
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 761-772.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0329
王春伟, 王燕, 段天坤, 苏雅馨, 袁胜楠, 任璐, 赵晓军, 王美琴*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-11-06
修回日期:2024-12-09
出版日期:2025-03-25
发布日期:2025-03-25
通讯作者:
基金资助:
WANG Chunwei, WANG Yan, DUAN Tiankun, SU Yaxin, YUAN Shengnan, REN Lu, ZHAO Xiaojun, WANG Meiqin*( )
)
Received:2024-11-06
Revised:2024-12-09
Published:2025-03-25
Online:2025-03-25
摘要:
前期研究发现异辛醇能够显著抑制番茄灰霉病菌(灰葡萄孢Botrytis cinerea)菌丝的生长。为进一步明确异辛醇对番茄灰霉病菌的抑菌机理,采用双皿对扣法测定异辛醇对灰葡萄孢菌丝生长、孢子萌发和菌核形成的影响,利用激光扫描共聚焦显微技术观察异辛醇处理后灰葡萄孢体内DNA含量和活性氧自由基水平变化,采用紫外分光光度计检测异辛醇对番茄灰霉病菌菌丝酶活性及产草酸能力的影响。测定了异辛醇对番茄果实灰霉病的防效,并检测了异辛醇对番茄果实防御酶活性的影响。结果表明:异辛醇对番茄灰霉病菌菌丝生长有明显抑制作用。20 μL · L-1异辛醇处理后,灰霉病菌孢子萌发抑制率达100%,菌核的形成被显著抑制;灰霉病菌菌丝DNA荧光强度值明显降低,而活性氧自由基的荧光强度值显著提高。番茄果实中的超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)、多聚半乳糖醛酸酶(PG)、β-1,3-葡聚糖酶(β-1,3-GA)和几丁质酶(CHI)活性均低于对照;毒力因子草酸的分泌能力显著降低。异辛醇对番茄灰霉病的防治效果为77.19%,可以提高番茄果实体内防御酶SOD、CAT、CHI、过氧化物酶(POD)和苯丙氨酸解氨酶(PAL)活性。异辛醇通过破坏番茄灰霉病菌菌丝的正常生理活性,有效抑制番茄灰霉病菌的生长,还可以诱导番茄果实的抗病性。
王春伟, 王燕, 段天坤, 苏雅馨, 袁胜楠, 任璐, 赵晓军, 王美琴. 异辛醇对番茄灰霉病菌的抑菌机理研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 761-772.
WANG Chunwei, WANG Yan, DUAN Tiankun, SU Yaxin, YUAN Shengnan, REN Lu, ZHAO Xiaojun, WANG Meiqin. Antifungal Mechanism of Isooctyl Alcohol on Botrytis cinerea Causing Tomato Gray Mold[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(3): 761-772.
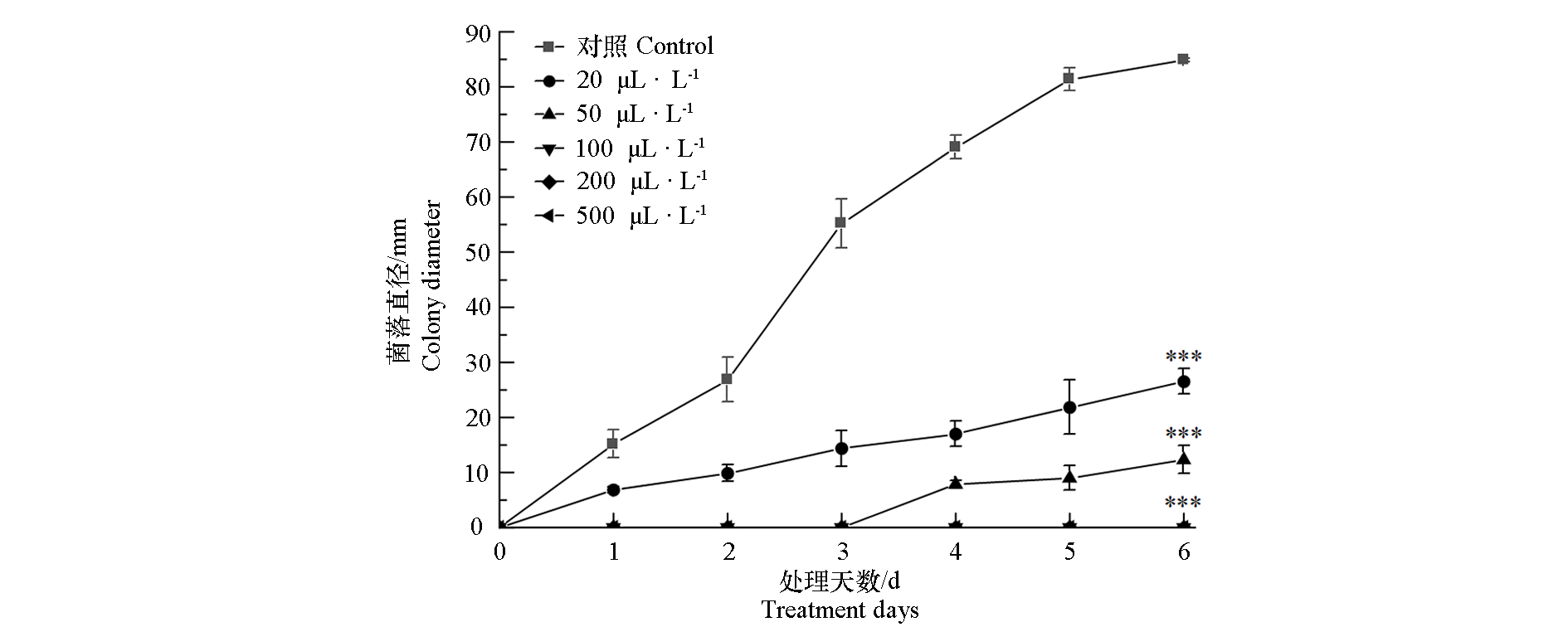
图1 不同浓度(20、50、100、200和500 μL · L-1)异辛醇处理对番茄灰霉病菌菌丝生长的影响 ***代表经Student’s t-test 检验各处理与对照间在0.001水平有显著差异
Fig. 1 Effects of isooctyl alcohol different concentrations(20,50,100,200 and 500 μL · L-1)on mycelial growth of Botrytis cinerea of tomato *** represented significant differences between treatment and control at 0.001 levels as calculated by Student’s t-test
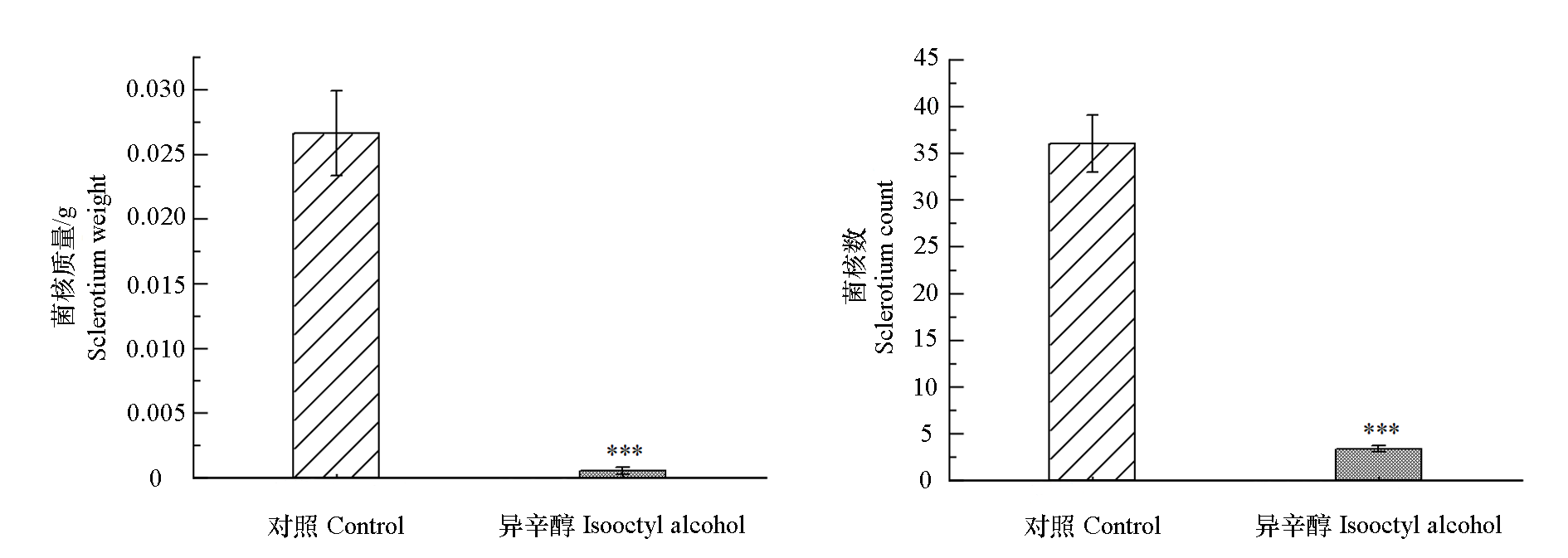
图3 异辛醇(20 μL · L-1)处理对番茄灰霉病菌菌核质量和数量的影响 数据均以平均值 ± 标准误(n = 3)表示,采用Student’s t-test检验比较差异显著性,*** P < 0.001
Fig. 3 Effect of isooctyl alcohol(20 μL · L-1)on sclerotium weight and sclerotium number of Botrytis cinerea of tomato Values are mean ± standard error(n = 3). Statistical analysis was conducted by Student’s t-test method. *** P < 0.001
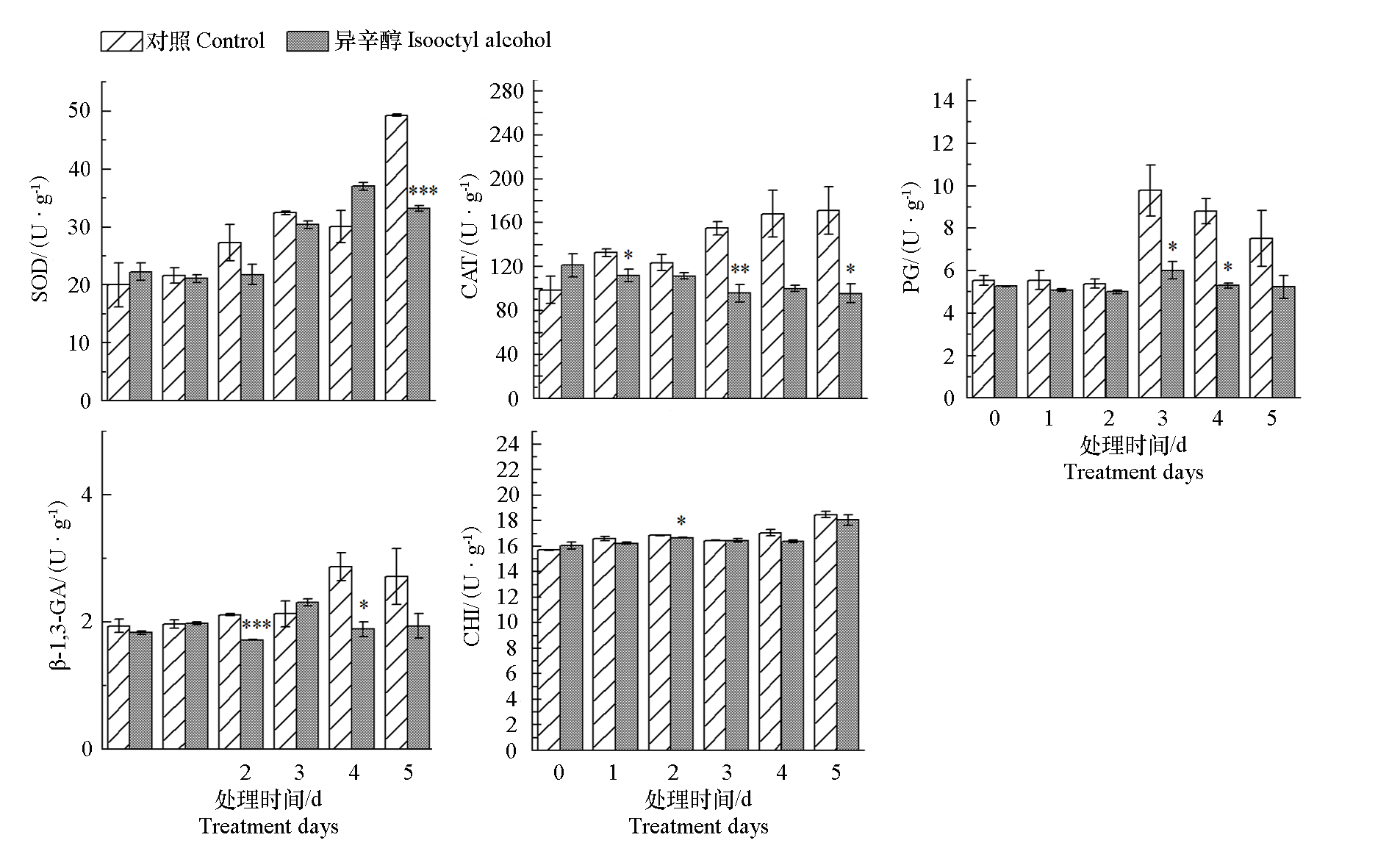
图5 异辛醇(20 μL · L-1)处理对番茄灰霉病菌菌丝酶活性的影响 *和***分别代表 Student’s t-test检验在P < 0.05和P < 0.001水平上处理与对照有显著差异
Fig. 5 Effect of isooctyl alcohol(20 μL · L-1)on enzyme activities of Botrytis cinerea * and *** represented significant differences at 0.05 and 0.001 levels as calculated by Student’s t-test

图6 异辛醇(20 μL · L-1)处理对番茄灰霉病菌草酸含量的影响 数据均以平均值 ± 标准误(n = 3)表示,采用Student’s t-test检验比较差异显著性,** P < 0.01,***P < 0.001
Fig. 6 Effect of isooctyl alcohol(20 μL · L-1)on oxalic acid content of Botrytis cinerea Values are mean ± standard error(n = 3). Statistical analysis was conducted by Student’s t-test method. ** P < 0.01,***P < 0.001
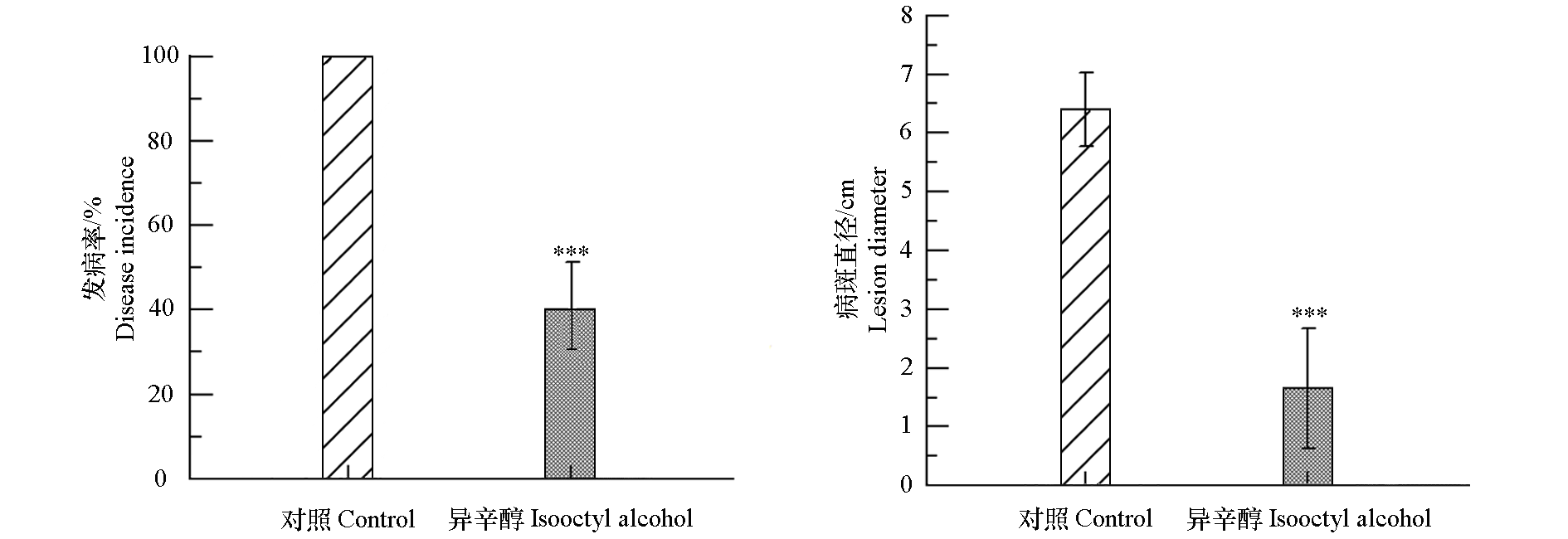
图7 异辛醇(20 μL · L-1)对番茄灰霉病发病率和病斑直径的影响 数据均以平均值 ± 标准误(n = 3)表示,采用Student’s t-test检验比较差异显著性,***P < 0.001
Fig. 7 Effects of isooctyl alcohol(20 μL · L-1)on incidence and lesion diameter of tomato Values are mean ± standard error(n = 3). Statistical analysis was conducted by Student’s t-test method. ***P < 0.001

图8 异辛醇(20 μL · L-1)处理对番茄防御酶活性的影响 *、**和***分别代表 Student’s t-test 检验在P < 0.05,P < 0.01和P < 0.001水平上有显著差异
Fig. 8 Effects of isooctyl alcohol on the activities of tomato defense enzyme *,** and *** represented significant differences at 0.05,0.01 and 0.001 levels as calculated by Student’s t-test
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
|
包华, 李康, 钟睦琪, 郝智慧. 2022. 胡椒碱对番茄灰霉病菌抑制作用及其机理研究. 中国农业大学学报, 27 (9):117-124.
|
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00060 pmid: 25750643 |
| [7] |
|
|
董晓南, 吕红梅, 赵立群, 何秉青, 张姣姣, 赵冰, 郭仰东, 张娜. 2024. SlMAPKKK43调控番茄对灰霉病的抗性. 园艺学报, 51 (2):309-320.
|
|
| [8] |
|
|
窦勇. 2023. Ε-聚赖氨酸对苹果采后青霉病的控制及其机制研究[博士论文]. 镇江: 江苏大学.
|
|
| [9] |
|
|
段立珍, 汪建飞, 赵建荣. 2007. 比色法测定菠菜中草酸含量的条件研究. 安徽农业科学, 35 (3):632-633,643.
|
|
| [10] |
doi: 10.16409/j.cnki.2095-039x.2023.02.068 |
|
段天坤, 王燕, 袁佳琪, 苏雅馨, 史璐欣, 王琳, 苏健, 王美琴, 王春伟. 2023. 异辛醇对灰葡萄孢的抑菌作用及转录组分析. 中国生物防治学报, 39 (6):1434-1445.
doi: 10.16409/j.cnki.2095-039x.2023.02.068 |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
|
付麟雲, 李晶, 李娜, 刘锦霞, 丁品, 聂垚琰, 武建荣, 杨成. 2024. 链霉菌SS9-1 发酵条件优化及其对番茄灰霉病的防治效果研究. 中国生物防治学报, 40 (1):126-136.
|
|
| [13] |
|
|
顾桂飞. 2022. 蛇床子素对Monilinia fructicola的生物活性及抑菌机制初探[硕士论文]. 贵阳: 贵州大学.
|
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
|
黄蓉, 胡建坤, 黄瑞荣. 2017. 酵母挥发性物质环辛四烯抑制灰霉菌的研究. 中国生物防治学报, 33 (2):266-272.
|
|
| [17] |
|
|
贾淑鑫, 李金, 闫思远, 郭苗苗, 王若彤, 顾沛雯. 2024. 嗜线虫镰刀菌NQ8GⅡ4对枸杞根腐病的防效及其机制研究. 园艺学报, 51 (3):631-642.
|
|
| [18] |
doi: 10.16409/j.cnki.2095-039x.2023.02.028 |
|
李博雅, 鲁姸璇, 谢家贝, 施李鸣, 张克诚, 葛蓓孛, 冉隆贤. 2023. 武夷菌素防治葡萄灰霉病的作用及机理. 中国生物防治学报, 39 (3):676-683.
doi: 10.16409/j.cnki.2095-039x.2023.02.028 |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
|
刘婧, 马汇泉, 刘东武, 董瑾, 杨晓. 2008. Bacillus cereus B-02对Botrytis cinerea拮抗机理的研究. 菌物学报, 27 (6):930-939.
|
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
|
刘信强. 2020. 灰葡萄孢菌核形成相关基因的挖掘和功能研究[博士论文]. 武汉: 华中农业大学.
|
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
|
邵文勇. 2018. 灰葡萄孢(Botrytis cinerea)对氟啶胺抗药性风险及敏感性相关基因功能的研究[博士论文]. 南京: 南京农业大学.
|
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
|
燕霞飞, 郑长英, 李凯月, 万方浩, 王俊平. 2017. 球孢白僵菌在重金属Cd(Ⅱ)作用下抗氧化酶系变化. 环境昆虫学报, 39 (5):992-999.
|
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
|
余红凤, 张琳, 毕钰, 王志刚, 徐伟慧, 黄欣冉, 郭嘉仪. 2024. 一株西瓜枯萎病生防菌Bacillus methylotrophicus的筛选、鉴定及抑菌物质分析. 微生物学通报, 51 (2):534-553.
|
|
| [34] |
|
|
余璐, 魏琛, 张凯歌, 林亲录, 王青云. 2023. 枯草芽孢杆菌PW2产挥发性物质对赭曲霉的抑制作用. 食品科学, 44 (14):125-133.
|
|
| [35] |
doi: 10.16409/j.cnki.2095-039x.2023.02.057 |
|
张金奎, 徐生军, 李继平, 马娅楠, 荆卓琼, 郭致杰, 郑果. 2023. 生防细菌HMQ20YJ04发酵条件优化及其对番茄灰霉病的效果评价. 中国生物防治学报, 39 (6):1418-1433.
doi: 10.16409/j.cnki.2095-039x.2023.02.057 |
|
| [36] |
|
|
张文静, 徐大勇, 吴倩琳, 杨佛, 信丙越, 曾昕, 李峰. 2024. 拮抗番茄灰霉病的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌XDY66基因组分析. 园艺学报, 51 (6):1413-1425.
|
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
|
钟涛, 王智荣, 杜木英. 2021. 微生物源挥发性物质防治采后果蔬病害的研究进展. 微生物学报, 61 (7):1771-1785.
|
|
| [42] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0418 URL |
|
周洁, 李甜竹, 刘汝懿, 李陈浩, 袁泽南, 李建明. 2023. 空气湿度与土壤含水量耦合对番茄灰霉病的影响. 园艺学报, 50 (8):1779-1792.
|
| [1] | 陆秀萍, 汤智超, 唐文琨, 毛妃凤, 张万萍, 李经纬. 13种类病毒RNA/DNA基因组对番茄的侵染性鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 749-760. |
| [2] | 李芮, 王稳, 杜明辉, 刘根忠, 马方放, 包志龙. SlBON1调控番茄植株营养生长机制的研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 73-87. |
| [3] | 韩荧, 段颖, 牛一杰, 李衍素, 贺超兴, 孙敏涛, 王君, 李强, 陈双臣, 闫妍. 腐殖酸生物降解地膜提高番茄品质的转录代谢机制研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1758-1772. |
| [4] | 龚小雅, 李贤, 周新刚, 吴凤芝. 分蘖洋葱伴生番茄诱导的根际微生物对根结线虫病的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1913-1926. |
| [5] | 孟思达, 韩磊磊, 相恒佐, 朱美玉, 冯珍, 叶云珠, 孙美华, 李艳冰, 赵利萍, 谭昌华, 齐明芳, 李天来. 番茄心室数的调控机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1649-1664. |
| [6] | 马星云, 范冰丽, 唐光彩, 贾芝琪, 李营, 薛东齐, 张世文. DXR调控番茄叶绿体发育、花色与果实着色机制初探[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1241-1255. |
| [7] | 张文静, 徐大勇, 吴倩琳, 杨佛, 信丙越, 曾昕, 李峰. 拮抗番茄灰霉病的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌XDY66基因组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1413-1425. |
| [8] | 王永珍, 张剑国, 刘彩虹, 李思蓓, 吕甜甜. 番茄新品种‘圆红212’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1435-1436. |
| [9] | 刘泽营, 孙帅, 刘志强, 崔霞, 李仁. 番茄尖果脐突变体的生理特性及其候选基因分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 982-992. |
| [10] | 李品, 甘宁, 陈家伟, 项思翔, 沈静漪, 欧阳波, 卢永恩. 番茄自然群体磷利用效率分析及耐低磷种质筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 993-1004. |
| [11] | 杨婷, 席德慧, 夏明, 李佳楠. α-苦瓜素基因提高番茄对烟草花叶病毒抗性的机理研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1126-1136. |
| [12] | 胡志峰, 邵景成, 张莉. 番茄新品种‘陇番15号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 917-918. |
| [13] | 刘根忠, 李方曼, 葛平飞, 陶金宝, 张星雨, 叶志彪, 张余洋. 番茄抗坏血酸含量相关QTL定位及候选基因鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 219-228. |
| [14] | 董舒超, 洪骏, 凌嘉怡, 谢紫欣, 张胜军, 赵丽萍, 宋刘霞, 王银磊, 赵统敏. 番茄抗旱性的全基因组关联分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 229-238. |
| [15] | 徐琴, 王嘉颖, 张曼楠, 萧志浩, 郑涵楷, 卢永恩, 王涛涛, 张余洋, 张俊红, 叶志彪, 叶杰. 番茄苗期耐盐相关遗传位点鉴定及分子标记开发[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 239-252. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司