
园艺学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 67-76.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0047
田茂森1,2,*, 周震2,*, 王海敬2, 崔霞2,**( ), 孙帅2,**(
), 孙帅2,**( )
)
收稿日期:2023-03-28
修回日期:2023-07-24
出版日期:2024-01-25
发布日期:2024-01-16
通讯作者:
作者简介:基金资助:
TIAN Maosen1,2, ZHOU Zhen2, WANG Haijing2, CUI Xia2,**( ), SUN Shuai2,**(
), SUN Shuai2,**( )
)
Received:2023-03-28
Revised:2023-07-24
Published:2024-01-25
Online:2024-01-16
摘要:
为了挖掘调控番茄果实柠檬酸含量的关键基因,以栽培番茄(Solanum lycopersicum ‘Moneymaker’)和野生醋栗番茄(Solanum pimpinellifolium‘PI365967’)为亲本构建的重组自交系群体为材料,利用混池重测序技术挖掘到6个控制柠檬酸含量的QTL。其中位于6号染色体末端的主效QTL qCA6.1表型贡献率高达19.28%。为对该位点进行定位,从重组自交系群体中挑选出2份柠檬酸含量差异较大,且只在主效位点存在基因型差异的株系作为亲本,构建BC2F2定位群体,通过交换单株后代鉴定,将定位区间缩小到342 kb区间内,并开发了连锁分子标记,为后续克隆基因奠定了基础,也为改良番茄果实柠檬酸含量提供了重要选择标记。
田茂森, 周震, 王海敬, 崔霞, 孙帅. 调控番茄果实柠檬酸含量的基因定位[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(1): 67-76.
TIAN Maosen, ZHOU Zhen, WANG Haijing, CUI Xia, SUN Shuai. Mapping of Gene Regulating Citric Acid Content in Tomato Fruit[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(1): 67-76.
| 标记名称 | 正向引物(5′-3′) | 反向引物(5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Primer name | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
| M1 | AAGCCATGCTACCATTGCTAGCT | AACCCATGCTTCAATGGTGAG |
| M2 | TCTTGGTTACCGAGAGTTATAGCTTCTACG | ACTCGATCAACTGTGCTACATTAGATG |
| M3 | ACCTGTCCAGAAAAACTGAAC | TCTGTTACTTGAGCTGAGC |
| M4 | TTCTTCTCTCGTTCTCCTCC | TCGAGATCATCAATTTCCAAGGTCATTGGTG |
| M5 | TGTGTAAGCTTGGTCGATG | ACTTAACGTGCTCGATGAAG |
| M6 | TGCTTGAAGTCTCCTGATCATCC | TCCAACTATTGCCCATGATTTCCTG |
| M7 | TTCTTCTCTCGTTCTCCTCC | TCGAGATCATCAATTTCCAAGGTCATTGGTG |
表1 主要标记的序列信息
Table 1 Primer sequences of major markers
| 标记名称 | 正向引物(5′-3′) | 反向引物(5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Primer name | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
| M1 | AAGCCATGCTACCATTGCTAGCT | AACCCATGCTTCAATGGTGAG |
| M2 | TCTTGGTTACCGAGAGTTATAGCTTCTACG | ACTCGATCAACTGTGCTACATTAGATG |
| M3 | ACCTGTCCAGAAAAACTGAAC | TCTGTTACTTGAGCTGAGC |
| M4 | TTCTTCTCTCGTTCTCCTCC | TCGAGATCATCAATTTCCAAGGTCATTGGTG |
| M5 | TGTGTAAGCTTGGTCGATG | ACTTAACGTGCTCGATGAAG |
| M6 | TGCTTGAAGTCTCCTGATCATCC | TCCAACTATTGCCCATGATTTCCTG |
| M7 | TTCTTCTCTCGTTCTCCTCC | TCGAGATCATCAATTTCCAAGGTCATTGGTG |
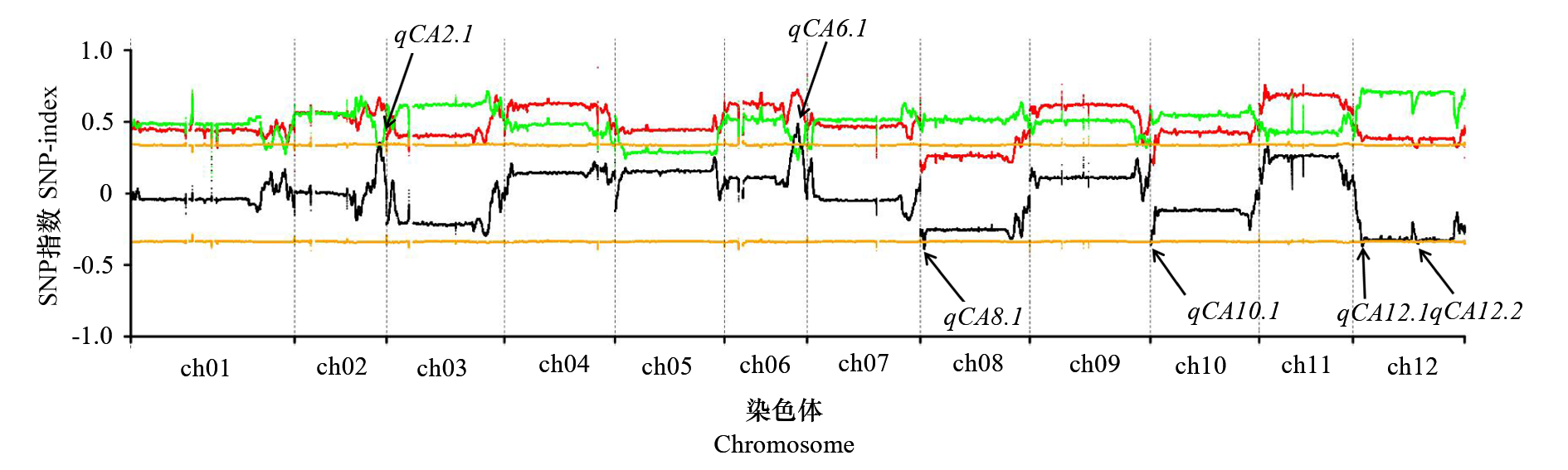
图3 BSA混池测序结果 黑色线条表示Δ(SNP-index)值,红色线条表示高酸池SNP-index值,绿色线条表示低酸池SNP-index值,橘色线条表示95%置信区间,箭头指示可能含有果实柠檬酸含量QTL的区域。
Fig. 3 BSA sequencing results Black line representation Δ(SNP-index) value,red line indicate high acid pool SNP-index values,green line indicate high acid pool SNP-index values,orange line represents the 95% confidence interval. Arrows indicate the regions that may contain QTL for fruit citric acid content.
| 位点 | 分子标记 | 染色体 | 物理位置/kb | 表型变异贡献率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QTL | Molecular marker | Chromosome | Postion on SL2.50 | PVE |
| qCA2.1 | M8 | 2 | 51 038 ~ 51 377 | 6.11 |
| qCA6.1 | M9 | 6 | 41 515 ~ 45 404 | 19.28 |
| qCA8.1 | M10 | 8 | 2 079 ~ 2 746 | 1.51 |
| qCA10.1 | M11 | 10 | 199 ~ 499 | 2.08 |
| qCA12.1 | M12 | 12 | 5 236 ~ 6 213 | 1.70 |
| qCA12.2 | M13 | 12 | 38 976 ~ 39 425 | 2.44 |
表2 BSA测序得到的QTL位点
Table 2 QTL loci obtained from BSA sequencing
| 位点 | 分子标记 | 染色体 | 物理位置/kb | 表型变异贡献率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QTL | Molecular marker | Chromosome | Postion on SL2.50 | PVE |
| qCA2.1 | M8 | 2 | 51 038 ~ 51 377 | 6.11 |
| qCA6.1 | M9 | 6 | 41 515 ~ 45 404 | 19.28 |
| qCA8.1 | M10 | 8 | 2 079 ~ 2 746 | 1.51 |
| qCA10.1 | M11 | 10 | 199 ~ 499 | 2.08 |
| qCA12.1 | M12 | 12 | 5 236 ~ 6 213 | 1.70 |
| qCA12.2 | M13 | 12 | 38 976 ~ 39 425 | 2.44 |

图4 亲本SL204与SL209果实外观(A)、果实质量(B)、柠檬酸含量(C)及近等基因系群体构建(D)
Fig. 4 Fruit images (A),Fruit weight (B),citric acid content (C) between parents SL204 and SL209 and construction of NILs (D) ** P < 0.01.
| 单株编号 Plant number | 分子标记Molecular marker | 柠檬酸含量/(mg · g-1 FW) Citric acid content | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | M5 | M6 | ||
| 21N16-204 | M | M | M | M | M | M | 9.03 ± 1.26 |
| 21N16-209 | P | P | P | P | P | P | 18.55 ± 1.69 |
| 21N16-3 | M | P | P | P | P | P | 16.36 ± 1.80 |
| 21N16-14 | M | M | M | M | P | P | 8.68 ± 1.65 |
| 21N16-17 | M | M | M | M | P | P | 10.51 ± 0.28 |
| 21N16-2 | P | P | M | M | M | M | 8.77 ± 0.87 |
表3 qCA6.1位点关键单株鉴定
Table 3 Key progeny plant test of qCA6.1
| 单株编号 Plant number | 分子标记Molecular marker | 柠檬酸含量/(mg · g-1 FW) Citric acid content | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | M5 | M6 | ||
| 21N16-204 | M | M | M | M | M | M | 9.03 ± 1.26 |
| 21N16-209 | P | P | P | P | P | P | 18.55 ± 1.69 |
| 21N16-3 | M | P | P | P | P | P | 16.36 ± 1.80 |
| 21N16-14 | M | M | M | M | P | P | 8.68 ± 1.65 |
| 21N16-17 | M | M | M | M | P | P | 10.51 ± 0.28 |
| 21N16-2 | P | P | M | M | M | M | 8.77 ± 0.87 |
| 基因组版本 | 基因编号 | 是否在果实中表达 | 基因注释 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genome | Gene ID | Expression in fruit | Annotation |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073210 | 是Yes | 远红损伤反应性家族蛋白Far-red impaired responsive family protein |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073220 | 否No | 柱头特异性蛋白(片段)Stigma-specific protein (Fragment) |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073230 | 是Yes | 类tRNA二氢尿苷合酶2蛋白 tRNA-dihydrouridine synthase 2-like protein |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073240 | 是Yes | 乙酰木聚糖酯酶A Acetyl xylan esterase A |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073250 | 否No | 未知蛋白 Unknown Protein |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073260 | 否No | NAD依赖型差向异构酶/脱水酶 NAD-dependent epimerase/dehydratase |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073270 | 是Yes | 高尔基体膜蛋白tvp23 Golgi apparatus membrane protein tvp23 |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073280 | 是Yes | LL二氨基苯甲酸氨基转移酶LL-diaminopimelate aminotransferase |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073290 | 是Yes | 类Gun4蛋白Gun4-like protein |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073300 | 是Yes | 60S核糖体蛋白L2760S ribosomal protein L27 |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073310 | 是Yes | 类核糖体L9蛋白 Ribosomal L9-like protein |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073320 | 是Yes | GDP-L-半乳糖磷酸化酶1 GDP-L-galactose phosphorylase 1 |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073330 | 是Yes | 赖氨酰tRNA合成酶 Lysyl-tRNA synthetase |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073340 | 是Yes | 类Ariadne泛素连接酶 Ariadne-like ubiquitin ligase |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073350 | 否No | 钙依赖性蛋白激酶2 Calcium-dependent protein kinase 2 |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073360 | 是Yes | 未知蛋白Unknown Protein |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073370 | 是Yes | 40S核糖体蛋白S18 40S ribosomal protein S18 |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073380 | 是Yes | UPF0558蛋白C1orf156同源物 UPF0558 protein C1orf156 homolog |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073390 | 是Yes | 法尼基转移酶/I型香叶基香叶基转移酶α亚基 Farnesyltransferase/type I geranylgeranyltransferase α subunit |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073400 | 是Yes | 类核酸内切酶III蛋白1 Endonuclease III-like protein 1 |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073410 | 是Yes | 类γAPH1分泌酶亚基 Gamma-secretase subunit APH1-like |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073420 | 是Yes | 肌醇转运蛋白2 Myo-inositol transporter 2 |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073430 | 是Yes | 40S核糖体蛋白S29 40S ribosomal protein S29 |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073440 | 否No | 未知蛋白Unknown Protein |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073450 | 是Yes | Os11g0282300蛋白(片段),功能未知 Os11g0282300 protein (Fragment),unknown function |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073460 | 是Yes | 谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶 Glutathione peroxidase |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073470 | 是Yes | 生物素合成酶 Biotin synthase |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073480 | 否No | 光敏反应型NPH3家族蛋白 Phototropic-responsive NPH3 family protein |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073490 | 是Yes | 未知蛋白Unknown Protein |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073500 | 是Yes | 未知蛋白Unknown Protein |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073510 | 是Yes | 起始点识别复合物亚基2 Origin recognition complex subunit 2 |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073520 | 是Yes | 35个溶质载体家族成员F1 Solute carrier family 35 member F1 |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073530 | 是Yes | 类AGO4蛋白 Argonaute4-like |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073540 | 是Yes | 类AGO4蛋白 Argonaute4-like |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073550 | 是Yes | 类La相关蛋白 La-related protein-like |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073560 | 否No | 异戊酰辅酶A脱氢酶 Isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073570 | 否No | 细胞色素P450 Cytochrome P450 |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073580 | 否No | 1-氨基环丙烷-1-羧酸氧化酶1 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate oxidase 1 |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073590 | 否No | 水通道蛋白Z跨膜水通道 Aquaporin Z transmembrane water channel |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073600 | 是Yes | 泛素相关/TS-N 结构域蛋白 Ubiquitin-associated /TS-N domain-containing protein |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073610 | 否No | 细胞周期蛋白B1 Cyclin B1 |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073620 | 是Yes | 亚钼嘌呤合酶催化亚基 Molybdopterin synthase catalytic subunit |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073630 | 是Yes | 细胞分裂蛋白激酶9 Cell division protein kinase 9 |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073640 | 否No | MYB转录因子 MYB transcription factor |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073650 | 是Yes | WD重复蛋白 WD-repeat protein |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073660 | 是Yes | 类非特异性脂质转移蛋白蛋白 Non-specific lipid-transfer protein-like protein |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073670 | 是Yes | 蛋白质FAR1相关序列3 Protein FAR1-RELATED SEQUENCE 3 |
表4 定位区间内的基因列表及注释信息
Table 4 Gene list and annotation information in the mapped regions
| 基因组版本 | 基因编号 | 是否在果实中表达 | 基因注释 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genome | Gene ID | Expression in fruit | Annotation |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073210 | 是Yes | 远红损伤反应性家族蛋白Far-red impaired responsive family protein |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073220 | 否No | 柱头特异性蛋白(片段)Stigma-specific protein (Fragment) |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073230 | 是Yes | 类tRNA二氢尿苷合酶2蛋白 tRNA-dihydrouridine synthase 2-like protein |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073240 | 是Yes | 乙酰木聚糖酯酶A Acetyl xylan esterase A |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073250 | 否No | 未知蛋白 Unknown Protein |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073260 | 否No | NAD依赖型差向异构酶/脱水酶 NAD-dependent epimerase/dehydratase |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073270 | 是Yes | 高尔基体膜蛋白tvp23 Golgi apparatus membrane protein tvp23 |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073280 | 是Yes | LL二氨基苯甲酸氨基转移酶LL-diaminopimelate aminotransferase |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073290 | 是Yes | 类Gun4蛋白Gun4-like protein |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073300 | 是Yes | 60S核糖体蛋白L2760S ribosomal protein L27 |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073310 | 是Yes | 类核糖体L9蛋白 Ribosomal L9-like protein |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073320 | 是Yes | GDP-L-半乳糖磷酸化酶1 GDP-L-galactose phosphorylase 1 |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073330 | 是Yes | 赖氨酰tRNA合成酶 Lysyl-tRNA synthetase |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073340 | 是Yes | 类Ariadne泛素连接酶 Ariadne-like ubiquitin ligase |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073350 | 否No | 钙依赖性蛋白激酶2 Calcium-dependent protein kinase 2 |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073360 | 是Yes | 未知蛋白Unknown Protein |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073370 | 是Yes | 40S核糖体蛋白S18 40S ribosomal protein S18 |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073380 | 是Yes | UPF0558蛋白C1orf156同源物 UPF0558 protein C1orf156 homolog |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073390 | 是Yes | 法尼基转移酶/I型香叶基香叶基转移酶α亚基 Farnesyltransferase/type I geranylgeranyltransferase α subunit |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073400 | 是Yes | 类核酸内切酶III蛋白1 Endonuclease III-like protein 1 |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073410 | 是Yes | 类γAPH1分泌酶亚基 Gamma-secretase subunit APH1-like |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073420 | 是Yes | 肌醇转运蛋白2 Myo-inositol transporter 2 |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073430 | 是Yes | 40S核糖体蛋白S29 40S ribosomal protein S29 |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073440 | 否No | 未知蛋白Unknown Protein |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073450 | 是Yes | Os11g0282300蛋白(片段),功能未知 Os11g0282300 protein (Fragment),unknown function |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073460 | 是Yes | 谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶 Glutathione peroxidase |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073470 | 是Yes | 生物素合成酶 Biotin synthase |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073480 | 否No | 光敏反应型NPH3家族蛋白 Phototropic-responsive NPH3 family protein |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073490 | 是Yes | 未知蛋白Unknown Protein |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073500 | 是Yes | 未知蛋白Unknown Protein |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073510 | 是Yes | 起始点识别复合物亚基2 Origin recognition complex subunit 2 |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073520 | 是Yes | 35个溶质载体家族成员F1 Solute carrier family 35 member F1 |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073530 | 是Yes | 类AGO4蛋白 Argonaute4-like |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073540 | 是Yes | 类AGO4蛋白 Argonaute4-like |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073550 | 是Yes | 类La相关蛋白 La-related protein-like |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073560 | 否No | 异戊酰辅酶A脱氢酶 Isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073570 | 否No | 细胞色素P450 Cytochrome P450 |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073580 | 否No | 1-氨基环丙烷-1-羧酸氧化酶1 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate oxidase 1 |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073590 | 否No | 水通道蛋白Z跨膜水通道 Aquaporin Z transmembrane water channel |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073600 | 是Yes | 泛素相关/TS-N 结构域蛋白 Ubiquitin-associated /TS-N domain-containing protein |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073610 | 否No | 细胞周期蛋白B1 Cyclin B1 |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073620 | 是Yes | 亚钼嘌呤合酶催化亚基 Molybdopterin synthase catalytic subunit |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073630 | 是Yes | 细胞分裂蛋白激酶9 Cell division protein kinase 9 |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073640 | 否No | MYB转录因子 MYB transcription factor |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073650 | 是Yes | WD重复蛋白 WD-repeat protein |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073660 | 是Yes | 类非特异性脂质转移蛋白蛋白 Non-specific lipid-transfer protein-like protein |
| SL2.50 | Solyc06g073670 | 是Yes | 蛋白质FAR1相关序列3 Protein FAR1-RELATED SEQUENCE 3 |
| [1] |
doi: 10.1111/ppl.2011.141.issue-3 URL |
| [2] |
doi: 10.1111/nph.2017.215.issue-2 URL |
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
doi: 10.1111/tpj.2012.70.issue-4 URL |
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.1007/s10681-018-2295-z |
| [7] |
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324 pmid: 19451168 |
| [8] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19705-w |
| [9] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2021.09.001 pmid: 34555548 |
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
doi: 10.1101/gr.107524.110 pmid: 20644199 |
| [12] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.112.209619 pmid: 23166354 |
| [13] |
doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(03)00156-5 pmid: 12781773 |
| [14] |
pmid: 24894148 |
| [15] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.055632 pmid: 18441213 |
| [16] |
doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2007.04.009 pmid: 17434786 |
| [17] |
doi: 10.1111/tpj.2013.74.issue-1 URL |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1126/science.aal1556 pmid: 28126817 |
| [19] |
doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2017.04.010 URL |
| [20] |
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01286 pmid: 27617019 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00792 URL |
| [22] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0709 URL |
|
赵永, 朱红菊, 杨东东, 龚成胜, 刘文革. 2022. 果实柠檬酸代谢研究进展. 园艺学报, 49 (12):2579-2596.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0709 URL |
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.1111/tpj.2018.95.issue-2 URL |
| [24] |
|
|
张绍铃, 贾璐婷, 王利斌, 张臻. 2019. 园艺作物果实液泡糖、酸转运与转化研究进展. 南京农业大学学报, 42 (4):583-593.
|
| [1] | 陆秀萍, 汤智超, 唐文琨, 毛妃凤, 张万萍, 李经纬. 13种类病毒RNA/DNA基因组对番茄的侵染性鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 749-760. |
| [2] | 王春伟, 王燕, 段天坤, 苏雅馨, 袁胜楠, 任璐, 赵晓军, 王美琴. 异辛醇对番茄灰霉病菌的抑菌机理研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 761-772. |
| [3] | 陈亚娟, 金鑫, 杨江山, 戴子博, 李斗, 邵璋. 黄腐酸钾对‘蛇龙珠’葡萄果实糖酸代谢及香味物质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 406-422. |
| [4] | 李芮, 王稳, 杜明辉, 刘根忠, 马方放, 包志龙. SlBON1调控番茄植株营养生长机制的研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 73-87. |
| [5] | 韩荧, 段颖, 牛一杰, 李衍素, 贺超兴, 孙敏涛, 王君, 李强, 陈双臣, 闫妍. 腐殖酸生物降解地膜提高番茄品质的转录代谢机制研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1758-1772. |
| [6] | 龚小雅, 李贤, 周新刚, 吴凤芝. 分蘖洋葱伴生番茄诱导的根际微生物对根结线虫病的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1913-1926. |
| [7] | 孟思达, 韩磊磊, 相恒佐, 朱美玉, 冯珍, 叶云珠, 孙美华, 李艳冰, 赵利萍, 谭昌华, 齐明芳, 李天来. 番茄心室数的调控机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1649-1664. |
| [8] | 赵崇斌, 张苇胤, 李舒庆, 郭乙含, 徐红霞, 陈俊伟, 杨向晖, 彭泽. 枇杷果、叶、花相关性状QTL定位分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1189-1200. |
| [9] | 马星云, 范冰丽, 唐光彩, 贾芝琪, 李营, 薛东齐, 张世文. DXR调控番茄叶绿体发育、花色与果实着色机制初探[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1241-1255. |
| [10] | 张文静, 徐大勇, 吴倩琳, 杨佛, 信丙越, 曾昕, 李峰. 拮抗番茄灰霉病的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌XDY66基因组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1413-1425. |
| [11] | 王永珍, 张剑国, 刘彩虹, 李思蓓, 吕甜甜. 番茄新品种‘圆红212’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1435-1436. |
| [12] | 刘泽营, 孙帅, 刘志强, 崔霞, 李仁. 番茄尖果脐突变体的生理特性及其候选基因分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 982-992. |
| [13] | 李品, 甘宁, 陈家伟, 项思翔, 沈静漪, 欧阳波, 卢永恩. 番茄自然群体磷利用效率分析及耐低磷种质筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 993-1004. |
| [14] | 杨婷, 席德慧, 夏明, 李佳楠. α-苦瓜素基因提高番茄对烟草花叶病毒抗性的机理研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1126-1136. |
| [15] | 李斗, 王宇航, 王春恒, 金鑫, 杨江山, 陈亚娟, 戴子博, 冯丽丹. GABA对葡萄叶片光合色素及糖含量和果实风味的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 815-831. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司