
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (11): 2121-2132.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0847
• Original article • Next Articles
CHEN Chen, LIU Chenghui, SHI Lijia, JIANG Aili( ), HU Wenzhong(
), HU Wenzhong( )
)
Received:2021-06-11
Revised:2021-08-06
Published:2021-12-02
Contact:
JIANG Aili,HU Wenzhong
E-mail:jal@dlnu.edu.cn;hwz@dlnu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
CHEN Chen, LIU Chenghui, SHI Lijia, JIANG Aili, HU Wenzhong. An Analysis of Alternative Splicing Events During Browning Inhibition of Fresh-cut Apples by Hydrogen Sulfide Treatment[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(11): 2121-2132.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0847
| 基因 Gene | 上游引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 下游引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| PPO | GTGGCTTGCGGTATTATTGGT | GATGCTCGGTTTCCCTCAA |
| POD | CCAACCTCGCAACCCTAATCT | CACTGAGACTGGCCTAATGTGTG |
| PAL | CGCTGGAGTGTTTGGAAGTG | AGTAGCCTTGGAGGAGTGTGTTG |
| PLD | GTCTTGATCTTTGTGATGGTCGTT | GGTTGTCTTGGAGCCTTGGT |
| LOX | AGCTTGGGCTGAAAATCCTGT | ACAACGCCTGCTCCAACTCT |
| NADH脱氢酶基因NADH dehydrogenase | TGGTATCGGACTGGGGTAGG | ATGTGCGTCCAAGTGTTTGTG |
| 18s RNA | GATTCCGGTGCCCAGAAGT | CCAGCAGCTTCCATTCCAA |
Table 1 Sequences of specific primers used for quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis
| 基因 Gene | 上游引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 下游引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| PPO | GTGGCTTGCGGTATTATTGGT | GATGCTCGGTTTCCCTCAA |
| POD | CCAACCTCGCAACCCTAATCT | CACTGAGACTGGCCTAATGTGTG |
| PAL | CGCTGGAGTGTTTGGAAGTG | AGTAGCCTTGGAGGAGTGTGTTG |
| PLD | GTCTTGATCTTTGTGATGGTCGTT | GGTTGTCTTGGAGCCTTGGT |
| LOX | AGCTTGGGCTGAAAATCCTGT | ACAACGCCTGCTCCAACTCT |
| NADH脱氢酶基因NADH dehydrogenase | TGGTATCGGACTGGGGTAGG | ATGTGCGTCCAAGTGTTTGTG |
| 18s RNA | GATTCCGGTGCCCAGAAGT | CCAGCAGCTTCCATTCCAA |
| 样品Sample | Raw reads 原始数据 | Clean reads 有效数据 | 质量值 ≥ 20的 碱基所占比例/% Q20 | 质量值 ≥ 30的 碱基所占比例/% Q30 | GC含量所占 的比例/% GC content | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 处理 Treatment | 天数/d Day | ||||||
| H2O | 0 | 60 422 744 | 59 865 744 | 99.61 | 95.03 | 47.50 | |
| 51 249 354 | 50 902 542 | 99.75 | 95.56 | 47.00 | |||
| 44 214 706 | 43 903 682 | 99.73 | 95.47 | 47.00 | |||
| 6 | 44 706 736 | 44 404 318 | 99.66 | 95.07 | 47.00 | ||
| 40 462 228 | 40 210 134 | 99.66 | 95.04 | 47.00 | |||
| 47 660 554 | 47 291 638 | 99.70 | 95.33 | 47.00 | |||
| H2S | 0 | 45 000 228 | 44 602 378 | 99.71 | 95.17 | 47.00 | |
| 50 155 628 | 49 585 722 | 99.74 | 95.94 | 47.00 | |||
| 45 750 610 | 45 333 712 | 99.73 | 95.78 | 47.00 | |||
| 6 | 47 041 536 | 46 731 660 | 99.67 | 95.17 | 47.00 | ||
| 46 388 294 | 46 024 028 | 99.76 | 95.62 | 47.00 | |||
| 52 755 840 | 52 352 240 | 99.43 | 96.58 | 47.00 | |||
Table 1 Quality summary of sequencing data
| 样品Sample | Raw reads 原始数据 | Clean reads 有效数据 | 质量值 ≥ 20的 碱基所占比例/% Q20 | 质量值 ≥ 30的 碱基所占比例/% Q30 | GC含量所占 的比例/% GC content | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 处理 Treatment | 天数/d Day | ||||||
| H2O | 0 | 60 422 744 | 59 865 744 | 99.61 | 95.03 | 47.50 | |
| 51 249 354 | 50 902 542 | 99.75 | 95.56 | 47.00 | |||
| 44 214 706 | 43 903 682 | 99.73 | 95.47 | 47.00 | |||
| 6 | 44 706 736 | 44 404 318 | 99.66 | 95.07 | 47.00 | ||
| 40 462 228 | 40 210 134 | 99.66 | 95.04 | 47.00 | |||
| 47 660 554 | 47 291 638 | 99.70 | 95.33 | 47.00 | |||
| H2S | 0 | 45 000 228 | 44 602 378 | 99.71 | 95.17 | 47.00 | |
| 50 155 628 | 49 585 722 | 99.74 | 95.94 | 47.00 | |||
| 45 750 610 | 45 333 712 | 99.73 | 95.78 | 47.00 | |||
| 6 | 47 041 536 | 46 731 660 | 99.67 | 95.17 | 47.00 | ||
| 46 388 294 | 46 024 028 | 99.76 | 95.62 | 47.00 | |||
| 52 755 840 | 52 352 240 | 99.43 | 96.58 | 47.00 | |||
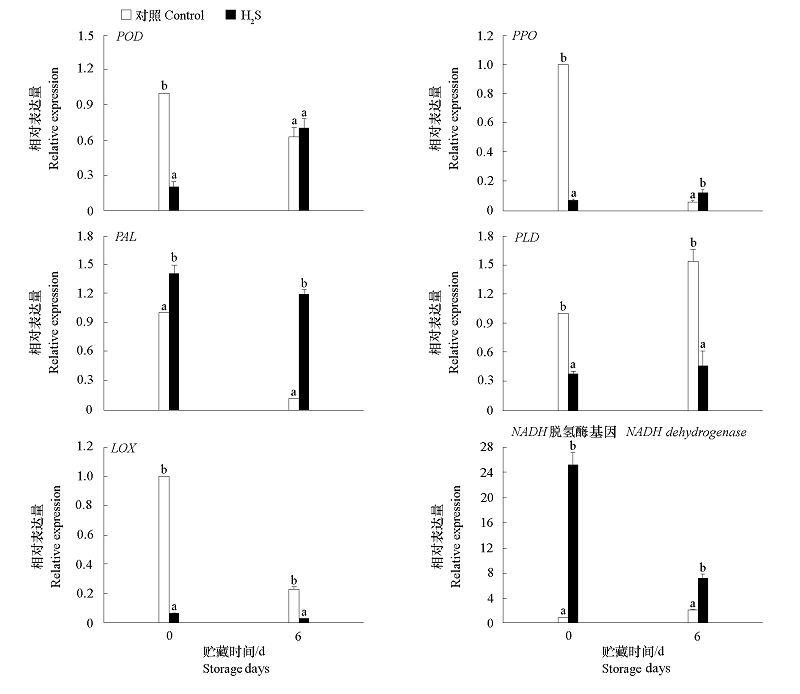
Fig. 6 Effect of H2S treatment on the expression of browning related genes in fresh cut apples Different alphabets are significantly(P < 0.05)different among different treated samples.
| [1] |
Hu Wenzhong, Jiang Aili, Liu Chenghui, Zhao Lei. 2018. Physiological mechanism for browning inhibition in fresh-cut apple by cysteine. Food Science, 39 (3):282-288. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.1111/jfds.1974.39.issue-2 URL |
| 陈晨, 胡文忠, 姜爱丽, 刘程惠, 赵蕾. 2018. 半胱氨酸控制鲜切苹果褐变的生理机制. 食品科学, 39 (3):282-288. | |
| [2] |
Cortellino G, Gobbi S, Bianchi G, Rizzolo A. 2015. Modified atmosphere packaging for shelf life extension of fresh-cut apples. Trends in Food Science and Technology, 46 (2):320-330.
doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2015.06.002 URL |
| [3] |
Docimo T, Francese G, de Palma M, Mennella D, Toppion L, Scalzo P L, Mennella G, Tucci M. 2016. Insights in the fruit flesh browning mechanisms in Solanum melongena genetic lines with opposite postcut behavior. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 64 (22):4675-4685.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b00662 pmid: 27198496 |
| [4] | Feng Yalan, Xiong Ying, Zhang Jun, Yuan Jiale, Cai Aishan, Ma Chao. 2020. Role of alternative splicing in plant development and abiotic stress responses. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 34 (1):62-70. (in Chinese) |
| 冯雅岚, 熊瑛, 张均, 原佳乐, 蔡艾杉, 马超. 2020. 可变剪切在植物发育和非生物胁迫响应中的作用. 核农学报, 34 (1):62-70. | |
| [5] |
Franck C, Lammertyn J, Ho Q T, Verboven P, Verlinden B, Nicolai B M. 2007. Browning disorders in pear fruit. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 43 (1):1-13.
doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2006.08.008 URL |
| [6] | Hancock J T, Whiteman M. 2014. Hydrogen sulfide and cell signaling: team player or referee? Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 78:37-42. |
| [7] |
Hu H, Shen W, Li P. 2014. Effects of hydrogen sulphide on quality and antioxidant capacity of mulberry fruit. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 49:399-409.
doi: 10.1111/ijfs.12313 URL |
| [8] |
Hu L, Hu S L, Wu J, Li Y H, Zheng J L, Wei Z J, Liu J, Wang H L, Liu Y S, Zhang H. 2012. Hydrogen sulfide prolongs postharvest shelf life of strawberry and plays an antioxidative role in fruits. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 60:8684-8693.
doi: 10.1021/jf300728h URL |
| [9] | Huang Ling, Li Qiongying, Wei Shugu, Lai Jia, Dai Shundong, Zhang Qianfang, Zeng Hualan, Liu Jia, Ye Pengsheng. 2019. Identification and difference analysis of the alternative splicing event in the hermaphroditic flowers and male flowers of Asparagus officinalis. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 46 (8):1503-1518. (in Chinese) |
| 黄玲, 李琼英, 韦树谷, 赖佳, 代顺冬, 张骞方, 曾华兰, 刘佳, 叶鹏盛. 2019. 芦笋两性花与雄花中发生可变剪接基因的差异分析. 园艺学报, 46 (8):1503-1518. | |
| [10] |
Jiang J, Jiang L, Zhang L, Luo H, Opiyo A M, Yu Z. 2012. Changes of protein profile in fresh-cut lotus tuber before and after browning. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 60 (15):3955-3965.
doi: 10.1021/jf205303y pmid: 22455495 |
| [11] | Jin Z, Pei Y. 2015. Physiological implications of hydrogen sulfide in plants: pleasant exploration behind its unpleasant odour. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2015:397502. |
| [12] |
Laloum T, Martín G, Duque P. 2018. Alternative splicing control of abiotic stress responses. Trends in Plant Science, 23:140-150.
doi: S1360-1385(17)30218-2 pmid: 29074233 |
| [13] |
Landrigan M, Morris S C, Eamus D, McGlasson W B. 1996. Postharvest water relationships and tissue browning of rambutan fruit. Scientia Horticulturae, 66 (3-4):201-208.
doi: 10.1016/S0304-4238(96)00915-6 URL |
| [14] |
Liang D, Wang C, Tocmo R, Wu H, Deng L W, Huang D. 2015. Hydrogen sulphide(H2S)releasing capacity of essential oils isolated from organosulphur rich fruits and vegetables. Journal of Functional Foods, 14:634-640.
doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2015.02.007 URL |
| [15] |
Lin Y, Lin Y, Lin H, Chen Y, Wang H, Shi J. 2018. Application of propyl gallate alleviates pericarp browning in harvested longan fruit by modulating metabolisms of respiration and energy. Food Chemistry, 240:863-869.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.07.118 URL |
| [16] |
Mellidou I, Buts K, Hatoum D, Ho Q T, Johnston J W, Watkins C B, Schaffer R J, Gapper N E, Giovannoni J J, Rudell D R, Hertog M L, Nicolai B M. 2014. Transcriptomic events associated with internal browning of apple during postharvest storage. BMC Plant Biology, 14:328.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-014-0328-x URL |
| [17] | Milani J, Hamedi M. 2004. Susceptibility of five apple cultivars to enzymatic browning. International Postharvest Symposium,2221-2226. |
| [18] | Qiao D, Yang C, Chen J, Guo Y, Li Y, Niu S, Cao K, Chen Z. 2019. Comprehensive identification of the full-length transcripts and alternative splicing related to the secondary metabolism pathways in the tea plant(Camellia sinensis). Scientific Reports, 9 (1):1-13. |
| [19] |
Rawyler A, Pavelic D, Gianinazzi C, Oberson J, Braendle R. 1999. Membrane lipid integrity relies on a threshold of ATP production rate in potato cell cultures submitted to anoxia. Plant Physiology, 120 (1):93-300.
doi: 10.1104/pp.120.1.93 URL |
| [20] |
Reddy A S N, Marquez Y, Kalyna M, Barta A. 2013. Complexity of the alternative splicing landscape in plants. The Plant Cell, 25 (10):3657-3683.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.117523 URL |
| [21] |
Saquet A A, Streif J, Bangerth F. 2003. Energy metabolism and membrane lipid alterations in relation to brown heart development in‘Conference’pears during delayed controlled atmosphere storage. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 30 (2):123-132.
doi: 10.1016/S0925-5214(03)00099-1 URL |
| [22] |
Sun Y, Zhang W, Zeng T, Nie Q, Zhang F, Zhu L. 2015. Hydrogen sulfide inhibits enzymatic browning of fresh-cut lotus root slices by regulating phenolic metabolism. Food Chemistry, 177:376-381.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.01.065 URL |
| [23] | Tan Yitan, Zeng Kaifang. 2014. Effects of combined treatment with ascorbic acid,cysteine and CaCl2 on browning of fresh-cut taro. Food Science, 35 (4):231-235. (in Chinese) |
| 谭谊谈, 曾凯芳. 2014. 抗坏血酸、半胱氨酸与氯化钙复合处理对鲜切芋艿褐变的影响. 食品科学, 35 (4):231-235. | |
| [24] |
Toivonen P M A, Brummell D A. 2008. Biochemical bases of appearance and texture changes in fresh-cut fruit and vegetables. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 48 (1):1-14.
doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2007.09.004 URL |
| [25] |
Wang R. 2002. Two’s company,three’sa crowd: can H2S be the third endogenous gaseous transmitter? The FASEB Journal, 16:1792-1798.
doi: 10.1096/fsb2.v16.13 URL |
| [26] | Zhang Xiaoyan, Liu Aiwen, Ji Qiyan, Peng Yong. 2020. Effect of heat treatment combined with γ-aminobutyric acid on the physiology property and quality of fresh-cut apples. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 41 (14):265-269,275. (in Chinese) |
| 张小燕, 刘艾雯, 籍奇岩, 彭勇. 2020. 热处理结合γ-氨基丁酸对鲜切苹果生理特性和品质的影响. 食品工业科技, 41 (14):265-269,275. | |
| [27] |
Zhang J L, Hu L Y, Hu K D, Wu J, Yang F, Zhang H. 2016. Hydrogen sulfide alleviates senescence of fresh-cut apple by regulating antioxidant defense system and senescence-related gene expression. HortScience, 51:152-158.
doi: 10.21273/HORTSCI.51.2.152 URL |
| [28] | Zhou Qi, Zhou Fuhui, Hu Wenzhong, Zhao Lei, Xu Yuanyuan. 2019. Correlation between enzymatic browning inhibition by UV-C treatment and reactive oxygen species metabolism of fresh-cut apples. Food Science, 40 (5):110-117. (in Chinese) |
| 周琪, 陈晨, 周福慧, 胡文忠, 赵蕾, 许源源. 2019. 短波紫外线控制鲜切苹果褐变与其活性氧代谢的相关性. 食品科学, 40 (5):110-117. |
| [1] | YU Tingting, LI Huan, NING Yuansheng, SONG Jianfei, PENG Lulin, JIA Junqi, ZHANG Weiwei, and YANG Hongqiang. Genome-wide Identification of GRAS Gene Family in Apple and Expression Analysis of Its Response to Auxin [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 397-409. |
| [2] | HAN Xiaolei, ZHANG Caixia, LIU Kai, YANG An, YAN Jiadi, LI Wuxing, KANG Liqun, and CONG Peihua. A New Mid-ripening Apple Cultivar‘Zhongping Youlei’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 1-2. |
| [3] | SUN Simiao, WANG Kun, GAO Yuan, WANG Dajiang, and LI Lianwen. A New Ornamental Crabapple Cultivar‘Zichen’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 267-268. |
| [4] | HAN Xiaolei, ZHANG Caixia, LIU Kai, YAN Jiadi, LI Wuxing, KANG Liqun, and CONG Peihua. A New Mid-ripening Apple Cultivar‘Pingyou 2’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S1): 1-2. |
| [5] | WANG Qiang, CONG Peihua, and LIU Xiaofeng. A New Late Ripening Apple Cultivar‘Huayou Tianwa’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S1): 3-4. |
| [6] | WANG Qiang, CONG Peihua, and LIU Xiaofeng. A New Mid-ripening Apple Cultivar‘Huayou Baomi’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S1): 5-6. |
| [7] | YANG Ling, CONG Peihua, WANG Qiang, LI Wuxing, and KANG Liqun. A New Mid-ripening Apple Cultivar‘Huafeng’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S1): 7-8. |
| [8] | LIU Chuanhe, HE Han, SHAO Xuehua, LAI Duo, KUANG Shizi, XIAO Weiqiang, LIU Yan. A New Pineapple Cultivar‘Yuetong’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(9): 2053-2054. |
| [9] | GAO Yanlong, WU Yuxia, ZHANG Zhongxing, WANG Shuangcheng, ZHANG Rui, ZHANG De, WANG Yanxiu. Bioinformatics Analysis of Apple ELO Gene Family and Its Expression Analysis Under Low Temperature Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1621-1636. |
| [10] | LIU Chaoyang, LIAO Zhichan, LU Xinxin, HE Yehua. Identification of CslD Gene Family in Pineapple and Functional Analysis of AcoCslD2a [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1650-1662. |
| [11] | ZHENG Xiaodong, XI Xiangli, LI Yuqi, SUN Zhijuan, MA Changqing, HAN Mingsan, LI Shaoxuan, TIAN Yike, WANG Caihong. Effects and Regulating Mechanism of Exogenous Brassinosteroids on the Growth of Malus hupehensis Under Saline-alkali Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1401-1414. |
| [12] | XIA Yan, HUANG Song, WU Xueli, LIU Yiqi, WANG Miaomiao, SONG Chunhui, BAI Tuanhui, SONG Shangwei, PANG Hongguang, JIAO Jian, ZHENG Xianbo. Identification and Analysis of Apple Viruses Diseases Based on Virome Sequencing Technology [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1415-1428. |
| [13] | LIU Zhaoxia, ZHANG Xin, WANG Lu, MA Yuting, CHEN Qian, ZHU Zhanling, GE Shunfeng, JIANG Yuanmao. Effects of Fertilizer Hole Application Sites on Fine Root Growth,15N Absorption and Utilization,Yield and Quality of Apple Trees [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1545-1556. |
| [14] | MA Weifeng, LI Yanmei, MA Zonghuan, CHEN Baihong, MAO Juan. Identification of Apple POD Gene Family and Functional Analysis of MdPOD15 Gene [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1181-1199. |
| [15] | FENG Chen, HUANG Xuewang, LI Xingliang, ZHOU Jia, LI Tianhong. Comparative Study on Drought Resistance of Different Apple Dwarfing Rootstock and Scion Combinations [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(5): 945-957. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd