
园艺学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (7): 1535-1546.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0431
汪红秀1, 周上铃2, 何绍国3, 田再泽3, 马静华3, 彭良志1, 淳长品1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-12-15
修回日期:2023-04-03
出版日期:2023-07-25
发布日期:2023-07-26
通讯作者:
基金资助:
WANG Hongxiu1, ZHOU Shangling2, HE Shaoguo3, TIAN Zaize3, MA Jinghua3, PENG Liangzhi1, CHUN Changpin1,*( )
)
Received:2022-12-15
Revised:2023-04-03
Published:2023-07-25
Online:2023-07-26
摘要:
以四川安岳和重庆铜梁70个尤力克柠檬果园的果实和叶片为试验材料,测定其果实品质和叶片主要营养元素,通过建立柠檬果实品质综合评价模型,将柠檬果园分为优质果园和普通果园,根据果园等级制定尤力克柠檬叶片营养诊断标准。结果表明:果实品质主成分分析提取了4个主成分,其累计贡献率为80.54%,根据主成分分析结果计算各个果园综合评分并排序,作为划分果园等级的指标。对柠檬叶片营养元素研究表明,N、K、Zn、B营养元素遵循正态分布,P、Ca、Mg、S、Fe、Mn、Cu近似χ2分布;对于符合正态分布的元素采用4点5分段的概率分级法,将其分为缺乏、偏低、适宜、偏高和过量5个级别,对于不符合正态分布的元素参考优质果园的叶片营养元素值和现有标准进行矫正,初步制定了尤力克柠檬叶片营养元素的诊断标准。
汪红秀, 周上铃, 何绍国, 田再泽, 马静华, 彭良志, 淳长品. 尤力克柠檬叶片营养元素标准的研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(7): 1535-1546.
WANG Hongxiu, ZHOU Shangling, HE Shaoguo, TIAN Zaize, MA Jinghua, PENG Liangzhi, CHUN Changpin. Study on the Standard of Nutrient Elements Contents in Eureka Lemon Leaves[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(7): 1535-1546.
| 项目 Iteam | 平均值 Mean | 最大值 Maximum | 最小值 Minimum | 变异系数/% CV | 标准差 SD | 主成分Principal component | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||||||
| 单果质量/g Single fruit weigh(SFW) | 161.21 | 226.49 | 105.28 | 18.39 | 29.65 | -0.692 | -0.302 | -0.081 | 0.585 |
| 果皮厚度/mm Peel thickness(PT) | 6.42 | 8.48 | 4.28 | 12.28 | 0.79 | 0.576 | 0.357 | 0.550 | -0.326 |
| 果形指数Fruit shape index(FSI) | 1.25 | 1.52 | 1.02 | 6.82 | 0.09 | 0.513 | 0.285 | -0.265 | 0.251 |
| 果汁率/% Juice rate(JR) | 32.60 | 70.53 | 24.80 | 18.09 | 5.90 | 0.152 | -0.147 | 0.792 | 0.503 |
| 可溶性固形物/% Soluble solids content(TSS) | 8.13 | 10.05 | 6.60 | 7.99 | 0.65 | 0.859 | 0.007 | 0.058 | 0.267 |
| 可滴定酸/% Titratable acid content(TA) | 5.96 | 7.01 | 5.34 | 6.40 | 0.38 | 0.676 | 0.033 | -0.238 | 0.344 |
| 维生素C/(mg ·L-1) Vitamin C content | 492.27 | 674.98 | 350.68 | 15.37 | 7.56 | 0.816 | 0.224 | -0.245 | 0.102 |
| 果面亮度L | 79.78 | 87.57 | 44.48 | 8.93 | 7.12 | 0.705 | -0.553 | -0.246 | -0.097 |
| 红绿色差a* | -5.56 | -3.21 | -18.02 | 42.98 | 2.39 | -0.008 | 0.954 | 0.079 | 0.087 |
| 黄蓝色差b* | 47.37 | 55.59 | 29.75 | 8.78 | 4.16 | 0.507 | -0.694 | 0.257 | -0.176 |
| 特征值 Eigenvalue | 3.710 | 2.070 | 1.260 | 1.010 | |||||
| 贡献率/% Contribution rate | 37.110 | 20.720 | 12.590 | 10.120 | |||||
| 累计贡献率/% Cumulative contribution rate | 37.110 | 57.830 | 70.420 | 80.540 | |||||
表1 果实品质数据特征与主成分分析
Table 1 Fruit quality characteristics and principal component analysis of data
| 项目 Iteam | 平均值 Mean | 最大值 Maximum | 最小值 Minimum | 变异系数/% CV | 标准差 SD | 主成分Principal component | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||||||
| 单果质量/g Single fruit weigh(SFW) | 161.21 | 226.49 | 105.28 | 18.39 | 29.65 | -0.692 | -0.302 | -0.081 | 0.585 |
| 果皮厚度/mm Peel thickness(PT) | 6.42 | 8.48 | 4.28 | 12.28 | 0.79 | 0.576 | 0.357 | 0.550 | -0.326 |
| 果形指数Fruit shape index(FSI) | 1.25 | 1.52 | 1.02 | 6.82 | 0.09 | 0.513 | 0.285 | -0.265 | 0.251 |
| 果汁率/% Juice rate(JR) | 32.60 | 70.53 | 24.80 | 18.09 | 5.90 | 0.152 | -0.147 | 0.792 | 0.503 |
| 可溶性固形物/% Soluble solids content(TSS) | 8.13 | 10.05 | 6.60 | 7.99 | 0.65 | 0.859 | 0.007 | 0.058 | 0.267 |
| 可滴定酸/% Titratable acid content(TA) | 5.96 | 7.01 | 5.34 | 6.40 | 0.38 | 0.676 | 0.033 | -0.238 | 0.344 |
| 维生素C/(mg ·L-1) Vitamin C content | 492.27 | 674.98 | 350.68 | 15.37 | 7.56 | 0.816 | 0.224 | -0.245 | 0.102 |
| 果面亮度L | 79.78 | 87.57 | 44.48 | 8.93 | 7.12 | 0.705 | -0.553 | -0.246 | -0.097 |
| 红绿色差a* | -5.56 | -3.21 | -18.02 | 42.98 | 2.39 | -0.008 | 0.954 | 0.079 | 0.087 |
| 黄蓝色差b* | 47.37 | 55.59 | 29.75 | 8.78 | 4.16 | 0.507 | -0.694 | 0.257 | -0.176 |
| 特征值 Eigenvalue | 3.710 | 2.070 | 1.260 | 1.010 | |||||
| 贡献率/% Contribution rate | 37.110 | 20.720 | 12.590 | 10.120 | |||||
| 累计贡献率/% Cumulative contribution rate | 37.110 | 57.830 | 70.420 | 80.540 | |||||
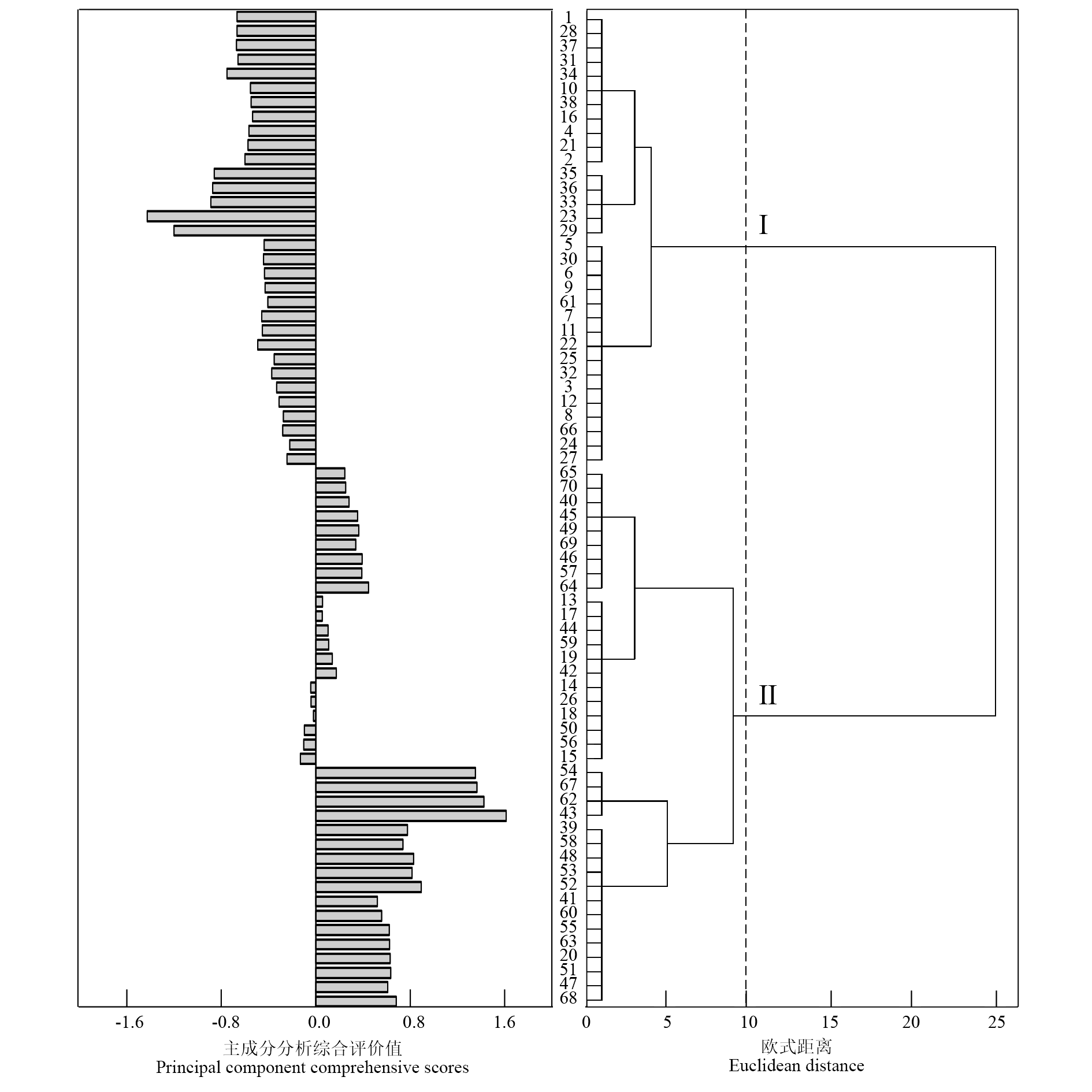
图1 尤力克柠檬果园(编号1 ~ 70)果实品质主成分分析综合评价值(左)及其Ward聚类(欧氏距离)图(右)
Fig. 1 Principal component comprehensive scores of fruit quality(left)and its Ward clustering(Euclidean distance)Plot(right)in Eureka lemon orchards(No. 1-70)
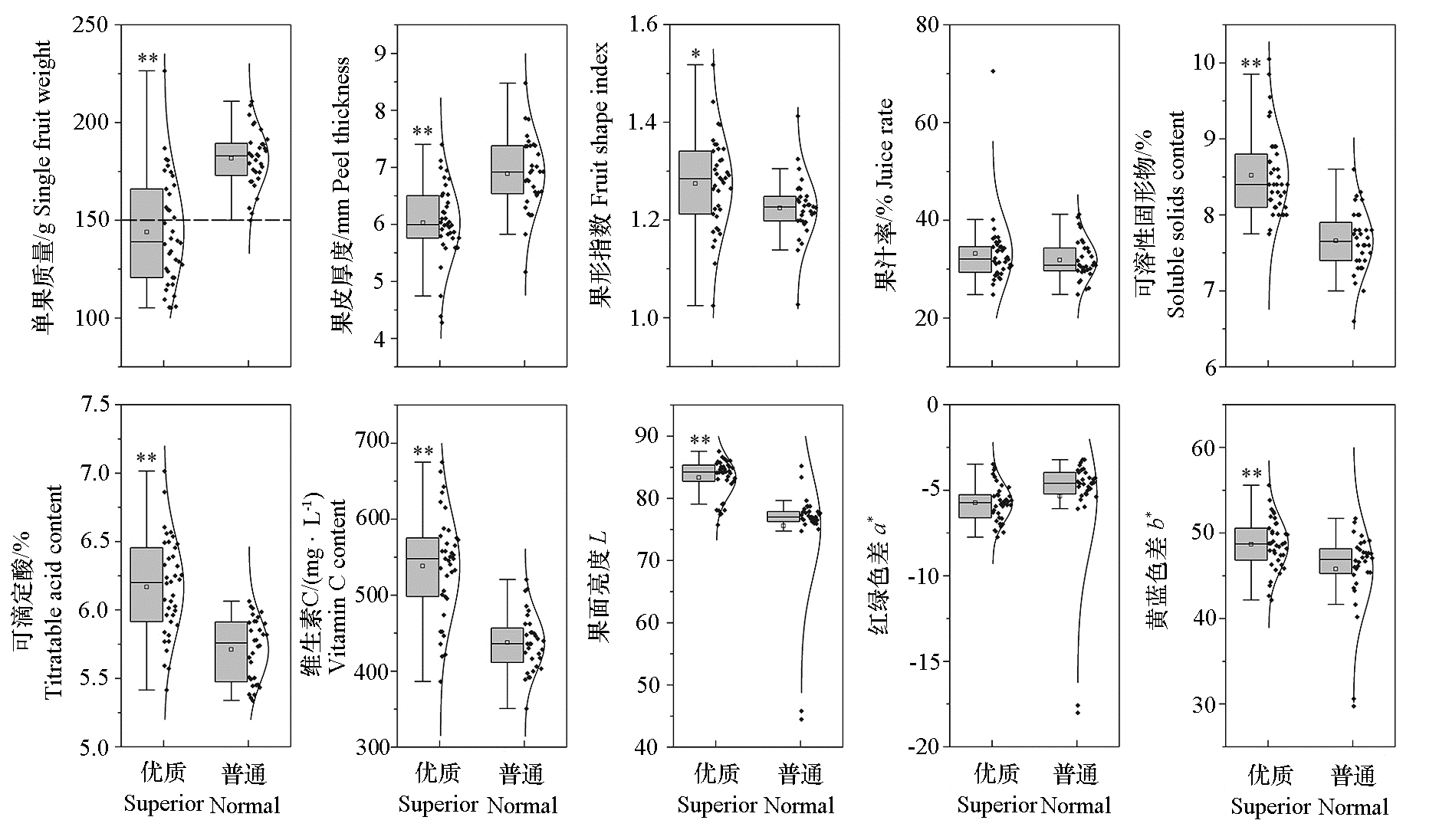
图2 尤力克柠檬优质果园(n = 38)和普通果园(n = 32)的果实品质 使用t检验计算P值。* 表示在0.05水平差异显著;** 表示在0.01水平差异显著。
Fig. 2 Fruit quality in superior(n = 38)and normal(n = 32)orchards of Eureka lemon P values were calculated using t-test. * indicates significantly difference at 0.05 level;** indicates significantly difference at 0.01 level.
| 元素 Element | 西班牙柠檬适宜值参考 Spanish lemon suitable value reference | 优质果园不同养分等级占比/% Percentage of different nutrient levels in superior quality orchards | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 缺乏 Deficiency | 偏低 Lower | 适宜 Normal | 偏高 Higher | 过量 Excess | ||
| N/% | 2.30 ~ 2.50 | 52.63 | 34.21 | 10.53 | 2.63 | 0 |
| P/% | 0.10 ~ 0.12 | 0 | 5.26 | 86.85 | 7.89 | 0 |
| K/% | 0.90 ~ 1.10 | 15.79 | 47.37 | 36.84 | 0 | 0 |
| Ca/% | 3.50 ~ 5.00 | 0 | 5.26 | 71.05 | 23.69 | 0 |
| Mg/% | 0.40 ~ 0.50 | 60.53 | 31.58 | 7.89 | 0 | 0 |
| S/% | — | 0 | 0 | 89.47 | 10.53 | 0 |
| Fe/(mg · kg-1) | 80.00 ~ 150.00 | 0 | 5.26 | 81.58 | 10.53 | 2.63 |
| Mn/(mg · kg-1) | 40.00 ~ 80.00 | 0 | 0 | 100.00 | 0 | 0 |
| Zn/(mg · kg-1) | — | 26.31 | 60.53 | 13.16 | 0 | 0 |
| Cu/(mg · kg-1) | — | 0 | 36.84 | 60.53 | 2.63 | 0 |
| B/(mg · kg-1) | — | 0 | 2.63 | 92.11 | 5.26 | 0 |
表2 西班牙柠檬叶营养元素含量参考及优质果园营养元素含量状况
Table 2 Reference of nutrient elements in Spanish lemon leaves and nutrient elements in superior quality orchards
| 元素 Element | 西班牙柠檬适宜值参考 Spanish lemon suitable value reference | 优质果园不同养分等级占比/% Percentage of different nutrient levels in superior quality orchards | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 缺乏 Deficiency | 偏低 Lower | 适宜 Normal | 偏高 Higher | 过量 Excess | ||
| N/% | 2.30 ~ 2.50 | 52.63 | 34.21 | 10.53 | 2.63 | 0 |
| P/% | 0.10 ~ 0.12 | 0 | 5.26 | 86.85 | 7.89 | 0 |
| K/% | 0.90 ~ 1.10 | 15.79 | 47.37 | 36.84 | 0 | 0 |
| Ca/% | 3.50 ~ 5.00 | 0 | 5.26 | 71.05 | 23.69 | 0 |
| Mg/% | 0.40 ~ 0.50 | 60.53 | 31.58 | 7.89 | 0 | 0 |
| S/% | — | 0 | 0 | 89.47 | 10.53 | 0 |
| Fe/(mg · kg-1) | 80.00 ~ 150.00 | 0 | 5.26 | 81.58 | 10.53 | 2.63 |
| Mn/(mg · kg-1) | 40.00 ~ 80.00 | 0 | 0 | 100.00 | 0 | 0 |
| Zn/(mg · kg-1) | — | 26.31 | 60.53 | 13.16 | 0 | 0 |
| Cu/(mg · kg-1) | — | 0 | 36.84 | 60.53 | 2.63 | 0 |
| B/(mg · kg-1) | — | 0 | 2.63 | 92.11 | 5.26 | 0 |
| 元素 Element | 缺乏 Deficiency | 偏低 Lower | 适宜 Normal | 偏高 Higher | 过量 Excess |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N/% | < 2.00 | 2.00 ~ 2.21 | 2.21 ~ 2.50 | 2.50 ~ 2.71 | > 2.71 |
| P/% | < 0.10 | 0.10 ~ 0.12 | 0.12 ~ 0.16 | 0.16 ~ 0.30 | > 0.30 |
| K/% | < 0.65 | 0.65 ~ 0.80 | 0.80 ~ 1.01 | 1.01 ~ 1.17 | > 1.17 |
| Ca/% | < 3.50 | 3.50 ~ 4.35 | 4.35 ~ 4.95 | 4.95 ~ 5.00 | > 5.00 |
| Mg/% | < 0.20 | 0.20 ~ 0.40 | 0.40 ~ 0.50 | 0.50 ~ 0.70 | > 0.70 |
| S/% | < 0.14 | 0.14 ~ 0.20 | 0.20 ~ 0.40 | 0.40 ~ 0.50 | > 0.50 |
| Fe/(mg · kg-1) | < 35.00 | 35.00 ~ 80.00 | 80.00 ~ 120.00 | 120.00 ~ 200.00 | > 200.00 |
| Mn/(mg · kg-1) | < 18.00 | 18.00 ~ 25.00 | 25.00 ~ 100.00 | 100.00 ~ 300.00 | > 300.00 |
| Zn/(mg · kg-1) | < 14.40 | 14.40 ~ 17.74 | 17.74 ~ 22.37 | 22.37 ~ 25.71 | > 25.71 |
| Cu/(mg · kg-1) | < 5.00 | 5.00 ~ 6.00 | 6.00 ~ 16.00 | 16.00 ~ 20.00 | > 20.00 |
| B/(mg · kg-1) | < 37.82 | 37.82 ~ 56.06 | 56.06 ~ 81.33 | 81.33 ~ 99.57 | > 99.57 |
表3 柠檬叶分析营养诊断标准值
Table 3 The standard value on analysis and diagnosis of nutrient element in leaves of lemon
| 元素 Element | 缺乏 Deficiency | 偏低 Lower | 适宜 Normal | 偏高 Higher | 过量 Excess |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N/% | < 2.00 | 2.00 ~ 2.21 | 2.21 ~ 2.50 | 2.50 ~ 2.71 | > 2.71 |
| P/% | < 0.10 | 0.10 ~ 0.12 | 0.12 ~ 0.16 | 0.16 ~ 0.30 | > 0.30 |
| K/% | < 0.65 | 0.65 ~ 0.80 | 0.80 ~ 1.01 | 1.01 ~ 1.17 | > 1.17 |
| Ca/% | < 3.50 | 3.50 ~ 4.35 | 4.35 ~ 4.95 | 4.95 ~ 5.00 | > 5.00 |
| Mg/% | < 0.20 | 0.20 ~ 0.40 | 0.40 ~ 0.50 | 0.50 ~ 0.70 | > 0.70 |
| S/% | < 0.14 | 0.14 ~ 0.20 | 0.20 ~ 0.40 | 0.40 ~ 0.50 | > 0.50 |
| Fe/(mg · kg-1) | < 35.00 | 35.00 ~ 80.00 | 80.00 ~ 120.00 | 120.00 ~ 200.00 | > 200.00 |
| Mn/(mg · kg-1) | < 18.00 | 18.00 ~ 25.00 | 25.00 ~ 100.00 | 100.00 ~ 300.00 | > 300.00 |
| Zn/(mg · kg-1) | < 14.40 | 14.40 ~ 17.74 | 17.74 ~ 22.37 | 22.37 ~ 25.71 | > 25.71 |
| Cu/(mg · kg-1) | < 5.00 | 5.00 ~ 6.00 | 6.00 ~ 16.00 | 16.00 ~ 20.00 | > 20.00 |
| B/(mg · kg-1) | < 37.82 | 37.82 ~ 56.06 | 56.06 ~ 81.33 | 81.33 ~ 99.57 | > 99.57 |
| [1] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2005.05.017 URL |
| [2] |
|
|
安贵阳, 范崇辉, 杜志辉, 郁俊谊, 邓丰产, 史联让. 2006. 苹果叶营养元素含量的影响因素分析. 园艺学报, 33 (1):12-16.
|
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.1080/00103629509369402 URL |
| [4] |
Chongqing Administration of Quality and Technology Supervision. 2013. The citrus of leaf nutrition diagnosis formulated fertilization technology regulations. DB50/T487-2012. Beijing: China Agriculture Press. (in Chinese)
|
|
重庆市质量技术监督局. 2013. 柑橘营养诊断配方施肥技术规程. DB50/T487-2012. 北京: 中国农业出版社.
|
|
| [5] |
|
|
樊卫国, 潘学军, 杨婳若, 陈红, 官纪元, 周禹佳, 穆瑞, 何春丽. 2022. 刺梨叶片营养元素与果实产量、维生素C含量的相关性及营养诊断标准值的建立. 贵州大学学报 (自然科学版), 39 (2):7-16.
|
|
| [6] |
|
|
范志懿, 刘佳嘉. 2020. 果树叶片营养诊断方法研究进展. 山西农业科学, 48 (12):2017-2022.
|
|
| [7] |
|
|
付行政, 彭良志, 邢飞, 凌丽俐, 淳长品, 江才伦, 曹立. 2014. 柑橘缺锌研究进展与展望. 果树学报, 31 (1):132-139.
|
|
| [8] |
General Administration of Quality Supervision,Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. 2011. Citrus fresh fruit inspection methods. GB/T 8210-2011. Beijing: Standards Press of China. (in Chinese)
|
|
国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 2011. 柑桔鲜果检验方法. GB/T 8210-2011. 北京: 中国标准出版社.
|
|
| [9] |
General Administration of Quality Supervision,Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. 2013. Lemon. GB/T 29370-2012. Beijing: Standards Press of China. (in Chinese)
|
|
国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 2013. 柠檬. GB/T 29370-2012. 北京: 中国标准出版社.
|
|
| [10] |
|
|
黄艳, 涂勋良, 马晓丽, 王进, 吕秀兰. 2019. 四川安岳8个柠檬品种果实品质分析. 食品工业科技, 40 (14):83-88.
|
|
| [11] |
|
|
贾学梅. 2017. 纽荷尔脐橙挂果能力对茎杆注射糖类和激素保果处理响应[硕士论文]. 重庆: 西南大学.
|
|
| [12] |
|
|
刘孟军. 1992. 桃树部分经济性状的种内变异及其分级标准研究. 北京农学院学报, 7 (2):98-104.
|
|
| [13] |
|
|
刘孟军. 1996. 枣树数量性状的概率分级研究. 园艺学报, 23 (2):105-109.
|
|
| [14] |
|
|
刘文欢. 2021. 基于养分平衡的柑橘高产优质叶片矿质营养诊断与施肥决策研究[硕士论文]. 重庆: 西南大学.
|
|
| [15] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-1071 |
|
鲁雅楠, 诸葛雅贤, 裴清圆, 马吾丹, 樊秀彩, 刘崇怀, 管乐, 房经贵. 2019. 葡萄种质资源果穗穗形调查与综合评价. 园艺学报, 46 (8):1593-1603.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-1071 |
|
| [16] |
doi: 10.1080/01904169309364613 URL |
| [17] |
|
|
牟红梅, 于强, 李庆余, 王义菊, 姜福东, 李元军, 薛敏, 王兆龙. 2019. 基于主成分分析的烟台地区西洋梨果实品质综合评价. 果树学报, 36 (8):1084-1092.
|
|
| [18] |
|
|
国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 2017. 食品中抗坏血酸的测定. GB 5009.86-2016. 北京: 中国标准出版社.
|
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.21273/HORTSCI.28.10.1041 URL |
| [20] |
|
|
阮科, 朱礼乾, 沈鑫健, 周上铃, 彭良志, 凌丽俐, 黄涛江, 刘文华, 淳长品. 2019. 奉节脐橙园土壤养分状况普查及其与叶片养分和产量相关性研究. 果树学报, 36 (4):458-467.
|
|
| [21] |
|
|
沈兆敏. 2014. 我国柠檬生产现状、优势机遇及发展对策建议. 果农之友,( 7):3-4,18.
|
|
| [22] |
The State Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision. 1990. Determination of titratable acidity of fruit and vegetable products. GB/T 12293- 1990. Beijing: Standards Press of China. (in Chinese)
|
|
国家技术监督局.
|
|
| [23] |
The State Forestry Administration of the People's Republic of China. 1999a. Determination of total nitrogen in forest plants and forest litter. LY/T 1269-1999. Beijing: State Forestry Administration of China. (in Chinese)
|
|
国家林业局. 1999a. 森林植物与森林枯枝落叶层全氮的测定. LY/T 1269-1999 北京: 国家林业局.
|
|
| [24] |
The State Forestry Administration of the People’s Republic of China. 1999b. etermination of total silicon,iron,aluminum,calcium,magnesium,potassium,sodium,phosphorus,sulfur,manganese,copper,and zinc in forest plants and forest litter. LY/T 1270-1999. Beijing: State Forestry Administration of China. (in Chinese)
|
|
国家林业局. 1999b. 森林植物与森林枯枝落叶层全硅、铁、铝、钙、镁、钾、钠、磷、硫、锰、铜、锌的测定. LY/T 1270-1999. 北京: 国家林业局.
|
|
| [25] |
The State Forestry Administration of the People's Republic of China. 1999c. Determination of total boron in forest plants and forest litter. LY/T 1273-1999. Beijing:State Forestry Administration of China. (in Chinese)
|
|
国家林业局. 1999c. 森林植物与森林枯枝落叶层全硼的测定. LY/T 1273-1999. 北京: 国家林业局.
|
|
| [26] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2004.01.025 URL |
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
|
王莉, 叶小梅, 杜静, 张应鹏, 蔺经, 奚永兰, 孔祥平. 2021. 江苏省苏翠1号梨叶养分标准值初探. 江苏农业学报, 37 (5):1278-1284.
|
|
| [29] |
|
|
谢祝英, 席志鸿, 钟全斌, 庄恩及, 王汉良, 金佩芳, 蔡奚平. 1982. 果树叶片中钾、钙、镁、铜、铁、锌、锰七个元素分析方法的研究——原子吸收分光光度法. 中国果树,(4):49-52,13.
|
|
| [30] |
|
|
薛鑫, 石胜友, 侯世奎. 2020. 龙眼‘蜀冠’ב大乌圆’杂交后代果实品质性状多样性分析及综合评价. 园艺学报, 47 (5):827-836.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2019-0531 |
|
| [31] |
|
|
杨惠栋, 淳长品, 彭良志, 付行政, 凌丽俐, 江才伦, 曹立, 袁高鹏, 张梦娇. 2016. 奉节脐橙树体营养状况研究. 中国南方果树, 45 (2):10-15.
|
|
| [32] |
|
|
杨葳. 2012. 紫色丘陵区土壤养分空间变异及肥力评价研究[硕士论文]. 重庆: 西南大学.
|
|
| [33] |
|
|
张继舟, 李云影, 袁磊, 吕品, 于志民, 王立民, 张悦. 2019. 大兴安岭地区笃斯越橘果实成熟期叶片矿质元素营养诊断. 果树学报, 36 (9):1161-1170.
|
|
| [34] |
|
|
张新生, 冉辛拓, 陈湖, 王召元, 傅友. 2008. 燕山山区苹果叶片氮、磷、钾含量标准范围的确定. 河北农业科学,( 8):14-15,24.
|
|
| [35] |
|
|
赵慧琴, 石立, 刘金山, 林海明. 2020. SPSS软件计算主成分分析的缺陷与纠正. 统计与决策, 36 (15):56-59.
|
|
| [36] |
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2018.12.014 |
|
郑永强, 王娅, 杨琼, 贾学梅, 何绍兰, 邓烈, 谢让金, 易时来, 吕强, 马岩岩. 2018. 重庆三峡库区鲍威尔脐橙花期叶片矿质营养诊断. 中国农业科学, 51 (12):2378-2390.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2018.12.014 |
|
| [37] |
|
|
周开隆, 叶荫民. 2010. 中国果树志 · 柑橘卷. 北京:中国林业出版社:203-204.
|
|
| [38] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0627 |
|
周高峰, 李碧娴, 付燕玲, 管冠, 姚锋先, 刘桂东. 2019. ‘南丰蜜橘’缺铁、锰、锌的症状及其光合特性和营养状况研究. 园艺学报, 46 (4):691-700.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0627 |
|
| [39] |
|
|
周鑫斌, 石孝均, 温明霞, 王秀英, 孙彭寿, 李伟, 戴亨林, 淳长品. 2011. 三峡重庆库区甜橙叶片矿质营养丰缺状况调查. 园艺学报, 38 (10):1847-1856.
|
| [1] | 樊 娟, 沈松真, 苗青青, 张乐辉, 姚恩鹏, 裴卓强. 番茄新品种‘卫红 16 号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 65-66. |
| [2] | 张印, 胡路艳, 王淑明, 景丹龙, 郭启高, 梁国鲁. ABA调控果实成熟研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(9): 1889-1898. |
| [3] | 何义仲, 庞尧, 孙浩谦, 李欣宇, 王振豪, 钱卫, 张印, 何发, 尹杭, 赖恒鑫, 淳长品, 付行政, 彭良志. 果实抗坏血酸生物合成、代谢循环及其调控的研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(9): 1899-1915. |
| [4] | 丁捷, 刘春燕, 黄彭, 李红莹, 陈黎维, 蒲小燕, 刘耀文, 秦文. 蓝莓保鲜技术研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(9): 1944-1958. |
| [5] | 刘金莹, 孔令喜, 王威浩, 秦国政, 王豫颖. 草莓果实香气物质生物合成研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(9): 1959-1970. |
| [6] | 张巧丽, 陈笛, 宋艳萍, 朱鸿亮, 罗云波, 曲桂芹. 番茄果实叶绿素代谢转录调控网络研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(9): 2031-2047. |
| [7] | 莫雨杏, 周 艳, 林润婷, 多泳星, 张 涛, 刘锴栋. 番木瓜CpWRI3参与调控果实成熟过程中脂肪酸合成[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1637-1648. |
| [8] | 张 茜, 赵秋燕, 谷志佳, 黄海泉, 鄢 波, 黄美娟, . 四川西南地区凤仙花属植物花粉微形态研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1664-1678. |
| [9] | 代红军, 魏 强, 贺 琰, 汪月宁, 王振平. 油菜素内酯对高温胁迫下葡萄花色苷合成及果实品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1711-1722. |
| [10] | 王 文, 张柯楠, 方莫扉, 丁思悦, 王雪飞, 惠竹梅, . 果袋颜色对‘赤霞珠’葡萄果皮花色苷积累的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1723-1738. |
| [11] | 陈敏, 吴天利, 吕远达, 姜波, 闫化学, 李娟, 钟云. 不同砧木红江橙容器栽培生长和果实品质分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(7): 1547-1562. |
| [12] | 杨孟霞, 刘晓林, 曹雪, 魏凯, 宁宇, 杨沛, 李珊珊, 陈紫月, 王孝宣, 国艳梅, 杜永臣, 李君明, 刘磊, 李鑫, 黄泽军. 番茄CRISPR/Cas9介导的多基因编辑技术体系构建与应用[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(6): 1215-1229. |
| [13] | 周成, 方怡, 周锦杨, 黄企浩, 盘永坚, 史千千, 倪慧娴, 杨震峰, 宋春波. 低温诱导的桃果实采后膜脂代谢变化与冷害的关系[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(6): 1305-1317. |
| [14] | 郭静, 廖满余, 金燕, 马小川, 张芬, 卢晓鹏, 邓子牛, 盛玲. 柑橘转录因子CsbHLH3调控柠檬酸代谢的功能解析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(5): 947-958. |
| [15] | 周平, 郭瑞, 颜少宾, 金光. 外源山梨醇影响桃叶片和果实糖代谢的分子机制研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(5): 959-971. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司