
园艺学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 1241-1255.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0774
马星云, 范冰丽, 唐光彩, 贾芝琪, 李营, 薛东齐, 张世文*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-01-26
修回日期:2024-04-19
出版日期:2024-12-18
发布日期:2024-06-21
通讯作者:
基金资助:
MA Xingyun, FAN Bingli, TANG Guangcai, JIA Zhiqi, LI Ying, XUE Dongqi, ZHANG Shiwen*( )
)
Received:2024-01-26
Revised:2024-04-19
Published:2024-12-18
Online:2024-06-21
摘要:
在植物的生长发育过程中,类胡萝卜素对叶、花、果的着色有着重要影响,是果实发育过程中的主要色素物质。1-脱氧-D-木酮糖-5-磷酸还原异构酶基因(DXR)参与了类胡萝卜素的合成,构建番茄DXR基因编辑株系和超量表达株系,发现基因编辑株系叶片呈现黄色甚至白色,叶片的叶绿素含量和最大PSⅡ的光能转换效率显著降低,细胞叶绿体发育受到影响,类囊体数量减少;花瓣边缘白化,红熟期果实颜色变为橙色甚至黄色,果实番茄红素、类黄酮等含量有不同程度降低。而超量表达株系与野生型对照相比无明显差异,但可溶性固形物含量明显增多。通过转录组测序发现,SlDXR与类黄酮生物合成、类胡萝卜素生物合成等途径相关。推测SlDXR可能通过调控萜类化合物的合成来影响番茄果实着色。
马星云, 范冰丽, 唐光彩, 贾芝琪, 李营, 薛东齐, 张世文. DXR调控番茄叶绿体发育、花色与果实着色机制初探[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1241-1255.
MA Xingyun, FAN Bingli, TANG Guangcai, JIA Zhiqi, LI Ying, XUE Dongqi, ZHANG Shiwen. Preliminary Study on the Mechanism of DXR Regulating Chloroplast Development Flower Color and Fruit Coloring in Tomato[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1241-1255.
| 基因序列 Primer name | 正向引物序列(5′-3′) Forward primer sequence | 反向引物序列(5′-3′) Reverse primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Actin | GTCCTCTTCCAGCCATCCAT | ACCACTGAGCACAATGTTACCG |
| Solyc03g114340(DXR) | AAGGCAGAGTTGGGATGGTC | TTGTCCGGATTCTCAGCGAC |
| Solyc04g012120(14-3-3) | GAGCTAGGAGAGCATCGTGG | GCAACTTGAGGATGCCGTTAC |
| Solyc03g034180(14-3-3) | TGATGATGCCATCGCAGAGC | TCATCCGTGGTATCAGAAGTCC |
| Solyc01g079620(MYB12) | GGGCATCAAGAGAGGCAGAT | AACGACCTCCAAGAGCCTTC |
| Solyc11g013110(FLS) | AAGATTTGGCCTCCTCCTGC | TCCAAACCAAGCCCAAGTGA |
| Solyc04g040190(LCYB) | GTGCTCGATGCAACTGGCTT | GGTGCTCTTCCACTTCAGCC |
| Solyc12g008980(LCYE) | TGGTGTATGGGAGGACGAGT | AACTCTTCCATAGGCACGGC |
| Solyc05g010320(CHI) | GAATCCTCTGGGCTCCAACA | ACACACCGATCGCAGTAAAC |
表1 qRT-PCR所用引物序列
Table 1 Sequence of primers used for qRT-PCR
| 基因序列 Primer name | 正向引物序列(5′-3′) Forward primer sequence | 反向引物序列(5′-3′) Reverse primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Actin | GTCCTCTTCCAGCCATCCAT | ACCACTGAGCACAATGTTACCG |
| Solyc03g114340(DXR) | AAGGCAGAGTTGGGATGGTC | TTGTCCGGATTCTCAGCGAC |
| Solyc04g012120(14-3-3) | GAGCTAGGAGAGCATCGTGG | GCAACTTGAGGATGCCGTTAC |
| Solyc03g034180(14-3-3) | TGATGATGCCATCGCAGAGC | TCATCCGTGGTATCAGAAGTCC |
| Solyc01g079620(MYB12) | GGGCATCAAGAGAGGCAGAT | AACGACCTCCAAGAGCCTTC |
| Solyc11g013110(FLS) | AAGATTTGGCCTCCTCCTGC | TCCAAACCAAGCCCAAGTGA |
| Solyc04g040190(LCYB) | GTGCTCGATGCAACTGGCTT | GGTGCTCTTCCACTTCAGCC |
| Solyc12g008980(LCYE) | TGGTGTATGGGAGGACGAGT | AACTCTTCCATAGGCACGGC |
| Solyc05g010320(CHI) | GAATCCTCTGGGCTCCAACA | ACACACCGATCGCAGTAAAC |
| 引物名称 Primer name | 正向引物序列(5′-3′) Forward primer sequence | 反向引物序列(5′-3′) Reverse primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| CP098-SlDXR | AATCTAACAGTGTAGTTTGTGAGCCAGGAAGGCAGAGTTGTTTTAGAGCTAGAAATAGC | CTATTTCTAGCTCTAAAACTGCTCCCCAGGTATAATCTCCAAACTACACTGTTAGATTC |
| pHellgate8-SlDXR | CATTTGGAGAGGACACGCTCGAGATGGCCCTCAATTTGCTTTCTC | TCTCATTAAAGCAGGACTCTAGATACAAGAGCTGGACTCAAACCAGAT |
| pCAMBIA1302-SlDXR-GFP | ACGGGGGACTCTTGACCATGGATGGCCCTCAATTTGCTTTCTC | AAGTTCTTCTCCTTTACTAGTTACAAGAGCTGGACTCAAACCAGAT |
| pMV2-SlDXR | TGCATCCAACGCGTTGGGAGCTCGCCTGCATCACACCCGTAT | GCCTTCGCCATTCTAGACTCGAGGCTATGTGTCTCGTTGTGGC |
表2 表达载体所用引物序列
Table 2 Sequence of primers used for expression vectors
| 引物名称 Primer name | 正向引物序列(5′-3′) Forward primer sequence | 反向引物序列(5′-3′) Reverse primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| CP098-SlDXR | AATCTAACAGTGTAGTTTGTGAGCCAGGAAGGCAGAGTTGTTTTAGAGCTAGAAATAGC | CTATTTCTAGCTCTAAAACTGCTCCCCAGGTATAATCTCCAAACTACACTGTTAGATTC |
| pHellgate8-SlDXR | CATTTGGAGAGGACACGCTCGAGATGGCCCTCAATTTGCTTTCTC | TCTCATTAAAGCAGGACTCTAGATACAAGAGCTGGACTCAAACCAGAT |
| pCAMBIA1302-SlDXR-GFP | ACGGGGGACTCTTGACCATGGATGGCCCTCAATTTGCTTTCTC | AAGTTCTTCTCCTTTACTAGTTACAAGAGCTGGACTCAAACCAGAT |
| pMV2-SlDXR | TGCATCCAACGCGTTGGGAGCTCGCCTGCATCACACCCGTAT | GCCTTCGCCATTCTAGACTCGAGGCTATGTGTCTCGTTGTGGC |
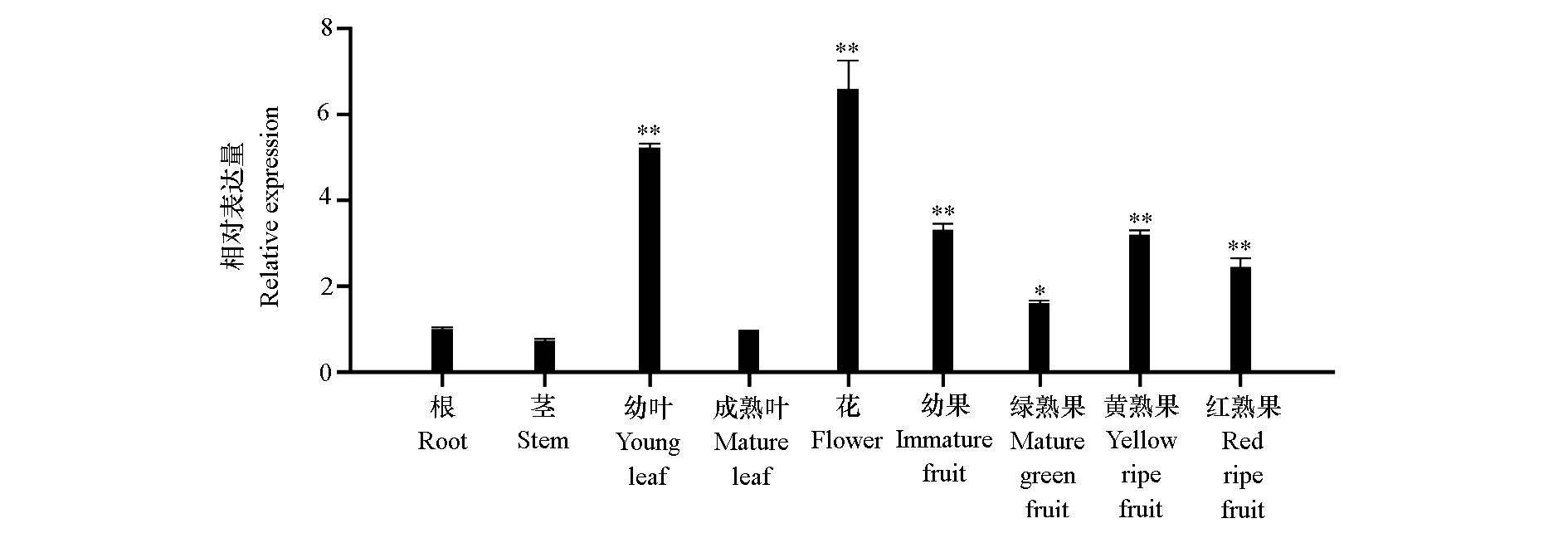
图1 SlDXR 在番茄各个组织中的表达量 各组织与根中相对表达量相比。
Fig. 1 Relative expression of SlDXR in various tissues of tomato Comparison of relative expression levels between tissues and roots. t-test,* P < 0.05;** P < 0.01

图3 番茄SlDXR在烟草中的亚细胞定位 叠加1为GFP荧光与叶绿体荧光的叠加图;叠加2为明场、GFP荧光和叶绿体荧光的叠加图。
Fig. 3 Subcellular localization of tomato SlDXR in tobacco Superposition 1 represents the superposition of GFP fluorescence and chloroplast fluorescence;Superimposed 2 generations of brighfield,GFP fluorescence and chloroplast fluorescence.

图4 番茄野生型(WT)、T0代SlDXR编辑株系(CR)和超量表达株系(OE)株系的鉴定 A:基因编辑载体CP098阳性检测;B:超量表达载体pHellsgate8阳性检测;C:CRISPR/Cas9基因编辑SlDXR的靶点和突变位点;D:CR株系的SlDXR基因序列。
Fig. 4 Identification and gene expression detection of tomato wild type(WT),T0 generation SlDXR edited lines(CR)and overexpressed lines(OE) A:Positive detection of gene editing vector CP098;B:Positive detection of overexpression lines vector pHellsgate8;C:Target and mutation sites of CRISPR/ Cas9 gene editing SlDXR;D:SlDXR gene sequence of CR lines.

图6 番茄野生型(WT)、SlDXR编辑株系(CR)和超量表达株系(OE)的表型与光合相关指标测定 A:T0代阳性植株;B:T2代叶片叶绿素荧光成像;C:叶片最大PSⅡ的光能转换效率;D:叶片叶绿素含量。** P < 0.01。
Fig. 6 Phenotypic and photosynthetic related indexes determination of tomato wild type(WT),SlDXR edited(CR)and overexpressed(OE)lines A:T0 generation positive plants;B:T2 generation leaf chlorophyll fluorescence imaging;C:The light energy conversion efficiency of the maximum PSⅡof the leaves;D:Chlorophyll content in leaves. ** P < 0.01.
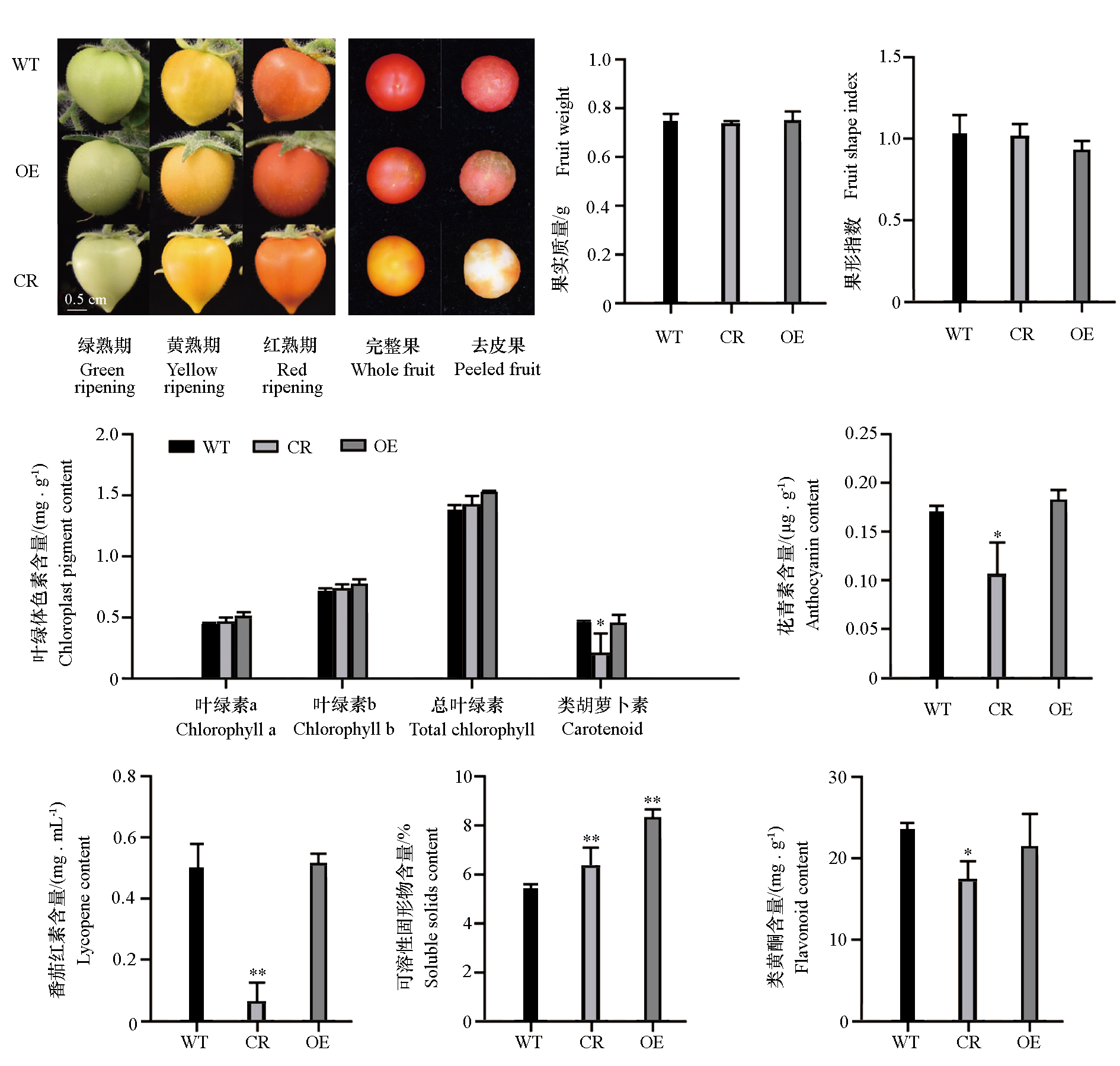
图8 番茄野生型(WT)、SlDXR编辑株系(CR)和超量表达株系(OE)果实表型及其相关生理指标
Fig. 8 Fruit phenotype and related physiological indexes of tomato wild type(WT),SlDXR edited(CR)and overexpression lines(OE) * P < 0.05;** P < 0.01.
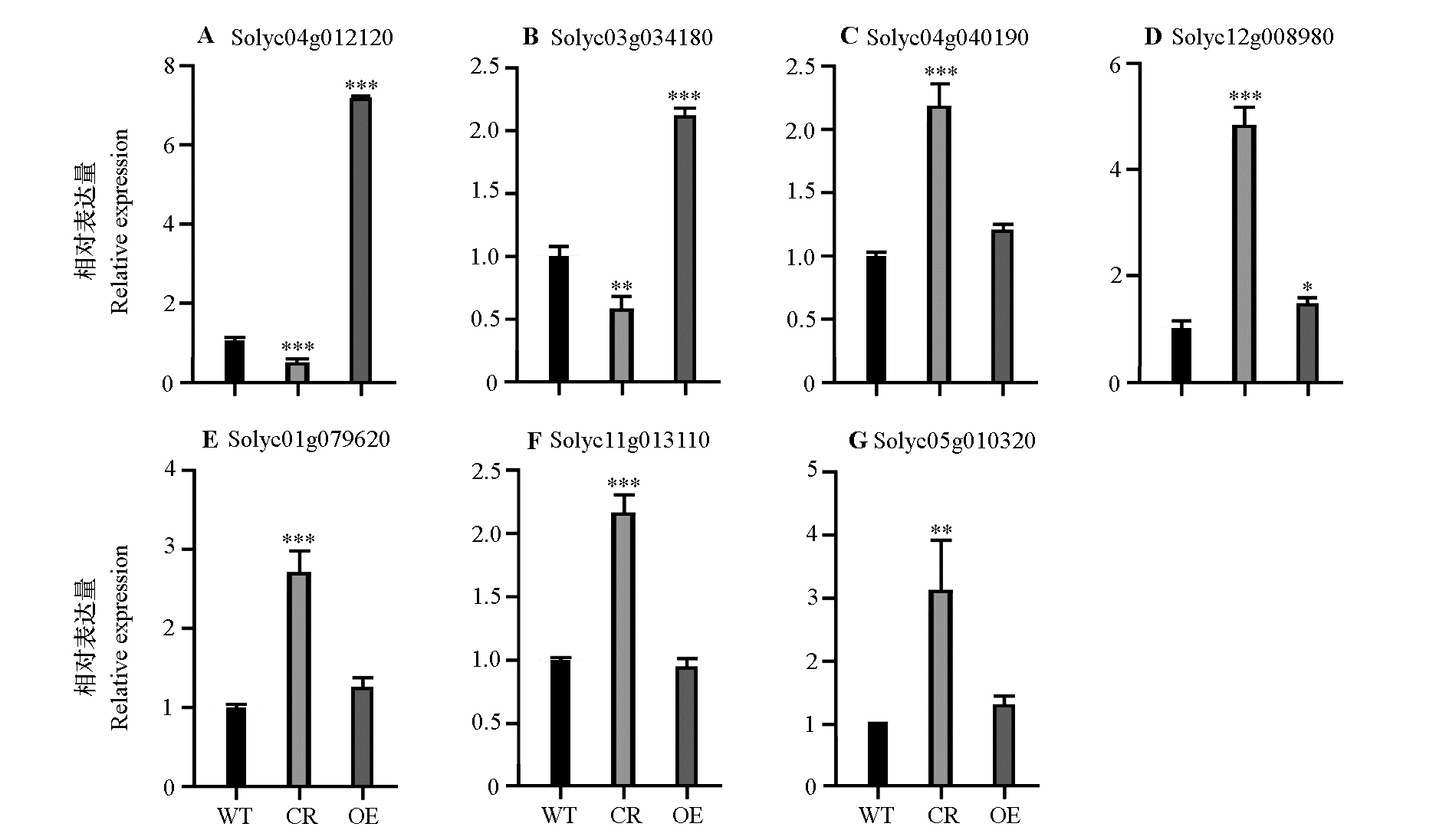
图9 SlDXR相关基因在番茄野生型(WT)、SlDXR编辑株系(CR)和超量表达株系(OE)叶片(A、B)和红熟果实(C ~ G)中的表达量
Fig. 9 Relative expression levels of SlDXR-related genes in tomato wild type(WT),SlDXR edited(CR)and overexpressed(OE)lines in leaves(A,B)and red ripe fruits(C-G) ** P < 0.01;*** P < 0.001.
| [1] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.109.147322 pmid: 19906891 |
| [2] |
pmid: 16941216 |
| [3] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0063 |
|
陈同强, 张天柱, 王晓卓. 2022. 光照对番茄果实中番茄红素生物合成的调控研究进展. 园艺学报, 49 (4):907-923.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0063 |
|
| [4] |
|
|
戴翔, 刘伟伟, 林光号. 2022. 蓝莓果实色素含量的分析. 浙江农业科学, 63 (12):2917-2920.
doi: 10.16178/j.issn.0528-9017.20220153 |
|
| [5] |
|
|
丁飞. 2022. SlFolB调控番茄叶绿体发育的表观遗传机理解析[博士论文]. 郑州: 河南农业大学.
|
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
|
高红岩, 梅晓宏, 苏夜阳, 朱本忠, 罗云波. 2005. 番茄红素及其生物合成途径的研究. 食品科技,(8):42-45.
|
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
|
郭亚飞, 王君雅, 郭飞, 倪德江. 2018. 茶树1-脱氧-D-木酮糖-5-磷酸合成酶基因CsDXS1的克隆与表达分析. 生物技术通报, 34 (1):144-152.
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2017-0652 |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
doi: 10.1263/jbb.105.518 pmid: 18558344 |
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
doi: 10.1073/pnas.240454797 pmid: 11078528 |
| [38] |
|
|
张丽, 陈丰酆, 王红霞, 廖乐琴, 张鹏, 周全卢, 康乐. 2023. 甘薯类胡萝卜素的代谢调控研究进展. 农业生物技术学报, 31 (8):1719-1729.
|
|
| [39] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0110 |
|
张巧丽, 陈笛, 宋艳萍, 朱鸿亮, 罗云波, 曲桂芹. 2023. 番茄果实叶绿素代谢转录调控网络研究进展. 园艺学报, 50 (9):2031-2047.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0110 |
|
| [40] |
|
|
张世文. 2018. 番茄抗热基因LrgB及果实硬度调控基因的研究[博士论文]. 武汉: 华中农业大学.
|
|
| [41] |
|
|
张伟, 梁成伟. 2014. 植物类异戊二烯合成途径的研究进展. 山东化工, 43 (5):57-58.
|
|
| [42] |
|
|
张文才. 2023. 不同海拔藏波罗花中萜类和黄酮类化合物及其合成相关基因表达的研究[硕士论文]. 林芝: 西藏大学.
|
|
| [43] |
|
|
张新业, 王雨欣, 孙艳香, 朱姝, 王聪艳, 李文静. 2021. 胡萝卜类黄酮含量的测定及DcCHS基因家族的鉴定分析. 西北农业学报, 30 (4):572-581.
|
|
| [44] |
|
|
周颖, 李冰樱, 李学宝. 2012. 14-3-3蛋白对植物发育的调控作用. 植物学报, 47 (1):55-64.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1259.2012.00055 |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0531 |
|
陆晨飞, 高月霞, 黄河, 戴思兰. 2022. 植物类胡萝卜素代谢及调控研究进展. 园艺学报, 49 (12):2559-2578.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0531 |
|
| [18] |
doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201119062 |
|
罗金凤, 任美燕, 陈敬鑫, 丁晓雯. 2011. 番茄红素的生理功能及保持其稳定性方法的研究进展. 食品科学, 32 (19):279-283.
doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201119062 |
|
| [19] |
|
|
罗志丹. 2015. 番茄果实颜色与质地调控基因SlSGR1和nsLTP的功能鉴定[博士论文]. 武汉: 华中农业大学.
|
|
| [20] |
|
|
欧阳波. 2003. 几种病程相关蛋白基因转化番茄的研究[博士论文]. 武汉: 华中农业大学.
|
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
|
邱见方. 2023. 番茄转录因子PHYTOCLOCK1( SlPCL1) 基因的耐旱和耐寒功能研究[硕士论文]. 重庆: 西南大学.
|
|
| [24] |
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.01089.x pmid: 11532167 |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1039/a709175c pmid: 10584331 |
| [26] |
|
|
阮美颖. 2014. 紫色番茄果实主要色素积累、果色遗传规律及种质创新研究[硕士论文]. 金华: 浙江师范大学.
|
|
| [27] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.107.100305 pmid: 17478633 |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0913 |
|
王晋, 王新宇, 沈渊博, 张清花, 娄茜棋, 张世杰, 赵攀, 梁燕. 2022. 番茄果实叶绿体发育调控及其应用的研究进展. 园艺学报, 49 (12):2669-2682.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0913 |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
|
徐萌. 2018. 番茄果实早期发育重要调控因子的发掘与功能分析[硕士论文]. 北京: 中国农业科学院.
|
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
|
杨小飞, 郭房庆. 2014. 高温逆境下植物叶片衰老机理研究进展. 植物生理学报, 50 (9):1285-1292.
|
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [1] | 夏志磊, 俞冰昕, 杨 梦, 连子林, 官利兰, 何艺超, 颜爽爽, 曹必好, 邱正坤, . 茄子绿果基因的精细定位及其KASP标记开发[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2008-2018. |
| [2] | 韩荧, 段颖, 牛一杰, 李衍素, 贺超兴, 孙敏涛, 王君, 李强, 陈双臣, 闫妍. 腐殖酸生物降解地膜提高番茄品质的转录代谢机制研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1758-1772. |
| [3] | 龚小雅, 李贤, 周新刚, 吴凤芝. 分蘖洋葱伴生番茄诱导的根际微生物对根结线虫病的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1913-1926. |
| [4] | 王晨雨, 刘孟军, 王立新, 刘志国, . CRISPR/Cas9技术研究进展及其在园艺植物中的应用进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1439-1454. |
| [5] | 孟思达, 韩磊磊, 相恒佐, 朱美玉, 冯 珍, 叶云珠, 孙美华, 李艳冰, 赵利萍, 谭昌华, 齐明芳, 李天来. 番茄心室数的调控机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1649-1664. |
| [6] | 江 睿, 周胜军, 朱育强, 王 欣, 谭继宏, 王华森, 张 鹏, . 瓜类作物CRISPR/Cas9基因编辑技术应用研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1683-1694. |
| [7] | 田歌, 刘建廷, 高传彩, 赵雪惠, 樊永信, 李森, 张寒啸, 陈修德, 李玲, 李冬梅. UV-B对设施油桃叶片叶绿素生物合成的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1332-1344. |
| [8] | 张文静, 徐大勇, 吴倩琳, 杨佛, 信丙越, 曾昕, 李峰. 拮抗番茄灰霉病的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌XDY66基因组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1413-1425. |
| [9] | 王永珍, 张剑国, 刘彩虹, 李思蓓, 吕甜甜. 番茄新品种‘圆红212’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1435-1436. |
| [10] | 邓淑芳, 刘倩, 刘玲, 陈鸥, 王文军, 曾凯芳, 邓丽莉. 蜜橘CcHY5的克隆及其对果实转色功能的研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 939-955. |
| [11] | 刘泽营, 孙帅, 刘志强, 崔霞, 李仁. 番茄尖果脐突变体的生理特性及其候选基因分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 982-992. |
| [12] | 李品, 甘宁, 陈家伟, 项思翔, 沈静漪, 欧阳波, 卢永恩. 番茄自然群体磷利用效率分析及耐低磷种质筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 993-1004. |
| [13] | 王文娇, 邢军杰, 申成丞, 李斌. 黄瓜蜡质基因CsCER1调控因子CsCOL5的筛选及其功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1005-1016. |
| [14] | 杨婷, 席德慧, 夏明, 李佳楠. α-苦瓜素基因提高番茄对烟草花叶病毒抗性的机理研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1126-1136. |
| [15] | 胡志峰, 邵景成, 张莉. 番茄新品种‘陇番15号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 917-918. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司