
园艺学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (11): 2483-2494.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-1008
• 遗传育种·种质资源·分子生物学 • 下一篇
杨娟博, 郭丽丽, 卢世雄, 苟惠敏, 王帅珽, 曾宝珍, 毛娟*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-07-18
修回日期:2024-08-29
出版日期:2024-12-12
发布日期:2024-11-25
通讯作者:
基金资助:
YANG Juanbo, GUO Lili, LU Shixiong, GOU Huimin, WANG Shuaiting, ZENG Baozhen, MAO Juan*( )
)
Received:2024-07-18
Revised:2024-08-29
Published:2024-12-12
Online:2024-11-25
摘要:
为了研究GH3.17在草莓中对盐胁迫的响应,克隆了FaGH3.17,分析其进化关系、编码蛋白的理化性质等,进行烟草亚细胞定位以及拟南芥异源过表达,验证其在盐胁迫中的功能。结果表明,FaGH3.17为酸性且不稳定的疏水性非分泌性蛋白,主要定位在细胞核和细胞膜。FaGH3.17与蕨麻的亲缘关系最近。盐胁迫下,异源过表达FaGH3.17拟南芥株系的电导率、MDA含量、H2O2含量均高于野生型,分别升高了15.43%、42.97%、18.86%,而Pro含量、POD、SOD及CAT活性均显著低于野生型,分别降低了13.28%、15.42%、14.22%、19.87%,并且盐响应相关基因的相对表达量均显著降低,表明异源过表达FaGH3.17显著降低了拟南芥的抗氧化酶活性和渗透调节物质含量,预示着GH3.17可能会减弱植株的耐盐性。
杨娟博, 郭丽丽, 卢世雄, 苟惠敏, 王帅珽, 曾宝珍, 毛娟. 草莓FaGH3.17基因的克隆及功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(11): 2483-2494.
YANG Juanbo, GUO Lili, LU Shixiong, GOU Huimin, WANG Shuaiting, ZENG Baozhen, MAO Juan. Cloning and Functional Analysis of FaGH3.17 Gene in Strawberry[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(11): 2483-2494.
| 基因 Gene | 上游引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 下游引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| FaGH3.17 | ACAGTTGATCTGGTGGATGTGAAGC | ACGGAACTGAGGAGCATTGTTGTG |
| AtHKT1 | GTCTCTGCCATCACCGTCTCTTC | GCCACCGAGGAACATGAGGATAG |
| AtSOS1 | TCATCTCCCGCCGCATTATCAC | GATTGCTCTTGCTCTCGTCTCAAC |
| AtNHX1 | TTGACAAGTGGAGATCCGTGAGTG | TGCTCTTCCAACCATGACCAGAC |
| AtAPX1 | CTCTGGGACGATGCCACAAG | CTCGACCAAAGGACGGAAAA |
| AtActin2 | CTGGCCTACGTGGCACTTGACTT | AGCGATGGCTGGAACAGAAC |
表1 实时荧光定量引物序列
Table 1 Sequence of real-time fluorescence quantitative primers
| 基因 Gene | 上游引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 下游引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| FaGH3.17 | ACAGTTGATCTGGTGGATGTGAAGC | ACGGAACTGAGGAGCATTGTTGTG |
| AtHKT1 | GTCTCTGCCATCACCGTCTCTTC | GCCACCGAGGAACATGAGGATAG |
| AtSOS1 | TCATCTCCCGCCGCATTATCAC | GATTGCTCTTGCTCTCGTCTCAAC |
| AtNHX1 | TTGACAAGTGGAGATCCGTGAGTG | TGCTCTTCCAACCATGACCAGAC |
| AtAPX1 | CTCTGGGACGATGCCACAAG | CTCGACCAAAGGACGGAAAA |
| AtActin2 | CTGGCCTACGTGGCACTTGACTT | AGCGATGGCTGGAACAGAAC |

图4 FaGH3.17异源过表达拟南芥的鉴定(A)及其盐胁迫15 d的表型(B) M:DL2000 marker;+:阳性对照;-:阴性对照;WT:野生型;OE:异源过表达株系。下同。
Fig. 4 Identification of FaGH3.17 heterologously overexpressing Arabidopsis thaliana(A)and phenotypic observation of overexpressing Arabidopsis thaliana under salt stress 15 days(B) M:DL2000 marker;+:Positive control;-:Negative control;WT:Wild type;OE:Heterologous overexpression strain. The same below.
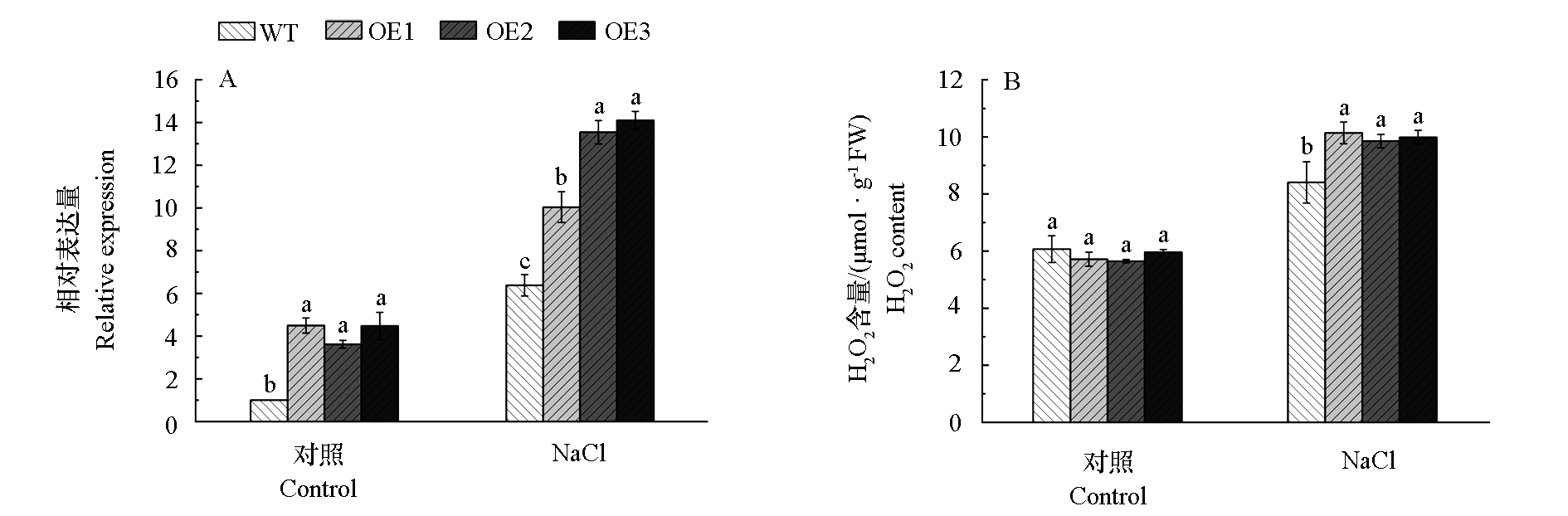
图5 盐胁迫15 d后FaGH3.17在野生型和异源过表达拟南芥中的表达量(A)及过氧化氢含量(B) 小写字母代表显著性水平(P < 0.05)。下同。
Fig. 5 Analysis of FaGH3.17 heterologously expression(A)and hydrogen peroxide content(B)in overexpressing Arabidopsis thaliana after salt stress 15 days Lowercase letters represent significance level at P < 0.05. The same below.

图6 FaGH3.17异源过表达拟南芥在盐胁迫下的细胞质膜渗透性分析
Fig. 6 Analysis of cytoplasmic membrane permeability under salt stress in FaGH3.17 heterologously overexpressing Arabidopsis thaliana

图7 盐胁迫下FaGH3.17异源过表达拟南芥中抗氧化酶的活性
Fig. 7 Determination of antioxidant enzyme activities of FaGH3.17 heterologously overexpressing Arabidopsis thaliana under salt stress
| [1] |
doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.3310 pmid: 10600390 |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-16240-5 pmid: 29162903 |
| [5] |
|
|
郭丽丽, 卢世雄, 乃国洁, 任家玄, 苟惠敏, 陈佰鸿, 毛娟. 2023. 凤梨草莓和森林草莓GH3基因家族的鉴定与表达分析. 植物生理学报, 59 (3):579-598.
|
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.1007/BF00410211 pmid: 24254049 |
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
|
姜丽娟. 2022. 苹果MdMYB94及其靶基因MdGH3.6的抗旱功能分析[博士论文]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学.
|
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
|
刘慧洁. 2020. 水稻花期特异表达的转录因子OsbZIPX的功能研究[硕士论文]. 金华: 浙江师范大学.
|
|
| [15] |
|
|
刘晓东, 王若仲, 焦彬彬, 代培红, 李月. 2016. 拟南芥IAA酰胺合成酶GH3-6负调控干旱和盐胁迫的反应. 植物学报, 51 (5):586-593.
doi: 10.11983/CBB15223 |
|
| [16] |
|
|
刘勇, 王泽琼, 龚林忠, 王富荣, 王会良, 艾小艳, 何华平. 2020. 桃乙烯应答因子PpERF1a的克隆与功能分析. 园艺学报, 47 (6):1165-1171.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2019-0872 |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.6.5.645 pmid: 8038604 |
| [18] |
|
|
卢世雄. 2021. 葡萄Trihelix转录因子家族鉴定及VvTrihelix5响应盐胁迫功能研究[硕士论文]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学.
|
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
|
马梦楠, 刘媛, 马锋旺, 邹养军. 2021. 苹果MdGH3-2/12在盐胁迫下的功能分析. 干旱地区农业研究, 39 (6):39-52.
|
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1701 pmid: 21959131 |
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.026690 pmid: 15659623 |
| [27] |
|
|
苏代发, 童江云, 杨俊誉, 陈杉艳, 罗志伟, 沈雪梅, 赖泳红,
|
|
| [28] |
|
|
孙涛, 柴团耀, 刘戈宇, 张玉秀. 2008. 植物GH3基因家族研究进展. 生物工程学报,(11):1860-1866.
|
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0743 |
|
孙雪丽, 刘范, 田娜, 项蕾蕾, 郝向阳, 王云, 彭丽云, 王天池, 程春振, 赖钟雄. 2019. 香蕉Aux/IAA基因家族的全基因组鉴定及表达分析. 园艺学报, 46 (10):1919-1935.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0743 |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
|
王楚侨, 黄一梅, 罗弦, 贾永霞, 唐姗姗. 2023. 外源ABA对低温胁迫下火龙果苗活性氧代谢的影响. 西北植物学报, 43 (8):1344-1351.
|
|
| [33] |
|
|
谢小芳, 黄勤怡, 吴为人. 2010. 植物GH3基因家族的生物信息学分析. 基因组学与应用生物学, 29 (5):829-837.
|
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
|
杨建宇. 2022. 外源亚精胺在增强番茄盐碱胁迫耐性中信号转导和转录调控功能研究[博士论文]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学.
|
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
|
袁馨, 徐云鹤, 张雨培, 单楠, 陈楚英, 万春鹏, 开文斌, 翟夏琬, 陈金印, 甘增宇. 2023. 猕猴桃后熟过程中ABA响应结合因子AcAREB1调控AcGH3.1的表达. 园艺学报, 50 (1):53-64.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-1086 |
|
| [38] |
|
|
曾洪学. 2015. 盐胁迫条件下草莓的生理生态表现及提高草莓耐盐性的途径. 黑龙江农业科学,(3):43-46.
|
|
| [39] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2016-0388 |
|
曾文芳, 王小贝, 潘磊, 牛良, 鲁振华, 崔国朝, 王志强. 2017. 桃Aux/IAA家族基因鉴定及在果实成熟过程中的表达分析. 园艺学报, 44 (2):233-244.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2016-0388 |
|
| [40] |
|
|
曾亚, 丁新华, 沈祥陵, 李香花, 王石平. 2008. 水稻抗病基因介导的抗白叶枯病反应中蛋白质表达谱的比较分析. 中国水稻科学,(3):234-242.
|
|
| [41] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0932 |
|
翟含含, 翟宇杰, 田义, 张叶, 杨丽, 温陟良, 陈海江. 2023. 桃SAUR家族基因分析及PpSAUR5功能鉴定. 园艺学报, 50 (1):1-14.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0932 |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
|
朱宇斌, 孔莹莹, 王君晖. 2014. 植物生长素响应基因SAUR的研究进展. 生命科学, 26 (4):407-413.
|
| [1] | 刘宇香, 韩风庆, 赵鑫雨, 刘玉梅, 李占省, 方智远, . 青花菜侧枝调控基因BoBRC1的克隆及功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 1997-2007. |
| [2] | 李文静, 石 硕, 张 郝, 张江燕, 宋思豪, 杨爱珍, 沈元月, 郭家选, 高 凡, . 外源NO与腐胺对草莓幼苗抗旱性的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2131-2142. |
| [3] | 丁新伦, 张 洁, 吴祖建. 草莓上新发现的病毒研究现状与展望[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1639-1648. |
| [4] | 王佩云, 李子昂, 白杨, 杨萍, 尹承芃, 李传荣, 张馨文, 宋秀华. ‘海黄’牡丹芳樟醇合酶基因PsTPS14的克隆及功能验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1273-1283. |
| [5] | 仲钊江, 吴震, 周蓉, 朱为民, 杨学东, 于筱薇, 徐艳, 高扬杨, 蒋芳玲. 番茄果胶裂解酶基因SlPL参与调控裂果机制研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 295-308. |
| [6] | 冯志娟, 刘娜, 张古文, 卜远鹏, 王斌, 龚亚明. 菜用大豆GmDi19-3启动子对盐胁迫和外源ABA、MeJA的响应[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(12): 2791-2799. |
| [7] | 袁青云, 韩昱, 贺巍, 苏会, 班秋艳, 吴春来, 周琼琼, 徐文静, 王丽鸳, 张芬. 茶树CsNPF6.1/6.3基因克隆及ABA转运功能验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(12): 2817-2828. |
| [8] | 杨雪, 胡进红, 李晶晶, 章英才, 王玲霞, 梁文裕. 宁夏枸杞TGA2转化拟南芥增强其耐盐性[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(12): 2829-2842. |
| [9] | 赵 霞, 李 刚, 刘丽锋, 胡盼盼, 宋艳红, 周厚成. 草莓新品种‘华丰 1 号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 35-36. |
| [10] | 刘金莹, 孔令喜, 王威浩, 秦国政, 王豫颖. 草莓果实香气物质生物合成研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(9): 1959-1970. |
| [11] | 高鹏飞, 高冰, 冯郑红, 吴建慧. 绢毛委陵菜PsWRKY40的克隆与耐镉功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(6): 1269-1283. |
| [12] | 阚丽平, 石晓倩, 杨晗, 金雨濛, 陈丽妍, 张丽娟, 徐阳春, 沈其荣, 董彩霞. 梨果实钾转运体基因PbKT12的克隆与功能验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(4): 713-723. |
| [13] | 袁华招, 庞夫花, 王静, 蔡伟建, 夏瑾, 赵密珍. 草莓花色苷物质鉴定及关键基因表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(4): 791-801. |
| [14] | 饶智雄, 安玉艳, 曹荣祥, 唐泉, 汪良驹. 外源ALA缓解ABA抑制草莓根系伸长生长的机理研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(3): 461-474. |
| [15] | 宋艳红, 陈亚铎, 张晓玉, 宋盼, 刘丽锋, 李刚, 赵霞, 周厚成. 森林草莓FvbHLH130转录因子调控植株提前开花[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 295-306. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司