1800473.
doi: 10.1002/smtd.v3.3 URL |
| [12] |
Li J F, Norville J E, Aach J, McCormack M, Zhang D D, Bush J, Church G M, Sheen J. 2013. Multiplex and homologous recombination-mediated genome editing in Arabidopsis and Nicotiana benthamiana using guide RNA and Cas9. Nature Biotechnology, 31(8):688-691.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.2654 URL |
| [13] |
Ma C, Liu M, Li Q, Jun Si, Ren X, Song H. 2019. Efficient BoPDSgene editing in cabbage by the CRISPR/Cas9 system. Horticultural Plant Journal, 5(4):164-169.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2019.04.001 URL |
| [14] | Ma X, Liu Y G. 2016. CRISPR/Cas9-based multiplex genome editing in monocot and dicot plants. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology,115:31.6.1-31. 6.21. |
| [15] | Malnoy M, Viola R, Jung M H, Koo O J, Kim S, Kim J S, Velasco R, Kanchiswamy C N. 2016. DNA-free genetically edited grapevine and apple protoplast using CRISPR/Cas9 ribonucleoproteins. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7:1904. |
| [16] |
Mao Y F, Zhang H, Xu N F, Zhang B T, Gou F, Zhu J K. 2013. Application of the CRISPR/Cas system for efficient genome engineering in plants. Molecular Plant, 6(6):2008-2011.
doi: 10.1093/mp/sst121 URL |
| [17] | Nakajima I, Ban Y, Azuma A, Onoue N, Moriguchi T, Yamamoto T, Toki S, Endo M. 2017. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeted mutagenesis in grape. PLoS ONE, 12(5):16. |
| [18] |
Nekrasov V, Staskawicz B, Weigel D, Jones J D G, Kamoun S. 2013. Targeted mutagenesis in the model plant Nicotiana benthamiana using Cas9 RNA-guided endonuclease. Nature Biotechnology, 31(8):691-693.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.2655 URL |
| [19] |
Nishitani C, Hirai N, Komori S, Wada M, Okada K, Osakabe K, Yamamoto T, Osakabe Y. 2016. Efficient genome editing in apple using a CRISPR/Cas9 system. Scientific Reports, 6:31481.
doi: 10.1038/srep31481 URL |
| [20] |
Peng A, Chen S, Lei T, Xu L, He Y, Wu L, Yao L, Zou X. 2017. Engineering canker-resistant plants through CRISPR/Cas9-targeted editing of the susceptibility gene CsLOB1 promoter in citrus. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 15(12):1509-1519.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.2017.15.issue-12 URL |
| [21] |
Ren C, Liu X J, Zhang Z, Wang Y, Duan W, Li S H, Liang Z C. 2016. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated efficient targeted mutagenesis in Chardonnay(Vitis vinifera L.). Scientific Reports, 6:32289.
doi: 10.1038/srep32289 URL |
| [22] | Shan Qiwei, Gao Caixia. 2015. Recent advances in plant genome editing and its derivatives. Hereditas, 37(10):953-973. (in Chinese) |
| 单奇伟, 高彩霞. 2015. 植物基因组编辑及衍生技术最新研究进展. 遗传, 37(10):953-973. | |
| [23] |
Shan Q W, Wang Y P, Li J, Zhang Y, Chen K L, Liang Z, Zhang K, Liu J X, Xi J J, Qiu J L, Gao C X. 2013. Targeted genome modification of crop plants using a CRISPR-Cas system. Nature Biotechnology, 31(8):686-688.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.2650 URL |
| [24] |
Svitashev S, Young J K, Schwartz C, Gao H R, Falco S C, Cigan A M. 2015. Targeted mutagenesis,precise gene editing,and site-specific gene insertion in maize using Cas9 and guide RNA. Plant Physiology, 169(2):931-945.
doi: 10.1104/pp.15.00793 URL |
| [25] |
Tian S, Jiang L, Gao Q, Zhang J, Zong M, Zhang H, Ren Y, Guo S, Gong G, Liu F, Xu Y. 2017. Efficient CRISPR/Cas9-based gene knockout in watermelon. Plant Cell Reports, 36(3):399-406.
doi: 10.1007/s00299-016-2089-5 URL |
| [26] | Wang Fujun, Zhao Kaijun. 2018. Progress and challenge of crop genetic improvement via genome editing. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 51(1):1-16. (in Chinese) |
| 王福军, 赵开军. 2018. 基因组编辑技术应用于作物遗传改良的进展与挑战. 中国农业科学, 51(1):1-16. | |
| [27] |
Wang X, Tu M, Wang D, Liu J, Li Y, Li Z, Wang Y, Wang X. 2018. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated efficient targeted mutagenesis in grape in the first generation. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 16(4):844-855.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.2018.16.issue-4 URL |
| [28] |
Wang Y P, Cheng X, Shan Q W, Zhang Y, Liu J X, Gao CX, Qiu J L. 2014. Simultaneous editing of three homoeoalleles in hexaploid bread wheat confers heritable resistance to powdery mildew. Nature Biotechnology, 32(9):947-951.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.2969 URL |
| [29] |
Wang Z, Wang S, Li D, Zhang Q, Li L, Zhong C, Liu Y, Huang H. 2018. Optimized paired-sgRNA/Cas9 cloning and expression cassette triggers high-efficiency multiplex genome editing in kiwifruit. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 16(8):1424-1433.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.2018.16.issue-8 URL |
| [30] |
Wu J, Wang Z, Shi Z, Zhang S, Ming R, Zhu S, Khan M, Tao S, Korban S, Wang H, Chen N, Nishio T, Xu X, Cong L, Qi K, Huang X, Wang Y, Zhao X, Wu J, Deng C, Gou C, Zhou W, Yin H, Qin G, Sha Y, Tao Y, Chen H, Yang Y, Song Y, Zhan D, Wang J, Li L, Dai M, Gu C, Wang Y, Shi D, Wang X, Zhang H, Zeng L, Zheng D, Wang C, Chen M, Wang G, Xie L, Sovero V, Sha S, Huang W, Zhang S, Zhang M, Sun J, Xu L, Li Y, Liu X, Li Q, Shen J, Wang J, Paull R, Bennetzen J, Zhang S. 2013. The genome of the pear(Pyrus bretschneideriRehd.). Genome Research, 23:396-408.
doi: 10.1101/gr.144311.112 URL |
| [31] | Yang Lushan, Guo Ye, Hu Yang, Wen Yingqiang. 2020. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mutagenesis of VviEDR2 results in enhanced resistance to powdery mildew in grapevine (Vitis vinifera) . Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47(4):623-634. (in Chinese) |
| 杨禄山, 郭晔, 胡洋, 文颖强. 2020. 利用CRISPR/Cas9系统敲除葡萄中VviEDR2提高对白粉病的抗性. 园艺学报, 47(4):623-634. | |
| [32] |
Yang Q, Yang B, Li J, Wang Y, Tao R, Yang F, Wu X, Yan X, Ahmad M, Shen J, Bai S, Teng Y. 2020. ABA-responsive ABRE-BINDING FACTOR3 activates DAM3 expression to promote bud dormancy in Asian pear. Plant Cell and Environment, 43(6):1360-1375.
doi: 10.1111/pce.v43.6 URL |
| [33] | Zheng Aihong, Zhang Fen, Jiang Min, Yuan Qiao, Jiang Leiyu, Chen Qing, Tang Haoru, Sun Bo. 2019. Targeted editing of BoaZDSby CRISPR/Cas9 technology in Chinese kale . Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 46(1):57-64. (in Chinese) |
| 郑爱红, 张芬, 江敏, 袁巧, 江雷雨, 陈清, 汤浩茹, 孙勃. 2019. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术靶向编辑芥蓝BoaZDS. 园艺学报, 46(1):57-64. | |
| [34] | Zou Xiuping, Fan Di, Peng Aihong, He Yongrui, Xu Lanzhen, Lei Tiangang, Yao Lixiao, Li Qiang, Luo Keming, Chen Shanchun. 2019 CRISPR/Cas9-mediated editing of multiple sites in the citrus CsLOB1 promoter . Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 46(2):337-344. (in Chinese) |
| 邹修平, 范迪, 彭爱红, 何永睿, 许兰珍, 雷天刚, 姚利晓, 李强, 罗克明, 陈善春. 2019. CRISPR/Cas9介导柑橘CsLOB1基因启动子的多位点编辑. 园艺学报, 46(2):337-344. |
| [1] | 宋健坤, 杨英杰, 李鼎立, 马春晖, 王彩虹, 王 然. 梨新品种‘鲁秀’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 3-4. |
| [2] | 董星光, 曹玉芬, 张 莹, 田路明, 霍宏亮, 齐 丹, 徐家玉, 刘 超, 王立东. 抗寒脆肉梨新品种‘玉翠香’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 5-6. |
| [3] | 欧春青, 姜淑苓, 王 斐, 马 力, 张艳杰, 刘振杰. 早熟梨新品种‘兴梨蜜水’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 7-8. |
| [4] | 张艳杰, 王 斐, 欧春青, 马 力, 姜淑苓, 刘振杰. 梨新品种‘中梨玉脆3’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 9-10. |
| [5] | 范 净, 陈启亮, 张靖国, 杨晓平, 杜 威, 田 瑞, 周德平, 胡红菊, . 中熟红皮砂梨新品种‘金彤’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 11-12. |
| [6] | 王苏珂, 李秀根, 杨 健, 王 龙, 苏艳丽, 张向展, 薛华柏. 红皮梨新品种‘丹霞红’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 13-14. |
| [7] | 王 斐, 欧春青, 张艳杰, 马 力, 姜淑苓. 晚熟耐贮梨新品种‘华秋’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 9-10. |
| [8] | 宋健坤, 李鼎立, 杨英杰, 马春晖, 王彩虹, 王 然. 梨新品种‘琴岛红’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 11-12. |
| [9] | 郭伟珍, 赵京献, 李莹. 中早熟梨新品种‘美玉’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(9): 2051-2052. |
| [10] | 刘金明, 郭彩华, 袁星, 亢超, 全绍文, 牛建新. 梨Dof家族基因鉴定及其在宿存与脱落萼片中的表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(8): 1637-1649. |
| [11] | 张婉青, 张红晓, 廉小芳, 李昱莹, 郭丽丽, 侯小改. ‘凤丹’牡丹愈伤组织分化和生根诱导中的DNA甲基化分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(8): 1735-1746. |
| [12] | 陶鑫, 朱荣香, 贡鑫, 吴磊, 张绍铃, 赵建荣, 张虎平. 梨果糖激酶基因PpyFRK5在果实蔗糖积累中的作用[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(7): 1429-1440. |
| [13] | 左鑫, 李铭铭, 李欣容, 苗春妍, 李炎枋, 杨旭, 张重义, 王丰青. CRISPR/Cas9技术在天目地黄RcPDS1基因编辑中的应用[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(7): 1532-1544. |
| [14] | 张秋悦, 刘昌来, 于晓晶, 杨甲定, 封超年. 盐胁迫条件下杜梨叶片差异表达基因qRT-PCR内参基因筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(7): 1557-1570. |
| [15] | 邱可立, 王玉民, 何金铃, 俞红, 潘海发, 盛玉, 谢庆梅, 陈红莉, 周晖, 张金云. 桃漆酶家族基因鉴定及PpLAC21功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(6): 1351-1362. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司