
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 463-478.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0056
• Genetic & Breeding·Germplasm Resources·Molecular Biology • Next Articles
ZHOU Ping, YAN Shaobin, GUO Rui, JIN Guang*( )
)
Received:2023-03-29
Revised:2023-11-30
Online:2024-03-25
Published:2024-03-22
Contact:
JIN Guang
ZHOU Ping, YAN Shaobin, GUO Rui, JIN Guang. Identification and Expressional Analysis of MGT Gene Family in Prunus persica[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(3): 463-478.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0056
| 基因 Gene | ID | 染色体 Chromosome | 氨基酸数 Number of amino acids | 分子量/kD MW | 等电点 pI | 跨膜域 Transmem- brane | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PpMGT1 | Prupe.1G027800 | Chr1 | 393 | 43.71 | 4.64 | 2 | 质膜,叶绿体 Plasma membrane,chloroplast |
| PpMGT2 | Prupe.1G287300 | Chr1 | 433 | 47.53 | 4.98 | 2 | 高尔基体,细胞质 Golgi,cytoplasm |
| PpMGT3 | Prupe.1G575700 | Chr1 | 455 | 50.79 | 5.14 | 2 | 叶绿体,线粒体 Chloroplast,mitochondrion |
| PpMGT4 | Prupe.3G100200 | Chr3 | 472 | 53.39 | 5.30 | 1 | 高尔基体,细胞质 Golgi,cytoplasm |
| PpMGT5 | Prupe.6G116100 | Chr6 | 452 | 50.71 | 6.21 | 2 | 质膜,叶绿体 Plasma membrane,chloroplast |
| PpMGT6 | Prupe.8G147300 | Chr8 | 491 | 54.70 | 4.64 | 2 | 叶绿体,细胞质 Chloroplast,cytoplasm |
| PpMGT7 | Prupe.8G147400 | Chr8 | 460 | 51.20 | 4.84 | 2 | 叶绿体,液泡 Chloroplast,vacuole |
| PpMGT8 | Prupe.8G231400 | Chr8 | 435 | 48.81 | 4.54 | 2 | 质膜,叶绿体 Plasma membrane,chloroplast |
Table 1 The properties of PpMGTs
| 基因 Gene | ID | 染色体 Chromosome | 氨基酸数 Number of amino acids | 分子量/kD MW | 等电点 pI | 跨膜域 Transmem- brane | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PpMGT1 | Prupe.1G027800 | Chr1 | 393 | 43.71 | 4.64 | 2 | 质膜,叶绿体 Plasma membrane,chloroplast |
| PpMGT2 | Prupe.1G287300 | Chr1 | 433 | 47.53 | 4.98 | 2 | 高尔基体,细胞质 Golgi,cytoplasm |
| PpMGT3 | Prupe.1G575700 | Chr1 | 455 | 50.79 | 5.14 | 2 | 叶绿体,线粒体 Chloroplast,mitochondrion |
| PpMGT4 | Prupe.3G100200 | Chr3 | 472 | 53.39 | 5.30 | 1 | 高尔基体,细胞质 Golgi,cytoplasm |
| PpMGT5 | Prupe.6G116100 | Chr6 | 452 | 50.71 | 6.21 | 2 | 质膜,叶绿体 Plasma membrane,chloroplast |
| PpMGT6 | Prupe.8G147300 | Chr8 | 491 | 54.70 | 4.64 | 2 | 叶绿体,细胞质 Chloroplast,cytoplasm |
| PpMGT7 | Prupe.8G147400 | Chr8 | 460 | 51.20 | 4.84 | 2 | 叶绿体,液泡 Chloroplast,vacuole |
| PpMGT8 | Prupe.8G231400 | Chr8 | 435 | 48.81 | 4.54 | 2 | 质膜,叶绿体 Plasma membrane,chloroplast |

Fig. 1 Multiple protein sequence alignment of the PpMGTs The η symbols refer to 310-helix,and squiggles and arrows indicate α-helices and β-strands. TT letters show β-turns.
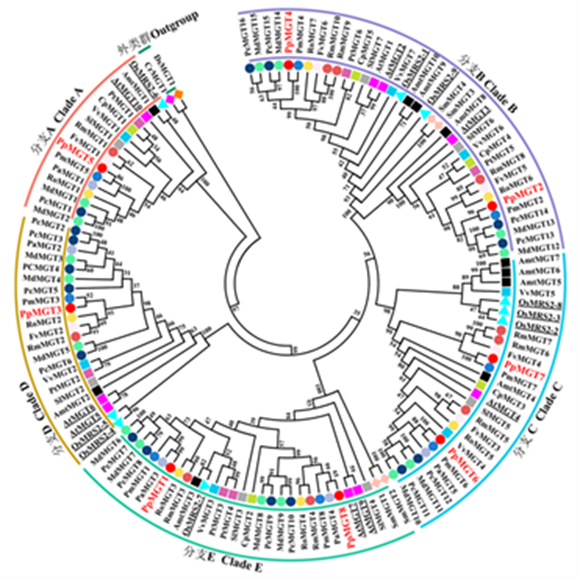

Fig. 2 Evolutionary analysis of MGT family members Prunus persica(Pp, ),Arabidopsis thaliana(At, ),Oryza sativa(Os, ),Carica papaya(Cp, ),Populus trichocarpa(Pt, ),Solanum lycopersicum(Sl, ),Vitis vinifera(Vv, ),Amborella trichopoda(Amt, ),Malus × domestica(Md, ),Pyrus communis(Pc, ),Prunus mume(Pm, ),Rubus occidentalis(Ro, ),Fragaria vesca(Fv, ),Prunus avium(Pa, ),Rosa multiflora (Rm, ),Selaginella moellendorffii(Sm, ),Chlamydomonas reinhardti(Cr, ),and Dunaliella salina(Ds, ).
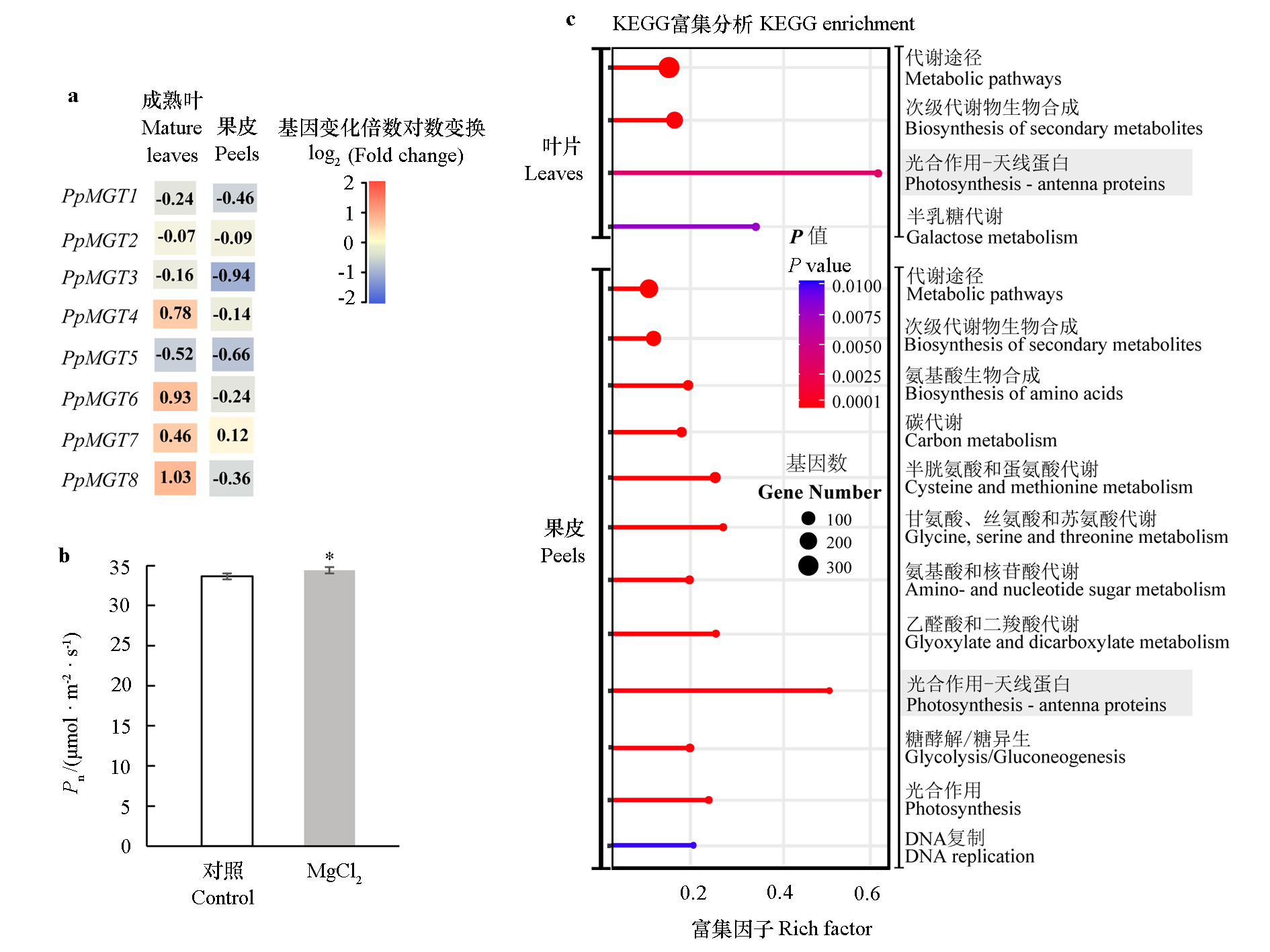
Fig. 7 Gene expressional changes(a),photosynthetic rate comparison(b)and metabolic pathway enrichment analysis(c)after magnesium treatment * represents a significant difference between treatment and control group(Student t-test).

Fig. 8 Expressional changes of Light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein complex(LHC)genes(a)and their correlative relations to MGTs transcriptional changes(b) Symbols * or ** indicate that the corresponding genes were differentially expressed in control-treatment comparisons at P < 0.05 or P < 0.01 levels,analyzing by DEseq2.
| [27] |
doi: 10.1038/s41477-020-0686-3 pmid: 32541951 |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
doi: S1674-2052(17)30380-5 pmid: 29275166 |
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
doi: 10.1021/bi4007397 pmid: 23781956 |
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
doi: S1674-2052(17)30296-4 pmid: 28989088 |
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [48] |
|
|
王勇军. 2019. 甘蔗MGT基因家族鉴定与缺镁胁迫的转录组动力学研究[硕士论文]. 福州: 福建农林大学.
|
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0506 |
|
文婷, 李婧, 张家琪, 魏仪, 祝文睿, 倪德江, 王明乐. 2023. 树镁转运子基因CsMGT6的表达和功能鉴定. 园艺学报, 50 (10):2171-2182.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0506 |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
|
许迎港, 邹智, 郭静远, 孔华, 朱国鹏, 郭安平. 2022. 番木瓜镁离子转运蛋白基因CpMGT1的克隆与功能分析. 热带作物学报, 43 (6):1114-1121.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2022.06.003 |
|
| [55] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
|
丛悦玺, 骆东峰, 陈坤明, 蒋立希, 郭万里. 2012. 生物镁离子转运体研究进展. 农业生物技术学报, 20 (7):837-848.
|
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erl201 pmid: 17101715 |
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
|
周平, 林志楷, 郭瑞, 颜少宾, 张小丹, 马昕怡, 金光. 2021. 低温处理对桃树叶片基因表达及类黄酮合成代谢的影响. 农业生物技术学报, 29 (7):1283-1294.
|
|
| [15] |
doi: 10.1093/aob/mcu245 pmid: 25550144 |
| [16] |
pmid: 12753976 |
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0197 |
|
贾亚敏, 徐浩, 胡文朗, 王玉雯, 叶欣, 陈立松, 李延, 郭九信. 2022. 缺镁对柑橘苗铁的吸收及亚细胞分布和化学形态的影响. 园艺学报, 49 (5):973-983.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0197 |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [1] | REN Siyuan, CHEN Sen, LONG Zhijian, WANG Boya, TANG Dengguo, WANG Zhengqian, YANG Bin, HU Shanglian, and CAO Ying, . Nitrogen Allocation Characteristics and Expression of Related Genes During Corm-Forming Stage of Amorphophallus konjac [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(9): 2019-2030. |
| [2] | CUI Yiqiong, LI Ju, LIU Xiaoqi, WANG Junwen, TANG Zhongqi, WU Yue, XIAO Xuemei, YU Jihua. Effects of Water Deficiency on Sucrose and Starch Metabolism of Substrate Culture Tomato in Greenhouse [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(11): 2607-2619. |
| [3] | HAN Shiwen, LIU Tao, WANG Liping, LI Nanyang, WANG Suna, and WANG Xing, . Genome-Wide Identification and Stress-Responsive Expression Analysis of the Cucumber SRS Gene Family [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(10): 2281-2296. |
| [4] | YOU Qian, LIU Xiao, LIU Mengmeng, LIU Dan, BO Chen, ZHU Yanfang, DUAN Yongbo, XUE Jianping, ZHANG Aimin, and XUE Tao. Identification and Bioinformatics Analysis of the HSF Family Gene in Pinellia ternata [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(10): 2371-2385. |
| [5] | YE Yufan, WANG Yujie, FU Qianyuan, WANG Lu, HAO Xinyuan, DING Changqing, WANG Xinchao, CAO Hongli, LI Nana. Cloning and Expression Analysis of Mg-Chelatase H Subunit Gene CsChlH in Tea Plant(Camellia sinensis) [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(1): 91-102. |
| [6] | PAN Jiajia, ZHANG Dongmei, MENG Jian, GAO Sunan, ZHU Kaijie, LIU Junwei, LI Guohuai. Optimization and Validation of PpPDS Gene Silencing Induced by Prunus Necrotic Ring Spot Virus in Prunus persica [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(7): 1587-1600. |
| [7] | WANG Xiaochen, NIE Ziye, LIU Xianju, DUAN Wei, FAN Peige, LIANG Zhenchang. Effects of Abscisic Acid on Monoterpene Synthesis in‘Jingxiangyu’Grape Berries [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 237-249. |
| [8] | SHEN Yuxiao, ZOU Jinyu, LUO Ping, SHANG Wenqian, LI Yonghua, HE Songlin, WANG Zheng, SHI Liyun. Genome-wide Identification and Abiotic Stress Response Analysis of PP2C Family Genes in Rosa chinensis‘Old Blush’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(10): 2139-2156. |
| [9] | WEN Ting, LI Jing, ZHANG Jiaqi, WEI Yi, ZHU Wenrui, NI Dejiang, WANG Mingle. Expression and Functional Identification of Magnesium Transporter Gene CsMGT6 in Camellia sinensis [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(10): 2171-2182. |
| [10] | ZHAI Hanhan, ZHAI Yujie, TIAN Yi, ZHANG Ye, YANG Li, WEN Zhiliang, CHEN Haijiang. Genome-wide Identification of Peach SAUR Gene Family and Characterization of PpSAUR5 Gene [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(1): 1-14. |
| [11] | ZHANG Qiuyue, LIU Changlai, YU Xiaojing, YANG Jiading, FENG Chaonian. Screening of Reference Genes for Differentially Expressed Genes in Pyrus betulaefolia Plant Under Salt Stress by qRT-PCR [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1557-1570. |
| [12] | JIA Yamin, XU Hao, HU Wenlang, WANG Yuwen, YE Xin, CHEN Lisong, LI Yan, GUO Jiuxin. Magnesium Deficiency Altered in Iron Absorption,Subcellular Distribution,and Chemical Forms in Citrus Seedlings [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(5): 973-983. |
| [13] | LI Yamei, MA Fuli, ZHANG Shanqi, HUANG Jinqiu, CHEN Mengting, ZHOU Junyong, SUN Qibao, SUN Jun. Optimization of Jujube Callus Transformation System and Application of ZjBRC1 in Regulating ZjYUCCA Expression [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(4): 749-757. |
| [14] | WANG Ying, AI Penghui, LI Shuailei, KANG Dongru, LI Zhongai, WANG Zicheng. Identification and Expression Analysis of Genes Related to DNA Methylation in Chrysanthemum × morifolium and C. nankingense [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(4): 827-840. |
| [15] | LÜ Yan, DUAN Weijun. TaqMan MGB-based Real-time Fluorescence PCR Method for the Rapid Detection of Ciborinia camelliae [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(3): 663-670. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd