
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (11): 2620-2632.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0413
• Cultivation·Physiology & Biochemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LU Jianzeng, ZHOU Liyan, HUANG Xinyi, WU Fengzhi, GAO Danmei*( )
)
Received:2024-06-21
Revised:2024-09-05
Online:2024-12-12
Published:2024-11-25
Contact:
GAO Danmei
LU Jianzeng, ZHOU Liyan, HUANG Xinyi, WU Fengzhi, GAO Danmei. Effects of Carbon Pool Strength on Plant Growth and Potassium Uptake of Tomato Intercropped with Potato-Onion[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(11): 2620-2632.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0413

Fig. 1 Effects of shading,defoliation and size adjustment on growth of tomato intercropped with potato-onion under pot experiment CK:Normal control. Student’s t-test was used for the mean comparison between treatments. * indicated significant differences between treatments and the control(P < 0.05).

Fig. 2 Effects of shading,defoliation and size adjustment on mycorrhizal infection rate in tomato intercropped with potato-onion under pot experiment CK:Normal control. Student’s t-test was used for the mean comparison between treatments. * indicated significant differences between treatments and the control(P < 0.05).

Fig. 3 Effects of shading,defoliation and size adjustment on potassium content in leaves and roots of tomato intercropped with potato-onion under pot experiment CK:Normal control. Student’s t-test was used for the mean comparison between treatments. * indicated significant differences between treatments and the control(P < 0.05).

Fig. 4 Effects of shading,defoliation and size adjustment on available potassium of soil in tomato intercropped with potato-onion under pot experiment CK:Normal control. Student’s t-test was used for the mean comparison between treatments. * different lowercase letters indicated significant differences between treatments and the control(P < 0.05).
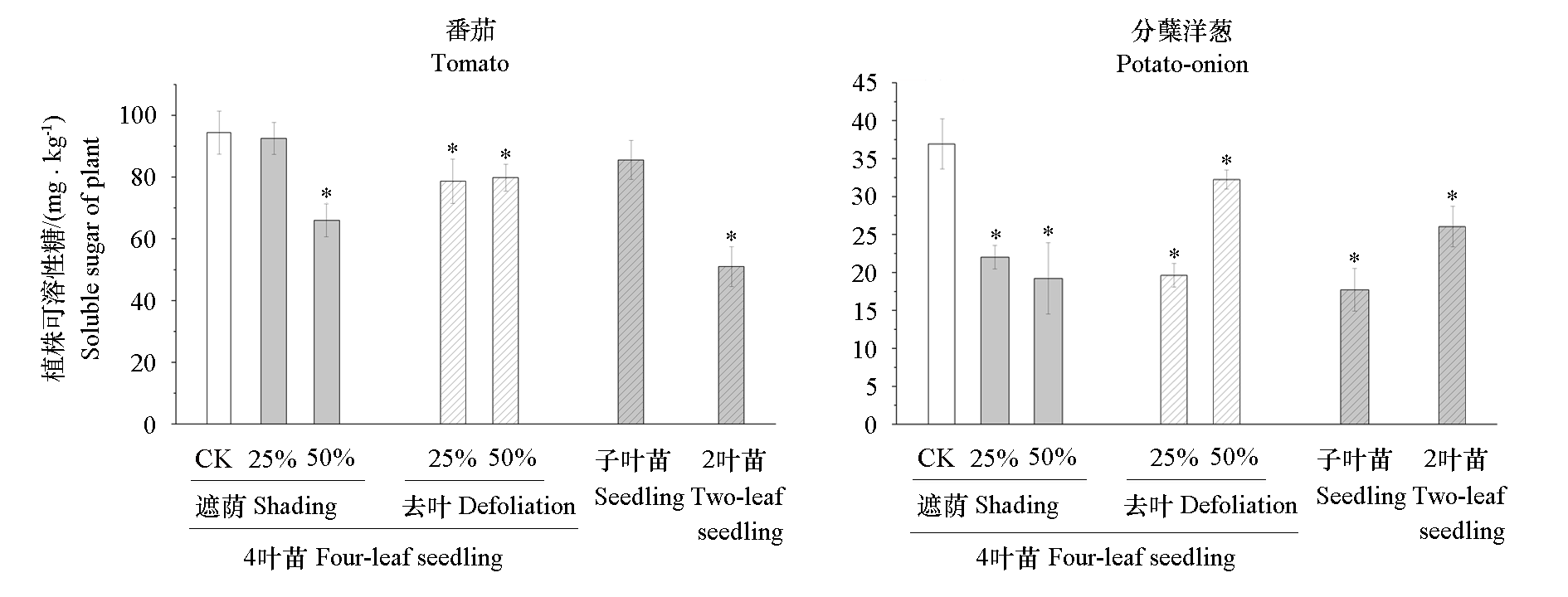
Fig. 5 Effects of shading,defoliation and size adjustment on soluble sugar of plant in tomato intercropped with potato-onion under pot experiment CK:Normal control. Student’s t-test was used for the mean comparison between treatments. * indicated significant differences between treatments and the control(P < 0.05).
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
|
鲍士旦. 2000. 土壤农化分析. 3版. 北京:中国农业出版社:263-268.
|
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
|
曹本福, 姜海霞, 刘丽, 陆引罡, 王茂胜. 2021. 丛枝菌根菌丝网络在植物互作中的作用机制研究进展. 应用生态学报, 32 (9):3385-3396.
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202111.032 |
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.1007/s004420050072 pmid: 28307168 |
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0604 |
|
董桑婕, 葛诗蓓, 李岚, 贺丽群, 范飞军, 齐振宇, 喻景权, 周艳虹. 2022. 不同光质补光对辣椒幼苗生长、丛枝菌根共生和磷吸收的影响. 园艺学报, 49 (8):1699-1712.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0604 |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
doi: 10.1111/nph.12827 pmid: 24787049 |
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
|
葛诗蓓, 姜小春, 王羚羽, 喻景权, 周艳虹. 2020. 园艺植物丛枝菌根抗非生物胁迫的作用机制研究进展. 园艺学报, 47 (9):1752-1776.
|
|
| [14] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0306 |
|
龚小雅, 李贤, 周新刚, 吴凤芝. 2024. 分蘖洋葱伴生番茄诱导的根际微生物对根结线虫病的影响. 园艺学报, 51 (8):1913-1926.
|
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
|
胡海玲, 马钰雯, 耿赫阳, 陈晓璇, 石聪聪, 王英男, 王竞红, 蔺吉祥. 2022. 丛枝菌根真菌AMF提高植物抗逆性的组学技术研究进展. 植物营养与肥料学报, 28 (10):1928-1936.
|
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
|
郎林杰, 杨持. 1997. 遮光和去叶处理对羊草(Leymus chinensis)无性系分株间碳物质转移的影响. 内蒙古大学学报(自然科学版), 28 (3):430-434.
|
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2010.00956.x pmid: 20722732 |
| [21] |
|
|
李敏, 刘润进, 李晓林. 2004. 大田条件下丛枝菌根真菌对西瓜生长和枯萎病的影响. 植物病理学报, 34 (5):472-473.
|
|
| [22] |
|
|
李威, 程智慧, 孟焕文, 周静, 梁静, 刘雪娇. 2012. 轮作不同蔬菜对大棚番茄连作基质中微生物与酶及后茬番茄的影响. 园艺学报, 39 (1):73-80.
|
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-1036 |
|
梁圣敏, 张菲, 吴强盛. 2023. 丛枝菌根真菌通过调节枳根系多胺提高抗旱性. 园艺学报, 50 (12):2680-2688.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-1036 |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2021-0050 |
|
马俊卿, 侯宁, 孙晨瑜, 杨怡森, 覃圣峰, 王勇, 刘璐, 廖虹霖, 黄京华. 2022. 宿主不同对丛枝菌根真菌扩繁效应的影响. 中国农学通报,(1):7-14.
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2021-0050 |
|
| [26] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.1990.tb00476.x pmid: 33874272 |
| [27] |
doi: 10.1111/nph.12351 pmid: 23738787 |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.02209.x pmid: 17725554 |
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
|
屈明华, 俞元春, 李生, 张金池. 2019. 丛枝菌根真菌对矿质养分活化作用研究进展. 浙江农林大学学报, 36 (2):394-405.
|
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
pmid: 15221523 |
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
|
谭德水, 金继运, 黄绍文. 2008. 长期施钾与秸秆还田对西北区不同种植制度下作物产量及土壤钾素的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 14 (5):886-893.
|
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
van der Heijden M G A,Martin F M,Selosse M A,Sanders I R. 2015. Mycorrhizal ecology and evolution:the past,the present,and the future. New Phytologist, 205 (4):1406-1423.
doi: 10.1111/nph.13288 pmid: 25639293 |
| [39] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.112.195727 pmid: 22517410 |
| [40] |
|
|
王海燕, 盛月凡, 李前进, 王玫, 潘凤兵, 陈学森, 沈向, 尹承苗, 毛志泉. 2019. 葱、芥菜和小麦轮作对老龄苹果园土壤环境的影响. 园艺学报, 46 (11):2224-2238.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2019-0048 |
|
| [41] |
|
|
王明泉, 苏俊, 李春霞, 龚士琛, 闫淑琴, 李国良, 扈光辉, 任洪雷. 2014. 不同密度及施肥量对玉米品种龙单42产量的影响. 黑龙江农业科学,(5):49-51.
|
|
| [42] |
doi: 10.1111/nph.12125 pmid: 23356215 |
| [43] |
doi: 10.1111/nph.14041 pmid: 27265515 |
| [44] |
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202010.029 |
|
战丽杰, 张宏宝, 李宗泰, 孟伟, 徐伟, 李凌浩. 2020. 遮荫处理对芍药幼苗生长和矿质营养积累的影响. 应用生态学报, 31 (10):3473-3479..
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202010.029 |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
|
张晶, 王姣爱, 党建友, 张定一. 2013. 播期对小麦主茎及分蘖农艺性状,产量和品质的影响. 农学学报, 3 (10):1.
|
|
| [47] |
|
|
张山泉, 陈川, 徐沭, 殷士学. 2003. 硫酸-过氧化氢消化法测定植株氮磷钾方法的改进. 土壤,(2):174-175.
|
|
| [48] |
doi: 10.1111/nph.13025 pmid: 25243653 |
| [1] | HAN Ying, DUAN Ying, NIU Yijie, LI Yansu, HE Chaoxing, SUN Mintao, WANG Jun, LI Qiang, CHEN Shuangchen, YAN Yan. Transcription Metabolic Mechanism of Humic Acid Biodegradable Plastic Film to Improving the Fruit Quality of Tomato in the Greenhouse [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1758-1772. |
| [2] | GONG Xiaoya, LI Xian, ZHOU Xingang, WU Fengzhi. Effect of Rhizosphere Microorganisms Induced by Potato-Onion on Tomato Root-Knot Nematode Disease [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1913-1926. |
| [3] | MENG Sida, HAN Leilei, XIANG Hengzuo, ZHU Meiyu, FENG Zhen, YE Yunzhu, SUN Meihua, LI Yanbing, ZHAO Liping, TAN Changhua, QI Mingfang, and LI Tianlai. Research Progress on the Mechanism of Regulating the Number of Tomato Locules [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(7): 1649-1664. |
| [4] | MA Xingyun, FAN Bingli, TANG Guangcai, JIA Zhiqi, LI Ying, XUE Dongqi, ZHANG Shiwen. Preliminary Study on the Mechanism of DXR Regulating Chloroplast Development Flower Color and Fruit Coloring in Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1241-1255. |
| [5] | ZHANG Wenjing, XU Dayong, WU Qianlin, YANG Fo, XIN Bingyue, ZENG Xin, LI Feng. Genome Analysis of Bacillus velezensis XDY66,an Antagonist of Tomato Botrytis cinerea [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1413-1425. |
| [6] | WANG Yongzhen, ZHANG Jianguo, LIU Caihong, LI Sibei, LÜ Tiantian. A New Tomato Hybrid Cultivar‘Yuanhong 212’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1435-1436. |
| [7] | LIU Zeying, SUN Shuai, LIU Zhiqiang, CUI Xia, LI Ren. Mapping of the Sharp Blossom-end Gene and Screening of Candidate Gene in Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(5): 982-992. |
| [8] | LI Pin, GAN Ning, CHEN Jiawei, XIANG Sixiang, SHEN Jingyi, OUYANG Bo, LU Yong’en. Analysis of Phosphorus Utilization Efficiency in Natural Population of Tomato and Screening of Low Phosphorus Tolerant Germplasm [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(5): 993-1004. |
| [9] | YANG Ting, XI Dehui, XIA Ming, LI Jianan. Studies on the Mechanism of α-Momordicin Gene Enhancing Tomato Resistance to Tobacco Mosaic Virus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(5): 1126-1136. |
| [10] | HU Zhifeng, SHAO Jingcheng, and ZHANG Li. A New Tomato Cultivar‘Longfan 15’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(4): 917-918. |
| [11] | LIU Genzhong, LI Fangman, GE Pingfei, TAO Jinbao, ZHANG Xingyu, YE Zhibiao, ZHANG Yuyang. QTL Mapping and Candidate Gene Identification Related to Ascorbic Acid Content in Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(2): 219-228. |
| [12] | DONG Shuchao, HONG Jun, LING Jiayi, XIE Zixin, ZHANG Shengjun, ZHAO Liping, SONG Liuxia, WANG Yinlei, ZHAO Tongmin. Genome-wide Association Studies of Drought Tolerance in Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(2): 229-238. |
| [13] | XU Qin, WANG Jiaying, ZHANG Mannan, XIAO Zhihao, ZHENG Hankai, LU Yong'en, WANG Taotao, ZHANG Yuyang, ZHANG Junhong, YE Zhibiao, YE Jie. Identification of Genetic Loci and Molecular Marker Development of Salt Tolerance in Tomato Seedlings [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(2): 239-252. |
| [14] | YANG Liang, LIU Huan, MA Yanqin, LI Ju, WANG Hai'e, ZHOU Yujie, LONG Haicheng, MIAO Mingjun, LI Zhi, CHANG Wei. Creating High Lycopene Fruit Using CRISPR/Cas9 Technology in Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(2): 253-265. |
| [15] | YAN Chaofan, SUN Xuemei, ZHONG Qiwen, SHAO Dengkui, DENG Changrong, WEN Junqin. Identification and Bioinformatics Analysis of 20S Proteasome Gene Family in Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(2): 266-280. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd