
园艺学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 538-556.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2025-0861
魏永路, 叶广英, 高洁, 金建鹏, 陆楚桥, 李杰, 谢琦, 苟亚军, 朱根发*( ), 杨凤玺*(
), 杨凤玺*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-09-15
修回日期:2025-12-18
出版日期:2026-02-25
发布日期:2026-02-12
基金资助:
WEI Yonglu, YE Guangying, GAO Jie, JIN Jianpeng, LU Chuqiao, LI Jie, XIE Qie, GOU Yajun, ZHU Genfa( ), YANG Fengxi(
), YANG Fengxi( )
)
Received:2025-09-15
Revised:2025-12-18
Published:2026-02-25
Online:2026-02-12
摘要:
以腋唇兰(Maxillaria tenuifolia)为研究对象,系统分析了其4个花器官(萼片、花瓣、唇瓣和合蕊柱)的花香成分及代谢特征。通过气相色谱—质谱联用技术(GC-MS)对各花器官中的挥发性有机化合物进行测定,并结合转录组数据筛选了参与关键花香成分合成的候选基因。结果表明,在鉴定出的31种香气成分中,萼片中的挥发性物质最为丰富(30种),总含量最高,达到96.55 μg · g-1 FW。基于相对气味活度值(relative odor activity values,ROAV)分析,确定δ-癸内酯、马索亚内酯和δ-杜松烯为腋唇兰的主要香气成分,共同赋予其椰奶与草药融合的香气。转录组分析显示,多个与花香合成相关的差异表达基因主要富集于萜类、苯丙烷类、类黄酮以及脂肪酸代谢等通路。通过整合代谢与转录数据,进一步筛选出5个候选调控基因,分别为FAD、HMGR、MYB、TPS、WRKY,这些基因在腋唇兰花香合成调控网络中可能发挥关键作用。
魏永路, 叶广英, 高洁, 金建鹏, 陆楚桥, 李杰, 谢琦, 苟亚军, 朱根发, 杨凤玺. 腋唇兰花香成分鉴定和关键调控基因挖掘[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 538-556.
WEI Yonglu, YE Guangying, GAO Jie, JIN Jianpeng, LU Chuqiao, LI Jie, XIE Qie, GOU Yajun, ZHU Genfa, YANG Fengxi. Integrated Metabolome and Transcriptome Analysis of Floral Scent in Maxillaria tenuifolia[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2026, 53(2): 538-556.
| 类别 Category | 基因名称 Gene name | 序列ID Sequence ID | 正向引物序列(5′-3′) Forward primer sequence | 反向引物序列(5′-3′) Reverse primer sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 结构基因 Structural gene | TPS | Mte34245 | CTGCATCGTCAATCCTGTCA | CACTTAAGGACGGAGAGCAC |
| HMGR | Mte37089 | ATAAAGCTCCTCACCCCCTT | GTCGGAAGCCTGGACTTTAG | |
| FAD | Mte38831 | ATCCTCCATTCCCTGGTTCA | TATAGATTGGGCCGTAGGGG | |
| 转录因子 Transcription factor | WRKY | Mte37746 | CCCGAAGAGTGATGGTTCTG | TCCAGCTATAGCCGTCATCA |
| MYB | Mte39919 | TTCACCAAAATGTACCGCCA | TGTCACAAATCTCCCCTCCT |
表1 腋唇兰花香挥发性有机化合物生物合成相关基因及其引物
Table 1 Floral volatile organic compounds (VOCs) biosynthesis-related genes in Maxillaria tenuifolia and their primer sequences
| 类别 Category | 基因名称 Gene name | 序列ID Sequence ID | 正向引物序列(5′-3′) Forward primer sequence | 反向引物序列(5′-3′) Reverse primer sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 结构基因 Structural gene | TPS | Mte34245 | CTGCATCGTCAATCCTGTCA | CACTTAAGGACGGAGAGCAC |
| HMGR | Mte37089 | ATAAAGCTCCTCACCCCCTT | GTCGGAAGCCTGGACTTTAG | |
| FAD | Mte38831 | ATCCTCCATTCCCTGGTTCA | TATAGATTGGGCCGTAGGGG | |
| 转录因子 Transcription factor | WRKY | Mte37746 | CCCGAAGAGTGATGGTTCTG | TCCAGCTATAGCCGTCATCA |
| MYB | Mte39919 | TTCACCAAAATGTACCGCCA | TGTCACAAATCTCCCCTCCT |
| 样本 Sample | 萜类 Terpenoids | 酯类 Esters | 醛类 Aldehydes | 醇类 Alcohols | 酮类 Ketones | 酸类 Acids | 烷烃类 Alkanes | 其他 Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 萼片 Sepal | 33.92 | 16.84 | 12.43 | 10.69 | 5.01 | 6.3 | 7.71 | 7.11 |
| 花瓣 Petal | 21.03 | 22.48 | 9.12 | 9.90 | — | — | 17.64 | 19.85 |
| 唇瓣 Lip | 31.69 | 29.32 | 6.85 | 0.91 | 5.96 | — | 18.09 | 7.18 |
| 合蕊柱 Column | 44.36 | 3.37 | 10.08 | 1.53 | — | — | 23.09 | 17.57 |
表2 腋唇兰萼片、花瓣、唇瓣和合蕊柱VOC相对含量
Table 2 The relative contents of VOCs in sepals,petals,Lips and columns of Maxillaria tenuifolia %
| 样本 Sample | 萜类 Terpenoids | 酯类 Esters | 醛类 Aldehydes | 醇类 Alcohols | 酮类 Ketones | 酸类 Acids | 烷烃类 Alkanes | 其他 Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 萼片 Sepal | 33.92 | 16.84 | 12.43 | 10.69 | 5.01 | 6.3 | 7.71 | 7.11 |
| 花瓣 Petal | 21.03 | 22.48 | 9.12 | 9.90 | — | — | 17.64 | 19.85 |
| 唇瓣 Lip | 31.69 | 29.32 | 6.85 | 0.91 | 5.96 | — | 18.09 | 7.18 |
| 合蕊柱 Column | 44.36 | 3.37 | 10.08 | 1.53 | — | — | 23.09 | 17.57 |
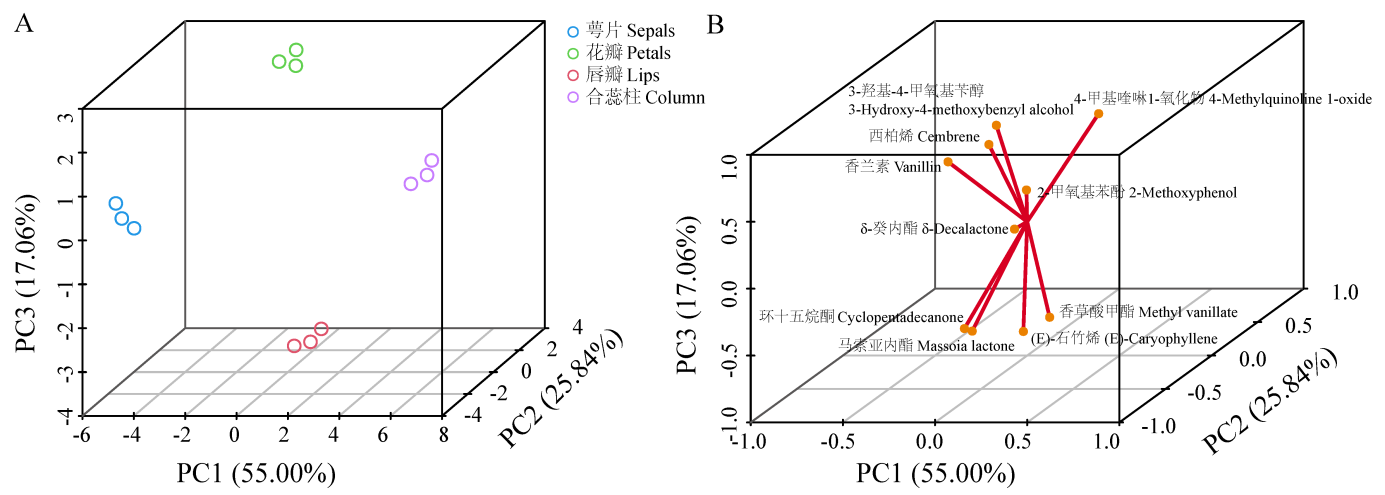
图1 腋唇兰花器官的三维主成分分析(A)及前10个挥发性化合物的载荷分布(B)
Fig. 1 Three-dimensional principal component analysis(A)of floral organs in Maxillaria tenuifolia and loading distribution of the TOP10 volatile organic compounds(B)
| 挥发性成分分类 Volatile component classification | 组分 Component | 萼片 Sepal | 花瓣 Petal | 唇瓣 Lip | 合蕊柱 Column |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 萜类 Terpenoids | α-松油烯 α-Terpinene | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | — | — |
| D-柠檬烯 D-Limonene | 0.04 ± 0.01 | — | — | — | |
| α-古巴烯 α-Copaene | 2.79 ± 0.64 | 0.53 ± 0.08 | 1.18 ± 0.22 | 4.41 ± 0.92 | |
| (E)-石竹烯 (E)-Caryophyllene | 18.26 ± 1.44 | 5.53 ± 0.54 | 23.13 ± 0.45 | 21.76 ± 2.00 | |
| δ-杜松烯 δ-Cadinene | 1.42 ± 0.15 | 3.05 ± 0.15 | 3.16 ± 0.16 | 13.16 ± 1.8 | |
| 石竹烯氧化物 Caryophyllene oxide | 0.60 ± 0.01 | 1.72 ± 0.05 | 1.66 ± 0.10 | 4.83 ± 0.4 | |
| α-蒎烯 α-Pinene | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.2 ± 0.06 | |
| 月桂烯 Myrcene | 0.1 ± 0.00 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | — | |
| 长叶烯 Longifolene | 0.07 ± 0.01 | — | — | — | |
| α-红没药醇 α-Bisabolol* | 4.22 ± 0.22 | — | — | — | |
| 西柏烯 Cembrene* | 6.32 ± 0.19 | 10.02 ± 0.65 | 2.45 ± 0.03 | — | |
| 酯类 Esters | δ-癸内酯 δ-Decalactone | 13.69 ± 0.8 | 21.71 ± 1.76 | 21.32 ± 1.19 | — |
| 肉桂酸异丙酯Isopropyl 3-phenylpropenoate* | 0.92 ± 0.01 | — | — | 2.95 ± 0.13 | |
| 马索亚内酯 Massoia lactone* | 1.24 ± 0.1 | — | 1.69 ± 0.18 | — | |
| 戊酸甲酯 Methyl pentanoate* | 0.99 ± 0.12 | 0.77 ± 0.05 | 0.75 ± 0.08 | 0.42 ± 0.06 | |
| 香草酸甲酯 Methyl vanillate* | — | — | 5.56 ± 0.17 | — | |
| 醛类 Aldehydes | 壬醛 Nonanal | 6.18 ± 0.71 | 3.91 ± 0.13 | 6.32 ± 0.18 | 9.03 ± 0.48 |
| 香兰素 Vanillin* | 6.16 ± 1.07 | 5.04 ± 0.3 | — | — | |
| (E)-2-庚烯醛 (E)-2-Heptenal* | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.29 ± 0.01 | 0.64 ± 0.05 | |
| 2-辛烯醛 2-Octenal* | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | 0.41 ± 0.03 | |
| 醇类 Alcohols | 香叶基香叶醇 Geranylgeraniol* | 5.08 ± 0.44 | 0.33 ± 0.04 | — | — |
| 3-羟基-4-甲氧基苄醇 3-Hydroxy-4-methoxybenzyl alcohol* | 4.82 ± 0.45 | 8.88 ± 0.65 | — | — | |
| 4-甲基-1-戊醇 4-Methyl-1-pentanol* | 0.63 ± 0.01 | 0.58 ± 0.04 | 0.8 ± 0.06 | 1.53 ± 0.04 | |
| (E)-2-辛烯-1-醇 (E)-2-Octen-1-ol* | 0.1 ± 0.02 | — | — | — | |
| 1-辛醇 1-Octanol* | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.11 ± 0.02 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | — | |
| 酮类 Ketones | 环十五烷酮 Cyclopentadecanone | 5.01 ± 0.88 | — | 5.96 ± 0.41 | — |
| 酸类 Acids | 壬酸 Nonanoic acid* | 4.93 ± 0.81 | — | — | — |
| 神经酸 Neric acid* | 1.37 ± 0.12 | — | — | — | |
| 烷烃类 Alkanes | 角鲨烷 Squalane* | 7.71 ± 1.06 | 17.64 ± 0.56 | 18.09 ± 0.88 | 23.09 ± 0.13 |
| 其他 Others | 4-甲基喹啉1-氧化物 4-Methylquinoline 1-oxide* | 6.95 ± 0.45 | 19.48 ± 1.08 | 6.91 ± 0.26 | 17.57 ± 1.47 |
| 2-甲氧基苯酚 2-Methoxyphenol* | 0.16 ± 0.01 | 0.37 ± 0.02 | 0.27 ± 0.01 | — |
表3 腋唇兰不同花器官花香成分种类及含量
Table 3 Volatile components types and contents in different floral organs of Maxillaria tenuifolia
| 挥发性成分分类 Volatile component classification | 组分 Component | 萼片 Sepal | 花瓣 Petal | 唇瓣 Lip | 合蕊柱 Column |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 萜类 Terpenoids | α-松油烯 α-Terpinene | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | — | — |
| D-柠檬烯 D-Limonene | 0.04 ± 0.01 | — | — | — | |
| α-古巴烯 α-Copaene | 2.79 ± 0.64 | 0.53 ± 0.08 | 1.18 ± 0.22 | 4.41 ± 0.92 | |
| (E)-石竹烯 (E)-Caryophyllene | 18.26 ± 1.44 | 5.53 ± 0.54 | 23.13 ± 0.45 | 21.76 ± 2.00 | |
| δ-杜松烯 δ-Cadinene | 1.42 ± 0.15 | 3.05 ± 0.15 | 3.16 ± 0.16 | 13.16 ± 1.8 | |
| 石竹烯氧化物 Caryophyllene oxide | 0.60 ± 0.01 | 1.72 ± 0.05 | 1.66 ± 0.10 | 4.83 ± 0.4 | |
| α-蒎烯 α-Pinene | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.2 ± 0.06 | |
| 月桂烯 Myrcene | 0.1 ± 0.00 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | — | |
| 长叶烯 Longifolene | 0.07 ± 0.01 | — | — | — | |
| α-红没药醇 α-Bisabolol* | 4.22 ± 0.22 | — | — | — | |
| 西柏烯 Cembrene* | 6.32 ± 0.19 | 10.02 ± 0.65 | 2.45 ± 0.03 | — | |
| 酯类 Esters | δ-癸内酯 δ-Decalactone | 13.69 ± 0.8 | 21.71 ± 1.76 | 21.32 ± 1.19 | — |
| 肉桂酸异丙酯Isopropyl 3-phenylpropenoate* | 0.92 ± 0.01 | — | — | 2.95 ± 0.13 | |
| 马索亚内酯 Massoia lactone* | 1.24 ± 0.1 | — | 1.69 ± 0.18 | — | |
| 戊酸甲酯 Methyl pentanoate* | 0.99 ± 0.12 | 0.77 ± 0.05 | 0.75 ± 0.08 | 0.42 ± 0.06 | |
| 香草酸甲酯 Methyl vanillate* | — | — | 5.56 ± 0.17 | — | |
| 醛类 Aldehydes | 壬醛 Nonanal | 6.18 ± 0.71 | 3.91 ± 0.13 | 6.32 ± 0.18 | 9.03 ± 0.48 |
| 香兰素 Vanillin* | 6.16 ± 1.07 | 5.04 ± 0.3 | — | — | |
| (E)-2-庚烯醛 (E)-2-Heptenal* | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.29 ± 0.01 | 0.64 ± 0.05 | |
| 2-辛烯醛 2-Octenal* | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | 0.41 ± 0.03 | |
| 醇类 Alcohols | 香叶基香叶醇 Geranylgeraniol* | 5.08 ± 0.44 | 0.33 ± 0.04 | — | — |
| 3-羟基-4-甲氧基苄醇 3-Hydroxy-4-methoxybenzyl alcohol* | 4.82 ± 0.45 | 8.88 ± 0.65 | — | — | |
| 4-甲基-1-戊醇 4-Methyl-1-pentanol* | 0.63 ± 0.01 | 0.58 ± 0.04 | 0.8 ± 0.06 | 1.53 ± 0.04 | |
| (E)-2-辛烯-1-醇 (E)-2-Octen-1-ol* | 0.1 ± 0.02 | — | — | — | |
| 1-辛醇 1-Octanol* | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.11 ± 0.02 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | — | |
| 酮类 Ketones | 环十五烷酮 Cyclopentadecanone | 5.01 ± 0.88 | — | 5.96 ± 0.41 | — |
| 酸类 Acids | 壬酸 Nonanoic acid* | 4.93 ± 0.81 | — | — | — |
| 神经酸 Neric acid* | 1.37 ± 0.12 | — | — | — | |
| 烷烃类 Alkanes | 角鲨烷 Squalane* | 7.71 ± 1.06 | 17.64 ± 0.56 | 18.09 ± 0.88 | 23.09 ± 0.13 |
| 其他 Others | 4-甲基喹啉1-氧化物 4-Methylquinoline 1-oxide* | 6.95 ± 0.45 | 19.48 ± 1.08 | 6.91 ± 0.26 | 17.57 ± 1.47 |
| 2-甲氧基苯酚 2-Methoxyphenol* | 0.16 ± 0.01 | 0.37 ± 0.02 | 0.27 ± 0.01 | — |
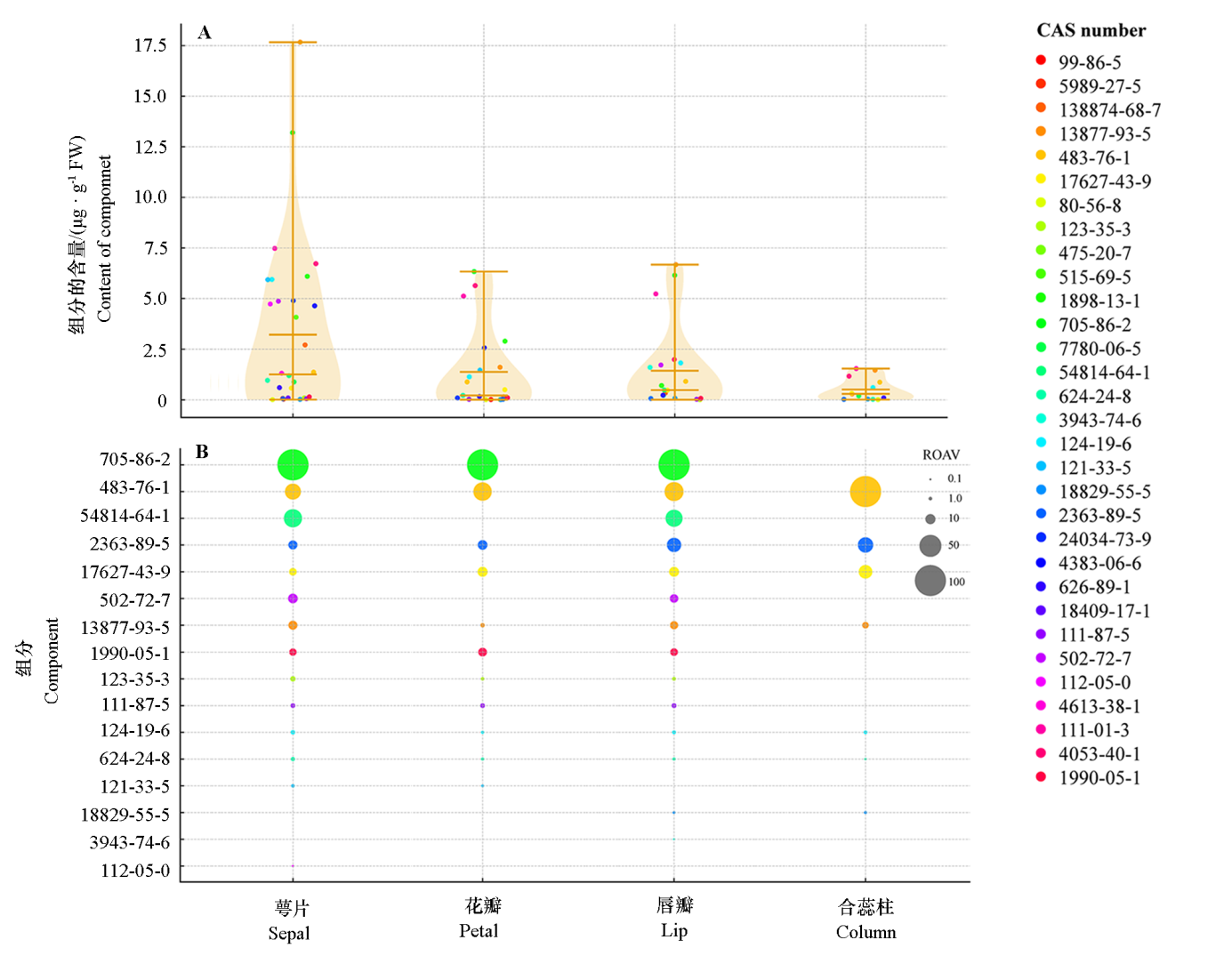
图2 腋唇兰4个花器官VOC含量与ROAV分布 A:基于半定量结果绘制的小提琴图;每个散点代表一种 VOC。B:ROAV气泡图,仅显示 ROAV ≥ 0.1,每个气泡代表一种VOC
Fig. 2 Distributions of VOC abundance and ROAV across the four floral organs A:Violin plots of semi-quantitative abundances with zeros removed,each dot denotes one volatile organic compound(VOC);B:ROAV bubble plot,only ROAV ≥ 0.1 are shown,each bubble denotes one VOC
| 挥发性成分 Volatile component | ROAV | CAS号 CAS number | 香味描述 Aroma description | 香味类型 Odor type | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 萼片 Sepal | 花瓣 Petal | 唇瓣 Lip | 合蕊柱 Column | ||||
| α-松油烯 α-Terpinene | 99-86-5 | 松木香、柑橘香 Piney,citrusy | 木香型 Woody1,2 | ||||
| D-柠檬烯 D-Limonene | 5989-27-5 | 柑橘味 Citrusy | 果香型 Fruity2,3 | ||||
| α-古巴烯 α-Copaene | 138874-68-7 | 木质香、辛辣香 Woody,spicy | 木香型 Woody1,2 | ||||
| (E)-石竹烯 (E)-Caryophyllene | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | 13877-93-5 | 丁香味、胡椒香 Clove-like,peppery | 香料型 Spicy1,2 |
| δ-杜松烯 δ-Cadinene | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | 483-76-1 | 百里香、草本香 Thyme,Herbal | 草药香型 Herbal1,2 |
| 石竹烯氧化物 Caryophyllene oxide | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | 17627-43-9 | 甜香、清新香、木质香 Sweet,fresh,woody | 木香型 Woody1,2 |
| α-蒎烯 α-Pinene | 80-56-8 | 松木香 Piney | 木香型 Woody3 | ||||
| 月桂烯 Myrcene | ≥ 1 | 0.1 ~ 1.0 | ≥ 1 | 123-35-3 | 草本香、柑橘香 Herbal,citrusy | 草药香型 Herbal1 | |
| 长叶烯 Longifolene | 475-20-7 | 木质香 Woody | 木香型 Woody1 | ||||
| α-红没药醇 α-Bisabolol | 515-69-5 | 花香、甜香 Floral,sweet | 花香型 Floral1,2 | ||||
| 西柏烯 Cembrene | 1898-13-1 | 木质香 Woody | 木香型 Woody4 | ||||
| δ-癸内酯 δ-Decalactone | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | 705-86-2 | 奶香、椰子香 Creamy,Coconut-like | 奶香型 Creamy1,2 | |
| 肉桂酸异丙酯 Isopropyl 3- phenylpropenoate | 7780-06-5 | 甜香、花香 Sweet,Floral | 花香型 Floral1,2 | ||||
| 马索亚内酯 Massoia lactone | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | 54814-64-1 | 椰香、甜香 Coconut-like,Sweet | 果香型 Fruity1 | ||
| 戊酸甲酯 Methyl pentanoate | ≥1 | 0.1 ~ 1.0 | 0.1 ~ 1.0 | 0.1 ~ 1.0 | 624-24-8 | 果香、甜香 Fruity,Sweet | 果香型 Fruity1,2 |
| 香草酸甲酯 Methyl vanillate | 3943-74-6 | 甜香、香草香 Sweet,vanilla-like | 甜香型 Sweet1,2 | ||||
| 壬醛 Nonanal | ≥ 1 | 0.1 ~ 1.0 | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | 124-19-6 | 柑橘香、脂肪香 Citrusy,waxy | 果香型 Fruity1,2 |
| 香兰素 Vanillin | 121-33-5 | 甜香、香草香 Sweet,vanilla-like | 甜香型 Sweet2 | ||||
| (E)-2-庚烯醛 (E)-2-Heptenal | 0.1 ~ 1.0 | 0.1 ~ 1.0 | 18829-55-5 | 青草香、脂肪香 Green,fatty | 清香型 Green1,2 | ||
| 2-辛烯醛 2-Octenal | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | 2363-89-5 | 脂肪香、青草香 Fatty,green | 清香型 Green1,2 |
| 香叶基香叶醇 Geranylgeraniol | 24034-73-9 | 花香、木质香 Floral,woody | 花香型 Floral1,2 | ||||
| 3-羟基-4-甲氧基苄醇 3-Hydroxy-4-methoxybenzyl alcohol | 4383-06-6 | 甜香、香草香 Sweet,vanilla-like | 甜香型 Sweet1,4 | ||||
| 4-甲基-1-戊醇 4-Methyl-1-pentanol | 626-89-1 | 果香、甜香 Fruity,sweet | 果香型 Fruity2 | ||||
| (E)-2-辛烯-1-醇 (E)-2-Octen-1-ol | 18409-17-1 | 蘑菇香、青草香 Mushroom-like,green | 清香型 Green1 | ||||
| 1-辛醇 1-Octanol | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | 111-87-5 | 脂肪香、柑橘香 Waxy,citrusy | 果香型 Fruity1,2 | |
| 环十五烷酮 Cyclopentadecanone | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | 502-72-7 | 麝香 Musky | 麝香型 Musky1,2 | ||
| 壬酸 Nonanoic acid | 0.1 ~ 1.0 | 112-5-0 | 脂肪香、奶酪香 Fatty,cheesy | 脂肪香型 Fatty1 | |||
| 神经酸 Neric acid | 4613-38-1 | 花香 Floral | 花香型 Floral5 | ||||
| 角鲨烷 Squalane | 111-01-3 | 无味、滋润质感 Odorless, moisturizing texture | 无味型 Odorless2 | ||||
| 4-甲基喹啉1-氧化物 4-Methylquinoline 1-oxide | 4053-40-1 | 焦香 Burnt | 焦香型 Burnt1,2 | ||||
| 2-甲氧基苯酚 2-Methoxyphenol | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | 1990-05-1 | 烟熏香、甜香 Smoky,sweet | 烟熏香型 Smoky1,2 | |
表4 腋唇兰花器官挥发性成分香型特征
Table 4 Aroma type characteristics of volatile compounds in floral organs of Maxillaria tenuifolia
| 挥发性成分 Volatile component | ROAV | CAS号 CAS number | 香味描述 Aroma description | 香味类型 Odor type | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 萼片 Sepal | 花瓣 Petal | 唇瓣 Lip | 合蕊柱 Column | ||||
| α-松油烯 α-Terpinene | 99-86-5 | 松木香、柑橘香 Piney,citrusy | 木香型 Woody1,2 | ||||
| D-柠檬烯 D-Limonene | 5989-27-5 | 柑橘味 Citrusy | 果香型 Fruity2,3 | ||||
| α-古巴烯 α-Copaene | 138874-68-7 | 木质香、辛辣香 Woody,spicy | 木香型 Woody1,2 | ||||
| (E)-石竹烯 (E)-Caryophyllene | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | 13877-93-5 | 丁香味、胡椒香 Clove-like,peppery | 香料型 Spicy1,2 |
| δ-杜松烯 δ-Cadinene | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | 483-76-1 | 百里香、草本香 Thyme,Herbal | 草药香型 Herbal1,2 |
| 石竹烯氧化物 Caryophyllene oxide | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | 17627-43-9 | 甜香、清新香、木质香 Sweet,fresh,woody | 木香型 Woody1,2 |
| α-蒎烯 α-Pinene | 80-56-8 | 松木香 Piney | 木香型 Woody3 | ||||
| 月桂烯 Myrcene | ≥ 1 | 0.1 ~ 1.0 | ≥ 1 | 123-35-3 | 草本香、柑橘香 Herbal,citrusy | 草药香型 Herbal1 | |
| 长叶烯 Longifolene | 475-20-7 | 木质香 Woody | 木香型 Woody1 | ||||
| α-红没药醇 α-Bisabolol | 515-69-5 | 花香、甜香 Floral,sweet | 花香型 Floral1,2 | ||||
| 西柏烯 Cembrene | 1898-13-1 | 木质香 Woody | 木香型 Woody4 | ||||
| δ-癸内酯 δ-Decalactone | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | 705-86-2 | 奶香、椰子香 Creamy,Coconut-like | 奶香型 Creamy1,2 | |
| 肉桂酸异丙酯 Isopropyl 3- phenylpropenoate | 7780-06-5 | 甜香、花香 Sweet,Floral | 花香型 Floral1,2 | ||||
| 马索亚内酯 Massoia lactone | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | 54814-64-1 | 椰香、甜香 Coconut-like,Sweet | 果香型 Fruity1 | ||
| 戊酸甲酯 Methyl pentanoate | ≥1 | 0.1 ~ 1.0 | 0.1 ~ 1.0 | 0.1 ~ 1.0 | 624-24-8 | 果香、甜香 Fruity,Sweet | 果香型 Fruity1,2 |
| 香草酸甲酯 Methyl vanillate | 3943-74-6 | 甜香、香草香 Sweet,vanilla-like | 甜香型 Sweet1,2 | ||||
| 壬醛 Nonanal | ≥ 1 | 0.1 ~ 1.0 | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | 124-19-6 | 柑橘香、脂肪香 Citrusy,waxy | 果香型 Fruity1,2 |
| 香兰素 Vanillin | 121-33-5 | 甜香、香草香 Sweet,vanilla-like | 甜香型 Sweet2 | ||||
| (E)-2-庚烯醛 (E)-2-Heptenal | 0.1 ~ 1.0 | 0.1 ~ 1.0 | 18829-55-5 | 青草香、脂肪香 Green,fatty | 清香型 Green1,2 | ||
| 2-辛烯醛 2-Octenal | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | 2363-89-5 | 脂肪香、青草香 Fatty,green | 清香型 Green1,2 |
| 香叶基香叶醇 Geranylgeraniol | 24034-73-9 | 花香、木质香 Floral,woody | 花香型 Floral1,2 | ||||
| 3-羟基-4-甲氧基苄醇 3-Hydroxy-4-methoxybenzyl alcohol | 4383-06-6 | 甜香、香草香 Sweet,vanilla-like | 甜香型 Sweet1,4 | ||||
| 4-甲基-1-戊醇 4-Methyl-1-pentanol | 626-89-1 | 果香、甜香 Fruity,sweet | 果香型 Fruity2 | ||||
| (E)-2-辛烯-1-醇 (E)-2-Octen-1-ol | 18409-17-1 | 蘑菇香、青草香 Mushroom-like,green | 清香型 Green1 | ||||
| 1-辛醇 1-Octanol | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | 111-87-5 | 脂肪香、柑橘香 Waxy,citrusy | 果香型 Fruity1,2 | |
| 环十五烷酮 Cyclopentadecanone | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | 502-72-7 | 麝香 Musky | 麝香型 Musky1,2 | ||
| 壬酸 Nonanoic acid | 0.1 ~ 1.0 | 112-5-0 | 脂肪香、奶酪香 Fatty,cheesy | 脂肪香型 Fatty1 | |||
| 神经酸 Neric acid | 4613-38-1 | 花香 Floral | 花香型 Floral5 | ||||
| 角鲨烷 Squalane | 111-01-3 | 无味、滋润质感 Odorless, moisturizing texture | 无味型 Odorless2 | ||||
| 4-甲基喹啉1-氧化物 4-Methylquinoline 1-oxide | 4053-40-1 | 焦香 Burnt | 焦香型 Burnt1,2 | ||||
| 2-甲氧基苯酚 2-Methoxyphenol | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | ≥ 1 | 1990-05-1 | 烟熏香、甜香 Smoky,sweet | 烟熏香型 Smoky1,2 | |
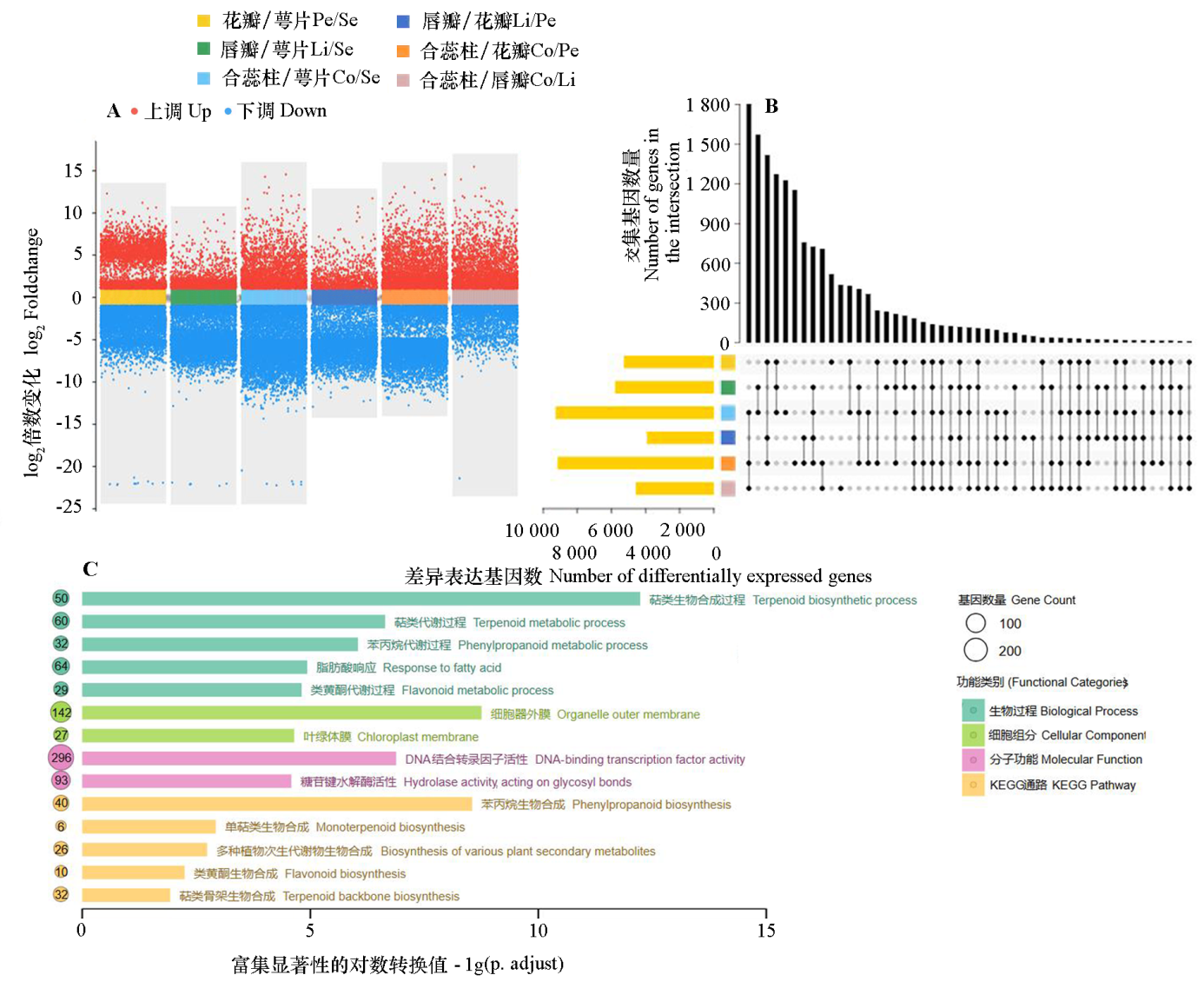
图3 腋唇兰4个花器官的转录组分析 A:不同花器官两两比较的差异表达基因(DEG)火山图;B:差异表达基因的Upset图。C:差异表达基因的GO与KEGG富集分析结果。Pe:花瓣;Li:唇瓣;Se:萼片;Co:合蕊柱
Fig. 3 Transcriptome analysis of four tissue parts of floral organs in Maxillaria tenuifolia A:Volcano plots of differentially expressed genes(DEGs)for pairwise comparisons between tissue parts;B:Upset diagram of DEGs;C:GO and KEGG enrichment analysis of DEGs. Pe:Petal;Li:Lip;Se:Sepal;Co:Column

图4 腋唇兰花香成分的主要生物合成途径 ADH:乙醇脱氢酶;DMAPP:二甲烯丙基焦磷酸酯;FAD:脂肪酸脱氢酶;FPP:法尼基焦磷酸;FPPS:法尼基焦磷酸合酶;GGPP:牻牛儿基牻牛儿基焦磷酸;GGPPS:牻牛儿基牻牛儿基焦磷酸合酶;GPP:牻牛儿基焦磷酸;GPPS:牻牛儿基牻牛儿基焦磷酸合酶;HPL:氢过氧化物裂解酶;IPP:异戊二烯焦磷酸;LOX:脂氧合酶;TPS:萜烯合酶;PAL:苯丙氨酸解氨酶;MEP:甲基赤藓糖醇-4-磷酸途径;MVA:甲羟戊酸途径;Pe:花瓣;Li:唇瓣;Se:萼片;Co:合蕊柱
Fig. 4 Major biosynthetic pathways of aroma compounds in Maxillaria tenuifolia ADH:Alcohol dehydrogenase;DMAPP:Dimethylallyl diphosphate;FAD:Fatty acid desaturase;FPP:Farnesyl diphosphate;FPPS:Farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase;GGPP:Geranylgeranyl diphosphate;GGPPS:Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase;GPP:Geranyl diphosphate;GPPS:Geranyl pyrophosphate synthase;HPL:Hydroperoxide lyase;IPP:Isopentenyl diphosphate;LOX:Lipoxygenase; TPS:Terpene synthase;PAL:phenylalanine ammonia lyase;MEP:methylerythritol 4-phosphate;MVA:Mevalonate;Pe:Petal;Li:Lip;Se:Sepal;Co:Column
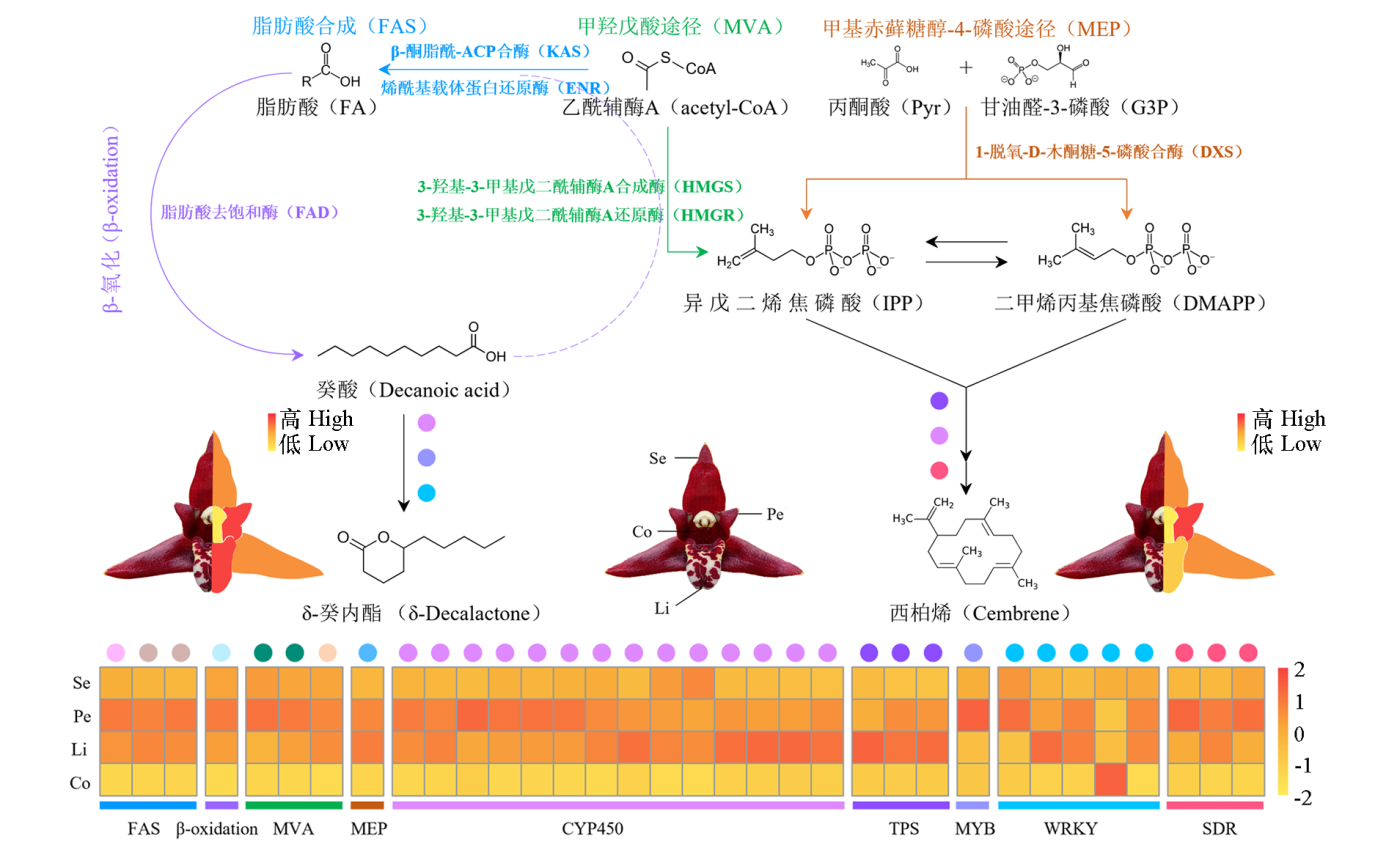
图9 脂肪酸合成途径(FAS)、甲羟戊酸途径(MVA)和甲基赤藓糖醇-4-磷酸途径(MEP)在腋唇兰花器官中合成酯类和萜类化合物的示意图 紫色箭头表示β-氧化循环;蓝色和绿色字体表示FAS和MVA途径中的关键酶基因,橙色字体表示MEP途径的关键酶。下方热图展示了这些基因在不同花器官中的转录表达水平(黄色至红色表示从低到高)。中央花瓣图像展示了δ-癸内酯和西柏烯在不同花器官中的相对丰度差异。Pe:花瓣;Li:唇瓣;Se:萼片;Co:合蕊柱
Fig. 9 Schematic diagram of fatty acid synthesis(FAS),the mevalonate pathway(MVA),and the methylerythritol phosphate pathway (MEP)involved in ester and terpenoid biosynthesis in floral organs of Maxillaria tenuifolia The purple arrow represents the β-oxidation cycle;blue and green labels denote key enzyme genes in the FAS and MVA pathways,while orange labels indicate enzymes of the MEP pathway. The heatmap illustrates the transcript levels of these genes across floral organs(yellow to red indicating low to high expression). The central petal image highlights the relative abundance differences. of δ-decalactone and caryophyllene among distinct floral tissues. Pe:Petal;Li:Lip;Se:Sepal;Co:Column
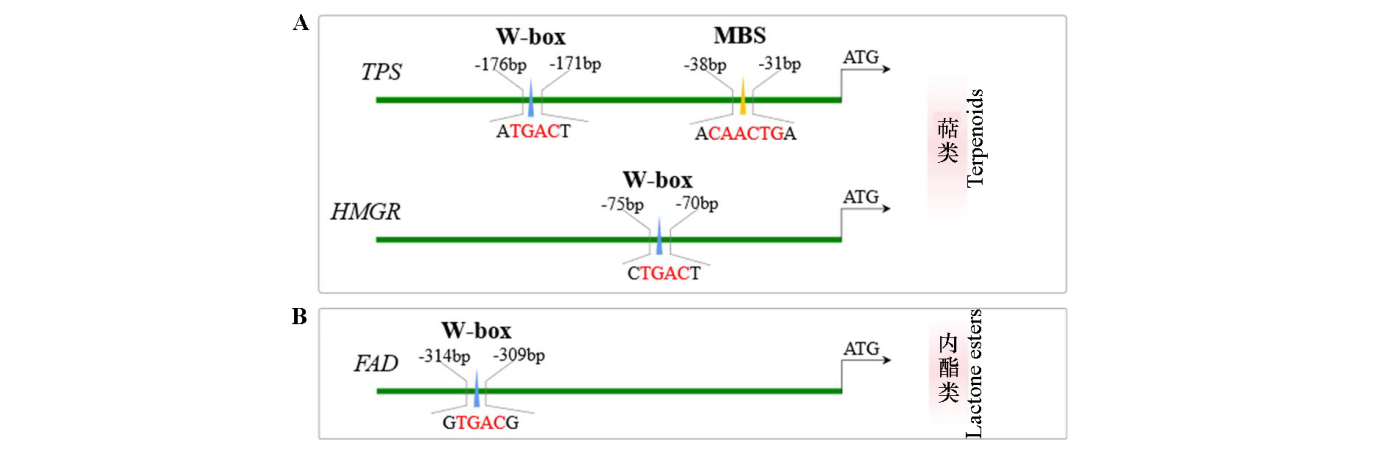
图10 腋唇兰花香气关键基因的调控模式 A:萜类化合物合成关键基因TPS与HMGR启动子中的WRKY结合位点(W-box)及MYB结合位点(MBS)分布;B:内酯类化合物合成关键基因FAD启动子中的WRKY结合位点(W-box)分布
Fig. 10 Regulatory landscape of key floral scent genes in Maxillaria tenuifolia A:Distribution of WRKY(W-box)and MYB(MBS)binding motifs within the promoter regions of the terpenoid biosynthetic genes TPS and HMGR. B:WRKY(W-box)motif distribution within the promoter of the lactone-related gene FAD
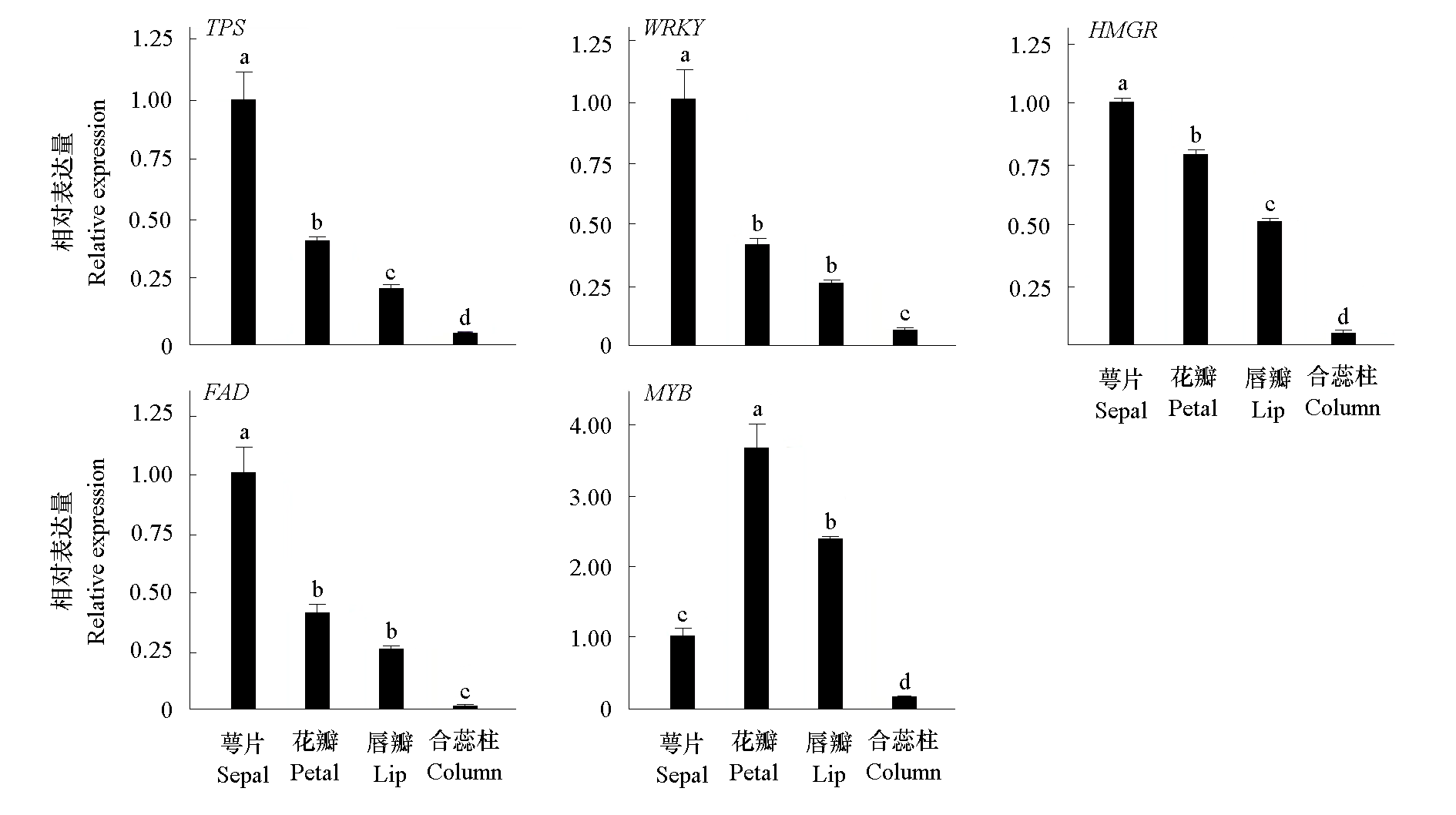
图11 腋唇兰花香气关键基因的组织表达分析 经单因素方差分析,不同字母表示Tukey检验下P < 0.05的显著性差异
Fig. 11 Tissue-specific expression of key floral scent genes in Maxillaria tenuifolia Statistical significance was evaluated using one-way ANOVA,followed by Tukey’s post hoc test,with different lowercase letters indicating significant differences at P < 0.05
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
|
刘登勇, 周光宏, 徐幸莲. 2008. 确定食品关键风味化合物的一种新方法:“ROAV”法. 食品科学,(7):370-374.
|
|
| [27] |
|
|
刘国梅, 郭淑慧, 孙璇, 姚琳, 张高扬, 杜春芳. 2024. 改良CTAB法提取不同作物总RNA技术研究. 中国农学通报, 40:28-35.
|
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
|
马迪, 肖文芳, 李佐, 张俊卫, 陈和明, 吕复兵. 2023. 兰科植物花香成分研究进展. 中国农学通报, 39 (16):52-60.
|
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
|
谢光明, 李秀梅, 刘进平. 2021. 咖啡兰繁殖与栽培. 中国花卉园艺,(5):54-55.
|
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
|
邹晶晶, 蔡璇, 曾祥玲, 郑日如, 王彩云. 2017. 桂花不同品种开花过程中香气活性物质的变化. 园艺学报, 44 (8):1517-1534.
|
| [1] | 王芳, 范燕萍. 观赏植物花香性状形成及调控机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 359-385. |
| [2] | 谢雨滢, 施婷婷, 杨秀莲, 王良桂, 岳远征. 花香的生物功能及其合成机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 386-396. |
| [3] | 赵雨晴, 唐菲鸿, 郑仕杰, 官泽恩, 吴建凯, 刘仲健, 彭东辉, 兰思仁, 赵凯, 周育真. 兰花“花香”物质研究进展:从合成机制到进化驱动[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 412-436. |
| [4] | 牛童非, 杨迪, 马慧丽, 郭丽丽, 侯小改. 牡丹花香的生物合成及调控研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 447-466. |
| [5] | 岳芝伊, 李心, 王昊宁, 张启翔, 孙丽丹. 梅花花香研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 467-480. |
| [6] | 付琪, 尚均忠, 裴文文, 刘国梁, 景维坤, 张颢, 蹇洪英, 邱显钦, 唐开学, 晏慧君. 月季花香物质合成基因及其演化机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 481-495. |
| [7] | 黄雅雯, 黄洪峰, 王智灵, 陈思雨, 张世琦, 洪波, 顾钊宇. 菊花花香突变体香气成分鉴定与萜烯合酶基因表达特性分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 513-524. |
| [8] | 沈言, 夏子轶, 冷平生, 马波, 胡增辉. ‘西伯利亚’百合LiMYB4的克隆及在萜烯合成中的功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 525-537. |
| [9] | 李崇晖, 洪小雨, 陆顺教, 廖易, 尹俊梅. 基于代谢组与转录组联合分析解析秋石斛花香形成机制[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 557-573. |
| [10] | 刘庭函, 张一凡, 陈沄毅, 周利君, 刘雨晨, 吴思惠, 罗乐, 于超. 巨花蔷薇杂交子代花香成分解析与释香部位研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 585-597. |
| [11] | 陈艺荃, 樊荣辉, 林兵, 陈燕, 吴建设, 钟淮钦. 山茶花花香生物合成相关基因的实时荧光定量PCR内参基因的筛选及验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 598-612. |
| [12] | 刘玉婷, 付雪梅, 胡一航, 陈龙清. 蜡梅花香转运相关ABCG基因的筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 613-634. |
| [13] | 康婧博, 温欢, 吴群, 敖义俊, 陈嘉景, 刘园, 徐娟. 七种香橙种质挥发性物质比较分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(1): 25-40. |
| [14] | 李雪, 蔡中虎, 高俊燕, 陈嘉景, 刘园, 徐娟. 云南巍山不同采收季广东香水柠檬(Citrus medica)挥发性物质差异分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(9): 2439-2452. |
| [15] | 李诗, 兰嘉仪, 杨廷, 付稳, 朱程红, 杨莎, 徐昊, 刘峰, 熊程, 邹学校, 戴雄泽. 辣椒挥发性物质研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(8): 2133-2154. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司