
园艺学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (8): 1735-1746.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0547
张婉青, 张红晓, 廉小芳, 李昱莹, 郭丽丽, 侯小改*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-05-19
修回日期:2022-08-17
出版日期:2022-08-25
发布日期:2022-09-05
通讯作者:
侯小改
E-mail:hkdhxg@haust.edu.cn
基金资助:
ZHANG Wanqing, ZHANG Hongxiao, LIAN Xiaofang, LI Yuying, GUO Lili, HOU Xiaogai*( )
)
Received:2022-05-19
Revised:2022-08-17
Online:2022-08-25
Published:2022-09-05
Contact:
HOU Xiaogai
E-mail:hkdhxg@haust.edu.cn
摘要:
牡丹愈伤组织分化率低和组培苗生根困难一直是其再生体系建立的两大制约因素。利用甲基化敏感扩增多态性(MSAP)技术,对‘凤丹’非胚性与胚性愈伤组织、未生根与生根组培苗的DNA甲基化进行了比较分析。结果表明,非胚性和胚性愈伤组织的DNA甲基化水平均以全甲基化水平较高,二者的超甲基化位点数相差较大,与非胚性愈伤组织相比,胚性愈伤组织分化引起由全甲基化转变为超甲基化的占比多达33.45%;与未生根组培苗相比,组培苗生根过程是以去甲基化模式占比最多,为38.41%。因此推测,‘凤丹’胚性愈伤组织分化较少,可能与其超甲基化的形成有关;而组培苗生根可能与其去甲基化有关。
中图分类号:
张婉青, 张红晓, 廉小芳, 李昱莹, 郭丽丽, 侯小改. ‘凤丹’牡丹愈伤组织分化和生根诱导中的DNA甲基化分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(8): 1735-1746.
ZHANG Wanqing, ZHANG Hongxiao, LIAN Xiaofang, LI Yuying, GUO Lili, HOU Xiaogai. Analysis of DNA Methylation Related to Callus Differentiation and Rooting Induction of Paeonia ostii‘Fengdan’[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1735-1746.
| 接头和引物 Adapters and primers | EcoRⅠ(E) (5′-3′) | HpaⅡ/MspⅠ(H/M) (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Adapter‐Ⅰ | CTCGTAGACTGCGTACC | GACGATGAGTCCTGAG |
| Adapter‐Ⅱ | AATTGGTACGCAGTCTA | TACTCAGGACTCAT |
| 预扩增Pre-amplification | GACTGCGTACCAATTC | GATGAGTCCTGAGCGG |
| 选择性扩增 Selective amplification | E + AAC | HM + AGC |
| E + AAT | HM + AGG | |
| E + ATG | HM + ATA | |
| E + AGG | HM + CAT | |
| E + ACG | HM + CTA | |
| E + CAA | HM + CTC | |
| E + CAT | HM + CTG | |
| E + GTG | ||
| E + GTT | ||
| E + TCA | ||
| E + TCC | ||
| E + TCG |
表1 MSAP体系建立的接头和引物信息
Table 1 MSAP system established adapter and primer information
| 接头和引物 Adapters and primers | EcoRⅠ(E) (5′-3′) | HpaⅡ/MspⅠ(H/M) (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Adapter‐Ⅰ | CTCGTAGACTGCGTACC | GACGATGAGTCCTGAG |
| Adapter‐Ⅱ | AATTGGTACGCAGTCTA | TACTCAGGACTCAT |
| 预扩增Pre-amplification | GACTGCGTACCAATTC | GATGAGTCCTGAGCGG |
| 选择性扩增 Selective amplification | E + AAC | HM + AGC |
| E + AAT | HM + AGG | |
| E + ATG | HM + ATA | |
| E + AGG | HM + CAT | |
| E + ACG | HM + CTA | |
| E + CAA | HM + CTC | |
| E + CAT | HM + CTG | |
| E + GTG | ||
| E + GTT | ||
| E + TCA | ||
| E + TCC | ||
| E + TCG |
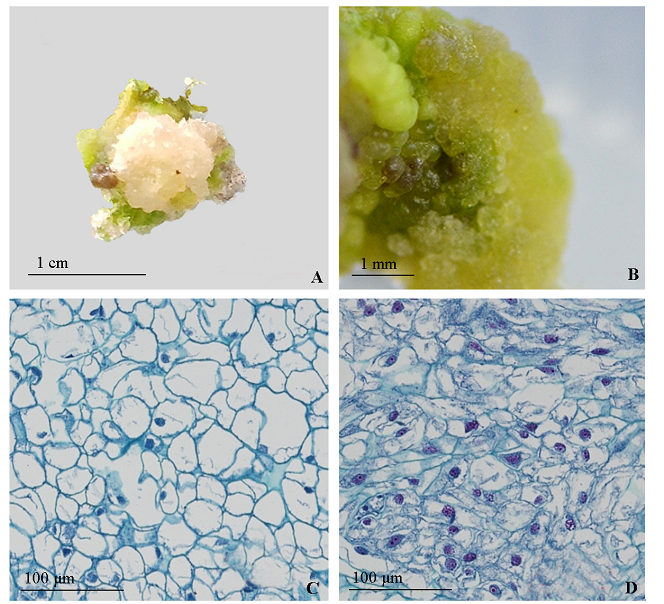
图1 ‘凤丹’愈伤组织诱导 A:非胚性愈伤组织;B:胚性愈伤组织;C:非胚性细胞;D:胚性细胞。
Fig. 1 Callus induction of Paeonia ostii‘Fengdan’ A:Non-embryogenic callus;B:Embryogenic callus;C:Non-embryonic cells;D:Embryonic cells.
| 培养基 Medium | 浓度/(mg · L-1)Concentration | 愈伤增殖率/% Callus proliferation rate | 胚性愈伤比率/% Embryogenic callus ratio | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAA | 6-BA | TDZ | 2,4-D | IBA | 水解酪蛋白 Hydrolyzed casein | ||||
| WPM | 0.05 | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | 87.22 ± 4.08 a | 8.89 ± 5.88 ab | |||
| WPM | 0.02 | 0 | 0.05 | 0 | 72.67 ± 2.61 c | 5.00 ± 5.00 cd | |||
| MS | 0 | 2.0 | 0.30 | 0 | 71.94 ± 2.96 c | 0 d | |||
| WPM | 0.05 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0 | 83.61 ± 3.50 ab | 0 d | |||
| MS | 0.1 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0 | 80.27 ± 3.06 abc | 3.33 ± 3.33 cd | |||
| 1/2MS | 0.1 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0 | 71.11 ± 3.38 c | 6.95 ± 4.52 bc | |||
| MS | 0.3 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 100 | 74.79 ± 6.75 bc | 13.33 ± 4.02 a | |||
表2 ‘凤丹’不同处理诱导愈伤组织增殖率和胚性愈伤组织比率
Table 2 Different treatments of Paeonia ostii‘Fengdan’induce callus proliferation rate and embryogenic callus rate
| 培养基 Medium | 浓度/(mg · L-1)Concentration | 愈伤增殖率/% Callus proliferation rate | 胚性愈伤比率/% Embryogenic callus ratio | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAA | 6-BA | TDZ | 2,4-D | IBA | 水解酪蛋白 Hydrolyzed casein | ||||
| WPM | 0.05 | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | 87.22 ± 4.08 a | 8.89 ± 5.88 ab | |||
| WPM | 0.02 | 0 | 0.05 | 0 | 72.67 ± 2.61 c | 5.00 ± 5.00 cd | |||
| MS | 0 | 2.0 | 0.30 | 0 | 71.94 ± 2.96 c | 0 d | |||
| WPM | 0.05 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0 | 83.61 ± 3.50 ab | 0 d | |||
| MS | 0.1 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0 | 80.27 ± 3.06 abc | 3.33 ± 3.33 cd | |||
| 1/2MS | 0.1 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0 | 71.11 ± 3.38 c | 6.95 ± 4.52 bc | |||
| MS | 0.3 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 100 | 74.79 ± 6.75 bc | 13.33 ± 4.02 a | |||
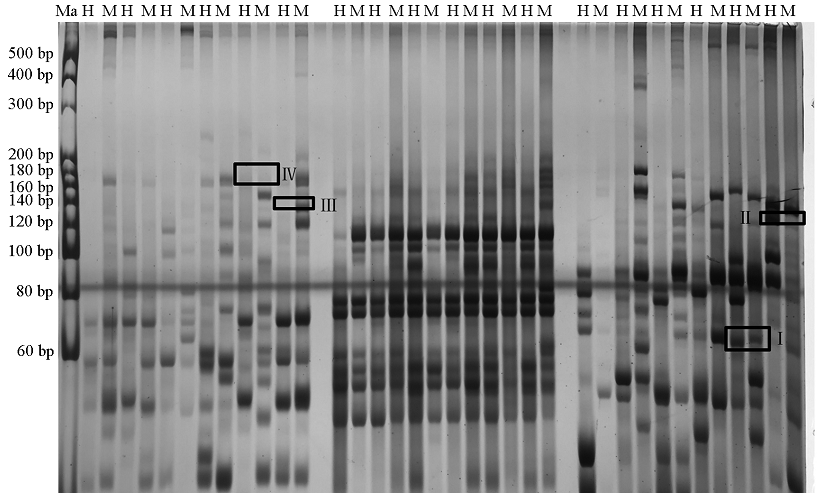
图3 ‘凤丹’愈伤组织MASP扩增的聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳检测结果 Ma:DNA marker DL20;H:HpaⅡ酶切片段;M:MspⅠ酶切片段。
Fig. 3 Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis detection results of MASP amplification of Paeonia ostii‘Fengdan’callus Ma:DNA marker DL20;H:HpaⅡdigestion fragment;M:MspⅠdigestion fragment.
| 愈伤组织 Callus | 条带数(%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ 非甲基化Un-methylation | Ⅱ 半甲基化Hemi-methylation | Ⅲ 全甲基化Full-methylation | Ⅳ 超甲基化Hyper-methylation | |
| 胚性Embryogenic | 388(26.39) | 383(26.05) | 428(29.12) | 271(18.44) |
| 非胚性Non-embryogenic | 352(23.94) | 322(21.90) | 358(24.35) | 438(29.80) |
表3 ‘凤丹’胚性愈伤组织与非胚性愈伤组织的甲基化水平
Table 3 Methylation level of embryogenic callus and non-embryogenic callus of Paeonia ostii‘Fengdan’
| 愈伤组织 Callus | 条带数(%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ 非甲基化Un-methylation | Ⅱ 半甲基化Hemi-methylation | Ⅲ 全甲基化Full-methylation | Ⅳ 超甲基化Hyper-methylation | |
| 胚性Embryogenic | 388(26.39) | 383(26.05) | 428(29.12) | 271(18.44) |
| 非胚性Non-embryogenic | 352(23.94) | 322(21.90) | 358(24.35) | 438(29.80) |
| 模式 Mode | 占比/% Percentage | 类型 Type | 非胚性愈伤带型 Non-embryogenic callus type | 胚性愈伤带型 Embryogenic callus type | 条带数 Number of strip | % | 甲基化变化 Methylation changes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | M | H | M | ||||||
| 无变化 No change | 22.04 | A1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 139 | 42.90 | 非→非Un-→Un- |
| A2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 99 | 30.56 | 半→半Hemi-→Hemi- | ||
| A3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 86 | 26.54 | 全→全Full-→Full- | ||
| 去甲基化 Demethylation | 28.78 | B1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 69 | 16.31 | 半→非Hemi-→Un- |
| B2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 83 | 19.62 | 全→非Full-→Un- | ||
| B3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 61 | 14.42 | 超→非Hper-→Un- | ||
| B4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 87 | 20.57 | 超→半Hper-→Hemi- | ||
| B5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 123 | 29.08 | 超→全Hper-→Full- | ||
| 甲基化 Methylation | 40.48 | C1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 76 | 12.77 | 非→半Un-→Hemi- |
| C2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 81 | 13.61 | 非→全Un-→Full- | ||
| C3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 92 | 15.46 | 非→超Un-→Hper- | ||
| C4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 147 | 24.71 | 半→超Hemi-→Hper- | ||
| C5 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 199 | 33.45 | 全→超Full-→Hper- | ||
表4 ‘凤丹’胚性愈伤组织与非胚性愈伤组织甲基化模式变异
Table 4 Variations in methylation patterns of embryogenic callus and non-embryogenic callus of Paeonia ostii‘Fengdan’
| 模式 Mode | 占比/% Percentage | 类型 Type | 非胚性愈伤带型 Non-embryogenic callus type | 胚性愈伤带型 Embryogenic callus type | 条带数 Number of strip | % | 甲基化变化 Methylation changes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | M | H | M | ||||||
| 无变化 No change | 22.04 | A1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 139 | 42.90 | 非→非Un-→Un- |
| A2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 99 | 30.56 | 半→半Hemi-→Hemi- | ||
| A3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 86 | 26.54 | 全→全Full-→Full- | ||
| 去甲基化 Demethylation | 28.78 | B1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 69 | 16.31 | 半→非Hemi-→Un- |
| B2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 83 | 19.62 | 全→非Full-→Un- | ||
| B3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 61 | 14.42 | 超→非Hper-→Un- | ||
| B4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 87 | 20.57 | 超→半Hper-→Hemi- | ||
| B5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 123 | 29.08 | 超→全Hper-→Full- | ||
| 甲基化 Methylation | 40.48 | C1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 76 | 12.77 | 非→半Un-→Hemi- |
| C2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 81 | 13.61 | 非→全Un-→Full- | ||
| C3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 92 | 15.46 | 非→超Un-→Hper- | ||
| C4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 147 | 24.71 | 半→超Hemi-→Hper- | ||
| C5 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 199 | 33.45 | 全→超Full-→Hper- | ||
| 组培苗 Callus | 条带数(%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ 非甲基化Un-methylation | Ⅱ 半甲基化Hemi-methylation | Ⅲ 全甲基化Full-methylation | Ⅳ 超甲基化Hyper-methylation | |
| 生根Rooted | 447(27.49) | 378(23.25) | 452(27.80) | 349(21.46) |
| 未生根Unrooted | 347(21.34) | 497(30.57) | 355(21.83) | 427(26.26) |
表5 ‘凤丹’未生根组培苗与生根组培苗甲基化水平
Table 5 Methylation level of Paeonia ostii‘Fengdan’unrooted tissue culture seedlings and rooted tissue culture seedlings
| 组培苗 Callus | 条带数(%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ 非甲基化Un-methylation | Ⅱ 半甲基化Hemi-methylation | Ⅲ 全甲基化Full-methylation | Ⅳ 超甲基化Hyper-methylation | |
| 生根Rooted | 447(27.49) | 378(23.25) | 452(27.80) | 349(21.46) |
| 未生根Unrooted | 347(21.34) | 497(30.57) | 355(21.83) | 427(26.26) |
| 模式 Mode | 占比/% Percentage | 类型 Types | 未生根组培苗 Unrooted tissue culture seedlings | 生根组培苗 Rooting tissue culture seedlings | 条带数 Number of strips | % | 甲基化变化 Methylation changes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | M | H | M | ||||||
| 无变化 No change | 18.37 | A1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 133 | 44.63 | 非→非Un-→Un- |
| A2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 97 | 32.55 | 半→半Hemi-→Hemi- | ||
| A3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 68 | 22.82 | 全→全Full-→Full- | ||
| 去甲基化 Demethy- lation | 38.41 | B1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 103 | 16.53 | 半→非Hemi-→Un- |
| B2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 97 | 15.57 | 全→非Full-→Un- | ||
| B3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 114 | 18.30 | 超→非Hper-→Un- | ||
| B4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 122 | 19.58 | 超→半Hper-→Hemi- | ||
| B5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 187 | 30.02 | 超→全Hper-→Full- | ||
| 甲基化 Methylation | 30.15 | C1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 81 | 16.56 | 非→半Un-→Hemi- |
| C2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 63 | 12.88 | 非→全Un-→Full- | ||
| C3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 70 | 14.31 | 非→超Un-→Hper- | ||
| C4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 163 | 33.33 | 半→超Hemi-→Hper- | ||
| C5 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 112 | 22.90 | 全→超Full-→Hper- | ||
表6 ‘凤丹’未生根组培苗与生根组培苗甲基化模式变异
Table 6 Variations in methylation patterns of Paeonia ostii‘Fengdan’unrooted tissue culture seedlings and rooted tissue culture seedlings
| 模式 Mode | 占比/% Percentage | 类型 Types | 未生根组培苗 Unrooted tissue culture seedlings | 生根组培苗 Rooting tissue culture seedlings | 条带数 Number of strips | % | 甲基化变化 Methylation changes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | M | H | M | ||||||
| 无变化 No change | 18.37 | A1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 133 | 44.63 | 非→非Un-→Un- |
| A2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 97 | 32.55 | 半→半Hemi-→Hemi- | ||
| A3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 68 | 22.82 | 全→全Full-→Full- | ||
| 去甲基化 Demethy- lation | 38.41 | B1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 103 | 16.53 | 半→非Hemi-→Un- |
| B2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 97 | 15.57 | 全→非Full-→Un- | ||
| B3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 114 | 18.30 | 超→非Hper-→Un- | ||
| B4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 122 | 19.58 | 超→半Hper-→Hemi- | ||
| B5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 187 | 30.02 | 超→全Hper-→Full- | ||
| 甲基化 Methylation | 30.15 | C1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 81 | 16.56 | 非→半Un-→Hemi- |
| C2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 63 | 12.88 | 非→全Un-→Full- | ||
| C3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 70 | 14.31 | 非→超Un-→Hper- | ||
| C4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 163 | 33.33 | 半→超Hemi-→Hper- | ||
| C5 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 112 | 22.90 | 全→超Full-→Hper- | ||
| [1] |
Bai C M, Fang M H, Zhai B Q, Ma L L, Fu A Z, Gao L P, Kou X H, Meng D M, Wang Q, Zheng S F, Zuo J H. 2021. Regulations of m6A methylation on tomato fruit chilling injury. Horticultural Plant Journal, 7 (5):434-442.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2021.05.005 URL |
| [2] | Cheng Yu-fei, Ji Wen, Wang Jian-wen, Feng Li-guo, Zhu Xiang-tao. 2021. Induction and germination of somatic embryos of Paeonia suffruticosa ‘Fengdanbai’. Molecular Plant Breeding, 19 (17):5775-5781. (in Chinese) |
| 程雨飞, 季雯, 王建文, 冯立国, 朱向涛. 2021. ‘凤丹白’牡丹体细胞胚的诱导及萌发. 分子植物育种, 19 (17):5775-5781. | |
| [3] | Ding Ming-li. 2008. Studyies on DNA methylation during dedifferentiation of mature wheat embryos[M. D. Dissertation]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 丁明丽. 2008. 小麦成熟胚脱分化过程的DNA甲基化研究[硕士论文]. 郑州: 河南农业大学. | |
| [4] | Du Yi-ming, Zhong Yuan, Shang Hong-qin, Cheng Fang-yun. 2020. Callus induction and differentiation from the filaments of Paeonia ostii‘Feng Dan’. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 40 (4):514-522. (in Chinese) |
| 杜一鸣, 钟原, 尚宏芹, 成仿云. 2020. ‘凤丹’牡丹花丝愈伤组织诱导及分化研究. 植物研究, 40 (4):514-522. | |
| [5] |
Gao J, Xue J Q, Xue Y Q, Liu R, Ren X X, Wang S L, Zhang X X. 2020. Transcriptome sequencing and identification of key callus browning-related genes from petiole callus of tree peony(Paeonia suffruticosa cv. Kao)cultured on media with three browning inhibitors. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 149:36-49.
doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.01.029 URL |
| [6] | Hong De-yuan, Pan Kai-yu. 2005. Additional taxonomic notes on Paeonia sect. Moutan(Paeoniaceae). Journal of Systematics and Evolution (formerly Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica), 1 (3):284-287. (in Chinese) |
| 洪德元, 潘开玉. 2005. 芍药属牡丹组分类补注. 植物分类学报, 1 (3):284-287. | |
| [7] | Jin Chun-yi, Jin Hua, Lu Ying-ying, Li Xin-Lin, Bai Xin-lei, Zou Ji-xiang. 2019. Embryogenic callus induction plant regeneration and ultrastructure of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 41 (5):563-568. (in Chinese) |
| 金纯伊, 金华, 卢影影, 李新林, 白鑫磊, 邹吉祥. 2019. 文冠果胚性愈伤组织的诱导与植株再生及超微结构. 吉林农业大学学报, 41 (5):563-568. | |
| [8] | Li Sheng-nan, Liang Hua, Qiu Shuai, Ji Kun, Wang Yu-kai, Yang Fu-rong, Zhao Bo-wen, Li Xue-lin. 2021. DNA methylation analysis during cotton callus differentiation. Molecular Plant Breeding, 19 (7):2265-2272. (in Chinese) |
| 李胜楠, 梁华, 丘帅, 纪坤, 王煜凯, 杨馥熔, 赵博文, 李雪林. 2021. 棉花愈伤组织分化过程中的DNA甲基化分析. 分子植物育种, 19 (7):2265-2272. | |
| [9] | Li Xiang-nan. 2017. Preliminary analysis of DNA methylation levels and patterns in dwarf rootstock of Prunus mahaleb[M. D. Dissertation]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University. (in Chinese) |
| 李向男. 2017. 马哈利樱桃矮化砧的DNA甲基化水平及模式初步分析[硕士论文]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学. | |
| [10] | Lian Xiao-fang, Li Yu-ying, Zhang Wan-qing, Guo Li-li, Zhang You-fu, Hou Xiao-gai. 2020. Establishment of Paeonia ostii‘Fengdan’embryo culture system and analysis of methylation variation in malformed embryo culture seedlings. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 49 (11):110-119. (in Chinese) |
| 廉小芳, 李昱莹, 张婉青, 郭丽丽, 张有福, 侯小改. 2020. 凤丹牡丹胚培养体系建立及初代畸形苗甲基化变异分析. 河南农业科学, 49 (11):110-119. | |
| [11] |
Liu H J, Ma L L, Yang X R, Zhang L, Zeng X, Xie S P, Peng H W, Gao S B, Lin H J, Pan G T, Wu Y R, Shen Y O. 2017. Integrative analysis of DNA methylation,mRNAs,and small RNAs during maize embryo dedifferentiation. BMC Plant Biology, 17 (1):1-12.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-016-0951-9 URL |
| [12] | Liu Peng-fei, Qiao Guang, Liu Tao, Peng Zhi-jun, Cai Yong-qiang, Wen Xiao-peng. 2016a. On optimization of MSAP analysis system and assessment of DNA methylation in in vitro pitaya. Journal of Southwest University(Natural Science Edition), 38 (9):34-40. (in Chinese) |
| 刘鹏飞, 乔光, 刘涛, 彭志军, 蔡永强, 文晓鹏. 2016a. 火龙果MSAP体系的优化及组培苗DNA甲基化检测. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 38 (9):34-40. | |
| [13] | Liu Peng-fei, Qiao Guang, Wen Xiao-peng. 2016b. DNA methylation variation of in vitro pitaya shoots and its response to exogenous GA application. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 35 (5):18-26. (in Chinese) |
| 刘鹏飞, 乔光, 文晓鹏. 2016b. 火龙果组培苗DNA甲基化变化及应答赤霉素效应. 华中农业大学学报, 35 (5):18-26. | |
| [14] | Liu Rong, Ci Huiting, Ren Xiuxia, Gao Jie, Wang Shunli, Zhang Xiuxin. 2022. Optimization of callus induction from immature embryo and establishment regeneration system of Paeonia ostii‘Fengdan’. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 49 (1):166-174. (in Chinese) |
| 刘蓉, 慈惠婷, 任秀霞, 高洁, 王顺利, 张秀新. 2022. ‘凤丹’牡丹幼胚愈伤组织诱导的优化和再生体系的建立. 园艺学报, 49 (1):166-174. | |
| [15] |
Lukens L N, Zhan S H. 2007. The plant genome’s methylation status and response to stress:implications for plant improvement. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 10 (3):317-322.
pmid: 17468039 |
| [16] | Lü Xiao-ting. 2012. Research of DNA methylation during the formation of calli induced from apple(Malus domestica)leaves[M. D. Dissertation]. Qingdao: Qingdao Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 吕晓婷. 2012. 苹果愈伤组织形成过程中DNA甲基化的研究[硕士论文]. 青岛: 青岛农业大学. | |
| [17] | Miao Gao-jian. 2009. The embryogenic callus inducation and plant regeneration in rice tissue culture are respectively accompanied by decrease in cytosine methylation and restoration[M. D. Dissertation]. Changchun: Northeast Normal University. (in Chinese) |
| 苗高健. 2009. 水稻胚性愈伤组织诱导和植株再生伴随DNA胞嘧啶甲基化的减少和恢复[硕士论文]. 长春: 东北师范大学. | |
| [18] | Miao Xu-jing, Wen Zhuang, Wen Xiao-peng. 2018. Changes of DNA methylation level and patterns in tissue culture seedlings of strawberry (Fragaria ananassa‘Akihime’)in response to cold acclimation. Journal of Mountain Agriculture and Biology, 37 (2):7-13,45. (in Chinese) |
| 苗徐静, 文壮, 文晓鹏. 2018. 冷驯化草莓组培苗DNA甲基化水平及模式的变化. 山地农业生物学报, 37 (2):7-13,45. | |
| [19] | Nie Yuan-yuan, Qu Ze-jing, Ruan Sheng-qiang, Yang Shan-xiao, Zhou Zhen-kai. 2017. Benefit evaluation on comprehensive standardization of eco-agricultural industry— Taking Tongling peony as an example. Journal of West Anhui University, 33 (5):113-117. (in Chinese) |
| 聂媛媛, 曲泽静, 阮胜强, 杨善啸, 周振凯. 2017. 生态农业产业综合标准化效益评价研究——以铜陵凤丹为例. 皖西学院学报, 33 (5):113-117. | |
| [20] |
Shang W Q, Wang Z, He S L, He D, Liu Y P, Fu Z Z. 2017. Research on the relationship between phenolic acids and rooting of tree peony(Paeonia suffruticosa)plantlets in vitro. Scientia Horticulturae, 224:53-60.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2017.04.038 URL |
| [21] |
Wang Jian-yong, Zou Yong-mei, Ge Yan-bin, Wang Kai, Xi Meng-li. 2021. Advance on epigenetic modification during plant callus induction. Biotechnology Bulletin, 37 (8):253-262. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2020-1302 |
|
王建勇, 邹永梅, 葛言彬, 王凯, 席梦利. 2021. 植物愈伤组织诱导过程中的表观遗传修饰研究进展. 生物技术通报, 37 (8):253-262.
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2020-1302 |
|
| [22] | Wang Meng-meng, Bu Xiang-pan, Zhang Qian, Huo Jin-ru, Chao Long-jun, Wang Hua-fang. 2018. Study on in vitro rapid propagation technology on Paeonia ostii var. lishizheni. Molecular Plant Breeding, 16 (2):526-534. (in Chinese) |
| 王蒙蒙, 卜祥潘, 张倩, 霍瑾茹, 晁龙军, 王华芳. 2018. ‘凤丹’离体快繁工厂化技术研究. 分子植物育种, 16 (2):526-534. | |
| [23] |
Wang Wen-guo, Li Rui, Zhu Jia-yi, Wang Sheng-hua, Chen Fang. 2010. DNA methylation-mediated regulation of OsMAPK2 gene expression in rice callus formation. Hereditas(Beijing), 32 (12):1275-1280. (in Chinese)
pmid: 21513154 |
|
王文国, 李锐, 朱珈仪, 王胜华, 陈放. 2010. 水稻愈伤组织形成过程中甲基化对OsMAPK2的表达调控. 遗传, 32 (12):1275-1280.
pmid: 21513154 |
|
| [24] | Wang Xin, Cheng Fang-yun, Zhong Yuan, Wen Shu-sheng, Li Liu-zemu, Huang Nong-zhang. 2016. Establishment of in vitro rapid propagation system for Tree Peony(Paeonia ostii). Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 52 (5):101-110. (in Chinese) |
| 王新, 成仿云, 钟原, 文书生, 李刘泽木, 黄弄璋. 2016. 凤丹牡丹鳞芽离体培养与快繁技术. 林业科学, 52 (5):101-110. | |
| [25] | Wang Yu. 2020. Analysis of DNA methylation of multicolor petal of Paeonia Suffruticosa based on MSAP[M. D. Dissertation]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 王玉. 2020. 基于MSAP的牡丹复色花DNA甲基化分析[硕士论文]. 泰安: 山东农业大学. | |
| [26] | Wang Zhao-lu. 2014. Effects of different hormones and polyamines on the induction of embryogenic callus of Paeonia suffruticosa[M. D. Dissertation]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 王照路. 2014. 不同激素和多胺类物质对牡丹胚性愈伤组织诱导的影响[硕士论文]. 郑州: 河南农业大学. | |
| [27] | Wang Zheng, Yang Da-juan, He Song-lin, Mao Cang-cang, Meng Xin-ya, He Dan. 2018. Effects of different treatments on physiological biochemical properties of early somatic embryogenesis of Paeonia suffruticosa Andr. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 47 (3):105-111. (in Chinese) |
| 王政, 杨大娟, 何松林, 毛仓仓, 孟新亚, 贺丹. 2018. 不同处理对牡丹体细胞胚发生早期生理生化的影响. 河南农业科学, 47 (3):105-111. | |
| [28] | Wei Dong-xia. 2017. Somatic embryogenesis and callus re-differentiation of Herbaceous Peony[M. D. Dissertation]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University. (in Chinese) |
| 魏冬霞. 2017. 芍药体细胞胚诱导和愈伤组织再分化研究[硕士论文]. 北京: 北京林业大学. | |
| [29] |
Wen S S, Chen L, Tian R N. 2020. Micropropagation of tree peony(Paeonia section Moutan):a review. Plant Cell,Tissue and Organ Culture, 141 (1):1-14.
doi: 10.1007/s11240-019-01747-8 URL |
| [30] |
Wen S S, Cheng F Y, Zhong Y, Wang X, Li L Z, Zhang Y X, Qiu J M. 2016. Efficient protocols for the micropropagation of tree peony(Paeonia suffruticosa‘Jin Pao Hong’,P. Suffruticosa‘Wu Long Peng Sheng’,and P. × lemoinei‘High Noon’)and application of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi to improve plantlet establishment. Scientia Horticulturae, 201:10-17.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2016.01.022 URL |
| [31] | Wu Fang. 2013. The research of cutting rooting and transplanting of tissue culture of HASKAOP[M. D. Dissertation]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 吴芳. 2013. 日本小果树HASKAOP组培苗的扦插生根及带根苗移栽条件的研究[硕士论文]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学. | |
| [32] | Wu Xia-lei. 2019. Optimization of somatic embryogenesis system of Cunninghamia lanceolata Hook[M. D. Dissertation]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University. (in Chinese) |
| 吴夏雷. 2019. 杉木合子胚体细胞胚胎发生体系优化研究[硕士论文]. 北京: 北京林业大学. | |
| [33] | Xu Sheng, Zhang Xin, Liu Decai, Gu Tingting. 2020. Identification and functional analysis of N6-adenine methylation(6mA)methyltransferase genes in Fragaria vesca. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47 (11):2194-2206. (in Chinese) |
| 徐昇, 张鑫, 刘德才, 顾婷婷. 2020. 森林草莓6mA 甲基转移酶基因鉴定及功能分析. 园艺学报, 47 (11):2194-2206. | |
| [34] | Yao Pei-juan, Li Ji-hong, Qi Xiao, Xing Shi-yan. 2013. DNA Methylation in somatic embryogenesis of Erica carnea L. Acta Plant Physiology Journal, 49 (12):1413-1420. (in Chinese) |
| 姚培娟, 李际红, 亓晓, 邢世岩. 2013. 欧石楠体细胞胚发生过程中的DNA甲基化. 植物生理学报, 49 (12):1413-1420. | |
| [35] | Yin Ming-hua, Liao Yu, Wan Zhi-ting. 2019. MSAP analysis of genomic DNA methylation of virus-free plantlets by cryotherapy of Red Bud Taro. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 28 (1):132-138. (in Chinese) |
| 尹明华, 廖玉, 万志庭. 2019. 红芽芋超低温疗法脱毒苗基因组DNA甲基化的MSAP分析. 西北农业学报, 28 (1):132-138. | |
| [36] |
Zeng F S, Sun F K, Liang N S, Zhao X T, Luo W, Zhan Y G. 2015. Dynamic change of DNA methylation and cell redox state at different micropropagation phases in birch. Trees, 29 (3):917-930.
doi: 10.1007/s00468-015-1174-7 URL |
| [37] | Zhai Chun-mei, Meng Xiang-ying, Fu Jing-Ju, Qin Zhen, Meng Yong-hai. 2020. Research progress of peony bark in modern pharmacy. Information on Traditional Chinese Medicine, 37 (1):109-114. (in Chinese) |
| 翟春梅, 孟祥瑛, 付敬菊, 秦蓁, 孟永海. 2020. 牡丹皮的现代药学研究进展. 中医药信息, 37 (1):109-114. | |
| [38] |
Zhang L, Guo D L, Guo L L, Guo Q, Wang H F, Hou X G. 2019. Construction of a high-density genetic map and QTLs mapping with GBS from the interspecific F1 population of P. ostii‘Fengdan Bai’and P. suffruticosa‘Xin Riyuejin’. Scientia Horticulturae, 246:190-200.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2018.10.039 |
| [39] | Zhang Yong, Deng Ke-jun, Zhang Tao, Peng Jin-hua, Zhou Jian-ping, Ren Zheng-long. 2009. Analysis on genomic DNA methylation modification of rye by methylation-sensitive amplification polymorphism. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 29 (4):559-564. (in Chinese) |
| 张勇, 邓科君, 张韬, 彭金华, 周建平, 任正隆. 2009. 黑麦基因组DNA甲基化修饰位点的MSAP分析. 麦类作物学报, 29 (4):559-564. | |
| [40] | Zhu Hua-guo. 2009. Morphological and genetic analysis of somatic embryogenesis and cloning and expressional analysis of related genes during initial cellular dedifferentiation in cotton[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 朱华国. 2009. 棉花体细胞胚胎发生形态、遗传分析及初始脱分化相关基因的克隆与表达分析[博士论文]. 武汉: 华中农业大学. |
| [1] | 李瑞雅, 宋程威, 牛童非, 魏祯祯, 郭丽丽, 侯小改. ‘海黄’牡丹花挥发性物质释放规律及PsGDS的克隆与表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 331-344. |
| [2] | 邵凤清, 罗秀荣, 王奇, 张宪智, 王文彩. 果实成熟过程中的DNA甲基化调控研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 197-208. |
| [3] | 何智宏, 何丽霞, 张延东, 杨国州, 李 睿, 徐晶晶, 瞿 丹, 李京璟. 牡丹新品种‘余霞散绮’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 219-220. |
| [4] | 赵海军, 盖树鹏, 晁 振, 闫闪闪, 房义福, 张 佩. 牡丹新品种‘福照粉蓝’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 221-222. |
| [5] | 邱可立, 王玉民, 何金铃, 俞红, 潘海发, 盛玉, 谢庆梅, 陈红莉, 周晖, 张金云. 桃漆酶家族基因鉴定及PpLAC21功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(6): 1351-1362. |
| [6] | 李亚梅, 马福利, 张山奇, 黄锦秋, 陈梦婷, 周军永, 孙其宝, 孙俊. 酸枣愈伤组织转化体系构建及在ZjBRC1调控ZjYUCCA表达中的应用[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(4): 749-757. |
| [7] | 王莹, 艾鹏慧, 李帅磊, 康冬茹, 李忠爱, 王子成. 菊花和菊花脑DNA甲基化相关酶基因鉴定及表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(4): 827-840. |
| [8] | 周陈平, 杨敏, 郭金菊, 邝瑞彬, 杨护, 黄炳雄, 魏岳荣. 番木瓜成熟过程中全基因组DNA甲基化和转录组变化分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(3): 519-532. |
| [9] | 程世平, 姚鹏强, 耿喜宁, 刘春洋, 谢丽华. 高温诱导牡丹产生未减数花粉[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(3): 581-589. |
| [10] | 聂文锋, 王金玉, 高春娟, 陈学好. 表观遗传修饰调控园艺植物果实发育研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(3): 671-686. |
| [11] | 郭鑫, 成仿云, 钟原, 成信云, 陶熙文. 紫斑牡丹花色表型数量分类研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(1): 86-99. |
| [12] | 务俊月, 孙雪言, 杨振华, 罗璐, 莫翠园, 马爱民. 虎奶菇菌丝体和菌核基因组甲基化分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(1): 148-156. |
| [13] | 刘蓉, 慈惠婷, 任秀霞, 高洁, 王顺利, 张秀新. ‘凤丹’牡丹幼胚愈伤组织诱导的优化和再生体系的建立[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(1): 166-174. |
| [14] | 叶 康, 胡永红, 张 颖. 牡丹新品种‘金琉鹤舞’[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(S2): 2959-2960. |
| [15] | 叶 康, 胡永红, 张 颖. 牡丹新品种‘银粟紫染’[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(S2): 2961-2962. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司