
园艺学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 447-466.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2025-0961
牛童非1, 杨迪1,3, 马慧丽2, 郭丽丽1, 侯小改1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-11-14
修回日期:2026-01-06
出版日期:2026-02-25
发布日期:2026-02-12
基金资助:
NIU Tongfei1, YANG Di1,3, MA Huili2, GUO Lili1, HOU Xiaogai1( )
)
Received:2025-11-14
Revised:2026-01-06
Published:2026-02-25
Online:2026-02-12
摘要:
牡丹(Paeonia Sect. Moutan DC.)花型硕大、花色艳丽,且香气类型丰富,极具观赏价值。近年来,解析牡丹香气成分、培育芳香牡丹品种日益成为研究热点。本文中系统综述了牡丹花香的研究进展,包括牡丹花香成分的采集方法、香气合成与释放的影响因素以及关键香气物质的合成途径,并对未来研究方向进行展望,以期为牡丹花香育种与产业化应用提供理论参考。
牛童非, 杨迪, 马慧丽, 郭丽丽, 侯小改. 牡丹花香的生物合成及调控研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 447-466.
NIU Tongfei, YANG Di, MA Huili, GUO Lili, HOU Xiaogai. Advances in Floral Aroma Biosynthesis and Regulation in Tree Peony[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2026, 53(2): 447-466.
| 采集方法 Collection method | 优势 Advantage | 局限 Limitation | 牡丹应用场景 Applications in tree peony | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水蒸气蒸馏法 Steam Distillation,SD | 经典提取方法,成本低;无溶剂残留Classical extraction method,low cost;no solvent residue. | 极性萜烯和化学活性化合物可能会损失;耗时;产量低Polar terpenes and chemically active compounds may be lost;time-consuming;yield low | 适合提取水溶性极性挥发物,适合精油工业化制备Suitable for extracting water-soluble polar volatiles,suitable for essential oil industrial-scale preparation | Ormeño et al., |
| 溶剂萃取法 Solvent extraction,SE | 简单易行,可富集弱挥发性成分;无需加热,所需植物材料较少;质量优于水蒸气蒸馏法Simple and easy,can enrich weakly volatile components;no heating required,required plant material less;quality superior to steam distillation | 需要大量溶剂;溶剂易残留,难除去;可能共提取非挥发性物质Requires large amount of solvent;solvent easily remains,difficult to remove;may co-extract non-volatile substances | 适合提取精油或植物提取物中的挥发性成分Suitable for extracting volatile components from essential oils or plant extracts | Ormeño et al., |
| 同时蒸馏萃取 Simulatancous distillation extraction,SDE | 成本较低,操作简单;溶剂用量少,能较好保留易挥发成分Cost relatively low,operation simple;solvent amount small,can better retain volatile components | 耗时,且高温破坏热敏性成分;溶剂可能有残留Time-consuming,and high temperature damages heat-sensitive components;solvent may have residue | 适合提取非含氧单萜以及需要高效、完全提取的挥发物Suitable for extracting non-oxygenated monoterpenes and volatiles requiring efficient,complete extraction | Ormeño et al., |
| 超临界流体萃取 Supercritical fluid extraction,SFE | 绿色高效,无溶剂残留;保留热敏性成分Green and efficient,no solvent residue; retains heat-sensitive components | 设备昂贵,成本高;不可避免共提取蜡质;牡丹花瓣含油率极低,需要精油含量更高的牡丹新品种的大量花瓣Equipment expensive,cost high;unavoidable co-extraction of waxes;tree peony petals oil yield extremely low,requires large quantity of petals from new tree peony varieties with higher essential oil content | 适合提取倍半萜、亲脂性成分,制作高品质香料Suitable for extracting sesquiterpenes,lipophilic components,producing high-quality perfume | Ormeño et al., |
| 顶空固相微萃取 Headspace solid phase micro-extraction,HS-SPME | 灵敏度高,可有效富集目标成分且用量少,萃取手柄和纤维头可多次使用,不与样品直接接触,能有效减少样品中非挥发性成分对萃取的干扰Sensitivity high,can effectively enrich target components and dosage small,extraction handle and fiber can be used multiple times,does not directly contact the sample,can effectively reduce interference from sample non-volatile components on the extraction | 不能提取成分,仅适用于定性/半定量分析,难以精确定量;结果受纤维涂层、温度、时间、湿度等多种因素影响,需要严格优化和控制条件;对痕量成分检测能力有限Cannot extract components,only suitable for qualitative/semi-quantitative analysis,difficult to accurately quantify;results affected by fiber coating,temperature,time,humidity and other factors,requires strict optimization and control of conditions;detection capability for trace components limited | 适合珍贵样品的挥发性成分采集Suitable for precious samples volatile component collection | 郝守进 等, |
| 动态顶空取样法 Dynamic headspace sampling,DHS | 非破坏性,原位采集;可富集低浓度挥发性成分;数据真实;可连续采样;所用材料可多次使用Non-destructive,in-situ sampling;can enrich low-concentration volatile components;data authentic;allows continuous sampling;materials used can be reused multiple times | 吸附剂种类影响挥发性成分吸附效果;设备携带不便Adsorbent type affects volatile component adsorption effect;equipment portability poor | 适合种植在实验室外且株型较大的植株,适合时间序列分析Suitable for those plants that are to be planted outside the laboratory and have a large plant size,suitable for time series analysis | Tholl et al., |
表1 常见花香采集方法比较
Table 1 Comparison of common methods for collecting flower fragrance
| 采集方法 Collection method | 优势 Advantage | 局限 Limitation | 牡丹应用场景 Applications in tree peony | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水蒸气蒸馏法 Steam Distillation,SD | 经典提取方法,成本低;无溶剂残留Classical extraction method,low cost;no solvent residue. | 极性萜烯和化学活性化合物可能会损失;耗时;产量低Polar terpenes and chemically active compounds may be lost;time-consuming;yield low | 适合提取水溶性极性挥发物,适合精油工业化制备Suitable for extracting water-soluble polar volatiles,suitable for essential oil industrial-scale preparation | Ormeño et al., |
| 溶剂萃取法 Solvent extraction,SE | 简单易行,可富集弱挥发性成分;无需加热,所需植物材料较少;质量优于水蒸气蒸馏法Simple and easy,can enrich weakly volatile components;no heating required,required plant material less;quality superior to steam distillation | 需要大量溶剂;溶剂易残留,难除去;可能共提取非挥发性物质Requires large amount of solvent;solvent easily remains,difficult to remove;may co-extract non-volatile substances | 适合提取精油或植物提取物中的挥发性成分Suitable for extracting volatile components from essential oils or plant extracts | Ormeño et al., |
| 同时蒸馏萃取 Simulatancous distillation extraction,SDE | 成本较低,操作简单;溶剂用量少,能较好保留易挥发成分Cost relatively low,operation simple;solvent amount small,can better retain volatile components | 耗时,且高温破坏热敏性成分;溶剂可能有残留Time-consuming,and high temperature damages heat-sensitive components;solvent may have residue | 适合提取非含氧单萜以及需要高效、完全提取的挥发物Suitable for extracting non-oxygenated monoterpenes and volatiles requiring efficient,complete extraction | Ormeño et al., |
| 超临界流体萃取 Supercritical fluid extraction,SFE | 绿色高效,无溶剂残留;保留热敏性成分Green and efficient,no solvent residue; retains heat-sensitive components | 设备昂贵,成本高;不可避免共提取蜡质;牡丹花瓣含油率极低,需要精油含量更高的牡丹新品种的大量花瓣Equipment expensive,cost high;unavoidable co-extraction of waxes;tree peony petals oil yield extremely low,requires large quantity of petals from new tree peony varieties with higher essential oil content | 适合提取倍半萜、亲脂性成分,制作高品质香料Suitable for extracting sesquiterpenes,lipophilic components,producing high-quality perfume | Ormeño et al., |
| 顶空固相微萃取 Headspace solid phase micro-extraction,HS-SPME | 灵敏度高,可有效富集目标成分且用量少,萃取手柄和纤维头可多次使用,不与样品直接接触,能有效减少样品中非挥发性成分对萃取的干扰Sensitivity high,can effectively enrich target components and dosage small,extraction handle and fiber can be used multiple times,does not directly contact the sample,can effectively reduce interference from sample non-volatile components on the extraction | 不能提取成分,仅适用于定性/半定量分析,难以精确定量;结果受纤维涂层、温度、时间、湿度等多种因素影响,需要严格优化和控制条件;对痕量成分检测能力有限Cannot extract components,only suitable for qualitative/semi-quantitative analysis,difficult to accurately quantify;results affected by fiber coating,temperature,time,humidity and other factors,requires strict optimization and control of conditions;detection capability for trace components limited | 适合珍贵样品的挥发性成分采集Suitable for precious samples volatile component collection | 郝守进 等, |
| 动态顶空取样法 Dynamic headspace sampling,DHS | 非破坏性,原位采集;可富集低浓度挥发性成分;数据真实;可连续采样;所用材料可多次使用Non-destructive,in-situ sampling;can enrich low-concentration volatile components;data authentic;allows continuous sampling;materials used can be reused multiple times | 吸附剂种类影响挥发性成分吸附效果;设备携带不便Adsorbent type affects volatile component adsorption effect;equipment portability poor | 适合种植在实验室外且株型较大的植株,适合时间序列分析Suitable for those plants that are to be planted outside the laboratory and have a large plant size,suitable for time series analysis | Tholl et al., |
| 化合物Compounds | 品种Cultivar | 气味特征Odour profile | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 单萜类Monoterpenes | |||
| 芳樟醇Linalool | ‘海黄’‘格桑黄’‘黄水晶’、大花黄牡丹 P. suffruticosa‘Highnoon’,P. ludlowii‘Gesanghuang’,P. suffruticosa ‘Huangshuijing’,P. ludlowii | 花香、甜香、柑橘香 Floral,sweet,citrus | 孙苗, |
| 香茅醇Citronellol | ‘银粉金鳞’‘冠群芳’‘香玉’‘肉芙蓉’‘初乌’ P. suffruticosa‘Yinfen Jinlin’,P. suffruticosa‘Guanqunfang’,P. suffruticosa ‘Xiangyu’, P. suffruticosa‘Roufurong’,P. suffruticosa‘Chuwu’ | 花香、玫瑰香、柑橘香 Flora,rose,citrus | 周海梅 等, |
| 橙花醇Nerol | ‘赵粉’‘脂红’‘凤丹’P. suffruticosa‘Zhaofen’,P. suffruticosa‘Zhihong’,P. ostii‘Fengdan’ | 天然橙花气味、甜香、柑橘香、玉兰香Natural neroli,sweet,citrus,magnolia | 刘爽 等, |
| 香叶醇Geraniol | ‘千堆雪’‘墨润绝伦’‘粉中冠’‘赛雪塔’ P. suffruticosa‘Qianduixue’,P. suffruticosa‘Morun Juelun’,P. suffruticosa‘Fenzhongguan’,P. suffruticosa ‘Saixueta’ | 甜美的花香、水果香、玫瑰香、柑橘香 Sweet floral,fruity,rose,citrus | 张红磊, |
| 罗勒烯Ocimene | ‘格桑绿’‘鲁菏红’‘脂红’‘首案红’ P. ludlowii‘Gesanglv’,P. suffruticosa‘Luhehong’,P. suffruticosa‘Zhihong’,P. suffruticosa‘Shouanhong’ | 绿色、热带气息、木质香、花香、 柑橘香 Green,tropical,woody,floral,citrus | 张红磊, |
| 倍半萜类Sesquiterpenes | |||
| 大根香叶烯D Germacrene D | ‘姚黄’‘粉楼台’‘银红巧对’‘春雪’‘二乔’P. suffruticosa‘Yaohuang’,P. suffruticosa‘Fenloutai’,P. suffruticosa‘Yinhong Qiaodui’,P. suffruticosa‘Chunxue’,P. suffruticosa‘Erqiao’ | 木质味、辛辣味 Woody,spicy | 周海梅 等, |
| β-石竹烯β-Caryophyllene | ‘蓝宝石’‘水晶白’‘紫二乔’ P. suffruticosa‘Lanbaoshi’,P. suffruticosa‘Shuijingbai’,P. suffruticosa‘Zierqiao’ | 丁香、木本、坚果、果皮、粉椒味道 Clove,woody,nut,skin,powdery peppery | 李莹莹 等, |
| α-法尼烯α-Farnesene | ‘乌金耀辉’‘百园紫’‘海黄’‘大棕紫’ P. suffruticosa‘Wujin Yaohui’,P. suffruticosa ‘Baiyuanzi’,P. suffruticosa‘Highnoon’,P. suffruticosa‘Dazongzi’ | 清新绿色植物味、热带水果味 Fresh green vegetative,tropical fruity | 周海梅 等, |
| β-波旁烯β-Bourbonene | 大花黄牡丹P. ludlowii | 草本、木本味道Herbaceous,woody | 徐慧, |
| 苯丙素类/苯环类Benzenoids/phenylpropanoids | |||
| 对二甲氧基苯1,4-Dimethoxybenzene | ‘书生捧墨’‘银红巧对’‘首案红’‘藏枝红’ P. suffruticosa‘Shusheng Pengmo’,P. suffruticosa ‘Yinhong Qiaodui’,P. suffruticosa‘Shouanhong’,P. suffruticosa‘Cangzhihong’ | 新刈的干草、茴香、绿山楂 New mown hay,anisic,green hawthorn | 张红磊, |
| 1,3,5-三甲氧基苯1,3,5-Trimethoxybenzene | ‘粉楼台’‘蓝宝石’‘脂红’‘葛巾紫’ P. suffruticosa‘Fenloutai’,P. suffruticosa‘Lanbaoshi’,P. suffruticosa‘Zhihong’,P. suffruticosa‘Gejinzi’ | 酚类、甜三叶草 Phenolic,sweet clover | 张静 等, |
| 苯乙醇Phenylethyl alcohol | ‘天香’‘冠艳群芳’‘十八号’‘黄水晶’P. suffruticosa ‘Tianxiang’,P. suffruticosa‘Guanyan Qunfang’,P. suffruticosa‘Shibahao’,P. suffruticosa‘Huangshuijing’ | 花香、玫瑰、蜂蜜、甜、新鲜 Floral,rose,honey,sweet,fresh | 张红磊, |
| 乙酸苯乙酯 Acetic acid, 2-phenylethyl ester | ‘一品红’‘冠群芳’‘墨楼争辉’‘花二乔’P. suffruticosa‘Yipinhong’,P. suffruticosa ‘Guanqunfang’,P. suffruticosa‘Molou Zhenghui’,P. suffruticosa‘Huaerqiao’ | 甜、蜂蜜、花香、玫瑰 Sweet,honey,floral,rose | 李莹莹 等, |
| 甲基丁香酚Methyleugenol | ‘粉面桃腮’‘春雪’‘赛雪塔’‘雪莲’P. suffruticosa ‘Fenmian Taosai’,P. suffruticosa‘Chunxue’, P. suffruticosa‘Saixueta’,P. suffruticosa‘Xuelian’ | 辛辣、肉桂、丁香、霉味、蔬菜、蜡质、胡椒Spicy,cinnamon,clove,musty,vegetable,waxy,peppery | 孙强, |
| 脂肪酸衍生物Fatty acid derivatives | |||
| 己酸乙酯Acetic acid, hexyl ester | ‘京飞红’‘醉桃’‘雪海冰心’‘首案红’ P. suffruticosa‘Jingfeihong’,P. suffruticosa‘Zuitao’,P. suffruticosa‘Xuehai Bingxin’,P. suffruticosa‘Shouanhong’ | 苹果、香蕉、草、香草、梨 Apple,banana,grass,herb,pear | 张静 等, |
| 乙酸香茅酯Citronellyl acetate | ‘香玉’‘粉面桃腮’‘白鹤展翅’‘雪海冰心’P. suffruticosa‘Xiangyu’,P. suffruticosa‘Fenmian Taosai’,P. suffruticosa‘Baihe Zhanchi’, P. suffruticosa‘Xuehai Bingxin’ | 花香、芳香、玫瑰 Floral,fragant,rose | 张玲, |
| 乙酸香叶酯Geranyl acetate | ‘春雪’‘丛中笑’‘宏图’‘红霞争辉’ P. suffruticosa‘Chunxue’,P. suffruticosa ‘Congzhongxiao’,P. suffruticosa‘Hongtu’, P. suffruticosa‘Hongxia Zhenghui’ | 花香、玫瑰、薰衣草、绿色、蜡质 Floral,rose,lavender,green,waxy | 孙强, |
| 壬醛Nonanal | ‘海黄’‘天香’‘春雪’‘凤丹白’ P. suffruticosa‘Highnoon’,P. suffruticosa‘Tianxiang’,P. suffruticosa‘Chunxue’,P. ostii‘Fengdanbai’ | 柑橘味,蜡质,清新的绿色的柠檬皮,黄瓜的油脂味 Citrus,waxy,fresh slightly green lemon peel like nuance,cucumber fattiness | 孙强, |
| 十五烷Pentadecane | ‘凤丹’‘洛阳红’‘赵粉’‘海黄’ P. ostii‘Fengdan’,P. suffruticosa‘Luoyanghong’,P. suffruticosa‘Zhaofen’,P. suffruticosa‘Highnoon’ | 气味极其微弱或近乎无味 Weak or odorless | 周海梅 等, |
表2 牡丹中常见的挥发性化合物
Table 2 Common volatile compounds in tree peony
| 化合物Compounds | 品种Cultivar | 气味特征Odour profile | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 单萜类Monoterpenes | |||
| 芳樟醇Linalool | ‘海黄’‘格桑黄’‘黄水晶’、大花黄牡丹 P. suffruticosa‘Highnoon’,P. ludlowii‘Gesanghuang’,P. suffruticosa ‘Huangshuijing’,P. ludlowii | 花香、甜香、柑橘香 Floral,sweet,citrus | 孙苗, |
| 香茅醇Citronellol | ‘银粉金鳞’‘冠群芳’‘香玉’‘肉芙蓉’‘初乌’ P. suffruticosa‘Yinfen Jinlin’,P. suffruticosa‘Guanqunfang’,P. suffruticosa ‘Xiangyu’, P. suffruticosa‘Roufurong’,P. suffruticosa‘Chuwu’ | 花香、玫瑰香、柑橘香 Flora,rose,citrus | 周海梅 等, |
| 橙花醇Nerol | ‘赵粉’‘脂红’‘凤丹’P. suffruticosa‘Zhaofen’,P. suffruticosa‘Zhihong’,P. ostii‘Fengdan’ | 天然橙花气味、甜香、柑橘香、玉兰香Natural neroli,sweet,citrus,magnolia | 刘爽 等, |
| 香叶醇Geraniol | ‘千堆雪’‘墨润绝伦’‘粉中冠’‘赛雪塔’ P. suffruticosa‘Qianduixue’,P. suffruticosa‘Morun Juelun’,P. suffruticosa‘Fenzhongguan’,P. suffruticosa ‘Saixueta’ | 甜美的花香、水果香、玫瑰香、柑橘香 Sweet floral,fruity,rose,citrus | 张红磊, |
| 罗勒烯Ocimene | ‘格桑绿’‘鲁菏红’‘脂红’‘首案红’ P. ludlowii‘Gesanglv’,P. suffruticosa‘Luhehong’,P. suffruticosa‘Zhihong’,P. suffruticosa‘Shouanhong’ | 绿色、热带气息、木质香、花香、 柑橘香 Green,tropical,woody,floral,citrus | 张红磊, |
| 倍半萜类Sesquiterpenes | |||
| 大根香叶烯D Germacrene D | ‘姚黄’‘粉楼台’‘银红巧对’‘春雪’‘二乔’P. suffruticosa‘Yaohuang’,P. suffruticosa‘Fenloutai’,P. suffruticosa‘Yinhong Qiaodui’,P. suffruticosa‘Chunxue’,P. suffruticosa‘Erqiao’ | 木质味、辛辣味 Woody,spicy | 周海梅 等, |
| β-石竹烯β-Caryophyllene | ‘蓝宝石’‘水晶白’‘紫二乔’ P. suffruticosa‘Lanbaoshi’,P. suffruticosa‘Shuijingbai’,P. suffruticosa‘Zierqiao’ | 丁香、木本、坚果、果皮、粉椒味道 Clove,woody,nut,skin,powdery peppery | 李莹莹 等, |
| α-法尼烯α-Farnesene | ‘乌金耀辉’‘百园紫’‘海黄’‘大棕紫’ P. suffruticosa‘Wujin Yaohui’,P. suffruticosa ‘Baiyuanzi’,P. suffruticosa‘Highnoon’,P. suffruticosa‘Dazongzi’ | 清新绿色植物味、热带水果味 Fresh green vegetative,tropical fruity | 周海梅 等, |
| β-波旁烯β-Bourbonene | 大花黄牡丹P. ludlowii | 草本、木本味道Herbaceous,woody | 徐慧, |
| 苯丙素类/苯环类Benzenoids/phenylpropanoids | |||
| 对二甲氧基苯1,4-Dimethoxybenzene | ‘书生捧墨’‘银红巧对’‘首案红’‘藏枝红’ P. suffruticosa‘Shusheng Pengmo’,P. suffruticosa ‘Yinhong Qiaodui’,P. suffruticosa‘Shouanhong’,P. suffruticosa‘Cangzhihong’ | 新刈的干草、茴香、绿山楂 New mown hay,anisic,green hawthorn | 张红磊, |
| 1,3,5-三甲氧基苯1,3,5-Trimethoxybenzene | ‘粉楼台’‘蓝宝石’‘脂红’‘葛巾紫’ P. suffruticosa‘Fenloutai’,P. suffruticosa‘Lanbaoshi’,P. suffruticosa‘Zhihong’,P. suffruticosa‘Gejinzi’ | 酚类、甜三叶草 Phenolic,sweet clover | 张静 等, |
| 苯乙醇Phenylethyl alcohol | ‘天香’‘冠艳群芳’‘十八号’‘黄水晶’P. suffruticosa ‘Tianxiang’,P. suffruticosa‘Guanyan Qunfang’,P. suffruticosa‘Shibahao’,P. suffruticosa‘Huangshuijing’ | 花香、玫瑰、蜂蜜、甜、新鲜 Floral,rose,honey,sweet,fresh | 张红磊, |
| 乙酸苯乙酯 Acetic acid, 2-phenylethyl ester | ‘一品红’‘冠群芳’‘墨楼争辉’‘花二乔’P. suffruticosa‘Yipinhong’,P. suffruticosa ‘Guanqunfang’,P. suffruticosa‘Molou Zhenghui’,P. suffruticosa‘Huaerqiao’ | 甜、蜂蜜、花香、玫瑰 Sweet,honey,floral,rose | 李莹莹 等, |
| 甲基丁香酚Methyleugenol | ‘粉面桃腮’‘春雪’‘赛雪塔’‘雪莲’P. suffruticosa ‘Fenmian Taosai’,P. suffruticosa‘Chunxue’, P. suffruticosa‘Saixueta’,P. suffruticosa‘Xuelian’ | 辛辣、肉桂、丁香、霉味、蔬菜、蜡质、胡椒Spicy,cinnamon,clove,musty,vegetable,waxy,peppery | 孙强, |
| 脂肪酸衍生物Fatty acid derivatives | |||
| 己酸乙酯Acetic acid, hexyl ester | ‘京飞红’‘醉桃’‘雪海冰心’‘首案红’ P. suffruticosa‘Jingfeihong’,P. suffruticosa‘Zuitao’,P. suffruticosa‘Xuehai Bingxin’,P. suffruticosa‘Shouanhong’ | 苹果、香蕉、草、香草、梨 Apple,banana,grass,herb,pear | 张静 等, |
| 乙酸香茅酯Citronellyl acetate | ‘香玉’‘粉面桃腮’‘白鹤展翅’‘雪海冰心’P. suffruticosa‘Xiangyu’,P. suffruticosa‘Fenmian Taosai’,P. suffruticosa‘Baihe Zhanchi’, P. suffruticosa‘Xuehai Bingxin’ | 花香、芳香、玫瑰 Floral,fragant,rose | 张玲, |
| 乙酸香叶酯Geranyl acetate | ‘春雪’‘丛中笑’‘宏图’‘红霞争辉’ P. suffruticosa‘Chunxue’,P. suffruticosa ‘Congzhongxiao’,P. suffruticosa‘Hongtu’, P. suffruticosa‘Hongxia Zhenghui’ | 花香、玫瑰、薰衣草、绿色、蜡质 Floral,rose,lavender,green,waxy | 孙强, |
| 壬醛Nonanal | ‘海黄’‘天香’‘春雪’‘凤丹白’ P. suffruticosa‘Highnoon’,P. suffruticosa‘Tianxiang’,P. suffruticosa‘Chunxue’,P. ostii‘Fengdanbai’ | 柑橘味,蜡质,清新的绿色的柠檬皮,黄瓜的油脂味 Citrus,waxy,fresh slightly green lemon peel like nuance,cucumber fattiness | 孙强, |
| 十五烷Pentadecane | ‘凤丹’‘洛阳红’‘赵粉’‘海黄’ P. ostii‘Fengdan’,P. suffruticosa‘Luoyanghong’,P. suffruticosa‘Zhaofen’,P. suffruticosa‘Highnoon’ | 气味极其微弱或近乎无味 Weak or odorless | 周海梅 等, |
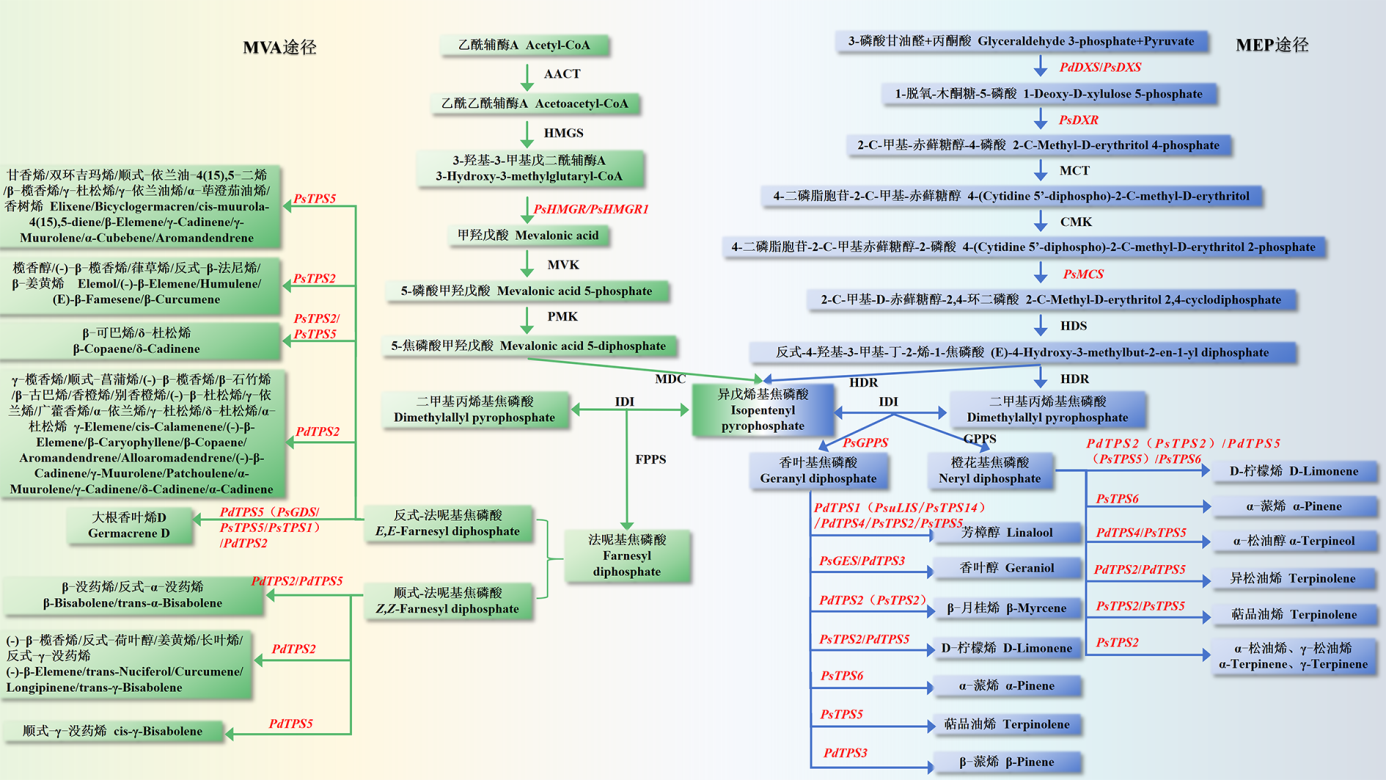
图1 牡丹萜类化合物生物合成途径(MVA和MEP) 红色字体代表在牡丹中已被克隆的基因。括号内的基因与括号前的基因为同一个基因。AACT:乙酰辅酶A乙酰基转移酶。HMGS:3-羟基-3-甲基戊二酰辅酶A合成酶。HMGR:3-羟基-3-甲基戊二酰辅酶A还原酶。MVK:甲羟戊酸激酶。PMK:磷酸甲羟戊酸激酶。MDC:甲羟戊酸焦磷酸脱羧酶。IDI:异戊烯基焦磷酸异构酶。FPPS:法尼基焦磷酸合成酶。GDS:大根香叶烯D合成酶。TPS:萜类合酶。DXS:1-脱氧-D-木酮糖-5-磷酸合成酶。DXR:1-脱氧-D-木酮糖-5-磷酸还原异构酶。MCT:2-C-甲基-D-赤藓醇-4-磷酸胞苷酰转移酶。CMK:4-二磷酸胞苷-2-C-甲基-D-赤藓糖醇激酶。MCS:2-C-甲基-D-赤藓糖醇-2,4-环二磷酸合成酶。HDS:4-羟基-3-甲基-2-丁烯基二磷酸合成酶。HDR:4-羟基-3-甲基-2-丁烯基二磷酸还原酶。 GPPS:香叶基焦磷酸合成酶。GES:香叶醇合成酶。LIS:芳樟醇合成酶
Fig. 1 Terpenoid biosynthesis pathway(MVA and MEP)in tree peony Genes in red have been cloned in tree peony. The genes in parentheses are the same as the genes before the parentheses. AACT:Acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase. HMGS:3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A synthase. HMGR:3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase. MVK:Mevalonate kinase. PMK:Phosphomevalonate kinase. MDC:Mevalonate diphosphate decarboxylase. IDI:Isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase. FPPS:Farnesyl diphosphate synthase. GDS:Germacrene D synthase. TPS:Terpene synthase. DXS:1-Deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase. DXR:1-Deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase. MCT:2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate cytidylyltransferase. CMK:4-(cytidine 5′-diphospho)-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase. MCS:2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase. HDS:4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate synthase. HDR:4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate reductase. GPPS:Geranyl diphosphate synthase. GES:Geraniol synthase. LIS:Linalool synthase
| 化合物 Compounds | 牡丹产品 Tree peony product | 功效 Efficacy | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 芳樟醇 Linalool | 鲜花精油、干花精油、干花芳香水 Fresh flower essential oil,dried flower essential oil,dried flower hydrosol | 花香气味,具有镇静、抗菌、抗炎、抗肿瘤等作用 It is characterized by a floral aroma as well as sedative,antibacterial,anti-inflammatory,and anti-tumor properties | 郑红富 等, |
| 氧化芳樟醇(呋喃型)Linalool oxide (furanoid) | 干花精油、干花芳香水Dried flower essential oil,dried flower hydrosol | 具有强烈的木香、花香和甜香的气息,是一种多香韵的香料,是目前食物、日化香精香料的主要来源 It possesses intense woody,floral,and sweet nuances,serving as a versatile fragrance material and a primary source for flavor and fragrance compounds in both food and personal care products | 谷运璀 等, |
| 松油醇 Terpineol | 鲜花精油 Fresh flower essential oil | 具有多种抑菌活性,也是重要的香料成分,广泛用于日化和食用香精It demonstrates various antimicrobial activities and is also valued as an important fragrance ingredient,widely used in both flavoring and fragrance formulations | 欧阳秋丽 等, |
| 橙花醇 Nerol | 鲜花精油 Fresh flower essential oil | 具有玫瑰和橙花香气,是一种能抑制微生物的香料成分,可用于消毒剂和护肤品 With rose and orange blossom notes,this ingredient serves as a fragrance with microbial growth-inhibiting properties,making it suitable for use in disinfectants and skincare products | 谢宇婷 等, |
| 1,3,5-三甲氧基苯 1,3,5-Trimethoxybenzene | 鲜花精油、干花精油、干花芳香水 Fresh flower essential oil,dried flower essential oil,dried flower hydrosol | 是现代茶香月季的主要成分,也是合成药物、香料和其他化学品的前体,具有药用价值 It is the definitive component that imparts the characteristic tea scent to modern roses and also serves as a key precursor in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals,fragrances,and other fine chemicals,with additional medicinal value | 李莹莹, |
表3 牡丹花香成分在牡丹产品中的应用与功效
Table 3 Application and efficacy of tree peony fragrance components in treepeony products
| 化合物 Compounds | 牡丹产品 Tree peony product | 功效 Efficacy | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 芳樟醇 Linalool | 鲜花精油、干花精油、干花芳香水 Fresh flower essential oil,dried flower essential oil,dried flower hydrosol | 花香气味,具有镇静、抗菌、抗炎、抗肿瘤等作用 It is characterized by a floral aroma as well as sedative,antibacterial,anti-inflammatory,and anti-tumor properties | 郑红富 等, |
| 氧化芳樟醇(呋喃型)Linalool oxide (furanoid) | 干花精油、干花芳香水Dried flower essential oil,dried flower hydrosol | 具有强烈的木香、花香和甜香的气息,是一种多香韵的香料,是目前食物、日化香精香料的主要来源 It possesses intense woody,floral,and sweet nuances,serving as a versatile fragrance material and a primary source for flavor and fragrance compounds in both food and personal care products | 谷运璀 等, |
| 松油醇 Terpineol | 鲜花精油 Fresh flower essential oil | 具有多种抑菌活性,也是重要的香料成分,广泛用于日化和食用香精It demonstrates various antimicrobial activities and is also valued as an important fragrance ingredient,widely used in both flavoring and fragrance formulations | 欧阳秋丽 等, |
| 橙花醇 Nerol | 鲜花精油 Fresh flower essential oil | 具有玫瑰和橙花香气,是一种能抑制微生物的香料成分,可用于消毒剂和护肤品 With rose and orange blossom notes,this ingredient serves as a fragrance with microbial growth-inhibiting properties,making it suitable for use in disinfectants and skincare products | 谢宇婷 等, |
| 1,3,5-三甲氧基苯 1,3,5-Trimethoxybenzene | 鲜花精油、干花精油、干花芳香水 Fresh flower essential oil,dried flower essential oil,dried flower hydrosol | 是现代茶香月季的主要成分,也是合成药物、香料和其他化学品的前体,具有药用价值 It is the definitive component that imparts the characteristic tea scent to modern roses and also serves as a key precursor in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals,fragrances,and other fine chemicals,with additional medicinal value | 李莹莹, |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
|
包秀霞, 廉勇, 包秀平. 2016. 植物花香气成分提取方法的比较研究进展. 北方农业学报, 44 (5):126-130.
|
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
|
陈美霞. 2005. 杏果实风味物质的组成及其遗传特性的研究[博士论文]. 泰安: 山东农业大学.
|
|
| [6] |
|
|
陈秀中, 王琪. 2001. 中华民族传统赏花理论探微. 北京林业大学学报, 23 (S1):16-21.
|
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
|
丁星文, 王珍珍, 王其刚, 蹇洪英, 陈敏, 李树发. 2022. 不同花色滇牡丹花香成分分析. 南方园艺, 33 (3):25-30.
|
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
|
符勇耀, 刘建玲, 朱艺勇, 徐文姬, 雷美艳, 杨利平. 2020. 卷丹转基因体系构建及岷江百合LrCCoAOMT的导入. 园艺学报, 47 (7):1345-1358.
|
|
| [14] |
|
|
高洁. 2012. 萱草再生体系的优化及农杆菌介导的遗传转化体系的建立[硕士论文]. 成都: 四川农业大学.
|
|
| [15] |
|
|
高洁, 张萍, 薛璟祺, 薛玉前, 王顺利, 张秀新. 2019. 酚类物质及其对木本植物组织培养褐变影响的研究进展. 园艺学报, 46 (9):1645-1654.
|
|
| [16] |
|
|
谷运璀, 钱莉群, 李步详, 宦月琴. 2013. 芳樟醇氧化物的合成. 香料香精化妆品,(S1):28-31.
|
|
| [17] |
|
|
郭耀东, 王佳蒙, 张昂, 岳田利. 2019. 商洛油用牡丹花精油挥发性成分SPME/GC-MS分析. 陕西农业科学, 65 (1):53-56.
|
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
|
郝瑞杰. 2014. 植物花香研究. 北京: 中国林业出版社:8-38.
|
|
| [20] |
|
|
郝守进, 崔九思, 戚其平. 1999. 固相微萃取技术在挥发性有机化合物分析中的应用进展. 环境与健康杂志,(4):57-60.
|
|
| [21] |
|
|
胡欣荃, 古今, 杨姝琦, 彭昌操. 2023. 木本植物再生和遗传转化的研究进展. 分子植物育种, 21 (16):5322-5329.
|
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
|
黄亚茹, 高芳, 迟韵阳, 廖圣良, 刘新亮, 杨海宽, 华小菊, 龚岚, 王宗德. 2022. 天然柠檬醛提取方法与生物活性研究进展. 南方农业学报, 53 (11):3217-3228.
|
|
| [24] |
|
|
黄玉清, 陈艺欣, 田厚军. 2012. 植物香气成分提取方法的研究进展. 江苏农业科学, 40 (7):245-247.
|
|
| [25] |
|
|
孔凡, 郝青, 刘政安, 舒庆艳. 2021. 凤丹牡丹花朵不同发育时期挥发性成分积累规律与蒸馏工艺研究. 亚热带植物科学, 50 (6):447-453.
|
|
| [26] |
|
|
雷高明, 李杰, 姚俊巧, 郑涛, 段冷昕, 李瑞芳, 李艳. 2019. 两种凤丹干花精油及芳香水挥发性成分比较研究. 香料香精化妆品,(3):7-11.
|
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
|
李学震, 刘光鹏, 马艳蕊, 姚旖旎, 孟园, 赵岩, 和法涛. 2023. “金花菌”(Aspergillus chevalieri)发酵牡丹花瓣过程中挥发性物质及酚酸类物质变化. 食品与发酵工业, 49 (19):304-311.
|
|
| [30] |
|
|
李军. 2016. 植物挥发性有机化合物研究方法进展. 生态环境学报, 25 (6):1076-1081.
|
|
| [31] |
|
|
李铭韧. 2010. 牡丹开花和衰老过程中香气物质含量及相关酶活性的变化[硕士论文]. 洛阳: 河南科技大学.
|
|
| [32] |
|
|
李秋棉, 罗均, 李雪萍, 陈维信. 2012. 果实香气物质的合成与代谢研究进展. 广东农业科学, 39 (19):104-107.
|
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
|
李荣琛, 李紫瑶, 白茹, 吴静, 窦德泉. 2021. 牡丹PsDXS基因克隆及表达分析. 分子植物育种, 19 (7):2177-2184.
|
|
| [35] |
|
|
李瑞雅, 宋程威, 牛童非, 魏祯祯, 郭丽丽, 侯小改. 2023. ‘海黄’牡丹花挥发性物质释放规律及PsGDS的克隆与表达分析. 园艺学报, 50 (2):331-344.
|
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
|
李莹莹. 2013. 静态顶空—气相色谱—质谱法测定4种牡丹花的挥发性成分. 理化检验(化学分册), 49 (3):334-336.
|
|
| [39] |
|
|
李莹莹, 王小文, 孙霞, 王文莉, 孙宪芝, 郑成淑. 2015. 中原牡丹品种主要花香挥发物的多元统计分析∥中国园艺学会观赏园艺专业委员会. 中国观赏园艺研究进展. 北京: 中国林业出版社:92-101.
|
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
|
李子昂. 2022. 基于转录组分析的牡丹花香萜类化合物合成途径相关基因的研究[硕士论文]. 泰安: 山东农业大学.
|
|
| [42] |
|
|
梁彩婷, 荣骅, 徐璐, 饶雨, 李军, 邓婷, 石向群, 高银祥. 2025. 基于HS-SPME-GC-MS分析宁州群体种和混合种制成的宁红茶挥发性成分差异. 食品工业科技, 46 (13):271-281.
|
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
|
刘建华, 董福英, 程传格, 谷颜杰, 李淑娥. 1999. 菏泽牡丹花挥发油化学成分分析. 山东化工,(3):37-38,20.
|
|
| [45] |
|
|
刘俊民, 吴震生, 朱宗磊, 李莹莹, 毛文岳. 2014. 牡丹鲜花精油的工业化提取及挥发性组分的GC-MS分析. 中国食物与营养, 20 (6):57-60.
|
|
| [46] |
|
|
刘爽, 沈红艳, 刘金宝, 武红玉, 高东升, 朱翠英, 付喜玲. 2019. 不同花色牡丹盛花期花瓣香气成分分析. 农业科学, 9 (8):603-611.
|
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
|
牛童非, 薛娴, 郭丽丽, 郁敏, 张晨洁, 徐鑫傲, 李瑞雅, 侯小改. 2023. 外源茉莉酸甲酯对温室牡丹‘洛阳红’挥发性成分及含量的影响. 林业科学, 59 (5):53-60.
|
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
|
欧阳秋丽, 贾雷, 陶能国, 何湘丽. 2014. α-松油醇对意大利青霉的抑制作用. 食品科学, 35 (11):32-35.
|
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
|
邱守昊, 张依倩, 赵俊赫, 宋兆辉. 2023. 水蒸气蒸馏法提取中药挥发油的研究进展. 天津药学, 35 (4):63-68.
|
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
|
孙苗. 2021. 牡丹花香TPS基因家族克隆及其功能分析[硕士论文]. 北京: 北京林业大学.
|
|
| [72] |
|
|
孙强. 2012. 凤丹花挥发性成分测定及化学计量学分析[硕士论文]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学.
|
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
|
王娟. 2014. 外源一氧化氮对温室牡丹花瓣挥发性成分的影响. 核农学报, 28 (9):1728-1735.
|
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
|
王衍彬, 陈雅丹, 秦玉川, 吴晓红, 黄旭波, 程俊文, 王丽玲, 方茹, 贺亮. 2024. 不同萃取方法下绿萼梅花蕾挥发性成分的差异研究. 浙江林业科技, 44 (1):33-41.
|
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
|
|
谢宇婷, 陈昭斌, 陈雯杰. 2020. 橙花醇的杀菌效果观察. 中国消毒学杂志, 37 (5):339-341.
|
|
| [85] |
|
|
徐慧. 2023. 大花黄牡丹花香成分分析及释香规律研究[硕士论文]. 林芝: 西藏农牧学院.
|
|
| [86] |
|
|
徐慧, 姚霞珍, 佟珂珂, 邢震, 李垚. 2023. 3种牡丹花器官不同部位挥发性成分分析. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 47 (3):63-69,1-5.
|
|
| [87] |
|
|
晏慧君, 王娟, 陈敏, 王其刚, 张颢. 2017. 月月粉(Rosa chinensis‘Pallida’)、大马士革蔷薇(R. damascene)、百叶蔷薇(R. centifolia)香气成分分析. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学版), 32 (1):78-82.
|
|
| [88] |
|
|
叶楚, 谢炳春, 李涛, 徐小万, 徐晓美, 王恒明, 吴智明, 衡周. 2023. 园艺作物香气成分及合成调控机理的研究进展. 广东农业科学, 50 (11):98-112.
|
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
|
|
于荟, 马文平, 刘延平, 李建新, 刘俊民. 2015. 顶空-气相色谱-质谱法分析牡丹鲜花精油中的挥发性成分. 食品科学, 36 (18):167-171.
|
|
| [91] |
|
|
尉洁净, 李媛, 熊群, 王炳晖. 2023. 柑橘属植物精油的提取技术与应用研究. 上海化工, 48 (3):43-45.
|
|
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
|
|
张红磊. 2011. 牡丹花期、花色及花香的变异研究[硕士论文]. 泰安: 山东农业大学.
|
|
| [94] |
|
|
张辉, 刘丰静, 李慧玲, 王定锋. 2012. 茶树挥发物的研究进展. 茶叶科学技术,(4):4-8.
|
|
| [95] |
|
|
张静, 周小婷, 胡立盼, 邹志荣. 2013. SPME-GC-MS测定不同品种牡丹花挥发性物质成分分析. 西北林学院学报, 28 (4):136-143.
|
|
| [96] |
|
|
张玲. 2019. 牡丹花香特异种质筛选及其花香形成关键基因挖掘[硕士论文]. 南京: 南京农业大学.
|
|
| [97] |
|
|
张少颖, 饶景萍, 任小林. 2007. 一氧化氮对瓶插月季呼吸作用及相关酶活性的影响. 园艺学报, 34 (1):183-188.
|
|
| [98] |
|
| [99] |
|
| [100] |
|
| [101] |
|
|
赵能, 原晓龙, 陈中华, 杨宇明, 王娟, 王毅. 2017. 滇牡丹1-脱氧-D-木酮糖-5-磷酸合酶(DXS)基因的克隆及功能分析. 基因组学与应用生物学, 36 (7):2919-2925.
|
|
| [102] |
|
|
赵书珂, 芦瑞, 刘琛琛, 杜方, 韩美玲. 2025. 植物花香挥发物释放规律及其提取和检测方法的研究进展. 江苏农业学报, 41 (3):615-624.
|
|
| [103] |
|
|
赵印泉, 周斯建, 彭培好, 潘会堂, 张启翔. 2011. 植物花香代谢调节与基因工程研究进展. 热带亚热带植物学报, 19 (4):381-390.
|
|
| [104] |
|
|
郑红富, 廖圣良, 范国荣, 司红燕, 陈尚钘, 王宗德. 2019. 芳樟精油的开发与利用研究进展. 广州化工, 47 (5):17-19,108.
|
|
| [105] |
|
| [106] |
|
|
周畅, 李玉红, 姚雷. 2015. 不同条件下提取牡丹花的成分及分析. 上海交通大学学报(农业科学版), 33 (5):28-33.
|
|
| [107] |
|
|
周海梅, 戚军超, 董苗菊, 李朴, 马锦琦. 2008. 固相微萃取-气相色谱-质谱分析牡丹花的挥发性成分. 化学分析计量, 17 (3):21-23.
|
|
| [108] |
|
| [109] |
|
|
周思雨. 2021. 瓦氏秋海棠高效再生及遗传转化技术的研究[硕士论文]. 苏州: 苏州大学.
|
| [1] | 王芳, 范燕萍. 观赏植物花香性状形成及调控机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 359-385. |
| [2] | 赵雨晴, 唐菲鸿, 郑仕杰, 官泽恩, 吴建凯, 刘仲健, 彭东辉, 兰思仁, 赵凯, 周育真. 兰花“花香”物质研究进展:从合成机制到进化驱动[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 412-436. |
| [3] | 岳芝伊, 李心, 王昊宁, 张启翔, 孙丽丹. 梅花花香研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 467-480. |
| [4] | 张鹏, 叶新茹, 栗华隆, 陈昱媛, 孙明, 唐玉超. ‘梨香’菊花香成分鉴定及香气特征分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 496-512. |
| [5] | 徐勇, 杨阳, 王若彤, 毛一茹, 冯立国. 外源褪黑素对玫瑰花香的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 574-584. |
| [6] | 何智宏, 杨国州, 李京璟, 唐小亚, 赵萍, 高斌斌, 李睿, 何丽霞. 牡丹新品种‘紫韵轮回’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 267-268. |
| [7] | 高斌斌, 何智宏, 杨国州, 李京璟, 唐小亚, 赵萍, 李睿, 何丽霞. 牡丹新品种‘茶花韵’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 269-270. |
| [8] | 邹沛姗, 郑锡荣, 胡 杏, 代色平, 倪建中. 野牡丹属新品种‘紫珊’和‘红妃’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 215-216. |
| [9] | 王心茹, 白帅帅, 孙雨乐, 武欣宇, 曾凤, 刘春英, 张玉喜, 盖树鹏, 袁延超. ‘凤丹’牡丹PoSnRK基因家族鉴定及其在花衰老中的表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(9): 2363-2376. |
| [10] | 冯玲佳, 刘毓婕, 何林彤, 王新超, 叶萌. 芳樟醇合成调控机制及其生态功能研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(8): 2270-2290. |
| [11] | 智慧, 杨菁菁, 罗建让. 牡丹96个品种表型多样性分析与观赏性综合评价[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 635-645. |
| [12] | 李超楠, 李璐, 高丹蕾, 乔红雍, 袁涛. 原产地与引种地大花黄牡丹根系和根际土壤的AMF群落差异[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 467-480. |
| [13] | 彭朝凤, 齐帅征, 耿喜宁, 姚鹏强, 谢丽华, 张钰, 陈明辉, 施江, 程世平. 不同倍性‘凤丹’牡丹叶片转录组差异表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(12): 3288-3302. |
| [14] | 黄嘉可, 洪思丹, 徐海华, 顾翠花. 紫薇花色呈色机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(12): 3412-3426. |
| [15] | 李冰敏, 谭广文, 刘晓洲, 李银, 谢腾芳, 汪子涵, 周仁超. 野牡丹新品种‘霁月’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(12): 3427-3428. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司