
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2022, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (8): 1673-1688.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0760
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
GUO Yan, ZHANG Shuhang, LI Ying, ZHANG Xinfang, WANG Yingjie, WANG Guangpeng*( )
)
Received:2022-04-19
Revised:2022-07-04
Online:2022-08-25
Published:2022-09-05
Contact:
WANG Guangpeng
E-mail:wangguangpeng430@163.com
CLC Number:
GUO Yan, ZHANG Shuhang, LI Ying, ZHANG Xinfang, WANG Yingjie, WANG Guangpeng. Diversity Analysis of Leaves Phenotypic Traits of Yanshan Chestnut[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1673-1688.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0760
| 序号 No. | 来源 Source | 名称 Name | 类型 Type | 序号 No. | 来源 Source | 名称 Name | 类型 Type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 昌黎Changli | 14-39 | A | 76 | 青龙Qinglong | 下庄4号Xiazhuang 4 | C | |
| 2 | 2-84 | A | 77 | 凤2 Feng 2 | C | |||
| 3 | D 5-71 | A | 78 | 去暑红-1 Qushuhong-1 | B | |||
| 4 | X 12-55 | A | 79 | 去暑红-2 Qushuhong-2 | B | |||
| 5 | X 12 | A | 80 | 白露Bailu | B | |||
| 6 | 何家坟5 Hejiafen 5 | A | 81 | 燕秋 Yanqiu | B | |||
| 7 | M 17-21 | A | 82 | YL-1 | B | |||
| 8 | 波叶栗Boyeli | B | 83 | 迁西Qianxi | 早3113 Zao 3113 | B | ||
| 9 | 三色栗Sanseli | B | 84 | 迁西壮栗Qianxi Zhuangli | B | |||
| 10 | M 18-16 | A | 85 | 迁西早红Qianxi Zaohong | B | |||
| 11 | 1209 | A | 86 | 石场子1-1 Shichangzi 1-1 | C | |||
| 12 | D 5-50 | A | 87 | 变异燕奎Bianyi Yankui | B | |||
| 13 | 园门实生Yuanmen Shisheng | A | 88 | 西寨2号Xizhai 2 | A | |||
| 14 | H 7-5 | A | 89 | 西寨1号Xizhai 1 | A | |||
| 15 | H 2-4 | A | 90 | 侯2 Hou 2 | A | |||
| 16 | X 49-70 | A | 91 | 贾古11Jiagu 1 | A | |||
| 17 | D 6-87 | A | 92 | 干2-2 Gan 2-2 | A | |||
| 18 | 早2 Zao 2 | B | 93 | 西变1 Xibian 1 | B | |||
| 19 | 明丰2号Mingfeng 2 | B | 94 | 石场子2-2 Shichangzi 2-2 | C | |||
| 20 | 早3 Zao 3 | B | 95 | 杨家峪13 Yangjiayu 13 | C | |||
| 21 | H 7-1 | A | 96 | 杨家峪5号Yangjiayu 5 | C | |||
| 22 | M替码实生 Tima Shisheng M | A | 97 | 牛1 Niu 1 | C | |||
| 23 | 南垂5号Nanchui 5 | B | 98 | 杨家峪1号Yangjiayu 1 | C | |||
| 24 | 848 | A | 99 | 长南庄2号Changnanzhuang 2 | C | |||
| 25 | 早1 Zao 1 | B | 100 | 杨家峪1-6 Yangjiayu 1-6 | C | |||
| 序号 No. | 来源 Source | 名称 Name | 类型 Type | 序号 No. | 来源 Source | 名称 Name | 类型 Type | |
| 26 | 昌黎Changli | 冀栗1号Jili 1 | B | 101 | 迁西Qianxi | 周家峪6号Zhoujiayu 6 | C | |
| 27 | 燕栗1号Yanli 1 | B | 102 | 大36 Da 36 | B | |||
| 28 | 宽城Kuancheng | 榆树沟1Yushugou 1 | C | 103 | 替码珍珠Tima Zhenzhu | B | ||
| 29 | 大桑园1号Dasangyuan 1 | C | 104 | 燕奎Yankui | B | |||
| 30 | 金1 Jin 1 | C | 105 | 燕山早丰Yanshan Zaofeng | B | |||
| 31 | 金2 Jin 2 | C | 106 | 燕光 Yanguang | B | |||
| 32 | 屈家早Qujiazao | A | 107 | 燕山短枝Yanshan Duanzhi | B | |||
| 33 | 崔1 Cui 1 | C | 108 | 迁安Qianan | 迁早2 Qianzao 2 | B | ||
| 34 | 艾峪口Aiyukou | C | 109 | 桑6 Sang 6 | C | |||
| 35 | 熊84 Xiong 84 | B | 110 | 桑1 Sang 1 | C | |||
| 36 | 塌山1号Tashan 1 | C | 111 | 迁早1 Qianzao 1 | B | |||
| 37 | 岔3 Cha 3 | C | 112 | 遵化Zunhua | 短刺大青Duanci Daqing | B | ||
| 38 | 浡1 Bo 1 | B | 113 | 遵玉Zunyu | B | |||
| 39 | 榆树沟2 Yushugou 2 | C | 114 | 西沟1 Xigou 1 | B | |||
| 40 | 燕宽Yankuan | B | 115 | 遵化短刺Zunhua Duanci | B | |||
| 41 | 下六Xialiu | C | 116 | 小官10 Xiaoguan 10 | B | |||
| 42 | 毛栗Maoli | B | 117 | 紫珀Zipo | B | |||
| 43 | 大板红Dabanhong | B | 118 | 遵古12 Zungu 12 | B | |||
| 44 | 燕金Yanjin | B | 119 | 达1-3 Da 1-3 | B | |||
| 45 | 兴隆Xinglong | 东优1号Dongyou 1 | C | 120 | 关堂64 Guantang 64 | C | ||
| 46 | 东优2号Dongyou 2 | C | 121 | 东陵明珠Dongling Mingzhu | B | |||
| 47 | 桥7 Qiao 7 | C | 122 | 塔54 Ta 54 | A | |||
| 48 | 兴隆短刺Xinglong Duanci | B | 123 | 东沟峪39 Donggouyu 39 | C | |||
| 49 | 晚早5 Wanzao 5 | B | 124 | 塔14 Ta 14 | C | |||
| 50 | 大31 Da 31 | B | 125 | 燕晶Yanjing | B | |||
| 51 | 陈中熟Chenzhongshu | C | 126 | 抚宁Funing | 抚古6 Fugu 6 | C | ||
| 52 | XL-001 | C | 127 | 抚古3 Fugu 3 | C | |||
| 53 | XL-002 | C | 128 | 抚宁薄皮Funing Baopi | B | |||
| 54 | 沙坡峪3号Shapoyu 3 | C | 129 | 燕明 Yanming | B | |||
| 55 | 龙湾1号Longwan 1 | A | 130 | 密云Miyun | 密古3 Migu 3 | C | ||
| 56 | 龙湾5号Longwan 5 | A | 131 | 密古1 Migu 1 | C | |||
| 57 | 大录洞Daludong | C | 132 | 密W1 MiW 1 | C | |||
| 58 | 赵杖子11 Zhaozhangzi 11 | C | 133 | 密丰1 Mifeng 1 | C | |||
| 59 | 沙坡峪1号Shapoyu 1 | C | 134 | 密古5 Migu 5 | C | |||
| 60 | 南天门乡Nantian Menxiang | C | 135 | 密丰2 Mifeng 2 | C | |||
| 61 | 大兰口Dalankou | C | 136 | 密张1 Mizhang 1 | C | |||
| 62 | 徐玉明1 Xuyuming 1 | C | 137 | 密大粒1 Midali 1 | C | |||
| 63 | 左贵生Zuoguisheng | C | 138 | 密Z-2 MiZ-2 | C | |||
| 64 | 陆南优1 Lunanyou 1 | C | 139 | 怀柔Huairou | 怀丰Huaifeng | B | ||
| 65 | 牛4 Niu 4 | C | 140 | 黑8 Hei 8 | B | |||
| 66 | 燕兴Yanxing | B | 141 | 短花Duanhua | B | |||
| 67 | 青龙Qinglong | 燕宝 Yanbao | B | 142 | 怀黄Huaihuang | B | ||
| 68 | YZ-1 | B | 143 | 京暑红Jingshuhong | B | |||
| 69 | 燕丽Yanli | B | 144 | 怀九Huaijiu | B | |||
| 70 | 白露母Bailumu | B | 145 | 北京8号Beijing 8 | B | |||
| 71 | 大青裂Daqinglie | B | 146 | 燕丰Yanfeng | B | |||
| 72 | 去暑红Qushuhong | B | 147 | 昌平Changpin | 燕平Yanping | B | ||
| 73 | 白底Baidi | B | 148 | 燕昌Yanchang | B | |||
| 74 | 青实Qingshi | B | 149 | 燕红Yanhong | B | |||
| 75 | 上52 Shang 52 | C |
Table 1 Type,name,source and number of 149 resources in Yanshan chestnut
| 序号 No. | 来源 Source | 名称 Name | 类型 Type | 序号 No. | 来源 Source | 名称 Name | 类型 Type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 昌黎Changli | 14-39 | A | 76 | 青龙Qinglong | 下庄4号Xiazhuang 4 | C | |
| 2 | 2-84 | A | 77 | 凤2 Feng 2 | C | |||
| 3 | D 5-71 | A | 78 | 去暑红-1 Qushuhong-1 | B | |||
| 4 | X 12-55 | A | 79 | 去暑红-2 Qushuhong-2 | B | |||
| 5 | X 12 | A | 80 | 白露Bailu | B | |||
| 6 | 何家坟5 Hejiafen 5 | A | 81 | 燕秋 Yanqiu | B | |||
| 7 | M 17-21 | A | 82 | YL-1 | B | |||
| 8 | 波叶栗Boyeli | B | 83 | 迁西Qianxi | 早3113 Zao 3113 | B | ||
| 9 | 三色栗Sanseli | B | 84 | 迁西壮栗Qianxi Zhuangli | B | |||
| 10 | M 18-16 | A | 85 | 迁西早红Qianxi Zaohong | B | |||
| 11 | 1209 | A | 86 | 石场子1-1 Shichangzi 1-1 | C | |||
| 12 | D 5-50 | A | 87 | 变异燕奎Bianyi Yankui | B | |||
| 13 | 园门实生Yuanmen Shisheng | A | 88 | 西寨2号Xizhai 2 | A | |||
| 14 | H 7-5 | A | 89 | 西寨1号Xizhai 1 | A | |||
| 15 | H 2-4 | A | 90 | 侯2 Hou 2 | A | |||
| 16 | X 49-70 | A | 91 | 贾古11Jiagu 1 | A | |||
| 17 | D 6-87 | A | 92 | 干2-2 Gan 2-2 | A | |||
| 18 | 早2 Zao 2 | B | 93 | 西变1 Xibian 1 | B | |||
| 19 | 明丰2号Mingfeng 2 | B | 94 | 石场子2-2 Shichangzi 2-2 | C | |||
| 20 | 早3 Zao 3 | B | 95 | 杨家峪13 Yangjiayu 13 | C | |||
| 21 | H 7-1 | A | 96 | 杨家峪5号Yangjiayu 5 | C | |||
| 22 | M替码实生 Tima Shisheng M | A | 97 | 牛1 Niu 1 | C | |||
| 23 | 南垂5号Nanchui 5 | B | 98 | 杨家峪1号Yangjiayu 1 | C | |||
| 24 | 848 | A | 99 | 长南庄2号Changnanzhuang 2 | C | |||
| 25 | 早1 Zao 1 | B | 100 | 杨家峪1-6 Yangjiayu 1-6 | C | |||
| 序号 No. | 来源 Source | 名称 Name | 类型 Type | 序号 No. | 来源 Source | 名称 Name | 类型 Type | |
| 26 | 昌黎Changli | 冀栗1号Jili 1 | B | 101 | 迁西Qianxi | 周家峪6号Zhoujiayu 6 | C | |
| 27 | 燕栗1号Yanli 1 | B | 102 | 大36 Da 36 | B | |||
| 28 | 宽城Kuancheng | 榆树沟1Yushugou 1 | C | 103 | 替码珍珠Tima Zhenzhu | B | ||
| 29 | 大桑园1号Dasangyuan 1 | C | 104 | 燕奎Yankui | B | |||
| 30 | 金1 Jin 1 | C | 105 | 燕山早丰Yanshan Zaofeng | B | |||
| 31 | 金2 Jin 2 | C | 106 | 燕光 Yanguang | B | |||
| 32 | 屈家早Qujiazao | A | 107 | 燕山短枝Yanshan Duanzhi | B | |||
| 33 | 崔1 Cui 1 | C | 108 | 迁安Qianan | 迁早2 Qianzao 2 | B | ||
| 34 | 艾峪口Aiyukou | C | 109 | 桑6 Sang 6 | C | |||
| 35 | 熊84 Xiong 84 | B | 110 | 桑1 Sang 1 | C | |||
| 36 | 塌山1号Tashan 1 | C | 111 | 迁早1 Qianzao 1 | B | |||
| 37 | 岔3 Cha 3 | C | 112 | 遵化Zunhua | 短刺大青Duanci Daqing | B | ||
| 38 | 浡1 Bo 1 | B | 113 | 遵玉Zunyu | B | |||
| 39 | 榆树沟2 Yushugou 2 | C | 114 | 西沟1 Xigou 1 | B | |||
| 40 | 燕宽Yankuan | B | 115 | 遵化短刺Zunhua Duanci | B | |||
| 41 | 下六Xialiu | C | 116 | 小官10 Xiaoguan 10 | B | |||
| 42 | 毛栗Maoli | B | 117 | 紫珀Zipo | B | |||
| 43 | 大板红Dabanhong | B | 118 | 遵古12 Zungu 12 | B | |||
| 44 | 燕金Yanjin | B | 119 | 达1-3 Da 1-3 | B | |||
| 45 | 兴隆Xinglong | 东优1号Dongyou 1 | C | 120 | 关堂64 Guantang 64 | C | ||
| 46 | 东优2号Dongyou 2 | C | 121 | 东陵明珠Dongling Mingzhu | B | |||
| 47 | 桥7 Qiao 7 | C | 122 | 塔54 Ta 54 | A | |||
| 48 | 兴隆短刺Xinglong Duanci | B | 123 | 东沟峪39 Donggouyu 39 | C | |||
| 49 | 晚早5 Wanzao 5 | B | 124 | 塔14 Ta 14 | C | |||
| 50 | 大31 Da 31 | B | 125 | 燕晶Yanjing | B | |||
| 51 | 陈中熟Chenzhongshu | C | 126 | 抚宁Funing | 抚古6 Fugu 6 | C | ||
| 52 | XL-001 | C | 127 | 抚古3 Fugu 3 | C | |||
| 53 | XL-002 | C | 128 | 抚宁薄皮Funing Baopi | B | |||
| 54 | 沙坡峪3号Shapoyu 3 | C | 129 | 燕明 Yanming | B | |||
| 55 | 龙湾1号Longwan 1 | A | 130 | 密云Miyun | 密古3 Migu 3 | C | ||
| 56 | 龙湾5号Longwan 5 | A | 131 | 密古1 Migu 1 | C | |||
| 57 | 大录洞Daludong | C | 132 | 密W1 MiW 1 | C | |||
| 58 | 赵杖子11 Zhaozhangzi 11 | C | 133 | 密丰1 Mifeng 1 | C | |||
| 59 | 沙坡峪1号Shapoyu 1 | C | 134 | 密古5 Migu 5 | C | |||
| 60 | 南天门乡Nantian Menxiang | C | 135 | 密丰2 Mifeng 2 | C | |||
| 61 | 大兰口Dalankou | C | 136 | 密张1 Mizhang 1 | C | |||
| 62 | 徐玉明1 Xuyuming 1 | C | 137 | 密大粒1 Midali 1 | C | |||
| 63 | 左贵生Zuoguisheng | C | 138 | 密Z-2 MiZ-2 | C | |||
| 64 | 陆南优1 Lunanyou 1 | C | 139 | 怀柔Huairou | 怀丰Huaifeng | B | ||
| 65 | 牛4 Niu 4 | C | 140 | 黑8 Hei 8 | B | |||
| 66 | 燕兴Yanxing | B | 141 | 短花Duanhua | B | |||
| 67 | 青龙Qinglong | 燕宝 Yanbao | B | 142 | 怀黄Huaihuang | B | ||
| 68 | YZ-1 | B | 143 | 京暑红Jingshuhong | B | |||
| 69 | 燕丽Yanli | B | 144 | 怀九Huaijiu | B | |||
| 70 | 白露母Bailumu | B | 145 | 北京8号Beijing 8 | B | |||
| 71 | 大青裂Daqinglie | B | 146 | 燕丰Yanfeng | B | |||
| 72 | 去暑红Qushuhong | B | 147 | 昌平Changpin | 燕平Yanping | B | ||
| 73 | 白底Baidi | B | 148 | 燕昌Yanchang | B | |||
| 74 | 青实Qingshi | B | 149 | 燕红Yanhong | B | |||
| 75 | 上52 Shang 52 | C |
| 质量性状 Quality trait | 赋值及性状特征描述Description and assignment of traits | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 7 | |
| 叶片形状 Leaf shape(LS) | 椭圆形 Oval | 长椭圆形 Long oval | 披针形 Lanceolate | 卵形 Egg shape | 倒卵形 Obovate | |
| 先端形状 Shape of leaf apex(LAS) | 急尖 Acute | 渐尖 Taper | ||||
| 叶基形状 Shape of leaf base(LBS) | 楔形 Cuneiform | 钝形 Obtuse | 心形 Heart-shaped | |||
| 叶缘特征 Leaf margin character(LMC) | 具短尖 Leaf margin with short apex | 具锯齿 Leaf margin with sawtooth | ||||
| 叶缘锯齿方向 Leaf margin sawtooth direction (LM) | 外向 Outward | 直向 Vertical | 内向 Inward | |||
Table 2 The description and assignment of leaf quality traits of chestnut
| 质量性状 Quality trait | 赋值及性状特征描述Description and assignment of traits | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 7 | |
| 叶片形状 Leaf shape(LS) | 椭圆形 Oval | 长椭圆形 Long oval | 披针形 Lanceolate | 卵形 Egg shape | 倒卵形 Obovate | |
| 先端形状 Shape of leaf apex(LAS) | 急尖 Acute | 渐尖 Taper | ||||
| 叶基形状 Shape of leaf base(LBS) | 楔形 Cuneiform | 钝形 Obtuse | 心形 Heart-shaped | |||
| 叶缘特征 Leaf margin character(LMC) | 具短尖 Leaf margin with short apex | 具锯齿 Leaf margin with sawtooth | ||||
| 叶缘锯齿方向 Leaf margin sawtooth direction (LM) | 外向 Outward | 直向 Vertical | 内向 Inward | |||
| 质量性状 Quality trait | 赋值频率/% Frequency of assignment | 变异系数/% CV | 多样性指数 H’ | 群体间F F among population | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | ||||
| 叶片形状LS | 34.90 | 61.07 | 2.68 | 1.34 | 0 | 34.44 | 0.82 | 1.21 | ||
| 先端形状LAS | 4.70 | 95.30 | 10.87 | 0.19 | 1.31 | |||||
| 叶基形状LBS | 26.17 | 70.47 | 3.36 | 27.93 | 0.71 | 1.46 | ||||
| 叶缘特征LMC | 0 | 100.00 | 0 | 0 | / | |||||
| 叶缘锯齿方向LM | 88.59 | 6.71 | 4.70 | 28.91 | 0.43 | 1.25 | ||||
| 平均Mean | 20.43 | 0.43 | / | |||||||
Table 3 Frequency distribution,diversity and variance analysis among population of leaf quality trait in Yanshan chestnut
| 质量性状 Quality trait | 赋值频率/% Frequency of assignment | 变异系数/% CV | 多样性指数 H’ | 群体间F F among population | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | ||||
| 叶片形状LS | 34.90 | 61.07 | 2.68 | 1.34 | 0 | 34.44 | 0.82 | 1.21 | ||
| 先端形状LAS | 4.70 | 95.30 | 10.87 | 0.19 | 1.31 | |||||
| 叶基形状LBS | 26.17 | 70.47 | 3.36 | 27.93 | 0.71 | 1.46 | ||||
| 叶缘特征LMC | 0 | 100.00 | 0 | 0 | / | |||||
| 叶缘锯齿方向LM | 88.59 | 6.71 | 4.70 | 28.91 | 0.43 | 1.25 | ||||
| 平均Mean | 20.43 | 0.43 | / | |||||||
| 数量性状 Quantitative trait | 均值 ± 标准差 Mean ± SD | 中位数 Median | 极小值 Min | 极大值 Max | 变异系数/% CV | 多样性 指数H’ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶柄长/mm Petiole length(PL) | 24.36 ± 2.91 | 24.56 | 16.75 | 30.78 | 11.96 | 2.09 |
| 叶片长/mm Leaf length(LL) | 179.38 ± 13.13 | 178.94 | 142.41 | 231.21 | 7.32 | 2.05 |
| 叶片宽/mm Leaf width(LW) | 71.94 ± 5.45 | 72.22 | 59.87 | 85.80 | 7.57 | 2.07 |
| 叶片长/宽Leaf length/width(L/W) | 2.51 ± 0.17 | 2.48 | 2.10 | 3.23 | 6.82 | 1.97 |
| 叶片面积/mm2 Leaf area(LA) | 8 567.87 ± 1 121.56 | 8 611.46 | 5 862.31 | 12 276.14 | 13.09 | 2.03 |
| 锯齿深度/mm Sawtooth depth(SWD) | 3.62 ± 1.02 | 3.57 | 1.13 | 6.63 | 28.32 | 2.08 |
| 锯齿与叶缘间角度 The angle between sawtooth and leaf margin(LSA) | 76.7 ± 9.58 | 76.99 | 54.44 | 97.03 | 12.49 | 2.03 |
| 叶脉间距/mm Spacing length of veins(VSL) | 1.13 ± 0.15 | 1.11 | 0.72 | 1.55 | 13.31 | 2.04 |
| 叶厚/μm Leaf thickness(LT) | 181.42 ± 16.25 | 179.88 | 143.52 | 240.14 | 8.96 | 2.06 |
| 上表皮细胞厚/μm Thickness of upper epidermis cell(UT) | 25.42 ± 2.88 | 25.20 | 17.22 | 36.05 | 11.32 | 2.03 |
| 上表皮细胞宽/μm Width of upper epidermis cell(UW) | 21.14 ± 2.06 | 21.12 | 16.02 | 29.43 | 9.76 | 2.00 |
| 栅栏组织厚度/μm Thickness of palisade tissue(PT) | 77.93 ± 8.86 | 77.32 | 59.96 | 106.27 | 11.37 | 2.06 |
| 海绵组织厚度/μm Thickness of spongy tissue(ST) | 60.78 ± 8.96 | 60.35 | 39.25 | 87.65 | 14.75 | 2.07 |
| 栅海比Thickness of palisade tissue/thickness of spongy tissue(PS) | 1.32 ± 0.20 | 1.30 | 0.94 | 2.11 | 15.08 | 2.00 |
| 下表皮细胞厚度/μm Thickness of lower epidermis cell(LET) | 5.65 ± 0.73 | 5.70 | 3.78 | 7.33 | 12.94 | 2.04 |
| 叶片结构紧密度/% Tightness of leaf tissue(LST) | 43.02 ± 3.07 | 43.16 | 34.38 | 54.57 | 7.13 | 2.02 |
| 叶片结构疏松度/% Looseness of leaf tissue(LL) | 33.36 ± 3.21 | 33.30 | 26.12 | 41.96 | 9.63 | 2.09 |
| 气孔长/μm Stoma length(SL) | 22.62 ± 1.06 | 22.55 | 19.61 | 25.26 | 4.69 | 2.06 |
| 气孔宽/μm Stoma width(SW) | 21.68 ± 0.98 | 21.70 | 17.96 | 24.37 | 4.52 | 2.00 |
| 气孔密度/(个 · mm-2)Stoma density(SD) | 948.69 ± 125.89 | 938.21 | 668.43 | 1 389.56 | 13.27 | 2.00 |
| 比叶质量/(g × 10-3 ·cm-2)Leaf mass per area(LM) | 10.61 ± 1.49 | 10.67 | 6.52 | 14.82 | 14.00 | 2.06 |
| 叶绿素含量/(mg · g-1)Chlorophyll content (CP) | 4.11 ± 0.31 | 4.11 | 3.40 | 4.93 | 7.42 | 2.08 |
| 保水力/% The water retention capacity(WRC) | 48.39 ± 7.83 | 48.84 | 19.48 | 72.80 | 16.18 | 2.02 |
| 平均Mean | 11.39 | 2.04 |
Table 4 Variation of leaf quantitative traits in Yanshan chestnut
| 数量性状 Quantitative trait | 均值 ± 标准差 Mean ± SD | 中位数 Median | 极小值 Min | 极大值 Max | 变异系数/% CV | 多样性 指数H’ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶柄长/mm Petiole length(PL) | 24.36 ± 2.91 | 24.56 | 16.75 | 30.78 | 11.96 | 2.09 |
| 叶片长/mm Leaf length(LL) | 179.38 ± 13.13 | 178.94 | 142.41 | 231.21 | 7.32 | 2.05 |
| 叶片宽/mm Leaf width(LW) | 71.94 ± 5.45 | 72.22 | 59.87 | 85.80 | 7.57 | 2.07 |
| 叶片长/宽Leaf length/width(L/W) | 2.51 ± 0.17 | 2.48 | 2.10 | 3.23 | 6.82 | 1.97 |
| 叶片面积/mm2 Leaf area(LA) | 8 567.87 ± 1 121.56 | 8 611.46 | 5 862.31 | 12 276.14 | 13.09 | 2.03 |
| 锯齿深度/mm Sawtooth depth(SWD) | 3.62 ± 1.02 | 3.57 | 1.13 | 6.63 | 28.32 | 2.08 |
| 锯齿与叶缘间角度 The angle between sawtooth and leaf margin(LSA) | 76.7 ± 9.58 | 76.99 | 54.44 | 97.03 | 12.49 | 2.03 |
| 叶脉间距/mm Spacing length of veins(VSL) | 1.13 ± 0.15 | 1.11 | 0.72 | 1.55 | 13.31 | 2.04 |
| 叶厚/μm Leaf thickness(LT) | 181.42 ± 16.25 | 179.88 | 143.52 | 240.14 | 8.96 | 2.06 |
| 上表皮细胞厚/μm Thickness of upper epidermis cell(UT) | 25.42 ± 2.88 | 25.20 | 17.22 | 36.05 | 11.32 | 2.03 |
| 上表皮细胞宽/μm Width of upper epidermis cell(UW) | 21.14 ± 2.06 | 21.12 | 16.02 | 29.43 | 9.76 | 2.00 |
| 栅栏组织厚度/μm Thickness of palisade tissue(PT) | 77.93 ± 8.86 | 77.32 | 59.96 | 106.27 | 11.37 | 2.06 |
| 海绵组织厚度/μm Thickness of spongy tissue(ST) | 60.78 ± 8.96 | 60.35 | 39.25 | 87.65 | 14.75 | 2.07 |
| 栅海比Thickness of palisade tissue/thickness of spongy tissue(PS) | 1.32 ± 0.20 | 1.30 | 0.94 | 2.11 | 15.08 | 2.00 |
| 下表皮细胞厚度/μm Thickness of lower epidermis cell(LET) | 5.65 ± 0.73 | 5.70 | 3.78 | 7.33 | 12.94 | 2.04 |
| 叶片结构紧密度/% Tightness of leaf tissue(LST) | 43.02 ± 3.07 | 43.16 | 34.38 | 54.57 | 7.13 | 2.02 |
| 叶片结构疏松度/% Looseness of leaf tissue(LL) | 33.36 ± 3.21 | 33.30 | 26.12 | 41.96 | 9.63 | 2.09 |
| 气孔长/μm Stoma length(SL) | 22.62 ± 1.06 | 22.55 | 19.61 | 25.26 | 4.69 | 2.06 |
| 气孔宽/μm Stoma width(SW) | 21.68 ± 0.98 | 21.70 | 17.96 | 24.37 | 4.52 | 2.00 |
| 气孔密度/(个 · mm-2)Stoma density(SD) | 948.69 ± 125.89 | 938.21 | 668.43 | 1 389.56 | 13.27 | 2.00 |
| 比叶质量/(g × 10-3 ·cm-2)Leaf mass per area(LM) | 10.61 ± 1.49 | 10.67 | 6.52 | 14.82 | 14.00 | 2.06 |
| 叶绿素含量/(mg · g-1)Chlorophyll content (CP) | 4.11 ± 0.31 | 4.11 | 3.40 | 4.93 | 7.42 | 2.08 |
| 保水力/% The water retention capacity(WRC) | 48.39 ± 7.83 | 48.84 | 19.48 | 72.80 | 16.18 | 2.02 |
| 平均Mean | 11.39 | 2.04 |

Fig. 1 Leaf thickness difference and anatomical structure of chestnut Red arrow indicates the cells infected by Plasmodiophora brassicae,the circular microscopic observation image is enlarged for the area marked with ※.
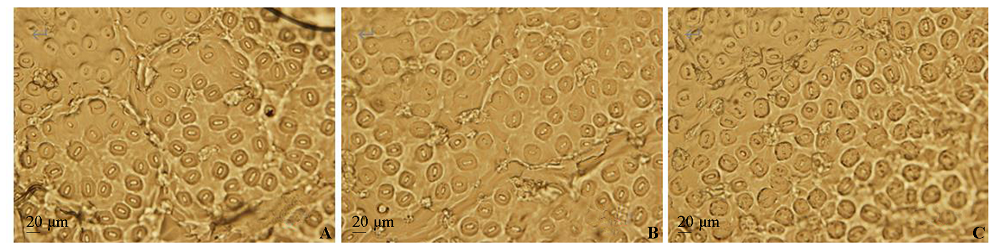
Fig. 2 Difference of stomatal density in lower epidermis of chestnut leaves A:Small(< 800 per mm2);B:Medium(800-1 000 per mm2);C:Large(> 1 000 per mm2).
| 数量性状 Quantitative trait | 方差分量Variance component | VST/% 表型分化系数 Phenotype differentition coefficient | F | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 群体间 Among populations | 群体内 Within populations | 随机误差 Random errors | 群体间 Among populations | 群体内 Within populations | |||
| 叶柄长/mm PL | 360.86 | 9690.56 | 7798.85 | 3.59 | 0.50 | 6.24** | |
| 叶片长/ mm LL | 20908.78 | 223721.98 | 259565.60 | 8.55 | 1.25 | 4.33** | |
| 叶片宽/ mm LW | 3250.06 | 36292.38 | 38088.95 | 8.22 | 1.20 | 4.79** | |
| 叶片长/宽L/W | 2.40 | 28.30 | 33.57 | 7.81 | 1.14 | 4.23** | |
| 叶片面积/mm2 LA | 142227019.94 | 1715222268.65 | 2055244859.42 | 7.66 | 1.11 | 4.19** | |
| 锯齿深度SWD | 26.16 | 440.05 | 216.35 | 5.61 | 0.82 | 4.39** | |
| 锯齿与叶缘间角度LSA | 2168.82 | 38550.73 | 11197.92 | 5.33 | 0.78 | 7.43** | |
| 叶脉间距/ mm VSL | 0.30 | 9.73 | 8.42 | 2.94 | 0.42 | 2.50** | |
| 数量性状 Quantitative trait | 方差分量Variance component | VST/% 表型分化系数 Phenotype differentition coefficient | F | ||||
| 群体间 Among populations | 群体内 Within populations | 随机误差 Random errors | 群体间 Among populations | 群体内 Within populations | |||
| 叶厚/μm LT | 10 194.91 | 103 144.17 | 90 269.85 | 9.00 | 1.84** | 2.54** | |
| 上表皮细胞厚度/μm UT | 290.47 | 3 155.57 | 2 945.68 | 8.43 | 1.22 | 1.78** | |
| 上表皮细胞宽度/μm UW | 135.06 | 1 507.29 | 2 263.51 | 8.22 | 1.20 | 1.48** | |
| 栅栏组织厚度/μm PT | 3 727.90 | 27 865.14 | 23 014.66 | 11.80 | 2.28** | 2.69** | |
| 海绵组织厚度/μm ST | 3 097.94 | 32 742.53 | 35 006.34 | 8.64 | 1.29 | 2.08** | |
| 栅海比PS | 1.12 | 16.69 | 18.56 | 6.27 | 0.91 | 2.00** | |
| 下表皮细胞厚度/μm LET | 15.13 | 211.61 | 295.57 | 6.67 | 0.99 | 1.59** | |
| 叶片结构紧密度/% LST | 386.64 | 3 451.47 | 4 484.62 | 10.07 | 1.72* | 1.71** | |
| 叶片结构疏松度/% LL | 130.90 | 4 518.32 | 5 460.81 | 2.82 | 0.40 | 1.84** | |
| 气孔长/μm SL | 47.24 | 534.97 | 570.79 | 8.11 | 1.02 | 2.83** | |
| 气孔宽/μm SW | 39.50 | 439.92 | 570.35 | 8.24 | 1.06 | 2.33** | |
| 气孔密度/(个 · mm-2)SD | 1 187 576.14 | 7 039 419.69 | 5 362 440.33 | 14.44 | 2.16** | 3.96** | |
| 比叶质量/(g × 10-3 ·cm-2) LM | 7.81 | 90.39 | 49.12 | 7.95 | 1.15 | 9.24** | |
| 叶绿素含量/(mg · g-1)CP | 98.61 | 881.42 | 342.22 | 10.06 | 1.54 | 5.56** | |
| 保水力/% WRC | 2 459.43 | 24 745.84 | 7 159.81 | 9.04 | 1.37 | 7.46** | |
| 平均 | 6 237 475.92 | 74 903 205.54 | 89 612 898.32 | 7.80 | / | / | |
Table 5 Differentiation coefficient and variance analysis of quantitative traits of Yanshan chestnut leaves
| 数量性状 Quantitative trait | 方差分量Variance component | VST/% 表型分化系数 Phenotype differentition coefficient | F | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 群体间 Among populations | 群体内 Within populations | 随机误差 Random errors | 群体间 Among populations | 群体内 Within populations | |||
| 叶柄长/mm PL | 360.86 | 9690.56 | 7798.85 | 3.59 | 0.50 | 6.24** | |
| 叶片长/ mm LL | 20908.78 | 223721.98 | 259565.60 | 8.55 | 1.25 | 4.33** | |
| 叶片宽/ mm LW | 3250.06 | 36292.38 | 38088.95 | 8.22 | 1.20 | 4.79** | |
| 叶片长/宽L/W | 2.40 | 28.30 | 33.57 | 7.81 | 1.14 | 4.23** | |
| 叶片面积/mm2 LA | 142227019.94 | 1715222268.65 | 2055244859.42 | 7.66 | 1.11 | 4.19** | |
| 锯齿深度SWD | 26.16 | 440.05 | 216.35 | 5.61 | 0.82 | 4.39** | |
| 锯齿与叶缘间角度LSA | 2168.82 | 38550.73 | 11197.92 | 5.33 | 0.78 | 7.43** | |
| 叶脉间距/ mm VSL | 0.30 | 9.73 | 8.42 | 2.94 | 0.42 | 2.50** | |
| 数量性状 Quantitative trait | 方差分量Variance component | VST/% 表型分化系数 Phenotype differentition coefficient | F | ||||
| 群体间 Among populations | 群体内 Within populations | 随机误差 Random errors | 群体间 Among populations | 群体内 Within populations | |||
| 叶厚/μm LT | 10 194.91 | 103 144.17 | 90 269.85 | 9.00 | 1.84** | 2.54** | |
| 上表皮细胞厚度/μm UT | 290.47 | 3 155.57 | 2 945.68 | 8.43 | 1.22 | 1.78** | |
| 上表皮细胞宽度/μm UW | 135.06 | 1 507.29 | 2 263.51 | 8.22 | 1.20 | 1.48** | |
| 栅栏组织厚度/μm PT | 3 727.90 | 27 865.14 | 23 014.66 | 11.80 | 2.28** | 2.69** | |
| 海绵组织厚度/μm ST | 3 097.94 | 32 742.53 | 35 006.34 | 8.64 | 1.29 | 2.08** | |
| 栅海比PS | 1.12 | 16.69 | 18.56 | 6.27 | 0.91 | 2.00** | |
| 下表皮细胞厚度/μm LET | 15.13 | 211.61 | 295.57 | 6.67 | 0.99 | 1.59** | |
| 叶片结构紧密度/% LST | 386.64 | 3 451.47 | 4 484.62 | 10.07 | 1.72* | 1.71** | |
| 叶片结构疏松度/% LL | 130.90 | 4 518.32 | 5 460.81 | 2.82 | 0.40 | 1.84** | |
| 气孔长/μm SL | 47.24 | 534.97 | 570.79 | 8.11 | 1.02 | 2.83** | |
| 气孔宽/μm SW | 39.50 | 439.92 | 570.35 | 8.24 | 1.06 | 2.33** | |
| 气孔密度/(个 · mm-2)SD | 1 187 576.14 | 7 039 419.69 | 5 362 440.33 | 14.44 | 2.16** | 3.96** | |
| 比叶质量/(g × 10-3 ·cm-2) LM | 7.81 | 90.39 | 49.12 | 7.95 | 1.15 | 9.24** | |
| 叶绿素含量/(mg · g-1)CP | 98.61 | 881.42 | 342.22 | 10.06 | 1.54 | 5.56** | |
| 保水力/% WRC | 2 459.43 | 24 745.84 | 7 159.81 | 9.04 | 1.37 | 7.46** | |
| 平均 | 6 237 475.92 | 74 903 205.54 | 89 612 898.32 | 7.80 | / | / | |
| 性状Trait | LS | LAS | LBS | LSD | PL | LL | LW | L/W | LA | SWD | LSA | VSL | LT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 先端形状LAS | 0.051 | 1 | |||||||||||
| 叶基形状LBS | 0.139 | 0.155 | 1 | ||||||||||
| 叶缘锯齿方向LSD | 0.170* | -0.058 | 0.042 | 1 | |||||||||
| 叶柄长/mm PL | 0.019 | 0.018 | -0.023 | -0.023 | 1 | ||||||||
| 叶片长/mm LL | 0.177* | 0.146 | -0.167* | 0.000 | 0.020 | 1 | |||||||
| 叶片宽/mm LW | -0.200* | 0.022 | -0.076 | 0.015 | -0.150 | 0.598** | 1 | ||||||
| 叶片长/宽L/W | 0.424** | 0.137 | -0.099 | -0.028 | 0.199* | 0.410** | -0.481** | 1 | |||||
| 叶片面积/mm2 LA | -0.012 | 0.081 | -0.091 | 0.060 | -0.051 | 0.824** | 0.913** | -0.141 | 1 | ||||
| 锯齿深度SWD | -0.050 | 0.009 | 0.027 | -0.394** | -0.055 | 0.215** | 0.201* | 0.023 | 0.124 | 1 | |||
| 锯齿与叶缘间角度 LSA | 0.026 | 0.109 | 0.161 | -0.226** | 0.121 | 0.103 | 0.125 | -0.035 | 0.144 | -0.011 | 1 | ||
| 叶脉间距/mm VSL | 0.020 | 0.146 | 0.109 | -0.196* | -0.069 | 0.268** | 0.287** | -0.034 | 0.321** | 0.284** | 0.276** | 1 | |
| 性状Trait | LS | LAS | LBS | LSD | PL | LL | LW | L/W | LA | SWD | LSA | VSL | LT |
| 叶厚/μm LT | 0.112 | -0.006 | 0.116 | 0.073 | 0.270** | -0.061 | -0.079 | 0.022 | -0.063 | -0.112 | 0.051 | -0.026 | 1 |
| 上表皮细胞厚度/μm UT | -0.018 | -0.072 | 0.061 | 0.157 | 0.198* | 0.024 | 0.026 | 0.001 | 0.026 | -0.040 | 0.134 | 0.047 | 0.394** |
| 上表皮细胞宽度/μm UW | 0.162* | -0.003 | 0.041 | 0.188* | 0.106 | -0.035 | -0.057 | 0.041 | -0.058 | 0.020 | 0.023 | -0.089 | 0.385** |
| 栅栏组织厚度/μm PT | 0.227** | -0.063 | 0.081 | 0.128 | 0.199* | 0.010 | -0.088 | 0.109 | -0.041 | -0.077 | -0.002 | -0.086 | 0.781** |
| 海绵组织厚度/μm ST | -0.034 | 0.087 | 0.094 | 0.008 | 0.208* | -0.137 | -0.086 | -0.057 | -0.093 | -0.052 | 0.018 | 0.032 | 0.780** |
| 栅海比PS | 0.209* | -0.144 | -0.035 | 0.131 | -0.078 | 0.146 | 0.023 | 0.141 | 0.059 | -0.016 | -0.049 | -0.120 | -0.187* |
| 下表皮细胞厚度/μm LET | -0.046 | 0.107 | 0.144 | -0.070 | 0.002 | -0.236** | -0.191* | -0.059 | -0.199* | -0.071 | 0.027 | -0.023 | 0.183* |
| 叶片结构紧密度/% LST | 0.230** | -0.096 | -0.022 | 0.120 | -0.028 | 0.085 | -0.048 | 0.148 | 0.005 | 0.012 | -0.080 | -0.119 | -0.017 |
| 叶片结构疏松度/% LL | -0.140 | 0.147 | 0.049 | -0.052 | 0.071 | -0.148 | -0.065 | -0.096 | -0.083 | 0.018 | -0.021 | 0.085 | 0.272** |
| 气孔长/μm SL | -0.013 | -0.110 | 0.173* | -0.016 | 0.041 | -0.243** | -0.098 | -0.167* | -0.146 | -0.076 | -0.014 | -0.027 | 0.305** |
| 气孔宽/μm SW | 0.034 | 0.014 | 0.088 | -0.031 | 0.103 | -0.037 | -0.152 | 0.129 | -0.124 | 0.000 | 0.125 | 0.066 | 0.152 |
| 气孔密度/(个 · mm-2) SD | 0.002 | -0.075 | -0.010 | -0.173* | 0.109 | -0.198* | -0.216** | 0.034 | -0.200* | -0.018 | -0.053 | -0.146 | 0.089 |
| 比叶质量/ (g × 10-3 · cm-2) LM | 0.071 | 0.058 | 0.062 | 0.084 | 0.122 | -0.139 | -0.130 | -0.005 | -0.108 | -0.112 | 0.017 | -0.115 | 0.042 |
| 叶绿素含量/ (mg · g-1)CP | 0.082 | 0.026 | -0.163* | 0.049 | -0.006 | 0.042 | 0.042 | 0.001 | 0.035 | -0.021 | 0.062 | 0.067 | 0.034 |
| 叶片保水力/% WRC | 0.144 | -0.031 | 0.049 | 0.101 | -0.013 | 0.061 | 0.050 | 0.009 | 0.049 | 0.053 | 0.056 | 0.185* | 0.240** |
| 性状Trait | UT | UW | PT | ST | PS | LET | LST | LL | SL | SW | SD | LM | CP |
| 上表皮细胞宽度/μm UW | 0.389** | 1 | |||||||||||
| 栅栏组织厚度/μm PT | 0.313** | 0.397** | 1 | ||||||||||
| 海绵组织厚度/μm ST | 0.144 | 0.224** | 0.416** | 1 | |||||||||
| 栅海比PS | 0.087 | 0.086 | 0.354** | -0.680** | 1 | ||||||||
| 下表皮细胞厚度/μm LET | 0.099 | -0.109 | 0.086 | 0.236** | -0.223** | 1 | |||||||
| 叶片结构紧密度/% LST | -0.001 | 0.147 | 0.608** | -0.320** | 0.813** | -0.113 | 1 | ||||||
| 叶片结构疏松度/% LL | -0.143 | -0.023 | -0.087 | 0.810** | -0.886** | 0.220** | -0.486** | 1 | |||||
| 气孔长/μm SL | 0.017 | 0.159 | 0.270** | 0.230** | -0.034 | 0.123 | 0.057 | 0.070 | 1 | ||||
| 气孔宽/μm SW | 0.100 | 0.076 | 0.122 | 0.072 | 0.009 | 0.074 | -0.016 | -0.023 | 0.362** | 1 | |||
| 气孔密度/ (个 · mm-2)SD | -0.290** | -0.132 | 0.013 | 0.145 | -0.163* | 0.141 | -0.096 | 0.138 | 0.122 | -0.134 | 1 | ||
| 比叶质量/ (g × 10-3 ·cm-2)LM | 0.026 | 0.005 | 0.016 | 0.099 | -0.087 | 0.114 | -0.029 | 0.114 | -0.031 | 0.059 | 0.126 | 1 | |
| 叶绿素含量/(mg · g-1) CP | -0.007 | 0.031 | 0.177* | -0.071 | 0.211** | -0.109 | 0.236** | -0.136 | -0.049 | -0.051 | -0.063 | -0.196* | 1 |
| 叶片保水力/% WRC | 0.309** | 0.057 | 0.192* | -0.033 | 0.002 | -0.111 | -0.049 | -0.046 | -0.230** | -0.128 | -0.190* | -0.002 | 0.107 |
Table 6 Analysis of correlation between leaves phenotypic traits in Yanshan chestnut
| 性状Trait | LS | LAS | LBS | LSD | PL | LL | LW | L/W | LA | SWD | LSA | VSL | LT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 先端形状LAS | 0.051 | 1 | |||||||||||
| 叶基形状LBS | 0.139 | 0.155 | 1 | ||||||||||
| 叶缘锯齿方向LSD | 0.170* | -0.058 | 0.042 | 1 | |||||||||
| 叶柄长/mm PL | 0.019 | 0.018 | -0.023 | -0.023 | 1 | ||||||||
| 叶片长/mm LL | 0.177* | 0.146 | -0.167* | 0.000 | 0.020 | 1 | |||||||
| 叶片宽/mm LW | -0.200* | 0.022 | -0.076 | 0.015 | -0.150 | 0.598** | 1 | ||||||
| 叶片长/宽L/W | 0.424** | 0.137 | -0.099 | -0.028 | 0.199* | 0.410** | -0.481** | 1 | |||||
| 叶片面积/mm2 LA | -0.012 | 0.081 | -0.091 | 0.060 | -0.051 | 0.824** | 0.913** | -0.141 | 1 | ||||
| 锯齿深度SWD | -0.050 | 0.009 | 0.027 | -0.394** | -0.055 | 0.215** | 0.201* | 0.023 | 0.124 | 1 | |||
| 锯齿与叶缘间角度 LSA | 0.026 | 0.109 | 0.161 | -0.226** | 0.121 | 0.103 | 0.125 | -0.035 | 0.144 | -0.011 | 1 | ||
| 叶脉间距/mm VSL | 0.020 | 0.146 | 0.109 | -0.196* | -0.069 | 0.268** | 0.287** | -0.034 | 0.321** | 0.284** | 0.276** | 1 | |
| 性状Trait | LS | LAS | LBS | LSD | PL | LL | LW | L/W | LA | SWD | LSA | VSL | LT |
| 叶厚/μm LT | 0.112 | -0.006 | 0.116 | 0.073 | 0.270** | -0.061 | -0.079 | 0.022 | -0.063 | -0.112 | 0.051 | -0.026 | 1 |
| 上表皮细胞厚度/μm UT | -0.018 | -0.072 | 0.061 | 0.157 | 0.198* | 0.024 | 0.026 | 0.001 | 0.026 | -0.040 | 0.134 | 0.047 | 0.394** |
| 上表皮细胞宽度/μm UW | 0.162* | -0.003 | 0.041 | 0.188* | 0.106 | -0.035 | -0.057 | 0.041 | -0.058 | 0.020 | 0.023 | -0.089 | 0.385** |
| 栅栏组织厚度/μm PT | 0.227** | -0.063 | 0.081 | 0.128 | 0.199* | 0.010 | -0.088 | 0.109 | -0.041 | -0.077 | -0.002 | -0.086 | 0.781** |
| 海绵组织厚度/μm ST | -0.034 | 0.087 | 0.094 | 0.008 | 0.208* | -0.137 | -0.086 | -0.057 | -0.093 | -0.052 | 0.018 | 0.032 | 0.780** |
| 栅海比PS | 0.209* | -0.144 | -0.035 | 0.131 | -0.078 | 0.146 | 0.023 | 0.141 | 0.059 | -0.016 | -0.049 | -0.120 | -0.187* |
| 下表皮细胞厚度/μm LET | -0.046 | 0.107 | 0.144 | -0.070 | 0.002 | -0.236** | -0.191* | -0.059 | -0.199* | -0.071 | 0.027 | -0.023 | 0.183* |
| 叶片结构紧密度/% LST | 0.230** | -0.096 | -0.022 | 0.120 | -0.028 | 0.085 | -0.048 | 0.148 | 0.005 | 0.012 | -0.080 | -0.119 | -0.017 |
| 叶片结构疏松度/% LL | -0.140 | 0.147 | 0.049 | -0.052 | 0.071 | -0.148 | -0.065 | -0.096 | -0.083 | 0.018 | -0.021 | 0.085 | 0.272** |
| 气孔长/μm SL | -0.013 | -0.110 | 0.173* | -0.016 | 0.041 | -0.243** | -0.098 | -0.167* | -0.146 | -0.076 | -0.014 | -0.027 | 0.305** |
| 气孔宽/μm SW | 0.034 | 0.014 | 0.088 | -0.031 | 0.103 | -0.037 | -0.152 | 0.129 | -0.124 | 0.000 | 0.125 | 0.066 | 0.152 |
| 气孔密度/(个 · mm-2) SD | 0.002 | -0.075 | -0.010 | -0.173* | 0.109 | -0.198* | -0.216** | 0.034 | -0.200* | -0.018 | -0.053 | -0.146 | 0.089 |
| 比叶质量/ (g × 10-3 · cm-2) LM | 0.071 | 0.058 | 0.062 | 0.084 | 0.122 | -0.139 | -0.130 | -0.005 | -0.108 | -0.112 | 0.017 | -0.115 | 0.042 |
| 叶绿素含量/ (mg · g-1)CP | 0.082 | 0.026 | -0.163* | 0.049 | -0.006 | 0.042 | 0.042 | 0.001 | 0.035 | -0.021 | 0.062 | 0.067 | 0.034 |
| 叶片保水力/% WRC | 0.144 | -0.031 | 0.049 | 0.101 | -0.013 | 0.061 | 0.050 | 0.009 | 0.049 | 0.053 | 0.056 | 0.185* | 0.240** |
| 性状Trait | UT | UW | PT | ST | PS | LET | LST | LL | SL | SW | SD | LM | CP |
| 上表皮细胞宽度/μm UW | 0.389** | 1 | |||||||||||
| 栅栏组织厚度/μm PT | 0.313** | 0.397** | 1 | ||||||||||
| 海绵组织厚度/μm ST | 0.144 | 0.224** | 0.416** | 1 | |||||||||
| 栅海比PS | 0.087 | 0.086 | 0.354** | -0.680** | 1 | ||||||||
| 下表皮细胞厚度/μm LET | 0.099 | -0.109 | 0.086 | 0.236** | -0.223** | 1 | |||||||
| 叶片结构紧密度/% LST | -0.001 | 0.147 | 0.608** | -0.320** | 0.813** | -0.113 | 1 | ||||||
| 叶片结构疏松度/% LL | -0.143 | -0.023 | -0.087 | 0.810** | -0.886** | 0.220** | -0.486** | 1 | |||||
| 气孔长/μm SL | 0.017 | 0.159 | 0.270** | 0.230** | -0.034 | 0.123 | 0.057 | 0.070 | 1 | ||||
| 气孔宽/μm SW | 0.100 | 0.076 | 0.122 | 0.072 | 0.009 | 0.074 | -0.016 | -0.023 | 0.362** | 1 | |||
| 气孔密度/ (个 · mm-2)SD | -0.290** | -0.132 | 0.013 | 0.145 | -0.163* | 0.141 | -0.096 | 0.138 | 0.122 | -0.134 | 1 | ||
| 比叶质量/ (g × 10-3 ·cm-2)LM | 0.026 | 0.005 | 0.016 | 0.099 | -0.087 | 0.114 | -0.029 | 0.114 | -0.031 | 0.059 | 0.126 | 1 | |
| 叶绿素含量/(mg · g-1) CP | -0.007 | 0.031 | 0.177* | -0.071 | 0.211** | -0.109 | 0.236** | -0.136 | -0.049 | -0.051 | -0.063 | -0.196* | 1 |
| 叶片保水力/% WRC | 0.309** | 0.057 | 0.192* | -0.033 | 0.002 | -0.111 | -0.049 | -0.046 | -0.230** | -0.128 | -0.190* | -0.002 | 0.107 |
| 数量性状 Quantitative trait | 主成分Principle components | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | |
| 叶柄长/mm PL | 0.272 | 0.214 | 0.155 | 0.424 | 0.119 | 0.051 | -0.237 | 0.229 | -0.227 |
| 叶片长/mm LL | -0.542 | -0.105 | 0.595 | 0.391 | 0.128 | 0.296 | -0.090 | -0.092 | -0.009 |
| 叶片宽/mm LW | -0.487 | -0.335 | 0.660 | -0.360 | -0.038 | 0.119 | -0.204 | 0.011 | 0.004 |
| 叶片长/宽L/W | -0.045 | 0.271 | -0.100 | 0.845 | 0.177 | 0.187 | 0.136 | -0.122 | -0.017 |
| 叶片面积/mm2 LA | -0.527 | -0.269 | 0.703 | -0.072 | 0.045 | 0.232 | -0.236 | 0.026 | -0.033 |
| 锯齿深度/mm SWD | -0.195 | -0.164 | 0.207 | 0.108 | 0.118 | 0.050 | 0.314 | -0.264 | 0.501 |
| 锯齿与叶缘间角度/°LSA | -0.028 | -0.051 | 0.286 | 0.070 | 0.368 | -0.304 | -0.029 | 0.577 | -0.151 |
| 叶脉间距/mm VSL | -0.163 | -0.262 | 0.453 | 0.062 | 0.236 | -0.210 | 0.398 | 0.211 | 0.250 |
| 叶厚/μm LT | 0.835 | 0.435 | 0.521 | -0.044 | -0.070 | 0.142 | 0.002 | 0.028 | 0.014 |
| 上表皮细胞厚度/μm UT | 0.141 | 0.404 | 0.415 | 0.073 | -0.121 | -0.546 | -0.217 | -0.046 | 0.093 |
| 上表皮细胞宽度/μm UW | 0.200 | 0.470 | 0.298 | -0.051 | -0.057 | -0.130 | -0.080 | -0.390 | -0.151 |
| 栅栏组织厚度/μm PT | 0.255 | 0.796 | 0.370 | -0.112 | -0.044 | 0.287 | 0.038 | 0.077 | 0.130 |
| 海绵组织厚度/μm ST | 0.635 | -0.062 | 0.453 | 0.002 | -0.100 | 0.197 | 0.077 | -0.043 | -0.029 |
| 栅海比PS | -0.664 | 0.691 | -0.181 | -0.098 | 0.046 | 0.037 | -0.055 | 0.063 | 0.105 |
| 下表皮细胞厚度/μm LET | 0.418 | -0.043 | -0.083 | -0.110 | 0.123 | -0.053 | -0.040 | 0.299 | 0.493 |
| 叶片结构紧密度/% LT | -0.396 | 0.728 | -0.080 | -0.127 | 0.005 | 0.285 | 0.055 | 0.073 | 0.180 |
| 叶片结构疏松度/% LL | 0.701 | -0.506 | 0.215 | 0.055 | -0.084 | 0.166 | 0.122 | -0.080 | -0.047 |
| 气孔长/μm SL | 0.351 | 0.235 | 0.027 | -0.279 | 0.720 | 0.105 | 0.104 | -0.132 | -0.088 |
| 气孔宽/μm SW | 0.181 | 0.204 | 0.047 | 0.018 | 0.500 | -0.241 | 0.088 | -0.153 | -0.075 |
| 气孔密度/(个 · mm-2)SD | 0.302 | -0.102 | -0.289 | 0.022 | 0.022 | 0.549 | -0.008 | 0.302 | 0.112 |
| 比叶质量/(g × 10-3 · cm-2)LM | 0.235 | -0.005 | -0.133 | 0.116 | 0.078 | 0.009 | -0.603 | 0.143 | 0.308 |
| 叶绿素含量/mg · g-1 CP | -0.186 | 0.250 | 0.094 | -0.088 | -0.211 | 0.064 | 0.482 | 0.297 | -0.359 |
| 保水力/% WRC | 0.078 | 0.208 | 0.250 | 0.183 | -0.517 | -0.350 | 0.163 | 0.110 | 0.190 |
| 特征值(λ)Eigen value | 3.782 | 3.102 | 2.790 | 1.551 | 1.414 | 1.398 | 1.234 | 1.114 | 1.013 |
| 贡献率/% Contribution rate | 16.443 | 13.487 | 12.130 | 6.743 | 6.150 | 6.078 | 5.367 | 4.842 | 4.406 |
| 累计贡献率/% Cumulative contribution rate | 16.443 | 29.930 | 42.060 | 48.803 | 54.953 | 61.031 | 66.398 | 71.240 | 75.646 |
Table 7 Principal components matrix
| 数量性状 Quantitative trait | 主成分Principle components | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | |
| 叶柄长/mm PL | 0.272 | 0.214 | 0.155 | 0.424 | 0.119 | 0.051 | -0.237 | 0.229 | -0.227 |
| 叶片长/mm LL | -0.542 | -0.105 | 0.595 | 0.391 | 0.128 | 0.296 | -0.090 | -0.092 | -0.009 |
| 叶片宽/mm LW | -0.487 | -0.335 | 0.660 | -0.360 | -0.038 | 0.119 | -0.204 | 0.011 | 0.004 |
| 叶片长/宽L/W | -0.045 | 0.271 | -0.100 | 0.845 | 0.177 | 0.187 | 0.136 | -0.122 | -0.017 |
| 叶片面积/mm2 LA | -0.527 | -0.269 | 0.703 | -0.072 | 0.045 | 0.232 | -0.236 | 0.026 | -0.033 |
| 锯齿深度/mm SWD | -0.195 | -0.164 | 0.207 | 0.108 | 0.118 | 0.050 | 0.314 | -0.264 | 0.501 |
| 锯齿与叶缘间角度/°LSA | -0.028 | -0.051 | 0.286 | 0.070 | 0.368 | -0.304 | -0.029 | 0.577 | -0.151 |
| 叶脉间距/mm VSL | -0.163 | -0.262 | 0.453 | 0.062 | 0.236 | -0.210 | 0.398 | 0.211 | 0.250 |
| 叶厚/μm LT | 0.835 | 0.435 | 0.521 | -0.044 | -0.070 | 0.142 | 0.002 | 0.028 | 0.014 |
| 上表皮细胞厚度/μm UT | 0.141 | 0.404 | 0.415 | 0.073 | -0.121 | -0.546 | -0.217 | -0.046 | 0.093 |
| 上表皮细胞宽度/μm UW | 0.200 | 0.470 | 0.298 | -0.051 | -0.057 | -0.130 | -0.080 | -0.390 | -0.151 |
| 栅栏组织厚度/μm PT | 0.255 | 0.796 | 0.370 | -0.112 | -0.044 | 0.287 | 0.038 | 0.077 | 0.130 |
| 海绵组织厚度/μm ST | 0.635 | -0.062 | 0.453 | 0.002 | -0.100 | 0.197 | 0.077 | -0.043 | -0.029 |
| 栅海比PS | -0.664 | 0.691 | -0.181 | -0.098 | 0.046 | 0.037 | -0.055 | 0.063 | 0.105 |
| 下表皮细胞厚度/μm LET | 0.418 | -0.043 | -0.083 | -0.110 | 0.123 | -0.053 | -0.040 | 0.299 | 0.493 |
| 叶片结构紧密度/% LT | -0.396 | 0.728 | -0.080 | -0.127 | 0.005 | 0.285 | 0.055 | 0.073 | 0.180 |
| 叶片结构疏松度/% LL | 0.701 | -0.506 | 0.215 | 0.055 | -0.084 | 0.166 | 0.122 | -0.080 | -0.047 |
| 气孔长/μm SL | 0.351 | 0.235 | 0.027 | -0.279 | 0.720 | 0.105 | 0.104 | -0.132 | -0.088 |
| 气孔宽/μm SW | 0.181 | 0.204 | 0.047 | 0.018 | 0.500 | -0.241 | 0.088 | -0.153 | -0.075 |
| 气孔密度/(个 · mm-2)SD | 0.302 | -0.102 | -0.289 | 0.022 | 0.022 | 0.549 | -0.008 | 0.302 | 0.112 |
| 比叶质量/(g × 10-3 · cm-2)LM | 0.235 | -0.005 | -0.133 | 0.116 | 0.078 | 0.009 | -0.603 | 0.143 | 0.308 |
| 叶绿素含量/mg · g-1 CP | -0.186 | 0.250 | 0.094 | -0.088 | -0.211 | 0.064 | 0.482 | 0.297 | -0.359 |
| 保水力/% WRC | 0.078 | 0.208 | 0.250 | 0.183 | -0.517 | -0.350 | 0.163 | 0.110 | 0.190 |
| 特征值(λ)Eigen value | 3.782 | 3.102 | 2.790 | 1.551 | 1.414 | 1.398 | 1.234 | 1.114 | 1.013 |
| 贡献率/% Contribution rate | 16.443 | 13.487 | 12.130 | 6.743 | 6.150 | 6.078 | 5.367 | 4.842 | 4.406 |
| 累计贡献率/% Cumulative contribution rate | 16.443 | 29.930 | 42.060 | 48.803 | 54.953 | 61.031 | 66.398 | 71.240 | 75.646 |
| [1] | Bacilieri R, Ducousso A, Kremer A. 1995. Genetic,morphological,ecological and phenological differentiation between Quercus petraea(Matt.) Liebl. and Quercus robur L. in a mixed stand of northwest of France. Silvae Genetica, 44 (1):1-9. |
| [2] | Cheng Li-li, Su Shu-chai, Qin Ling, liu Jian-li, Yin Wei-lun. 2006. Construction of AFLP reaction system in leaves of Castanea mollissima in the Yanshan Mountains. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 28 (6):35-39. (in Chinese) |
| 程丽莉, 苏淑钗, 秦岭, 刘建立, 尹伟伦. 2006. 燕山板栗叶片基因组AFLP反应体系建立. 北京林业大学学报, 28 (6):35-39. | |
| [3] | Cheng Shi-ming, Gu Wan-chun. 2006, Studies on phenotypical characteristics gradient variation of Melia azedarach. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 42 (5):29-35. (in Chinese) |
| 程诗明, 顾万春. 2006. 苦楝表型性状梯度变异的研究. 林业科学, 42 (5):29-35. | |
| [4] | Cui Si-ming, Hao Ya-han, Zhou Wei, Ren Ying, Zhou Peng, Chen Xiao-yang. 2020. Variation of leaf morphological characters of Broussonetia papyrifera from different provenances. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 40 (5):104-110. (in Chinese) |
| 崔思明, 郝亚涵, 周玮, 任颖, 周鹏, 陈晓阳. 2020. 构树不同种源叶性状变异研究. 中南林业科技大学学报, 40 (5):104-110. | |
| [5] | Guo Su-juan, Wu Yan-qi. 2018. Leaf anatomical structure characteristics and drought resistance of Chinese chestnut. Journal of northwest A & F University(Nat. Sci. Ed.), 46 (9):1-9. (in Chinese) |
| 郭素娟, 武燕奇. 2018. 板栗叶片解剖结构特征及其与抗旱性的关系. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 46 (9):1-9. | |
| [6] | Guo Yan, Zhang Shuhang, LI Ying, Zhang Xinfang, Wang Guangpeng. 2020. Studies on the leaf morphology,anatomical structure and drought resistance evaluation of 238 Chinese chestnut varieties(strains). Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47 (6):1033-1046. (in Chinese) |
| 郭燕, 张树航, 李颖, 张馨方, 王广鹏. 2020. 中国板栗238份品种(系)叶片形态、解剖结构及其抗旱性评价. 园艺学报, 47 (6):1033-1046 | |
| [7] | Jian Xi-bing, Gong Bang-chu, Liu Qing-zhong, Chen-Xin, Wu Kai-yun, Deng Quan-en, Tang Dan. 2014. Phenotypic diversity of important agronomic traits of local cultivars of Chinese chestnut. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 41(4):641-652. (in Chinese) |
| 江锡兵, 龚榜初, 刘庆忠, 陈新, 吴开云, 邓全恩, 汤丹. 2014. 中国板栗地方品种重要农艺性状的表型多样性. 园艺学报, 41 (4):641-652. | |
| [8] | Jing Jian-yong, Xie Gang-gang, Ouyang Li-ting, Chen Xi, Ma Bai-qiang, Geng Wen-juan. 2020. Analysis on diversity of phenotypic traits of wild Prunus domestica in Xinjiang. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 29 (2):28-37. (in Chinese) |
| 经建永, 颉刚刚, 欧阳丽婷, 陈曦, 马百强, 耿文娟. 2020. 新疆野生欧洲李表型性状多样性分析. 植物资源与环境学报, 29 (2):28-37. | |
| [9] | Li Hon-guo, Chen Da-zhen, Xu Jing-shi, Liu Guang-jin, Pang Xiao-dong, Ye Jin-hui. 2019. Phenotypic diversity and variation in natural populations of Erythrophleum fordii,an endangered plant species. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 55 (4):69-82. (in Chinese) |
| 李洪果, 陈达镇, 许靖诗, 刘光金, 庞晓东, 叶金辉. 2019. 濒危植物格木天然种群的表型多样性及变异. 林业科学, 55 (4):69-82. | |
| [10] | Li Shan, Gan Xiao-hong, Han Hong-yan, Xu Ning, Hou Zheng-yang, Chen Yang, Deng Xiao-juan. 2016. Leaf phenotypic traits of Tetracentron sinense,an endangered plant species. Forest Research, 29 (5):687-697. (in Chinese) |
| 李珊, 甘小洪, 憨宏艳, 许宁, 侯正扬, 陈杨, 邓晓娟. 2016. 濒危植物水青树叶的表型性状变异. 林业科学研究, 29 (5):687-697. | |
| [11] | Li xiao-yu, Ralf Müller-Xing, Shahid Khan, Zheng yu-cai, Li yu-hua, Xing qian. 2019. Development of plant leaf margin:advances in research. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 35 (1):50-56. (in Chinese) |
| 李晓屿, Ralf Müller-Xing, Shahid Khan, 郑玉彩, 李玉花, 邢倩. 2019. 植物叶缘锯齿发育的研究进展. 中国农学通报, 35 (1):50-56. | |
| [12] | Li Ying, Zhang Shuhang, Guo Yan, Zhang Xinfang, Yan Xiguang, Wang Guangpeng. 2019. Genetic diversity analysis of several phenotypic traits related to biennial bearing branch in Chinese chestnut. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 46 (3):453-463. (in Chinese) |
| 李颖, 张树航, 郭燕, 张馨方, 闫希光, 王广鹏. 2019. 中国板栗9个结果母枝相关表型性状遗传多样性研究. 园艺学报, 46 (3):453-463. | |
| [13] | Liu Ya-bin, Guo Su-juan. 2020. Leaf functional traits of 41 chestnut germplasms in Qianxi region. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 48 (4):8-14. (in Chinese) |
| 刘亚斌, 郭素娟. 2020. 迁西地区39份板栗种质叶片的功能性状多样性. 东北林业大学学报, 48 (4):8-14. | |
| [14] | Maguylo K, Bassett C. 2012. Phenotyping M. sieversii collections from Kazakhstan for leaf traits and tree architecture,(1058):335-341. |
| [15] | Shang Shuai-bin, Guo Jun-jie, Wang Chun-sheng, Zhao Zhi-gang, Zeng Jie. 2015. Phenotypic variations in natural populations of Vatica mangachapoi in Hainan,China. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 51 (2):154-161. (in Chinese) |
| 尚帅斌, 郭俊杰, 王春胜, 赵志刚, 曾杰. 2015. 海南岛青梅天然居群表型变异. 林业科学, 51 (2):154-161. | |
| [16] | Shu Zhan, Zhang Xiao-Su, Chen Juan, Chen Gen-yun, Xu Da-quan. 2010. The simplification of chlorophyll content measurement. Plant Physiology Communications, 46 (4):399-402. |
| 舒展, 张晓素, 陈娟, 陈根云, 许大全. 2010. 叶绿素含量测定的简化. 植物生理学通讯, 46 (4):399-402. (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | State Forestry Bureau. 2009. Guidelines for the conduct of tests for distinctness,uniformity and stability-chestnut(Castanea mollissima Bl.):LY/T 1851-2009. Beijing: Standards Press of China, (in Chinese) |
| 国家林业局. 2009. 植物新品种特异性、一致性、稳定性测试指南板栗: LY/T 1851—2009. 北京: 中国标准出版社. | |
| [18] | Sun Zhi-chao, Cheng Hui, Guo Wen-lei, Wang Hong-hong, Wang Zheng-jia. 2015. Analysis of drought resistance of branch and leaf structure in Carya cathayensis. Journal of Fruit Science, 32 (4):633-640. (in Chinese) |
| 孙志超, 程慧, 郭文磊, 王红红, 王正加. 2015. 山核桃枝叶耐旱特性分析. 果树学报, 32 (4):633-640. | |
| [19] |
Tian Hua, Kang Ming, Yao Xiao-hong, Huang Hong-wen. 2009. Genetic diversity in natural populations of Castanea mollissima inferred from nuclear SSR markers. Biodiversity Science, 17 (3):296-302. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09043 URL |
|
田华, 康明, 李丽, 姚小洪, 黄宏文. 2009. 中国板栗自然居群微卫星(SSR)遗传多样性. 生物多样性, 17 (3):296-302.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09043 |
|
| [20] | Wang Guang-peng, Lu Feng-qing, Kong De-jun. 2016. Highly effective cultivation and control technique of main pests and diseases of chestnut. Beijing: China Agriculture Press:81-84. (in Chinese) |
| 王广鹏, 陆凤勤, 孔德军. 2016. 板栗高效栽培技术与主要病虫害防治. 北京: 中国农业出版社:81-84. | |
| [21] | Wang Yong-kang, Wu Guo-liang, Zhao Ai-ling, Li Deng-ke. 2014. Phenotypic genetic diversity of jujube germplasm resources. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 50 (10):33-41. (in Chinese) |
| 王永康, 吴国良, 赵爱玲, 李登科. 2014. 枣种质资源的表型遗传多样性. 林业科学, 50 (10):33-41. | |
| [22] |
Wani G A, Shah M A, Tekeu H. 2020. Phenotypic variability and genetic giversity of phragmites australis in quebec and kashmir reveal contrasting population structure. Plants, 9 (10):1392.
doi: 10.3390/plants9101392 URL |
| [23] | Xie Yi-qing, Huang Ru-zhu, Li Zhi-zhen, Huang Yong, Yang Zong-wu. 2009. Genetic variation of natural populations of Betula luminifera in fujian and its relationship with the habita. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 45 (9):60-65. (in Chinese) |
| 谢一青, 黄儒珠, 李志真, 黄勇, 杨宗武. 2009. 福建光皮桦野生种群遗传变异及其与生境的关系. 林业科学, 45 (9):60-65. | |
| [24] | Xu Yang, Chen Xiao-hong, Zhao An-jiu. 2015. Drought resistance evaluation and leaf anatomical structures of four species of Malus plants in western Sichuan Plateau. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 35 (11):2227-2234. (in Chinese) |
| 徐扬, 陈小红, 赵安玖. 2015. 川西高原4种苹果属植物叶片解剖结构与其抗旱性分析. 西北植物学报, 35 (11):2227-2234. | |
| [25] | Xu Yong-jie, Han Hua-bai, Wang Hua, Chen Ling-na, Ma Qing-guo, Pei Dong. 2016. Phenotypic and genetic diversities of nuts of walnut(Juglans regia)populations originated from seedlings in Daba Mountains. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 52 (5):111-119. (in Chinese) |
| 徐永杰, 韩华柏, 王滑, 陈凌娜, 马庆国, 裴东. 2016. 大巴山区核桃实生居群的坚果表型和遗传多样性. 林业科学, 52 (5):111-119. | |
| [26] | Zeng Jie, Zheng Hai-shui, Gan Si-ming, Bai Jia-yu. 2005. Phenotypic variation in natural populations of Betula alnoides in Guangxi,China. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 41 (2):59-65. (in Chinese) |
| 曾杰, 郑海水, 甘四明, 白嘉雨. 2005. 广西西南桦天然居群的表型变异. 林业科学, 41 (2):59-65. | |
| [27] | Zhang Shen-mei, Xi Jian-wei, Hong Jun-yan, Xia Guo-hua, Li Yan, Huang Xing-zhao, Zhu Xian-fu, Huang Jian-qin. 2020. A study on phenotypic diversity of fruit and leaf traits in Carya dabieshanensis. Forest Research, 33 (1):152-161. (in Chinese) |
| 张深梅, 奚建伟, 洪俊彦, 夏国华, 李岩, 黄兴召, 朱先富, 黄坚钦. 2020. 大别山山核桃果实与叶片性状的表型多样性研究. 林业科学研究, 33 (1):152-161. | |
| [28] | Zhang Xiao-quan, Xu Zhi-wen, Kan Hong-ying, Zhang Lin, Zhang Yun-yun, Guo Chuan-bin. 2017. Effects of stalk positions and natural dehydration after priming on water retention capacity of flue-cured tobacco leaves. Acta Tabacaria Sinica, 23 (4):33-39. (in Chinese) |
| 张小全, 许志文, 阚洪赢, 张林, 张鋆鋆, 郭传滨. 2017. 不同叶位和离体失水时间对烤烟叶片保水能力的影响. 中国烟草学报, 23 (4):33-39. | |
| [29] | Zhang Xin-fang, Zhang Shu-hang, Li Ying, Guo Yan, Wang Guang-peng. 2020a. Genetic diversity analysis of castanea mollissima germplasm resources based on SSR markers. Molecular Plant Breeding, 18 (15):5164-5175. (in Chinese) |
| 张馨方, 张树航, 李颖, 郭燕, 王广鹏. 2020a. 基于SSR标记的板栗种质资源遗传多样性分析. 分子植物育种, 18 (15):5164-5175. | |
| [30] | Zhang Xin-fang, Zhang Shu-hang, Li Ying, Guo Yan, Wang Guan-gpeng. 2020b. Genetic diversity analysis of chestnut germplasm in Yanshan region based on SSR markers. Journal of China Agricultural University, 25 (4):61-67. (in Chinese) |
| 张馨方, 张树航, 李颖, 郭燕, 王广鹏. 2020b. 基于SSR标记的燕山板栗种质资源遗传多样性分析. 中国农业大学学报, 25 (4):61-67. | |
| [31] | Zhang Ying, Cao Yu-fen, Huo Hong-liang, Xu Jia-yu, Tian Lu-ming, Dong Xing-guang, Qi Dan, Zhang Xiao-shuang, Liu Chao, Wang Li-dong. 2018. Diversity of pear germplasm resources based on twig and leaf phenotypic traits. Scientia Agricultura sinica, 51 (17):3353-3369. (in Chinese) |
| 张莹, 曹玉芬, 霍宏亮, 徐家玉, 田路明, 董星光, 齐丹, 张小双, 刘超, 王立东. 2018. 基于枝条和叶片表型性状的梨种质资源多样性. 中国农业科学, 51 (17):3353-3369. | |
| [32] | Zhang Yun-yue, Ma Chang-geng, Lin Mu-jiu, Li Bai-hai. 2001. Study on one of genetic variations for ginkgo biloba in China the variation of breeding frutt-stong characters among and within population. Scientia Silvae Sinicae,(37):36-40. (in Chinese) |
| 张云跃, 马常耕, 林睦就, 李柏海. 2001. 我国银杏遗传变异研究之一种核性状的群体间和群体内变异. 林业科学,(37):36-40. | |
| [33] | Zhou Lian-di, Lan Yan-ping, Cao Qing-chang, Li Shu-ying, Lan Wei-zong. 2005. Geographical variation of morphologic characteristics of Castanea mollissima seeds and legumes. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 21 (9):136-139. (in Chinese) |
| 周连第, 兰彦平, 曹庆昌, 李淑英, 兰卫宗. 2005. 板栗叶片性状表型多样性研究. 林业科学, 21 (9):136-139. |
| [1] | WANG Rui, HONG Wenjuan, LUO Hua, ZHAO Lina, CHEN Ying, and WANG Jun, . Construction of SSR Fingerprints of Pomegranate Cultivars and Male Parent Identification of Hybrids [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 265-278. |
| [2] | JIANG Yu, TU Xunliang, and HE Junrong. Analysis of Differential Expression Genes in Leaves of Leaf Color Mutant of Chinese Orchid [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 371-381. |
| [3] | LIANG Jiali, WU Qisong, CHEN Guangquan, ZHANG Rong, XU Chunxiang, and FENG Shujie, . Identification of the Neopestalotiopsis musae Pathogen of Banana Leaf Spot Disease [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 410-420. |
| [4] | WANG Mengmeng, SUN Deling, CHEN Rui, YANG Yingxia, ZHANG Guan, LÜ Mingjie, WANG Qian, XIE Tianyu, NIU Guobao, SHAN Xiaozheng, TAN Jin, and YAO Xingwei, . Construction and Evaluation of Cauliflower Core Collection [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 421-431. |
| [5] | PENG Yufu, OUYANG Xueling, YE Chuan, CHEN Hualing, PENG Yong, WANG Guohang, KONG Lingpu, LE Jun, and PENG Huohui, . A New Acer cordatum Cultivar‘Huoyan’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 269-270. |
| [6] | BI Sisheng, ZHANG Lanying, WANG Hongyong, WANG Zhenmeng, MA Bingyao, GAO Wei, and LIU Guimin, . A New Northern Red Oak Cultivar‘Golden Prince' [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S1): 179-180. |
| [7] | JIANG Yajun, CHEN Jiajia, TAN Bin, ZHENG Xianbo, WANG Wei, ZHANG Langlang, CHENG Jun, FENG Jiancan. Function Exploration of PpIDD11 in Regulating Peach Flower Development [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(9): 1841-1852. |
| [8] | WU Fan, JIANG Junhao, LU Shan, ZHANG Nan, QIU Shuai, WEI Jianfen, SHEN Baichun. Research Progress on Germplasm Resources and Utilization of Hydrangea in China [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(9): 2037-2050. |
| [9] | CHEN Lilang, YANG Tianzhang, CAI Ruping, LIN Xiaoman, DENG Nankang, CHE Haiyan, LIN Yating, KONG Xiangyi. Molecular Detection and Identification of Viruses from Passiflora edulis in Hainan [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1785-1794. |
| [10] | LÜ Zhengxin, HE Yanqun, JIA Dongfeng, HUANG Chunhui, ZHONG Min, LIAO Guanglian, ZHU Yi, YUAN Kaichang, LIU Chuanhao, XU Xiaobiao. Genetic Diversity Analysis of Phenotypic Traits for Kiwifruit Germplasm Resources [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1571-1581. |
| [11] | ZHANG Lugang, LU Qianqian, HE Qiong, XUE Yihua, MA Xiaomin, MA Shuai, NIE Shanshan, YANG Wenjing. Creation of Novel Germplasm of Purple-orange Heading Chinese Cabbage [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1582-1588. |
| [12] | LI Pingping, ZHANG Xiang, LIU Yuting, XIE Zhihe, ZHANG Ruihao, ZHAO Kai, LÜ Junheng, WANG Ziran, WEN Jinfen, ZOU Xuexiao, DENG Minghua. Studies on the Relationship Between Pigment Composition and Fruit Coloration of 63 Peppers [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1589-1601. |
| [13] | LU Tao, YU Hongjun, LI Qiang, JIANG Weijie. Effects of Leaf and Fruit Quantity Regulation on Growth,Fruit Quality and Yield of Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1261-1274. |
| [14] | CAI Zhixiang, YAN Juan, SU Ziwen, XU Ziyuan, ZHANG Minghao, SHEN Zhijun, YANG Jun, MA Ruijuan, YU Mingliang. Evaluation of Main Phenolic Compounds in Different Types of Peach Germplasm Resources [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(5): 1008-1022. |
| [15] | LI Dongze, LUO Fangliang, FENG Yuanyuan, ZHANG Lu, HU Shaoqing, CUI Qi. A New Osmanthus fragrans Cultivar‘Luocai 16’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(5): 1179-1180. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd