
园艺学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (9): 1899-1915.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0490
何义仲1,*, 庞尧2,*, 孙浩谦2, 李欣宇2, 王振豪2, 钱卫2, 张印2, 何发3, 尹杭1, 赖恒鑫1, 淳长品1, 付行政1, 彭良志1,**( )
)
收稿日期:2023-04-02
修回日期:2023-08-13
出版日期:2023-09-25
发布日期:2023-09-26
通讯作者:
作者简介:基金资助:
HE Yizhong1, PANG Yao2, SUN Haoqian2, LI Xinyu2, WANG Zhenhao2, QIAN Wei2, ZHANG Yin2, HE Fa3, YIN Hang1, LAI Hengxin1, CHUN Changpin1, FU Xingzheng1, PENG Liangzhi1,**( )
)
Received:2023-04-02
Revised:2023-08-13
Published:2023-09-25
Online:2023-09-26
Contact:
**(E-mail:pengliangzhi@cric.cn)
摘要:
对不同果实抗坏血酸(AsA,维生素C)积累特点、生物学功能和合成途径等进行了综述,分析了AsA受遗传与外在因素如光照、糖和激素等影响的共性问题,阐述转录因子、microRNA、DNA甲基化和翻译后修饰方式调控果实AsA合成与循环途径相关基因的模式,以期为后续果实AsA形成机制研究提供参考。
何义仲, 庞尧, 孙浩谦, 李欣宇, 王振豪, 钱卫, 张印, 何发, 尹杭, 赖恒鑫, 淳长品, 付行政, 彭良志. 果实抗坏血酸生物合成、代谢循环及其调控的研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(9): 1899-1915.
HE Yizhong, PANG Yao, SUN Haoqian, LI Xinyu, WANG Zhenhao, QIAN Wei, ZHANG Yin, HE Fa, YIN Hang, LAI Hengxin, CHUN Changpin, FU Xingzheng, PENG Liangzhi. Recent Advances in the Biosynthesis,Recycling and Regulation of Ascorbic Acid in Fruit[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(9): 1899-1915.
| 科 Family | 材料 Material | 每100 g或100 mL含量/mg Content per 100 g or 100 mL | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 禾本科Gramineae | 水稻Rice(Foliar) | ND ~ 4.65 | Ji et al., |
| 小麦Wheat | 0.54 ~ 0.38 | Nicolò et al., | |
| 玉米Maize | 10.11 ~ 22.17 | 杨若明和李玉田, | |
| 豆科Legume | 大豆Soybean | 3.52 ~ 7.47 | Kumar et al., |
| 茄科Solanaceae | 马铃薯Potato | 7.54 ~ 28.58 | Jiménez et al., |
| 蔷薇科Rosaceae | 刺梨Chestnut rose | 1 290.00 ~ 2 000.00 | Huang et al., |
| 玫瑰果Rose hip | 1 273.64 ~ 2 264.00 | 韩云和管正学, | |
| 金樱子Cherokee rose | 700.00 ~ 900.00 | 佘祥威 等, | |
| 木瓜Papaya | 31.50 ~ 62.50 | Farina et al., | |
| 草莓Strawberry | 28.80 ~ 88.70 | Mezzetti et al., | |
| 苹果Apple | 1.05 ~ 27.85 | Mellidou et al., | |
| 樱桃Cherry | 8.40 ~ 17.60 | Gündogdu & Bilge, | |
| 枇杷Loquat | 6.50 ~ 14.80 | Cai et al., | |
| 桃Peach | 1.00 ~ 14.00 | Gil et al., | |
| 梨Pear | 1.32 ~ 3.59 | Curi et al., | |
| 李Plum | 3.00 ~ 10.00 | Gil et al., | |
| 金虎尾科Malpighiaceae | 针叶樱桃Acerola | 800.00 ~ 4 000.00 | Nagy & Shaw, |
| 猕猴桃科Actinidiaceae | 猕猴桃Kiwifruit | 29.00 ~ 2 140.00 | Huang et al., |
| 胡桃科Juglandaceae | 核桃Walnut | 410.00 ~ 1 800.00 | Pyke et al., |
| 胡颓子科Elaeagnaceae | 沙棘Sea-buckthorn | 10.00 ~ 1 320.00 | 吕荣森, |
| 鼠李科Rhamnaceae | 枣Chinese jujube | 166.47 ~ 808.83 | 刘孟军和汪民, |
| 芸香科Rutaceae | 柑橘Citrus | 15.90 ~ 62.00 | Claudie et al., |
| 桃金娘科Myrtaceae | 番石榴 Guava | 136.50 ~ 220.40 | Adrees et al., |
| 柿科Ebenaceae | 柿Persimmon | 11.66 ~ 12.32 | Cardoso et al., |
| 漆树科Anacardiaceae | 杧果Mango | 17.01 ~ 50.71 | Sellamuthu et al., |
| 无患子科Sapindaceae Juss | 龙眼Longan | 44.65 ~ 79.23 | Wall, |
| 荔枝Litchi | 21.00 ~ 36.00 | Wall, | |
| 葡萄科Vitaceae | 葡萄Grape | 12.33 ~ 30.80 | Derradji et al., |
| 酢浆草科Oxalidaceae | 杨桃Carambola | 17.50 ~ 20.50 | Luximon et al., |
| 凤梨Bromeliaceae | 菠萝Pineapple | 5.08 ~ 33.57 | Lu et al., |
| 芭蕉科Musaceae | 香蕉Banana | 2.10 ~ 18.70 | Wall, |
| 番木瓜科 Caricaceae | 番木瓜Papaya | 36.30 ~ 67.80 | Wall, |
| 茄科Solanaceae | 番茄Tomato | 1.07 ~ 38.80 | Bhandari et al., |
表1 不同植物材料的果实或其他食用部位的AsA含量
Table 1 The content of AsA in the fruit or other edible tissues of different types of plant materials
| 科 Family | 材料 Material | 每100 g或100 mL含量/mg Content per 100 g or 100 mL | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 禾本科Gramineae | 水稻Rice(Foliar) | ND ~ 4.65 | Ji et al., |
| 小麦Wheat | 0.54 ~ 0.38 | Nicolò et al., | |
| 玉米Maize | 10.11 ~ 22.17 | 杨若明和李玉田, | |
| 豆科Legume | 大豆Soybean | 3.52 ~ 7.47 | Kumar et al., |
| 茄科Solanaceae | 马铃薯Potato | 7.54 ~ 28.58 | Jiménez et al., |
| 蔷薇科Rosaceae | 刺梨Chestnut rose | 1 290.00 ~ 2 000.00 | Huang et al., |
| 玫瑰果Rose hip | 1 273.64 ~ 2 264.00 | 韩云和管正学, | |
| 金樱子Cherokee rose | 700.00 ~ 900.00 | 佘祥威 等, | |
| 木瓜Papaya | 31.50 ~ 62.50 | Farina et al., | |
| 草莓Strawberry | 28.80 ~ 88.70 | Mezzetti et al., | |
| 苹果Apple | 1.05 ~ 27.85 | Mellidou et al., | |
| 樱桃Cherry | 8.40 ~ 17.60 | Gündogdu & Bilge, | |
| 枇杷Loquat | 6.50 ~ 14.80 | Cai et al., | |
| 桃Peach | 1.00 ~ 14.00 | Gil et al., | |
| 梨Pear | 1.32 ~ 3.59 | Curi et al., | |
| 李Plum | 3.00 ~ 10.00 | Gil et al., | |
| 金虎尾科Malpighiaceae | 针叶樱桃Acerola | 800.00 ~ 4 000.00 | Nagy & Shaw, |
| 猕猴桃科Actinidiaceae | 猕猴桃Kiwifruit | 29.00 ~ 2 140.00 | Huang et al., |
| 胡桃科Juglandaceae | 核桃Walnut | 410.00 ~ 1 800.00 | Pyke et al., |
| 胡颓子科Elaeagnaceae | 沙棘Sea-buckthorn | 10.00 ~ 1 320.00 | 吕荣森, |
| 鼠李科Rhamnaceae | 枣Chinese jujube | 166.47 ~ 808.83 | 刘孟军和汪民, |
| 芸香科Rutaceae | 柑橘Citrus | 15.90 ~ 62.00 | Claudie et al., |
| 桃金娘科Myrtaceae | 番石榴 Guava | 136.50 ~ 220.40 | Adrees et al., |
| 柿科Ebenaceae | 柿Persimmon | 11.66 ~ 12.32 | Cardoso et al., |
| 漆树科Anacardiaceae | 杧果Mango | 17.01 ~ 50.71 | Sellamuthu et al., |
| 无患子科Sapindaceae Juss | 龙眼Longan | 44.65 ~ 79.23 | Wall, |
| 荔枝Litchi | 21.00 ~ 36.00 | Wall, | |
| 葡萄科Vitaceae | 葡萄Grape | 12.33 ~ 30.80 | Derradji et al., |
| 酢浆草科Oxalidaceae | 杨桃Carambola | 17.50 ~ 20.50 | Luximon et al., |
| 凤梨Bromeliaceae | 菠萝Pineapple | 5.08 ~ 33.57 | Lu et al., |
| 芭蕉科Musaceae | 香蕉Banana | 2.10 ~ 18.70 | Wall, |
| 番木瓜科 Caricaceae | 番木瓜Papaya | 36.30 ~ 67.80 | Wall, |
| 茄科Solanaceae | 番茄Tomato | 1.07 ~ 38.80 | Bhandari et al., |
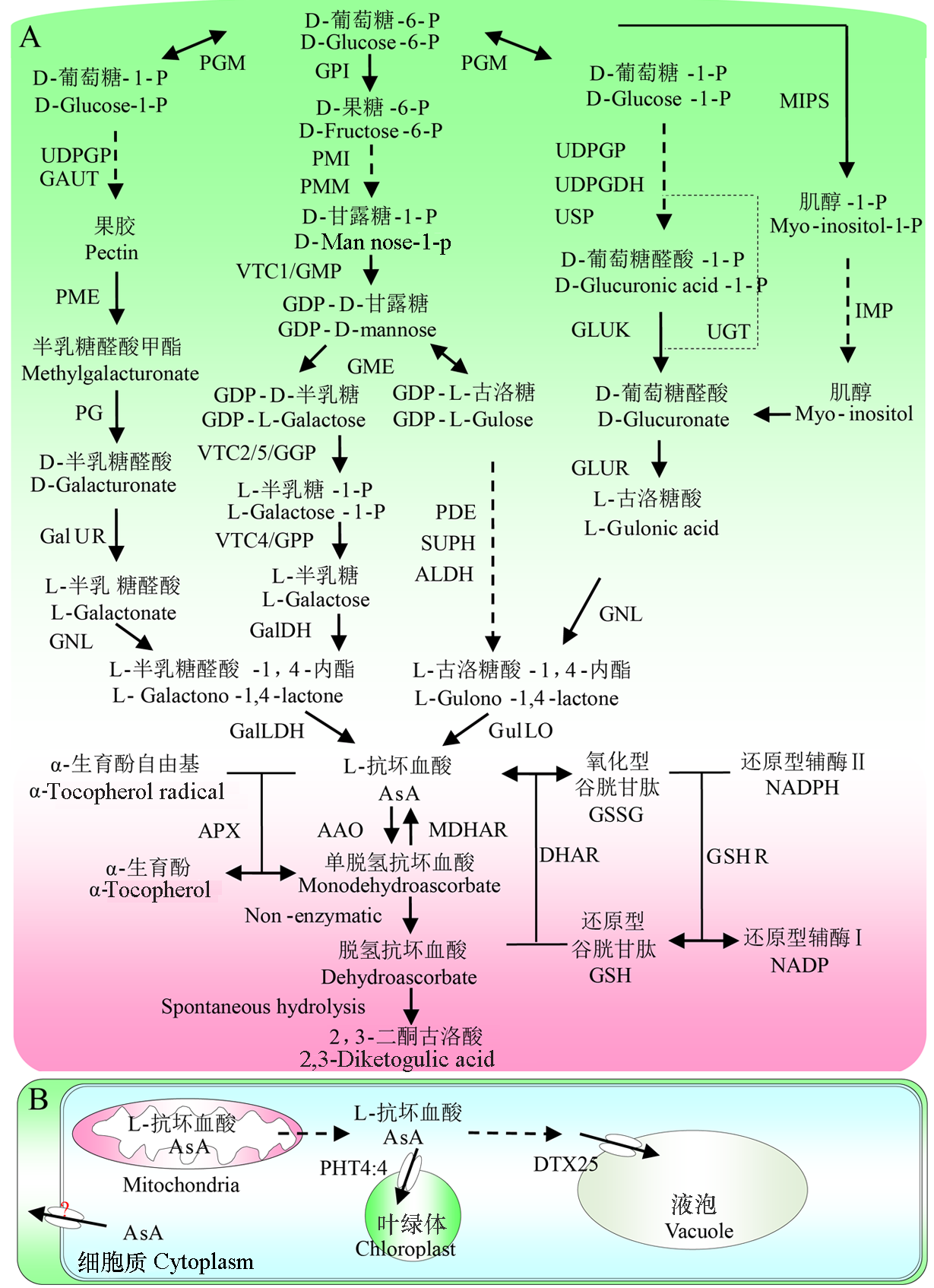
图1 AsA的生物合成、代谢循环(A)和细胞内转运(B)途径 (刘永立 等,2006;Mellidou & Kanellis,2017;Fenech et al.,2019;Foyer et al.,2020;Chaturvedi et al.,2022)。 PGM:磷酸葡萄糖变位酶;UDPGP:UDP-葡萄糖焦磷酸化酶;UDPGDH:UDP-葡萄糖6-脱氢酶;GAUT:半乳糖醛酸转移酶;PME:果胶酯酶;PG:聚半乳糖醛酸酶;GalUR:半乳糖醛酸还原酶;GNL:葡萄糖酸内酯酶;GLDH:L-半乳糖-1,4-内酯脱氢酶;GPI:6-磷酸葡萄糖异构酶;PMI:6-磷酸甘露糖异构酶;PMM:磷酸甘露糖变位酶;VCT1/GMP:GDP-D-甘露糖焦磷酸酶;GME:GDP-D-甘露糖3,5-差向异构酶;VCT2/VCT5/GGP:GDP-L-半乳糖磷酸化酶;VCT4/GPP:L-半乳糖-1-磷酸磷酸酶;GalDH:L-半乳糖脱氢酶;PDE:磷酸二酯酶;SUPH:糖磷酸酶;ALDH:L-古洛糖酸-1,4-内酯脱氢酶;GulLO:L-古洛糖酸内酯氧化酶;PsUSP:UDP-糖焦磷酸化酶;UGT:UDP-葡萄糖醛酸转移酶;GLUK:葡萄糖醛酸激酶;GLUR:葡萄糖醛酸还原酶;MIPS:肌醇3-磷酸合酶;IMP:肌醇单磷酸酶;MIOX:肌醇加氧酶;APX:L-抗坏血酸过氧化物酶;AAO:L-抗坏血酸氧化酶;MDHAR:单脱氢抗坏血酸还原酶;DHAR:脱氢抗坏血酸还原酶;GSHR:谷胱甘肽还原酶。
Fig. 1 AsA biosynthesis,regeneration(A)and intracellular transport(B) PGM:Phosphoglucomutase;UDPGP:UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase;UDPGDH:UDP-glucose 6-dehydrogenase;GAUT:Galacturonosyltransferase;PME:Pectinesterase;PG:Polygalacturonase;GalUR:Galacturonic acid reductase;GNL:Gluconolactonase;GLDH:L-galactono-1,4-lactone dehydrogenase;GPI:Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase;PMI:Mannose-6-phosphate isomerase;PMM:Phosphomannomutase;VCT1/GMP:GDP-D-mannose pyrophorylase;GME:GDP-D-mannose 3,5-epimerase;VCT2/VCT5/GGP:GDP-L-galactose phosphorylase;VCT4/GPP:L-galactose-1-phosphate phosphatase;GalDH:L-galactose dehydrogenase;PDE:Phosphodiesterase;SUPH:Sugar-phosphatase;ALDH:L-gulono-1,4-lactone dehydrogenase;GulLO:L-gulonolactone oxidase;PsUSP:UDP-sugar pyrophosphorylase;UGT:UDP-glucuronosyltransferase;GLUK:Glucuronokinase;GLUR:Glucuronate reductase;MIPS:myo-Inositol-3-phosphate synthase;IMP:myo-Inositol monophosphatase;MIOX:myo-Inositol oxygenase;APX:L-ascorbate peroxidase;AAO:L-ascorbate oxidase;MDHAR:Monodehydroascorbate reductase;DHAR:Dehydroascorbate reductase;GSHR:Glutathione reductase.
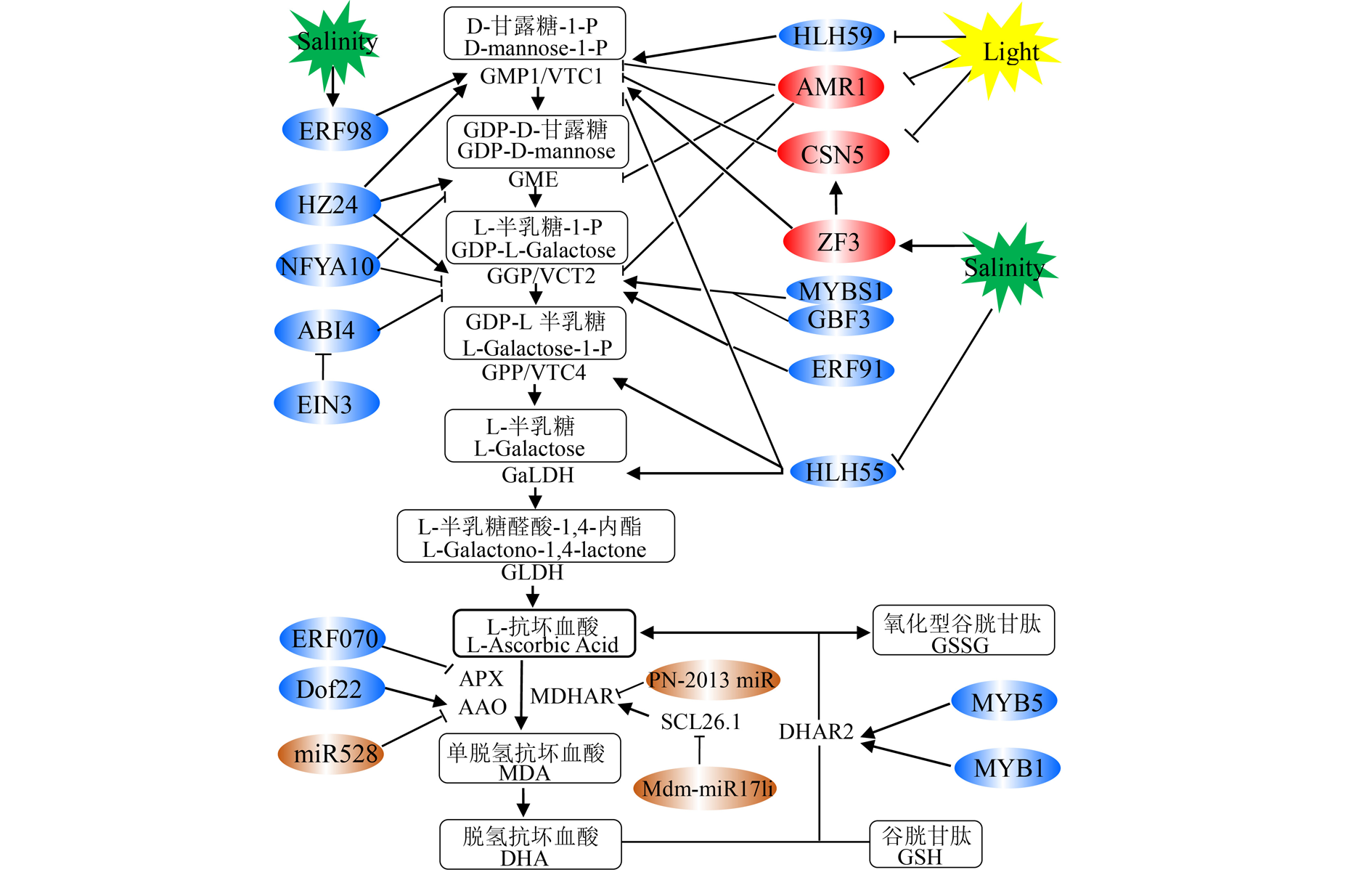
图2 AsA的生物合成与代谢循环途径的调控网络 蓝白色椭圆:转录因子;红白色椭圆:翻译后调控因子;棕白色椭圆:小RNA。
Fig. 2 The regulatory network of AsA biosynthesis and regeneration White-blue ellipse:transcription factor;White-red ellipse:post-translational regulation factor;White-blue ellipse:microRNAs. (Zhang et al.,2012;Mellidou & Kanellis,2017;Yu et al.,2021;Liu et al.,2022).
| [1] |
doi: 10.20455/ros.2017.861 pmid: 30112455 |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.1007/s00425-020-03345-x |
| [4] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.107.106500 pmid: 17921340 |
| [5] |
doi: 10.1007/s00425-014-2044-z pmid: 24567029 |
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2017.04.005 URL |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
pmid: 5481396 |
| [10] |
doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2008.11.034 pmid: 19059408 |
| [11] |
doi: 10.3390/agronomy11112293 URL |
| [12] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.73.1.41 pmid: 16663182 |
| [13] |
doi: 10.1007/s13580-016-0144-3 URL |
| [14] |
doi: 10.1007/s13580-017-0362-3 URL |
| [15] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.04.148 URL |
| [16] |
doi: 10.1007/s10725-014-9988-7 URL |
| [17] |
doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2010.08.020 URL |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1021/jf900385a pmid: 19397288 |
| [19] |
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.10.109 URL |
| [20] |
doi: 10.1007/s12298-022-01172-w |
| [21] |
|
|
陈朋朋. 2015. 不同覆盖与亏水对梨枣树的影响[硕士论文]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学.
|
|
| [22] |
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2021.111063 URL |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1021/jf0402983 URL |
| [24] |
doi: 10.1590/fst.23420 URL |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0010 URL |
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03266.x URL |
| [28] |
doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2008.01.017 URL |
| [29] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.108.130948 URL |
| [30] |
doi: S0308-8146(17)30014-6 pmid: 28193406 |
| [31] |
doi: 10.3390/agronomy10040501 URL |
| [32] |
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.02006 URL |
| [33] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.11.001 pmid: 24269602 |
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
doi: 10.1016/S0176-1617(96)80271-9 URL |
| [36] |
pmid: 12376632 |
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
doi: 10.1021/jf020136b URL |
| [39] |
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.514828 pmid: 24347170 |
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
|
韩凤波, 曾祥云. 2013. 植物生长调节剂对酸浆果实生长及维生素C含量的影响. 江苏农业科学, 41 (2):156-158.
|
|
| [43] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0110 URL |
|
韩敏, 曹逼力, 刘树森, 徐坤. 2019. 低温胁迫下番茄幼苗根穗互作对其抗坏血酸—谷胱甘肽循环的影响. 园艺学报, 46 (1):65-73.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0110 URL |
|
| [44] |
|
|
韩云, 管正学. 1991. 野玫瑰果的营养成份分析. 食品科学,(12):38-40.
|
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
doi: S0308-8146(19)30658-2 pmid: 31054680 |
| [47] |
doi: 10.3390/agronomy11040764 URL |
| [48] |
doi: 10.1016/S0981-9428(00)00782-8 URL |
| [49] |
doi: 10.1111/tpj.2016.85.issue-1 URL |
| [50] |
doi: 10.21273/HORTSCI.39.6.1165 URL |
| [51] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2014.03.010 pmid: 25019249 |
| [52] |
doi: 10.1021/jf049398z URL |
| [53] |
doi: 10.1038/171348a0 |
| [54] |
doi: 10.1023/A:1009680818138 URL |
| [55] |
doi: 10.1007/s10068-013-0162-1 URL |
| [56] |
doi: S0981-9428(18)30005-6 pmid: 29331889 |
| [57] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2008.08.004 URL |
| [58] |
doi: 10.1021/jf020421v URL |
| [59] |
doi: 10.1111/tpj.v109.2 URL |
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2009.10.019 URL |
| [62] |
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2014.12.002 pmid: 25575999 |
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2012.11.009 pmid: 23267462 |
| [65] |
doi: 10.21273/HORTSCI.41.1.59 URL |
| [66] |
|
|
李良良, 安华明. 2016. Ca2+和Cu2+对刺梨果实AsA代谢相关基因表达的影响. 园艺学报, 43 (7):1377-1382.
|
|
| [67] |
|
|
李明军, 刘军, 梁东, 郭春苗, 马锋旺. 2011. 猕猴桃GalUR表达与抗坏血酸积累的关系. 园艺学报, 38 (9):15-23.
|
|
| [68] |
doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190526-307 |
|
李勋兰, 洪林, 杨蕾, 王武, 韩国辉, 农江飞, 谭平. 2020. 11个柑橘品种果实营养成分分析与品质综合评价. 食品科学, 41 (8):228-233.
doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190526-307 |
|
| [69] |
doi: 10.1111/pbi.12863 pmid: 29193661 |
| [70] |
doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-07308-0 |
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-187 pmid: 22583865 |
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2022.110940 URL |
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
doi: S0308-8146(18)30772-6 pmid: 29784307 |
| [77] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2014.06.027 URL |
| [78] |
doi: 10.1111/pbi.2013.12.issue-1 URL |
| [79] |
|
|
刘婧愉, 滕瑞敏, 李辉, 刘昊, 庄静. 2020. 茶树DHAR酶基因的克隆与非生物胁迫响应分析. 园艺学报, 47 (5):983-994.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2019-0684 URL |
|
| [80] |
|
|
刘孟军, 汪民. 2009. 中国枣种质资源. 北京: 中国林业出版社.
|
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
|
|
刘永立, 胡海涛, 兰大伟. 2006. 维生素C的生物合成及其基因调控研究进展. 果树学报, 23 (3):431-436.
|
|
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.103.033936 pmid: 14976233 |
| [85] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erw260 URL |
| [86] |
doi: 10.3390/molecules19068518 URL |
| [87] |
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0010 URL |
| [88] |
|
|
吕荣森. 1990. 中国沙棘属植物资源研究. 园艺学报, 17 (3):177-184.
|
|
| [89] |
|
|
马福生, 康绍忠, 王密侠, 庞秀明, 王金凤, 李志军. 2006. 调亏灌溉对温室梨枣树水分利用效率与枣品质的影响. 农业工程学报, 22 (1):37-43.
|
|
| [90] |
doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiab427 URL |
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.06.001 pmid: 20621498 |
| [93] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.112.203786 pmid: 23001142 |
| [94] |
|
| [95] |
|
| [96] |
pmid: 15509850 |
| [97] |
doi: 10.1038/ncomms6928 |
| [98] |
doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-6708-8 pmid: 32252624 |
| [99] |
|
| [100] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2005.09.002 URL |
| [101] |
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01386 URL |
| [102] |
pmid: 15520028 |
| [103] |
doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.12.002 URL |
| [104] |
pmid: 15234991 |
| [105] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0486 URL |
|
彭银霞, 张颖, 朱康友, 孙鑫, 张克敏, 孙周平, 齐明芳, 李天来, 王峰. 2022. 园艺作物抗坏血酸生物合成中光的调控作用研究综述. 园艺学报, 49 (11):2502-2518.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0486 URL |
|
| [106] |
doi: S0308-8146(18)31375-X pmid: 30236710 |
| [107] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.103.022798 pmid: 12857842 |
| [108] |
|
| [109] |
doi: 10.1023/B:PLAN.0000023671.99451.1d URL |
| [110] |
|
| [111] |
|
|
任宗君. 2019. DNA甲基化对番茄果实抗坏血酸合成积累的调控研究[硕士论文]. 武汉: 华中农业大学.
|
|
| [112] |
doi: 10.1111/jfq.2013.36.issue-6 URL |
| [113] |
|
|
佘祥威, 李来庚, 王平, 欧阳玉珍. 1988. 金樱子果实的营养成分及其利用研究. 园艺学报, 15 (4):240-244.
|
|
| [114] |
|
| [115] |
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2021.07.002 URL |
| [116] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.106.091413 pmid: 17277090 |
| [117] |
doi: 10.1080/09168451.2019.1608808 URL |
| [118] |
|
| [119] |
doi: 10.1002/jsfa.9280 pmid: 30047146 |
| [120] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2006.01.002 URL |
| [121] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2005.12.001 URL |
| [122] |
doi: 10.1007/s00299-011-1009-y URL |
| [123] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.106880 URL |
| [124] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c01096 pmid: 34339211 |
| [125] |
doi: 10.1023/A:1005992829284 URL |
| [126] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.20.00476 URL |
| [127] |
doi: 10.1038/30728 URL |
| [128] |
doi: 10.4161/psb.6.10.17036 URL |
| [129] |
doi: 10.1111/pce.v42.3 URL |
| [130] |
|
|
熊江, 卢晓鹏, 李静, 肖玉明, 曹雄军, 谢深喜. 2014. 水分胁迫对果实品质的影响研究进展. 湖南农业科学, 18 (18):56-60.
|
|
| [131] |
doi: 10.1038/ng.2472 |
| [132] |
|
| [133] |
|
|
杨若明, 李玉田. 2001. 鲜食玉米营养成分的分析研究. 食品科技,(1):67-68.
|
|
| [134] |
doi: 10.3390/antiox11010153 URL |
| [135] |
|
| [136] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.18.01250 pmid: 30723177 |
| [137] |
|
| [138] |
doi: 10.1007/s00299-010-0939-0 URL |
| [139] |
|
| [140] |
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2021.01.010 URL |
| [141] |
|
|
张书轩, 李良良, 鲁敏, 安华明. 2018. 三种植物生长调节剂对刺梨果实维生素C积累及其代谢基因表达的影响. 农业生物技术学报, 26 (4):606-615.
|
|
| [142] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.109.138453 URL |
| [143] |
|
|
张雪, 杨曼, 安华明, 黄伟, 刘卫. 2012. 外源Ca2+、Mg2+、Cu2+和吖啶黄素对刺梨果实维生素C合成的影响. 中国农业科学, 45 (6):1144-1149.
|
|
| [144] |
|
| [145] |
doi: 10.3390/plants10010176 URL |
| [146] |
doi: 10.1111/tpj.2012.71.issue-2 URL |
| [147] |
doi: 10.1111/pbi.v20.6 URL |
| [148] |
|
| [149] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109673 URL |
| [1] | 张印, 胡路艳, 王淑明, 景丹龙, 郭启高, 梁国鲁. ABA调控果实成熟研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(9): 1889-1898. |
| [2] | 刘金莹, 孔令喜, 王威浩, 秦国政, 王豫颖. 草莓果实香气物质生物合成研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(9): 1959-1970. |
| [3] | 张巧丽, 陈笛, 宋艳萍, 朱鸿亮, 罗云波, 曲桂芹. 番茄果实叶绿素代谢转录调控网络研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(9): 2031-2047. |
| [4] | 莫雨杏, 周艳, 林润婷, 多泳星, 张涛, 刘锴栋. 番木瓜CpWRI3参与调控果实成熟过程中脂肪酸合成[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1637-1648. |
| [5] | 王文, 张柯楠, 方莫扉, 丁思悦, 王雪飞, 惠竹梅. 果袋颜色对‘赤霞珠’葡萄果皮花色苷积累的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1723-1738. |
| [6] | 汪红秀, 周上铃, 何绍国, 田再泽, 马静华, 彭良志, 淳长品. 尤力克柠檬叶片营养元素标准的研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(7): 1535-1546. |
| [7] | 陈敏, 吴天利, 吕远达, 姜波, 闫化学, 李娟, 钟云. 不同砧木红江橙容器栽培生长和果实品质分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(7): 1547-1562. |
| [8] | 杨孟霞, 刘晓林, 曹雪, 魏凯, 宁宇, 杨沛, 李珊珊, 陈紫月, 王孝宣, 国艳梅, 杜永臣, 李君明, 刘磊, 李鑫, 黄泽军. 番茄CRISPR/Cas9介导的多基因编辑技术体系构建与应用[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(6): 1215-1229. |
| [9] | 周成, 方怡, 周锦杨, 黄企浩, 盘永坚, 史千千, 倪慧娴, 杨震峰, 宋春波. 低温诱导的桃果实采后膜脂代谢变化与冷害的关系[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(6): 1305-1317. |
| [10] | 周平, 郭瑞, 颜少宾, 金光. 外源山梨醇影响桃叶片和果实糖代谢的分子机制研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(5): 959-971. |
| [11] | 李中瀚, 唐美玲, 郑秋玲, 刘明慧, 康慧, 高振, 杜远鹏. 聚乙烯编织物Coverlys TF150®覆盖对‘蜜光’葡萄果实品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(5): 1073-1084. |
| [12] | 吕若亚, 李云, 郑永钦, 邓晓玲, 郑正. 黄龙病菌在柑橘果实橘络中的分布[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(5): 1110-1117. |
| [13] | 阚丽平, 石晓倩, 杨晗, 金雨濛, 陈丽妍, 张丽娟, 徐阳春, 沈其荣, 董彩霞. 梨果实钾转运体基因PbKT12的克隆与功能验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(4): 713-723. |
| [14] | 唐海霞, 裴广营, 张琼, 王中堂. 枣果实相关性状QTL定位分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(4): 754-764. |
| [15] | 常晓晓, 郭新波, 叶宇童, 彭程, 陈慧琼, 潘建平, 邱继水, 陆育生. ‘早丰黄皮’和‘鸡心黄皮’果实糖、酸和多酚及抗氧化活性差异分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(4): 778-790. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司