
园艺学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 613-634.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2025-0926
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2025-12-14
修回日期:2026-01-09
出版日期:2026-02-25
发布日期:2026-02-12
基金资助:
LIU Yuting, FU Xuemei, HU Yihang, CHEN Longqing( )
)
Received:2025-12-14
Revised:2026-01-09
Published:2026-02-25
Online:2026-02-12
摘要:
运用生物信息学技术,鉴定出蜡梅(Chimonanthus praecox)44个CpABCG基因,初步探讨蜡梅ABCG亚家族的特性及相关花香释放机制。结果表明,44个CpABCG家族成员均含具有疏水作用的跨膜结构域(TMD)和能够与水结合的核苷酸结合域(NBD);保守基序分析显示,Motif 1、Motif 3和Motif 4是ABCG家族的特征基序;共线性分析表明CpABCG和梅花ABCG亲缘关系更为紧密;CpABCG的启动子中含有光、植物生长发育、非生物胁迫和植物激素响应元件;qRT-PCR结果显示,CpABCG1.2、CpABCG9.1和CpABCG25.2三个基因在花中高表达,表达模式和蜡梅花香释放规律关系密切;外源花香抑制剂处理后,花香释放总量明显减少,而内源挥发性物质同比增多;结合表达水平变化,推测CpABCG1.2和CpABCG9.1可能在蜡梅花花香挥发性化合物跨膜运输中发挥重要作用。
刘玉婷, 付雪梅, 胡一航, 陈龙清. 蜡梅花香转运相关ABCG基因的筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 613-634.
LIU Yuting, FU Xuemei, HU Yihang, CHEN Longqing. Screening of ABCG Genes Related to the Transport of Volatile Compounds in Chimonanthus praecox[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2026, 53(2): 613-634.
| 目的基因 Gene name | 上游引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 下游引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| CpABCG1.2 | ACGAGCTTTGGAGAAGTGGA | ACAAAGGGAAAGCGCAATGT |
| CpABCG1.3 | GTTCCAAGATGGACGCCTGA | GGTATCCACGTCAACTCGCA |
| CpABCG6 | ATTCAATCGGTCATGGCAGC | GCTTCCCACGTGATATGCTG |
| CpABCG9.1 | CGCCAAAATGACAGCGGAAA | CGGCTCGCCATTGTAGGTTA |
| CpABCG9.2 | CTGGCAAACAGAAGGCATCG | AGTGAGGAGGGTCGTTTTGC |
| CpABCG14 | GAGATTCTGGCAATGCTGGG | CCTGTACGCCTTTTCATGGG |
| CpABCG20 | ATCGCCGATCTTCCTACGTT | TGTAGCCCACCATCACATGT |
| CpABCG21 | TACGGTGGTCGAAATGGCAA | GAGCCCGATCCAGCTTAGAC |
| CpABCG22.2 | GTCGAACCATGGCCTCCTAC | GGAGGTGGCGGTGAATTGTA |
| CpABCG25.1 | TGGATTCGTCACCCAAGACG | TCTCACATTTTCCGAGCCCC |
| CpABCG25.2 | TGAGGAGAAGGTGGTAGGGA | ATGACCTGTCCCACCTTGAG |
| CpABCG26 | CTTGCACTAATGGGCCCTTC | TCGGAAGTCTTAGAAGCGCA |
| CpABCG39.4 | GGCTGTCAACTGAACAACGT | CTGGGTTGGTGAATTGTGCA |
| CpRPL8 | ACATTGCCGACCATGAGATTG | CACTTGCCCGAGTTACCTTT |
表1 本试验中RT-qPCR 反应的引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequence of RT-qPCR reaction in this study
| 目的基因 Gene name | 上游引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 下游引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| CpABCG1.2 | ACGAGCTTTGGAGAAGTGGA | ACAAAGGGAAAGCGCAATGT |
| CpABCG1.3 | GTTCCAAGATGGACGCCTGA | GGTATCCACGTCAACTCGCA |
| CpABCG6 | ATTCAATCGGTCATGGCAGC | GCTTCCCACGTGATATGCTG |
| CpABCG9.1 | CGCCAAAATGACAGCGGAAA | CGGCTCGCCATTGTAGGTTA |
| CpABCG9.2 | CTGGCAAACAGAAGGCATCG | AGTGAGGAGGGTCGTTTTGC |
| CpABCG14 | GAGATTCTGGCAATGCTGGG | CCTGTACGCCTTTTCATGGG |
| CpABCG20 | ATCGCCGATCTTCCTACGTT | TGTAGCCCACCATCACATGT |
| CpABCG21 | TACGGTGGTCGAAATGGCAA | GAGCCCGATCCAGCTTAGAC |
| CpABCG22.2 | GTCGAACCATGGCCTCCTAC | GGAGGTGGCGGTGAATTGTA |
| CpABCG25.1 | TGGATTCGTCACCCAAGACG | TCTCACATTTTCCGAGCCCC |
| CpABCG25.2 | TGAGGAGAAGGTGGTAGGGA | ATGACCTGTCCCACCTTGAG |
| CpABCG26 | CTTGCACTAATGGGCCCTTC | TCGGAAGTCTTAGAAGCGCA |
| CpABCG39.4 | GGCTGTCAACTGAACAACGT | CTGGGTTGGTGAATTGTGCA |
| CpRPL8 | ACATTGCCGACCATGAGATTG | CACTTGCCCGAGTTACCTTT |
| 基因名称 Gene name | 长度/bp Length of CDS | 等电点 Theoretical (pI) | 分子量/kD Molecular weight | 氨基酸数 Number of amino acid | 亲水系数 GRAVY | 不稳定系数 Instability index | 信号肽 Signal peptide | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization | 类型 Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CpABCG1.1 | 2 232 | 8.90 | 82.59 | 743 | -0.051 | 45.95 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG1.2 | 2 229 | 8.75 | 82.26 | 742 | -0.043 | 46.12 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG1.3 | 2 364 | 8.60 | 86.73 | 787 | -0.010 | 46.63 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG1.4 | 2 145 | 9.02 | 79.74 | 714 | 0.107 | 36.60 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG3 | 2 172 | 8.98 | 80.80 | 723 | 0.197 | 42.75 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG5.1 | 2 211 | 8.68 | 81.94 | 736 | 0.082 | 41.88 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG5.2 | 1 959 | 8.41 | 73.56 | 652 | 0.056 | 45.77 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG6 | 2 247 | 9.59 | 82.79 | 748 | 0.117 | 41.47 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG8 | 1 782 | 9.21 | 65.75 | 593 | 0.410 | 49.37 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG9.1 | 1 761 | 8.37 | 65.12 | 586 | 0.209 | 38.68 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG9.2 | 966 | 7.63 | 34.83 | 321 | -0.058 | 31.55 | 无No | 质膜/高尔基体 Plas/golg | WBC |
| CpABCG11.1 | 2 229 | 8.94 | 82.62 | 742 | -0.070 | 44.90 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG11.2 | 2 094 | 9.04 | 77.71 | 697 | 0.165 | 34.51 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG14 | 1 992 | 8.54 | 74.14 | 663 | 0.050 | 44.36 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG15 | 2 088 | 9.36 | 77.85 | 695 | 0.041 | 46.45 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG17.1 | 2 169 | 9.51 | 81.28 | 722 | -0.014 | 40.40 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG17.2 | 2 187 | 9.21 | 82.01 | 728 | -0.085 | 42.97 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG18 | 2 414 | 9.03 | 90.93 | 803 | -0.112 | 43.72 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG20 | 2 286 | 9.04 | 84.25 | 761 | 0.120 | 42.68 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG21 | 2 034 | 9.01 | 75.41 | 677 | -0.057 | 43.57 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG22.1 | 2 196 | 9.10 | 81.22 | 731 | 0.069 | 34.65 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG22.2 | 1 965 | 8.53 | 73.40 | 654 | 0.160 | 42.80 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG22.3 | 2 235 | 9.15 | 82.50 | 744 | 0.009 | 34.24 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG25.1 | 1 947 | 9.13 | 71.70 | 648 | 0.143 | 38.56 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG25.2 | 1 869 | 6.48 | 68.92 | 622 | 0.189 | 38.45 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG26 | 1 911 | 9.25 | 72.63 | 636 | -0.120 | 45.59 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG31.1 | 4 311 | 6.92 | 164.08 | 1 436 | 0.063 | 40.34 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG31.2 | 4 002 | 9.01 | 149.07 | 1 333 | 0.185 | 35.94 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG32 | 2 172 | 6.37 | 81.98 | 723 | 0.020 | 38.03 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG34 | 4 416 | 6.39 | 166.47 | 1 471 | 0.058 | 38.26 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG39.1 | 4 059 | 8.27 | 152.16 | 1 352 | 0.033 | 40.48 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG39.2 | 4 167 | 8.31 | 157.99 | 1 388 | 0.026 | 42.55 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG39.3 | 3 909 | 7.81 | 147.66 | 1 302 | 0.079 | 41.67 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG39.4 | 4 356 | 8.27 | 163.79 | 1 451 | 0.030 | 40.50 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG39.5 | 4 356 | 8.00 | 163.87 | 1 451 | 0.027 | 39.37 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG39.6 | 4 314 | 7.49 | 162.94 | 1 437 | 0.062 | 35.65 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG39.7 | 4 314 | 8.37 | 162.21 | 1 437 | 0.039 | 37.01 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG39.8 | 4 224 | 8.78 | 158.83 | 1 407 | 0.025 | 35.73 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG39.9 | 4 206 | 8.89 | 158.29 | 1 401 | 0.014 | 37.71 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG39.10 | 2 079 | 6.32 | 78.08 | 692 | -0.002 | 38.27 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG39.11 | 4 365 | 6.60 | 163.87 | 1 454 | 0.077 | 38.39 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG39.12 | 4 347 | 8.41 | 163.47 | 1 448 | 0.017 | 36.28 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG41 | 3 879 | 8.69 | 146.26 | 1 292 | 0.114 | 40.77 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG42 | 4 491 | 8.70 | 169.63 | 1 496 | -0.031 | 38.12 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
表2 CpABCG基因家族信息及编码蛋白基本理化性质
Table 2 CpABCG gene family information and basic physicochemical properties of encoded proteins
| 基因名称 Gene name | 长度/bp Length of CDS | 等电点 Theoretical (pI) | 分子量/kD Molecular weight | 氨基酸数 Number of amino acid | 亲水系数 GRAVY | 不稳定系数 Instability index | 信号肽 Signal peptide | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization | 类型 Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CpABCG1.1 | 2 232 | 8.90 | 82.59 | 743 | -0.051 | 45.95 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG1.2 | 2 229 | 8.75 | 82.26 | 742 | -0.043 | 46.12 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG1.3 | 2 364 | 8.60 | 86.73 | 787 | -0.010 | 46.63 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG1.4 | 2 145 | 9.02 | 79.74 | 714 | 0.107 | 36.60 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG3 | 2 172 | 8.98 | 80.80 | 723 | 0.197 | 42.75 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG5.1 | 2 211 | 8.68 | 81.94 | 736 | 0.082 | 41.88 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG5.2 | 1 959 | 8.41 | 73.56 | 652 | 0.056 | 45.77 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG6 | 2 247 | 9.59 | 82.79 | 748 | 0.117 | 41.47 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG8 | 1 782 | 9.21 | 65.75 | 593 | 0.410 | 49.37 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG9.1 | 1 761 | 8.37 | 65.12 | 586 | 0.209 | 38.68 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG9.2 | 966 | 7.63 | 34.83 | 321 | -0.058 | 31.55 | 无No | 质膜/高尔基体 Plas/golg | WBC |
| CpABCG11.1 | 2 229 | 8.94 | 82.62 | 742 | -0.070 | 44.90 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG11.2 | 2 094 | 9.04 | 77.71 | 697 | 0.165 | 34.51 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG14 | 1 992 | 8.54 | 74.14 | 663 | 0.050 | 44.36 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG15 | 2 088 | 9.36 | 77.85 | 695 | 0.041 | 46.45 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG17.1 | 2 169 | 9.51 | 81.28 | 722 | -0.014 | 40.40 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG17.2 | 2 187 | 9.21 | 82.01 | 728 | -0.085 | 42.97 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG18 | 2 414 | 9.03 | 90.93 | 803 | -0.112 | 43.72 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG20 | 2 286 | 9.04 | 84.25 | 761 | 0.120 | 42.68 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG21 | 2 034 | 9.01 | 75.41 | 677 | -0.057 | 43.57 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG22.1 | 2 196 | 9.10 | 81.22 | 731 | 0.069 | 34.65 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG22.2 | 1 965 | 8.53 | 73.40 | 654 | 0.160 | 42.80 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG22.3 | 2 235 | 9.15 | 82.50 | 744 | 0.009 | 34.24 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG25.1 | 1 947 | 9.13 | 71.70 | 648 | 0.143 | 38.56 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG25.2 | 1 869 | 6.48 | 68.92 | 622 | 0.189 | 38.45 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG26 | 1 911 | 9.25 | 72.63 | 636 | -0.120 | 45.59 | 无No | 质膜Plas | WBC |
| CpABCG31.1 | 4 311 | 6.92 | 164.08 | 1 436 | 0.063 | 40.34 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG31.2 | 4 002 | 9.01 | 149.07 | 1 333 | 0.185 | 35.94 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG32 | 2 172 | 6.37 | 81.98 | 723 | 0.020 | 38.03 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG34 | 4 416 | 6.39 | 166.47 | 1 471 | 0.058 | 38.26 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG39.1 | 4 059 | 8.27 | 152.16 | 1 352 | 0.033 | 40.48 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG39.2 | 4 167 | 8.31 | 157.99 | 1 388 | 0.026 | 42.55 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG39.3 | 3 909 | 7.81 | 147.66 | 1 302 | 0.079 | 41.67 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG39.4 | 4 356 | 8.27 | 163.79 | 1 451 | 0.030 | 40.50 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG39.5 | 4 356 | 8.00 | 163.87 | 1 451 | 0.027 | 39.37 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG39.6 | 4 314 | 7.49 | 162.94 | 1 437 | 0.062 | 35.65 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG39.7 | 4 314 | 8.37 | 162.21 | 1 437 | 0.039 | 37.01 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG39.8 | 4 224 | 8.78 | 158.83 | 1 407 | 0.025 | 35.73 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG39.9 | 4 206 | 8.89 | 158.29 | 1 401 | 0.014 | 37.71 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG39.10 | 2 079 | 6.32 | 78.08 | 692 | -0.002 | 38.27 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG39.11 | 4 365 | 6.60 | 163.87 | 1 454 | 0.077 | 38.39 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG39.12 | 4 347 | 8.41 | 163.47 | 1 448 | 0.017 | 36.28 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG41 | 3 879 | 8.69 | 146.26 | 1 292 | 0.114 | 40.77 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
| CpABCG42 | 4 491 | 8.70 | 169.63 | 1 496 | -0.031 | 38.12 | 无No | 质膜Plas | PDR |
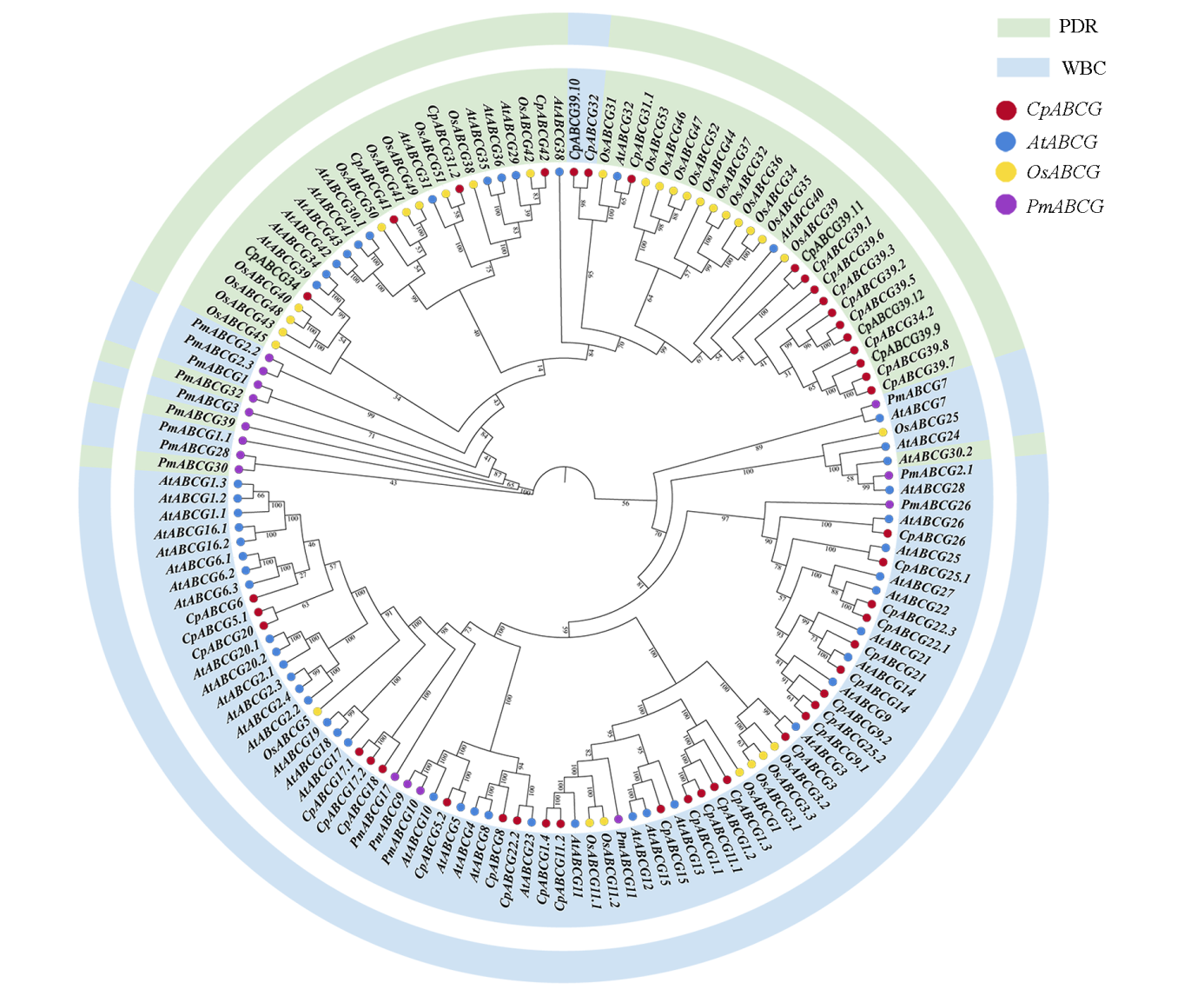
图1 蜡梅(Cp)、拟南芥(At)、水稻(At)和梅花(Pm)ABCG蛋白的系统进化树
Fig. 1 Phylogenetic tree of ABCG proteins in Chimonanthus praecox(Cp),Arabidopsis thaliana(At),Oryza sativa(At)and Prunus mume(Pm)
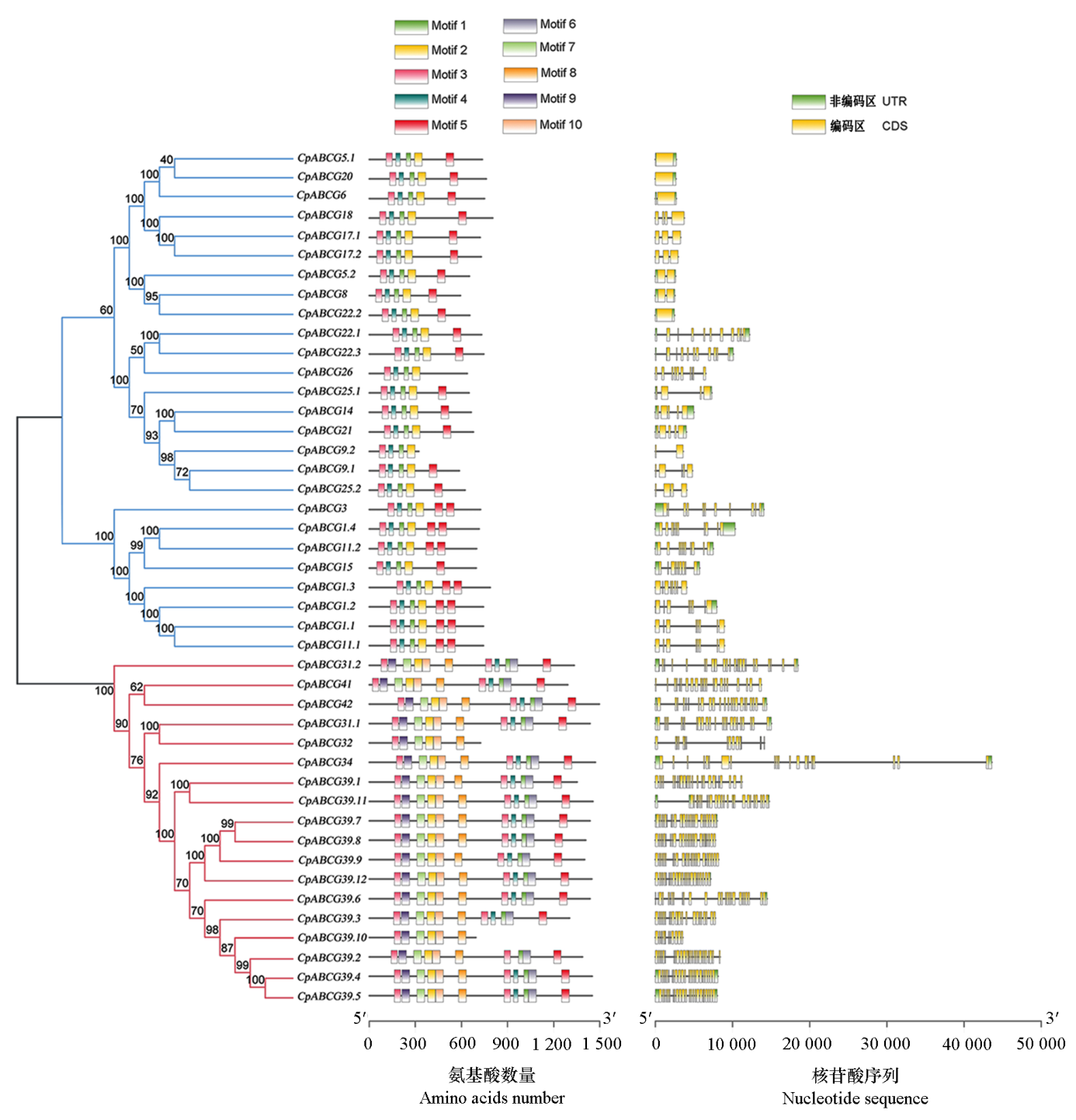
图2 CpABCG基因家族保守基序及基因结构分析 WBC型和PDR型的基因分别用蓝色线条和红色线条表示
Fig. 2 Conserved motif and gene structure of CpABCG gene family The WBC and PDR genes are represented by blue and red lines,respectively
| 基序名称 Motif | 标识 Logo | 期望值 E-value | 位点 Sites | 宽度 Width |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Motif1 | | 3.8e-823 | 44 | 29 |
| Motif2 | | 2.5e-1050 | 43 | 50 |
| Motif3 | | 1.3e-892 | 44 | 41 |
| Motif4 | | 7.3e-707 | 44 | 29 |
| Motif5 | | 3.0e-821 | 40 | 50 |
| Motif6 | | 2.7e-653 | 16 | 50 |
| Motif 7 | | 4.0e-609 | 16 | 50 |
| Motif 8 | | 9.9e-583 | 18 | 50 |
| Motif 9 | | 2.2e-542 | 15 | 50 |
| Motif 10 | | 1.8e-555 | 18 | 50 |
表3 44个蜡梅CpABCG基因家族成员的保守基序汇总
Table 3 Summary of conserved motifs of 44 members of CpABCG gene family in Chimonanthus praecox
| 基序名称 Motif | 标识 Logo | 期望值 E-value | 位点 Sites | 宽度 Width |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Motif1 | | 3.8e-823 | 44 | 29 |
| Motif2 | | 2.5e-1050 | 43 | 50 |
| Motif3 | | 1.3e-892 | 44 | 41 |
| Motif4 | | 7.3e-707 | 44 | 29 |
| Motif5 | | 3.0e-821 | 40 | 50 |
| Motif6 | | 2.7e-653 | 16 | 50 |
| Motif 7 | | 4.0e-609 | 16 | 50 |
| Motif 8 | | 9.9e-583 | 18 | 50 |
| Motif 9 | | 2.2e-542 | 15 | 50 |
| Motif 10 | | 1.8e-555 | 18 | 50 |

图3 蜡梅 ABCG 基因家族染色体定位 具有片段复制的CpABCG基因用红色字体表示,串联复制以红线表示
Fig. 3 Chromosomal localizationof the CpABCG family members in Chimonanthus praecox CpABCG genes with fragment duplication are shown in red fonts,and tandem duplication is shown in red lines
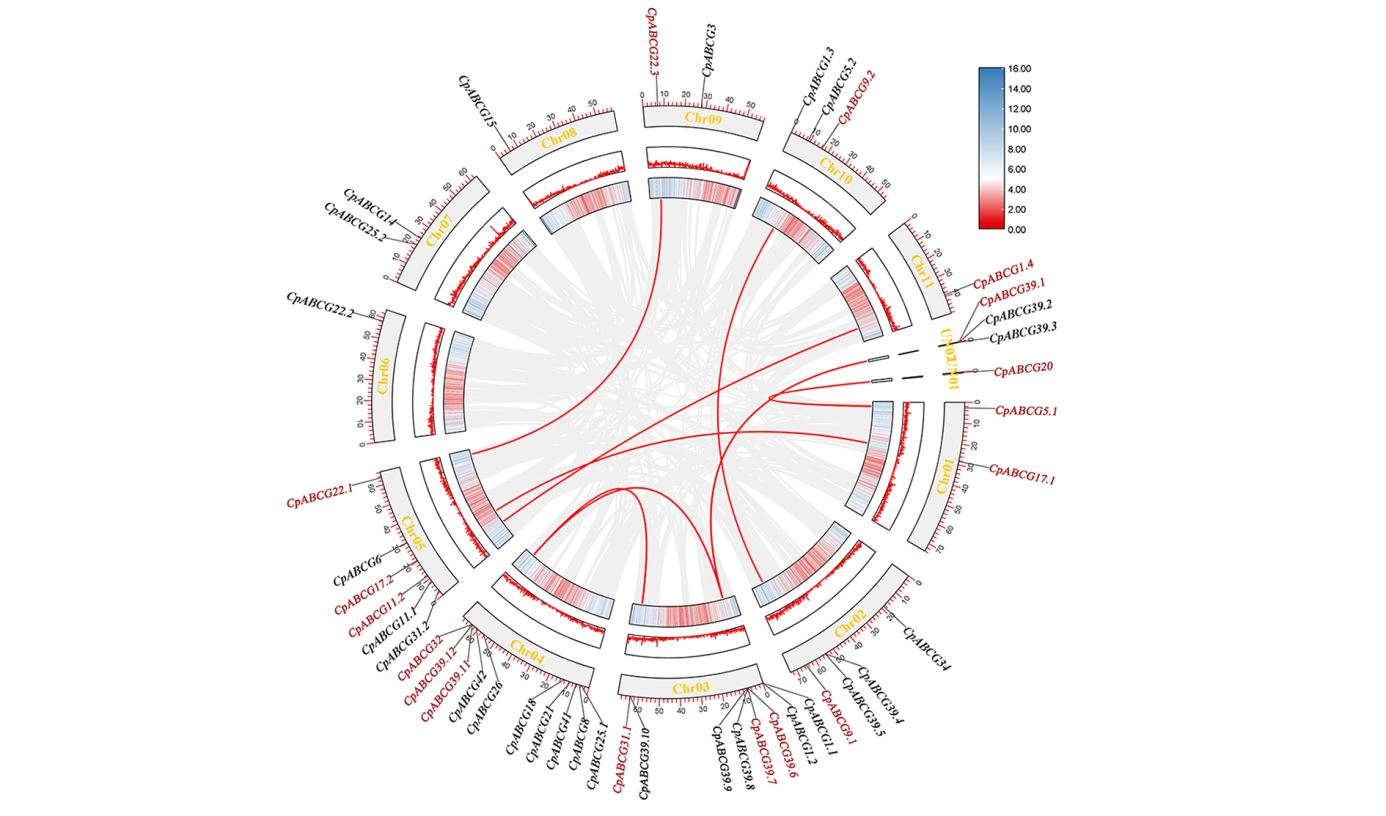
图4 蜡梅ABCG基因复制分析 外侧方框代表染色体骨架,中间和内侧方框表示基因密度,每个基因在染色体骨架上的大致分布用短黑线标出,红色线表示CpABCG的片段复制基因对
Fig. 4 Replication events of the CpABCG family members in Chimonanthus praecox The outer box represents the chromosome skeleton,the middle and inner boxes indicate gene density,and the approximate distribution of each CpABCG gene is marked on the chromosome skeleton by a short black line,the red line indicates the segmental duplication gene pairs of the CpABCG
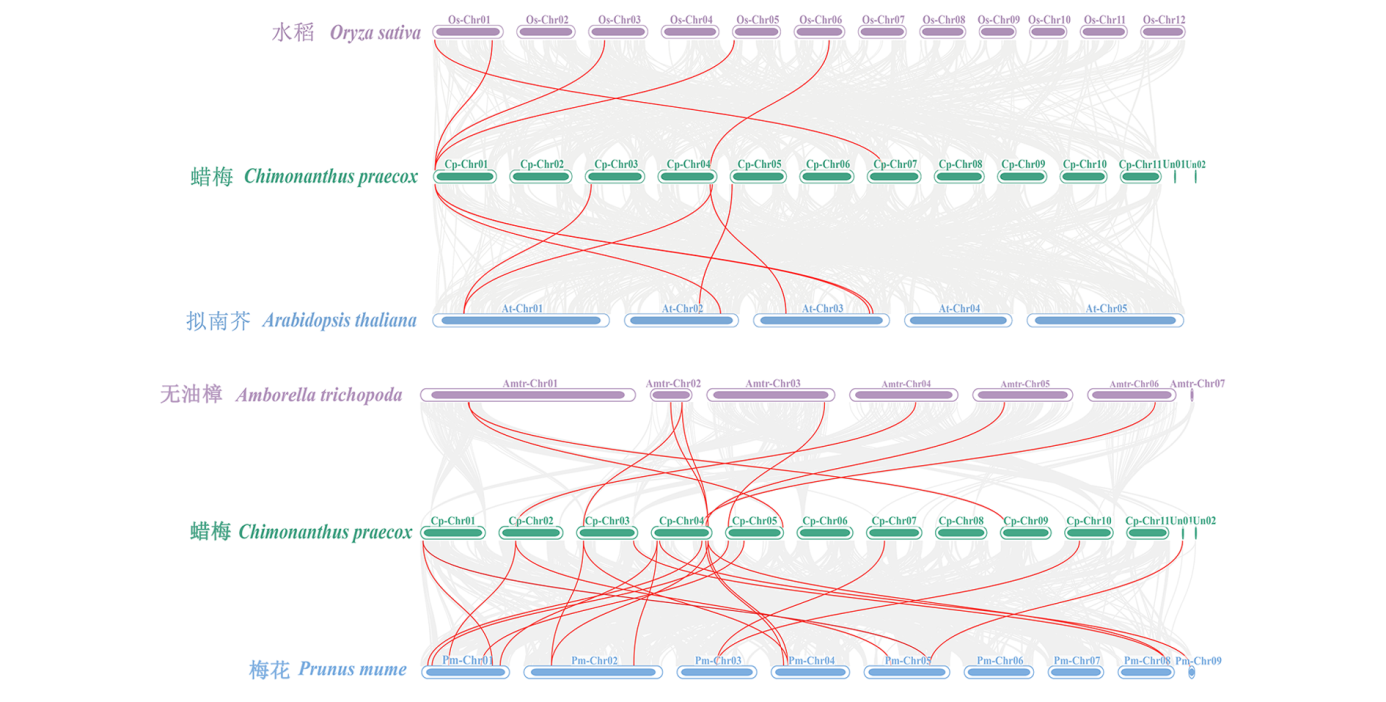
图5 CpABCG基因不同物种间共线性分析 背景中灰色线条表示蜡梅与其他物种之间的共线性区块,红色线条突出了CpABCG基因对
Fig. 5 Covariance analysis of CpABCG genes in different species Gray lines indicate blocks of covariance between Chimonanthus praecox and other species,and red lines highlight CpABCG gene pairs

图6 CpABCG基因家族启动子顺式作用元件分析 WBC型和PDR型的基因分别用蓝色线条和红色线条表示
Fig. 6 Analysis of cis-acting elements of CpABCG gene family promoters The WBC and PDR genes are represented by blue and red lines,respectively
| 类型 Type | 功能 Function | 顺式作用元件 cis-Acting element | 数量 Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| 植物生长发育 Plant growth and development | DNA 结合蛋白(ATBP-1)结合位点 Binding site of AT-rich DNA binding protein(ATBP-1) | AT-rich element | 2 |
| MYBHv1结合位点 MYBHv1 binding site | CCAAT-box | 26 | |
| 玉米醇溶蛋白代谢调节 Zein metabolism regulation | O2-site | 34 | |
| 分生组织表达 Meristem expression | CAT-box,NON-box | 31 | |
| 光响应元件 Light responsive element | AE-box,ATC-Motif,chs-CMA1a,MRE,G-Box,ACE,3-AF1 binding site,CAG-Motif | 405 | |
| 胚乳表达 Endosperm expression | GCN4_Motif | 14 | |
| 细胞周期调节 Cell cycle regulation | MSA-like | 6 | |
| 栅栏叶肉细胞分化 Differentiation of the palisade mesophyll cells | HD-Zip 1 | 4 | |
| 昼夜节律控制 Ircadian control | circadian | 14 | |
| 胁迫响应 Biological and abiotic stress | 低温响应 Low-temperature responsiveness | LTR | 23 |
| 防御和胁迫响应 Defense and stress responsiveness | TC-rich repeats | 9 | |
| 干旱诱导 Drought-inducibility | MBS | 37 | |
| 与缺氧特异性诱导有关的增强子元件,厌氧诱导所必需的调节元件 Anoxic specific inducibility,anaerobic induction | GC-Motif,ARE | 66 | |
| 激素响应 Hormones | 脱落酸响应 Abscisic acid responsiveness | TCA-element | 94 |
| 赤霉素响应 Gibberellin-responsive element | CARE;TATC-box | 49 | |
| 茉莉酸甲酯响应 The MeJA-responsiveness | CGTCA-Motif | 190 | |
| 生长素响应 Auxin-responsive element | AuxRR-core,TGA-element | 29 | |
| 水杨酸响应 Salicylic acid responsiveness | SARE | 23 |
表4 CpABCG基因家族启动子顺式作用元件分类
Table 4 Classification of cis-acting elements of CpABCG gene family promoters
| 类型 Type | 功能 Function | 顺式作用元件 cis-Acting element | 数量 Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| 植物生长发育 Plant growth and development | DNA 结合蛋白(ATBP-1)结合位点 Binding site of AT-rich DNA binding protein(ATBP-1) | AT-rich element | 2 |
| MYBHv1结合位点 MYBHv1 binding site | CCAAT-box | 26 | |
| 玉米醇溶蛋白代谢调节 Zein metabolism regulation | O2-site | 34 | |
| 分生组织表达 Meristem expression | CAT-box,NON-box | 31 | |
| 光响应元件 Light responsive element | AE-box,ATC-Motif,chs-CMA1a,MRE,G-Box,ACE,3-AF1 binding site,CAG-Motif | 405 | |
| 胚乳表达 Endosperm expression | GCN4_Motif | 14 | |
| 细胞周期调节 Cell cycle regulation | MSA-like | 6 | |
| 栅栏叶肉细胞分化 Differentiation of the palisade mesophyll cells | HD-Zip 1 | 4 | |
| 昼夜节律控制 Ircadian control | circadian | 14 | |
| 胁迫响应 Biological and abiotic stress | 低温响应 Low-temperature responsiveness | LTR | 23 |
| 防御和胁迫响应 Defense and stress responsiveness | TC-rich repeats | 9 | |
| 干旱诱导 Drought-inducibility | MBS | 37 | |
| 与缺氧特异性诱导有关的增强子元件,厌氧诱导所必需的调节元件 Anoxic specific inducibility,anaerobic induction | GC-Motif,ARE | 66 | |
| 激素响应 Hormones | 脱落酸响应 Abscisic acid responsiveness | TCA-element | 94 |
| 赤霉素响应 Gibberellin-responsive element | CARE;TATC-box | 49 | |
| 茉莉酸甲酯响应 The MeJA-responsiveness | CGTCA-Motif | 190 | |
| 生长素响应 Auxin-responsive element | AuxRR-core,TGA-element | 29 | |
| 水杨酸响应 Salicylic acid responsiveness | SARE | 23 |
| 基因名称 Gene name | 同源基因 Homologous gene | 功能 Function | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| CpABCG1.2 CpABCG1.3 | PhABCG1 | 将挥发性苯类/苯丙素类化合物转运到花瓣表皮细胞外,促进矮牵牛花香物质的释放 Volatile benzenes/phenylpropyl compounds were transported to the outside ofpetal epidermal cells to promote the release of floral substances in petunia | Adebesin et al., |
| AtABCG1 | 参与木栓质和花粉壁细胞外屏障形成,还可影响拟南芥生殖器官中生长素的信号传导 Involved in the formation of extracellular barriers and modulation of auxin signaling in Arabidopsis reproductive organs | Liu et al., | |
| AcABCG1 | 参与重金属/逆境胁迫响应 Involvement in heavy metal/stress response | 李季肤 等, | |
| MsABCG1 | 通过调节生理指标提高植物抗旱性 The drought resistance of plants can be improved by regulating physiological indexes | 李媛英, | |
| CpABCG14 CpABCG21 CpABCG9.1 CpABCG9.2 CpABCG25.2 | PmABCG9 | 转运苯甲醇 Transport benzyl alcohol | 郝瑞杰 等, |
| AtABCG9 | 促进花粉表面甾醇苷的运输从而调控花粉壁的成熟 Promote pollen surface steryl glycoside transport to regulate pollen wall maturation | Choi et al., | |
| OsABCG9 | 参与水稻蜡质积累 Involved in rice wax accumulation | Nguyen et al., | |
| CpABCG26 | PmABCG2 | 参与苯甲醛转运 Transport benzaldehyde | 常珺, |
表5 不同物种相关同源基因功能研究
Table 5 Functional Studies on Related Homolog Genes in different species
| 基因名称 Gene name | 同源基因 Homologous gene | 功能 Function | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| CpABCG1.2 CpABCG1.3 | PhABCG1 | 将挥发性苯类/苯丙素类化合物转运到花瓣表皮细胞外,促进矮牵牛花香物质的释放 Volatile benzenes/phenylpropyl compounds were transported to the outside ofpetal epidermal cells to promote the release of floral substances in petunia | Adebesin et al., |
| AtABCG1 | 参与木栓质和花粉壁细胞外屏障形成,还可影响拟南芥生殖器官中生长素的信号传导 Involved in the formation of extracellular barriers and modulation of auxin signaling in Arabidopsis reproductive organs | Liu et al., | |
| AcABCG1 | 参与重金属/逆境胁迫响应 Involvement in heavy metal/stress response | 李季肤 等, | |
| MsABCG1 | 通过调节生理指标提高植物抗旱性 The drought resistance of plants can be improved by regulating physiological indexes | 李媛英, | |
| CpABCG14 CpABCG21 CpABCG9.1 CpABCG9.2 CpABCG25.2 | PmABCG9 | 转运苯甲醇 Transport benzyl alcohol | 郝瑞杰 等, |
| AtABCG9 | 促进花粉表面甾醇苷的运输从而调控花粉壁的成熟 Promote pollen surface steryl glycoside transport to regulate pollen wall maturation | Choi et al., | |
| OsABCG9 | 参与水稻蜡质积累 Involved in rice wax accumulation | Nguyen et al., | |
| CpABCG26 | PmABCG2 | 参与苯甲醛转运 Transport benzaldehyde | 常珺, |
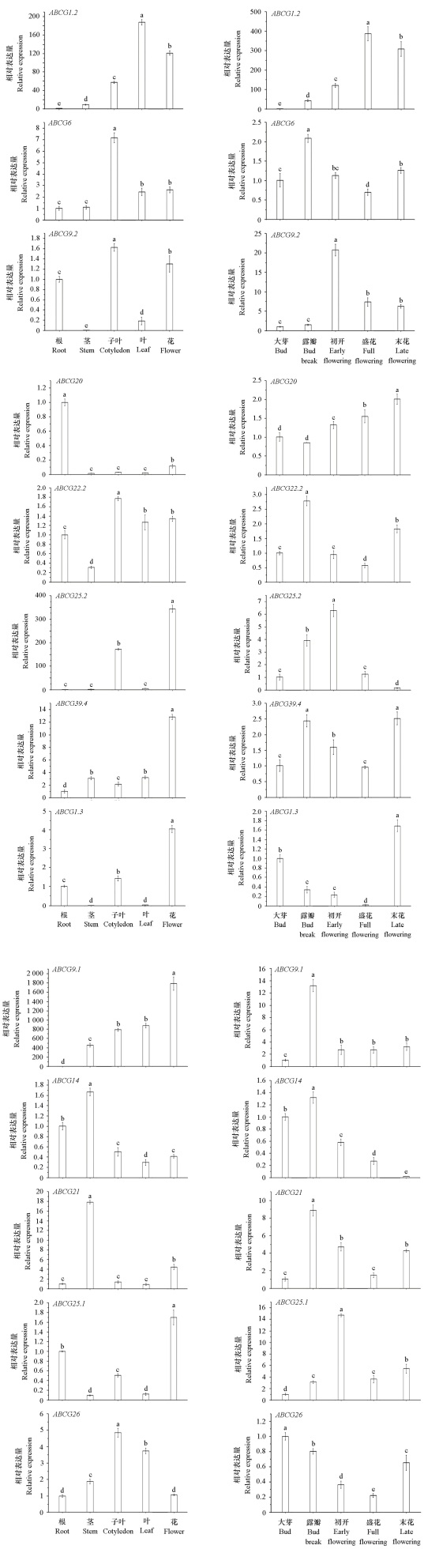
图9 候选CpABCG基因不同部位不同时间相对表达量分析 邓肯氏单因素方差分析,不同小写字母表示各样本间差异显著(P < 0.05)
Fig. 9 Analysis of relative expression of candidate CpABCG gene in different parts and time One-way ANOVA,Duncan’s test. Different lowercase letters indicate significant among different samples at 0.05 level
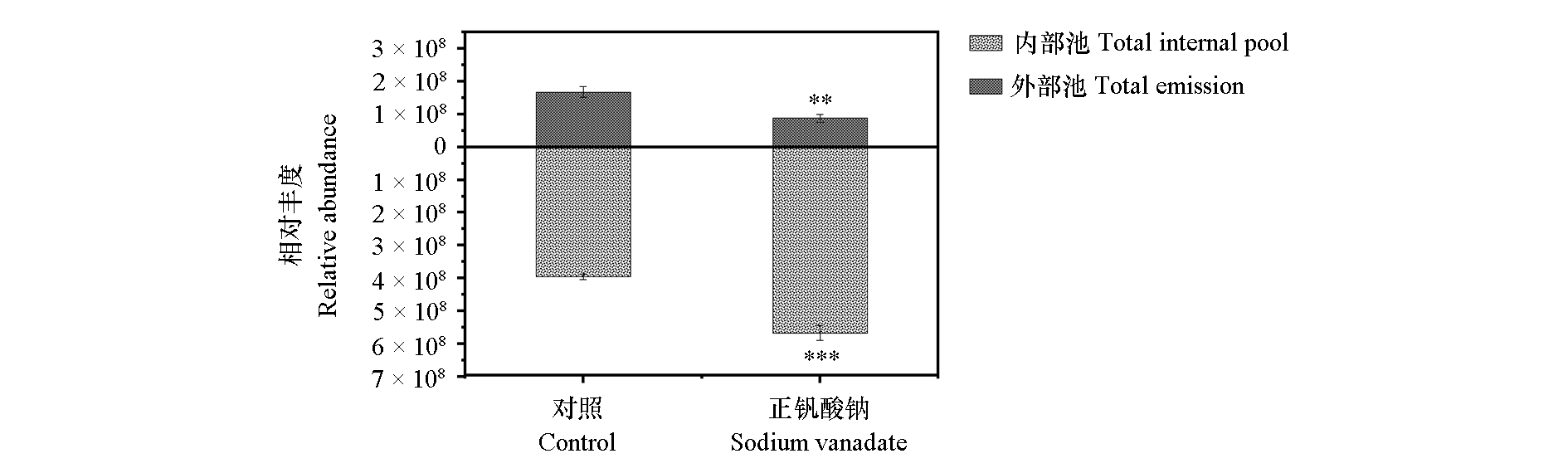
图10 外部释放和内源花香总量 t检验。**,***分别表示处理间差异显著(P < 0.01,P < 0.001)
Fig. 10 Comparison of total amount of external release and endogenous flower fragrance between experimental group and control group t-test. **,*** indicate significant differences(P < 0.01,P < 0.001)
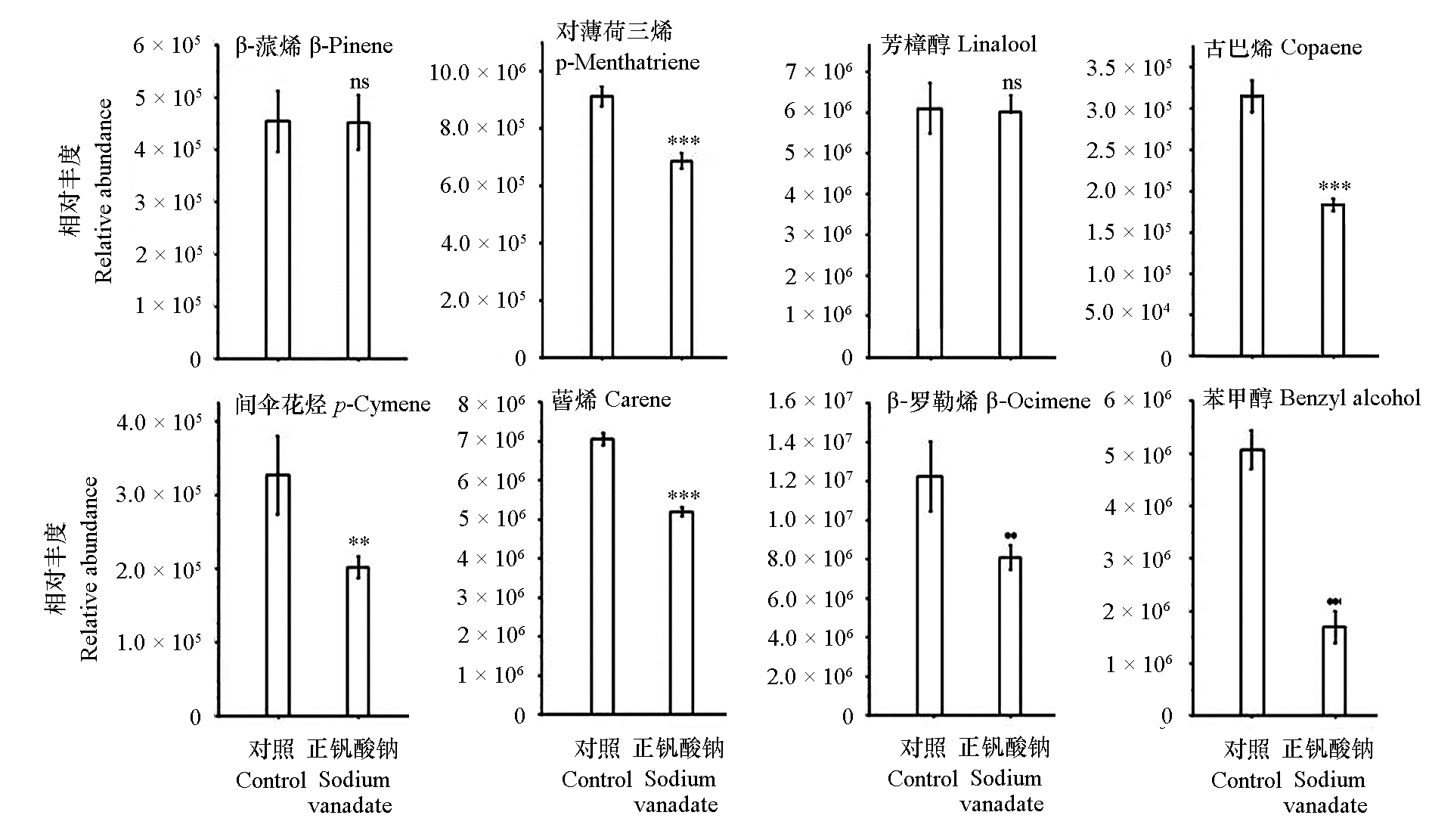
图11 主要花香成分外部挥发情况 t检验。**,***和ns分别表示处理间的差异显著性(P < 0.01,P < 0.001,P > 0.05)。下同
Fig. 11 External volatilization of main floral components t-test. **,***,and ns indicate significant differences between treatments,respectively(P < 0.01,P < 0.001,P > 0.05). The same below
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
|
常珺. 2023. 梅花苯甲醛转运相关ABCG基因的挖掘与功能分析[硕士论文]. 太原: 山西农业大学.
|
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
|
丁冬会, 张雨朋, 周人玲, 席武洋, 耿旎周, 常玮, 赵青平, 刘嘉斐, 杨树琼. 2024. 绿豆7S球蛋白基因鉴定及在籽粒发育中的表达分析. 食品科学, 45 (12):109-115.
|
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
|
郝瑞杰, 邱晨, 耿晓云, 贾浩田, 张雅静, 常珺, 冯新新. 2023. 梅花PmABCG9在苯甲醇挥发中的功能分析. 中国农业科学, 56 (13):2574-2585.
|
|
| [18] |
|
|
胡荻. 2016. 小报春(Primula forbesii)花香成分以及发香部位研究[硕士论文]. 雅安: 四川农业大学.
|
|
| [19] |
|
|
胡桂婷, 杨丽媛, 任广兵, 赵宏波. 2025. 3种蜡梅属植物花香物质及白天释放节律. 浙江农林大学学报, 42 (1):124-132.
|
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
|
李航航. 2020. 木豆ABCG转运蛋白抵御非生物胁迫的作用机制研究[硕士论文]. 北京: 北京林业大学.
|
|
| [22] |
|
|
李季肤, 韩佳芮, 贾怡丹, 张郎织, 王文强, 王志勇, 陈志坚. 2019. 地毯草铝响应基因AcABCG1的克隆与表达分析. 草地学报, 27 (5):1147-1153.
|
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
|
李莹莹. 2012. 萜烯类与苯丙酸类花香挥发物的生物合成与调节. 生物技术, 22 (2):86-90.
|
|
| [25] |
|
|
李媛英. 2021. 紫花苜蓿ABC转运蛋白基因(MsABCG1)的克隆及功能分析[硕士论文]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学.
|
|
| [26] |
|
|
李紫阳, 杨克彬, 朱成磊, 刘燕, 郭栋, 肖晓燕, 高志民. 2023. 毛竹ABCG基因鉴定及其表达模式研究. 核农学报, 37 (5):917-926.
|
|
| [27] |
|
|
林玉雪, 胡一航, 蔡月琴, 熊瑜, 陈龙清, 谯正林. 2025. 荷花GRF基因家族鉴定及外源GA3和NAA处理表达分析. 西南农业学报, 38 (5):938-949.
|
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
|
刘艳青, 赵永芳. 2017. ABC转运蛋白结构与转运机制的研究进展. 生命科学, 29 (3):223-229.
|
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
|
钱晓慧, 陈龙清, 李彪, 施蕊. 2021. 云南地区不同基因型蜡梅花香气成分分析. 西南农业学报, 34 (4):834-841.
|
|
| [37] |
|
|
邱晨, 常珺, 王帅兵, 范丽娜, 贾浩田, 郝瑞杰. 2022. 不同外源调节剂对梅花花香性状的影响. 江西农业学报, 34 (12):46-52.
|
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
|
田敬璞. 2019. 蜡梅花香生物合成途径及单萜合成酶基因功能的解析[博士论文]. 武汉: 华中农业大学.
|
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
|
闫超凡, 孙雪梅, 钟启文, 邵登魁, 邓昌蓉, 文军琴. 2024. 番茄20S蛋白酶体基因家族鉴定及生物信息学分析. 园艺学报, 51 (2):266-280.
|
|
| [44] |
|
|
杨姝婷. 2021. 梅花花香挥发的部位差异分析及ABCG基因的表达研究[硕士论文]. 太原: 山西农业大学.
|
|
| [45] |
|
|
余莉. 2013. 蜡梅花挥发性组分与花色色素分析[硕士论文]. 武汉: 华中农业大学.
|
|
| [46] |
|
|
张雅静. 2022. 梅花苯甲醇挥发相关基因PmABCG9的功能解析[硕士论文]. 太原: 山西农业大学.
|
|
| [47] |
|
|
张雅静, 郝瑞杰, 杨姝婷, 张忠强, 常珺, 邱晨. 2022. 3种花香调节剂对矮牵牛花香性状的影响. 山西农业科学,(3):346-355.
|
|
| [48] |
|
|
周明芹, 向林, 陈龙清. 2007. 蜡梅花香及花色色素成分的初步研究. 北京林业大学学报,(1):22-25.
|
| [1] | 王芳, 范燕萍. 观赏植物花香性状形成及调控机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 359-385. |
| [2] | 谢雨滢, 施婷婷, 杨秀莲, 王良桂, 岳远征. 花香的生物功能及其合成机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 386-396. |
| [3] | 赵雨晴, 唐菲鸿, 郑仕杰, 官泽恩, 吴建凯, 刘仲健, 彭东辉, 兰思仁, 赵凯, 周育真. 兰花“花香”物质研究进展:从合成机制到进化驱动[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 412-436. |
| [4] | 牛童非, 杨迪, 马慧丽, 郭丽丽, 侯小改. 牡丹花香的生物合成及调控研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 447-466. |
| [5] | 岳芝伊, 李心, 王昊宁, 张启翔, 孙丽丹. 梅花花香研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 467-480. |
| [6] | 付琪, 尚均忠, 裴文文, 刘国梁, 景维坤, 张颢, 蹇洪英, 邱显钦, 唐开学, 晏慧君. 月季花香物质合成基因及其演化机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 481-495. |
| [7] | 沈言, 夏子轶, 冷平生, 马波, 胡增辉. ‘西伯利亚’百合LiMYB4的克隆及在萜烯合成中的功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 525-537. |
| [8] | 魏永路, 叶广英, 高洁, 金建鹏, 陆楚桥, 李杰, 谢琦, 苟亚军, 朱根发, 杨凤玺. 腋唇兰花香成分鉴定和关键调控基因挖掘[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 538-556. |
| [9] | 李崇晖, 洪小雨, 陆顺教, 廖易, 尹俊梅. 基于代谢组与转录组联合分析解析秋石斛花香形成机制[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 557-573. |
| [10] | 刘庭函, 张一凡, 陈沄毅, 周利君, 刘雨晨, 吴思惠, 罗乐, 于超. 巨花蔷薇杂交子代花香成分解析与释香部位研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 585-597. |
| [11] | 陈艺荃, 樊荣辉, 林兵, 陈燕, 吴建设, 钟淮钦. 山茶花花香生物合成相关基因的实时荧光定量PCR内参基因的筛选及验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 598-612. |
| [12] | 孙俊明, 李晓云, 朱莹, 娄倩, 陈红武. 不同品种有髯鸢尾(Iris × barbata)花挥发性成分的GC-IMS分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(6): 1619-1632. |
| [13] | 汪锦, 高丽, 贺红宇, 涂勋良, 蒋彧. 兰属种间杂种花香成分特征分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(4): 897-907. |
| [14] | 付琪, 王丹, 景维坤, 张颢, 王慧纯, 蹇洪英, 邱显钦, 王其刚, 唐开学, 晏慧君. 月季类胡萝卜素裂解双加氧酶基因RcCCD4在花香合成中的功能[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 623-634. |
| [15] | 汪进萱, 倪莹, 孟昕, 冷卓, 马波, 冷平生, 吴静, 胡增辉. 紫丁香SoCHR35参与罗勒烯合成的功能解析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(10): 2655-2665. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司