
园艺学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (7): 1389-1401.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0478
• 遗传育种·种质资源·分子生物学 • 下一篇
收稿日期:2023-01-17
修回日期:2023-04-07
出版日期:2023-07-25
发布日期:2023-07-26
通讯作者:
基金资助:
LIU Hui, YIN Xiangjing, FANG Jinghao, GAO Min, LI Zhi, WANG Xiping*( )
)
Received:2023-01-17
Revised:2023-04-07
Published:2023-07-25
Online:2023-07-26
摘要:
以中国野生山葡萄(Vitis amurensis Rupr.)‘通化3号’和刺葡萄(V. davidii Foex.)‘塘尾’为材料,克隆得到芪合成酶基因VaSTS19和VdSTS19。序列分析发现VaSTS19和VdSTS19的编码区均为1 179 bp,编码392个氨基酸,定位于16号染色体,二者核苷酸和氨基酸序列相似性分别为98.81%和98.21%。亚细胞定位结果显示VaSTS19和VdSTS19均定位于细胞膜、细胞质和细胞核。将35S强启动子连接VaSTS19和VdSTS19转入番茄能显著促进STS19的表达及番茄中白藜芦醇的合成和积累。分别从两种材料中克隆得到VaSTS19和VdSTS19的启动子。顺式作用元件分析表明,二者启动子中均包含多个胁迫应答元件、激素应答元件及光应答元件。序列分析发现二者启动子序列与欧洲葡萄VST2启动子序列同源性为60%。转基因烟草叶片中二者不同长度启动子片段对SA和MeJA诱导响应明显。结果表明STS19的表达模式和白藜芦醇的合成可能与其上游启动子类型和调控有关。
刘慧, 殷向静, 方景浩, 高敏, 李智, 王西平. 中国野生葡萄芪合成酶基因STS19及其启动子的克隆与功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(7): 1389-1401.
LIU Hui, YIN Xiangjing, FANG Jinghao, GAO Min, LI Zhi, WANG Xiping. Cloning and Functional Analysis of the CDS and Promoter of Synthase Gene STS19 in Chinese Wild Grapevine[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(7): 1389-1401.
| 用途 | 引物名称 | 上游引物(5′-3′) | 下游引物(5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Use | Primer name | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
| 半定量分析RT-PCR | STS5/6a | GTGGGGCTACAAATTGAGTGAAAG | GGCGAAACTGTAAGAACTTGATGTC |
| STS7 | GGAGGGATTGTAATTTAGTGATCGT | CGCCAAGAACTTGAAGTCTCACT | |
| STS9 | CCCTATCATAAAATTGAGGGATTG | GGGCATTTCAAGAATATAAAACAA | |
| STS10 | CGATCATAACATTGAGGGATTGTAG | GGGGATACAACTTTTCAGGAAAC | |
| STS 15/21 | CGCCCTAAATCTTTTATTCCTATCC | CCCACAGAATGACAAGTACTTGCA | |
| STS16/22 a | CCTTCTGAAACTGCTTTGGACTCT | GGGTTGCGATAACTTCGTTATTGT | |
| STS17/23/24 a | CGGGTTTGATATCTGAAAACATAGAG | GGGAAGATGATTTCATGGTGATATATC | |
| STS19 | CGGGCTAATTTGAAAAATATGTAAAA | CGGTAAGGGTCATAGTGCAGCT | |
| STS20/28/30 | CGCTTGAGGAGCACCCAAAC | CCGATCCAATGATTACAGCTGC | |
| STS27/29 | CCGCCCTATTATGTTGAATAGGAGT | GGGTTTAGGGAATCTTCAAGATGAT | |
| STS31 | CGGGGTTATTTATCTCCTAAACTAAT | CCGTTTAATTTGAGCTCACCAAG | |
| STS32 | CAAACCATGAGAGTCCAAGTTCCC | GCGACACGTTGGTGTTCAAGTAGA | |
| STS35 a | TGCTGCATAGCGTTCCTCCA | CCCCACATGAACACAACATCAATA | |
| STS36 | CGGGTATAAATTAAGTGAAGGGGAA | GGGGGGATAATGAAACAGTGAGATA | |
| STS37 a | CCCATAGAGAAATGCTTGACCCA | CCGACTTGATTACAAGCCAAATTTA | |
| STS38 a | TGCCACGGGTACAAATTGAGTTA | GGAAGCCCTCCAGCAATCAGT | |
| STS39/43 | CGCCTATCGAAACTGTTGTGCTAC | CCCCCTTGAAACTCATCTTTTTAAT | |
| STS41/45 | CCCGTATTTCATCACATTGGTAA | GGCAACTTGAAACTCATCTTCTTA | |
| STS42 | CCCCAATTGATAAAACTCTTGTAGTA | CCCCTTTTAGTTTGAGCTAATCAC | |
| STS46 | GGGGGGTTACAAATTAAGAGCAATA | GGGTGACTCAGGTACAAATCCAAAT | |
| STS47 | CCCGTGAGGTAAAGAAGAATGGTC | GCCGCAGTCTAACAATGACTTGAA | |
| STS48 | GGGGCAGTAATGTAATCAAATAGGG | CCCTGGGAACTTCAAACTCATCAT | |
| 基因克隆Gene cloning | STS19-clone | ATGGCGTCTGTGGAGGAAA | TTAGTTGGAATCTGTACCA |
| 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization | STS19-GFP | AGCTCGGTACCCGGGGATCCATGGCGTCTGTGGAGGAAATTAGAAA | ACCATGGTGTCGACTCTAGAGTTGGAATCTGTACCAACGCTATGG |
| 转基因番茄鉴定Identification of transgenic tomato | 2300 | CAATCCCACTATCCTTCGC | TGCCAAATGTTTGAACGATC |
| 启动子克隆 Promoter amplification | PSTS19 | GAATTCTATAATTAGTGCGGGGCG | GACGTCTCCACAGACGCCATTG |
| 不同长度启动子片段克隆 | PVaSTS19-D5(P621) | GAATTCCCCTCAAAGTGGTATTTG | GACGTCTCCACAGACGCCATTG |
| Cloning of promoter deletion | PVaSTS19-D4(P851) | GAATTCCCTCCATAATTACAGCTC | GACGTCTCCACAGACGCCATTG |
| fragments | PVaSTS19-D3(P1197) | GAATTCCGCAATCATGGTAATTTT | GACGTCTCCACAGACGCCATTG |
| PVaSTS19-D2(P1384) | GAATTCCCCGTTTATTAAAATTAAACC | GACGTCTCCACAGACGCCATTG | |
| PVdSTS19-S5(P589) | GAATTCCAAAGAAGTTCCGATATTAA | GACGTCTCCACAGACGCCATTG | |
| PVdSTS19-S4(P868) | CTGCAGTCCACAGACGCCATTGAT | GACGTCTCCACAGACGCCATTG | |
| PVdSTS19-S3(P1194) | GAATTCCGCAATCATGGTAATTTT | GACGTCTCCACAGACGCCATTG | |
| PVdSTS19-S2(P1381) | GAATTCCCCGTTTATTAAAATTAAACC | GACGTCTCCACAGACGCCATTG |
表1 本研究所用引物
Table 1 Primer sequences used in this study
| 用途 | 引物名称 | 上游引物(5′-3′) | 下游引物(5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Use | Primer name | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
| 半定量分析RT-PCR | STS5/6a | GTGGGGCTACAAATTGAGTGAAAG | GGCGAAACTGTAAGAACTTGATGTC |
| STS7 | GGAGGGATTGTAATTTAGTGATCGT | CGCCAAGAACTTGAAGTCTCACT | |
| STS9 | CCCTATCATAAAATTGAGGGATTG | GGGCATTTCAAGAATATAAAACAA | |
| STS10 | CGATCATAACATTGAGGGATTGTAG | GGGGATACAACTTTTCAGGAAAC | |
| STS 15/21 | CGCCCTAAATCTTTTATTCCTATCC | CCCACAGAATGACAAGTACTTGCA | |
| STS16/22 a | CCTTCTGAAACTGCTTTGGACTCT | GGGTTGCGATAACTTCGTTATTGT | |
| STS17/23/24 a | CGGGTTTGATATCTGAAAACATAGAG | GGGAAGATGATTTCATGGTGATATATC | |
| STS19 | CGGGCTAATTTGAAAAATATGTAAAA | CGGTAAGGGTCATAGTGCAGCT | |
| STS20/28/30 | CGCTTGAGGAGCACCCAAAC | CCGATCCAATGATTACAGCTGC | |
| STS27/29 | CCGCCCTATTATGTTGAATAGGAGT | GGGTTTAGGGAATCTTCAAGATGAT | |
| STS31 | CGGGGTTATTTATCTCCTAAACTAAT | CCGTTTAATTTGAGCTCACCAAG | |
| STS32 | CAAACCATGAGAGTCCAAGTTCCC | GCGACACGTTGGTGTTCAAGTAGA | |
| STS35 a | TGCTGCATAGCGTTCCTCCA | CCCCACATGAACACAACATCAATA | |
| STS36 | CGGGTATAAATTAAGTGAAGGGGAA | GGGGGGATAATGAAACAGTGAGATA | |
| STS37 a | CCCATAGAGAAATGCTTGACCCA | CCGACTTGATTACAAGCCAAATTTA | |
| STS38 a | TGCCACGGGTACAAATTGAGTTA | GGAAGCCCTCCAGCAATCAGT | |
| STS39/43 | CGCCTATCGAAACTGTTGTGCTAC | CCCCCTTGAAACTCATCTTTTTAAT | |
| STS41/45 | CCCGTATTTCATCACATTGGTAA | GGCAACTTGAAACTCATCTTCTTA | |
| STS42 | CCCCAATTGATAAAACTCTTGTAGTA | CCCCTTTTAGTTTGAGCTAATCAC | |
| STS46 | GGGGGGTTACAAATTAAGAGCAATA | GGGTGACTCAGGTACAAATCCAAAT | |
| STS47 | CCCGTGAGGTAAAGAAGAATGGTC | GCCGCAGTCTAACAATGACTTGAA | |
| STS48 | GGGGCAGTAATGTAATCAAATAGGG | CCCTGGGAACTTCAAACTCATCAT | |
| 基因克隆Gene cloning | STS19-clone | ATGGCGTCTGTGGAGGAAA | TTAGTTGGAATCTGTACCA |
| 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization | STS19-GFP | AGCTCGGTACCCGGGGATCCATGGCGTCTGTGGAGGAAATTAGAAA | ACCATGGTGTCGACTCTAGAGTTGGAATCTGTACCAACGCTATGG |
| 转基因番茄鉴定Identification of transgenic tomato | 2300 | CAATCCCACTATCCTTCGC | TGCCAAATGTTTGAACGATC |
| 启动子克隆 Promoter amplification | PSTS19 | GAATTCTATAATTAGTGCGGGGCG | GACGTCTCCACAGACGCCATTG |
| 不同长度启动子片段克隆 | PVaSTS19-D5(P621) | GAATTCCCCTCAAAGTGGTATTTG | GACGTCTCCACAGACGCCATTG |
| Cloning of promoter deletion | PVaSTS19-D4(P851) | GAATTCCCTCCATAATTACAGCTC | GACGTCTCCACAGACGCCATTG |
| fragments | PVaSTS19-D3(P1197) | GAATTCCGCAATCATGGTAATTTT | GACGTCTCCACAGACGCCATTG |
| PVaSTS19-D2(P1384) | GAATTCCCCGTTTATTAAAATTAAACC | GACGTCTCCACAGACGCCATTG | |
| PVdSTS19-S5(P589) | GAATTCCAAAGAAGTTCCGATATTAA | GACGTCTCCACAGACGCCATTG | |
| PVdSTS19-S4(P868) | CTGCAGTCCACAGACGCCATTGAT | GACGTCTCCACAGACGCCATTG | |
| PVdSTS19-S3(P1194) | GAATTCCGCAATCATGGTAATTTT | GACGTCTCCACAGACGCCATTG | |
| PVdSTS19-S2(P1381) | GAATTCCCCGTTTATTAAAATTAAACC | GACGTCTCCACAGACGCCATTG |
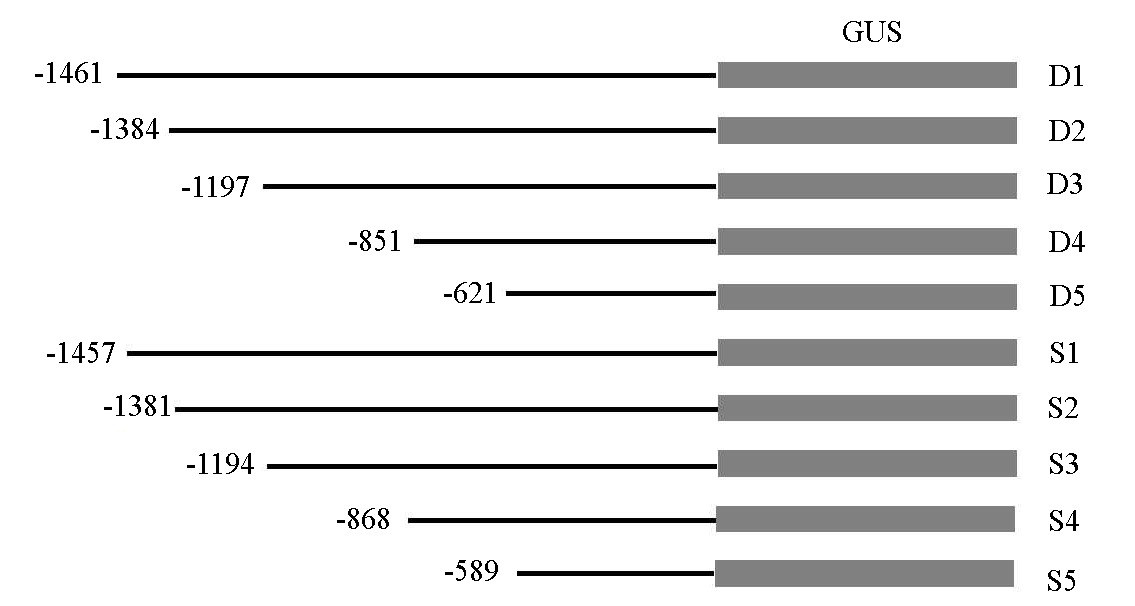
图1 VaSTS19和VdSTS19不同长度启动子片段 D1 ~ D5表示VaSTS19不同长度启动子片段;S1 ~ S5表示VdSTS19不同长度启动子片段。下同。
Fig. 1 Schematic representation of promoter fragments of different lengths of VaSTS19 and VdSTS19 D1-D5 indicate the promoter fragments of different lengths of VaSTS19;S1-S5 indicate the promoter fragments of different lengths of VdSTS19. The same below.

图2 STS家族基因在葡萄不同组织器官(A)和不同发育时期果实(B)中的表达 A:1 ~ 8分别为‘通化3号’根、茎、叶、花序、果皮、果肉、种子和卷须; B:1 ~ 3分别为‘塘尾’绿果期,转色期和成熟期果实;4 ~ 6为‘通化3号’绿果期、转色期和成熟期果实。
Fig. 2 Tissue specific expression profile analysis (A) and fruit development period expression (B) of STS genes A:Vitis amurensis‘Tonghua 3’. 1,root;2,stem;3,leaf;4,flower;5,pericarp;6,flesh;7,seed;8,tendril. B:1-3:Grapevine fruit of green,veraison and mature stages in V. davidii‘Tangwei’;4-6:Grapevine fruit of green,veraison and mature stages in V. amurensis‘Tonghua 3’.

图4 番茄的转基因遗传转化过程(A)和PCR扩增鉴定转化番茄植株(B) a:种子萌发长出子叶;b:子叶预培养;c:侵染后共培养;d:转化后形成的愈伤组织;e:产生的抗性芽;f和g:抗性芽生根;h:移栽。M:DNA marker DL2000;1 ~ 6:转化VaSTS19的转基因株系;7 ~ 12:转化VdSTS19的转基因株系;13 ~ 17:转化空载体2300的转基因株系;18、19:野生型株系。
Fig. 4 Transformation process of transgenic tomatos(A)and PCR verifies the recombinant plasmid in transformed tomato(B) a:Cotyledon germination;b:Cotyledon precultured;c:Co-culture after infection;d:Callus formed after transformation;e:Resistant shoots generate;f and g:Resistant bud rooting;h:Transplanting to the greenhouse. M:Indicates DNA marker DL 2000;Lane 1-6:Indicate the transgenic plants of VaSTS19;Lane 7-12:Indicate the transgenic plants of VdSTS19;Lane 13-17:Indicate the transgenic plants of 2300;Lane 18,19:Indicate wild type tomato.
| 转基因名称 Gene name | 转基因株系 Line | 绿果期 Green | 转色期 Veraison | 成熟期 Mature |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VaSTS19 | L1 | nd | 3.71 ± 0.58 a | 3.61 ± 0.41 a |
| L2 | nd | 3.63 ± 0.67 a | 2.68 ± 0.29 b | |
| L3 | nd | 2.84 ± 0.16 b | 4.29 ± 0.36 a | |
| VdSTS19 | L1 | nd | 3.83 ± 0.13 a | 3.99 ± 0.14 a |
| L2 | nd | 3.98 ± 0.25 a | 3.67 ± 0.47 a | |
| L3 | nd | 4.15 ± 0.55 a | 4.03 ± 0.40 a | |
| 2300 | L1 | nd | nd | nd |
| WT | nd | nd | nd |
表2 转基因和野生型(WT)番茄不同发育时期白藜芦醇的含量
Table 2 Resveratrol concentration in transgenic and wild type (WT) tomatoes μg · g-1
| 转基因名称 Gene name | 转基因株系 Line | 绿果期 Green | 转色期 Veraison | 成熟期 Mature |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VaSTS19 | L1 | nd | 3.71 ± 0.58 a | 3.61 ± 0.41 a |
| L2 | nd | 3.63 ± 0.67 a | 2.68 ± 0.29 b | |
| L3 | nd | 2.84 ± 0.16 b | 4.29 ± 0.36 a | |
| VdSTS19 | L1 | nd | 3.83 ± 0.13 a | 3.99 ± 0.14 a |
| L2 | nd | 3.98 ± 0.25 a | 3.67 ± 0.47 a | |
| L3 | nd | 4.15 ± 0.55 a | 4.03 ± 0.40 a | |
| 2300 | L1 | nd | nd | nd |
| WT | nd | nd | nd |

图5 VaSTS19和VdSTS19的启动子的序列比对 红色方框表示转录起始位点(+1);背景绿色的元件代表两个启动子序列中所共有的元件,粉色和红色分别表示‘通化3号’和‘塘尾’STS19启动子序列上特有元件。方向向左的箭头表明所标注元件与启动子方向相反;向下或向上的箭头表示启动子缺失体的起始位点。
Fig. 5 A comparison of the VaSTS19 and VdSTS19 promoter sequences The translational start sites(+1)are shown in red box. Motifs with significant similarity to previously identified cis-acting elements in both species are shaded in green. Motifs found only in VaSTS19 or VdSTS19 promoters are respectively shaded in pink or red. Arrowheads pointing to the left represent the reverse direction of cis-elements compared to promoter orientation. Other arrows represent start point of 5′-deleted derivatives.
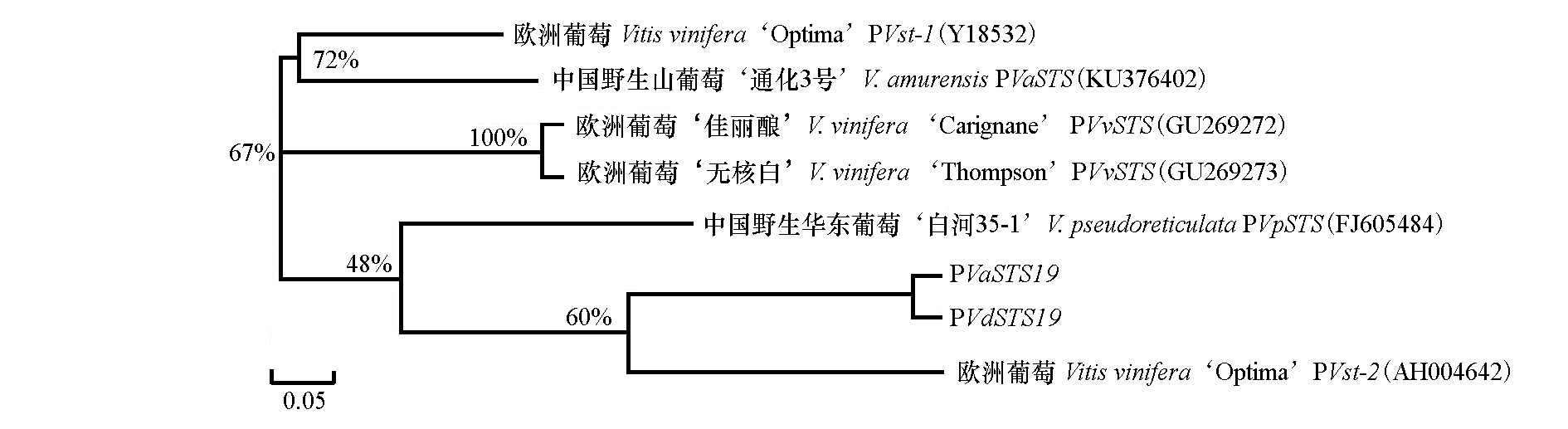
图6 不同葡萄种间芪合成酶基因启动子序列的聚类 标尺代表每单位长度发生0.05次剪辑替换,结点处的数字代表自展值(1 000次重复)。
Fig. 6 A phylogenetic tree based on a ClustalX multiple sequence alignment of STS promoters from a range of grape species The scale bar represents 0.05 substitutions per site and the numbers next to the nodes are bootstrap values from 1 000 replicates.
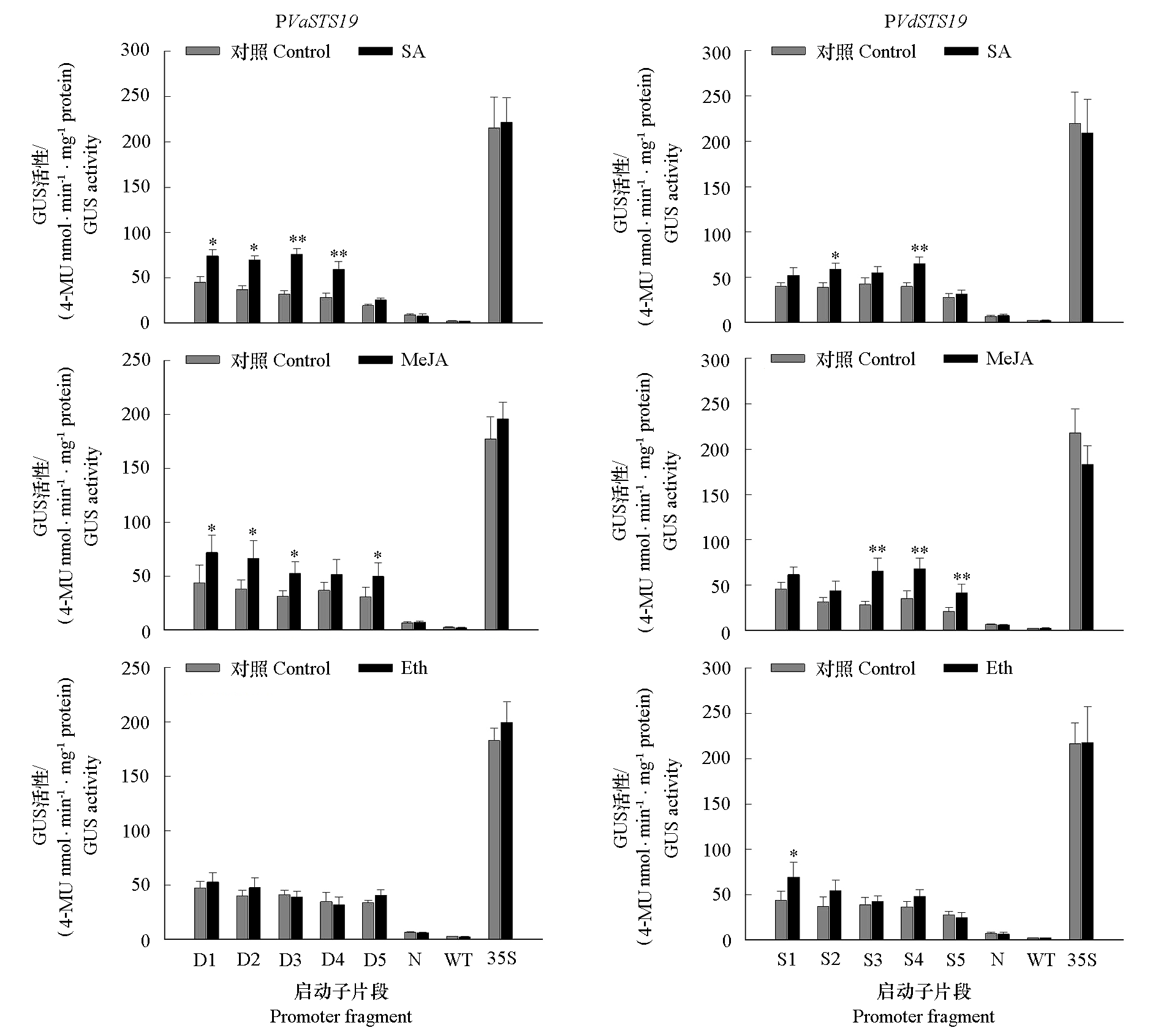
图7 不同激素处理下VaSTS19和VdSTS19不同长度启动子片段GUS活性分析 GUS活性值来自3次不同的重复试验。WT表示野生型,N表示阴性对照(不含启动子),35S表示阳性对照(内含CaMV35S启动子)。两组间的显著性分析采用单侧t检测进行分析,*表示显著(α = 0.05),**极显著(α = 0.01)。
Fig. 7 GUS activity analysis of promoter fragments of different lengths of VaSTS19 and VdSTS19 in response to hormone treatment in transiently transformed tobacco leaves Mean GUS activity(± SE)is averaged from triplicate experiments. WT:Wild type;N:Negative control(no promoter);35S:Positive control (CaMV35S promoter). Significant difference test were evaluated using a one-sided paired t test(**α = 0.01,or at *α = 0.05).
| [1] |
doi: 10.1007/s11103-008-9435-0 pmid: 19083153 |
| [2] |
pmid: 15359598 |
| [3] |
doi: 10.1111/pce.1982.5.issue-5 URL |
| [4] |
doi: 10.1038/361153a0 |
| [5] |
doi: 10.1007/s11816-018-0494-7 |
| [6] |
doi: 10.3390/ijms19102985 URL |
| [7] |
doi: 10.1002/biof.v36:5 URL |
| [8] |
doi: 10.1134/S1021443710030143 URL |
| [9] |
doi: 10.1007/s00299-014-1708-2 pmid: 25420769 |
| [10] |
doi: 10.1007/s00425-019-03276-2 |
| [11] |
|
|
刘梦琦, 吴凤颖, 王跃进. 2019. 中国野生毛葡萄芪合成酶基因表达与抗白粉病分析. 中国农业科学, 52 (14):2436-2449.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2019.14.005 |
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.1007/s00299-011-1110-2 URL |
| [13] |
doi: 10.1007/s11010-006-1260-7 URL |
| [14] |
doi: 10.1002/ptr.5644 pmid: 27196869 |
| [15] |
doi: 10.3390/ijms22052614 URL |
| [16] |
doi: 10.1021/jf070509e pmid: 17655245 |
| [17] |
doi: 10.1006/pmpp.1997.0123 URL |
| [18] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2019-0329 |
|
吴凤颖, 刘梦琦, 王跃进. 2020. 中国野生毛葡萄芪合酶基因抗白粉病功能分析. 园艺学报, 47 (2):205-219.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2019-0329 |
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.1007/s11240-015-0761-z URL |
| [20] |
|
|
徐伟荣. 2010. 中国野生华东葡萄芪合成酶基因其启动子克隆和功能分析[博士论文]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学.
|
|
| [21] |
doi: 10.1007/s00425-009-1062-8 URL |
| [22] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erq447 URL |
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0263 |
|
赵凯茜, 丁茜, 王跃进. 2020. 中国野生毛葡萄芪合酶基因VqSTS11和VqSTS23调控抗白粉病的研究. 园艺学报, 47 (7):1264-1276.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0263 |
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.1007/s00425-004-1343-1 URL |
| [1] | 吴伟民 , 王壮伟, 钱亚明, 王西成, 王 博, 闫莉春. 早熟鲜食葡萄新品种‘紫金红霞’ [J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 25-26. |
| [2] | 李松琦, 李旭飞, 李 敏, 刘海楠, 裴茂松, 韦同路, 郭大龙, 余义和. 葡萄细胞分裂素响应调节因子VlRRA1的克隆、表达及启动子活性分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1609-1621. |
| [3] | 代红军, 魏 强, 贺 琰, 汪月宁, 王振平. 油菜素内酯对高温胁迫下葡萄花色苷合成及果实品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1711-1722. |
| [4] | 王 文, 张柯楠, 方莫扉, 丁思悦, 王雪飞, 惠竹梅, . 果袋颜色对‘赤霞珠’葡萄果皮花色苷积累的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1723-1738. |
| [5] | 曹雄军, 韩佳宇, 成 果, 王 博, 马广仁, 林 玲, 谭宗琨, 黄秋秘, 陈 潇, 陈孚仪, 时晓芳, 盘丰平, 白先进, . 光照时数及强度对‘阳光玫瑰’葡萄产量形成的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1739-1746. |
| [6] | 高鹏飞, 高冰, 冯郑红, 吴建慧. 绢毛委陵菜PsWRKY40的克隆与耐镉功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(6): 1269-1283. |
| [7] | 秦嗣军, 张阔, 齐边斌, 于波, 吕德国. 外源碳对苹果根区土壤活性有机碳及植株生长的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(6): 1295-1304. |
| [8] | 王雯雯, 张强强, 李玲, 金婧, 王若彤, 顾沛雯. 葡萄白粉病菌潜伏侵染量Real-time PCR检测方法建立[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(6): 1368-1376. |
| [9] | 李中瀚, 唐美玲, 郑秋玲, 刘明慧, 康慧, 高振, 杜远鹏. 聚乙烯编织物Coverlys TF150®覆盖对‘蜜光’葡萄果实品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(5): 1073-1084. |
| [10] | 李玉梅, 娄玉穗, 王小龙, 马玉全, 王海波, 吕中伟. ‘夏黑’葡萄高品质果园植株叶片和土壤营养诊断研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(4): 864-874. |
| [11] | 俞沁含, 李俊铎, 崔莹, 王佳慧, 郑巧玲, 徐伟荣. 山葡萄转录因子VaMYB4a互作蛋白的筛选与鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(3): 508-522. |
| [12] | 马帅辉, 何光琪, 程一哲, 郭大龙. 5-azaC对‘巨峰’葡萄果实发育阶段mRNA可变剪接的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(3): 523-533. |
| [13] | 黄蓉, 董超, 姜娇, 秦义, 刘延琳, 宋育阳. 避雨栽培对‘赤霞珠’葡萄果表微生物多样性的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(3): 635-646. |
| [14] | 孙磊, 闫爱玲, 张国军, 王慧玲, 王晓玥, 任建成, 徐海英. 鲜食葡萄新品种‘瑞都摩指’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(3): 685-686. |
| [15] | 王晓晨, 聂子页, 刘先菊, 段伟, 范培格, 梁振昌. 脱落酸对‘京香玉’葡萄果实单萜物质合成的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 237-249. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司