
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (6): 1588-1598.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0895
• Cultivation?Physiology & Biochemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
YAN Lijuan1,2, OU Chenggang1, LIANG Chen1, HU Tiankuo1, LIU Xing1, YANG Jing2, LIN Guocang2, and ZHUANG Feiyun1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-11-29
Revised:2025-05-06
Online:2025-06-20
Published:2025-06-20
Contact:
and ZHUANG Feiyun
YAN Lijuan, OU Chenggang, LIANG Chen, HU Tiankuo, LIU Xing, YANG Jing, LIN Guocang, and ZHUANG Feiyun. Response of Premature Bolting of Carrots Under Different Low Temperature and Day Length[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(6): 1588-1598.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0895

Fig. 1 Comparison of temperature and day length in plastic shed of Shunyi,Beijing and premature bolting ratios of different carrot parents and their crosses A:The maximum and minimum temperature of a day during carrot growth in plastic shed;B:The days of minimum temperature below < 0,0-5 and 6-7 ℃ after carrot seedling;C:Day length during carrot growth,and the green dotted line showed that day length reaches 14 h;D and E showed premature bolting ratios of parents and their crosses,respectively. The orange and red lines represented the orange and red parents and their crosses,respectively. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05)by Duncan’s test. The same below
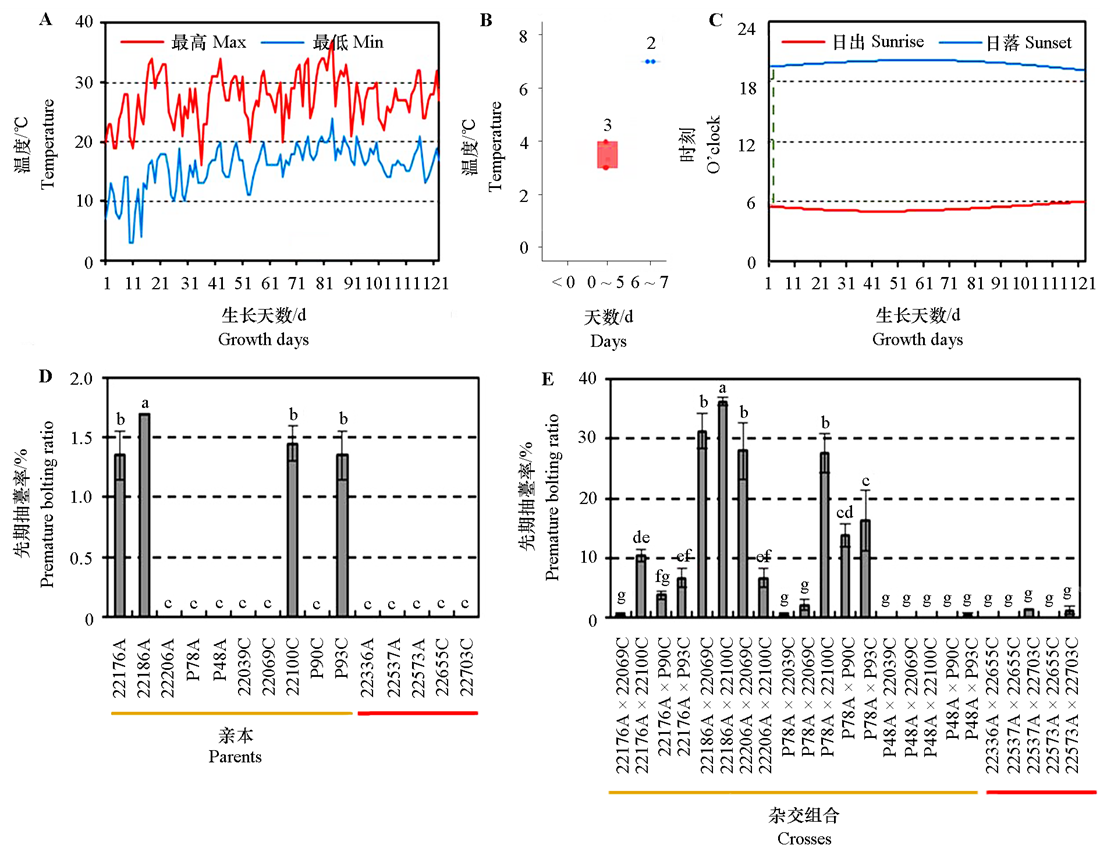
Fig. 2 Comparison of temperature and day length in Helingeer with premature bolting ratio of different carrot parents and their crosses A:The maximum and minimum temperature of a day during carrot growth;B:The days of minimum temperature below < 0,0-5 and 6-7 ℃ after carrot seedling;C:Day length during carrot growth,and the green dotted line showed that day length reaches 14 h;D and E showed premature bolting ratios of parents and their crosses,respectively
| 参数 Parameter | 方差分量 Variance component | 分量占比/% Proportion |
|---|---|---|
| 加性方差Additive variance(VA) | ND | ND |
| 显性方差Dominance variance(VD) | 5.36 ± 2.45* | 1.66 ± 2.48 |
| 加性 × 环境方差Additive × Environment interaction variance(VAE) | 106.02 ± 15.59** | 32.75 ± 3.78** |
| 显性 × 环境方差Dominance × Environment interaction variance(VDE) | 205.61 ± 24.71** | 63.52 ± 3.29** |
| 误差Error variance(VE) | 6.70 ± 2.96 | 2.07 ± 1.30 |
| 表型方差 Phenotype variance(Vp) | 323.69 ± 35.32** |
Table 1 Analysis of genetic variance components of parents and their crosses premature bolting
| 参数 Parameter | 方差分量 Variance component | 分量占比/% Proportion |
|---|---|---|
| 加性方差Additive variance(VA) | ND | ND |
| 显性方差Dominance variance(VD) | 5.36 ± 2.45* | 1.66 ± 2.48 |
| 加性 × 环境方差Additive × Environment interaction variance(VAE) | 106.02 ± 15.59** | 32.75 ± 3.78** |
| 显性 × 环境方差Dominance × Environment interaction variance(VDE) | 205.61 ± 24.71** | 63.52 ± 3.29** |
| 误差Error variance(VE) | 6.70 ± 2.96 | 2.07 ± 1.30 |
| 表型方差 Phenotype variance(Vp) | 323.69 ± 35.32** |
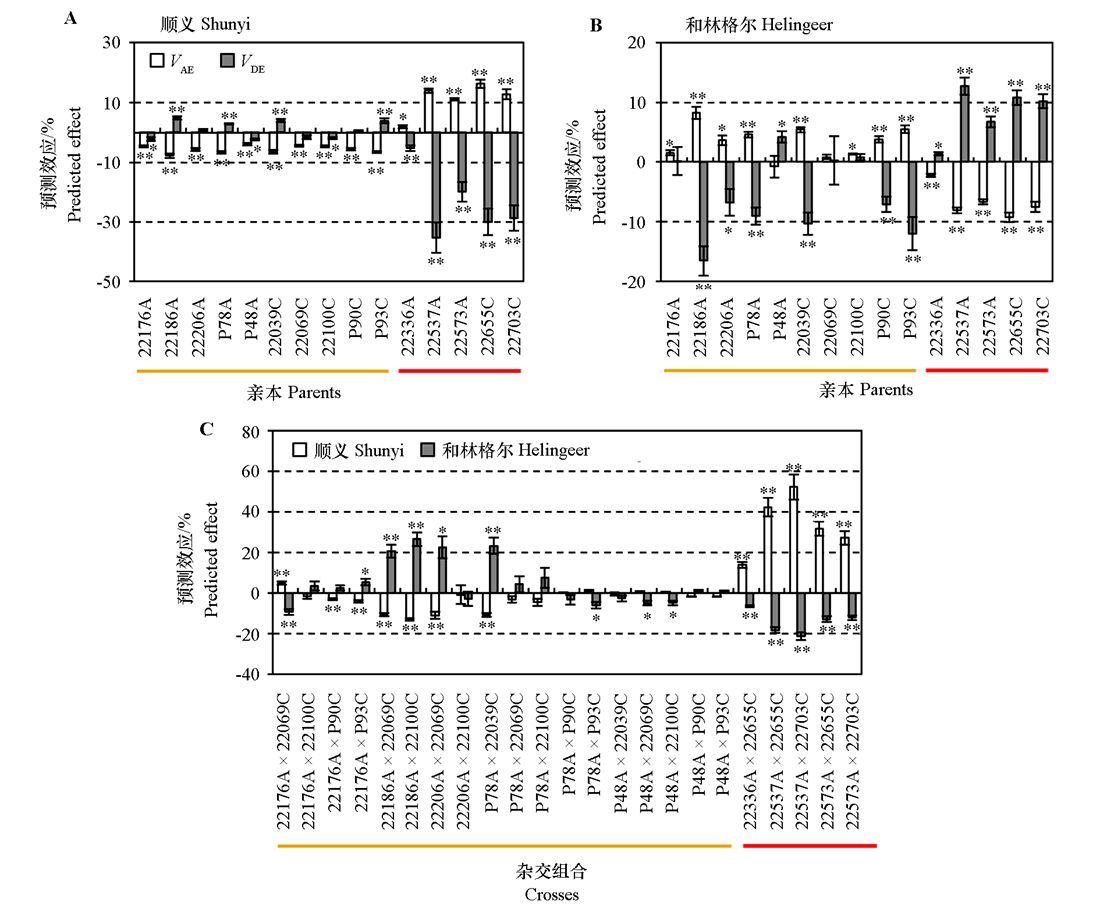
Fig. 3 Predicted heterosis of carrot parents and their crosses premature bolting ratios A and B:Predicted additive × environment effect(VAE)and dominant × environment effect(VDE)of different carrot parents premature bolting in Shunyi and Helingeer,respectively;C:Predicted VDE of their crosses premature bolting in Shunyi and Helingeer,respectively. The orange and purple lines represented the orange and red parents and their crosses,respectively. * and ** were significant at the level of 0.05 and 0.01,respectively
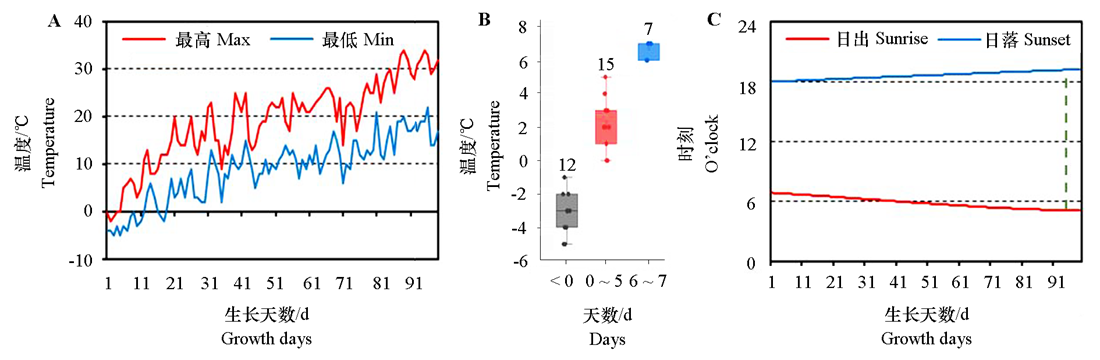
Fig. 4 Temperature in plastic shed of Yongqiao,Anhui A:The maximum and minimum temperature of a day during carrot growth;B:The days of minimum temperature below < 0,0-5 and 6-7 ℃ after carrot seedling;C:Day length during carrot growth,and the green dotted line showed that day length reaches 14 h
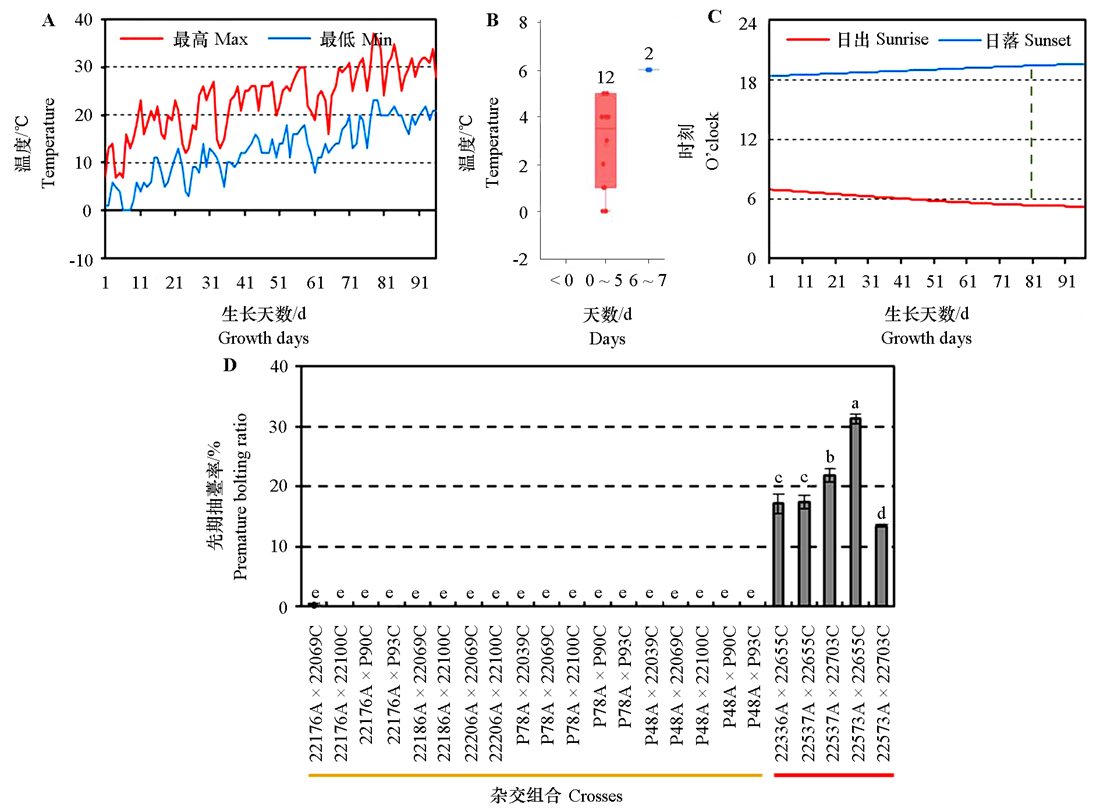
Fig. 6 Comparison of premature bolting ratios of crosses in small shed of Xiangfu,Henan A:The maximum and minimum temperature of a day during carrot growth;B:The days of minimum temperature below < 0,0-5 and 6-7 ℃ after carrot seedling;C:Day length during carrot growth,and the green dotted line showed that day length reaches 14 h; D:Premature bolting ratios of parents and their crosses,respectively

Fig. 7 Comparison of premature bolting ratios of crosses in Urumqi,Xinjiang A:The maximum and minimum temperature of a day during carrot growth;B:The days of minimum temperature below < 0,0-5 and 6-7 ℃ after carrot seedling;C:Day length during carrot growth,and the green dotted line showed that day length reaches 14 h; D:Premature bolting ratios of parents and their crosses,respectively
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
|
鲍生有, 欧承刚, 庄飞云, 陈劲枫, 赵志伟. 2010. 胡萝卜春季栽培先期抽薹的调查与分析. 中国蔬菜,(6):38-42.
|
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0985 |
|
崔建, 钟雄辉, 刘泽慈, 陈登辉, 李海龙, 韩睿, 乐祥庆, 康俊根, 王超. 2023. 结球甘蓝染色体片段替换系构建. 园艺学报, 50 (1):65-78.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0985 |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
|
方智远. 2017. 中国蔬菜育种学. 北京: 中国农业出版社.
|
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
|
毛笈华, 茅淑敏, 庄飞云, 欧承刚, 赵志伟, 鲍生有. 2013. 胡萝卜先期抽薹遗传及环境调控研究. 华北农学报, 28 (3):67-72.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7091.2013.03.013 |
|
| [16] |
|
|
缪旻珉, 汪李平. 2021. 蔬菜栽培学. 北京: 科学出版社.
|
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
|
肖炳光, 朱军, 卢秀萍, 白永富, 李永平. 2005. 烤烟主要农艺性状对产量的遗传贡献率分析. 遗传学报,32:1089-1093.
|
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
|
朱军. 1997. 遗传模型分析方法. 北京: 中国农业出版社.
|
|
| [25] |
|
|
庄飞云, 赵志伟, 李锡香, 胡鸿, 方智远. 2006. 中国地方胡萝卜品种资源的核心样品构建. 园艺学报, 33 (1):46-51.
|
| [1] | TIAN Hongmei, WANG Yuanlong, WANG Fei, PAN Hong, TAO Zhen, ZHANG Jian, WANG Pengcheng. A New Muskmelon Cultivar‘Jinzhongyuan Jintian’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 153-154. |
| [2] | XIAO Zhihao, ZHENG Hankai, ZHANG Mannan, TANG Huaiqian, WANG Jiaying, ZHANG Yuyang, ZHANG Junhong, YE Zhibiao, and YE Jie. Effects of Potassium on Growth and Development of Tomato Seedlings Under Abiotic Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(6): 1599-1618. |
| [3] | XING Zhigan, LEI Xiangzhao, WANG Haochen, FENG Mingxin, LI Jingwen, LIU Yujia, FANG Yulin, MENG Jiangfei. Physiological Response of Shine Muscat Grape Seedlings Grafted with Different Rootstocks to Combined Stress of Salt and Low Temperature [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(3): 693-704. |
| [4] | LUO Jiandong, QIU Mengqing, ZHOU Huimin, XIE Weiwei, Huang Haixin, LIU Jieqi, ZHANG Zimin, XU Jian, CHEN Chengjie, HE Yehua, LIU Chaoyang. Cloning and Functional Analysis of Pineapple AcZFP1 Gene Under Low Temperature Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(3): 495-508. |
| [5] | SUN Huiru, DANG Fengfeng, REN Min, ZHANG Jianing, FAN Bei, CHEN Guoliang, CHENG Guoting, WANG Yanfeng. Function Analysis of SlWRKY46 in Regulating Tomato Response to Low Temperature Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(12): 2758-2774. |
| [6] | WU Baizeng, JIANG Yuqing, HE Qi, HUANG Chenyang, ZHANG Lijiao, ZHAO Mengran. Study on the Regulation of Lactate Dehydrogenase on Mycelia Growth of Pleurotus ostreatus Under Low Temperature and Light [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(12): 2886-2894. |
| [7] | LI Renjie , YUAN Lingyun , CHEN Guohu , HOU Jinfeng , HUANG Xingxue , and WANG Chenggang, . [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(S1): 41-42. |
| [8] | ZHOU Cheng, FANG Yi, ZHOU Jinyang, HUANG Qihao, PAN Yongjian, SHI Qianqian, NI Huixian, YANG Zhenfeng, SONG Chunbo. The Relationship Between Membrane Lipid Metabolism and Chilling Injury of Postharvest Peach Fruit Induced by Low Temperature [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(6): 1305-1317. |
| [9] | MAO Kexin, AN Miao, WANG Hairong, WANG Shijin, LÜ Wei, GUO Yingtian, LI Jian, LI Guotian. Identification and Low Temperature Expression Analysis of MYB Transcription Factor Family in Kiwifruit [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(3): 534-548. |
| [10] | WANG Xuanzhen, CHEN Mindong, LIU Jianting, ZENG Meijuan, YE Xinru, LI Yongping, WEN Qingfang, ZHU Haisheng. Identification of Luffa Under Low Temperature and Weak Light Stress Gene Co-expression Modules by WGCNA [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(12): 2601-2618. |
| [11] | WANG Min, YANG Songguang, LIU Wei, HE Xiaoming, SHI Shaoqi, LIU Wenrui, CHEN Lin, JIANG Biao, PENG Qingwu. Response to Low Temperature Stress and Screening and Validation of Interaction Protein of CqCHP1 in Chieh-qua [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(11): 2376-2386. |
| [12] | LIN Haijiao, LIANG Yuchen, LI Ling, MA Jun, ZHANG Lu, LAN Zhenying, YUAN Zening. Exploration and Regulation Network Analysis of CBF Pathway Related Cold Tolerance Genes in Lavandula angustifolia [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(1): 131-144. |
| [13] | HUANG Shuping, TAN Jie, Chen Xia, ZHANG Hongyuan, LI Ye, WANG Benqi, CHEN Hao, WU Xuexia, and ZHANG Min, . A New Eggplant Cultivar‘Eqie 6’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 101-102. |
| [14] | NIE Xinmiao, LUAN Heng, FENG Gaili, WANG Chao, LI Yan, WEI Min. Effects of Silicon Nutrition and Grafting Rootstocks on Chilling Tolerance of Cucumber Seedlings [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1795-1804. |
| [15] | WANG Guangpeng, LIU Tongkun, XU Xinfeng, LI Zhubo, GAO Zhanyuan, HOU Xilin. Identification of LEA Family and Expression Analysis of Some Members Under Low-temperature Stress in Chinese Cabbage [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(2): 304-318. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd