
园艺学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (10): 2401-2412.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0742
陈冰, 程玉瑾, 孙宝箴, 宋建飞, 张玮玮, 杨洪强*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-05-31
修回日期:2024-07-03
出版日期:2024-10-25
发布日期:2024-10-21
通讯作者:
基金资助:
CHEN Bing, CHENG Yujin, SUN Baozhen, SONG Jianfei, ZHANG Weiwei, YANG Hongqiang*( )
)
Received:2024-05-31
Revised:2024-07-03
Published:2024-10-25
Online:2024-10-21
摘要:
以5年生‘富士’苹果树为试验材料,在土壤封冻前充分灌溉,于次年1月与4月取样分析根际土壤细菌群落组成结构及速效养分含量的变化。结果显示,封冻前灌水在提高土壤含水量、稳定土壤温度的同时,显著提高土壤速效养分含量,降低土壤有机质含量,增加根际土壤细菌群落的丰富度和多样性,降低土层之间及冬春季之间细菌群落的差异性。其中,土壤有效氮、磷、钾含量分别提高了15.83%、21.13%和8.22%,有机质含量降低了19.86%。此外,初春时期果树根系密度、根系活力和根系氮含量分别提升了10.3%、15.6%和13.3%。功能基因定量分析显示,封冻前灌水可以显著增加土壤细菌和真菌数量,包括氨氧化古菌、固氮菌和反硝化菌在内的氮功能菌群丰度分别提高了35.18%、18.12%和19.53%,增强土壤硝化与反硝化作用。
陈冰, 程玉瑾, 孙宝箴, 宋建飞, 张玮玮, 杨洪强. 封冻前灌水对‘富士’苹果根际细菌群落及速效养分的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(10): 2401-2412.
CHEN Bing, CHENG Yujin, SUN Baozhen, SONG Jianfei, ZHANG Weiwei, YANG Hongqiang. Effects of Irrigation Before Soil Freezing on Bacterial Community Composition and Available Nutrient Content in‘Fuji’Apple Rhizosphere[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(10): 2401-2412.
| 土层/cm Soil depth | 土壤有机质/% Soil organic matter | NH4+/(mg · kg-1) | NO3-/(mg · kg-1) | 有效P/(mg · kg-1) Available P | 有效K/(mg · kg-1) Available K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 ~ 20 | 3.21 | 14.45 | 48.32 | 33.02 | 121.80 |
| 20 ~ 40 | 3.12 | 15.62 | 47.59 | 34.27 | 90.44 |
| 40 ~ 60 | 1.82 | 14.10 | 50.46 | 27.41 | 54.14 |
表1 供试土壤的基本理化性质
Table 1 Primary soil properties of experimental site
| 土层/cm Soil depth | 土壤有机质/% Soil organic matter | NH4+/(mg · kg-1) | NO3-/(mg · kg-1) | 有效P/(mg · kg-1) Available P | 有效K/(mg · kg-1) Available K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 ~ 20 | 3.21 | 14.45 | 48.32 | 33.02 | 121.80 |
| 20 ~ 40 | 3.12 | 15.62 | 47.59 | 34.27 | 90.44 |
| 40 ~ 60 | 1.82 | 14.10 | 50.46 | 27.41 | 54.14 |
| 取样日期(M-D) Date of sample | 土层/ cm Soil depth | 处理 Treatment | 土壤含水量/% SRWC | 温度/℃ Temperature | O2/% | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01-05 | 0 ~ 20 | 对照Control | 63.12 ± 0.06 e | 0.83 ± 0.09 g | 17.17 ± 0.09 f | 7.26 ± 0.03 a |
| 灌水Irrigation | 79.42 ± 0.08 b | 1.23 ± 0.07 f | 15.73 ± 0.03 g | 7.15 ± 0.02 bc | ||
| 20 ~ 40 | 对照Control | 73.17 ± 0.08 c | 3.07 ± 0.09 e | 17.30 ± 0.06 f | 7.12 ± 0.02 bc | |
| 灌水Irrigation | 84.07 ± 0.04 a | 4.17 ± 0.09 c | 15.77 ± 0.03 g | 7.16 ± 0.01 b | ||
| 40 ~ 60 | 对照Control | 73.14 ± 0.08 c | 3.90 ± 0.06 d | 17.17 ± 0.09 f | 6.96 ± 0.01 ef | |
| 灌水Irrigation | 84.02 ± 0.07 a | 4.27 ± 0.03 c | 15.83 ± 0.03 g | 6.88 ± 0.02 g | ||
| 04-05 | 0 ~ 20 | 对照Control | 53.70 ± 0.06 h | 14.93 ± 0.03 a | 19.07 ± 0.09 b | 7.09 ± 0.02 cd |
| 灌水Irrigation | 57.78 ± 0.13 f | 15.00 ± 0.06 a | 18.37 ± 0.03 c | 7.10 ± 0.02 bcd | ||
| 20 ~ 40 | 对照Control | 53.67 ± 0.05 h | 14.67 ± 0.07 b | 19.33 ± 0.03 a | 7.00 ± 0.01 ef | |
| 灌水Irrigation | 65.06 ± 0.08 d | 14.67 ± 0.03 b | 17.77 ± 0.03 e | 7.03 ± 0.04 de | ||
| 40 ~ 60 | 对照Control | 56.22 ± 0.08 g | 14.70 ± 0.06 b | 18.13 ± 0.03 d | 6.95 ± 0.03 fg | |
| 灌水Irrigation | 64.89 ± 0.04 d | 14.63 ± 0.03 b | 17.27 ± 0.03 f | 6.99 ± 0.03 ef |
表2 封冻前灌水对土壤物理性质的影响
Table 2 Effects of irrigation before soil freezing on soil physical properties
| 取样日期(M-D) Date of sample | 土层/ cm Soil depth | 处理 Treatment | 土壤含水量/% SRWC | 温度/℃ Temperature | O2/% | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01-05 | 0 ~ 20 | 对照Control | 63.12 ± 0.06 e | 0.83 ± 0.09 g | 17.17 ± 0.09 f | 7.26 ± 0.03 a |
| 灌水Irrigation | 79.42 ± 0.08 b | 1.23 ± 0.07 f | 15.73 ± 0.03 g | 7.15 ± 0.02 bc | ||
| 20 ~ 40 | 对照Control | 73.17 ± 0.08 c | 3.07 ± 0.09 e | 17.30 ± 0.06 f | 7.12 ± 0.02 bc | |
| 灌水Irrigation | 84.07 ± 0.04 a | 4.17 ± 0.09 c | 15.77 ± 0.03 g | 7.16 ± 0.01 b | ||
| 40 ~ 60 | 对照Control | 73.14 ± 0.08 c | 3.90 ± 0.06 d | 17.17 ± 0.09 f | 6.96 ± 0.01 ef | |
| 灌水Irrigation | 84.02 ± 0.07 a | 4.27 ± 0.03 c | 15.83 ± 0.03 g | 6.88 ± 0.02 g | ||
| 04-05 | 0 ~ 20 | 对照Control | 53.70 ± 0.06 h | 14.93 ± 0.03 a | 19.07 ± 0.09 b | 7.09 ± 0.02 cd |
| 灌水Irrigation | 57.78 ± 0.13 f | 15.00 ± 0.06 a | 18.37 ± 0.03 c | 7.10 ± 0.02 bcd | ||
| 20 ~ 40 | 对照Control | 53.67 ± 0.05 h | 14.67 ± 0.07 b | 19.33 ± 0.03 a | 7.00 ± 0.01 ef | |
| 灌水Irrigation | 65.06 ± 0.08 d | 14.67 ± 0.03 b | 17.77 ± 0.03 e | 7.03 ± 0.04 de | ||
| 40 ~ 60 | 对照Control | 56.22 ± 0.08 g | 14.70 ± 0.06 b | 18.13 ± 0.03 d | 6.95 ± 0.03 fg | |
| 灌水Irrigation | 64.89 ± 0.04 d | 14.63 ± 0.03 b | 17.27 ± 0.03 f | 6.99 ± 0.03 ef |
| 取样日期/ (M-D) Date of sample | 土层/cm Soil depth | 处理 Treatment | 土壤有机质/% Soil organic matter | NH4+-N / (mg · kg-1) | NO3--N / (mg · kg-1) | 有效磷/(mg · kg-1) Available P | 速效钾/(mg · kg-1) Available K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01-05 | 0 ~ 20 | 对照 Control | 3.08 ± 0.03 a | 13.64 ± 0.61 d | 49.48 ± 0.97 g | 31.78 ± 1.90 fg | 128.86 ± 2.15 b |
| 灌水 Irrigation | 2.70 ± 0.01 b | 12.36 ± 0.30 e | 65.35 ± 1.16 e | 33.96 ± 1.90 ef | 118.10 ± 1.81 c | ||
| 20 ~ 40 | 对照 Control | 3.06 ± 0.03 a | 15.05 ± 0.54 c | 49.98 ± 1.08 g | 33.96 ± 2.18 ef | 94.13 ± 1.84 f | |
| 灌水 Irrigation | 2.76 ± 0.02 b | 16.69 ± 0.26 b | 56.74 ± 0.23 f | 35.20 ± 0.54 ef | 116.26 ± 1.82 c | ||
| 40 ~ 60 | 对照 Control | 1.69 ± 0.03 d | 14.14 ± 0.84 cd | 51.18 ± 0.27 g | 27.72 ± 1.08 g | 95.97 ± 1.84 ef | |
| 灌水 Irrigation | 1.29 ± 0.03 f | 18.05 ± 0.19 a | 55.95 ± 0.79f | 37.39 ± 2.18 de | 101.51 ± 1.80 de | ||
| 04-05 | 0 ~ 20 | 对照 Control | 2.75 ± 0.02 b | 8.45 ± 0.26 g | 75.04 ± 0.22 c | 49.54 ± 1.90 b | 131.29 ± 1.83 b |
| 灌水 Irrigation | 2.58 ± 0.03 c | 11.71 ± 0.20 ef | 86.83 ± 0.73 a | 60.45 ± 1.95 a | 141.08 ± 1.84 a | ||
| 20 ~ 40 | 对照 Control | 1.44 ± 0.03 e | 12.10 ± 0.10 ef | 65.57 ± 1.19 e | 32.71 ± 0.31 fg | 101.51 ± 1.82 e | |
| 灌水 Irrigation | 0.94 ± 0.03 g | 10.85 ± 0.27 f | 82.26 ± 1.87 b | 41.44 ± 1.56 cd | 105.19 ± 1.81 d | ||
| 40 ~ 60 | 对照 Control | 1.29 ± 0.03 f | 12.13 ± 0.53 ef | 64.89 ± 1.51 e | 32.40 ± 1.43 fg | 95.97 ± 1.80 ef | |
| 灌水 Irrigation | 0.87 ± 0.05 g | 11.16 ± 0.36 ef | 71.85 ± 1.31 d | 43.00 ± 1.36 c | 112.57 ± 3.20 c |
表3 封冻前灌水对土壤速效养分的影响
Table 3 Effects of irrigation before soil freezing on soil available nutrients
| 取样日期/ (M-D) Date of sample | 土层/cm Soil depth | 处理 Treatment | 土壤有机质/% Soil organic matter | NH4+-N / (mg · kg-1) | NO3--N / (mg · kg-1) | 有效磷/(mg · kg-1) Available P | 速效钾/(mg · kg-1) Available K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01-05 | 0 ~ 20 | 对照 Control | 3.08 ± 0.03 a | 13.64 ± 0.61 d | 49.48 ± 0.97 g | 31.78 ± 1.90 fg | 128.86 ± 2.15 b |
| 灌水 Irrigation | 2.70 ± 0.01 b | 12.36 ± 0.30 e | 65.35 ± 1.16 e | 33.96 ± 1.90 ef | 118.10 ± 1.81 c | ||
| 20 ~ 40 | 对照 Control | 3.06 ± 0.03 a | 15.05 ± 0.54 c | 49.98 ± 1.08 g | 33.96 ± 2.18 ef | 94.13 ± 1.84 f | |
| 灌水 Irrigation | 2.76 ± 0.02 b | 16.69 ± 0.26 b | 56.74 ± 0.23 f | 35.20 ± 0.54 ef | 116.26 ± 1.82 c | ||
| 40 ~ 60 | 对照 Control | 1.69 ± 0.03 d | 14.14 ± 0.84 cd | 51.18 ± 0.27 g | 27.72 ± 1.08 g | 95.97 ± 1.84 ef | |
| 灌水 Irrigation | 1.29 ± 0.03 f | 18.05 ± 0.19 a | 55.95 ± 0.79f | 37.39 ± 2.18 de | 101.51 ± 1.80 de | ||
| 04-05 | 0 ~ 20 | 对照 Control | 2.75 ± 0.02 b | 8.45 ± 0.26 g | 75.04 ± 0.22 c | 49.54 ± 1.90 b | 131.29 ± 1.83 b |
| 灌水 Irrigation | 2.58 ± 0.03 c | 11.71 ± 0.20 ef | 86.83 ± 0.73 a | 60.45 ± 1.95 a | 141.08 ± 1.84 a | ||
| 20 ~ 40 | 对照 Control | 1.44 ± 0.03 e | 12.10 ± 0.10 ef | 65.57 ± 1.19 e | 32.71 ± 0.31 fg | 101.51 ± 1.82 e | |
| 灌水 Irrigation | 0.94 ± 0.03 g | 10.85 ± 0.27 f | 82.26 ± 1.87 b | 41.44 ± 1.56 cd | 105.19 ± 1.81 d | ||
| 40 ~ 60 | 对照 Control | 1.29 ± 0.03 f | 12.13 ± 0.53 ef | 64.89 ± 1.51 e | 32.40 ± 1.43 fg | 95.97 ± 1.80 ef | |
| 灌水 Irrigation | 0.87 ± 0.05 g | 11.16 ± 0.36 ef | 71.85 ± 1.31 d | 43.00 ± 1.36 c | 112.57 ± 3.20 c |
| 取样日期/ (M-D) Date of sample | 土层/cm Soil depth | 处理 Treatment | 香农指数 Shannon | ACE | Chao1 | 覆盖指数 Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01-05 | 0 ~ 20 | 对照Control | 6.87 ± 0.01 c | 4022.35 ± 162.25 cd | 3962.09 ± 144.84 cd | 0.9783 |
| 灌水Irrigation | 6.98 ± 0.03 ab | 5044.61 ± 105.50 a | 4939.45 ± 111.26 a | 0.9697 | ||
| 20 ~ 40 | 对照Control | 6.73 ± 0.02 d | 3861.05 ± 140.15 cd | 3790.24 ± 123.66 cd | 0.9789 | |
| 灌水Irrigation | 7.01 ± 0.01 a | 4830.97 ± 103.70 a | 4760.91 ± 117.32 a | 0.9721 | ||
| 40 ~ 60 | 对照Control | 6.66 ± 0.01 de | 3920.75 ± 36.15 cd | 3886.33 ± 55.65 cd | 0.9779 | |
| 灌水Irrigation | 6.71 ± 0.06 de | 4291.09 ± 122.72 bc | 4194.42 ± 104.09 bc | 0.9748 | ||
| 04-05 | 0 ~ 20 | 对照Control | 6.84 ± 0.03 c | 4642.79 ± 80.98 ab | 4539.73 ± 62.66 ab | 0.9727 |
| 灌水Irrigation | 6.91 ± 0.00 bc | 4665.15 ± 102.21 ab | 4587.41 ± 91.75 ab | 0.9728 | ||
| 20 ~ 40 | 对照Control | 6.50 ± 0.02 f | 3784.16 ± 158.41 d | 3743.75 ± 133.20 d | 0.9789 | |
| 灌水Irrigation | 6.51 ± 0.03 f | 3960.74 ± 228.17 cd | 3879.69 ± 230.42 cd | 0.9775 | ||
| 40 ~ 60 | 对照Control | 6.45 ± 0.04 f | 3582.77 ± 69.64 d | 3552.87 ± 48.01 d | 0.9804 | |
| 灌水Irrigation | 6.63 ± 0.03 e | 3762.45 ± 210.85 d | 3739.95 ± 202.34 d | 0.9795 |
表4 封冻前灌水对根际土壤细菌Alpha多样性的影响
Table 4 Effect of irrigation before soil freezing on bacterial Alpha diversity in rhizosphere soil
| 取样日期/ (M-D) Date of sample | 土层/cm Soil depth | 处理 Treatment | 香农指数 Shannon | ACE | Chao1 | 覆盖指数 Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01-05 | 0 ~ 20 | 对照Control | 6.87 ± 0.01 c | 4022.35 ± 162.25 cd | 3962.09 ± 144.84 cd | 0.9783 |
| 灌水Irrigation | 6.98 ± 0.03 ab | 5044.61 ± 105.50 a | 4939.45 ± 111.26 a | 0.9697 | ||
| 20 ~ 40 | 对照Control | 6.73 ± 0.02 d | 3861.05 ± 140.15 cd | 3790.24 ± 123.66 cd | 0.9789 | |
| 灌水Irrigation | 7.01 ± 0.01 a | 4830.97 ± 103.70 a | 4760.91 ± 117.32 a | 0.9721 | ||
| 40 ~ 60 | 对照Control | 6.66 ± 0.01 de | 3920.75 ± 36.15 cd | 3886.33 ± 55.65 cd | 0.9779 | |
| 灌水Irrigation | 6.71 ± 0.06 de | 4291.09 ± 122.72 bc | 4194.42 ± 104.09 bc | 0.9748 | ||
| 04-05 | 0 ~ 20 | 对照Control | 6.84 ± 0.03 c | 4642.79 ± 80.98 ab | 4539.73 ± 62.66 ab | 0.9727 |
| 灌水Irrigation | 6.91 ± 0.00 bc | 4665.15 ± 102.21 ab | 4587.41 ± 91.75 ab | 0.9728 | ||
| 20 ~ 40 | 对照Control | 6.50 ± 0.02 f | 3784.16 ± 158.41 d | 3743.75 ± 133.20 d | 0.9789 | |
| 灌水Irrigation | 6.51 ± 0.03 f | 3960.74 ± 228.17 cd | 3879.69 ± 230.42 cd | 0.9775 | ||
| 40 ~ 60 | 对照Control | 6.45 ± 0.04 f | 3582.77 ± 69.64 d | 3552.87 ± 48.01 d | 0.9804 | |
| 灌水Irrigation | 6.63 ± 0.03 e | 3762.45 ± 210.85 d | 3739.95 ± 202.34 d | 0.9795 |

图1 封冻前灌水后根际土壤细菌群落组成分布图(A)和OTU水平Veen图(B) 20、40、60对应0 ~ 20、20 ~ 40、40 ~ 60 cm土层。下同。
Fig. 1 Rhizosphere soil bacterial community composition distribution diagram(A)and Venn diagram at OTU level(B) 20,40 and 60 correspond to soil layers of 0-20,20-40,and 40-60 cm. The same below.

图2 封冻前灌水处理后根际土壤细菌群落组成主坐标分析(A)和根际土壤细菌群落组成与根际土壤理化性质的冗余分析(B) SOM:土壤有机质;SRWC:土壤相对含水量;NH4+-N:铵态氮;NO3--N:硝态氮;AP:有效磷;AK:有效钾;O2:土壤氧气含量;pH:土壤pH;T:土壤温度。A中以样本间的距离大小反映样本群落的聚散程度。两样本点越接近,表明两样本物种组成越相似。B中从样品点向环境因子的箭头做投影,投影点到原点的距离代表环境因子对样本中细菌群落组成影响的大小。
Fig. 2 Principal component analysis of rhizosphere soil bacterial community after irrigation before freezing(A) and redundant analysis of rhizosphere soil bacterial community composition and physicochemical properties of rhizosphere soil(B) SOM:Soil organic matter;SRWC:Soil relative water content;NH4+-N:Ammonium nitrogen;NO3--N:Nitrate nitrogen;AP:Available phosphorus;AK:Available potassium;O2:Soil oxygen content;pH:Soil pH;T:Soil temperature. The distance between samples reflects the degree of clustering and dispersion of sample communities. The proximity of two sample points indicates a higher similarity in species composition(A). Projected from the sample point to the arrow of the environmental factors,the distance from the projection point to the origin represents the influence of environmental factors on the composition of the bacterial community in the sample(B).
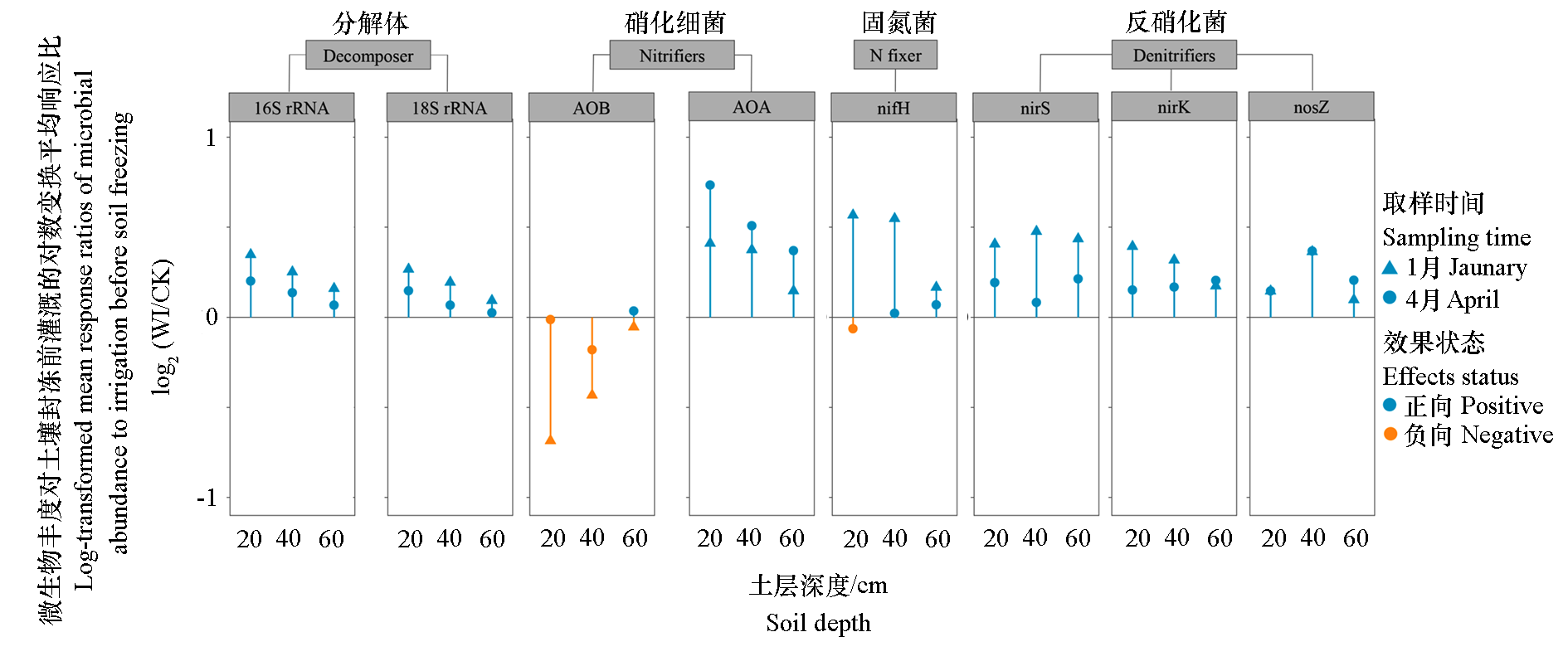
图4 封冻前灌水对根际土壤细菌(16S rRNA)、真菌(18S rRNA)和氮功能菌(AOB、AOA、nifH、nirS、nirK、nosZ)丰度的影响 CK:对照;WI:封冻前灌水;AOB:氨氧化细菌;AOA:氨氧化古菌;nifH:固氮菌;nirS、nirK、nosZ:反硝化菌。
Fig. 4 Effects of irrigation before soil freezing on abundance of bacteria(16S rRNA),fungi(18S rRNA)and N-cycling microbes(AOB,AOA,nifH,nirS,nirK,nosZ)in rhizosphere soil CK:Control;WI:Irrigation before soil freezing;AOB:Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria;AOA:Ammonia-oxidizing archaea;nifH:Nitrogen-fixing bacteria;nirS,nirK,nosZ:Denitrificans.
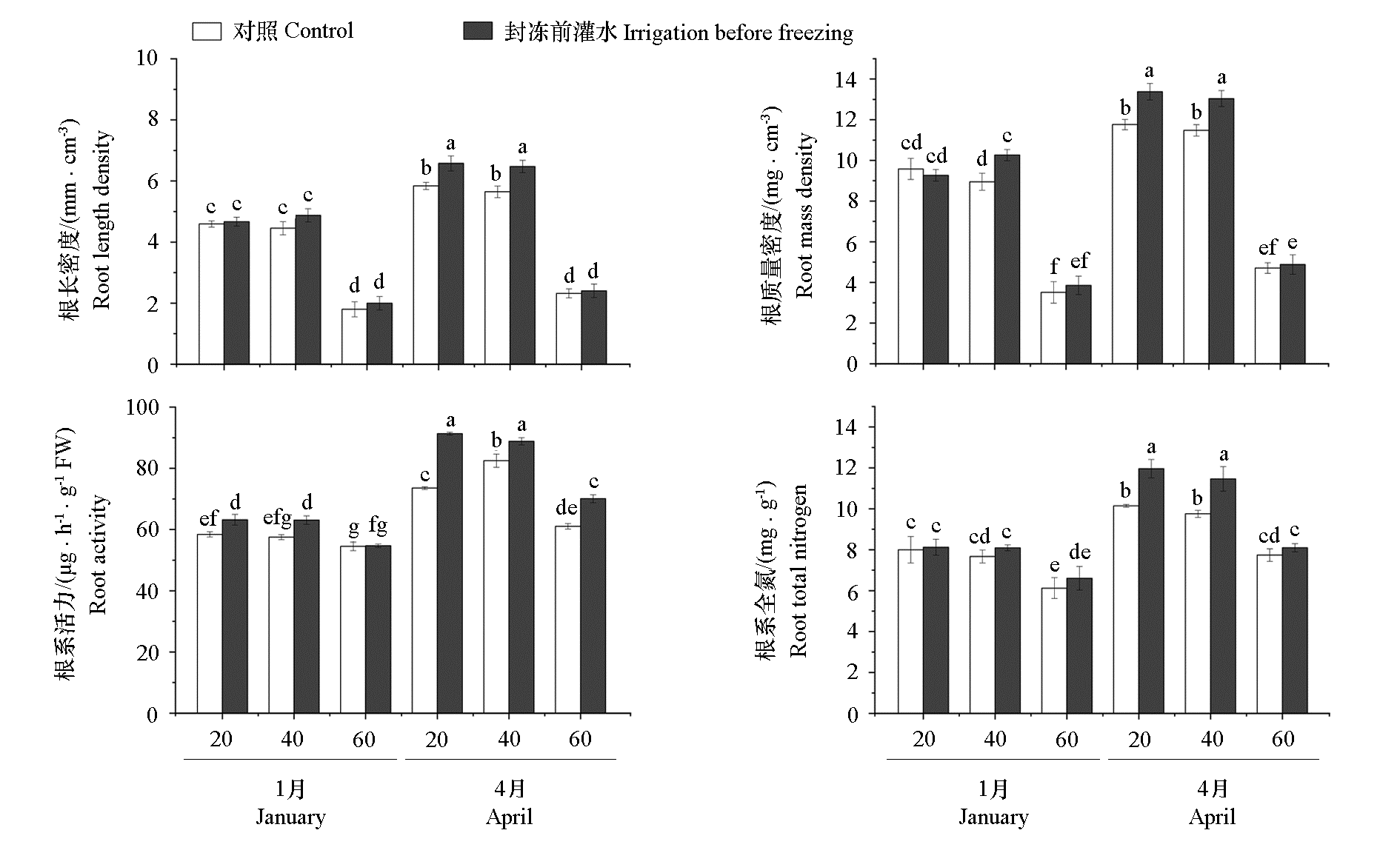
图5 封冻前灌水对0 ~ 20、20 ~ 40、40 ~ 60 cm土层苹果根系特征与根系氮含量的影响
Fig. 5 Effect of irrigation before freezing on root characteristics and root total nitrogen content of apple plants in 0-20,20-40,and 40-60 cm soil layers
| [1] |
|
|
白健, 李娜, 付春霞, 张志远, 王衍安, 束怀瑞. 2016. 苹果根域调控对土壤理化性质和根系生长的影响. 园艺学报, 43 (5):829-840.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2016-0098 |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
|
丁怡飞, 曹永庆, 姚小华, 吴鹏飞, 龚洪恩, 傅松玲, 张平安. 2018. 油茶—鼠茅草复合系统细根空间分布及地下竞争. 生态学杂志, 37 (4):981-986.
|
|
| [5] |
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2007.08.012 pmid: 17822944 |
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
|
郭钰, 姚佳峰, 董媛, 闫珏, 杨南, 冯泳翰, 魏曦, 梁文俊. 2023. 油松和刺槐纯林及混交林根系分布特征. 应用生态学报, 34 (11):2881-2888.
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202311.008 |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
|
贺纪正, 张丽梅. 2013. 土壤氮素转化的关键微生物过程及机制. 微生物学通报, 40 (1):98-108.
|
|
| [14] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2008.01786.x pmid: 18973618 |
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
|
李子忠, 王皓. 2010. 冬灌对农牧交错带人工草地越冬期土壤水热状况的影响. 干旱地区农业研究, 28 (4):7-13.
|
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
|
鲁如坤. 2000. 土壤农业化学分析方法. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社.
|
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
|
孙薇, 钱勋, 付青霞, 胡婷, 谷洁, 王小娟, 高华. 2013. 生物有机肥对秦巴山区核桃园土壤微生物群落和酶活性的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 19 (5):1224-1233.
|
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2014-1046 |
|
闫玉静, 白健, 付春霞, 范晓丹, 王衍安, 陈修德, 束怀瑞. 2015. 根域蓄水调控对苹果叶片光合特性和抗氧化酶活性的影响. 园艺学报, 42 (5):817-825.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2014-1046 |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
|
赵世杰, 史国安, 董新纯. 2002. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社.
|
|
| [34] |
|
| [1] | 邱辉, 朱德娟, 张永乐, 高玉洁, 李柳, 王国平, 洪霓. ACLSV外壳蛋白与梨两种E3泛素连接酶互作及亚细胞定位[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1715-1727. |
| [2] | 刘英浩, 李允, 吕伟静, 陈冉, 姜伟涛, 尹承苗, 毛志泉, 王艳芳. 不同温度烧制的生物炭对苹果连作土壤真菌群落结构的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1853-1867. |
| [3] | 李旭娇, 吕齐, 姚东东, 赵丰云, 王小非, 于坤. ‘烟富3’苹果不同砧木嫁接对其15N–尿素吸收利用的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1868-1880. |
| [4] | 田雯, 李子琛, 王霖, 王大江, 王昆, 孙思邈, 王广艺, 刘昭, 路翔, 冯建荣, 高源. 苹果重要性状全基因组关联分析研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1565-1579. |
| [5] | 刘成龙, 范旭东, 任芳, 张尊平, 胡国君, 董雅凤. 苹果病毒检测技术[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1580-1594. |
| [6] | 覃艮红, 袁洪波, 王卓妮, 史冰柯, 范洋洋, 王丽, 张猛, 涂洪涛, 徐超, 侯珲. 蜡样芽孢杆菌挥发物对苹果轮纹病菌的拮抗活性[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1403-1412. |
| [7] | 史冰柯, 王卓妮, 覃艮红, 黄天祥, 王丽, 涂洪涛, 袁洪波, 侯珲. 苹果轮纹病拮抗真菌Pa2的分离与鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1113-1125. |
| [8] | 高永臣, 苏新建, 余城, 刘铸, 毛柯, 邹养军, 龚小庆. 苹果树盘地布和药渣覆盖对土壤理化性质和细菌群落的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 587-600. |
| [9] | 林琭, 蔚露, 谢鹏, 李志强, 王红宁, 赵国平, 牛自勉. 矮化中间砧SC1对苹果光合特性及果实品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(12): 2871-2885. |
| [10] | 陈学森, 王楠, 彭福田, 毛志泉, 尹承苗, 姜远茂, 葛顺峰, 胡大刚, 李媛媛, 杜远鹏, 姚玉新, 张宗营. 中国重要落叶果树果实品质和熟期育种研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(1): 8-26. |
| [11] | 李少旋, 王芝云, 胡大刚, 朱 波, 韩明三, . 晚熟苹果新品种‘琴富 1 号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 1-2. |
| [12] | 孙燕霞, 唐 岩, 刘大亮, 赵玲玲, 张学勇, 刘学卿, Dorota Ewa Kruczynska, 程志娟, Sylwia Keller-Przybylkowicz, 宋来庆, . 早熟苹果新品种‘烟青玉’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 3-4. |
| [13] | 赵国栋, 贾林光, 陈东玫, 赵同生, 张新生, 张朝红, 李春敏, 付 友. 苹果新品种‘映红’ [J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 5-6. |
| [14] | 蔚 露, 牛自勉, 郭文龙, 林 琭, 李 全, 李志强, 王红宁, 李鸿雁 . 早熟苹果新品种‘夏露’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 7-8. |
| [15] | 孙志娟, 刘文杰, 郑晓东, 袭祥利, 马长青, 刘晓丽, 王彩虹, 田义轲. 褪黑素对盐碱胁迫下平邑甜茶幼苗生长的影响及其机制[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1697-1710. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司