
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2022, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (7): 1401-1414.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0499
• Research Papers • Next Articles
ZHENG Xiaodong1, XI Xiangli1, LI Yuqi1, SUN Zhijuan2, MA Changqing1, HAN Mingsan3, LI Shaoxuan3, TIAN Yike1, WANG Caihong1,**( )
)
Received:2022-01-17
Revised:2022-03-29
Online:2022-07-25
Published:2022-07-29
Contact:
WANG Caihong
E-mail:chw6068@126.com
CLC Number:
ZHENG Xiaodong, XI Xiangli, LI Yuqi, SUN Zhijuan, MA Changqing, HAN Mingsan, LI Shaoxuan, TIAN Yike, WANG Caihong. Effects and Regulating Mechanism of Exogenous Brassinosteroids on the Growth of Malus hupehensis Under Saline-alkali Stress[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1401-1414.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0499
| 基因名称 Gene name | 上游引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 下游引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| MhCAX5 | ACCAGTCTCACTCTTTGTGGCG | GAATATAATTGGTGGGAGGAGATAT |
| MhCHX15 | CCTCTTGGTACAGCATTGATAAAAA | GTTTGAACTTAATTTTGCAGCACA |
| MhSOS1 | TACATCATTTCTGGTATATCTTGTG | CAAGATGAAAATTAAGGTATTAGCA |
| MhALT1 | GTTGTTTTTTTGCTCTGACGACT | GTTGAACCACAAAACCCTGCT |
| MhSKOR | CATCCTGACAACTGGTGGTATCG | AAGTACCTCAGAGCAATCCGTTT |
| MhNHX4 | ACGAAACTCCTTTACTATACAGCCT | TGATACCACAGATAAGTGAGCATAG |
| MhAHA2 | AAAGTGTGAAGAAAGAGAAAATGC | AGTTCATTTGCTTGACATTCTTT |
| MhAHA8 | GGTCAAAAGTGTGTTGGTAAGCA | AAACCAAAATCCTCCAACAGC |
| MhMAPKKKa | GCTACATGGGACATGACATTACTAG | CCAAGATGTTCCTGCCTTTTAT |
| MhLECPK91 | TTCACCACTTATGCCAATGATAC | GGAACTGGAGATTCTTGCTTTTT |
| MhERF109 | ATGCCCTTCCATGCGAATAG | CTAGTTCATGGACAACCATGCC |
| MhNAC56 | ATGGAGTGCACCGACTCGTC | CTATCCCAAATTGGACTCAGAATAC |
| MhActin | CTTCAATGTGCCTGCCATGTAT | AATTTCCCGTTCAGCAGTAGTG |
Table 1 Primer sequences for qRT-PCR
| 基因名称 Gene name | 上游引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 下游引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| MhCAX5 | ACCAGTCTCACTCTTTGTGGCG | GAATATAATTGGTGGGAGGAGATAT |
| MhCHX15 | CCTCTTGGTACAGCATTGATAAAAA | GTTTGAACTTAATTTTGCAGCACA |
| MhSOS1 | TACATCATTTCTGGTATATCTTGTG | CAAGATGAAAATTAAGGTATTAGCA |
| MhALT1 | GTTGTTTTTTTGCTCTGACGACT | GTTGAACCACAAAACCCTGCT |
| MhSKOR | CATCCTGACAACTGGTGGTATCG | AAGTACCTCAGAGCAATCCGTTT |
| MhNHX4 | ACGAAACTCCTTTACTATACAGCCT | TGATACCACAGATAAGTGAGCATAG |
| MhAHA2 | AAAGTGTGAAGAAAGAGAAAATGC | AGTTCATTTGCTTGACATTCTTT |
| MhAHA8 | GGTCAAAAGTGTGTTGGTAAGCA | AAACCAAAATCCTCCAACAGC |
| MhMAPKKKa | GCTACATGGGACATGACATTACTAG | CCAAGATGTTCCTGCCTTTTAT |
| MhLECPK91 | TTCACCACTTATGCCAATGATAC | GGAACTGGAGATTCTTGCTTTTT |
| MhERF109 | ATGCCCTTCCATGCGAATAG | CTAGTTCATGGACAACCATGCC |
| MhNAC56 | ATGGAGTGCACCGACTCGTC | CTATCCCAAATTGGACTCAGAATAC |
| MhActin | CTTCAATGTGCCTGCCATGTAT | AATTTCCCGTTCAGCAGTAGTG |
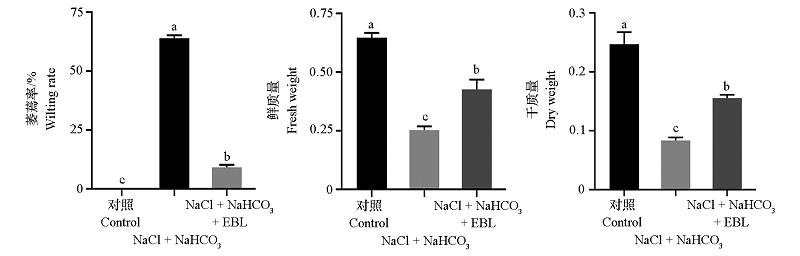
Fig. 2 Effects of saline-alkali stress and exogenous EBL treatment on wilting rate,fresh weight and dry weight of Malus hupehensis seedlingsDifferent lowercase letters indicate significant difference at the 0.05 probability level.
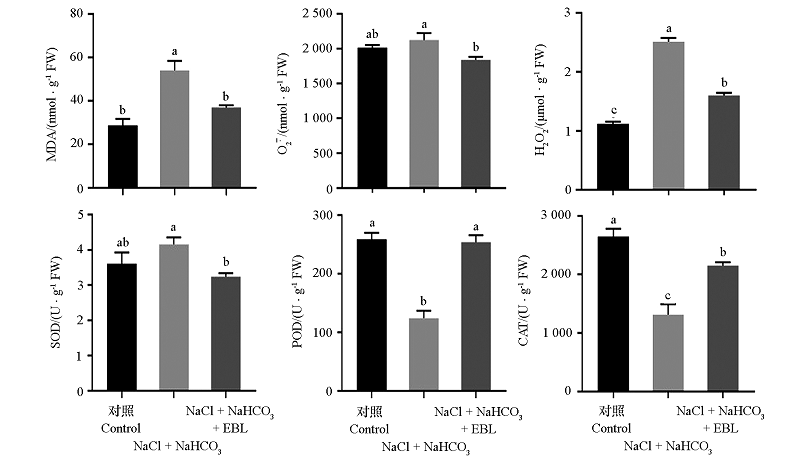
Fig. 6 Effects of saline-alkali stress and exogenous EBL treatment on the content of MDA,superoxide anion,H2O2 and the activities of autioxidant enzyme in Malus hupehensis
| [1] | Capula R, Valdez L A, Cartmill D L, Cartmill A D, Alia T I. 2016. Supplementary calcium and potassium improve the response of tomato(Solanum lycopersicum L.)to simultaneous alkalinity,salinity and boron stress. Communicates in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 47 (4):505-511. |
| [2] | Chen Guang-xin, Ding Dong, Li Qian, Chen Ying-xue, Wang Ye-Ning, Lü Chen-xi, Gao Hong-bo, Wu Xiao-lei. 2021. Growth of tomato seedlings under saline-alkali stress combined with GABA and CaCl2 effects of chlorophyll fluorescence parameters and reactive oxygen species. Chinese Vegetables,(7):48-55. (in Chinese) |
| 陈光鑫, 丁栋, 李倩, 陈迎雪, 王叶宁, 吕晨希, 高洪波, 吴晓蕾. 2021. GABA和CaCl2复配对盐碱胁迫下番茄幼苗生长、叶绿素荧光参数和活性氧的影响. 中国蔬菜,(7):48-55. | |
| [3] | Deng Ping, Zhao Ying, Wang Xia, Chen Qiu-you, Wu Min. 2021. Effects of salicylic acid on seed germination of quercus glauca under NaHCO3 stress in Karst region of Northwest Guangxi. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University(Natural Science Edition), 4 (7):1-13. (in Chinese) |
| 邓平, 赵英, 王霞, 陈秋佑, 吴敏. 2021. 水杨酸对NaHCO3胁迫下桂西北喀斯特地区青冈栎种子萌发的影响. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 4 (7):1-13. | |
| [4] |
Ding H, Lai J B, Wu Q, Zhang S C, Chen L, Dai Y S, Wang C F, Du J J, Xiao S, Yang C W. 2016. Jasmonate complements the function of Arabidopsis lipoxygenase 3 in salinity stress response. Plant Science, 244:1-7.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.11.009 pmid: 26810448 |
| [5] | Fan Cui-zhi, Wu Xin-yi, Guan Xin, Zheng Chun-fen, Zhao Hai-yan, Gu Zhi-zhuang, Liu Wei-cheng, Chen Jun, Zheng Qing-song. 2021. Effects of brassinolide soaking on seed germination of tomato under salt stress and its physiological mechanism. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41 (5):1857-1867. (in Chinese) |
| 范翠枝, 吴馨怡, 关欣, 郑春芳, 赵海燕, 顾志壮, 刘伟成, 陈军, 郑青松. 2021. 油菜素内酯浸种对盐胁迫番茄种子萌发的影响及其生理机制. 生态学报, 41 (5):1857-1867. | |
| [6] | Fan Wang-tao. 2020. Hazard and improvement method of soil salinization. Agriculture and Technology, 40 (23):114-116. (in Chinese) |
| 范王涛. 2020. 土壤盐碱化危害及改良方法研究. 农业与技术, 40 (23):114-116. | |
| [7] |
Guo R, Yang Z Z, Li F, Yan C R, Zhong X L, Liu Q, Xia X, Li H R, Zhao L. 2015. Comparative metabolic responses and adaptive strategies of wherat(Triticum aestivum)to salt and alkali stress. BMC Plant Biology, 15 (70):1-13.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-014-0410-4 URL |
| [8] | Guo Rui, Li Feng, Zhou Ji, Li Hao-ru, Xia Xu, Liu Qi. 2016. Physiological characteristics of flax in response to salt and alkali stress. Journal of Plant Ecology, 40 (1):69-79. (in Chinese) |
|
郭瑞, 李峰, 周际, 李昊儒, 夏旭, 刘琪. 2016. 亚麻响应盐、碱胁迫的生理特征. 植物生态学报, 40 (1):69-79.
doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2015.0240 |
|
| [9] |
Huang Hui-qiong. 2021. It is imperative to curb global soil degradation. Ecological Economics, 37 (2):5-8. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.1016/S0921-8009(00)00279-2 URL |
| 黄慧琼. 2021. 遏止全球土壤退化刻不容缓. 生态经济, 37 (2):5-8. | |
| [10] | Kou Jiang-tao. 2020. Physiological response of exogenous 2,4-epbrassinolide to salt tolerance in alfalfa seedlings. Acta Agriculturae Boreali Sinica, 35 (6):133-140. (in Chinese) |
| 寇江涛. 2020. 外源2,4-表油菜素内酯诱导紫花苜蓿幼苗耐盐性的生理响应. 华北农学报, 35 (6):133-140. | |
| [11] |
Li Bin, Huang Jin, Wang Li, Li Jin, Liang Yue-yang, Chen Ji. 2020. Effects of environmental stress and related plant hormones on root hair development in rice. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 34 (4):287-299. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2020.9138 |
|
李斌, 黄进, 王丽, 李瑾, 梁越洋, 陈稷. 2020. 环境胁迫及相关植物激素在水稻根毛发育过程中的作用. 中国水稻科学, 34 (4):287-299.
doi: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2020.9138 |
|
| [12] | Li H T, Liu H, Gao X S, Zhang H X. 2009. Knock-out of arabidopsis AtNHX4 gene enhances tolerance to salt stress. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 82 (3):37-41. |
| [13] | Li Qiao-li. 2020. Regulation of salt tolerance in cucumber by exogenous brassinolide[M. D. Dissertation]. Lanzhou: Northwest Normal University. (in Chinese) |
| 李巧丽. 2020. 外源油菜素内酯对黄瓜耐盐性的调控[硕士论文]. 兰州: 西北师范大学. | |
| [14] | Li Yao. 2020. Physiological and molecular mechanism of cold tolerance in Brassica napus induced by 24-epicbrassinolide vinegar[M. D. Dissertation]. Lanzhou: Northwest Normal University. (in Chinese) |
| [ 李瑶. 2020. 2,4-表油菜素内酯诱导油菜耐寒性的生理及分子机制研究[硕士论文]. 兰州: 西北师范大学. | |
| [15] | Liao Jie, Ren Hui-min, Liu Can-kui, Qi Guo-ning. 2021. Advances in plant physiology and molecular mechanisms of calcium signaling pathway under saline-alkali stress. Molecular Plant Breeding, 19 (6):2041-2047. (in Chinese) |
| 廖婕, 任慧敏, 柳参奎, 亓果宁. 2021. 盐碱胁迫下植物生理和钙信号通路分子机制的研究进展. 分子植物育种, 19 (6):2041-2047. | |
| [16] | Liu Feng-zhi, Wang Hai-bo, Hu Cheng-zhi. 2021. Present situation of main fruit trees industry in China and development countermeasures during the 14th Five-Year Plan. China Fruits,(1):1-5. (in Chinese) |
| 刘凤之, 王海波, 胡成志. 2021. 我国主要果树产业现状及“十四五”发展对策. 中国果树,(1):1-5. | |
| [17] | Liu Yue-yue, Huang Xiao-xuan, Geng Yan-Qiu, Guo Li-ying, Jin Feng, Shao Xi-wen. 2020. Effects of salt-alkali stress on growth and key enzymes of nitrogen metabolism in rice seedlings. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 42 (5):493-501. (in Chinese) |
| 刘月月, 黄小萱, 耿艳秋, 郭丽颖, 金峰, 邵玺文. 2020. 苏打盐碱胁迫对水稻幼苗生长及氮代谢关键酶的影响. 吉林农业大学学报, 42 (5):493-501. | |
| [18] | Mao Qing-lian, Wang Sheng. 2020. Research on the trend of domestic saline-alkali land treatment. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 59 (S1):302-306. (in Chinese) |
| 毛庆莲, 王胜. 2020. 国内盐碱地治理趋势探究浅析. 湖北农业科学, 59 (S1):302-306. | |
| [19] |
Nawaz F, Naeem M, Zulfiqar B, Akram A, Ashraf M Y, Raheel M, Shabbir R N, Hussain R A, Anwar I, Aurangzaib M. 2017. Understanding brassinosteroid-regulated mechanisms to improve stress tolerance in plants:a critical review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24 (19):15959-15975.
doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-9163-6 URL |
| [20] | Ning Peng, Wang Fei, Xiao Yu, Huang Xiao-xia. 2021. Effects of exogenous ABA and salt stress on growth and physiological characteristics of Chlorophyta silvum. Journal of Jiangxi Agricultural University, 43 (2):287-295. (in Chinese) |
| 宁朋, 王菲, 肖雨, 黄晓霞. 2021. 外源ABA与盐胁迫对银边吊兰生长及生理特性的影响. 江西农业大学学报, 43 (2):287-295. | |
| [21] |
Roosta H R. 2011. Interaction between water alkalinity and nutrient solution pH on the vegetative growth,chlorophyll fluorescence and leaf Mg,Fe,Mn and Zn concentrations in lettuce. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 34 (5):717-731.
doi: 10.1080/01904167.2011.540687 URL |
| [22] |
Santi S, Schmidt W. 2009. Dissecting iron deficiency induced proton extrusion in Arabidopsis roots. New Phytologist, 183 (4):1072-1084.
doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.02908.x URL |
| [23] | Sha Guang-li, Hao Yu-jin, Wan Shu-wei, Shu Huai-rui. 2015. Progress in varieties and applications of apple rootstock. Deciduous Fruits, 47 (3):2-6. (in Chinese) |
| 沙广利, 郝玉金, 万述伟, 束怀瑞. 2015. 苹果砧木种类及应用进展. 落叶果树, 47 (3):2-6. | |
| [24] |
Su Q F, Zheng X D, Tian Y K, Wang C H. 2020. Exogenous brassinolide alleviates salt stress in Malus hupehensis rehd by regulating the transcription of NHX-type Na+(K+)/H+ antiporters. Frontiers in Plant Science, 11:38.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00038 URL |
| [25] |
Wani A S, Tahir I, Ahmad S S, Dar R A, Nisar S. 2017. Efficacy of 24-epibrassinolide in improving the nitrogen metabolism and antioxidant system in chickpea cultivars under cadmium and or NaCl stress. Scientia Horticulture, 225:48-55.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2017.06.063 URL |
| [26] | Wang Hou-chen, Liu Chong, Lü Liang-xiao, Wang Xue-shan, Lin Chuan-qing. 2020. Several issues that should be paid special attention to in the large-scale construction of apple gardens. Northwest Horticulture(Fruit Tree),(5):5-7. (in Chinese) |
| 王厚臣, 刘崇, 吕亮晓, 王学山, 林传清. 2020. 苹果规模化建园应特别关注的几个问题. 西北园艺(果树),(5):5-7. | |
| [27] | Wang Quan-zhen, Liu Qian, Gao Ya-ni, Liu Xu. 2017 Advances in plant responses to saline-alkali stress. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37 (16):5565-5577. (in Chinese) |
| 王佺珍, 刘倩, 高娅妮, 柳旭. 2017. 植物对盐碱胁迫的响应机制研究进展. 生态学报, 37 (16):5565-5577. | |
| [28] | Wang Xin-liang, Wang Jian, Jia Jing-jing, Tang Li-ping. 2020. Research progress in response mechanism of fruit trees to saline-alkali stress. Journal of Hebei Agricultural Sciences, 24 (5):63-67. (in Chinese) |
| 王新亮, 王健, 贾晶晶, 唐立平. 2020. 果树响应盐碱胁迫机理的研究进展. 河北农业科学, 24 (5):63-67. | |
| [29] | Wu Xiao-wei. 2015. Effect and effect of microbial fertilizer on amelioration of saline-alkali soil in Weibei region[M. D. Dissertation]. Lanzhou: Northwest University. (in Chinese) |
| 吴晓卫. 2015. 微生物菌肥改良渭北地区盐碱化土壤作用及效果研究[硕士论文]. 兰州: 西北大学. | |
| [30] | Xiong Jun-lan, Kong Hai-yan, Bai Xue, Tan Rui-yue, Xiong Youcai, Chen Hong-bin. 2013. Effects of brassinosteroids on plant drought tolerance and their regulatory mechanisms. Journal of Lanzhou University(Natural Science), 49 (5):658-665. (in Chinese) |
| 熊俊兰, 孔海燕, 白雪, 谭瑞玥, 熊友才, 陈宏彬. 2013. 油菜素甾族化合物对植物干旱适应性的影响及调控机理. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 49 (5):658-665. | |
| [31] | Yan Dao-liang, Zhu Xiang-long, Yang Qiao-ling, Yue Chun-lei. 2014. Effects of salt stress on clonal growth and sodium and potassium ion balance of Lentinus edodes. Zhejiang Forestry Science and Technology, 34 (2):1-4. (in Chinese) |
| 闫道良, 朱祥龙, 杨巧玲, 岳春雷. 2014. 盐胁迫对香菇草克隆生长及其钠、钾离子平衡的影响. 浙江林业科技, 34 (2):1-4. | |
| [32] |
Yang J Y, Zheng W, Tian Y, Wu Y, Zhou D W. 2011. Effects of various mixed salt-alkaline stresses on growth,photosynthesis and photosynthetic pigment concentrations of Medicago ruthenium seedlings. Photosynthetic, 49 (2):275-284.
doi: 10.1007/s11099-011-0037-8 URL |
| [33] |
Yang Y, Guo Y. 2018. Elucidating the molecular mechanisms mediating plant salt stress responses. New Phytologist, 217 (2):523-539.
doi: 10.1111/nph.14920 URL |
| [34] |
Yusuf M, Fariduddin Q, Khan T, Hayat S. 2017. Epibrassinolide reverses the stress generated by combination of excess aluminum and salt in two wheat cultivars through altered proline metabolism and antioxidants. South African Journal of Botany, 112:391-398.
doi: 10.1016/j.sajb.2017.06.034 URL |
| [35] | Yang Zhen, Wang Bao-shan. 2015. Status quo of soil resources and improvement and utilization countermeasures. Journal of Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 47 (4):125-130. (in Chinese) |
| 杨真, 王宝山. 2015. 渍土资源现状及改良利用对策. 山东农业科学, 47 (4):125-130. | |
| [36] | Zhao Huai-yu, Lin Hong-xuan. 2020. Molecular mechanism of plant response to saline-alkali stress. Soil and Crops, 9 (2):103-113. (in Chinese) |
| 赵怀玉, 林鸿宣. 2020. 植物响应盐碱胁迫的分子机制. 土壤与作物, 9 (2):103-113. | |
| [37] |
Zhao Q, Ren Y R, Wang Q J, Wang X F, You C X, Hao Y J. 2016. Ubiquitination-related MdBT scaffold proteins target a bHLH transcription factor for iron homeostasis. Plant Physiology, 172 (3):1973-1988.
doi: 10.1104/pp.16.01323 URL |
| [38] |
Zheng X D, Zhao Y, Shan D Q, Shi K, Wang L, Li Q T, Wang N, Zhou J Z, Yao J Z, Xue Y, Fang S, Chu J F, Guo Y. 2018. MdWRKY9 overexpression confers intensive dwarfing in the M 26 rootstock of apple by directly inhibiting brassinosteroid synthetase MdDWF4 expression. New Phytologist, 217 (3):1086-1098.
doi: 10.1111/nph.14891 URL |
| [39] |
Zheng X D, Li Y Q, Xi X L, Ma C Q, Sun Z J, Yang X Q, Li X Y, Tian Y K, Wang C H. 2020. Exogenous Strigolactones alleviate KCl stress by regulating photosynthesis,ROS migration and ion transport in Malus hupehensis Rehd. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 159:113-122.
doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.12.015 URL |
| [40] | Zhu Hui-qin, Xie Wan-bing. 2013. Discussion on improvement measures of saline-alkali land. West China Exploration Engineering, 25 (3):123-127. (in Chinese) |
| 朱慧秦, 谢万兵. 2013. 浅谈盐碱地的改良措施. 西部探矿工程, 25 (3):123-127. |
| [1] | YU Tingting, LI Huan, NING Yuansheng, SONG Jianfei, PENG Lulin, JIA Junqi, ZHANG Weiwei, and YANG Hongqiang. Genome-wide Identification of GRAS Gene Family in Apple and Expression Analysis of Its Response to Auxin [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 397-409. |
| [2] | HAN Xiaolei, ZHANG Caixia, LIU Kai, YANG An, YAN Jiadi, LI Wuxing, KANG Liqun, and CONG Peihua. A New Mid-ripening Apple Cultivar‘Zhongping Youlei’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 1-2. |
| [3] | ZHANG Xiaoming, YAN Guohua, ZHOU Yu, WANG Jing, DUAN Xuwei, WU Chuanbao, and ZHANG Kaichun. A New Sweet Cherry Rootstock Cultivar‘Jingchun 2’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 31-32. |
| [4] | TIAN Hongmei, LIU Juan, ZHANG Changkun, TAO Zhen, ZHANG Jian, and WANG Pengcheng, . A New Pumpkin Cultivar‘Wanzhen 6’for Melon Rootstock [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 127-128. |
| [5] | SUN Simiao, WANG Kun, GAO Yuan, WANG Dajiang, and LI Lianwen. A New Ornamental Crabapple Cultivar‘Zichen’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 267-268. |
| [6] | HAN Xiaolei, ZHANG Caixia, LIU Kai, YAN Jiadi, LI Wuxing, KANG Liqun, and CONG Peihua. A New Mid-ripening Apple Cultivar‘Pingyou 2’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S1): 1-2. |
| [7] | WANG Qiang, CONG Peihua, and LIU Xiaofeng. A New Late Ripening Apple Cultivar‘Huayou Tianwa’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S1): 3-4. |
| [8] | WANG Qiang, CONG Peihua, and LIU Xiaofeng. A New Mid-ripening Apple Cultivar‘Huayou Baomi’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S1): 5-6. |
| [9] | YANG Ling, CONG Peihua, WANG Qiang, LI Wuxing, and KANG Liqun. A New Mid-ripening Apple Cultivar‘Huafeng’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S1): 7-8. |
| [10] | LIU Chuanhe, HE Han, SHAO Xuehua, LAI Duo, KUANG Shizi, XIAO Weiqiang, LIU Yan. A New Pineapple Cultivar‘Yuetong’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(9): 2053-2054. |
| [11] | GAO Yanlong, WU Yuxia, ZHANG Zhongxing, WANG Shuangcheng, ZHANG Rui, ZHANG De, WANG Yanxiu. Bioinformatics Analysis of Apple ELO Gene Family and Its Expression Analysis Under Low Temperature Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1621-1636. |
| [12] | LIU Chaoyang, LIAO Zhichan, LU Xinxin, HE Yehua. Identification of CslD Gene Family in Pineapple and Functional Analysis of AcoCslD2a [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1650-1662. |
| [13] | NIE Xinmiao, LUAN Heng, FENG Gaili, WANG Chao, LI Yan, WEI Min. Effects of Silicon Nutrition and Grafting Rootstocks on Chilling Tolerance of Cucumber Seedlings [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1795-1804. |
| [14] | XIA Yan, HUANG Song, WU Xueli, LIU Yiqi, WANG Miaomiao, SONG Chunhui, BAI Tuanhui, SONG Shangwei, PANG Hongguang, JIAO Jian, ZHENG Xianbo. Identification and Analysis of Apple Viruses Diseases Based on Virome Sequencing Technology [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1415-1428. |
| [15] | LIU Zhaoxia, ZHANG Xin, WANG Lu, MA Yuting, CHEN Qian, ZHU Zhanling, GE Shunfeng, JIANG Yuanmao. Effects of Fertilizer Hole Application Sites on Fine Root Growth,15N Absorption and Utilization,Yield and Quality of Apple Trees [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1545-1556. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd