
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 749-760.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0050
陆秀萍1,*, 汤智超1,*, 唐文琨1, 毛妃凤2, 张万萍1, 李经纬1,**( )
)
收稿日期:2024-11-08
修回日期:2025-01-09
出版日期:2025-03-25
发布日期:2025-03-25
通讯作者:
作者简介:*共同第一作者
基金资助:
LU Xiuping1, TANG Zhichao1, TANG Wenkun1, Mao Feifeng2, ZHANG Wanping1, LI Jingwei1,**( )
)
Received:2024-11-08
Revised:2025-01-09
Published:2025-03-25
Online:2025-03-25
摘要:
选取13种在园艺植物上报道较多的类病毒,将其人工合成的cDNA通过Sac I和Spe I酶切后,经T7酶体外转录为常规RNA基因组,同时利用PCR合成各类病毒DNA全长基因组,将RNA和DNA基因组机械摩擦接种于Ailsa Craig番茄苗上,并通过RT-PCR和RT-qPCR检测不同类病毒对番茄的侵染效率。分别以RNA和DNA形式进行类病毒基因组人工接种,结果表明,除了常规的RNA基因组外,类病毒DNA基因组亦具有侵染性,少量类病毒RNA和DNA基因组侵染性存在差异。总体来看,13种类病毒均可侵染番茄,并引起植株矮化、落叶、叶片卷曲、革质和黄化等病症。其中侵染性较强的为CChMVd、ELVd-1、PSTVd、TCDVd、TPMVd和HSVd,其在感染植株中滴度较高,引起的病情指数较高。PLMVd在植株内平均滴度较低,但致病性较高。侵染后RT-PCR检测产物与人工合成cDNA序列测序基本一致。
陆秀萍, 汤智超, 唐文琨, 毛妃凤, 张万萍, 李经纬. 13种类病毒RNA/DNA基因组对番茄的侵染性鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 749-760.
LU Xiuping, TANG Zhichao, TANG Wenkun, Mao Feifeng, ZHANG Wanping, LI Jingwei. Identification of Infectivity of 13 Viroid RNA and DNA Genomes of Tomato[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(3): 749-760.
| 序号 Number | 科 Family | 类病毒名称 Viroid name | 大小/bp Size | 基因编号 GenBank number | 缩写 Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 鳄梨日斑类病毒科 Avsunviroidae | 类苹果锤头类病毒 Apple hammerhead viroid-like | 434 | KR605506.1 | AHVd-like |
| 2 | 鳄梨日斑类病毒科 Avsunviroidae | 鳄梨日斑类病毒 Avocado sunblotch viroid | 247 | J02020.1 | ASBVd |
| 3 | 鳄梨日斑类病毒科Avsunviroidae | 菊花黄化花叶类病毒 Chrysanthemum chlorotic mottle viroid | 399 | Y14700.1 | CChMVd |
| 4 | 鳄梨日斑类病毒科 Avsunviroidae | 茄潜隐类病毒-1 Eggplant latent viroid-1 | 333 | AJ536613.1 | ELVd-1 |
| 5 | 鳄梨日斑类病毒科 Avsunviroidae | 茄潜隐类病毒-2 Eggplant latent viroid-2 | 335 | AJ536612.1 | ELVd-2 |
| 6 | 鳄梨日斑类病毒科 Avsunviroidae | 桃潜隐花叶类病毒 Peach latent mosaic viroid | 337 | M83545.1 | PLMVd |
| 7 | 马铃薯块茎纺锤体类病毒科 Pospiviroidae | 柑橘类病毒VII Citrus viroid VII | 368 | KX013549.1 | CVd VII |
| 8 | 马铃薯块茎纺锤体类病毒科 Pospiviroidae | 马铃薯块茎纺锤体类病毒 Potato spindle tuber viroid | 359 | V01465.1 | PSTVd |
| 9 | 马铃薯块茎纺锤体类病毒科 Pospiviroidae | 番茄顶矮缩类病毒 Tomato apical stunt viroid | 360 | K00818.1 | TASVd |
| 10 | 马铃薯块茎纺锤体类病毒科 Pospiviroidae | 番茄褪绿矮缩类病毒 Tomato chlorotic dwarf viroid | 360 | AF162131.1 | TCDVd |
| 11 | 马铃薯块茎纺锤体类病毒科 Pospiviroidae | 番茄雄植株类病毒 Tomato planta macho viroid | 360 | K00817.1 | TPMVd |
| 12 | 马铃薯块茎纺锤体类病毒科 Pospiviroidae | 啤酒花矮化类病毒 Hop stunt viroid | 302 | X06719.1 | HSVd |
| 13 | 鳄梨日斑类病毒科 Avsunviroidae | 苹果锈皮类病毒 Apple scar skin viroid | 329 | X17696.1 | ASSVd |
表1 13种合成类病毒种类及编号
Table 1 13 types of synthetic viroid species and numbers
| 序号 Number | 科 Family | 类病毒名称 Viroid name | 大小/bp Size | 基因编号 GenBank number | 缩写 Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 鳄梨日斑类病毒科 Avsunviroidae | 类苹果锤头类病毒 Apple hammerhead viroid-like | 434 | KR605506.1 | AHVd-like |
| 2 | 鳄梨日斑类病毒科 Avsunviroidae | 鳄梨日斑类病毒 Avocado sunblotch viroid | 247 | J02020.1 | ASBVd |
| 3 | 鳄梨日斑类病毒科Avsunviroidae | 菊花黄化花叶类病毒 Chrysanthemum chlorotic mottle viroid | 399 | Y14700.1 | CChMVd |
| 4 | 鳄梨日斑类病毒科 Avsunviroidae | 茄潜隐类病毒-1 Eggplant latent viroid-1 | 333 | AJ536613.1 | ELVd-1 |
| 5 | 鳄梨日斑类病毒科 Avsunviroidae | 茄潜隐类病毒-2 Eggplant latent viroid-2 | 335 | AJ536612.1 | ELVd-2 |
| 6 | 鳄梨日斑类病毒科 Avsunviroidae | 桃潜隐花叶类病毒 Peach latent mosaic viroid | 337 | M83545.1 | PLMVd |
| 7 | 马铃薯块茎纺锤体类病毒科 Pospiviroidae | 柑橘类病毒VII Citrus viroid VII | 368 | KX013549.1 | CVd VII |
| 8 | 马铃薯块茎纺锤体类病毒科 Pospiviroidae | 马铃薯块茎纺锤体类病毒 Potato spindle tuber viroid | 359 | V01465.1 | PSTVd |
| 9 | 马铃薯块茎纺锤体类病毒科 Pospiviroidae | 番茄顶矮缩类病毒 Tomato apical stunt viroid | 360 | K00818.1 | TASVd |
| 10 | 马铃薯块茎纺锤体类病毒科 Pospiviroidae | 番茄褪绿矮缩类病毒 Tomato chlorotic dwarf viroid | 360 | AF162131.1 | TCDVd |
| 11 | 马铃薯块茎纺锤体类病毒科 Pospiviroidae | 番茄雄植株类病毒 Tomato planta macho viroid | 360 | K00817.1 | TPMVd |
| 12 | 马铃薯块茎纺锤体类病毒科 Pospiviroidae | 啤酒花矮化类病毒 Hop stunt viroid | 302 | X06719.1 | HSVd |
| 13 | 鳄梨日斑类病毒科 Avsunviroidae | 苹果锈皮类病毒 Apple scar skin viroid | 329 | X17696.1 | ASSVd |
| 类病毒Viroid | 引物序列Primer sequence | 类病毒Viroid | 引物序列Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| AHVd-like | 5′-GAAGGCTATTAGCCTTCCTGATGAGT-3′ 5′-GACCGTCACGGGGGTGTTAAAAC-3′ | PSTVd | 5′-CGGAACTAAACTCGTGGTTCCTGTG-3′ 5′-AGGAACCAACTGCGGTTCCAAG-3′ |
| ASBVd | 5′-TTTATTAGAACAAGAAGTGAGGATATGAT-3′ 5′-CAAGATTTTGTAAAAAAACAATGAAGAT-3′ | TASVd | 5′-CGGGATCTTTCGTGAGGTTCCT-3′ 5′-AGGGACCATTCAGGGTTCC-3′ |
| CChMVd | 5′-GGCACCTGACGTCGGTGTC-3′ 5′-GACCTCTTGGGGGTTTCAAACC-3′ | TCDVd | 5′-CGGAACTAAACTCGTGGTTCCTGTG-3′ 5′-AGGAACCAACTGCGGTTCCAAG-3′ |
| ELVd-1 | 5′-GGGTGGTGTGTGCCACC-3′ 5′-TATGGGGAGAGGTCGTCCTCTATCT-3′ | TPMVd | 5′-CGGGATCTTTTCCTTGTGGTTCC-3′ 5′-AGGGACCCTTTTCGAAGGGT-3′ |
| ELVd-2 | 5′-GGGTGGTGTGTACCACCCCT-3′ 5′-TATGGGGAGAGGCCGTCCT-3′ | HSVd | 5′-CTGGGGAATTCTCGAGTTGC-3′ 5′-AGGGGCTCAAGAGAGGATC-3′ |
| PLMVd | 5′-GTCATAAGTTTCGTCGCATTTCAGC-3′ 5′-AAGAAGAGTTTCGTCTCATCTCAGAG-3′ | ASSVd | 5′-GGTAAACACCGTGCGGTTC-3′ 5′-GGGAAACACCTATTGTGTTTTACCC-3′ |
| CVd VII | 5′-TCGAGGACACTTCTGGTTCCTAT-3′ 5′-GGGACGACTCTAGGTCTCCCTT-3′ |
表2 类病毒全长引物序列
Table 2 Full-length primer sequences for viroids
| 类病毒Viroid | 引物序列Primer sequence | 类病毒Viroid | 引物序列Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| AHVd-like | 5′-GAAGGCTATTAGCCTTCCTGATGAGT-3′ 5′-GACCGTCACGGGGGTGTTAAAAC-3′ | PSTVd | 5′-CGGAACTAAACTCGTGGTTCCTGTG-3′ 5′-AGGAACCAACTGCGGTTCCAAG-3′ |
| ASBVd | 5′-TTTATTAGAACAAGAAGTGAGGATATGAT-3′ 5′-CAAGATTTTGTAAAAAAACAATGAAGAT-3′ | TASVd | 5′-CGGGATCTTTCGTGAGGTTCCT-3′ 5′-AGGGACCATTCAGGGTTCC-3′ |
| CChMVd | 5′-GGCACCTGACGTCGGTGTC-3′ 5′-GACCTCTTGGGGGTTTCAAACC-3′ | TCDVd | 5′-CGGAACTAAACTCGTGGTTCCTGTG-3′ 5′-AGGAACCAACTGCGGTTCCAAG-3′ |
| ELVd-1 | 5′-GGGTGGTGTGTGCCACC-3′ 5′-TATGGGGAGAGGTCGTCCTCTATCT-3′ | TPMVd | 5′-CGGGATCTTTTCCTTGTGGTTCC-3′ 5′-AGGGACCCTTTTCGAAGGGT-3′ |
| ELVd-2 | 5′-GGGTGGTGTGTACCACCCCT-3′ 5′-TATGGGGAGAGGCCGTCCT-3′ | HSVd | 5′-CTGGGGAATTCTCGAGTTGC-3′ 5′-AGGGGCTCAAGAGAGGATC-3′ |
| PLMVd | 5′-GTCATAAGTTTCGTCGCATTTCAGC-3′ 5′-AAGAAGAGTTTCGTCTCATCTCAGAG-3′ | ASSVd | 5′-GGTAAACACCGTGCGGTTC-3′ 5′-GGGAAACACCTATTGTGTTTTACCC-3′ |
| CVd VII | 5′-TCGAGGACACTTCTGGTTCCTAT-3′ 5′-GGGACGACTCTAGGTCTCCCTT-3′ |
| 类病毒Viroid | 引物序列Primer sequence | 类病毒Viroid | 引物序列Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| AHVd-like | 5′-CTATTAGCCTTCCTGATG-3′ 5′-GTGTAAGTCGTAGTCTATT-3′ | PSTVd | 5′-CGGTGGAAACAACTGAAG-3′ 5′-GTTCCAAGGGCTAAACAC-3′ |
| ASBVd | 5′-TCTGTTCCGACTTTCCGACTC-3′ 5′-TTCTTCCCATCTTTCCCTGA-3′ | TASVd | 5′-TTTCTTCTGGTTTCCTTC-3′ 5′-AGAGCAACAAAGATAGAG-3′ |
| CChMVd | 5′-CAGGAAACCCACTTCAGGTC-3′ 5′-TCCGAGGAGAATATCCAACG-3′ | TCDVd | 5′-GCTTGTGGAAGGCGAAAC-3′ 5′-AAGGAAGGAAACCGCAGAA-3′ |
| ELVd-1 | 5′-AGACCGAAAGGTCGAAATGG-3′ 5′-AAGGGACTCTTGGAGGAACG-3′ | TPMVd | 5′-CTGACCTCCTGACCAGAA-3′ 5′-AGTTCGCTCCAGGTTTCC-3′ |
| ELVd-2 | 5′-TACCACCCCTGATGAGTC-3′ 5′-GCTCTTGGAGGAACGATT-3′ | HSVd | 5′-AACAAGGCAGGGAGGAGACT-3′ 5′-GAAGAGCCAGGAGAAGGTAAAA-3′ |
| PLMVd | 5′-CCGTAGAAACTGGATTAC-3′ 5′-TTAGCACAGACTCTTCAT-3′ | ASSVd | 5′-CCGTGCGGTTCCTGTGGTTC-3′ 5′-GGTTAGTGCTGGCAGCTCCTTT-3′ |
| CVd VII | 5′-ACTGGAACTGCTTGCCTTGA-3′ 5′-CGGTCCATTGCCTTAGAATA-3′ |
表3 类病毒RT-qPCR引物序列
Table 3 Primary sequences for viroid RT-qPCR detection
| 类病毒Viroid | 引物序列Primer sequence | 类病毒Viroid | 引物序列Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| AHVd-like | 5′-CTATTAGCCTTCCTGATG-3′ 5′-GTGTAAGTCGTAGTCTATT-3′ | PSTVd | 5′-CGGTGGAAACAACTGAAG-3′ 5′-GTTCCAAGGGCTAAACAC-3′ |
| ASBVd | 5′-TCTGTTCCGACTTTCCGACTC-3′ 5′-TTCTTCCCATCTTTCCCTGA-3′ | TASVd | 5′-TTTCTTCTGGTTTCCTTC-3′ 5′-AGAGCAACAAAGATAGAG-3′ |
| CChMVd | 5′-CAGGAAACCCACTTCAGGTC-3′ 5′-TCCGAGGAGAATATCCAACG-3′ | TCDVd | 5′-GCTTGTGGAAGGCGAAAC-3′ 5′-AAGGAAGGAAACCGCAGAA-3′ |
| ELVd-1 | 5′-AGACCGAAAGGTCGAAATGG-3′ 5′-AAGGGACTCTTGGAGGAACG-3′ | TPMVd | 5′-CTGACCTCCTGACCAGAA-3′ 5′-AGTTCGCTCCAGGTTTCC-3′ |
| ELVd-2 | 5′-TACCACCCCTGATGAGTC-3′ 5′-GCTCTTGGAGGAACGATT-3′ | HSVd | 5′-AACAAGGCAGGGAGGAGACT-3′ 5′-GAAGAGCCAGGAGAAGGTAAAA-3′ |
| PLMVd | 5′-CCGTAGAAACTGGATTAC-3′ 5′-TTAGCACAGACTCTTCAT-3′ | ASSVd | 5′-CCGTGCGGTTCCTGTGGTTC-3′ 5′-GGTTAGTGCTGGCAGCTCCTTT-3′ |
| CVd VII | 5′-ACTGGAACTGCTTGCCTTGA-3′ 5′-CGGTCCATTGCCTTAGAATA-3′ |

图1 类病毒RNA和DNA基因组接种番茄叶片侵染情况检测 M:Marker;N为阴性对照;1 ~ 13依次为AHVd-like、ASBVd、CChMVd、ELVd-1、ELVd-2、PLMVd、CVd VII、PSTVd、TASVd、TCDVd、TPMVd、HSVd和ASSVd样本
Fig. 1 Detection of infection status of tomato leaves inoculated with viroid RNA and DNA genome M:Marker;N:Healthy plants negative control. 1-13 were AHVd-like,ASBVd,CChMVd,ELVd-1,ELVd-2,PLMVd,CVd VII,PSTVd,TASVd,TCDVd,TPMVd,HSVd and ASSVd samples
| 类病毒 Viroid | RNA基因组接种样本RNA genome infection samples | DNA基因组接种样本 DNA genome infection samples | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SacⅠ酶切SacⅠdigested | SacⅠ酶切SacⅠdigested | ||
| H2O(对照Control) | 0 i | 0 g | 0 h |
| AHVd-like | 0 i | 13.9 ± 1.8 f | 18.8 ± 1.6 g |
| ASBVd | 49.2 ±13.9 g | 0 g | 0 h |
| CChMVd | 916.4 ± 144.4 b | 247.8 ± 60.9 b | 101.8 ± 8.9 e |
| ELVd-1 | 283.6 ± 57.9 e | 83.9 ± 12.3 c | 323.8 ± 56.6 c |
| ELVd-2 | 100.5 ± 13.0 f | 33.1 ± 7.2 d | 153.4 ± 41.5 d |
| PLMVd | 228.2 ± 21.7 e | 36.9 ± 8.1 d | 18.2 ± 1.2 g |
| CVd Ⅶ | 0 i | 197.8 ± 30.5 b | 36.7 ± 1.2 f |
| PSTVd | 424.2 ± 42.6 d | 194.2 ± 38.2 b | 694.8 ± 58.9 a |
| TASVd | 50.7 ± 5.8 g | 12.5 ± 1.3 f | 17.0 ± 2.1 g |
| TCDVd | 656.7 ± 75.6 c | 407.0 ± 28.1 a | 428.8 ± 14.7 b |
| TPMVd | 2 011.8 ± 119.1 a | 0 g | 595.7 ± 98.0 a |
| HSVd | 219.1 ± 20.6 e | 111.8 ± 25.0 c | 100.2 ± 22.9 e |
| ASSVd | 28.1 ± 2.5 h | 19.2 ± 3.1 e | 0 h |
表4 Ailsa Craig番茄中各类病毒滴度RT-qPCR检测结果
Table 4 Results of RT-qPCR of various viroid titers in Ailsa Craig tomato
| 类病毒 Viroid | RNA基因组接种样本RNA genome infection samples | DNA基因组接种样本 DNA genome infection samples | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SacⅠ酶切SacⅠdigested | SacⅠ酶切SacⅠdigested | ||
| H2O(对照Control) | 0 i | 0 g | 0 h |
| AHVd-like | 0 i | 13.9 ± 1.8 f | 18.8 ± 1.6 g |
| ASBVd | 49.2 ±13.9 g | 0 g | 0 h |
| CChMVd | 916.4 ± 144.4 b | 247.8 ± 60.9 b | 101.8 ± 8.9 e |
| ELVd-1 | 283.6 ± 57.9 e | 83.9 ± 12.3 c | 323.8 ± 56.6 c |
| ELVd-2 | 100.5 ± 13.0 f | 33.1 ± 7.2 d | 153.4 ± 41.5 d |
| PLMVd | 228.2 ± 21.7 e | 36.9 ± 8.1 d | 18.2 ± 1.2 g |
| CVd Ⅶ | 0 i | 197.8 ± 30.5 b | 36.7 ± 1.2 f |
| PSTVd | 424.2 ± 42.6 d | 194.2 ± 38.2 b | 694.8 ± 58.9 a |
| TASVd | 50.7 ± 5.8 g | 12.5 ± 1.3 f | 17.0 ± 2.1 g |
| TCDVd | 656.7 ± 75.6 c | 407.0 ± 28.1 a | 428.8 ± 14.7 b |
| TPMVd | 2 011.8 ± 119.1 a | 0 g | 595.7 ± 98.0 a |
| HSVd | 219.1 ± 20.6 e | 111.8 ± 25.0 c | 100.2 ± 22.9 e |
| ASSVd | 28.1 ± 2.5 h | 19.2 ± 3.1 e | 0 h |
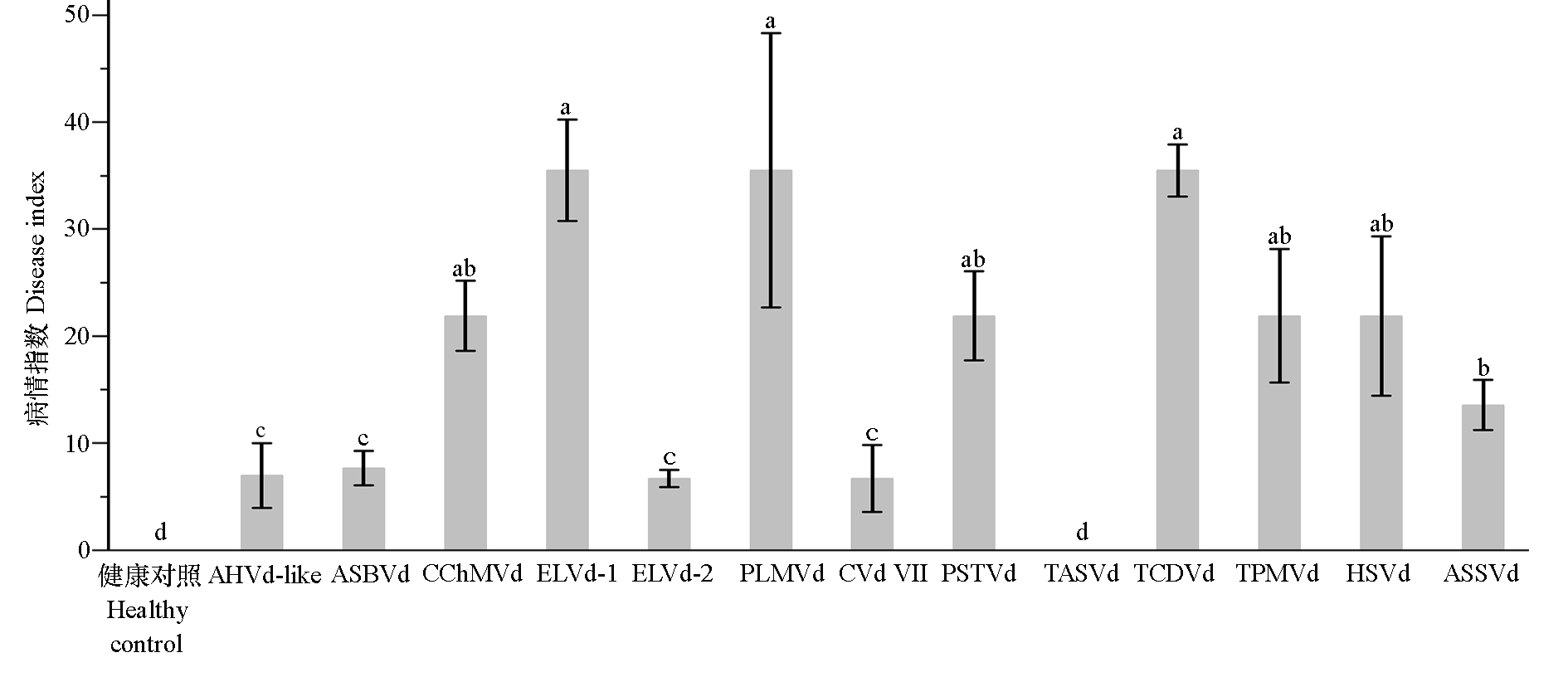
图4 13种类病毒侵染番茄病情指数统计 数据采用单因素方差分析,不同字母代表在P < 0.05水平上存在显著性差异
Fig. 4 Statistics of various viroid disease index in tomato The data was analyzed using one-way ANOVA,where different letters represent significant differences at the P < 0.05

图5 类病毒感染对Ailsa Craig番茄株高和叶片数的影响 数据采用单因素方差分析,不同字母代表在 P < 0.05 水平上存在显著性差异
Fig. 5 Effect of class viroid infection on Ailsa Craig tomato strain height and leaf number The data was analyzed using one-way ANOVA,where different letters represent significant differences at the P < 0.05
| 类病毒 Viroid | 基因编号 GenBank number | 比对率/% Match rate | 类病毒 Viroid | 基因编号 GenBank number | 比对率/% Match rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AHVd-like | KR605506.1 | 98.64 | PSTVd | V01465.1 | 97.01 |
| ASBVd | J02020.1 | 99.06 | TASVd | K00818.1 | 98.89 |
| CChMVd | Y14700.1 | 98.99 | TCDVd | AF162131.1 | 98.06 |
| ELVd-1 | AJ536613.1 | 99.09 | TPMVd | K00817.1 | 98.61 |
| ELVd-2 | AJ536612.1 | 99.24 | HSVd | X06719.1 | 98.68 |
| PLMVd | M83545.1 | 98.81 | ASSVd | X17696.1 | 99.46 |
| CVd Ⅶ | KX013549.1 | 99.46 |
表5 番茄内类病毒复制子序列比对结果
Table 5 Comparison results of replicon sequences of tomato viroid
| 类病毒 Viroid | 基因编号 GenBank number | 比对率/% Match rate | 类病毒 Viroid | 基因编号 GenBank number | 比对率/% Match rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AHVd-like | KR605506.1 | 98.64 | PSTVd | V01465.1 | 97.01 |
| ASBVd | J02020.1 | 99.06 | TASVd | K00818.1 | 98.89 |
| CChMVd | Y14700.1 | 98.99 | TCDVd | AF162131.1 | 98.06 |
| ELVd-1 | AJ536613.1 | 99.09 | TPMVd | K00817.1 | 98.61 |
| ELVd-2 | AJ536612.1 | 99.24 | HSVd | X06719.1 | 98.68 |
| PLMVd | M83545.1 | 98.81 | ASSVd | X17696.1 | 99.46 |
| CVd Ⅶ | KX013549.1 | 99.46 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.09.031 pmid: 18028975 |
| [4] |
|
|
陈海燕. 2018. 马铃薯卷叶病毒,S病毒与马铃薯纺锤形块茎类病毒的茎尖超低温保存研究[硕士论文]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学.
|
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2016.04.017 |
|
董艳娜, 郑银英, 徐文兴. 2016. 用草本植物番茄鉴定五种柑橘类病毒. 中国农业科学, 49 (4):784-790.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2016.04.017 |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
|
霍建勇. 2016. 中国番茄产业现状及安全防范. 蔬菜,(6):1-4.
|
|
| [11] |
|
|
李君明, 项朝阳, 王孝宣, 国艳梅, 黄泽军, 刘磊, 李鑫, 杜永臣. 2021. “十三五”我国番茄产业现状及展望. 中国蔬菜,(2):13-20.
|
|
| [12] |
|
|
刘茜. 2019. 类病毒在栗疫病菌中的侵染,复制和传播[硕士论文]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学.
|
|
| [13] |
|
|
吕典秋, 邱彩玲, 王绍鹏, 李勇, 高云飞. 2009. 马铃薯类病毒cDNA双体探针的研制及其在检测上的应用. 园艺学报, 36 (10):1538-1544.
|
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0766 URL |
|
聂睿涵, 孙曼丽, 冯迪, 宋谢天, 高俊燕, 郭莉娜, 邓秀新, 柴利军, 谢宗周, 叶俊丽. 2024. 云南柑橘5种常见病害发生分布调查及其规律分析. 园艺学报, 51 (11):2685-2700.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0766 URL |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
|
王进, 欧毅, 武峥, 代正林, 刘圣维. 2011. 高温胁迫对早熟梨生理效应和早期落叶的影响. 西南农业学报, 24 (2):6.
|
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
|
张知博. 2015. 木茼蒿(Argyranthemum)茎尖超低温保存与脱除菊花矮化类病毒(CSVd)的效应与机理研究[博士论文]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学.
|
|
| [23] |
|
|
张志想, 葛蓓孛, 潘嵩, 赵哲, 王红清, 李世访. 2011. 菊花矮化类病毒的分子检测与序列分析. 园艺学报, 38 (12):2349-2356.
|
| [1] | 刘勇, 王富荣, 王会良, 艾小艳, 朱炜, 张杨, 甘志猛, 龚林忠, 何华平. 武汉地区油蟠桃病毒种类的小RNA测序鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 727-736. |
| [2] | 王春伟, 王燕, 段天坤, 苏雅馨, 袁胜楠, 任璐, 赵晓军, 王美琴. 异辛醇对番茄灰霉病菌的抑菌机理研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 761-772. |
| [3] | 李芮, 王稳, 杜明辉, 刘根忠, 马方放, 包志龙. SlBON1调控番茄植株营养生长机制的研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 73-87. |
| [4] | 韩荧, 段颖, 牛一杰, 李衍素, 贺超兴, 孙敏涛, 王君, 李强, 陈双臣, 闫妍. 腐殖酸生物降解地膜提高番茄品质的转录代谢机制研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1758-1772. |
| [5] | 龚小雅, 李贤, 周新刚, 吴凤芝. 分蘖洋葱伴生番茄诱导的根际微生物对根结线虫病的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1913-1926. |
| [6] | 孟思达, 韩磊磊, 相恒佐, 朱美玉, 冯珍, 叶云珠, 孙美华, 李艳冰, 赵利萍, 谭昌华, 齐明芳, 李天来. 番茄心室数的调控机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1649-1664. |
| [7] | 马星云, 范冰丽, 唐光彩, 贾芝琪, 李营, 薛东齐, 张世文. DXR调控番茄叶绿体发育、花色与果实着色机制初探[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1241-1255. |
| [8] | 张文静, 徐大勇, 吴倩琳, 杨佛, 信丙越, 曾昕, 李峰. 拮抗番茄灰霉病的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌XDY66基因组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1413-1425. |
| [9] | 王永珍, 张剑国, 刘彩虹, 李思蓓, 吕甜甜. 番茄新品种‘圆红212’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1435-1436. |
| [10] | 刘泽营, 孙帅, 刘志强, 崔霞, 李仁. 番茄尖果脐突变体的生理特性及其候选基因分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 982-992. |
| [11] | 李品, 甘宁, 陈家伟, 项思翔, 沈静漪, 欧阳波, 卢永恩. 番茄自然群体磷利用效率分析及耐低磷种质筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 993-1004. |
| [12] | 杨婷, 席德慧, 夏明, 李佳楠. α-苦瓜素基因提高番茄对烟草花叶病毒抗性的机理研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1126-1136. |
| [13] | 胡志峰, 邵景成, 张莉. 番茄新品种‘陇番15号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 917-918. |
| [14] | 刘根忠, 李方曼, 葛平飞, 陶金宝, 张星雨, 叶志彪, 张余洋. 番茄抗坏血酸含量相关QTL定位及候选基因鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 219-228. |
| [15] | 董舒超, 洪骏, 凌嘉怡, 谢紫欣, 张胜军, 赵丽萍, 宋刘霞, 王银磊, 赵统敏. 番茄抗旱性的全基因组关联分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 229-238. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司