
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (8): 1758-1772.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0116
• Genetic & Breeding·Germplasm Resources·Molecular Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
HAN Ying1,2, DUAN Ying2, NIU Yijie2, LI Yansu2, HE Chaoxing2, SUN Mintao2, WANG Jun2, LI Qiang3,**( ), CHEN Shuangchen1,**(
), CHEN Shuangchen1,**( ), YAN Yan2,**(
), YAN Yan2,**( )
)
Received:2024-03-20
Revised:2024-06-19
Online:2024-08-25
Published:2024-08-21
Contact:
LI Qiang, CHEN Shuangchen, YAN Yan
HAN Ying, DUAN Ying, NIU Yijie, LI Yansu, HE Chaoxing, SUN Mintao, WANG Jun, LI Qiang, CHEN Shuangchen, YAN Yan. Transcription Metabolic Mechanism of Humic Acid Biodegradable Plastic Film to Improving the Fruit Quality of Tomato in the Greenhouse[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1758-1772.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0116
| 级别 Grade | 分数 Score | 风味口感评价标准 Evaluate standard of the taste in grafted tomato |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 9.0 ~ 10.0 | 口感甜,浓郁清香味,肉质软 Sweet taste,rich and clear fragrance,soft sarcocarp |
| 2 | 6.0 ~ 8.0 | 口感酸甜,有清香味,肉质软 Taste sour and sweet,clear fragrance,soft sarcocarp |
| 3 | 3.0 ~ 5.0 | 口感甜酸,略有清香味,肉质面 Taste sweet and sour,slightly fragrant,slightly hard sarcocarp |
| 4 | 0 ~ 2.0 | 口感酸,无清香味,肉质沙 Sour taste,no fragrance,hard sarcocarp |
Table 1 Standard of fruit tasty in tomato
| 级别 Grade | 分数 Score | 风味口感评价标准 Evaluate standard of the taste in grafted tomato |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 9.0 ~ 10.0 | 口感甜,浓郁清香味,肉质软 Sweet taste,rich and clear fragrance,soft sarcocarp |
| 2 | 6.0 ~ 8.0 | 口感酸甜,有清香味,肉质软 Taste sour and sweet,clear fragrance,soft sarcocarp |
| 3 | 3.0 ~ 5.0 | 口感甜酸,略有清香味,肉质面 Taste sweet and sour,slightly fragrant,slightly hard sarcocarp |
| 4 | 0 ~ 2.0 | 口感酸,无清香味,肉质沙 Sour taste,no fragrance,hard sarcocarp |
| 基因 Gene | 引物 Primer |
|---|---|
| Solyc09g075420 | F:5′-TATGGCCGACTGATTTCTGG-3′;R:5′-CCAAACCCTAACCCCTTTTCT-3′ |
| Solyc08g079480 | F:5′-TGGTCTCCAGAAAAAGCATCTAAAG-3′;R:5′- ACCTGTATGATAATTTGCCACAGC-3′ |
| Solyc08g078850 | F:5′- TAGATTTCGGTTTTTGATTGCG-3′;R:5′-CACAACTTCTTGGTGGATTTTTT-3′ |
| Solyc09g011810 | F:5′-GGTGGCATTTATGGTTATCCTAGA-3′;R:5′-TCCAATTTTTCAACTTCTTCTGTG-3′ |
| Solyc02g062340 | F:5′-ATTCCCCCTGCTGTCCCT-3′;R:5′-GAGCTGCCTCAACATTTTCTG-3′ |
| Solyc05g055840 | F:5′-GCGGACACTTTCTTTGTCTGG-3′;R:5′-CAATAGCTTGAACGCCTGGTA-3′ |
| Actin | F:5′-TGTCCCTATTTACGAGGGTTATGC-3′;R:5′-AGTTAAATCACGACCAGCAAGAT-3′ |
Table 2 qRT-PCR validation gene and primer information
| 基因 Gene | 引物 Primer |
|---|---|
| Solyc09g075420 | F:5′-TATGGCCGACTGATTTCTGG-3′;R:5′-CCAAACCCTAACCCCTTTTCT-3′ |
| Solyc08g079480 | F:5′-TGGTCTCCAGAAAAAGCATCTAAAG-3′;R:5′- ACCTGTATGATAATTTGCCACAGC-3′ |
| Solyc08g078850 | F:5′- TAGATTTCGGTTTTTGATTGCG-3′;R:5′-CACAACTTCTTGGTGGATTTTTT-3′ |
| Solyc09g011810 | F:5′-GGTGGCATTTATGGTTATCCTAGA-3′;R:5′-TCCAATTTTTCAACTTCTTCTGTG-3′ |
| Solyc02g062340 | F:5′-ATTCCCCCTGCTGTCCCT-3′;R:5′-GAGCTGCCTCAACATTTTCTG-3′ |
| Solyc05g055840 | F:5′-GCGGACACTTTCTTTGTCTGG-3′;R:5′-CAATAGCTTGAACGCCTGGTA-3′ |
| Actin | F:5′-TGTCCCTATTTACGAGGGTTATGC-3′;R:5′-AGTTAAATCACGACCAGCAAGAT-3′ |
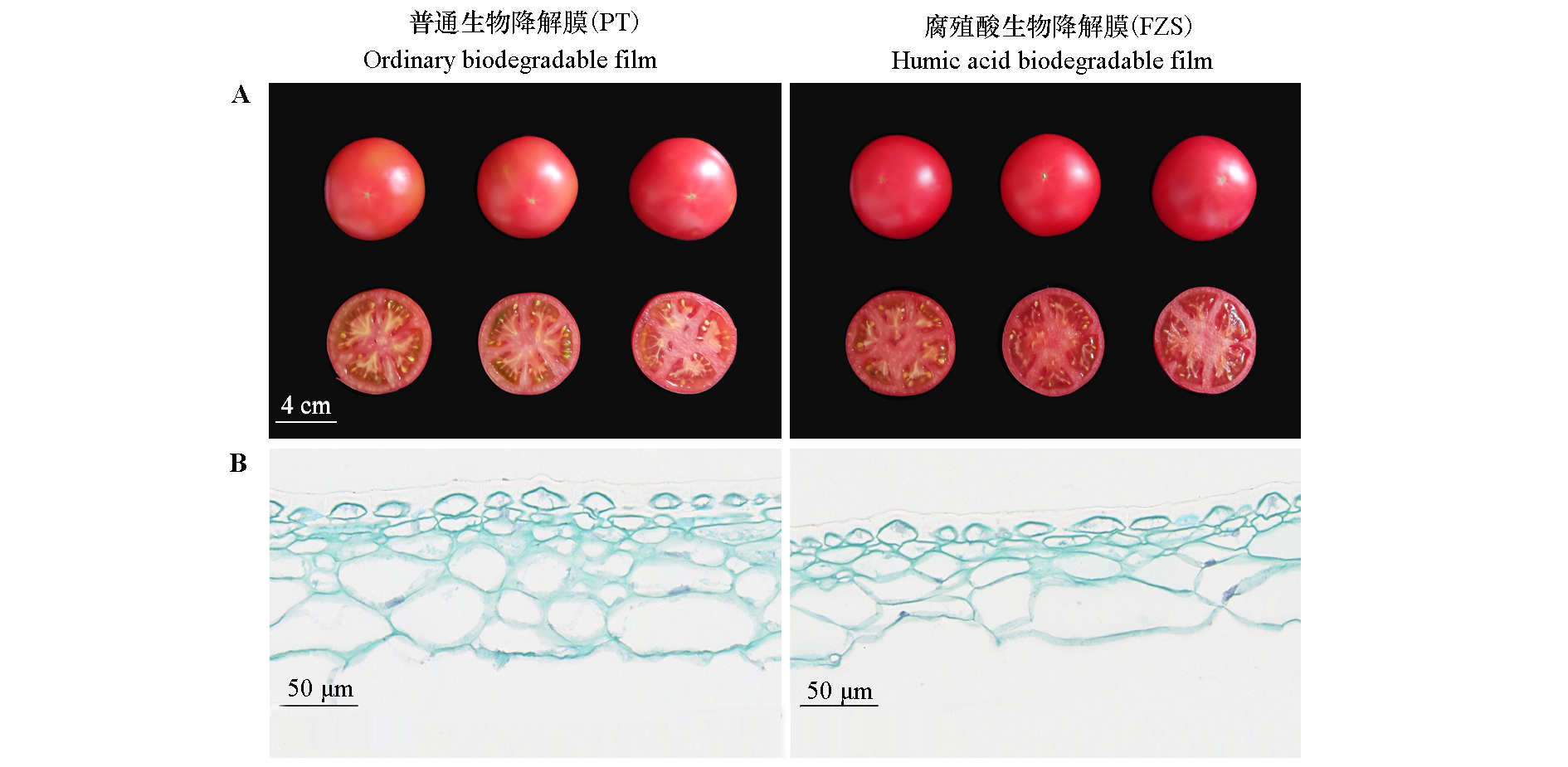
Fig. 1 Fruit phenotype(A)and pericarp cell(B)of tomato covered with ordinary biodegradable film(PT)and humic acid biodegradable film(FZS)55 d after pollination
| 处理 Treatment | 角质层厚度/μm Cutin thickness | 表皮层厚度/μm Epidermis thickness | 表皮细胞宽/μm Epidermal cell width | 薄壁细胞宽/μm Parenchyma cell width | 单位面积表皮细胞数 Number of epidermal cells per unit area | 单位面积薄壁细胞数 Number of parenchyma cells per unit area |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PT | 6.59 ± 0.83 | 75.73 ± 4.68 | 8.22 ± 2.50 | 17.92 ± 6.34 | 10.21 ± 2.06 | 32.17 ± 5.97 |
| FZS | 4.99 ± 0.67* | 42.42 ± 3.25* | 9.85 ± 2.42 | 15.23 ± 2.81 | 9.75 ± 1.59 | 23.13 ± 5.90* |
Table 3 Coverage of the effects of ordinary biodegradable film(PT)and humic acid biodegradable film(FZS)on the thickness of tomato fruit epidermal tissue
| 处理 Treatment | 角质层厚度/μm Cutin thickness | 表皮层厚度/μm Epidermis thickness | 表皮细胞宽/μm Epidermal cell width | 薄壁细胞宽/μm Parenchyma cell width | 单位面积表皮细胞数 Number of epidermal cells per unit area | 单位面积薄壁细胞数 Number of parenchyma cells per unit area |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PT | 6.59 ± 0.83 | 75.73 ± 4.68 | 8.22 ± 2.50 | 17.92 ± 6.34 | 10.21 ± 2.06 | 32.17 ± 5.97 |
| FZS | 4.99 ± 0.67* | 42.42 ± 3.25* | 9.85 ± 2.42 | 15.23 ± 2.81 | 9.75 ± 1.59 | 23.13 ± 5.90* |
| 处理 Treatment | 硬度 Hardness | 甜度 Sweetness | 酸度 Acidity | 风味 Flavor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PT | 8.30 ± 0.90 | 6.10 ± 1.13 | 7.50 ± 0.78 | 6.40 ± 1.28 |
| FZS | 5.50 ± 0.92* | 7.30 ± 0.90* | 5.90 ± 0.70* | 8.00 ± 0.88* |
Table 4 Flavor and taste scores of mature tomato fruits covered with ordinary biodegradable film(PT) and humic acid biodegradable film(FZS)
| 处理 Treatment | 硬度 Hardness | 甜度 Sweetness | 酸度 Acidity | 风味 Flavor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PT | 8.30 ± 0.90 | 6.10 ± 1.13 | 7.50 ± 0.78 | 6.40 ± 1.28 |
| FZS | 5.50 ± 0.92* | 7.30 ± 0.90* | 5.90 ± 0.70* | 8.00 ± 0.88* |
| 处理 Treatment | 果实硬度/(kg · cm-2) Fruit firmness | 维生素C/(mg · kg-1) Vitamin C | 可溶性糖/% Soluble sugar | 可溶性固形物/% Soluble solids | 番茄红素/(μg · g-1) Lycopene | 可滴定酸/% Titratable acid | 糖酸比 Sugar acid ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PT | 10.50 ± 0.31 | 1.48 ± 1.08 | 2.47 ± 0.03 | 7.83 ± 0.12 | 79.32 ± 2.81 | 5.81 ± 0.01 | 42.48 ± 0.64 |
| FZS | 9.80 ± 0.13* | 1.40 ± 0.17 | 2.71 ± 0.01* | 8.17 ± 0.06* | 90.39 ± 5.49* | 5.64 ± 0.07* | 48.09 ± 0.78* |
Table 5 Effects of ordinary biodegradable film(PT)and humic acid biodegradable film(FZS)on tomato fruit quality
| 处理 Treatment | 果实硬度/(kg · cm-2) Fruit firmness | 维生素C/(mg · kg-1) Vitamin C | 可溶性糖/% Soluble sugar | 可溶性固形物/% Soluble solids | 番茄红素/(μg · g-1) Lycopene | 可滴定酸/% Titratable acid | 糖酸比 Sugar acid ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PT | 10.50 ± 0.31 | 1.48 ± 1.08 | 2.47 ± 0.03 | 7.83 ± 0.12 | 79.32 ± 2.81 | 5.81 ± 0.01 | 42.48 ± 0.64 |
| FZS | 9.80 ± 0.13* | 1.40 ± 0.17 | 2.71 ± 0.01* | 8.17 ± 0.06* | 90.39 ± 5.49* | 5.64 ± 0.07* | 48.09 ± 0.78* |
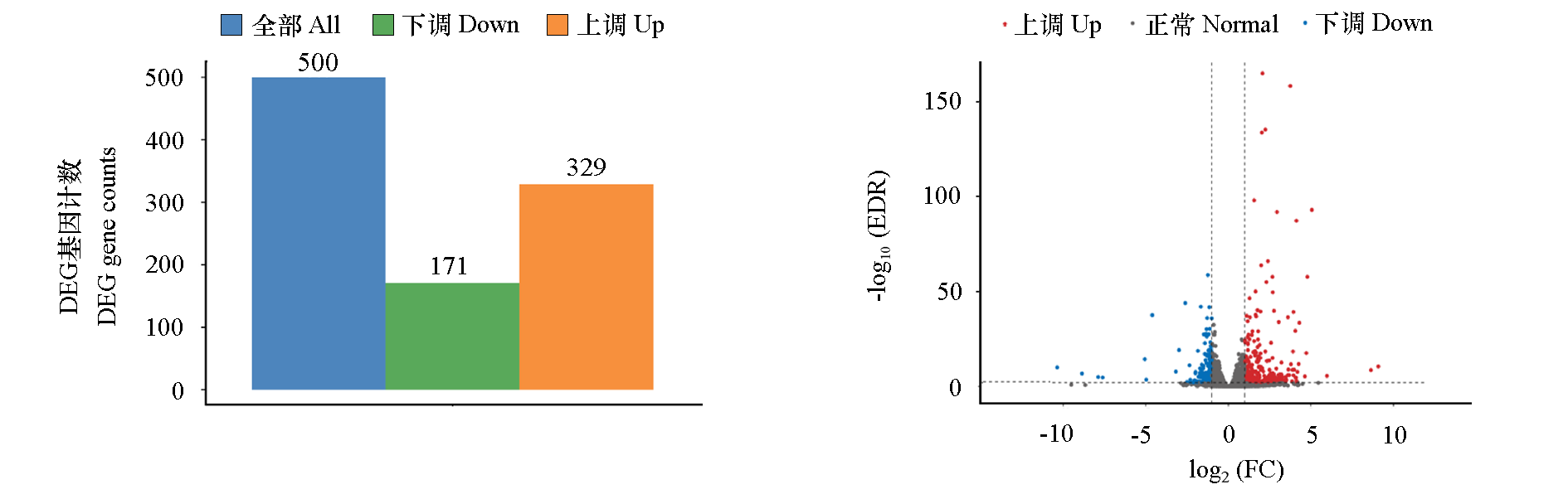
Fig. 2 Histogram and volcanic map of differentially expressed genes in tomato fruits covered with ordinary biodegradable film(PT)and humic acid biodegradable film(FZS)
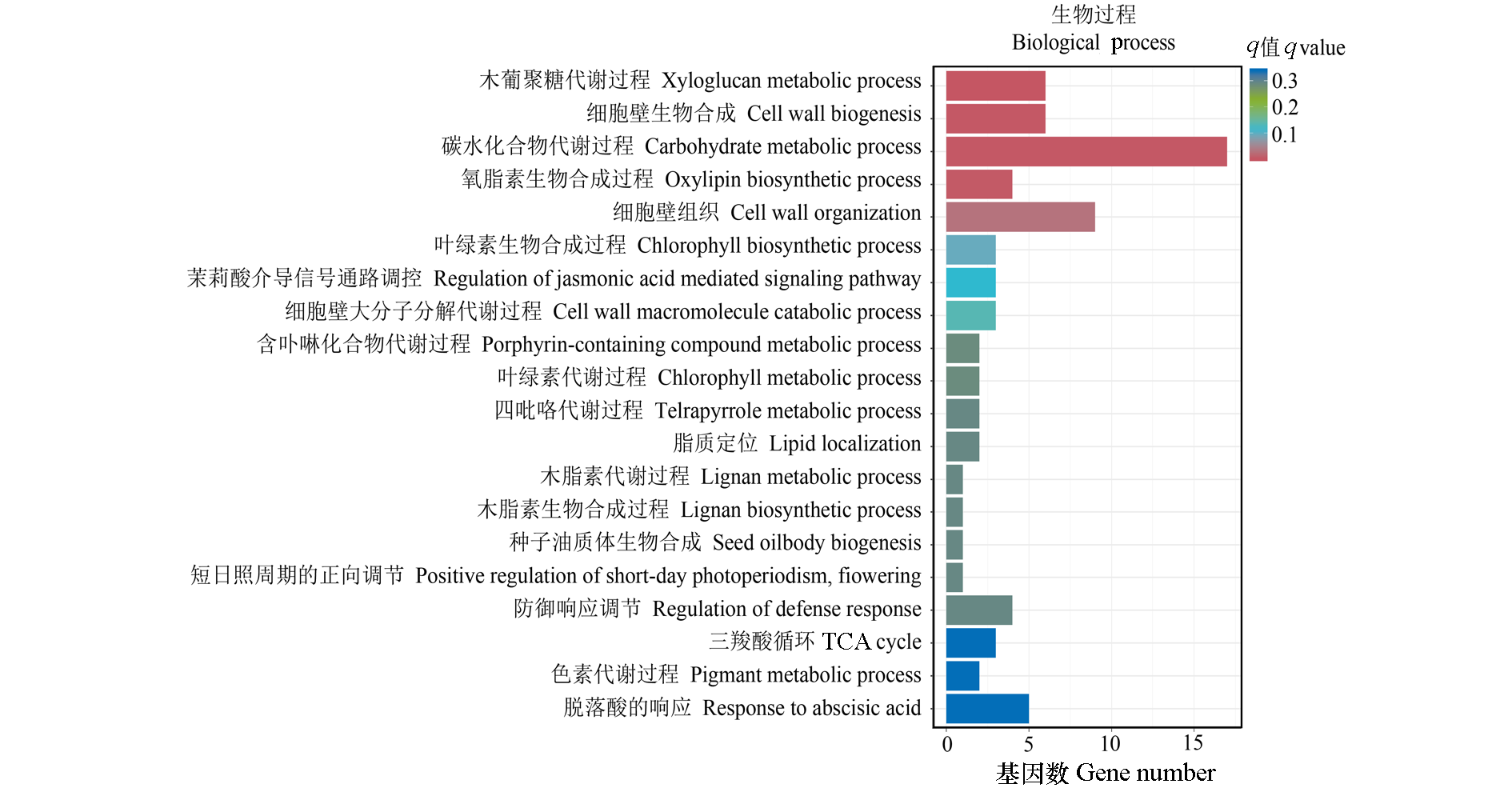
Fig. 3 Enrichment of go function of differentially expressed genes in tomato covered with ordinary biodegradable film(PT) and humic acid biodegradable film(FZS)
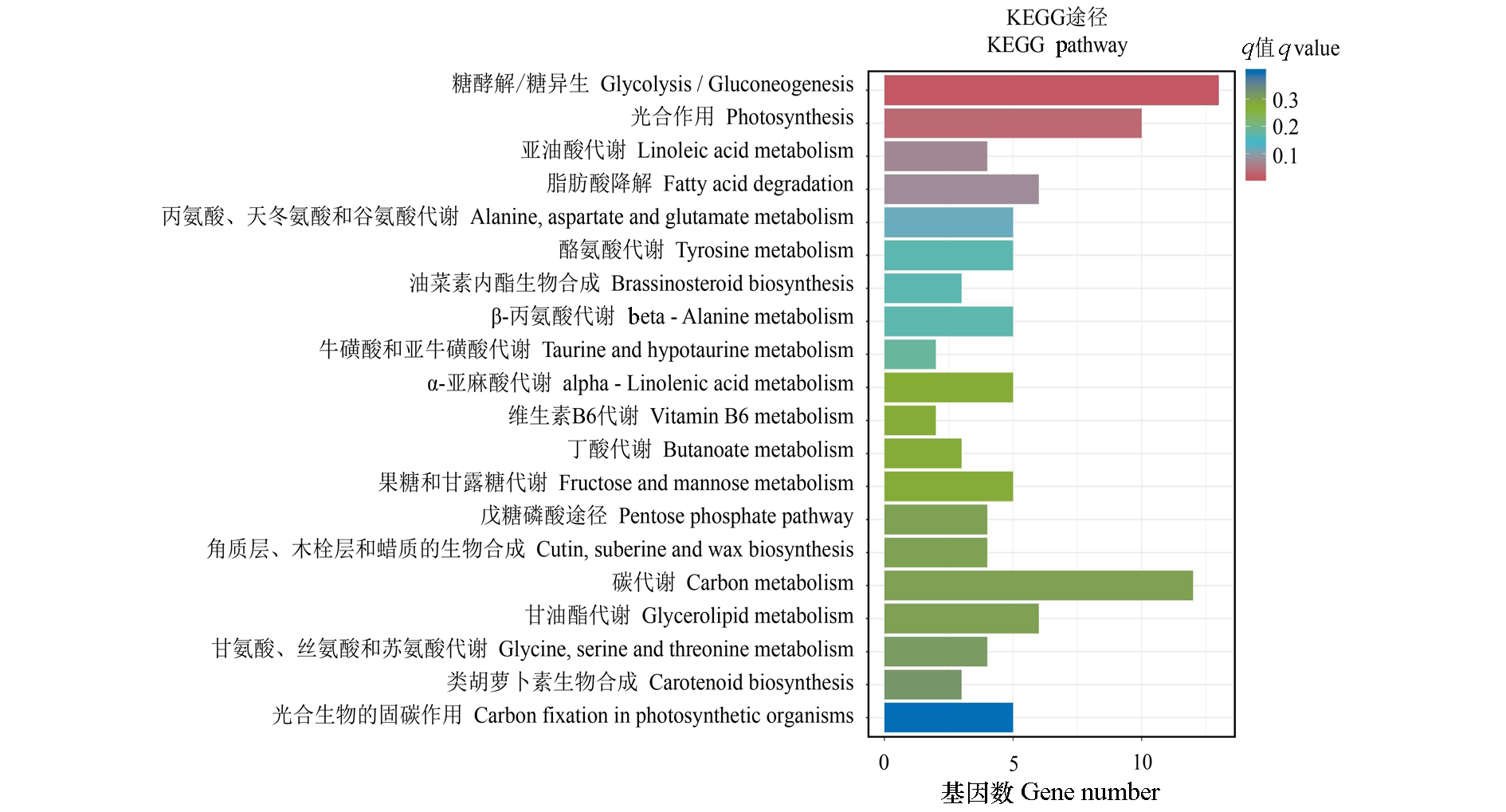
Fig. 4 KEGG functional enrichment of differentially expressed genes in tomato covered with ordinary biodegradable film(PT)and humic acid biodegradable film(FZS)
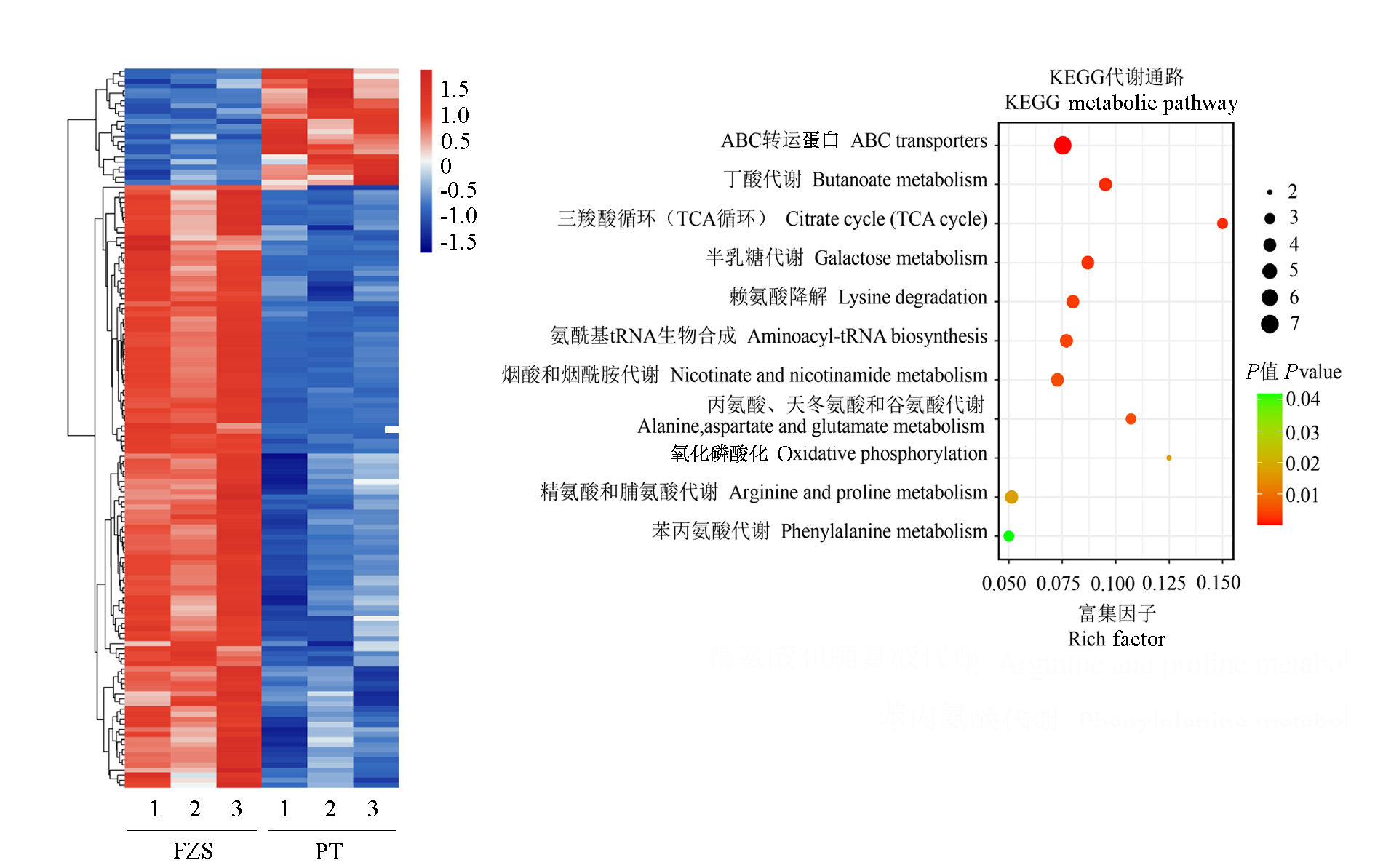
Fig.6 Clustering and KEGG enrichment of differential metabolites in tomato fruits covered with ordinary biodegradable film(PT) and humic acid biodegradable film(FZS)

Fig. 7 Common mapping pathways of transcription metabolism poor foreign bodies in tomato covered with ordinary biodegradable film(PT)and humic acid biodegradable film(FZS)
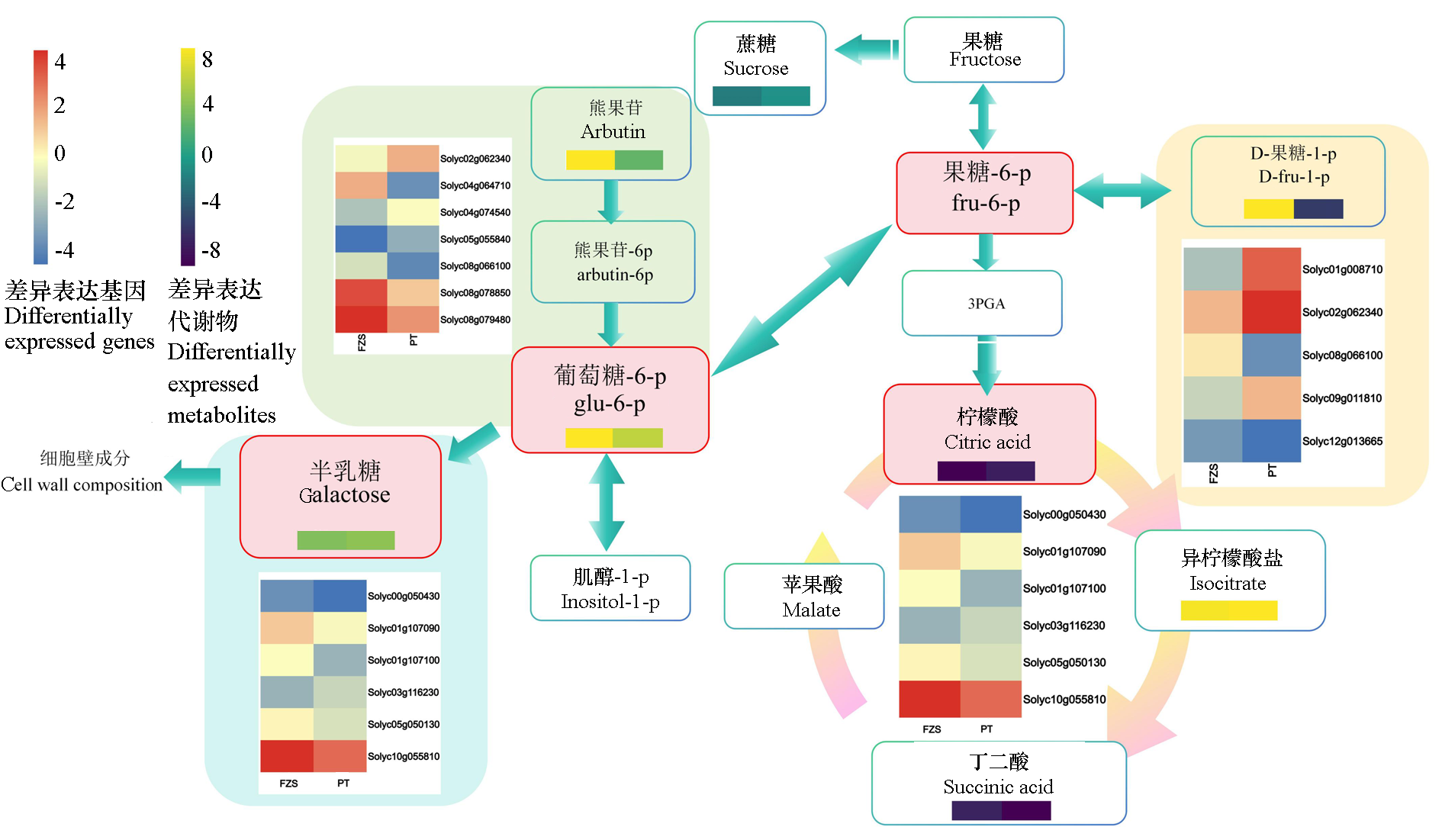
Fig. 8 Main common mapping pathways of transcription metabolism poor foreign bodies in tomato covered with ordinary biodegradable film(PT)and humic acid biodegradable film(FZS)
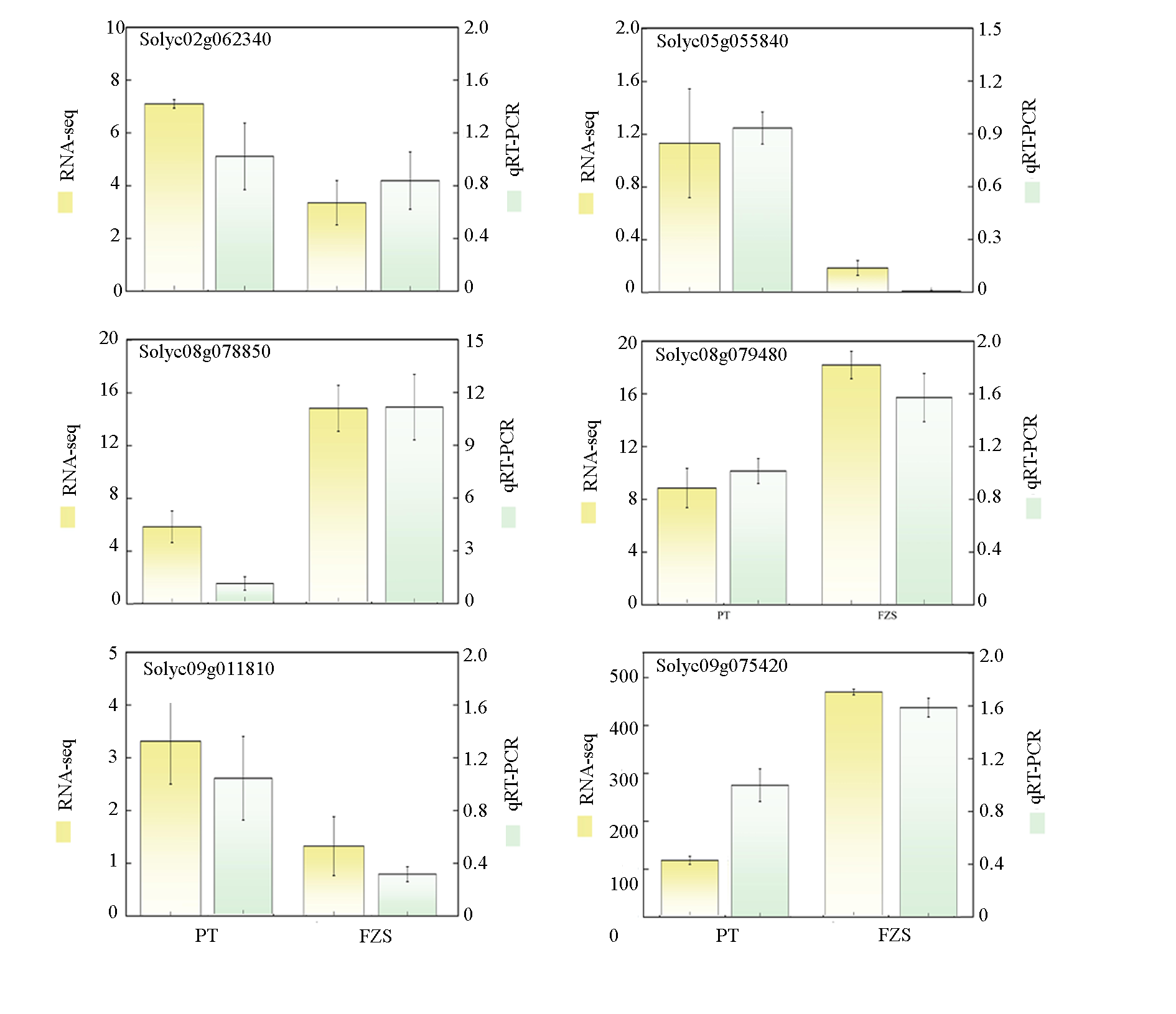
Fig. 9 qRT-PCR verification of tomato related gene expression levels covered with ordinary biodegradable film(PT) and humic acid biodegradable film(FZS)
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
|
李锡香. 2006. 番茄种质资源描述规范和数据标准. 北京: 中国农业出版社.
|
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
|
路露, 韩荧, 刘梓桐, 钱晶晶, 闫妍, 孙玉军. 2023. 两种新型生物降解地膜对番茄生长及土壤微生物、酶活性的影响. 山东农业科学, 55 (5):101-106.
|
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
|
丁凡, 严昌荣, 汪景宽. 2022. 黑土地保护中不容忽视的一个问题:地膜残留及其污染. 土壤通报, 53 (1):234-240.
|
|
| [8] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0047 |
|
田茂森, 周震, 王海敬, 崔霞, 孙帅. 2024. 调控番茄果实柠檬酸含量的基因定位. 园艺学报, 51 (1):67-76.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0047 |
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.1126/science.aal1556 pmid: 28126817 |
| [30] |
|
|
王斌, 万艳芳, 王金鑫, 孙九胜, 槐国龙, 崔磊, 张彦红, 魏彦宏, 刘国宏. 2019. PBAT型全生物降解膜对南疆番茄产量及土壤理化性质的影响. 农业资源与环境学报, 36 (5):640-648.
|
|
| [31] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0811 |
|
关思慧, 刘晨旭, 姚祝平, 万红建, 刁明, 程远. 2024. 腐植酸处理对樱桃番茄挥发性有机化合物成分和含量的影响. 园艺学报, 51 (2):346-360.
|
|
| [11] |
|
|
胡伟, 邵华伟, 孙九胜, 王新勇. 2014. Mater-Bi和PBS可生物降解膜降解特征及对加工番茄的影响. 北方园艺, 57 (22):36-38.
|
|
| [12] |
|
| [32] |
|
|
汪敏, 徐磊, 严旎娜, 蒋希芝, 冯敏, 张晓美, 陈罡, 徐寸发. 2022. 设施内PBAT/秸秆基地膜降解特性及对番茄生长的影响. 农业工程学报, 38 (5):184-193.
|
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
|
章永年, 张任飞, 孙晔, 郑恩来, 孙国祥, 汪小旵. 2021. 局部按压对不同成熟度番茄机械损伤的影响. 农业工程学报, 37 (11):292-298.
|
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
|
周春丽, 钟贤武, 范鸿冰, 吕玲琴, 苏虎, 李玉萍. 2012. 果蔬及其制品中可溶性总糖和还原糖的测定方法评价. 食品工业,(5):89-92.
|
| [1] | GONG Xiaoya, LI Xian, ZHOU Xingang, WU Fengzhi. Effect of Rhizosphere Microorganisms Induced by Potato-Onion on Tomato Root-Knot Nematode Disease [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1913-1926. |
| [2] | MENG Sida, HAN Leilei, XIANG Hengzuo, ZHU Meiyu, FENG Zhen, YE Yunzhu, SUN Meihua, LI Yanbing, ZHAO Liping, TAN Changhua, QI Mingfang, and LI Tianlai. Research Progress on the Mechanism of Regulating the Number of Tomato Locules [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(7): 1649-1664. |
| [3] | MA Xingyun, FAN Bingli, TANG Guangcai, JIA Zhiqi, LI Ying, XUE Dongqi, ZHANG Shiwen. Preliminary Study on the Mechanism of DXR Regulating Chloroplast Development Flower Color and Fruit Coloring in Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1241-1255. |
| [4] | ZHANG Wenjing, XU Dayong, WU Qianlin, YANG Fo, XIN Bingyue, ZENG Xin, LI Feng. Genome Analysis of Bacillus velezensis XDY66,an Antagonist of Tomato Botrytis cinerea [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1413-1425. |
| [5] | WANG Yongzhen, ZHANG Jianguo, LIU Caihong, LI Sibei, LÜ Tiantian. A New Tomato Hybrid Cultivar‘Yuanhong 212’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1435-1436. |
| [6] | LIU Zeying, SUN Shuai, LIU Zhiqiang, CUI Xia, LI Ren. Mapping of the Sharp Blossom-end Gene and Screening of Candidate Gene in Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(5): 982-992. |
| [7] | LI Pin, GAN Ning, CHEN Jiawei, XIANG Sixiang, SHEN Jingyi, OUYANG Bo, LU Yong’en. Analysis of Phosphorus Utilization Efficiency in Natural Population of Tomato and Screening of Low Phosphorus Tolerant Germplasm [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(5): 993-1004. |
| [8] | YANG Ting, XI Dehui, XIA Ming, LI Jianan. Studies on the Mechanism of α-Momordicin Gene Enhancing Tomato Resistance to Tobacco Mosaic Virus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(5): 1126-1136. |
| [9] | HU Zhifeng, SHAO Jingcheng, ZHANG Li. A New Tomato Cultivar‘Longfan 15’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(4): 917-918. |
| [10] | LIU Genzhong, LI Fangman, GE Pingfei, TAO Jinbao, ZHANG Xingyu, YE Zhibiao, ZHANG Yuyang. QTL Mapping and Candidate Gene Identification Related to Ascorbic Acid Content in Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(2): 219-228. |
| [11] | DONG Shuchao, HONG Jun, LING Jiayi, XIE Zixin, ZHANG Shengjun, ZHAO Liping, SONG Liuxia, WANG Yinlei, ZHAO Tongmin. Genome-wide Association Studies of Drought Tolerance in Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(2): 229-238. |
| [12] | XU Qin, WANG Jiaying, ZHANG Mannan, XIAO Zhihao, ZHENG Hankai, LU Yong'en, WANG Taotao, ZHANG Yuyang, ZHANG Junhong, YE Zhibiao, YE Jie. Identification of Genetic Loci and Molecular Marker Development of Salt Tolerance in Tomato Seedlings [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(2): 239-252. |
| [13] | YANG Liang, LIU Huan, MA Yanqin, LI Ju, WANG Hai'e, ZHOU Yujie, LONG Haicheng, MIAO Mingjun, LI Zhi, CHANG Wei. Creating High Lycopene Fruit Using CRISPR/Cas9 Technology in Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(2): 253-265. |
| [14] | YAN Chaofan, SUN Xuemei, ZHONG Qiwen, SHAO Dengkui, DENG Changrong, WEN Junqin. Identification and Bioinformatics Analysis of 20S Proteasome Gene Family in Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(2): 266-280. |
| [15] | ZHANG Wenhao, ZHANG Hui, LIU Yuting, WANG Yan, ZHANG Yingying, WANG Xinman, WANG Quanhua, ZHU Weimin, YANG Xuedong. Preliminary Transcriptome Analysis in Two Tomato Fruits Materials with Different Sugar Content [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(2): 281-294. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd