
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (6): 1599-1618.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0383
• Cultivation?Physiology & Biochemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
XIAO Zhihao1, ZHENG Hankai1, ZHANG Mannan1, TANG Huaiqian1, WANG Jiaying1, ZHANG Yuyang1,2, ZHANG Junhong1,2, YE Zhibiao1,2, and YE Jie1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-12-01
Revised:2025-03-19
Online:2025-06-20
Published:2025-06-20
Contact:
and YE Jie
XIAO Zhihao, ZHENG Hankai, ZHANG Mannan, TANG Huaiqian, WANG Jiaying, ZHANG Yuyang, ZHANG Junhong, YE Zhibiao, and YE Jie. Effects of Potassium on Growth and Development of Tomato Seedlings Under Abiotic Stress[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(6): 1599-1618.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0383
| K/mmol · L-1 | mg · L-1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KNO3 | NH4NO3 | Ca(NO3)2·4H2O | NH4H2PO4 | MgSO4·7H2O | CaCl2 | |
| 1.5 | 151.75 | 180.30 | 945.00 | 115.00 | 493.00 | 0 |
| 6.0 | 607.00 | 0 | 945.00 | 115.00 | 493.00 | 0 |
| 9.0 | 910.50 | 0 | 590.42 | 115.00 | 493.00 | 166.77 |
Table 1 Potassium low,medium and high concentration Hogland nutrient solution content of a large number of elements
| K/mmol · L-1 | mg · L-1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KNO3 | NH4NO3 | Ca(NO3)2·4H2O | NH4H2PO4 | MgSO4·7H2O | CaCl2 | |
| 1.5 | 151.75 | 180.30 | 945.00 | 115.00 | 493.00 | 0 |
| 6.0 | 607.00 | 0 | 945.00 | 115.00 | 493.00 | 0 |
| 9.0 | 910.50 | 0 | 590.42 | 115.00 | 493.00 | 166.77 |
| 基因名称Gene name | 引物(5′-3′)Primer | |
|---|---|---|
| Actin | F:ATGGCAGACGGAGAGGATATTCA | R:GCCTTTGCAATCCACATCTGCTG |
| LKT1 | F:ACTTGCCTCTCACCCTTTG | R:CCACACAGTTCTCAATGCC |
| HAK5 | F:CCGTGTTACGCGCCTTTAA | R:TCCTTTTTTACCGTTTCTTTTGAAG |
| HY5 | F:GCAAGCGACGAGTTCTAT | R:ATCTCCGGCACTCTTCTG |
| SlMYB15 | F:GCAGCAAGATTACCGGGAAG | R:TGGTGAGTTAGGAGCATGCA |
| SOS1 | F:GTGCAGTACAGATGCTTTTACTTG | R:AGGGCCACAACAGCCACAG |
| NHX1 | F:TGGCGAGATTGGGGGTGAGT | R:AACGACTCTCTTCAAGGAGATGACC |
| SlNAC6 | F:GAGGTGTTTCATGTGGTTAGGTGGAT | R:CGGCTTGCTGAGAAGACTGTTGC |
| SlAREB1 | F:TCCTTATGTGTTTAATGGTGGTTT | R:CATCGTTTTCTTCTTTTAGTTTCG |
| SlCBF1 | F:GAGTCGGAAGAAGTTTCAGG | R:TGTAGGCATCAGTTTCCAC |
| SlCBF3 | F:TGCCGGGTTTACTTACGAAT | R:TCAGCTTCCACATGATCTCC |
Table 2 Primer sequences for qRT-PCR
| 基因名称Gene name | 引物(5′-3′)Primer | |
|---|---|---|
| Actin | F:ATGGCAGACGGAGAGGATATTCA | R:GCCTTTGCAATCCACATCTGCTG |
| LKT1 | F:ACTTGCCTCTCACCCTTTG | R:CCACACAGTTCTCAATGCC |
| HAK5 | F:CCGTGTTACGCGCCTTTAA | R:TCCTTTTTTACCGTTTCTTTTGAAG |
| HY5 | F:GCAAGCGACGAGTTCTAT | R:ATCTCCGGCACTCTTCTG |
| SlMYB15 | F:GCAGCAAGATTACCGGGAAG | R:TGGTGAGTTAGGAGCATGCA |
| SOS1 | F:GTGCAGTACAGATGCTTTTACTTG | R:AGGGCCACAACAGCCACAG |
| NHX1 | F:TGGCGAGATTGGGGGTGAGT | R:AACGACTCTCTTCAAGGAGATGACC |
| SlNAC6 | F:GAGGTGTTTCATGTGGTTAGGTGGAT | R:CGGCTTGCTGAGAAGACTGTTGC |
| SlAREB1 | F:TCCTTATGTGTTTAATGGTGGTTT | R:CATCGTTTTCTTCTTTTAGTTTCG |
| SlCBF1 | F:GAGTCGGAAGAAGTTTCAGG | R:TGTAGGCATCAGTTTCCAC |
| SlCBF3 | F:TGCCGGGTTTACTTACGAAT | R:TCAGCTTCCACATGATCTCC |
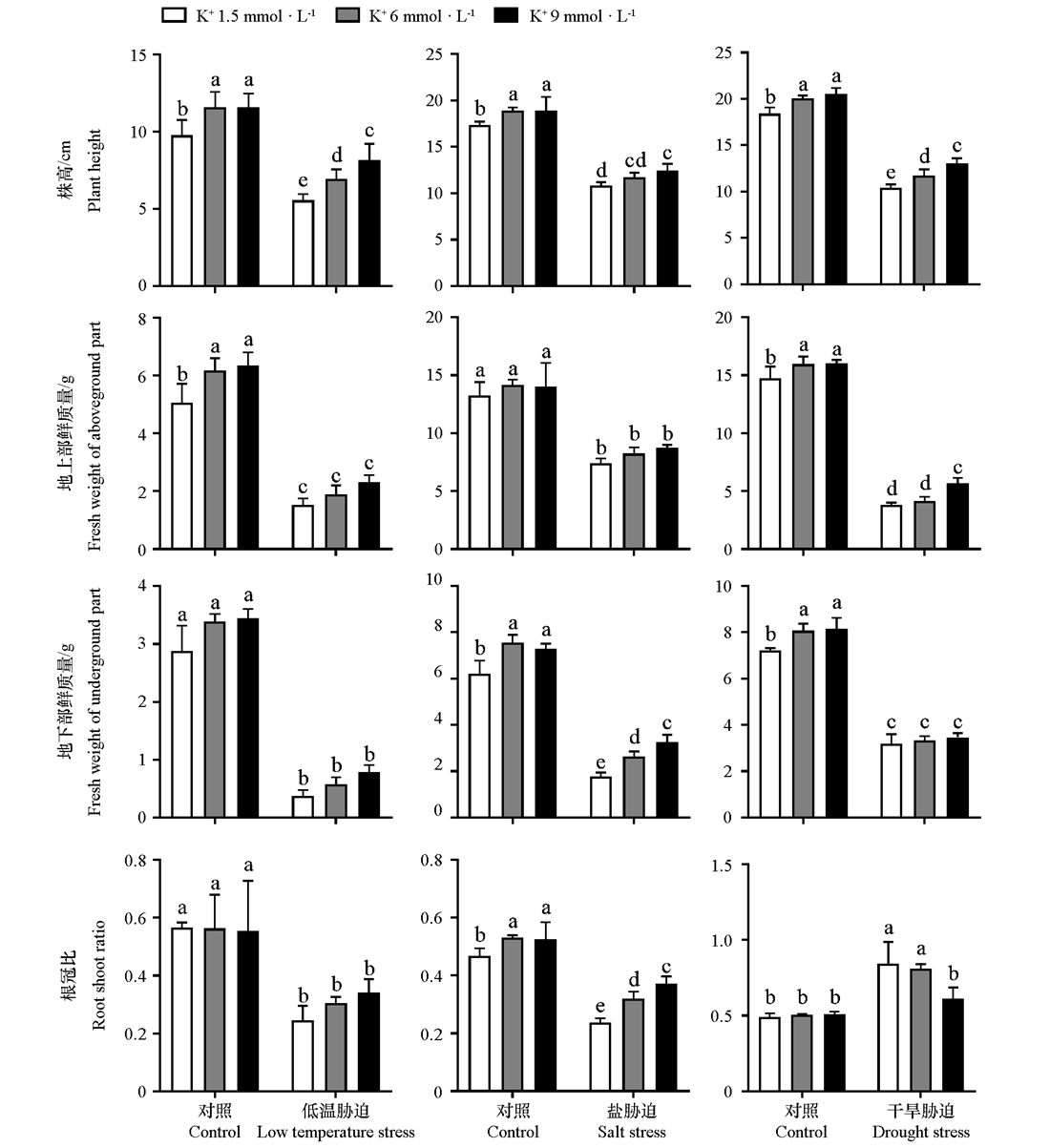
Fig. 1 Plant height,aboveground fresh weight,underground fresh weight and root-shoot ratio under different potassium concentrations and abiotic stresses Different lowercase letters on the bar chart indicated significant difference between treatments at 0.05 level. The same below
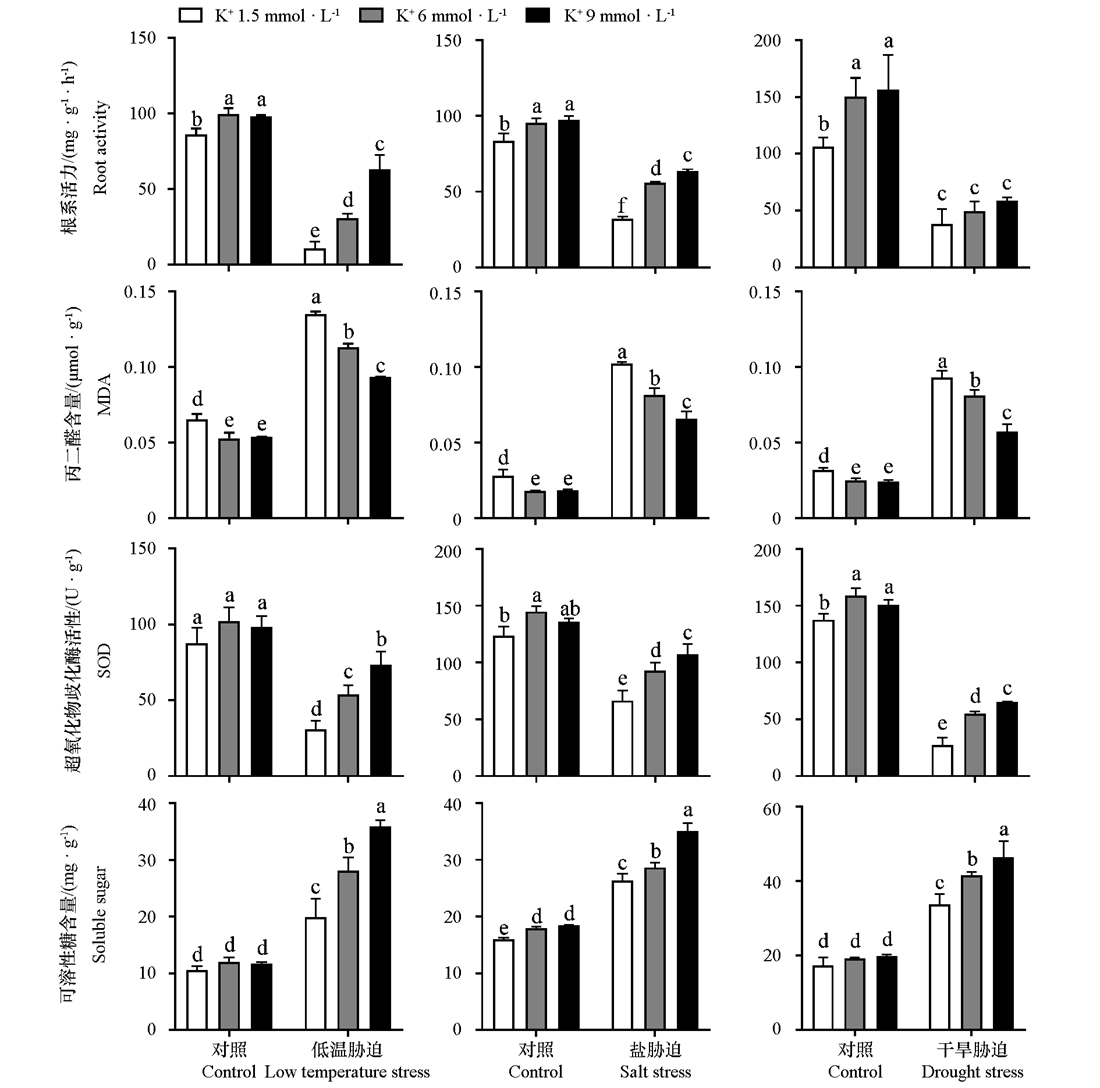
Fig. 3 Root activity and MDA content,SOD activity,soluble sugar content in leaves of abiotic stresses groups were treated with different potassium concentrations
| 处理Treatment | μ(X1) | μ(X2) | D值D-value | 排名Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干旱胁迫对照 + 中钾Drought stress control + Medium potassium | 1.000 | 0.412 | 0.930 | 1 |
| 干旱胁迫对照 + 高钾Drought stress control + High potassium | 0.993 | 0.442 | 0.927 | 2 |
| 盐胁迫对照 + 中钾Salt stress control + Medium potassium | 0.902 | 0.427 | 0.845 | 3 |
| 盐胁迫对照 + 高钾Salt stress control + High potassium | 0.858 | 0.444 | 0.808 | 4 |
| 干旱胁迫对照 + 低钾Drought stress control + Low potassium | 0.864 | 0.366 | 0.805 | 5 |
| 盐胁迫对照 + 低钾Salt stress control + Low potassium | 0.825 | 0.300 | 0.763 | 6 |
| 低温胁迫对照 + 中钾Low temperature stress control + Medium potassium | 0.531 | 0.357 | 0.510 | 7 |
| 低温胁迫对照 + 高钾Low temperature stress control + High potassium | 0.516 | 0.353 | 0.497 | 8 |
| 盐胁迫处理 + 高钾Salt stress + High potassium | 0.493 | 0.325 | 0.473 | 9 |
| 低温胁迫对照 + 低钾Low temperature stress control + Low potassium | 0.446 | 0.328 | 0.432 | 10 |
| 干旱胁迫处理 + 高钾Drought stress + High potassium | 0.328 | 0.838 | 0.389 | 11 |
| 盐胁迫处理 + 中钾Salt stress + Medium potassium | 0.404 | 0.204 | 0.380 | 12 |
| 干旱胁迫处理 + 中钾Drought stress + Medium potassium | 0.242 | 1.000 | 0.332 | 13 |
| 干旱胁迫处理 + 低钾Drought stress + Low potassium | 0.155 | 0.973 | 0.252 | 14 |
| 盐胁迫处理 + 低钾Salt stress + Low potassium | 0.271 | 0.078 | 0.248 | 15 |
| 低温胁迫处理 + 高钾Low temperature stress + High potassium | 0.194 | 0.304 | 0.207 | 16 |
| 低温胁迫处理 + 中钾Low temperature stress + Medium potassium | 0.120 | 0.149 | 0.123 | 17 |
| 低温胁迫处理 + 低钾Low temperature stress + Low potassium | 0 | 0 | 0 | 18 |
Table 3 Comprehensive evaluation of tomato growth under different treatments
| 处理Treatment | μ(X1) | μ(X2) | D值D-value | 排名Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干旱胁迫对照 + 中钾Drought stress control + Medium potassium | 1.000 | 0.412 | 0.930 | 1 |
| 干旱胁迫对照 + 高钾Drought stress control + High potassium | 0.993 | 0.442 | 0.927 | 2 |
| 盐胁迫对照 + 中钾Salt stress control + Medium potassium | 0.902 | 0.427 | 0.845 | 3 |
| 盐胁迫对照 + 高钾Salt stress control + High potassium | 0.858 | 0.444 | 0.808 | 4 |
| 干旱胁迫对照 + 低钾Drought stress control + Low potassium | 0.864 | 0.366 | 0.805 | 5 |
| 盐胁迫对照 + 低钾Salt stress control + Low potassium | 0.825 | 0.300 | 0.763 | 6 |
| 低温胁迫对照 + 中钾Low temperature stress control + Medium potassium | 0.531 | 0.357 | 0.510 | 7 |
| 低温胁迫对照 + 高钾Low temperature stress control + High potassium | 0.516 | 0.353 | 0.497 | 8 |
| 盐胁迫处理 + 高钾Salt stress + High potassium | 0.493 | 0.325 | 0.473 | 9 |
| 低温胁迫对照 + 低钾Low temperature stress control + Low potassium | 0.446 | 0.328 | 0.432 | 10 |
| 干旱胁迫处理 + 高钾Drought stress + High potassium | 0.328 | 0.838 | 0.389 | 11 |
| 盐胁迫处理 + 中钾Salt stress + Medium potassium | 0.404 | 0.204 | 0.380 | 12 |
| 干旱胁迫处理 + 中钾Drought stress + Medium potassium | 0.242 | 1.000 | 0.332 | 13 |
| 干旱胁迫处理 + 低钾Drought stress + Low potassium | 0.155 | 0.973 | 0.252 | 14 |
| 盐胁迫处理 + 低钾Salt stress + Low potassium | 0.271 | 0.078 | 0.248 | 15 |
| 低温胁迫处理 + 高钾Low temperature stress + High potassium | 0.194 | 0.304 | 0.207 | 16 |
| 低温胁迫处理 + 中钾Low temperature stress + Medium potassium | 0.120 | 0.149 | 0.123 | 17 |
| 低温胁迫处理 + 低钾Low temperature stress + Low potassium | 0 | 0 | 0 | 18 |
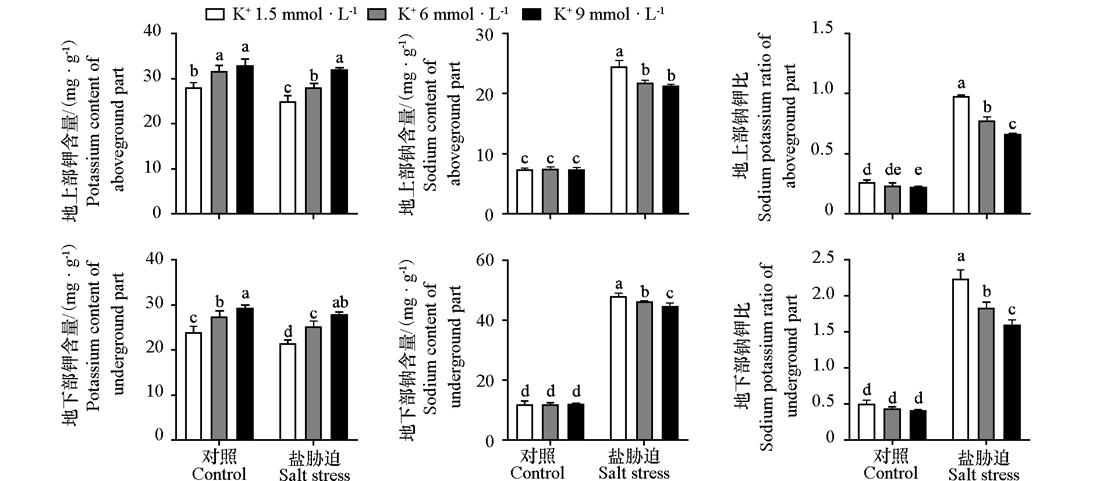
Fig. 5 Content of potassium and sodium,ratio of sodium and potassium in different parts of tomato under salt stress and different potassium concentration

Fig. 6 Expression of HAK5,LKT1,NHX1 and SOS1 genes in different parts of tomato under salt stress and different potassium concentration CK:Control;T:Treatment;L:Low potassium treatment;M:Medium potassium treatment;H:High potassium treatment. Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference between different treatments at 0.05 level during the same period. The same below

Fig. 7 Expression of HAK5,LKT1,SlMYB15,HY5,SlCBF1 and SlCBF3 genes in different parts of tomato under low temperature stress and different potassium concentration
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
|
车延辉. 2023. 外源钾离子缓解盐胁迫对烟草光合机构负面效应的生理与分子机制[博士论文]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学.
|
|
| [5] |
|
|
成京晋, 李浩, 早浩龙, 黄珍华, 海梅荣, 范伟. 2021. 植物响应低温胁迫的分子调控机制. 分子植物育种, 19 (9):3104-3115.
|
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
|
董舒超, 凌嘉怡, 赵丽萍, 宋刘霞, 王银磊, 赵统敏. 2023. 转录因子调控番茄抗旱性研究进展. 江苏农业科学, 51 (9):9-16.
|
|
| [8] |
|
|
杜志烨, 李明玉, 陈稷, 黄进. 2024. 植物胁迫相关蛋白功能研究进展. 植物学报, 59 (1):110-121.
doi: 10.11983/CBB23029 |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
|
方基建, 裴孝伯. 2010. 不同浓度的钾处理对丝瓜幼苗抗寒性的影响. 热带作物学报, 31 (4):561-566.
|
|
| [11] |
|
|
高欢. 2018. 亚低温对番茄幼苗钾吸收、转运及循环的影响[硕士论文]. 黑龙江: 东北农业大学.
|
|
| [12] |
|
|
高晓旭. 2011. 黄瓜、番茄幼苗下胚轴徒长制御及作用机理[硕士论文]. 北京: 中国农业科学院.
|
|
| [13] |
|
|
高玉青, 王文成. 2022. 不定根发生的形态学和生理学研究进展. 烟台果树,(4):1-5.
|
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
doi: 10.1002/bies.201200181 pmid: 23640876 |
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
|
郭书亚, 艾金祥, 陈虹宇, 邵烨瑶, 汪妍, 王倩, 叶怡彤, 张雅婷, 丁哲晓, 吴昊辰, 吴玉环, 张建新, 饶米德, 刘鹏. 2022. 基于主成分—聚类—逐步回归分析构建番茄苗期耐铝性综合评价体系. 植物学报, 57 (4):479-489.
doi: 10.11983/CBB22066 |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
|
何紫瑶, 陈其睿, 胡文诗, 谷贺贺, 宋毅, 叶晓磊, 张洋洋, 陆志峰, 任涛, 鲁剑巍. 2023. 不同钾素供应和光强对油菜叶片光合能力的影响. 中国油料作物学报,https://doi.org/10.19802/j.issn.1007-9084.2022354.
|
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.1126/science.280.5365.918 pmid: 9572739 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2024.240307 |
|
候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 2024. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析. 中国水稻科学, 38 (4):409-421.
doi: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2024.240307 |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
|
简伟. 2018. 番茄SlMYB75和SlNAC6转录因子在果实成熟及胁迫应答中的功能研究[博士论文]. 重庆: 重庆大学.
|
|
| [24] |
|
|
靳容, 张爱君, 史新敏, 唐忠厚, 陈晓光, 魏猛, 李洪民. 2014. 干旱胁迫下钾对甘薯幼苗光合特性及根系活力的影响. 江苏农业学报, 30 (5):992-996.
|
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
|
李海东, 纪聪聪, 徐一萍, 康涛, 陈建生, 张艳艳, 张玲, 李文金. 2024. 锌对花生活性氧代谢、衰老和产量的影响. 中国农学通报, 40 (4):20-25.
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2023-0117 |
|
| [27] |
|
|
李薇. 2023. 钾在缓解玉米冷害中的作用研究[硕士论文]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学.
|
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
|
刘畅. 2023. 小麦生长点的分化状态对小麦抗寒性影响的研究[硕士论文]. 黑龙江: 东北农业大学.
|
|
| [30] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.10.8.1391 pmid: 9707537 |
| [31] |
|
|
罗丽霞, 刘莹莹, 曾晓辉, 吴熙文, 汪波. 2024. 低温胁迫下小兰屿蝴蝶兰叶片转录组分析. 现代农业科技,(6):162-165.
|
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
doi: 10.1093/nar/29.9.e45 pmid: 11328886 |
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
|
秦娇娇. 2016. 温度对红王子锦带、金银花生理生态特征的影响[硕士论文]. 沈阳: 沈阳师范大学.
|
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
|
宋立金, 丁日升, 曹荷莉, 郭悦, 霍礼琪, 王嫣然, 武凝楠. 2022. 集成萌芽期生长和苗期生理指标高通鉴选番茄耐盐品种. 植物生理学报, 58 (4):733-745.
|
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-1264 |
|
田晓成, 祝令成, 邹晖, 李白云, 马锋旺, 李明军. 2023. 果实可溶性糖的积累模式及其调控研究进展. 园艺学报, 50 (4):885-895.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-1264 |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2024.01.007 pmid: 38335958 |
| [46] |
|
|
王学奎, 黄见良. 2015. 植物生理生化实验原理与技术. 3版. 北京: 高等教育出版社.
|
|
| [47] |
|
|
魏婧, 徐畅, 李可欣, 贺洪军, 徐启江. 2020. 超氧化物歧化酶的研究进展与植物抗逆性. 植物生理学报, 56 (12):2571-2584.
|
|
| [48] |
|
|
吴国江, 周伟, 余忠浩, 刘慧, 李昊, 卢顺丽, 刘祯源, 郭威宏, 周亚星. 2024. 内蒙古自治区高粱登记品种农艺性状及品质综合评价. 江苏农业科学, 52 (1):83-92.
|
|
| [49] |
|
|
夏颖, 姜存仓, 汪宵, 陈防. 2013. 低钾胁迫对棉花光合作用和光合产物分配的影响. 生态学杂志, 32 (6):1476-1482.
|
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
|
徐琴, 王嘉颖, 张曼楠, 萧志浩, 郑涵楷, 卢永恩, 王涛涛, 张余洋, 张俊红, 叶志彪, 叶杰. 2024. 番茄苗期耐盐相关遗传位点鉴定及分子标记开发. 园艺学报, 51 (2):239-252.
|
|
| [52] |
|
|
严圣杰, 刘雪, 黄一轩, 梅振浩, 王伟平, 黎妮, 刘志, 杨华, 张先文. 2024. 模拟干旱对不同耐旱能力水稻根系的影响. 分子植物育种, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20240312.1350.014.html.
|
|
| [53] |
|
|
杨晓燕, 夏体渊, 吴甜. 2023. 植物钾营养胁迫研究进展. 中国农学通报, 39 (18):101-106.
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2022-0495 |
|
| [54] |
|
|
张露月. 2020. SlMYB15转录因子调控番茄低温抗性的作用机制研究[博士论文]. 杭州: 浙江大学.
|
|
| [55] |
|
|
赵晴, 欧英卓, 胡诗钦, 周宇阳, 郭龙彪, 郝芷圻, 孟丽君, 刘长华. 2024. 水稻耐盐生理及分子机制研究进展. 中国农学通报, 40 (12):94-103.
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2023-0792 |
|
| [56] |
|
|
赵杨, 杨永青, 丁杨林, 张蘅, 谢彦杰, 赵春钊, 刘林川, 王鹏程. 2024. 植物非生物逆境学科发展综述. 植物生理学报, 60 (2):248-270.
|
|
| [57] |
|
|
周婷, 曾广宏, 刘碧颖, 廖慧璇, 张圆浩. 2024. 海滨乔木矮化现象及其环境因子驱动力. 生态学报, 44 (3):893-902.
|
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
|
朱波. 2020. 不同钾肥水平对油菜抗旱性的影响及其机理研究[博士论文]. 重庆: 西南大学.
|
|
| [60] |
|
|
朱波, 徐绮雯, 马淑敏, 刘帮艳, 段美春, 王龙昌. 2021. 干旱胁迫下施钾水平对油菜生长特性、籽粒品质和钾素利用的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 27 (6):1016-1026.
|
|
| [61] |
|
|
卓鑫鑫, 刘昆, 周舟, 邱园园, 余锋, 李思宇, 汪浩, 黄健, 朱安, 刘立军. 2023. 土壤微生物对水稻根系形态活力影响的研究进展. 东北农业科学, 48 (2):78-85.
|
| [1] | FAN Huidong, ZHENG Shijin, TIAN song, ZHENG Jianchao. A New Tomato F1 Hybrid‘Jifen 7’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 109-110. |
| [2] | ZHANG Liwei, DAI Zhongren, CHEN Qingqi, LEI Na, HUANG Jun, Hu Haijiang, MEN Wanjie. A New Tomato Cultivar‘Hayan Zhongfenguo 1’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 111-112. |
| [3] | XIONG Zili, SHI Jianlei, CHEN Yongbing, ZHANG Haili, SU Shiwen, ZAI Wenshan, YE Shuguang. A New Tomato Cultivar‘Ouxiu 202’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 113-114. |
| [4] | FANG Junyi, WU Weifeng, LU Qiao, LING Hongqing, and KONG Danyu. Screening and Identification for Bacterial Wilt Resistance Accession TK083 in Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(6): 1477-1487. |
| [5] | CONG Xin, HU Qianyuan, PANG Guibin, XU Lirong, XU Zhenghe, LIU Hongfei, PEI Xiangli. Effect of the Salinity of Irrigation Water on Growth,Yield,and Quality of Ziziphus jujuba‘Dongzao’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(3): 714-726. |
| [6] | LU Xiuping, TANG Zhichao, TANG Wenkun, Mao Feifeng, ZHANG Wanping, LI Jingwei. Identification of Infectivity of 13 Viroid RNA and DNA Genomes of Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(3): 749-760. |
| [7] | WANG Chunwei, WANG Yan, DUAN Tiankun, SU Yaxin, YUAN Shengnan, REN Lu, ZHAO Xiaojun, WANG Meiqin. Antifungal Mechanism of Isooctyl Alcohol on Botrytis cinerea Causing Tomato Gray Mold [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(3): 761-772. |
| [8] | CHEN Yajuan, JIN Xin, YANG Jiangshan, DAI Zibo, LI Dou, SHAO Zhang. Effects of Fulvic Acid Potassium on Sugar-Acid Metabolism and Aroma Substances in‘Cabernet Gernischt’Grape Berries [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(2): 406-422. |
| [9] | LI Rui, WANG Wen, DU Minghui, LIU Genzhong, MA Fangfang, BAO Zhilong. Mechanistic Studies on SlBON1-Regulated Plant Vegetative Growth in Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(1): 73-87. |
| [10] | WANG Shanshan, GUO Rui, HE Ling, WU Chunhong, CHEN Chanyou, WAN Heping, ZHAO Huixia. Identification of Long Cowpea Lhc Gene Family and Its Expression Analysis Under Salt Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(1): 111-122. |
| [11] | HAN Ying, DUAN Ying, NIU Yijie, LI Yansu, HE Chaoxing, SUN Mintao, WANG Jun, LI Qiang, CHEN Shuangchen, YAN Yan. Transcription Metabolic Mechanism of Humic Acid Biodegradable Plastic Film to Improving the Fruit Quality of Tomato in the Greenhouse [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1758-1772. |
| [12] | GONG Xiaoya, LI Xian, ZHOU Xingang, WU Fengzhi. Effect of Rhizosphere Microorganisms Induced by Potato-Onion on Tomato Root-Knot Nematode Disease [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1913-1926. |
| [13] | MENG Sida, HAN Leilei, XIANG Hengzuo, ZHU Meiyu, FENG Zhen, YE Yunzhu, SUN Meihua, LI Yanbing, ZHAO Liping, TAN Changhua, QI Mingfang, LI Tianlai. Research Progress on the Mechanism of Regulating the Number of Tomato Locules [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(7): 1649-1664. |
| [14] | MA Xingyun, FAN Bingli, TANG Guangcai, JIA Zhiqi, LI Ying, XUE Dongqi, ZHANG Shiwen. Preliminary Study on the Mechanism of DXR Regulating Chloroplast Development Flower Color and Fruit Coloring in Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1241-1255. |
| [15] | ZHANG Wenjing, XU Dayong, WU Qianlin, YANG Fo, XIN Bingyue, ZENG Xin, LI Feng. Genome Analysis of Bacillus velezensis XDY66,an Antagonist of Tomato Botrytis cinerea [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1413-1425. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd