
园艺学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (7): 1557-1570.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0376
张秋悦1, 刘昌来1,2,*( ), 于晓晶1, 杨甲定1, 封超年1,*(
), 于晓晶1, 杨甲定1, 封超年1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-03-25
修回日期:2022-04-27
出版日期:2022-07-25
发布日期:2022-07-29
通讯作者:
刘昌来,封超年
E-mail:clc2012@njfu.edu.cn;fcn@njfu.edu.cn
ZHANG Qiuyue1, LIU Changlai1,2,*( ), YU Xiaojing1, YANG Jiading1, FENG Chaonian1,*(
), YU Xiaojing1, YANG Jiading1, FENG Chaonian1,*( )
)
Received:2022-03-25
Revised:2022-04-27
Online:2022-07-25
Published:2022-07-29
Contact:
LIU Changlai,FENG Chaonian
E-mail:clc2012@njfu.edu.cn;fcn@njfu.edu.cn
摘要:
为了准确评价盐胁迫下杜梨(Pyrus betulaefolia Bunge.)目标基因表达量,筛选qRT-PCR适用内参基因。利用杜梨的全基因组注释信息和转录组测序数据,选择Actin2(Chr15.g01351)、EF1α-1(Chr3.g19898)、 EF1α-2(Chr4.g38173)、EF2(Chr5.g06899)、 GAPDH-1(Chr16.g30426)、 GAPDH-2(Chr13.g23532)、 TUBB(Chr5.g06472)、UBQ(Chr4.g40121)等8个候选基因,设计Actin2、EF1α-1、EF1α-2A、EF1α-2B、EF2、GAPDH-1、GAPDH-2、TUBB-A、TUBB-B、UBQE等10对qRT-PCR引物。首先对10对引物的扩增效率进行了测定,再以200 mmol · L-1的NaCl溶液对两个杜梨家系(盐城和连云港)幼苗进行0、24、48、72 h盐胁迫处理。提取叶片的总RNA,反转录合成cDNA,使用10对引物进行qRT-PCR扩增,根据扩增产物使用delta Ct、BestKeeper、geNorm和NormFinder 等4种评价内参基因稳定性的方法,对10对引物扩增产物的稳定性进行分析,并使用RefFinder软件对4种评价方法进行综合分析,以确定最稳定内参基因及其引物。利用筛选出的2对最优内参基因引物对(TUBB-A和GAPDH-1)对1个可能参与杜梨盐胁迫响应的HKT基因(Chr16.g29024)的表达情况进行分析,8个候选内参基因的FPKM值(Fragments PerKilobase Million)都大于30,不同盐处理时间下的FPKM变异系数为0.087 ~ 0.260;10对荧光定量PCR引物的扩增效率在91.82% ~ 112.99%之间,其中引物对TUBB-A和GAPDH-1的扩增效率最接近于100%;稳定性分析显示10对引物扩增产物的稳定性排序为GΑPDH-1、TUBB-Α、EF1α-1、TUBB-B、EF1α-2Α、EF2、UBQE、GΑPDH-2、Αctin2、EF1α-2B;不同引物对(TUBB-Α、TUBB-B和EF1α-2Α、EF1α-2B)对同一基因的扩增产物的稳定性存在明显差异;利用TUBB-A和GAPDH-1分析HKT基因的表达趋势没有差别。说明基因GΑPDH和TUBB适于作为杜梨盐胁迫下进行荧光定量PCR的内参基因,对应的GAPDH-1、TUBB-A引物对的扩增效果最好。
中图分类号:
张秋悦, 刘昌来, 于晓晶, 杨甲定, 封超年. 盐胁迫条件下杜梨叶片差异表达基因qRT-PCR内参基因筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(7): 1557-1570.
ZHANG Qiuyue, LIU Changlai, YU Xiaojing, YANG Jiading, FENG Chaonian. Screening of Reference Genes for Differentially Expressed Genes in Pyrus betulaefolia Plant Under Salt Stress by qRT-PCR[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1557-1570.
| 引物名称 Primer names | 基因名称 Gene name | 基因编号 Gene ID | 片段长度/bp Gene length | 来源 Source | 变异系数/% CV | 引物序列 Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EF1a-1 | EF1a-1 | Chr3.g19898 | 168 | 本研究设计 Designed in this study | 18.0 | F:CATCGAGAGGTTCGAGAAGG R:CCGGGAGCATCAATAACAGT |
| EF1a-2A | EF1a-2 | Chr4.g38173 | 167 | 蒲小秋 等, | 26.0 | F:GGTGTGAAGCAGATGATTTG R:TCACCCTCAAACCCAGATAT |
| EF1a-2B | EF1a-2 | Chr4.g38173 | 201 | 本研究设计 Designed in this study | 26.0 | F:AGGTCCACCAACCTTGACTG R:TGGACCAAAAGTGACAACCA |
| EF2 | EF2 | Chr5.g06899 | 179 | 本研究设计 Designed in this study | 8.7 | F:CCCAAGAGATGATCCCAAGA R:ACCCAGCAACAACAGAATCC |
| Actin2 | Actin2 | Chr15.g01351 | 101 | 蒲小秋 等, | 13.8 | F:CTTCAATGTGCCTGCCATGT R:TCACACCATCACCAGAGTCC |
| GAPDH-1 | GAPDH-1 | Chr16.g30426 | 171 | 本研究设计 Designed in this study | 17.9 | F:GTTCGTTGTTGGTGTGAACG R:GTCTTTTGGGTGGCAGTGAT |
| GAPDH-2 | GAPDH-2 | Chr13.g23532 | 123 | 张雪 等, | 11.2 | F:GAGGGTCTCATGACCACAGT R:TCCAGTGCTGCTAGGAATGA |
| TUBB-A | TUBB | Chr5.g06472 | 212 | 张雪 等, | 20.6 | F:CTGCTGTGTTCCGTGGTAAG R:CTGCTCGCTAACTCTCCTGA |
| TUBB-B | TUBB | Chr5.g06472 | 237 | 本研究设计 Designed in this study | 20.6 | F:ACCCGATAACTTCGTGTTCG R:AACATCATTCGATCCGGGTA |
| UBQE | UBQ | Chr4.g40121 | 140 | 本研究设计 Designed in this study | 8.8 | F:GGCAGAACTGCCTGCTAATC R:CGGTTTTGCTCGATAAGCTC |
| HKT | HKT | Chr16.g29024 | 197 | 本研究设计 Designed in this study | 63.9 | F:TGGGCTACTGTCATTTGCTG R:AACGGATTCACCGCTATGTC |
表1 候选内参基因及目的基因的引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences of candidate reference genes and target gene
| 引物名称 Primer names | 基因名称 Gene name | 基因编号 Gene ID | 片段长度/bp Gene length | 来源 Source | 变异系数/% CV | 引物序列 Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EF1a-1 | EF1a-1 | Chr3.g19898 | 168 | 本研究设计 Designed in this study | 18.0 | F:CATCGAGAGGTTCGAGAAGG R:CCGGGAGCATCAATAACAGT |
| EF1a-2A | EF1a-2 | Chr4.g38173 | 167 | 蒲小秋 等, | 26.0 | F:GGTGTGAAGCAGATGATTTG R:TCACCCTCAAACCCAGATAT |
| EF1a-2B | EF1a-2 | Chr4.g38173 | 201 | 本研究设计 Designed in this study | 26.0 | F:AGGTCCACCAACCTTGACTG R:TGGACCAAAAGTGACAACCA |
| EF2 | EF2 | Chr5.g06899 | 179 | 本研究设计 Designed in this study | 8.7 | F:CCCAAGAGATGATCCCAAGA R:ACCCAGCAACAACAGAATCC |
| Actin2 | Actin2 | Chr15.g01351 | 101 | 蒲小秋 等, | 13.8 | F:CTTCAATGTGCCTGCCATGT R:TCACACCATCACCAGAGTCC |
| GAPDH-1 | GAPDH-1 | Chr16.g30426 | 171 | 本研究设计 Designed in this study | 17.9 | F:GTTCGTTGTTGGTGTGAACG R:GTCTTTTGGGTGGCAGTGAT |
| GAPDH-2 | GAPDH-2 | Chr13.g23532 | 123 | 张雪 等, | 11.2 | F:GAGGGTCTCATGACCACAGT R:TCCAGTGCTGCTAGGAATGA |
| TUBB-A | TUBB | Chr5.g06472 | 212 | 张雪 等, | 20.6 | F:CTGCTGTGTTCCGTGGTAAG R:CTGCTCGCTAACTCTCCTGA |
| TUBB-B | TUBB | Chr5.g06472 | 237 | 本研究设计 Designed in this study | 20.6 | F:ACCCGATAACTTCGTGTTCG R:AACATCATTCGATCCGGGTA |
| UBQE | UBQ | Chr4.g40121 | 140 | 本研究设计 Designed in this study | 8.8 | F:GGCAGAACTGCCTGCTAATC R:CGGTTTTGCTCGATAAGCTC |
| HKT | HKT | Chr16.g29024 | 197 | 本研究设计 Designed in this study | 63.9 | F:TGGGCTACTGTCATTTGCTG R:AACGGATTCACCGCTATGTC |
| 引物名称 Primer name | 斜率(K) Slope | 决定系数 R2 | 扩增效率/% Amplification efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| EF1a-1 | -3.43 | 0.998 | 95.66 |
| EF1a-2A | -3.15 | 0.999 | 107.96 |
| EF1a-2B | -3.54 | 0.999 | 91.82 |
| EF2 | -3.43 | 0.998 | 95.66 |
| Actin2 | -3.43 | 0.998 | 95.66 |
| GAPDH-1 | -3.35 | 0.999 | 98.77 |
| GAPDH-2 | -3.21 | 0.999 | 104.95 |
| TUBB-A | -3.32 | 0.996 | 100.16 |
| TUBB-B | -3.05 | 0.989 | 112.99 |
| UBQE | -3.52 | 0.999 | 92.49 |
表2 候选内参基因载体特征和引物扩增效率
Table 2 The vector characteristics of candidate internal reference genes and amplification efficiency of primer pairs
| 引物名称 Primer name | 斜率(K) Slope | 决定系数 R2 | 扩增效率/% Amplification efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| EF1a-1 | -3.43 | 0.998 | 95.66 |
| EF1a-2A | -3.15 | 0.999 | 107.96 |
| EF1a-2B | -3.54 | 0.999 | 91.82 |
| EF2 | -3.43 | 0.998 | 95.66 |
| Actin2 | -3.43 | 0.998 | 95.66 |
| GAPDH-1 | -3.35 | 0.999 | 98.77 |
| GAPDH-2 | -3.21 | 0.999 | 104.95 |
| TUBB-A | -3.32 | 0.996 | 100.16 |
| TUBB-B | -3.05 | 0.989 | 112.99 |
| UBQE | -3.52 | 0.999 | 92.49 |
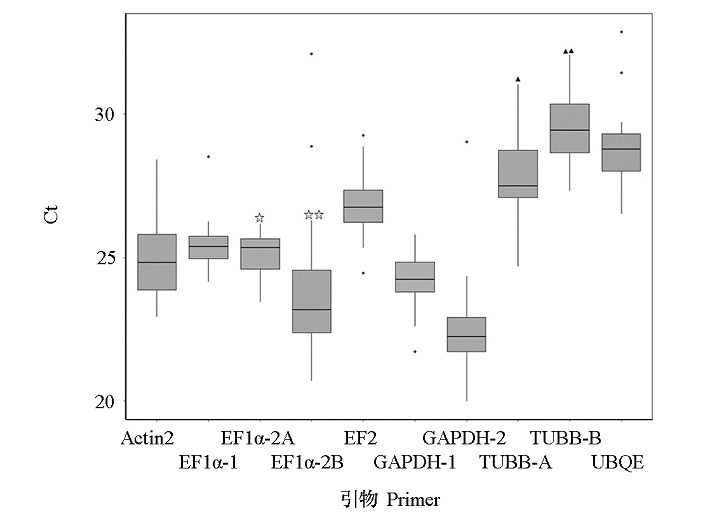
图4 24个叶片样品中候选内参基因引物扩增产物的Ct值分布☆和▲分别代表EF1α-2A与EF1α-2B引物扩增产物、TUBB-A与TUBB-B引物扩增产物的Ct值在P < 0.01水平下差异显著(t检验)。小黑点代表离散点。
Fig. 4 Ct value distribution of amplification products by primer pairs of candidate internal reference genes in 24 leaf samples☆ and ▲ represent the significant difference between PCR products using the primers of EF1α-2A and EF1α-2B,TUBB-A and TUBB-B,at P < 0.01 level,respectively. The little black spot represent the discrete value.

图5 delta Ct、NormFinder、geNorm法评价内参基因引物扩增稳定性
Fig. 5 Evaluation of the amplification stability of reference gene primers by delta Ct,NormFinder and geNorm
| 引物 Primer | 几何平均值 Geo mean | 算术平均值 AM | 最小值 Min | 最大值 Max | 相关系数 r | 标准偏差 SD | 变异系数/% CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH-1 | 24.24 | 24.26 | 21.71 | 25.79 | 0.870 | 0.75 | 3.09 |
| EF2 | 26.83 | 26.85 | 24.46 | 29.27 | 0.806 | 0.89 | 3.32 |
| UBQE | 28.81 | 28.84 | 26.52 | 32.87 | 0.697 | 0.86 | 2.98 |
| EF1α-1 | 25.39 | 25.40 | 24.15 | 28.52 | 0.688 | 0.56 | 2.21 |
| EF1α-2A | 25.18 | 25.19 | 23.44 | 26.18 | 0.640 | 0.57 | 2.27 |
| TUBB-B | 29.56 | 29.58 | 27.32 | 32.08 | 0.817 | 1.02 | 3.45 |
| TUBB-A | 27.79 | 27.82 | 24.68 | 31.04 | 0.890 | 1.04 | 3.72 |
| GAPDH-2 | 22.47 | 22.53 | 19.99 | 29.04 | 0.912 | 1.06 | 4.69 |
| Actin2 | 25.01 | 25.05 | 22.93 | 28.41 | 0.792 | 1.27 | 5.05 |
| EF1α-2B | 23.71 | 23.83 | 20.70 | 32.10 | 0.648 | 1.75 | 7.34 |
表3 BestKeeper方法评价候选内参基因稳定性
Table 3 Analysis results of expression stability of candidate reference genes by BestKeeper
| 引物 Primer | 几何平均值 Geo mean | 算术平均值 AM | 最小值 Min | 最大值 Max | 相关系数 r | 标准偏差 SD | 变异系数/% CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH-1 | 24.24 | 24.26 | 21.71 | 25.79 | 0.870 | 0.75 | 3.09 |
| EF2 | 26.83 | 26.85 | 24.46 | 29.27 | 0.806 | 0.89 | 3.32 |
| UBQE | 28.81 | 28.84 | 26.52 | 32.87 | 0.697 | 0.86 | 2.98 |
| EF1α-1 | 25.39 | 25.40 | 24.15 | 28.52 | 0.688 | 0.56 | 2.21 |
| EF1α-2A | 25.18 | 25.19 | 23.44 | 26.18 | 0.640 | 0.57 | 2.27 |
| TUBB-B | 29.56 | 29.58 | 27.32 | 32.08 | 0.817 | 1.02 | 3.45 |
| TUBB-A | 27.79 | 27.82 | 24.68 | 31.04 | 0.890 | 1.04 | 3.72 |
| GAPDH-2 | 22.47 | 22.53 | 19.99 | 29.04 | 0.912 | 1.06 | 4.69 |
| Actin2 | 25.01 | 25.05 | 22.93 | 28.41 | 0.792 | 1.27 | 5.05 |
| EF1α-2B | 23.71 | 23.83 | 20.70 | 32.10 | 0.648 | 1.75 | 7.34 |
| 评价方法 Method | 等级Ranking order(Better--Good--Average) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | |
| delta Ct | GΑPDH-1 | TUBB-Α | TUBB-B | EF2 | EF1α-1 | EF1α-2Α | UBQE | GΑPDH-2 | Αctin2 | EF1α-2B |
| BestKeeper | EF1α-1 | EF1α-2Α | GΑPDH-1 | UBQE | EF2 | TUBB-B | TUBB-Α | GΑPDH-2 | Αctin2 | EF1α-2B |
| NormFinder | GΑPDH-1 | TUBB-Α | EF2 | TUBB-B | EF1α-1 | EF1α-2Α | UBQE | GΑPDH-2 | Αctin2 | EF1α-2B |
| geNorm | GΑPDH-1 TUBB-Α | TUBB-B | EF1α-2Α | EF1α-1 | EF2 | Αctin2 | GΑPDH-2 | UBQE | EF1α-2B | |
| 综合评价 Comprehensive | GΑPDH-1 | TUBB-Α | EF1α-1 | TUBB-B | EF1α-2Α | EF2 | UBQE | GΑPDH-2 | Αctin2 | EF1α-2B |
表4 候选内参基因表达稳定性的RefFinder软件分析
Table 4 Expression stability of candidate reference genes analysed by RefFinder
| 评价方法 Method | 等级Ranking order(Better--Good--Average) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | |
| delta Ct | GΑPDH-1 | TUBB-Α | TUBB-B | EF2 | EF1α-1 | EF1α-2Α | UBQE | GΑPDH-2 | Αctin2 | EF1α-2B |
| BestKeeper | EF1α-1 | EF1α-2Α | GΑPDH-1 | UBQE | EF2 | TUBB-B | TUBB-Α | GΑPDH-2 | Αctin2 | EF1α-2B |
| NormFinder | GΑPDH-1 | TUBB-Α | EF2 | TUBB-B | EF1α-1 | EF1α-2Α | UBQE | GΑPDH-2 | Αctin2 | EF1α-2B |
| geNorm | GΑPDH-1 TUBB-Α | TUBB-B | EF1α-2Α | EF1α-1 | EF2 | Αctin2 | GΑPDH-2 | UBQE | EF1α-2B | |
| 综合评价 Comprehensive | GΑPDH-1 | TUBB-Α | EF1α-1 | TUBB-B | EF1α-2Α | EF2 | UBQE | GΑPDH-2 | Αctin2 | EF1α-2B |
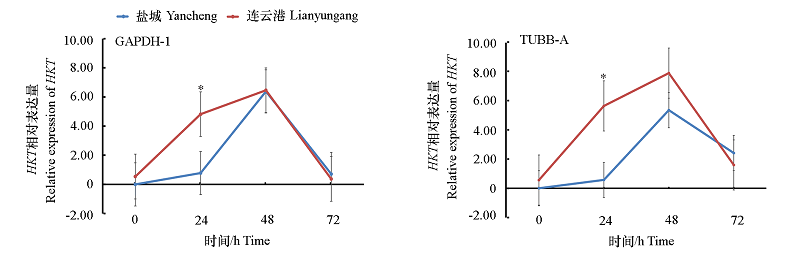
图6 以GAPDH-1和TUBB-A作为内参基因引物检测HKT的相对表达量* 代表在同一时间盐城与连云港杜梨家系中表达量具有显著性差异(P < 0.05)。
Fig. 6 Relative expression of HKT gene measured by using GAPDH-1 and TUBB-A as primer pairs of internal reference genes respectively* represent HKT expression significant difference of Pyrus betulaefolia Bunge. from Lianyungang and Yancheng at P < 0.05.
| [1] |
Andersen C L, Jensen J L, Ørntoft T F. 2004. Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data:a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization. Applied to Bladder and Colon Cancer Data Sets. Cancer Research, 64 (15):5245.
doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0496 URL |
| [2] |
Butterfield D A, Hardas S S, Lange M L B. 2010. Oxidatively modified glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase(GAPDH)and Alzheimer's Disease:many pathways to neurodegeneration. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, 20:369-393.
doi: 10.3233/JAD-2010-1375 pmid: 20164570 |
| [3] |
Chen J, Li X, Wang D, Li L, Zhou H, Liu Z, Wu J, Wang P, Jiang X, Fabrice M R, Zhang S, Wu J. 2015. Identification and testing of reference genes for gene expression analysis in pollen of Pyrus bretschneideri. Scientia Horticulturae, 190:43-56.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2015.04.010 URL |
| [4] | Chen Yangyang, Wu Xiao, Gu Chao, Yin Hao, Zhang Shaoling. 2018. Selection of reference genes in qRT-PCR of pear‘Dangshansuli’. China Fruits,(1):16-22. (in Chinese) |
| 陈杨杨, 吴潇, 谷超, 殷豪, 张绍铃. 2018. ‘砀山酥梨’实时荧光定量PCR内参基因的筛选. 中国果树,(1):16-22 | |
| [5] |
Dominguez R, Holmes K C. 2011. Actin structure and function. Annual Review of Biophysics, 40 (1):169-186.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-042910-155359 URL |
| [6] |
Dong X, Wang Z, Tian L, Zhang Y, Qi D, Huo H, Xu J, Li Z, Liao R, Shi M, Wahocho S A, Liu C, Zhang S, Tian Z, Cao Y. 2019. De novo assembly of a wild pear(Pyrus betuleafolia)genome. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 18 (2):581-595.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.13226 URL |
| [7] | Dubbelhuis P F, Meijer A J. 2002. Chapter 14 - Amino acid-dependent signal transduction. Sensing. Amsterdam:Elsevier:207-219. |
| [8] | Gao Haiming, Zhao Yanyan. 2020. Application progress of next generation and the third generation sequencing technology in genetic diagnosis. Current Biotechnology, 10 (6):646-654. (in Chinese) |
| 高海明, 赵彦艳. 2020. 二代及三代测序技术在遗传学诊断中的应用进展. 生物技术进展, 10 (6):646-654. | |
| [9] | Hou Lei, Chen Longjun. 2011. Effects of salt stress on epidermal cell expansion in leaves of Arabidopsis thaliana. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 39 (13):7615-7616. (in Chinese) |
| 侯蕾, 陈龙俊. 2011. 盐胁迫对拟南芥叶片和下表皮细胞大小的影响. 安徽农业科学, 39 (13):7615-7616. | |
| [10] | Hu Lisong, Wu Siting, Duan Xingshuai, Cen Yi, Su Yuefeng, Fan Rui, Wu Baoduo, Hao Chaoyun. 2020. The identification of internal control genes based on genome and transcriptome data in black pepper(Piper nigrum L.). Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 41 (10):2120-2129. (in Chinese) |
| 胡丽松, 吴思婷, 段兴帅, 岑怡, 苏岳峰, 范睿, 伍宝朵, 郝朝运. 2020. 基于基因组和转录组数据的胡椒内参基因鉴定. 热带作物学报, 41 (10):2120-2129. | |
| [11] | Jiang Lei, Li Huanyong, Zhang Qin, Zhang Huilong, Qiao Yanhui, Zhang Huaxin, Yang Xiuyan. 2020. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi on the growth and physiological metabolism of Pyrus betulaefolia Bunge seedlings under saline-alkaline stress. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University(Natural Science Edition), 44 (6):152-160. (in Chinese) |
| 姜磊, 李焕勇, 张芹, 张会龙, 乔艳辉, 张华新, 杨秀艳. 2020. AM真菌对盐碱胁迫下杜梨幼苗生长与生理代谢的影响. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 44 (6):152-160. | |
| [12] |
Lehmann S G, Bourgoin-Voillard S, Seve M, Rachidi W, Ayala A. 2017. Tubulin Beta-3 Chain as a new candidate protein biomarker of human skin aging:a preliminary study. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity,doi: 0.1155/2017/5140360.
doi: 0.1155/2017/5140360 URL |
| [13] |
Li H, Lin J, Yang Q, Li X, Chang Y. 2017. Comprehensive analysis of differentially expressed genes under salt stress in pear(Pyrus betulaefolia)using RNA-Seq. Plant Growth Regulation, 82 (3):409-420.
doi: 10.1007/s10725-017-0266-3 URL |
| [14] | Li Yongping, Ye Xinru, Wang Bin, Chen Meidong, Liu Jianting, Zhu Haisheng, Wen Qingfang. 2021. Cloning and selection evaluation of reference gene for quantitative real-time PCR in Hibiscus esculentus L. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 35 (1):60-71. (in Chinese) |
|
李永平, 叶新如, 王彬, 陈敏氡, 刘建汀, 朱海生, 温庆放. 2021. 黄秋葵实时荧光定量PCR内参基因的克隆与筛选评价. 核农学报, 35 (1):60-71.
doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2021.01.0060 |
|
| [15] | Liu Xiaofei, Yu Bo, Huang Lili, Sun Yingbo. 2020. Screening and validation of reference genes of Camellia azalea by quantitative real-time PCR. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 47 (12):203-211. (in Chinese) |
| 刘小飞, 于波, 黄丽丽, 孙映波. 2020. 杜鹃红山茶实时定量PCR内参基因筛选及验证. 广东农业科学, 47 (12):203-211. | |
| [16] | Ma Lina, Yang Jinbo, Ding Yifei, Li Yingkang. 2019. Research progress on three generations sequencing technology and its application. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 46 (8):2246-2256. (in Chinese) |
| 马丽娜, 杨进波, 丁逸菲, 李颖康. 2019. 三代测序技术及其应用研究进展. 中国畜牧兽医, 46 (8):2246-2256. | |
| [17] | Mou Lifei, Yu Xiaojing, Zhang Qiuyue, Feng Chaonian. 2020. Salt tolerance of four half-sib families of Pyrus betulaefolia Bunge from coastal areas. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University(Natural Science Edition), 44 (5):157-166. (in Chinese) |
| 缪李飞, 于晓晶, 张秋悦, 封超年. 2020. 4个杜梨半同胞家系苗期耐盐性分析. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 44 (5):157-166. | |
| [18] |
Pfaffl M W, Tichopad A, Prgomet C, Neuvians T P. 2004. Determination of stable housekeeping genes,differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity:BestKeeper-Excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations. Biotechnology Letters, 26 (6):509-515.
doi: 10.1023/B:BILE.0000019559.84305.47 URL |
| [19] | Pu Xiaoqiu, Tian Jia, Li Jiang, Zhang Yan, Li Peng, Tan Weiming, Jing Chunzhi. 2020. Analysis on expression stability of internal reference genes at cell division stage of pear fruits. Nonwood Forest Research, 38 (1):66-74. (in Chinese) |
| 蒲小秋, 田嘉, 李疆, 张艳, 李鹏, 覃伟铭, 井春芝. 2020. 梨果实细胞分裂期内参基因表达稳定性分析. 经济林研究, 38 (1):66-74. | |
| [20] | Qiao Yonggang, Wang Yongfei, Cao Yaping, He Jiaxin, Jia Mengjun, Li Zheng, Zhang Xinrui, Song Yun. 2020. Reference genes selection and related genes expression analysis under low and high temperature stress in Taraxacum officinale. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47 (6):1153-1164. (in Chinese) |
| 乔永刚, 王勇飞, 曹亚萍, 贺嘉欣, 贾孟君, 李政, 张鑫瑞, 宋芸. 2020. 药用蒲公英低温和高温胁迫下内参基因筛选与相关基因表达分析. 园艺学报, 47 (6):1153-1164. | |
| [21] |
Roger A J, Sandblom O, Doolittle W F, Philippe H. 1999. An evaluation of elongation factor 1 alpha as a phylogenetic marker for eukaryotes. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 16 (2):218-233.
pmid: 10028289 |
| [22] |
Silver N, Best S, Jiang J, Thein S L. 2006. Selection of housekeeping genes for gene expression studies in human reticulocytes using real-time PCR. BMC Molecular Biology, 7 (1):33.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-7-33 URL |
| [23] | Stone S L. 2016. Chapter 26-ubiquitination of plant transcription factors, Boston: Academic Press:395-409. |
| [24] |
Umadevi P, Suraby E J, Anandaraj M, Nepolean T. 2019. Identification of stable reference gene for transcript normalization in black pepper-Phytophthora capsici pathosystem. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants, 25 (4):945-952.
doi: 10.1007/s12298-019-00653-9 pmid: 31402818 |
| [25] | Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F. 2002. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biology, 3 (7):h31-h34. |
| [26] |
Wang Hao, Cai Qizhong, Liu Lu, Yang Quan, Zhou Liangyun. 2021. Reference gene screening for real-time quantitative PCR in Polygonum multiflorum. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 46 (1):80-85. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20201024.103 pmid: 33645055 |
|
王浩, 蔡启忠, 刘露, 杨全, 周良云. 2021. 何首乌实时荧光定量PCR内参基因筛选. 中国中药杂志, 46 (1):80-85.
pmid: 33645055 |
|
| [27] |
Wu H. 2018. Plant salt tolerance and Na+ sensing and transport. The Crop Journal, 6 (3):215-225.
doi: 10.1016/j.cj.2018.01.003 URL |
| [28] |
Xie F, Xiao P, Chen D, Xu L, Zhang B. 2012. miRDeepFinder:a miRNA analysis tool for deep sequencing of plant small RNAs. Plant Mol Biol, 80:75-84.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-012-9885-2 URL |
| [29] | Yang Ting, Xue Zhenzhen, Li Na, Lang Xiaoan, Li Lingfei, Zhong Chunmei. 2021. Reference genes selection and validation in Begonia masoniana leaves of different developmental stages. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 48 (11):2251-2261. (in Chinese) |
| 杨婷, 薛珍珍, 李娜, 郎校安, 李凌飞, 钟春梅. 2021. 铁十字秋海棠斑叶发育过程内参基因筛选及验证. 园艺学报, 48 (11):2251-2261. | |
| [30] | Ye Bihuan, Song Qiyan, Chen Youwu, Hu Chuanjiu, Du Guojian, Liao Rongjun, Li Haibo. 2020. Selection and validation of internal reference genes for qPCR in Polygonatum cyrtonema tubers at different development stages and in response to abiotic stress. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 45 (24):5967-5975. (in Chinese) |
| 杨阳, 叶碧欢, 宋其岩, 陈友吾, 胡传久, 杜国坚, 廖荣俊, 李海波. 2020. 多花黄精块茎发育和胁迫条件下qPCR内参基因的筛选与验证. 中国中药杂志, 45 (24):5967-5975. | |
| [31] | Zhang Xue, Wang Li, Ju Fei, Yang Shengjun. 2019. Reference gene screening for real-time quantitative PCR in red pear(Pyrus pyrifolia). Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 27 (2):361-370. (in Chinese) |
| 张雪, 王荔, 瞿飞, 杨胜俊. 2019. 红梨实时荧光定量PCR内参基因的筛选. 农业生物技术学报, 27 (2):361-370. | |
| [32] | Zhang Zhengrui, Zhang Yaohua, Wang Qiushi, Yu Hui, Yang Suxin. 2020. Screening and validation of reference genes for real-time quantitative PCR in soybean. Plant Physiology Communications, 56 (9):1963-1973. (in Chinese) |
| 张芷睿, 张耀华, 王秋实, 于慧, 杨素欣. 2020. 大豆实时荧光定量PCR内参基因的筛选与验证. 植物生理学报, 56 (9):1963-1973. |
| [1] | 侯天泽, 易双双, 张志群, 王健, 李崇晖. 秋石斛RT-qPCR内参基因的筛选与验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(11): 2489-2501. |
| [2] | 马璐琳, 段青, 崔光芬, 杜文文, 贾文杰, 王祥宁, 王继华, 陈发棣. 钝裂银莲花花色素合成相关基因qRT-PCR内参基因的筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(2): 377-388. |
| [3] | 杨婷, 薛珍珍, 李娜, 郎校安, 李凌飞, 钟春梅. 铁十字秋海棠斑叶发育过程内参基因筛选及验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(11): 2251-2261. |
| [4] | 李泳潭,张 军*,黄亚丽,范建敏,张益文,左力辉. 杜梨叶绿体基因组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2020, 47(6): 1021-1032. |
| [5] | 乔永刚*,王勇飞,曹亚萍,贺嘉欣,贾孟君,李 政,张鑫瑞,宋 芸. 药用蒲公英低温和高温胁迫下内参基因筛选与相关基因表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2020, 47(6): 1153-1164. |
| [6] | 宋晓波1,常英英1,刘 昊1,2,徐慧敏3,裴 东1,*. 核桃不定根发生阶段内参基因筛选与关键基因表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2019, 46(10): 1907-1918. |
| [7] | 刘晓婷1,2,*,王顺利2,*,薛璟祺2,薛玉前2,吕英民1,**,张秀新2,**. 朱顶红实时荧光定量PCR中不同组织器官内参基因的筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2018, 45(5): 919-930. |
| [8] | 张 欢,杨英杰,李鼎立,宋健坤,马春晖,王 然*. 杜梨根茎叶特异表达基因的RNA-Seq分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2018, 45(10): 1881-1894. |
| [9] | 庞强强1,2,3,李植良1,罗少波1,陈日远2,金庆敏1,黎振兴1,李德明3,孙保娟1,*,孙光闻2,*. 高温胁迫下茄子qRT-PCR内参基因筛选及稳定性分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2017, 44(3): 475-486. |
| [10] | 蒋婷婷, 高燕会, 童再康. 石蒜属植物实时荧光定量PCR内参基因的选择[J]. 园艺学报, 2015, 42(6): 1129-1138. |
| [11] | 刘传娇1,2,王顺利2,*,薛璟祺2,朱富勇2,任秀霞2,李名扬1,**,张秀新2,**. 牡丹泛素延伸蛋白基因ubiquitin克隆及其作为内参基因的研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2015, 42(10): 1983-1992. |
| [12] | 周晓慧 刘 军 庄 勇. 喀西茄内参基因实时荧光定量PCR表达稳定性评价[J]. 园艺学报, 2014, 41(8): 1731-1738. |
| [13] | 李 慧1,2,*,李刚波1,3,*,丛 郁4,常有宏1,2,**,蔺 经1,盛宝龙1. 杜梨类钙调磷酸酶B亚基蛋白基因PbCBL2的克隆和功能初探[J]. 园艺学报, 2013, 40(8): 1445-1455. |
| [14] | 梁 云, 袁素霞, 冯慧颖, 徐雷锋, 袁迎迎, 刘 春, 明 军. 百合肌动蛋白基因lilyActin 的克隆与表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2013, 40(7): 1318-1326. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司