
园艺学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (4): 791-801.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0066
收稿日期:2022-11-28
修回日期:2023-03-07
出版日期:2023-04-25
发布日期:2023-04-27
通讯作者:
*(E-mail:njzhao@163.com)
基金资助:
YUAN Huazhao, PANG Fuhua, WANG Jing, CAI Weijian, XIA Jin, ZHAO Mizhen( )
)
Received:2022-11-28
Revised:2023-03-07
Online:2023-04-25
Published:2023-04-27
Contact:
*(E-mail:njzhao@163.com)
摘要:
建立了应用HPLC-MS/MS快速分离、鉴定草莓花色苷的方法,并对不同果色12个草莓品种的成熟果实进行花色苷定量和定性分析,同时对比分析草莓(Fragaria × ananassa,八倍体)和森林草莓(F. vesca,二倍体)基因组中花色苷合成相关基因的数量和染色体定位,通过RNA-Seq和qRT-PCR分析它们在果实发育过程中的转录水平变化。在草莓中检测到8种花色苷,包括首次检测到的芍药素-3-葡萄糖苷、芍药素-丙二酰葡糖苷和芍药素-3-甲基丙二酰葡糖苷。不同果色草莓果实中总花色苷含量差异较大,均以天竺葵素-3-葡糖苷为主。草莓基因组包含73个花色苷合成相关基因,是森林草莓的3 ~ 4倍,均匀分布在4套亚基因组上。RNA-Seq结果显示整体上多拷贝基因在草莓果实中的表达水平没有显著差异,未发生明显的偏向性表达。花色苷合成关键路径基因(PAL1、CHS、CHI、F3H、DFR1、ANS、UFGT),转运基因(GST)和转录因子基因MYB10在草莓果实成熟过程中表达量显著增加,尤其是花色苷积累期,表明这些基因在草莓果实花色苷积累中起关键作用。
中图分类号:
袁华招, 庞夫花, 王静, 蔡伟建, 夏瑾, 赵密珍. 草莓花色苷物质鉴定及关键基因表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(4): 791-801.
YUAN Huazhao, PANG Fuhua, WANG Jing, CAI Weijian, XIA Jin, ZHAO Mizhen. Identification of Anthocyanin Compositions and Expression Analysis of Key Related Genes in Fragaria × ananassa[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(4): 791-801.
| 基因Gene | 正向引物(5′-3′)Forword primer | 反向引物(5′-3′)Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| FaPAL1 | CAGTGACCAACCATGTCCAG | TCCTCCAAATGCCTCAAATC |
| FaCHS | GCCTGAGAAGTTAGAAGCCACG | CGAACCCAAACAGAACACCC |
| FaCHI | AGCATCACCCTCTACCCTCAT | ACCCACTGCACCCATAGCTG |
| FaF3H | TGTGGCGTTTGAGTCCGAGA | TGACGAGCTGATGGGGTTGG |
| FaDFR1 | CAGGGTTTGAGTTCAAGTACAGC | TATCGCCATTCTCCTGCTTCT |
| FaANS | ATCTTCTCCTTGGGCGGCTC | AACATGGTTCCCGGTCTGCA |
| FaUFGT | CAAGCAATCCAACAGCTCAATC | GAAAACATACCCCTCCGGCAC |
| FaGST | CAAGTTCCAGCAATCGAAGA | TGGGAAGGATCACAAGTTGA |
| FaMYB10 | GAGAAGGCAAATGGCATCAT | TTCATCCTCTGCAAACTCTCC |
表1 qRT-PCR引物
Table 1 Primers used for qRT-PCR
| 基因Gene | 正向引物(5′-3′)Forword primer | 反向引物(5′-3′)Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| FaPAL1 | CAGTGACCAACCATGTCCAG | TCCTCCAAATGCCTCAAATC |
| FaCHS | GCCTGAGAAGTTAGAAGCCACG | CGAACCCAAACAGAACACCC |
| FaCHI | AGCATCACCCTCTACCCTCAT | ACCCACTGCACCCATAGCTG |
| FaF3H | TGTGGCGTTTGAGTCCGAGA | TGACGAGCTGATGGGGTTGG |
| FaDFR1 | CAGGGTTTGAGTTCAAGTACAGC | TATCGCCATTCTCCTGCTTCT |
| FaANS | ATCTTCTCCTTGGGCGGCTC | AACATGGTTCCCGGTCTGCA |
| FaUFGT | CAAGCAATCCAACAGCTCAATC | GAAAACATACCCCTCCGGCAC |
| FaGST | CAAGTTCCAGCAATCGAAGA | TGGGAAGGATCACAAGTTGA |
| FaMYB10 | GAGAAGGCAAATGGCATCAT | TTCATCCTCTGCAAACTCTCC |
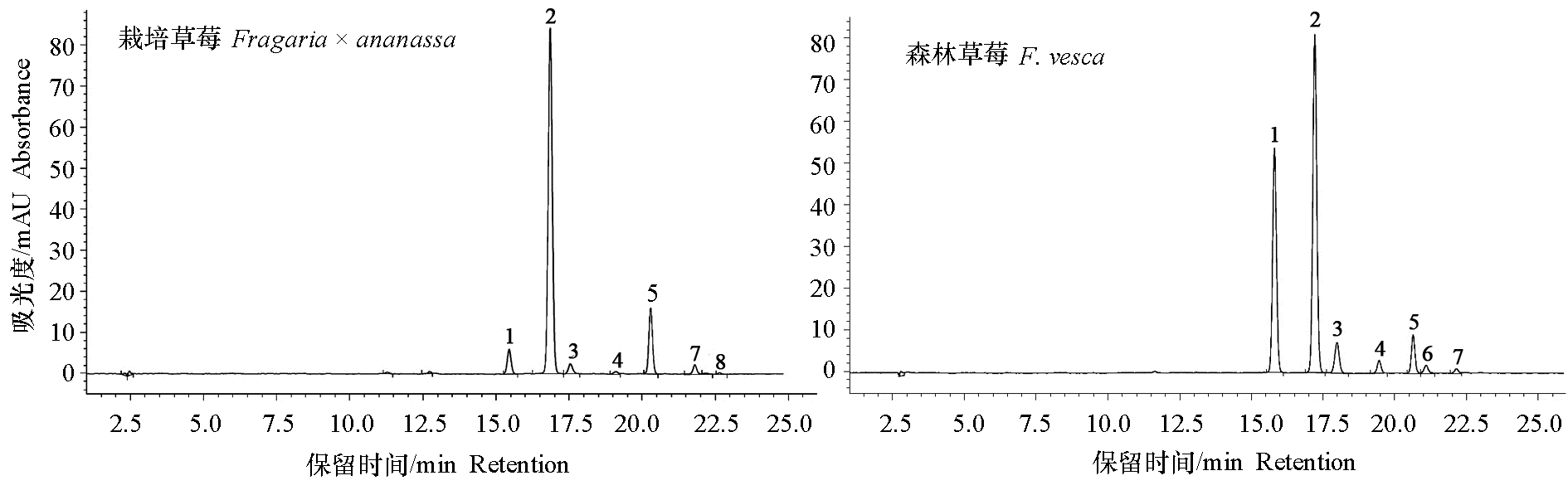
图1 栽培草莓和森林草莓果实花色苷在520 nm处的HPLC峰图
Fig. 1 Elution profile of anthocyanins in Fragaria × ananassa and F. vesca strawberry ripening fruit on HPLC under wavelength of 520 nm
| 组分 Peak No. | 保留时间/min Retention time | MS[M+H]/(m/z) | MS2/(m/z) | 化合物 Compound |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15.47 | 449 | 287 | 矢车菊素-3-葡糖苷* Cyanidin-3-glucoside* |
| 2 | 16.86 | 433 | 271 | 天竺葵素-3-葡糖苷* Pelargonidin-3-glucoside* |
| 3 | 17.73 | 463 | 301,286 | 芍药素-3-葡糖苷Peonidin-3-O-glucoside |
| 4 | 19.12 | 535 | 287 | 矢车菊素-丙二酰葡糖苷Cyanidin- malonylglucoside |
| 5 | 20.23 | 519 | 271 | 天竺葵素-丙二酰葡糖苷Pelargonidin-malonylglucoside |
| 6 | 20.73 | 549 | 301,286 | 芍药素-丙二酰葡糖苷Peonidin-malonylglucoside |
| 7 | 21.74 | 533 | 271 | 天竺葵素-3-甲基丙二酰基葡糖苷Pelargonidin-3-methylmalonylglucoside |
| 8 | 22.05 | 563 | 301,286 | 芍药素-3-甲基丙二酰基葡糖苷Peonidin-3-methylmalonylglucoside |
表2 草莓果实中花色苷成分的HPLC-MS/MS分析
Table 2 HPLC-MS/MS analysis of anthocyanins in strawberry fruit
| 组分 Peak No. | 保留时间/min Retention time | MS[M+H]/(m/z) | MS2/(m/z) | 化合物 Compound |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15.47 | 449 | 287 | 矢车菊素-3-葡糖苷* Cyanidin-3-glucoside* |
| 2 | 16.86 | 433 | 271 | 天竺葵素-3-葡糖苷* Pelargonidin-3-glucoside* |
| 3 | 17.73 | 463 | 301,286 | 芍药素-3-葡糖苷Peonidin-3-O-glucoside |
| 4 | 19.12 | 535 | 287 | 矢车菊素-丙二酰葡糖苷Cyanidin- malonylglucoside |
| 5 | 20.23 | 519 | 271 | 天竺葵素-丙二酰葡糖苷Pelargonidin-malonylglucoside |
| 6 | 20.73 | 549 | 301,286 | 芍药素-丙二酰葡糖苷Peonidin-malonylglucoside |
| 7 | 21.74 | 533 | 271 | 天竺葵素-3-甲基丙二酰基葡糖苷Pelargonidin-3-methylmalonylglucoside |
| 8 | 22.05 | 563 | 301,286 | 芍药素-3-甲基丙二酰基葡糖苷Peonidin-3-methylmalonylglucoside |

图2 不同果色的12个草莓品种成熟果实及其总花色苷含量(μg · g-1)
Fig. 2 Pictures and total contents of anthocyanins in ripe fruits of twelve strawberry cultivars with different fruit colors
| 品种 Cultivar | 各组分占比/% Percentage of each anthocyanin component | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |
| 四季香 Sijixiang | 4.25 ± 0.18 | 81.11 ± 3.42 | 6.05 ± 0.26 | ND | 8.59 ± 0.36 | ND | ND | ND |
| 明旭Mingxu | 3.32 ± 0.14 | 64.02 ± 2.71 | 6.15 ± 0.26 | 0.82 ± 0.03 | 22.93 ± 0.97 | ND | 2.76 ± 0.12 | ND |
| 97-17-1 | 5.47 ± 0.17 | 75.19 ± 2.28 | 7.18 ± 0.22 | ND | 12.16 ± 0.37 | ND | ND | ND |
| 97-4-17 | 5.11 ± 0.31 | 75.84 ± 4.54 | 8.52 ± 0.51 | ND | 10.53 ± 0.63 | ND | ND | ND |
| 甜查理 Sweet Charlie | 3.24 ± 0.17 | 70.65 ± 3.66 | 10.07 ± 0.52 | ND | 12.35 ± 0.64 | ND | 3.69 ± 0.19 | ND |
| 幸香 Sachinoka | 6.80 ± 0.49 | 79.23 ± 5.73 | 7.66 ± 0.55 | ND | ND | 0.87 ± 0.06 | ND | 5.44 ± 0.39 |
| 久59-1 Jiu 59-1 | 11.21 ± 0.69 | 78.46 ± 4.86 | 9.28 ± 0.57 | ND | ND | 1.05 ± 0.06 | ND | ND |
| 宁丰 Ningfeng | 9.83 ± 0.43 | 75.53 ± 3.29 | 14.64 ± 0.64 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 紫金久红 Zijin Jiuhong | 9.97 ± 0.59 | 83.17 ± 4.96 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | 6.86 ± 0.41 |
| 香Xiang | 10.54 ± 0.52 | 76.47 ± 3.75 | 12.99 ± 0.64 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 枥木少女 Tochiotome | 14.13 ± 0.92 | 72.38 ± 4.71 | 13.49 ± 0.88 | 1.23 ± 0.08 | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 桃熏Tokun | 14.00 ± 0.90 | 49.64 ± 3.20 | 15.27 ± 0.99 | ND | 21.09 ± 1.36 | ND | ND | ND |
| 平均值 Average | 8.16 ± 0.46 | 73.47 ± 3.93 | 10.12 ± 0.50 | 1.03 ± 0.06 | 14.61 ± 0.72 | 0.96 ± 0.06 | 3.23 ± 0.15 | 6.15 ± 0.04 |
表3 不同果色的12个草莓品种成熟果实中各花色苷组分占比
Table 3 Percentage of each anthocyanin component in the total content in twelve strawberry cultivars with different fruit colors
| 品种 Cultivar | 各组分占比/% Percentage of each anthocyanin component | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |
| 四季香 Sijixiang | 4.25 ± 0.18 | 81.11 ± 3.42 | 6.05 ± 0.26 | ND | 8.59 ± 0.36 | ND | ND | ND |
| 明旭Mingxu | 3.32 ± 0.14 | 64.02 ± 2.71 | 6.15 ± 0.26 | 0.82 ± 0.03 | 22.93 ± 0.97 | ND | 2.76 ± 0.12 | ND |
| 97-17-1 | 5.47 ± 0.17 | 75.19 ± 2.28 | 7.18 ± 0.22 | ND | 12.16 ± 0.37 | ND | ND | ND |
| 97-4-17 | 5.11 ± 0.31 | 75.84 ± 4.54 | 8.52 ± 0.51 | ND | 10.53 ± 0.63 | ND | ND | ND |
| 甜查理 Sweet Charlie | 3.24 ± 0.17 | 70.65 ± 3.66 | 10.07 ± 0.52 | ND | 12.35 ± 0.64 | ND | 3.69 ± 0.19 | ND |
| 幸香 Sachinoka | 6.80 ± 0.49 | 79.23 ± 5.73 | 7.66 ± 0.55 | ND | ND | 0.87 ± 0.06 | ND | 5.44 ± 0.39 |
| 久59-1 Jiu 59-1 | 11.21 ± 0.69 | 78.46 ± 4.86 | 9.28 ± 0.57 | ND | ND | 1.05 ± 0.06 | ND | ND |
| 宁丰 Ningfeng | 9.83 ± 0.43 | 75.53 ± 3.29 | 14.64 ± 0.64 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 紫金久红 Zijin Jiuhong | 9.97 ± 0.59 | 83.17 ± 4.96 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | 6.86 ± 0.41 |
| 香Xiang | 10.54 ± 0.52 | 76.47 ± 3.75 | 12.99 ± 0.64 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 枥木少女 Tochiotome | 14.13 ± 0.92 | 72.38 ± 4.71 | 13.49 ± 0.88 | 1.23 ± 0.08 | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 桃熏Tokun | 14.00 ± 0.90 | 49.64 ± 3.20 | 15.27 ± 0.99 | ND | 21.09 ± 1.36 | ND | ND | ND |
| 平均值 Average | 8.16 ± 0.46 | 73.47 ± 3.93 | 10.12 ± 0.50 | 1.03 ± 0.06 | 14.61 ± 0.72 | 0.96 ± 0.06 | 3.23 ± 0.15 | 6.15 ± 0.04 |

图3 花色苷合成关键基因在二倍体森林草莓(Fragaria vesca)和八倍体草莓(F. × ananassa)基因组(Subgenome 1 ~ 4)上的位置
Fig. 3 Chromosomal locations of genes involved in anthocyanins biosynthesis on the Fragaria vesca(2 ×)genome and four F. × ananassa(8×)subgenomes

图5 ‘红颊’草莓果实发育过程中花色苷合成相关基因表达的qRT-PCR检测 G1:小绿期;G2:中绿期;G3:大绿期;G4:白果期;G5:转色期;G6:半红;G7:全红。
Fig. 5 Real-time PCR analysis of expression for genes involved in anthocyanins biosynthesis during strawberry fruit development G1:Small green fruit stage;G2:Middle green fruit stage;G3:Big green fruit stage;G4:White fruit stage;G5:Turn red stage;G6:Half red stage;G7:Full red stage.
| [1] |
Aharoni A, de Vos C H, Wein M, Sun Z, Greco R, Kroon A, Mol J N, O'Connell A P. 2001. The strawberry FaMYB 1 transcription factor suppresses anthocyanin and flavonol accumulation in transgenic tobacco. Plant Journal, 28 (3):319-332.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.01154.x pmid: 11722774 |
| [2] |
Edger P P, Poorten T J, van Buren R, Hardigan M A, Colle M, McKain M R, Smith R D, Teresi S J, Nelson A D L, Wai C M, Alger E I, Bird K A, Yocca A E, Pumplin N, Ou S, Ben-Zvi G, Brodt A, Baruch K, Swale T, Shiue L. 2019. Origin and evolution of the octoploid strawberry genome. Nature Genetics, 51:541-547.
doi: 10.1038/s41588-019-0356-4 pmid: 30804557 |
| [3] |
Espley R V, Hellens R P, Putterill J, Stevenson D E, Kutty-Amma S, Allan A C. 2007. Red colouration in apple fruit is due to the activity of the MYB transcription factor,MdMYB10. The Plant Journal, 49:414-427.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.2007.49.issue-3 URL |
| [4] |
Gao Q, Luo H F, Li Y P, Liu Z C, Kang C Y. 2020. Genetic modulation of RAP alters fruit coloration in both wild and cultivated strawberry. Plant Biotechnol J, 18 (7):1550-1561.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.13317 pmid: 31845477 |
| [5] |
Griesser M, Hoffmann T, Bellido M L, Rosati C, Fink B, Kurtzer R, Aharoni A, Muñoz-Blanco J, Schwab W. 2008. Redirection of flavonoid biosynthesis through the down-regulation of an anthocyanidin glucosyltransferase in ripening strawberry fruit. Plant Physiology, 146 (4):1528-1539.
doi: 10.1104/pp.107.114280 pmid: 18258692 |
| [6] | Han Hai-hua, Liang Ming-zhi, Wang Li, Luo Qiong-xian, Zhao Tian-tian. 2011. Research progress of anthocyanin. Journal of Tea, 37 (4):217-220. (in Chinese) |
| 韩海华, 梁名志, 王丽, 罗琼仙, 赵甜甜. 2011. 花青素的研究进展及其应用. 茶叶, 37 (4):217-220. | |
| [7] |
Hegarty M J, Barker G L, Wilson I D, Abbott R J, Edwards K J, Hiscock S J. 2006. Transcriptome shock after interspecific hybridization in senecio is ameliorated by genome duplication. Current Biology, 16:1652-1659.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2006.06.071 pmid: 16920628 |
| [8] |
Hong Yanhong, Ye Qinghua, Li Zekun, Wang Wei, Xie Qian, Chen Qingxi, Chen Jianqing. 2021. Accumulation of anthocyanins in red-flowered strawberry‘Meihong’petals and expression analysis of MYB gene. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 48 (8):1470-1484. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0477 |
|
洪燕红, 叶清华, 李泽坤, 王威, 谢倩, 陈清西, 陈建清. 2021. 红花草莓‘莓红’花瓣花色苷积累及其MYB基因的表达分析. 园艺学报, 48 (8):1470-1484.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0477 |
|
| [9] |
Jiang Wei-wei, Ren Guo-feng. 2009. Review on anti-tumor effect of anthocyanin. Food Science, 30 (9):281-284. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-200909066 |
| 姜伟伟, 任国峰. 2009. 花色苷的抗肿瘤效应研究进展. 食品科学, 30 (9):281-284. | |
| [10] |
Li Lixian, Wang Shuo, Chen Ying, Wu Yingtao, Wang Yaqian, Fang Yue, Chen Xuesen, Tian Changping, Feng Shouqian. 2022. PavMYB10.1 promotes anthocyanin accumulation by positively regulating pavriant in sweet cherry. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 49 (5):1023-1030. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0732 |
|
李丽仙, 王烁, 陈莹, 邬滢涛, 王雅倩, 房月, 陈学森, 田长平, 冯守千. 2022. 甜樱桃PavMYB10.1促进PavRiant表达和花青苷积累. 园艺学报, 49 (5):1023-1030.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0732 |
|
| [11] | Lin B W, Gong C C, Song H F, Cui Y Y. 2017. Effects of anthocyanins on the prevention and treatment of cancer. British Journal of Pharmacology, 174 (11):1126-1128. |
| [12] |
Liu Jian-li, Liu Xiao, Cao Xiang-yu, Yu Hui, Yang Si-min, Sun Yu-hang. 2015. Purification and in vitro antioxidant activity of anthocyanins from Padus racemose. Food Science, 36 (15):5-10. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.1111/jfds.1971.36.issue-1 URL |
|
刘剑利, 刘晓, 曹向宇, 于慧, 杨思敏, 孙宇航. 2015. 稠李花色苷的纯化及体外抗氧化活性. 食品科学, 36 (15):5-10.
doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201515002 |
|
| [13] |
Lopes-da-Silva F, de Pascual-Teresa S, Rivas-Gonzalo J. 2002. Identification of anthocyanin pigments in strawberry(cv Camarosa)by LC using DAD and ESI-MS detection. European Food Research and Technology, 214:248-253.
doi: 10.1007/s00217-001-0434-5 URL |
| [14] |
Lopes-da-Silva F, Escribano-Bailón M T, Pérez-Alonso J J, Rivas-Gonzalo J, Santos-Buelga C. 2007. Anthocyanin pigments in strawberry. Food Science and Technology, 40 (2):374-382.
doi: 10.1590/fst.17419 URL |
| [15] | Luo Yun, Chen Zong-ling, Song Wei-tang, Wang Hong-qing. 2014. Identification and analysis for anthocyanins compositions in strawberry. Journal of China Agricultural Aniversity, 19 (5):86-94. (in Chinese) |
| 罗赟, 陈宗玲, 宋卫堂, 王红清. 2014. 草莓果实花色苷成分组成鉴定及分析. 中国农业大学学报, 19 (5):86-94. | |
| [16] |
Njuguna W, Liston A, Cronn R, Ashman T L, Bassil N. 2013. Insights into phylogeny,sex function and age of Fragaria based on whole chloroplast genome sequencing. Mol Phylogenet Evol, 66:17-29.
doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2012.08.026 pmid: 22982444 |
| [17] |
Opes-da-Silva F, de Pascual-Teresa S, Rivas-Gonzalo J, Santos-Buelga C. 2002. Identification of anthocyanin pigments in strawberry(cv Camarosa) by LC using DAD and ESI-MS detection. European Food Research and Technology, 214:248-253.
doi: 10.1007/s00217-001-0434-5 URL |
| [18] |
Paolocci F, Robbins M P, Passeri V, Hauck B, Morris P, Rubini A, Arcioni S, Damiani F. 2010. The strawberry transcription factor FaMYB1inhibits the biosynthesis of proanthocyanidins in Lotus corniculatus leaves. J Exp Bot, 62 (3):1189-1200.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erq344 URL |
| [19] |
Sun J H, Liu X J, Yang T B, Yang T B, Slovin J, Chen P. 2014. Profiling polyphenols of two diploid strawberry(Fragaria vesca)inbred lines using UHPLC-HRMS. Food Chemistry, 146:289-298.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.08.089 URL |
| [20] |
Wang H, Zhang H, Yang Y, Li M, Zhang Y, Liu J, Dong J, Li J, Butelli E, Xue Z, Wang A, Wang G, Martin C, Jin W. 2020. The control of red colour by a family of MYB transcription factors in octoploid strawberry(Fragaria × ananassa)fruits. Plant Biotechnol Journal, 18:1169-1184.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.v18.5 URL |
| [21] |
Wang Z G, Meng D, Wang A D, Li T L, Jiang S L, Cong P H, Li T Z. 2013. The methylation of the PcMYB 10 promoter is associated with green-skinned sport in max red bartlett pear. Plant Physiology, 162 (2):885-896.
doi: 10.1104/pp.113.214700 URL |
| [22] |
Yang Xiaofang, Zhang Zuying, Miao Lixiang, Zhang Yuchao, Shen Lan, Qin Qiaoping, Jiang Guihua. 2020. Preliminary analysis on the molecular differences of fruit colouring between yuexin strawberry and its somaclonal mutation. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47 (10):1999-2008. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2019-0996 URL |
| 杨肖芳, 张祖瑛, 苗立祥, 张豫超, 沈岚, 秦巧平, 蒋桂华. 2020. ‘越心’草莓组培突变体着色差异的分子机理初探. 园艺学报, 47 (10):1999-2008. | |
| [23] |
Yuan H Z, Pang F H, Cai W J, Chen X D, Zhao M Z, Yu H M. 2021. Genome-wide analysis of the invertase genes in strawberry(Fragaria × ananassa). Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 20 (10):2652-2665.
doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(20)63381-0 URL |
| [24] | Zhang Qiong, Wang Hong-qing, Leng Ping, Jia Le-xin. 2008. Mechanism of anthocyanins and flavonols in fruit development of strawberries. Journal of China Agricultural Aniversity, 35 (12):1735-1741. (in Chinese) |
| 张琼, 王红清, 冷平, 贾乐新. 2008. 草莓果实发育过程中花色苷和黄酮醇类物质的形成机制. 园艺学报, 35 (12):1735-1741. | |
| [25] | Zhao Mi-zhen, Wang Jin, Wang Zhuang-wei, Qian Ya-ming, Wu Wei-min. 2012. Development status of strawberry industry in the world and sustainable development countermeasures of Strawberry industry in Jiangsu,Zhejiang and Shanghai. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 40 (2):1-3. (in Chinese) |
| 赵密珍, 王静, 王壮伟, 钱亚明, 吴伟民. 2012. 世界草莓产业发展现状及江浙沪草莓产业可持续发展对策. 江苏农业科学, 40 (2):1-3. |
| [1] | 阚丽平, 石晓倩, 杨晗, 金雨濛, 陈丽妍, 张丽娟, 徐阳春, 沈其荣, 董彩霞. 梨果实钾转运体基因PbKT12的克隆与功能验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(4): 713-723. |
| [2] | 唐海霞, 裴广营, 张琼, 王中堂. 枣果实相关性状QTL定位分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(4): 754-764. |
| [3] | 常晓晓, 郭新波, 叶宇童, 彭程, 陈慧琼, 潘建平, 邱继水, 陆育生. ‘早丰黄皮’和‘鸡心黄皮’果实糖、酸和多酚及抗氧化活性差异分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(4): 778-790. |
| [4] | 李玉梅, 娄玉穗, 王小龙, 马玉全, 王海波, 吕中伟. ‘夏黑’葡萄高品质果园植株叶片和土壤营养诊断研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(4): 864-874. |
| [5] | 田晓成, 祝令成, 邹晖, 李白云, 马锋旺, 李明军. 果实可溶性糖的积累模式及其调控研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(4): 885-895. |
| [6] | 饶智雄, 安玉艳, 曹荣祥, 唐泉, 汪良驹. 外源ALA缓解ABA抑制草莓根系伸长生长的机理研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(3): 461-474. |
| [7] | 赖恒鑫, 李文广, 彭良志, 何义仲, 朱攀攀, 杨万云, 凌丽俐, 付行政, 淳长品, 曹立. 沃柑果实春夏季留树保鲜品质变化研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(3): 485-494. |
| [8] | 马帅辉, 何光琪, 程一哲, 郭大龙. 5-azaC对‘巨峰’葡萄果实发育阶段mRNA可变剪接的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(3): 523-533. |
| [9] | 宋艳红, 陈亚铎, 张晓玉, 宋盼, 刘丽锋, 李刚, 赵霞, 周厚成. 森林草莓FvbHLH130转录因子调控植株提前开花[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 295-306. |
| [10] | 朱炜, 曹津津, 陈曦, 张葳, 孙榕泽, 朱绍才, 赵家庚, 崔雅琦, 王宇暄, 于晓南. 芍药新品种‘粉罗裙’‘千重粉黛’‘笑春风’和‘碧叶粉荷’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 457-458. |
| [11] | 蒋靖东, 韦壮敏, 王楠, 朱晨桥, 叶俊丽, 谢宗周, 邓秀新, 柴利军. 山金柑四倍体资源的发掘与鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 27-35. |
| [12] | 杨植, 张川疆, 杨芯芳, 董梦怡, 王振磊, 闫芬芬, 吴翠云, 王玖瑞, 刘孟军, 林敏娟. 枣与酸枣杂交后代果实遗传倾向及混合遗传分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 36-52. |
| [13] | 何成勇, 赵晓丽, 许腾飞, 高德航, 李世访, 王红清. 草莓病毒1山东分离物全基因组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 153-160. |
| [14] | 邵凤清, 罗秀荣, 王奇, 张宪智, 王文彩. 果实成熟过程中的DNA甲基化调控研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 197-208. |
| [15] | 杨 雷, 李 莉, 董 辉, 冯 佳, 张建军, 范婧芳, 杨秋叶, 杨 莉, . 草莓新品种‘石莓11号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 79-80. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司