
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (7): 1402-1418.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0745
• Genetic & Breeding·Germplasm Resources·Molecular Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
MEI Yulin1,2, XU Jinjian1, JIANG Mengyue1, YU Junhai1, ZONG Yu1, CHEN Wenrong1, LIAO Fanglei1,2,*( ), GUO Weidong1,2,*(
), GUO Weidong1,2,*( )
)
Received:2022-11-21
Revised:2023-01-18
Published:2023-07-26
Contact:
LIAO Fanglei, GUO Weidong
MEI Yulin, XU Jinjian, JIANG Mengyue, YU Junhai, ZONG Yu, CHEN Wenrong, LIAO Fanglei, GUO Weidong. Identification of F1 Hybrids and Analysis of Fruit Shape Difference Between Fingered Citron and Citron[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(7): 1402-1418.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0745
| 引物序号 Primer code | 重复单元 Repeat motif | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence | 产物大小/bp Product size | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z1 | (AT)*8 | F:<M13>-TAACCTAGCATCCTCCAC | R:TATGCGGGTAAATCTCGT | 184 |
| Z5 | (TC)*10 | F:<M13>-CATTGATTCTTTCCTTCG | R:AAAATTAGCCAGAAACGT | 247 |
| Z7 | (TA)*9 | F:<M13>-TGATCTCCTCTGGCGAATG | R:CCTCCTCGTCACCATCCA | 277 |
| Z15 | (TC)*6 | F:<M13>-TCCCCTTCATTTATCCTT | R:TTTTGTTGATGGCGTTGG | 172 |
| Z17 | (CT)*8 | F:<M13>-ATGCAAGCCGCTTTTCTC | R:ACCCAAGATTCTGGTCAGG | 203 |
| Z24 | (AT)*18 | F:<M13>-ACCAGTCCTACGCATCAC | R:CCCGATACCCTGGATTTT | 260 |
| Z52 | (TA)*12 | F:<M13>-CTCCCACTGTCCCTTCGT | R:GCTTGCTGAGCGGATTTA | 186 |
| Z54 | (AT)*14 | F:<M13>-CATTAGAGTTCATTGGGAATA | R:TACCTTACGTTTTGTCGC | 254 |
| Z92 | (CT)*12 | F:<M13>-TACGGTATCAATTCCTTC | R:GGCATTATCAGACCCAAA | 312 |
| Z124 | (AG)*23 | F:<M13>-CCGATCATCAGGGACTACTA | R:CATCTCCAGCACCATTCTT | 316 |
| Z131 | (CT)*9 | F:<M13>-TATAAGGCAAGTGGGGTGA | R:GTGGCAACAAGAATACAAGAT | 161 |
| Z171 | (TA)*17 | F:<M13>-CTAAAGCGATCTTGACATA | R:GGACGGGACTTACTACCAG | 252 |
| Z178 | (AT)*11 | F:<M13>-GAGAACTTTTGTTTATTGGAG | R:TTCTTTCATGCTTCCGTTC | 165 |
| Z198 | (TAA)*13 | F:<M13>-GTAACTGGTGGATTTGTCG | R:CCATAGTCGGACCCTCTTT | 201 |
| Z199 | (TAA)*13 | F:<M13>-GTAACTGGTGGATTTGTCG | R:CCATAGTCGGACCCTCTTT | 220 |
| Z204 | (TG)*9 | F:<M13>-TGCTGGAAAGGAACGAAAC | R:CATTGCATGGCTGCTCATA | 244 |
| M13通用引物 <FAM>或<HEX>-TGTAAAACGACGGCCAGT | ||||
| M13 universal primer | ||||
Table 1 Information of 16 core SSR primers
| 引物序号 Primer code | 重复单元 Repeat motif | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence | 产物大小/bp Product size | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z1 | (AT)*8 | F:<M13>-TAACCTAGCATCCTCCAC | R:TATGCGGGTAAATCTCGT | 184 |
| Z5 | (TC)*10 | F:<M13>-CATTGATTCTTTCCTTCG | R:AAAATTAGCCAGAAACGT | 247 |
| Z7 | (TA)*9 | F:<M13>-TGATCTCCTCTGGCGAATG | R:CCTCCTCGTCACCATCCA | 277 |
| Z15 | (TC)*6 | F:<M13>-TCCCCTTCATTTATCCTT | R:TTTTGTTGATGGCGTTGG | 172 |
| Z17 | (CT)*8 | F:<M13>-ATGCAAGCCGCTTTTCTC | R:ACCCAAGATTCTGGTCAGG | 203 |
| Z24 | (AT)*18 | F:<M13>-ACCAGTCCTACGCATCAC | R:CCCGATACCCTGGATTTT | 260 |
| Z52 | (TA)*12 | F:<M13>-CTCCCACTGTCCCTTCGT | R:GCTTGCTGAGCGGATTTA | 186 |
| Z54 | (AT)*14 | F:<M13>-CATTAGAGTTCATTGGGAATA | R:TACCTTACGTTTTGTCGC | 254 |
| Z92 | (CT)*12 | F:<M13>-TACGGTATCAATTCCTTC | R:GGCATTATCAGACCCAAA | 312 |
| Z124 | (AG)*23 | F:<M13>-CCGATCATCAGGGACTACTA | R:CATCTCCAGCACCATTCTT | 316 |
| Z131 | (CT)*9 | F:<M13>-TATAAGGCAAGTGGGGTGA | R:GTGGCAACAAGAATACAAGAT | 161 |
| Z171 | (TA)*17 | F:<M13>-CTAAAGCGATCTTGACATA | R:GGACGGGACTTACTACCAG | 252 |
| Z178 | (AT)*11 | F:<M13>-GAGAACTTTTGTTTATTGGAG | R:TTCTTTCATGCTTCCGTTC | 165 |
| Z198 | (TAA)*13 | F:<M13>-GTAACTGGTGGATTTGTCG | R:CCATAGTCGGACCCTCTTT | 201 |
| Z199 | (TAA)*13 | F:<M13>-GTAACTGGTGGATTTGTCG | R:CCATAGTCGGACCCTCTTT | 220 |
| Z204 | (TG)*9 | F:<M13>-TGCTGGAAAGGAACGAAAC | R:CATTGCATGGCTGCTCATA | 244 |
| M13通用引物 <FAM>或<HEX>-TGTAAAACGACGGCCAGT | ||||
| M13 universal primer | ||||
| 基因 Gene | 序列号 ID | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence | 产物大小/bp Product size | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEP1 | Cm158770.1 | F:GCTTAGGCTTAGAGGAGTTG | R:GAATGAGCAGGTTGGTTG | 244 |
| SEP2 | Cm240370.1 | F:AGCGAACTCAGAGGAATC | R:ACCTAGTTGCTGCTCACC | 263 |
| SEP4 | Cm146780.1 | F:CCTGAGGAAGAAGTTGGAC | R:CGATAGAGGCTGAAAGAACC | 142 |
| SHP1 | Cm078390.1 | F:GGAATCGGCAGAGTCAGA | R:GCGTACTGGTGATTGGGT | 260 |
| SHP2 | Cm164940.1 | F:AATACTGGGTCTATCTGTGAA | R:TCTCGGCTATCTTTGCTC | 289 |
| SPL6 | Cm158790.1 | F:GACTCATCTGTTGACCCTT | R:CACTACCGACTTCACCATTA | 211 |
| SPL8 | Cm162720.1 | F:AGATGAAGCGACTCAAGAAT | R:GTGGGTGGGAGCGTAAGA | 286 |
| SPL9 | Cm119150.1 | F:TCTGATCGACTTCAGTGCATATC | R:AATTCCAGGACCAGAGAAACC | 208 |
| YABBY1A | Cm015380.1 | F:ATCCCAAATCCATCTCCGAAC | R:TGAATCGGTTGTACGCAGAG | 157 |
| YABBY1B | Cm112520.1 | F:ACTTCCCTCACATCCATTTCG | R:ACTACAACGAAACCCCAGC | 192 |
| YABBY4 | Cm075530.1 | F:CAAACATGGCTCACAAGGAAG | R:CTTCAAAGTTCCAAGCTCGC | 132 |
| YABBY5A | Cm147040.1 | F:TGCGAACACCCACTAACAAG | R:AATGGATGTGAGGGAAGTGTG | 198 |
| CRC | Cm158810.1 | F:CTCTCACCACTTCTCTCTTCTTC | R:AGAAGTTGCAGCGGACATAG | 204 |
| WOX1 | Cm275910.1 | F:ATTCTACTACGACTGCTATT | R:TCTCTCTTGTTTTGTTCACC | 190 |
| PRS | Cm223590.1 | F:CCATAAAGCAAGAGAGAGGC | R:AGCTGGGTTAGAAAAGGAAC | 190 |
| LUG | Cm111030.1 | F:CCCACCTCCTAAATGGCAATA | R:TAGCCGCATCATCCAAAGAA | 150 |
| AGL66 | Cm105600.1 | F:ATGTGAAGGAGAAATGCTGG | R:AATCTTTGGGTTGAGACTGG | 388 |
| AP2 | Cm077350.1 | F:AATCTAAAATAATTGCCCAA | R:AATAACTCAACTCACTCTGC | 324 |
| TIR1 | Cm233920.1 | F:GACGCAGCTCTACTCTCAGG | R:CTTTCTTGGTCCAGCAACAG | 204 |
| CsActin | Cs1g05000.1 | F:CCAAGCAGCATGAAGATCAA | R:ATCTGCTGGAAGGTGCTGAG | 101 |
Table 2 Information of qRT-PCR primers
| 基因 Gene | 序列号 ID | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence | 产物大小/bp Product size | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEP1 | Cm158770.1 | F:GCTTAGGCTTAGAGGAGTTG | R:GAATGAGCAGGTTGGTTG | 244 |
| SEP2 | Cm240370.1 | F:AGCGAACTCAGAGGAATC | R:ACCTAGTTGCTGCTCACC | 263 |
| SEP4 | Cm146780.1 | F:CCTGAGGAAGAAGTTGGAC | R:CGATAGAGGCTGAAAGAACC | 142 |
| SHP1 | Cm078390.1 | F:GGAATCGGCAGAGTCAGA | R:GCGTACTGGTGATTGGGT | 260 |
| SHP2 | Cm164940.1 | F:AATACTGGGTCTATCTGTGAA | R:TCTCGGCTATCTTTGCTC | 289 |
| SPL6 | Cm158790.1 | F:GACTCATCTGTTGACCCTT | R:CACTACCGACTTCACCATTA | 211 |
| SPL8 | Cm162720.1 | F:AGATGAAGCGACTCAAGAAT | R:GTGGGTGGGAGCGTAAGA | 286 |
| SPL9 | Cm119150.1 | F:TCTGATCGACTTCAGTGCATATC | R:AATTCCAGGACCAGAGAAACC | 208 |
| YABBY1A | Cm015380.1 | F:ATCCCAAATCCATCTCCGAAC | R:TGAATCGGTTGTACGCAGAG | 157 |
| YABBY1B | Cm112520.1 | F:ACTTCCCTCACATCCATTTCG | R:ACTACAACGAAACCCCAGC | 192 |
| YABBY4 | Cm075530.1 | F:CAAACATGGCTCACAAGGAAG | R:CTTCAAAGTTCCAAGCTCGC | 132 |
| YABBY5A | Cm147040.1 | F:TGCGAACACCCACTAACAAG | R:AATGGATGTGAGGGAAGTGTG | 198 |
| CRC | Cm158810.1 | F:CTCTCACCACTTCTCTCTTCTTC | R:AGAAGTTGCAGCGGACATAG | 204 |
| WOX1 | Cm275910.1 | F:ATTCTACTACGACTGCTATT | R:TCTCTCTTGTTTTGTTCACC | 190 |
| PRS | Cm223590.1 | F:CCATAAAGCAAGAGAGAGGC | R:AGCTGGGTTAGAAAAGGAAC | 190 |
| LUG | Cm111030.1 | F:CCCACCTCCTAAATGGCAATA | R:TAGCCGCATCATCCAAAGAA | 150 |
| AGL66 | Cm105600.1 | F:ATGTGAAGGAGAAATGCTGG | R:AATCTTTGGGTTGAGACTGG | 388 |
| AP2 | Cm077350.1 | F:AATCTAAAATAATTGCCCAA | R:AATAACTCAACTCACTCTGC | 324 |
| TIR1 | Cm233920.1 | F:GACGCAGCTCTACTCTCAGG | R:CTTTCTTGGTCCAGCAACAG | 204 |
| CsActin | Cs1g05000.1 | F:CCAAGCAGCATGAAGATCAA | R:ATCTGCTGGAAGGTGCTGAG | 101 |
| 重复类型 | 重复次数 Number of repeat | 总数 | 比例/% | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Repeat type | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | >12 | Total | Percentage |
| 二核苷酸Dinucleotide | — | 712 | 415 | 283 | 243 | 166 | 101 | 59 | 150 | 2 129 | 43.37 |
| 三核苷酸Trinucleotide | 1 322 | 605 | 311 | 131 | 49 | 35 | 18 | 8 | 22 | 2 501 | 50.95 |
| 四核苷酸Tetranucleotide | 115 | 36 | 7 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 166 | 3.38 |
| 五核苷酸Pentanucleotide | 20 | 8 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 31 | 0.63 |
| 六核苷酸Hexanucleotide | 59 | 13 | 7 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 82 | 1.67 |
| 总数Total | 1 516 | 1 374 | 743 | 420 | 295 | 203 | 119 | 67 | 172 | 4 909 | |
| 比例/% Percentage | 30.88 | 27.99 | 15.14 | 8.56 | 6.01 | 4.14 | 2.42 | 1.36 | 3.50 | 100.00 | |
Table 3 Distribution of SSRs with different repeat types and repeat numbers in transcriptomic sequence of fingered citron
| 重复类型 | 重复次数 Number of repeat | 总数 | 比例/% | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Repeat type | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | >12 | Total | Percentage |
| 二核苷酸Dinucleotide | — | 712 | 415 | 283 | 243 | 166 | 101 | 59 | 150 | 2 129 | 43.37 |
| 三核苷酸Trinucleotide | 1 322 | 605 | 311 | 131 | 49 | 35 | 18 | 8 | 22 | 2 501 | 50.95 |
| 四核苷酸Tetranucleotide | 115 | 36 | 7 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 166 | 3.38 |
| 五核苷酸Pentanucleotide | 20 | 8 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 31 | 0.63 |
| 六核苷酸Hexanucleotide | 59 | 13 | 7 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 82 | 1.67 |
| 总数Total | 1 516 | 1 374 | 743 | 420 | 295 | 203 | 119 | 67 | 172 | 4 909 | |
| 比例/% Percentage | 30.88 | 27.99 | 15.14 | 8.56 | 6.01 | 4.14 | 2.42 | 1.36 | 3.50 | 100.00 | |
| 重复类型 | 重复基序 | 所占比例/% |
|---|---|---|
| Repeat type | Repeat motif | Percentage |
| 二核苷酸 | AG/CT | 55.61 |
| Dinucleotide | AC/GT | 15.45 |
| AT/AT | 21.18 | |
| CG/CG | 0.75 | |
| 三核苷酸 | AAG/CTT | 24.32 |
| Trinucleotide | AGG/CCT | 4.37 |
| ACC/GGT | 5.19 | |
| AGC/CTG | 11.69 | |
| ATC/ATG | 16.06 | |
| CCG/CGG | 3.30 | |
| ACG/CGT | 2.48 | |
| AAC/GTT | 7.20 | |
| AAT/ATT | 24.20 | |
| ACT/AGT | 1.18 |
Table 4 Percentages of different repeat motifs among dinucleotide and trinucleotide repeats in transcriptomic sequence of fingered citron
| 重复类型 | 重复基序 | 所占比例/% |
|---|---|---|
| Repeat type | Repeat motif | Percentage |
| 二核苷酸 | AG/CT | 55.61 |
| Dinucleotide | AC/GT | 15.45 |
| AT/AT | 21.18 | |
| CG/CG | 0.75 | |
| 三核苷酸 | AAG/CTT | 24.32 |
| Trinucleotide | AGG/CCT | 4.37 |
| ACC/GGT | 5.19 | |
| AGC/CTG | 11.69 | |
| ATC/ATG | 16.06 | |
| CCG/CGG | 3.30 | |
| ACG/CGT | 2.48 | |
| AAC/GTT | 7.20 | |
| AAT/ATT | 24.20 | |
| ACT/AGT | 1.18 |
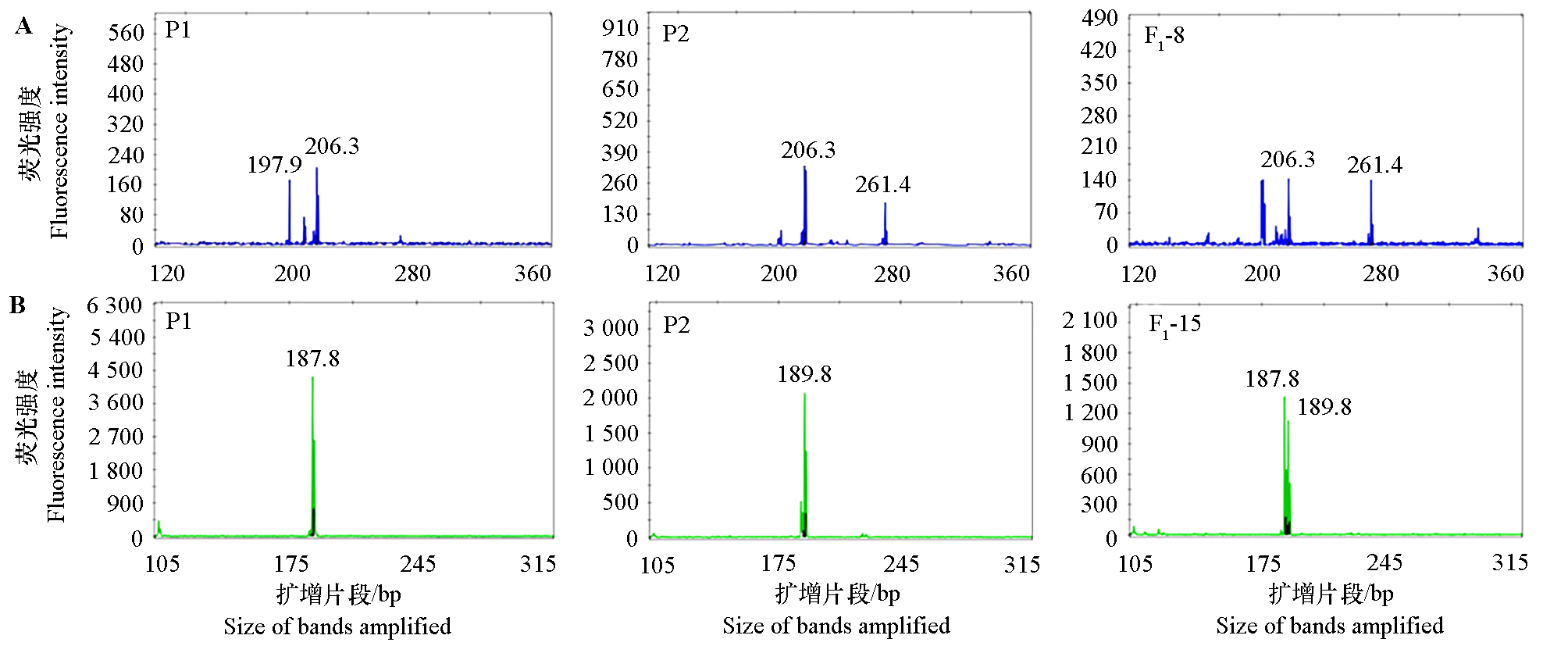
Fig. 1 Electropherogram of SSR locus and amplified allele sizes in base pairs of fingered citron(P1),citron(P2)and hybrid F1 lines A:The amplified products obtained in parents and F1-8 with the primer Z5;B:The amplified products obtained in parents and F1-15 with the primer Z15.
| 引物序号 Primer code | Na观测等位基因数 Observed number of alleles | Ne有效等位基因数 Effective number of alleles | Ho观测杂合度 Observed heterozygosity | He期望杂合度 Expected heterozygosity | Pi多态性信息量 Polymorphism information content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z1 | 28 | 21 | 1.000 | 0.981 | 0.956 |
| Z5 | 18 | 16 | 0.188 | 0.966 | 0.932 |
| Z7 | 17 | 14 | 0.429 | 0.963 | 0.924 |
| Z15 | 20 | 21 | 0.667 | 0.958 | 0.932 |
| Z17 | 28 | 17 | 0.941 | 0.988 | 0.957 |
| Z24 | 25 | 18 | 0.611 | 0.968 | 0.938 |
| Z52 | 19 | 14 | 0.929 | 0.968 | 0.930 |
| Z54 | 27 | 20 | 0.750 | 0.981 | 0.954 |
| Z92 | 25 | 19 | 0.526 | 0.977 | 0.949 |
| Z124 | 17 | 16 | 0.438 | 0.948 | 0.912 |
| Z131 | 32 | 21 | 0.952 | 0.986 | 0.961 |
| Z171 | 25 | 19 | 0.579 | 0.974 | 0.946 |
| Z178 | 26 | 19 | 0.474 | 0.982 | 0.954 |
| Z198 | 28 | 21 | 1.000 | 0.978 | 0.953 |
| Z199 | 30 | 21 | 0.762 | 0.985 | 0.960 |
| Z204 | 22 | 20 | 0.550 | 0.967 | 0.940 |
| 均值 Mean | 24.188 | 18.563 | 0.675 | 0.973 | 0.944 |
Table 5 Genetic diversity of F1 hybrids as revealed by core SSR primers
| 引物序号 Primer code | Na观测等位基因数 Observed number of alleles | Ne有效等位基因数 Effective number of alleles | Ho观测杂合度 Observed heterozygosity | He期望杂合度 Expected heterozygosity | Pi多态性信息量 Polymorphism information content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z1 | 28 | 21 | 1.000 | 0.981 | 0.956 |
| Z5 | 18 | 16 | 0.188 | 0.966 | 0.932 |
| Z7 | 17 | 14 | 0.429 | 0.963 | 0.924 |
| Z15 | 20 | 21 | 0.667 | 0.958 | 0.932 |
| Z17 | 28 | 17 | 0.941 | 0.988 | 0.957 |
| Z24 | 25 | 18 | 0.611 | 0.968 | 0.938 |
| Z52 | 19 | 14 | 0.929 | 0.968 | 0.930 |
| Z54 | 27 | 20 | 0.750 | 0.981 | 0.954 |
| Z92 | 25 | 19 | 0.526 | 0.977 | 0.949 |
| Z124 | 17 | 16 | 0.438 | 0.948 | 0.912 |
| Z131 | 32 | 21 | 0.952 | 0.986 | 0.961 |
| Z171 | 25 | 19 | 0.579 | 0.974 | 0.946 |
| Z178 | 26 | 19 | 0.474 | 0.982 | 0.954 |
| Z198 | 28 | 21 | 1.000 | 0.978 | 0.953 |
| Z199 | 30 | 21 | 0.762 | 0.985 | 0.960 |
| Z204 | 22 | 20 | 0.550 | 0.967 | 0.940 |
| 均值 Mean | 24.188 | 18.563 | 0.675 | 0.973 | 0.944 |

Fig. 2 The phenotype of fruit from fingered citron, citron and some F1 hybrids P1:Maternal citron;P2:Paternal fingered citron;F1-4 is hesperidium type;F1-7 is parents intermediate type;F1-2,F1-6 and F1-10 show finger fruit type.

Fig. 4 Paraffin sections of the visible bud stage,the petals emerging stage and the petals turning white stage of fingered citron and citron A(a)-C(c):1-3 mm flower buds in the visible bud stage;D(d)-E(e):4 mm and 5 mm flower buds in petals emerging stage;F(f):Ovule differentiation occurred in 7 mm flower buds at lantern petal stage;St:The stamen primordium;Pe:The petal primordium;Pi:The pistil primordium;Ca:The carpel;Ovules are in the black block.

Fig. 5 Heat map analysis of differential genes from the transcriptome data of fingered citron and citron S1:Visible bud stage;S2:Petals emerging stage;S3:Pre-anthesis stage;S4:The 3 days after anthesis.
| 基因 Gene | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient | 基因 Gene | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 现瓣期 Petals emerging stage | 即将开放期 Pre-anthesis stage | 现瓣期 Petals emerging stage | 即将开放期 Pre-anthesis stage | |||
| SEP1 | -0.358 | 0.086 | YABBY4 | 0.501 | 0.258 | |
| SEP2 | -0.645 | -0.775* | YABBY5A | 0.645 | 0.430 | |
| SEP4 | 0.788* | -0.430 | CRC | 0.358 | 0.775 | |
| SHP1 | -0.072 | -0.775* | WOX1 | 0.788* | -0.775* | |
| SHP2 | -0.645 | -0.775* | PRS | 0.620 | 0.430 | |
| SPL6 | -0.358 | 0.775* | LUG | -0.072 | -0.775* | |
| SPL8 | -0.501 | -0.430 | AGL66 | -0.358 | 0.086 | |
| SPL9 | 0.501 | 0.258 | AP2 | -0.501 | -0.602 | |
| YABBY1A | 0.358 | 0.258 | TIR1 | 0.501 | 0.775* | |
| YABBY1B | 0.501 | 0.258 | ||||
Table 6 Correlation analysis between the expression level of genes and the carpel feature
| 基因 Gene | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient | 基因 Gene | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 现瓣期 Petals emerging stage | 即将开放期 Pre-anthesis stage | 现瓣期 Petals emerging stage | 即将开放期 Pre-anthesis stage | |||
| SEP1 | -0.358 | 0.086 | YABBY4 | 0.501 | 0.258 | |
| SEP2 | -0.645 | -0.775* | YABBY5A | 0.645 | 0.430 | |
| SEP4 | 0.788* | -0.430 | CRC | 0.358 | 0.775 | |
| SHP1 | -0.072 | -0.775* | WOX1 | 0.788* | -0.775* | |
| SHP2 | -0.645 | -0.775* | PRS | 0.620 | 0.430 | |
| SPL6 | -0.358 | 0.775* | LUG | -0.072 | -0.775* | |
| SPL8 | -0.501 | -0.430 | AGL66 | -0.358 | 0.086 | |
| SPL9 | 0.501 | 0.258 | AP2 | -0.501 | -0.602 | |
| YABBY1A | 0.358 | 0.258 | TIR1 | 0.501 | 0.775* | |
| YABBY1B | 0.501 | 0.258 | ||||

Fig. 6 Expression analysis of differential expressed genes in fingered citron, citron and F1 generation hybrid in the pre-anthesis stage LSD,P < 0.05.
| 基因 Gene | AGL66 | AP2 | CRC | LUG | PRS | SEP1 | SEP2 | SEP4 | SHP1 | SHP2 | SPL6 | SPL9 | WOX1 | YABBY1A | YABBY1B | YABBY4 | YABBY5A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGL66 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| AP2 | 0.667 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| CRC | 0.667 | 0.333 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| LUG | 0.000 | 0.333 | -0.333 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| PRS | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 1 | ||||||||||||
| SEP1 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 1.000** | 1 | |||||||||||
| SEP2 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 1.000** | -0.333 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 1 | ||||||||||
| SEP4 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 1.000** | 1.000** | 0.667 | 1 | |||||||||
| SHP1 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 0.667 | 1 | ||||||||
| SHP2 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 1.000** | -0.333 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.333 | 1 | |||||||
| SPL6 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 1.000** | -0.333 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.333 | 1.000** | 1 | ||||||
| SPL9 | 0.000 | 0.333 | -0.333 | 1.000** | 0.000 | 0.000 | -0.333 | 0.000 | 0.333 | -0.333 | -0.333 | 1 | |||||
| WOX1 | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 1 | ||||
| YABBY1A | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 1.000** | 1.000** | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 0.667 | 1 | |||
| YABBY1B | 0.667 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.667 | 1 | ||
| YABBY4 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 1.000** | 1.000** | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 1 | |
| YABBY5A | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 1.000** | 1.000** | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 1.000** | 1 |
Table 7 Correlation analysis of differential genes expression between F1 generation hybrid and parent
| 基因 Gene | AGL66 | AP2 | CRC | LUG | PRS | SEP1 | SEP2 | SEP4 | SHP1 | SHP2 | SPL6 | SPL9 | WOX1 | YABBY1A | YABBY1B | YABBY4 | YABBY5A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGL66 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| AP2 | 0.667 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| CRC | 0.667 | 0.333 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| LUG | 0.000 | 0.333 | -0.333 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| PRS | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 1 | ||||||||||||
| SEP1 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 1.000** | 1 | |||||||||||
| SEP2 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 1.000** | -0.333 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 1 | ||||||||||
| SEP4 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 1.000** | 1.000** | 0.667 | 1 | |||||||||
| SHP1 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 0.667 | 1 | ||||||||
| SHP2 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 1.000** | -0.333 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.333 | 1 | |||||||
| SPL6 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 1.000** | -0.333 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.333 | 1.000** | 1 | ||||||
| SPL9 | 0.000 | 0.333 | -0.333 | 1.000** | 0.000 | 0.000 | -0.333 | 0.000 | 0.333 | -0.333 | -0.333 | 1 | |||||
| WOX1 | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 1 | ||||
| YABBY1A | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 1.000** | 1.000** | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 0.667 | 1 | |||
| YABBY1B | 0.667 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.667 | 1 | ||
| YABBY4 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 1.000** | 1.000** | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 1 | |
| YABBY5A | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 1.000** | 1.000** | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 1.000** | 1 |
| [1] |
doi: 10.1242/dev.126.11.2387 pmid: 10225998 |
| [2] |
|
|
陈民管. 2014. 佛手坐果及果形发育的初步研究[硕士论文]. 金华: 浙江师范大学.
|
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.1242/dev.126.12.2715 pmid: 10331982 |
| [4] |
|
|
陈小灵, 王念, 朱延林. 2012. 植物返祖现象研究. 上海农业学报, 28 (1):102-105.
|
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00331 URL |
| [7] |
|
|
董清华, 王西成, 赵密珍, 宋长年, 葛安静, 王静. 2011. 草莓EST-SSR标记开发及在品种遗传多样性分析中的应用. 中国农业科学, 44 (17):3603-3612.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2011.17.013 |
|
| [8] |
doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90551-9 pmid: 1675158 |
| [9] |
Editorial Committee of flora of China,Chinese Academy of Sciences. 1997. Flora of China. 43 (2). Beijing:Science Press:184. (in Chinese)
|
|
中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会. 1997. 中国植物志. 43 (2). 北京:科学出版社:184.
|
|
| [10] |
|
|
房经贵, 章镇, 马正强, 刘大钧, 王三红, Lavi U. 2000. AFLP标记在两个芒果品种间杂交Fl代的多态性及分离方式. 中国农业科学, 33 (3):19-24.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2000-33-3-22-27 |
|
| [11] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2017-0675 |
|
方茜, 张园园, 杨钰婷, 黄苗苗, 符巧丽, 周慧莎, 陈文荣, 宗宇, 郭卫东. 2018. 越橘叶片转录组SSR发掘及其多态性研究. 园艺学报, 45 (7):1359-1370.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2017-0675 |
|
| [12] |
|
|
方治伟, 李论. 2018. SSR分型技术研究进展. 生物化工, 4 (1):118-121.
|
|
| [13] |
doi: 10.1242/dev.01600 URL |
| [14] |
|
|
郭吉春, 叶乃兴, 何孝延. 2004. 茶树杂交一代展叶期的遗传变异. 茶叶科学,(4):255-259.
|
|
| [15] |
|
|
韩国辉, 向素琼, 汪卫星, 魏旭, 何波, 李晓林, 梁国鲁. 2010. 沙田柚杂交后代群体的 SSR 鉴定与遗传多样性分析. 中国农业科学, 43 (22):4678-4686.
|
|
| [16] |
|
|
韩晓霞. 2017. YABBY5和CRC基因在佛手果实发育中的功能初探[硕士论文]. 金华: 浙江师范大学.
|
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1242/dev.124.19.3845 pmid: 9367440 |
| [18] |
|
|
胡文舜, 黄爱萍, 姜帆, 蒋际, 陈秀萍, 郑少泉. 2015. 龙眼正反交后代的SSR鉴定及遗传多样性分析. 园艺学报, 42 (10):1899-1908.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2015-0131 |
|
| [19] |
pmid: 16625833 |
| [20] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1755-0998.2009.02778.x pmid: 21564987 |
| [21] |
pmid: 16391668 |
| [22] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.026666 URL |
| [23] |
|
|
李会勇, 王天宇, 黎裕, 石云素, 宋艳春, 陆平. 2005. TP-M13自动荧光检测法在高粱SSR基因型鉴定中的应用. 物遗传资源学报, 6 (1):68-70.
|
|
| [24] |
|
|
李响, 杨楠, 赵凯歌, 陈玉星, 唐锐君, 陈龙清. 2013. 蜡梅转录组EST-SSR标记开发与引物筛选. 北京林业大学学报, 35 (1):25-32.
|
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-9-35 URL |
| [26] |
doi: 10.1007/s11032-017-0693-x URL |
| [27] |
|
|
廖芳蕾, 陈民管, 桑丹, 陈文荣, 郭卫东. 2013. 佛手种质资源遗传多样性的ISSR 分析. 园艺学报, 40 (11):2222-2228.
|
|
| [28] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0502 |
|
廖芳蕾, 陈泽宇, 徐启越, 杨莉, 陈文荣, 郭卫东. 2018. 果形建成基因研究进展及其对佛手果形发育研究的启示. 园艺学报, 45 (9):1701-1714.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0502 |
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2016-0358 |
|
廖芳蕾, 韩晓霞, 陈文荣, 郭艳, 张晨晓, 陈泽宇, 周亚艳, 郭卫东. 2016. 佛手果形发育观察及果形相关基因表达分析. 园艺学报, 43 (11):2141-2150.
|
|
| [30] |
doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20211012.102 pmid: 34951256 |
|
刘航秀, 冯迪, 龙春瑞, 周先艳, 刘红明, 杨虹霞, 杜玉霞, 郭丽娜, 付小猛, 马兆成, 岳建强. 2021. 枸橼药用植物果实变异及地理分布研究. 中国中药杂志, 46 (23):6289-6293.
pmid: 34951256 |
|
| [31] |
|
|
刘升锐. 2016. 柑橘高密度遗传连锁图谱的构建及落叶性状的QTL定位[博士论文]. 武汉: 华中农业大学.
|
|
| [32] |
|
|
罗球, 张庆祥. 2020. SSR技术在果树上的应用. 江西农业,(10):36-38.
|
|
| [33] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.113209 pmid: 23821642 |
| [34] |
doi: 10.1038/72708 pmid: 10657137 |
| [35] |
doi: 10.1086/337805 URL |
| [36] |
|
|
王彬, 刘丽丽, 吴效芳. 2019. 孟德尔遗传定律中2种分离比的2个认识误区. 生物学通报, 54 (12):40-41.
|
|
| [37] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/eraa574 URL |
| [38] |
|
|
王静毅, 陈业渊, 刘伟良, 武耀廷. 2008. 香蕉EST-SSRs标记的开发与应用. 遗传, 30 (7):933-940.
|
|
| [39] |
doi: 10.1007/s11105-012-0519-2 URL |
| [40] |
|
|
伍涵宇. 2019. 光周期响应基因StYABBY1调控光合作用功能研究[硕士论文]. 银川: 宁夏大学.
|
|
| [41] |
|
|
鄢秀芹, 鲁敏, 安华明. 2015. 刺梨转录组SSR信息分析及其分子标记开发. 园艺学报, 42 (2):341-349.
|
|
| [42] |
|
|
杨梦婷, 黄洲, 干建平, 徐君驰, 庞基良. 2019. SSR分子标记的研究进展. 杭州师范大学学报(自然科学版), 18 (4):429-436.
|
|
| [43] |
doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-253 |
| [44] |
doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1300240 URL |
| [45] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2015-0659 |
|
张庆田, 李晓艳, 杨义明, 范书田, 艾军. 2016. 蓝靛果忍冬转录组SSR信息分析及其分子标记开发. 园艺学报, 43 (3):557-563.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2015-0659 |
|
| [46] |
doi: 10.1360/biodiv.060277 URL |
|
张田, 李作洲, 刘亚令, 姜正旺, 黄宏文. 2007. 猕猴桃属植物的cpSSR遗传多样性及其同域分布物种的杂交渐渗与同塑. 生物多样性, 15 (1):1-22.
doi: 10.1360/biodiv.060277 |
|
| [47] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0377 |
|
赵玉洁, 刘翠玉, 招雪晴, 汪钰莹, 闫明, 苑兆和. 2021. 石榴花器官发育相关基因PgWUS和PgBEL1克隆及其时空表达分析. 园艺学报, 48 (2):355-366.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0377 |
|
| [48] |
|
|
宗宇, 王月, 朱友银, 邵姁, 李永强, 郭卫东. 2016. 基于中国樱桃转录组的SSR分子标记开发与鉴定. 园艺学报, 43 (8):1566-1576.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2016-0005 |
| [1] | NIE Xinghua, ZHANG Yu, LIU Song, YANG Jiabin, HAO Yaqiong, LIU Yang, QIN Ling, and XING Yu. Study on Genetic Characteristics and Taxonomic Status of Wild Chinese Chestnut Based on Genome Re-sequencing [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(8): 1622-1636. |
| [2] | WANG Ping, SHENG Ling, YANG Jinpeng, ZHOU Linglei, JIN Yan, LUO Xuzhao, MA Xianfeng, DENG Ziniu. Evaluation of Resistance to Citrus Canker Disease in Hybrid Progeny of Red Pomelo and American Citron [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(4): 765-777. |
| [3] | SUN Zeshuo, JIANG Dongyue, LIU Xinhong, SHEN Xin, LI Yingang, QU Yufei, LI Yonghua. Cluster Analysis and Construction of DNA Fingerprinting of 42 Oriental Cultivars of Flowering Cherry Based on SSR Markers [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(3): 657-668. |
| [4] | WANG Rui, HONG Wenjuan, LUO Hua, ZHAO Lina, CHEN Ying, WANG Jun. Construction of SSR Fingerprints of Pomegranate Cultivars and Male Parent Identification of Hybrids [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 265-278. |
| [5] | LIU Yiping, NI Menghui, WU Fangfang, LIU Hongli, HE Dan, KONG Dezheng. Association Analysis of Organ Traits with SSR Markers in Lotus(Nelumbo nucifera) [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(1): 103-115. |
| [6] | ZHANG Kai, MA Mingying, WANG Ping, LI Yi, JIN Yan, SHENG Ling, DENG Ziniu, MA Xianfeng. Identification of HSP20 Family Genes in Citrus and Their Expression in Pathogen Infection Responses Citrus Canker [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1213-1232. |
| [7] | MA Mingying, HAO Chenxing, ZHANG Kai, XIAO Guihua, SU Hanying, WEN Kang, DENG Ziniu, MA Xianfeng. CsSWEET2a Promotes the Infection of Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1247-1260. |
| [8] | LI Chao, YANG Ying, CHEN Wei, ZHENG Heyun, LIAO Xinfu, SUN Yuping. Construction of DNA Fingerprinting and Clustering Analysis with SSR Markers for the Muskmelon of Xizhoumi Series [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(3): 622-632. |
| [9] | NIE Xinghua, LI Yiran, TIAN Shoule, WANG Xuefeng, SU Shuchai, CAO Qingqin, XING Yu, QIN Ling. Construction of DNA Fingerprint Map and Analysis of Genetic Diversity for Chinese Chestnut Cultivars(Lines) [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(11): 2313-2324. |
| [10] | CHEN Mingkun, CHEN Lu, SUN Weihong, MA Shanhu, LAN Siren, PENG Donghui, LIU Zhongjian, AI Ye. Genetic Diversity Analysis and Core Collection of Cymbidium ensifolium Germplasm Resources [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(1): 175-186. |
| [11] | SONG Yun, JIA Mengjun, CAO Yaping, LI Zheng, HE Jiaxin, WANG Yongfei, ZHANG Xinrui, QIAO Yonggang. Analysis on Chloroplast Genomic Characteristics of Forsythia suspensa [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(1): 187-199. |
| [12] | WANG Xin, LI Mingyang, TIAN Lin, LIU Dongyun. ISSR and rDNA-ITS Sequence Analysis of the Genetic Relationship of Clematis in Hebei Province [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(9): 1755-1767. |
| [13] | WANG Xiaoqing, MEI Yulin, LIU Jinlian, XU Jinjian, LI Yongqiang, CHEN Wenrong, ZONG Yu, SHAO Wenke, LIAO Fanglei, GUO Weidong. A New Fingered Citron Cultivar‘Cuizhi’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(8): 1639-1640. |
| [14] | DING Yunhua, Budahn Holger, ZHAO Hong, ZHAO Xiuyun. Accurate Identification of Radish Chromosome F in the Backcross Progeny of Brassica rapa and Rape-radish Chromosome F Addition Line [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(7): 1295-1303. |
| [15] | ZHAO Qing, DU Zhenzhen, LI Xixiang, SONG Jiangping, ZHANG Xiaohui, YANG Wenlong, JIA Huixia, WANG Haiping. Genetic Diversity of Garlic Germplasm Resources Based on SSRseq Molecular Markers [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(7): 1397-1408. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd