
园艺学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (8): 1715-1727.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0967
• 遗传育种·种质资源·分子生物学 • 下一篇
邱辉1,2, 朱德娟2, 张永乐2, 高玉洁2, 李柳2, 王国平1,2,*( ), 洪霓2,*(
), 洪霓2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-12-13
修回日期:2024-04-02
出版日期:2024-08-25
发布日期:2024-08-20
通讯作者:
基金资助:
QIU Hui1,2, ZHU Dejuan2, ZHANG Yongle2, GAO Yujie2, LI Liu2, WANG Guoping1,2,*( ), HONG Ni2,*(
), HONG Ni2,*( )
)
Received:2023-12-13
Revised:2024-04-02
Published:2024-08-25
Online:2024-08-20
摘要:
为深入了解苹果褪绿叶斑病毒(apple chlorotic leaf spot virus,ACLSV)与寄主植物的互作特性,构建了表达该病毒外壳蛋白(coat protein,CP)的诱饵载体pGBKT7-CP,采用酵母双杂交技术,从‘红香酥’梨cDNA文库中筛选出与ACLSV CP潜在互作的33种寄主因子。酵母双杂交和双分子荧光互补试验验证了CP与来自梨的两种RING型E3泛素连接酶(命名为MIEL和BOI)互作。亚细胞定位分析表明,CP与BOI具有相似的胞间连丝和细胞核分布特点,MIEL主要分布在内质网和细胞核。双分子荧光互补试验结果显示,CP与BOI互作不改变二者的亚细胞分布,而CP与MIEL互作信号分布与MIEL亚细胞定位相似。构建了这3种蛋白的截短突变体,发现含zf-CHY结构域(1 ~ 99 aa)的MIEL截短突变体可以与CP互作,而仅全长BOI可以与CP互作,CP截短突变体不能与这两种寄主蛋白互作。
邱辉, 朱德娟, 张永乐, 高玉洁, 李柳, 王国平, 洪霓. ACLSV外壳蛋白与梨两种E3泛素连接酶互作及亚细胞定位[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1715-1727.
QIU Hui, ZHU Dejuan, ZHANG Yongle, GAO Yujie, LI Liu, WANG Guoping, HONG Ni. Interaction Between the Coat Protein of Apple Chlorotic Leaf Spot Virus and Two E3 Ubiquitin Ligases of Pear and Their Subcellular Localization[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1715-1727.
| 分析方法 Assay | 基因 Gene | 引物(F/R,5′-3′) Primer |
|---|---|---|
| 酵母双杂交 | CP | GGAATTC CATATGATGGCAGCAGTTCTGAATCT/CCG GAATTCGATGCAAAGATCAGT |
| Y2H | MIEL | GGAATTC CATATGATGGAAGGCTCAGCCAATGAA/CCG GAATTCTTGAGGAAGAACCGGAGGGGC |
| BOI | GGAATTC CATATGATGGCTCTTCCCCGGCACCAT/CCG GAATTCCACATATACCTCCATGCCGAT | |
| 亚细胞定位 | CP | CTAG TCTAGAATGGCAGCAGTTCTGAATCT/ACGC GTCGACGATGCAAAGATCAGTTGAGAC |
| Localization | MIEL | CTAG TCTAGAATGGAAGGCTCAGCCAATGAA/ACGC GTCGACTTGAGGAAGAACCGGAGGGGC |
| BOI | CTAG TCTAGAATGGCTCTTCCCCGGCACCAT/ACGC GTCGACCACATATACCTCCATGCCGAT |
表1 用于基因克隆和载体构建的引物
Table 1 Primers used for gene cloning and vector construction
| 分析方法 Assay | 基因 Gene | 引物(F/R,5′-3′) Primer |
|---|---|---|
| 酵母双杂交 | CP | GGAATTC CATATGATGGCAGCAGTTCTGAATCT/CCG GAATTCGATGCAAAGATCAGT |
| Y2H | MIEL | GGAATTC CATATGATGGAAGGCTCAGCCAATGAA/CCG GAATTCTTGAGGAAGAACCGGAGGGGC |
| BOI | GGAATTC CATATGATGGCTCTTCCCCGGCACCAT/CCG GAATTCCACATATACCTCCATGCCGAT | |
| 亚细胞定位 | CP | CTAG TCTAGAATGGCAGCAGTTCTGAATCT/ACGC GTCGACGATGCAAAGATCAGTTGAGAC |
| Localization | MIEL | CTAG TCTAGAATGGAAGGCTCAGCCAATGAA/ACGC GTCGACTTGAGGAAGAACCGGAGGGGC |
| BOI | CTAG TCTAGAATGGCTCTTCCCCGGCACCAT/ACGC GTCGACCACATATACCTCCATGCCGAT |
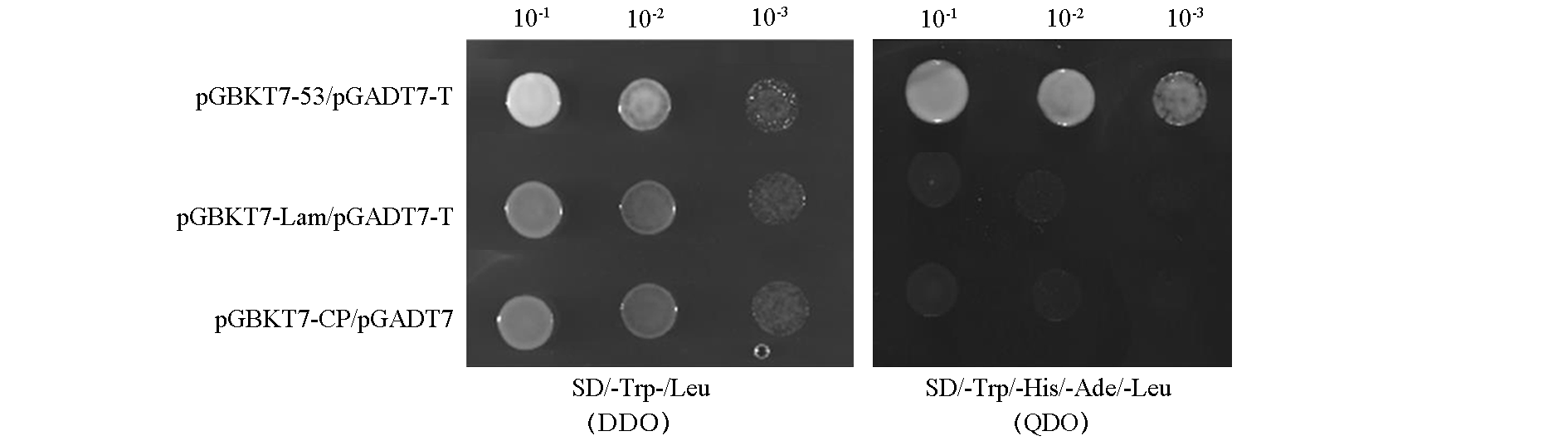
图1 诱饵载体pGBKT7-CP的毒性和自激活活性分析 DDO:二缺培养基;QDO:四缺培养基。
Fig. 1 Validation of toxicity and self-activation of bait vector pGBKT7-CP DDO:Double dropout;QDO:Quadruple dropout.
| 候选梨蛋白 Candidate protein | 登录号 Accession No. | 一致性/% Identity | 克隆数 Clone No. | 大小/bp Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BOI相关泛素蛋白连接酶2 Probable BOI-related E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase 2 | XM_009361505.2 | 93.00 | 18 | 1 026 |
| ATP依赖的Clp蛋白酶蛋白水解亚基6,叶绿体 ATP-dependent Clp protease proteolytic subunit 6,chloroplastic-like | XM_009351165.2 | 98.58 | 10 | 855 |
| 果糖二磷酸醛缩酶1,胞质型 Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase 1,cytoplasmic-like | XM_009354717.2 | 98.08 | 5 | 1 077 |
| 核酮糖二磷酸羧化酶/加氧酶激活酶,叶绿体Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activase,chloroplastic-like | XM_009345517.2 | 99.55 | 4 | 1 617 |
| E3泛素蛋白连接酶MIEL1 E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase MIEL1 | XM_018650219.1 | 98.93 | 4 | 804 |
| 假定E3泛素-蛋白连接酶UBR7 Putative E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase UBR7 | XM_009360328.2 | 93.90 | 1 | 1 239 |
| 核酮糖二磷酸羧化酶/加氧酶激活酶,叶绿体 Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activase,chloroplastic-like | XM_009366078.2 | 99.89 | 4 | 1 419 |
| 天冬氨酸蛋白酶A1-like Aspartic proteinase A1-like | XM_009355023.1 | 94.50 | 4 | 1 533 |
| 类甜蛋白1a Thaumatin-like protein 1a | XM_009345430.2 | 98.29 | 2 | 747 |
| LHCⅡ1型叶绿素ab结合蛋白 Chlorophyll a-b binding protein of LHCⅡ type 1 | XM_018648424.1 | 96.50 | 1 | 795 |
| 叶绿素ab结合蛋白CP29.1 Chlorophyll a-b binding protein CP29.1 | XM_009379505.2 | 91.96 | 1 | 861 |
| 克隆1118ab结合蛋白mRNA Clone 1118 a-b binding protein mRNA | KJ008964.1 | 98.41 | 1 | 816 |
| 半胱氨酸蛋白酶ATG4-like Cysteine protease ATG4-like | XM_009356387.2 | 97.54 | 1 | 1 464 |
| 半胱氨酸合成酶 Cysteine synthase | XM_009366277.2 | 92.62 | 1 | 978 |
| F-box/kelch-repeat蛋白At1g67480 F-box/kelch-repeat protein At1g67480 | XM_009374031.2 | 98.47 | 1 | 1 185 |
| LEC14B同源物 LEC14B homolog | XM_009353905.2 | 97.34 | 1 | 1 425 |
| 金属烟酰胺转运蛋白YSL2 Metal-nicotianamine transporter YSL2 | XM_018648503.1 | 97.22 | 1 | 1 998 |
| 甲基酯酶10 Methylesterase 10 | XM_009368119.2 | 99.89 | 1 | 825 |
| 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶13 Mitogen-activated protein kinase 13 | XM_009356240.2 | 98.04 | 1 | 1 104 |
| 磷脂酰肌醇4-激酶γ7 Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase gamma 7 | XM_009357275.2 | 97.77 | 1 | 1 926 |
| 可能无活性的紫色酸性磷酸酶27 Probable inactive purple acid phosphatase 27 | XM_009370253.2 | 98.40 | 1 | 1 923 |
| 锌指转录因子STOP1 Protein SENSITIVE TO PROTON RHIZOTOXICITY 1-like | XM_018645092.1 | 99.55 | 1 | 972 |
| 假定tRNA(胞苷(32)/鸟苷(34)-2′-O)-甲基转移酶 Putative tRNA (cytidine(32)/guanosine(34)-2′-O)-methyltransferase | XM_009371927.2 | 99.25 | 1 | 951 |
| 醌氧化还原酶PIG3 Quinone oxidoreductase PIG3 | XM_009379085.2 | 97.44 | 1 | 978 |
| 40S核糖体蛋白S3-3 40S ribosomal protein S3-3 | XM_009364296.2 | 98.99 | 1 | 717 |
| 60S核糖体蛋白L7-2样 60S ribosomal protein L7-2-like | XM_009347721.2 | 99.14 | 1 | 732 |
| 富含丝氨酸/精氨酸的剪接因子RS31 Serine/arginine-rich splicing factor RS31 | XM_009377158.2 | 97.58 | 1 | 777 |
| 茎特异性蛋白TSJT1 Stem-specific protein TSJT1 | XM_009365918.2 | 87.93 | 1 | 711 |
| 通用应激蛋白PHOS32-like Universal stress protein PHOS32-like | XM_009343181.2 | 99.34 | 1 | 693 |
| 尿卟啉原-ⅢC-甲基化转移酶 Uroporphyrinogen-III C-methyltransferase-like | XM_009356405.2 | 99.16 | 1 | 1 140 |
| 未知蛋白LOC103938811 Uncharacterized LOC103938811 | XM_009348858.2 | 95.47 | 1 | 489 |
| 未知蛋白LOC103952636 Uncharacterized LOC103952636 | XM_009364273.2 | 97.54 | 1 | 1 170 |
| 未知蛋白LOC103958759 Uncharacterized LOC103958759 | XM_009371077.2 | 97.74 | 1 | 606 |
表2 酵母双杂交鉴定出与 ACLSV CP 互作的候选梨蛋白
Table 2 ACLSV CP interacting proteins identified in the cDNA library of pear by yeast two hybridization
| 候选梨蛋白 Candidate protein | 登录号 Accession No. | 一致性/% Identity | 克隆数 Clone No. | 大小/bp Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BOI相关泛素蛋白连接酶2 Probable BOI-related E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase 2 | XM_009361505.2 | 93.00 | 18 | 1 026 |
| ATP依赖的Clp蛋白酶蛋白水解亚基6,叶绿体 ATP-dependent Clp protease proteolytic subunit 6,chloroplastic-like | XM_009351165.2 | 98.58 | 10 | 855 |
| 果糖二磷酸醛缩酶1,胞质型 Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase 1,cytoplasmic-like | XM_009354717.2 | 98.08 | 5 | 1 077 |
| 核酮糖二磷酸羧化酶/加氧酶激活酶,叶绿体Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activase,chloroplastic-like | XM_009345517.2 | 99.55 | 4 | 1 617 |
| E3泛素蛋白连接酶MIEL1 E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase MIEL1 | XM_018650219.1 | 98.93 | 4 | 804 |
| 假定E3泛素-蛋白连接酶UBR7 Putative E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase UBR7 | XM_009360328.2 | 93.90 | 1 | 1 239 |
| 核酮糖二磷酸羧化酶/加氧酶激活酶,叶绿体 Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activase,chloroplastic-like | XM_009366078.2 | 99.89 | 4 | 1 419 |
| 天冬氨酸蛋白酶A1-like Aspartic proteinase A1-like | XM_009355023.1 | 94.50 | 4 | 1 533 |
| 类甜蛋白1a Thaumatin-like protein 1a | XM_009345430.2 | 98.29 | 2 | 747 |
| LHCⅡ1型叶绿素ab结合蛋白 Chlorophyll a-b binding protein of LHCⅡ type 1 | XM_018648424.1 | 96.50 | 1 | 795 |
| 叶绿素ab结合蛋白CP29.1 Chlorophyll a-b binding protein CP29.1 | XM_009379505.2 | 91.96 | 1 | 861 |
| 克隆1118ab结合蛋白mRNA Clone 1118 a-b binding protein mRNA | KJ008964.1 | 98.41 | 1 | 816 |
| 半胱氨酸蛋白酶ATG4-like Cysteine protease ATG4-like | XM_009356387.2 | 97.54 | 1 | 1 464 |
| 半胱氨酸合成酶 Cysteine synthase | XM_009366277.2 | 92.62 | 1 | 978 |
| F-box/kelch-repeat蛋白At1g67480 F-box/kelch-repeat protein At1g67480 | XM_009374031.2 | 98.47 | 1 | 1 185 |
| LEC14B同源物 LEC14B homolog | XM_009353905.2 | 97.34 | 1 | 1 425 |
| 金属烟酰胺转运蛋白YSL2 Metal-nicotianamine transporter YSL2 | XM_018648503.1 | 97.22 | 1 | 1 998 |
| 甲基酯酶10 Methylesterase 10 | XM_009368119.2 | 99.89 | 1 | 825 |
| 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶13 Mitogen-activated protein kinase 13 | XM_009356240.2 | 98.04 | 1 | 1 104 |
| 磷脂酰肌醇4-激酶γ7 Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase gamma 7 | XM_009357275.2 | 97.77 | 1 | 1 926 |
| 可能无活性的紫色酸性磷酸酶27 Probable inactive purple acid phosphatase 27 | XM_009370253.2 | 98.40 | 1 | 1 923 |
| 锌指转录因子STOP1 Protein SENSITIVE TO PROTON RHIZOTOXICITY 1-like | XM_018645092.1 | 99.55 | 1 | 972 |
| 假定tRNA(胞苷(32)/鸟苷(34)-2′-O)-甲基转移酶 Putative tRNA (cytidine(32)/guanosine(34)-2′-O)-methyltransferase | XM_009371927.2 | 99.25 | 1 | 951 |
| 醌氧化还原酶PIG3 Quinone oxidoreductase PIG3 | XM_009379085.2 | 97.44 | 1 | 978 |
| 40S核糖体蛋白S3-3 40S ribosomal protein S3-3 | XM_009364296.2 | 98.99 | 1 | 717 |
| 60S核糖体蛋白L7-2样 60S ribosomal protein L7-2-like | XM_009347721.2 | 99.14 | 1 | 732 |
| 富含丝氨酸/精氨酸的剪接因子RS31 Serine/arginine-rich splicing factor RS31 | XM_009377158.2 | 97.58 | 1 | 777 |
| 茎特异性蛋白TSJT1 Stem-specific protein TSJT1 | XM_009365918.2 | 87.93 | 1 | 711 |
| 通用应激蛋白PHOS32-like Universal stress protein PHOS32-like | XM_009343181.2 | 99.34 | 1 | 693 |
| 尿卟啉原-ⅢC-甲基化转移酶 Uroporphyrinogen-III C-methyltransferase-like | XM_009356405.2 | 99.16 | 1 | 1 140 |
| 未知蛋白LOC103938811 Uncharacterized LOC103938811 | XM_009348858.2 | 95.47 | 1 | 489 |
| 未知蛋白LOC103952636 Uncharacterized LOC103952636 | XM_009364273.2 | 97.54 | 1 | 1 170 |
| 未知蛋白LOC103958759 Uncharacterized LOC103958759 | XM_009371077.2 | 97.74 | 1 | 606 |
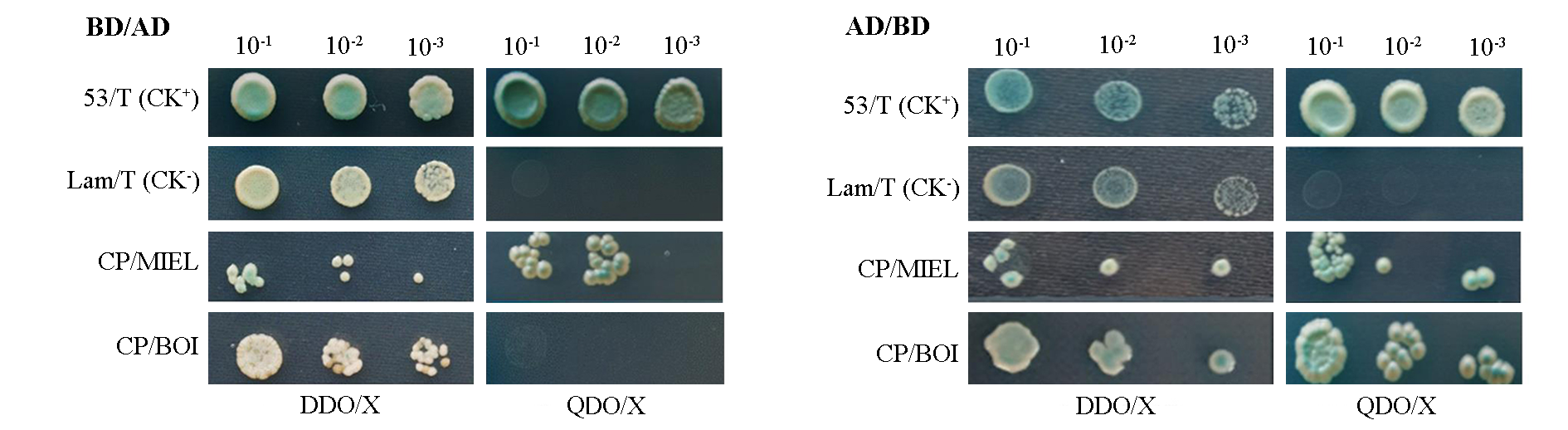
图2 酵母双杂交分析ACLSV CP与两种候选梨蛋白MIEL和BOI的相互作用 CK+:阳性对照;CK-:阴性对照。DDO/X:SD/-Trp/-Leu/X-α-Gal;QDO/X:SD/-Leu/-Trp/-His/-Ade/X-α-Gal。
Fig. 2 Yeast two hybridization assays for the interactions between ACLSV CP and each of two candidate pear proteins MIEL and BOI CK+:Positive control;CK-:Negative control. DDO/X:SD/-Trp/-Leu/X-α-Gal;QDO/X:SD/-Leu/-Trp/-His/-Ade/X-α-Gal.
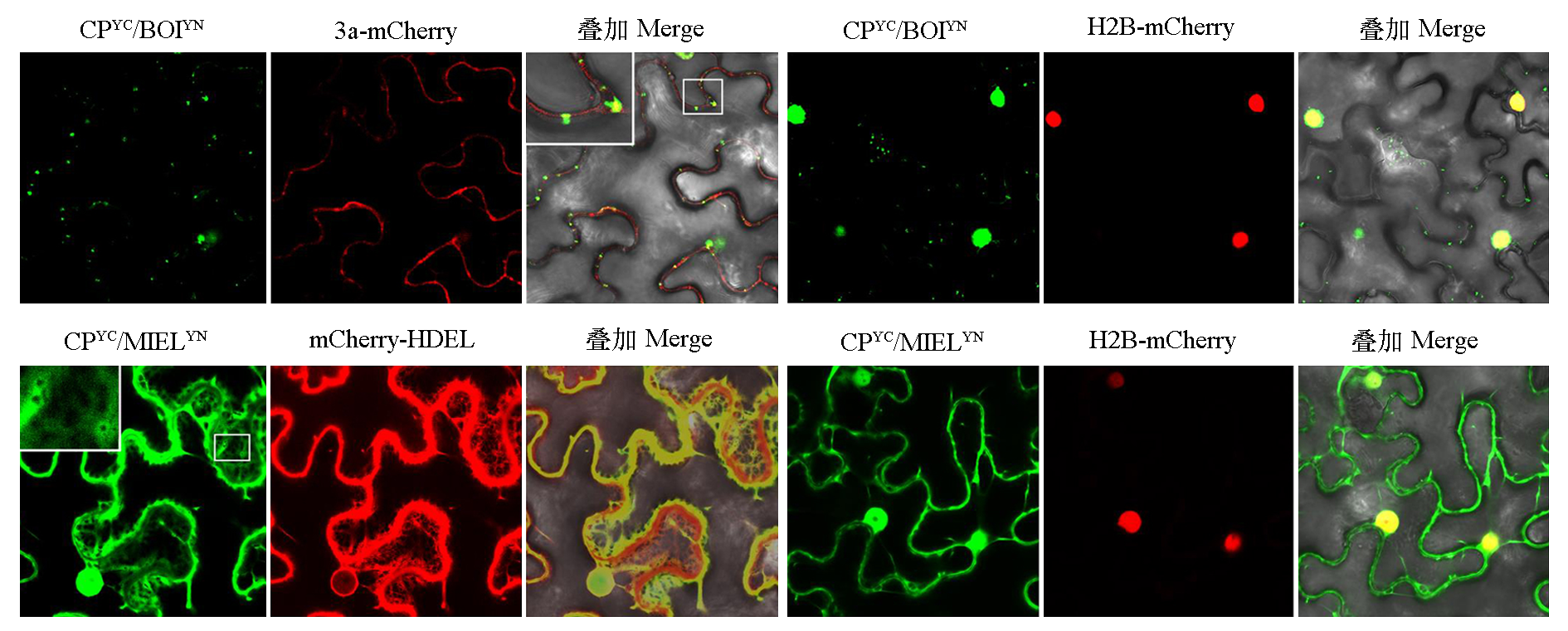
图3 双分子荧光互补试验检测ACLSV CP与BOI和MIEL在烟草表皮细胞中互作 3a-mCherry、mCherry-HDEL和H2B-mCherry分别用作胞间连丝、内质网和细胞核标记。
Fig. 3 Interactions of ACLSV CP with BOI and MIEL detected by bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC)assay in Nicotiana benthamiana epidermal cells The co-expressed 3a-mCherry,mCherry-HDEL and H2B-mCherry were used as plasmodesma,endoplasmic reticulum and nuclear markers,respectively.

图5 酵母双杂交分析ACLSV CP与两个梨蛋白BOI和MIEL的缺失突变体的互作 CK+:阳性对照;CK-:阴性对照。DDO/X:SD/-Trp/-Leu/X-α-Gal;QDO/X:SD/-Leu/-Trp/-His/-Ade/X-α-Gal.
Fig. 5 Yeast two hybridization analysis for the interactions of ACLSV CP with deletion mutants of two pear proteins BOI and MIEL CK+:Positive control;CK-:Negative control。DDO/X:SD/-Trp/-Leu/X-α-Gal;QDO/X:SD/-Leu/-Trp/-His/-Ade/X-α-Gal.

图6 ACLSV CP及寄主因子MIEL和BOI在本氏烟叶片表皮细胞中的分布特点 3a-mCherry、mCherry-HDEL和H2B-mCherry分别用作胞间连丝、内质网和细胞核标记。
Fig. 6 Subcellular distribution of ACLSV CP and host factors MIEL and BOI in Nicotiana benthamiana leaf epidermal cells The co-expressed 3a-mCherry,mCherry-HDEL and H2B-mCherry were used as plasmodesma,endoplasmic reticulum and nuclear markers,respectively.
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
pmid: 2219716 |
| [8] |
pmid: 9170508 |
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2014.24.005 |
|
何乙坤, 钟敏, 胡同乐, 王树桐, 段豪, 丁丽, 王亚南, 曹克强. 2014. 利用酵母双杂交筛选与苹果褪绿叶斑病毒CP互作的寄主因子. 中国农业科学, 47 (24):4821-4829.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2014.24.005 |
|
| [11] |
pmid: 26164936 |
|
何乙坤, 钟敏, 张瑜, 王亚南, 曹克强. 2015. 利用酵母双杂交筛选与苹果褪绿叶斑病毒 MP 互作的寄主因子. 病毒学报, 31 (2):124-131.
pmid: 26164936 |
|
| [12] |
Heden van Noort G J,
|
| [13] |
doi: 10.1128/JVI.00833-16 pmid: 27334588 |
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
|
李柳. 2023. 苹果茎痘病毒CP和TGB蛋白在该病毒运动和致病中的功能解析[博士论文]. 武汉: 华中农业大学.
|
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
doi: 10.1007/s00705-008-0076-z pmid: 18392552 |
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2015.08.005 pmid: 26298008 |
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
|
宋艳苏. 2011. 两种梨病毒CP基因原核表达及苹果褪绿叶斑病毒分子变异与其血清学多样性的关系[博士论文]. 武汉: 华中农业大学.
|
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2004.02.005 pmid: 15196553 |
| [37] |
doi: 10.1083/jcb.201304003 pmid: 23798728 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2010.04.002 pmid: 20471305 |
| [39] |
|
|
王亦栖, 颜爽爽, 余炳伟, 甘雨薇, 邱正坤, 朱张生, 陈长明, 曹必好. 2023. 茄子青枯病抗性相关的E3泛素连接酶基因的筛选及鉴定. 园艺学报, 50 (10):2271-2287.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0835 |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [1] | 吴 丹, 柳佳欣, 卓林熙, 李 钰, 罗 英, 周 勇, 杨有新, 余 婷, . CaWRKY39在辣椒响应疫霉菌侵染中的功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(10): 2297-2310. |
| [2] | 关夏玉, 陈细红, 郭菁, 吕浩阳, 梁晨媛, 高芳銮. 建兰花叶病毒的遗传变异及其寄主适应性[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(1): 203-212. |
| [3] | 李宇腾, 陈瑶, 任恒泽, 李聪聪, 王浩乾, 曹红利, 岳川, 郝心愿, 王新超. 茶树CsIDM的鉴定、表达分析及互作验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1679-1696. |
| [4] | 肖翔, 周储江, 金舒婉, 施丽愉, 杨震峰, 曹士锋, 陈伟. PpMADS2与PpMADS3协同调控黄肉桃果实类胡萝卜素积累机制的研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(6): 1173-1186. |
| [5] | 俞沁含, 李俊铎, 崔莹, 王佳慧, 郑巧玲, 徐伟荣. 山葡萄转录因子VaMYB4a互作蛋白的筛选与鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(3): 508-522. |
| [6] | 倪知游, 许林林, 杜建科, 王静, 汪涛, 潘娇艳, 赵密珍, 乔玉山. 绿色草莓S-RNase的体外表达及其互作蛋白FviFPA鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(12): 2577-2590. |
| [7] | 王敏, 杨松光, 刘微, 何晓明, 史绍琪, 刘文睿, 陈林, 江彪, 彭庆务. 节瓜CqCHP1的低温响应分析及互作蛋白的筛选与验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(11): 2376-2386. |
| [8] | 丁磊, 孙平平, 张磊, 李正男. 利用Y2H筛选西方烟中与苹果茎痘病毒CP互作的蛋白[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(11): 2509-2515. |
| [9] | 王亦栖, 颜爽爽, 余炳伟, 甘雨薇, 邱正坤, 朱张生, 陈长明, 曹必好. 茄子青枯病抗性相关的E3泛素连接酶基因的筛选及鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(10): 2271-2287. |
| [10] | 王沙, 张心慧, 赵玉洁, 李变变, 招雪晴, 沈雨, 董建梅, 苑兆和. 石榴花青苷合成相关基因PgMYB111的克隆与功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(9): 1883-1894. |
| [11] | 高玮林, 张力曼, 薛超玲, 张垚, 刘孟军, 赵锦. 枣E类MADS基因在花和果中的表达及其蛋白互作研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(4): 739-748. |
| [12] | 相立, 赵蕾, 王玫, 吕毅, 王艳芳, 沈向, 陈学森, 尹承苗, 毛志泉. 苹果MdWRKY74的克隆和功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(3): 482-492. |
| [13] | 陈健鑫, 魏玉倩, 唐婕, 竺永金, 马焕成, 伍建榕. 云南大理栽培春兰中ORSV和CymMV的分子检测及序列分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(3): 655-662. |
| [14] | 宋放, 李子璇, 王策, 王志静, 何利刚, 蒋迎春, 吴黎明, 白福玺. 柑橘菌根信号受体蛋白基因LYK2的克隆及功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(2): 281-292. |
| [15] | 谢思艺, 周承哲, 朱晨, 詹冬梅, 陈兰, 吴祖春, 赖钟雄, 郭玉琼. 茶树CsTIFY家族全基因组鉴定及非生物胁迫和激素处理中主要基因表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(1): 100-116. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司