
园艺学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (12): 2701-2712.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-1208
陈琪1( ), 李婷1, 陈佳琳1, 陈鸥1, 王文军1,2, 姚世响1,2, 曾凯芳1,2,3,*(
), 李婷1, 陈佳琳1, 陈鸥1, 王文军1,2, 姚世响1,2, 曾凯芳1,2,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-01-18
修回日期:2023-05-08
出版日期:2023-12-25
发布日期:2023-12-29
通讯作者:
基金资助:
CHEN Qi1( ), LI Ting1, CHEN Jialin1, CHEN Ou1, WANG Wenjun1,2, YAO Shixiang1,2, ZENG Kaifang1,2,3,*(
), LI Ting1, CHEN Jialin1, CHEN Ou1, WANG Wenjun1,2, YAO Shixiang1,2, ZENG Kaifang1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2023-01-18
Revised:2023-05-08
Published:2023-12-25
Online:2023-12-29
摘要:
为探究柑橘转录因子CsNAC2对果实绿霉病抗病性的影响,以‘锦橙447'为材料,克隆了CsNAC2的编码序列。通过生物信息分析、酵母单杂交、RNA-Seq、凝胶迁移实验和qRT-PCR,探究柑橘转录因子CsNAC2对果实绿霉病抗性的调控作用。结果表明,CsNAC2编码区序列为909 bp,编码302个氨基酸,其蛋白质分子量为34.40 kD。CsNAC2具备NAC家族转录因子的结构特点,在N端含有保守的NAC结构域。在柑橘果实上瞬时过表达CsNAC2能够有效降低果实绿霉病的发病率和病斑直径。转录组分析发现CsNAC2能够参与果实中多个与抗病相关的代谢途径,对木质素合成途径以及氨基酸和核苷酸糖代谢途径进行深入研究发现,CsNAC2能够分别结合这两个途径中的CsLAC7和CsEP3的启动子,瞬时过表达CsNAC2能够提高CsLAC7和CsEP3的表达量。上述结果表明,CsNAC2可能通过激活CsLAC7和CsEP3的表达,从而提高柑橘果实对绿霉病的抗性。
陈琪, 李婷, 陈佳琳, 陈鸥, 王文军, 姚世响, 曾凯芳. 柑橘CsNAC2在果实绿霉病抗病性中的功能和机制研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(12): 2701-2712.
CHEN Qi, LI Ting, CHEN Jialin, CHEN Ou, WANG Wenjun, YAO Shixiang, ZENG Kaifang. Studies on Function and Mechanism of CsNAC2 Transcription Factor in Resistance to Green Mold in Citrus[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(12): 2701-2712.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Sequence |
|---|---|
| CsNAC2-For | ATGACGGCTGAGTTACAGTTACCA |
| CsNAC2-Rev | TTAAAAGGGTTTCGGAAGGTACATGAA |
| CsNAC2-pGBKT7-For | AGGCCGAATTCCCGGGGATCCATGACGGCTGAGTTACAGTTACCA |
| CsNAC2-pGBKT7-Rev | CTAGTTATGCGGCCGCTGCAGTTAAAAGGGTTTCGGAAGGTACATGAA |
| CsNAC2-pEAQ-For | CAAATTCGCGACCGGTATGACGGCTGAGTTACAGTTACCA |
| CsNAC2-pEAQ-Rev | AGTTAAAGGCCTCGAGAAAGGGTTTCGGAAGGTACATGAA |
| CsNAC2-GST-For | GGTTCCGCGTGGATCCATGACGGCTGAGTTACAGTTACCA |
| CsNAC2-GST-Rev | AGTCACGATGCGGCCGCAAAGGGTTTCGGAAGGTACATGAA |
| CsLAC7-probe-For | AATTTTTCACGGCACTGCTTCAATTGTAATGCGTGTGTCAGTAG |
| CsLAC7-probe-Rev | TGCTGACAAGCTACTGACACACGCATTACAATTGAAGCAGTG |
| CsLAC7-mutant probe-For | AATTTTTAAAAGCACTAAAACAATTGTAATGAAAATGTCAGTAAAAAGTCAGCA |
| CsLAC7-mutant probe-Rev | TGCTGACTTTTTACTGACATTTTCATTACAATTGTTTTAGTGCTTTTAAAAATT |
| CsEP3-probe-For | TACTCGCTCGACAATAGATCCGTAGTCAACACGGAGGACAAGAA |
| CsEP3-probe-Rev | TTCTTGTCCTCCGTGTTGACTACGGATCTATTGTCGAGCGAGTA |
| CsEP3-mutant probe-For | TACTCGCTCGACAATAGATCAAAAGTCAAAAAAGAGGACAAGAA |
| CsEP3-mutant probe-Rev | TTCTTGTCCTCTTTTTTGACTTTTGATCTATTGTCGAGCGAGTA |
| CsLAC7-For | CCTGCAAAACACAGCGTTGA |
| CsLAC7-Rev | GTAGGGATCCCGTCCTGAAA |
| CsEP3-For | TGTGTCAAAACTCCGTTGCC |
| CsEP3-Rev | AGCACAATGAGACGGAGAACT |
| Action-For | ATCTGCTGGAAGGTGCTGAG |
| Action-Rev | CCAAGCAGCATGAAGATCAA |
表1 试验中所用引物序列
Table 1 Specific primer sequences used in experiments
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Sequence |
|---|---|
| CsNAC2-For | ATGACGGCTGAGTTACAGTTACCA |
| CsNAC2-Rev | TTAAAAGGGTTTCGGAAGGTACATGAA |
| CsNAC2-pGBKT7-For | AGGCCGAATTCCCGGGGATCCATGACGGCTGAGTTACAGTTACCA |
| CsNAC2-pGBKT7-Rev | CTAGTTATGCGGCCGCTGCAGTTAAAAGGGTTTCGGAAGGTACATGAA |
| CsNAC2-pEAQ-For | CAAATTCGCGACCGGTATGACGGCTGAGTTACAGTTACCA |
| CsNAC2-pEAQ-Rev | AGTTAAAGGCCTCGAGAAAGGGTTTCGGAAGGTACATGAA |
| CsNAC2-GST-For | GGTTCCGCGTGGATCCATGACGGCTGAGTTACAGTTACCA |
| CsNAC2-GST-Rev | AGTCACGATGCGGCCGCAAAGGGTTTCGGAAGGTACATGAA |
| CsLAC7-probe-For | AATTTTTCACGGCACTGCTTCAATTGTAATGCGTGTGTCAGTAG |
| CsLAC7-probe-Rev | TGCTGACAAGCTACTGACACACGCATTACAATTGAAGCAGTG |
| CsLAC7-mutant probe-For | AATTTTTAAAAGCACTAAAACAATTGTAATGAAAATGTCAGTAAAAAGTCAGCA |
| CsLAC7-mutant probe-Rev | TGCTGACTTTTTACTGACATTTTCATTACAATTGTTTTAGTGCTTTTAAAAATT |
| CsEP3-probe-For | TACTCGCTCGACAATAGATCCGTAGTCAACACGGAGGACAAGAA |
| CsEP3-probe-Rev | TTCTTGTCCTCCGTGTTGACTACGGATCTATTGTCGAGCGAGTA |
| CsEP3-mutant probe-For | TACTCGCTCGACAATAGATCAAAAGTCAAAAAAGAGGACAAGAA |
| CsEP3-mutant probe-Rev | TTCTTGTCCTCTTTTTTGACTTTTGATCTATTGTCGAGCGAGTA |
| CsLAC7-For | CCTGCAAAACACAGCGTTGA |
| CsLAC7-Rev | GTAGGGATCCCGTCCTGAAA |
| CsEP3-For | TGTGTCAAAACTCCGTTGCC |
| CsEP3-Rev | AGCACAATGAGACGGAGAACT |
| Action-For | ATCTGCTGGAAGGTGCTGAG |
| Action-Rev | CCAAGCAGCATGAAGATCAA |

图1 CsNAC2与其他物种中NAC转录因子的氨基酸序列比对分析 Mi:杧果;Cc:克莱门柚;Me:木薯;Cp:番木瓜。
Fig. 1 Comparison of amino acid sequences between CsNAC2 and NAC transcription factors in other species Mi:Mangifera indica;Cc:Citrus clementina;Me:Manihot esculenta;Cp:Carica papaya.
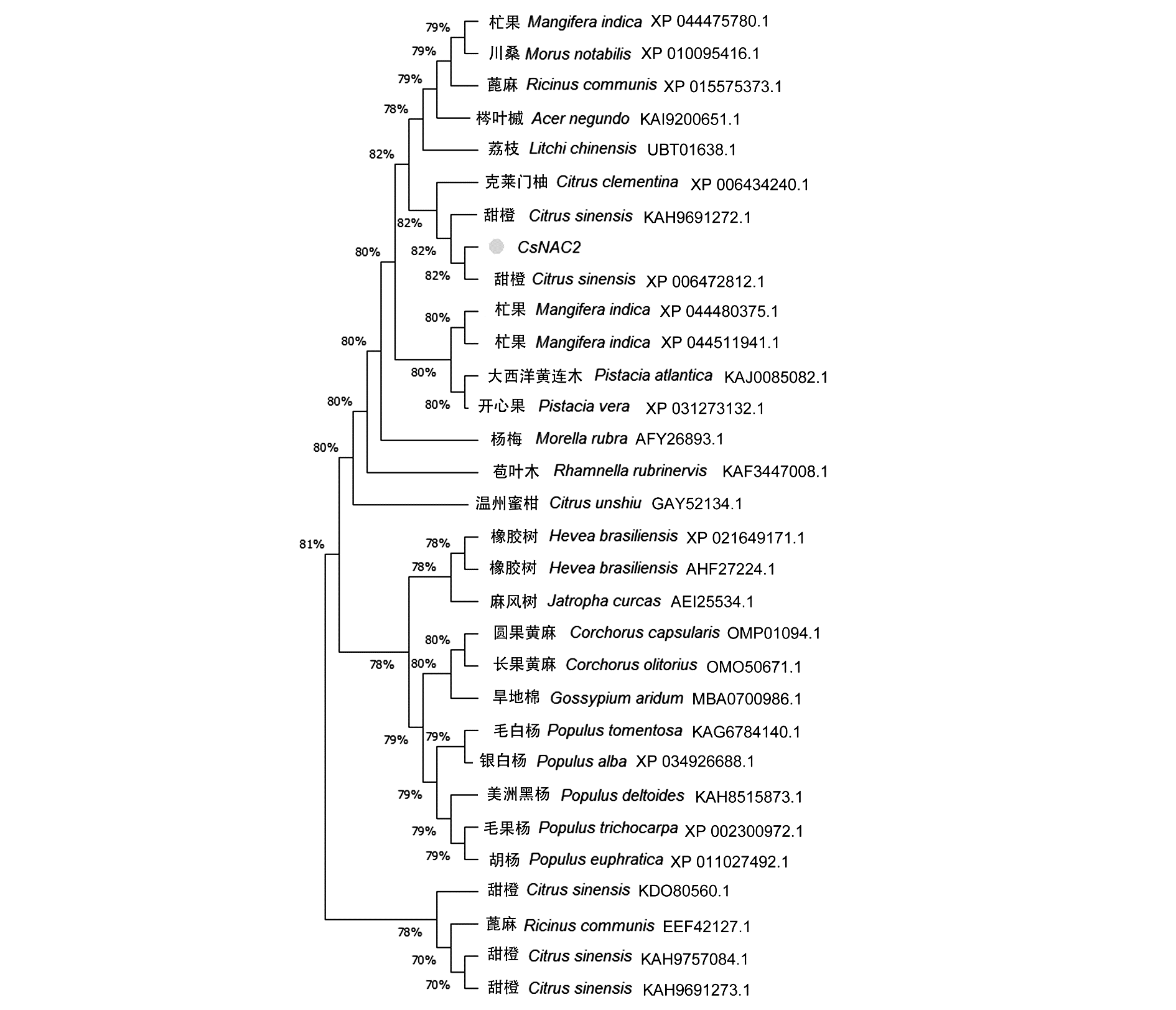
图2 CsNAC2与其他物种中NAC转录因子的进化关系 结点处数值表示自展值,值越大该节点置信度越高。
Fig. 2 The evolutionary relationship between CsNAC2 and NAC transcription factors in other species The value at the node represents the bootstrap value,and the larger the value,the higher the confidence of the node.
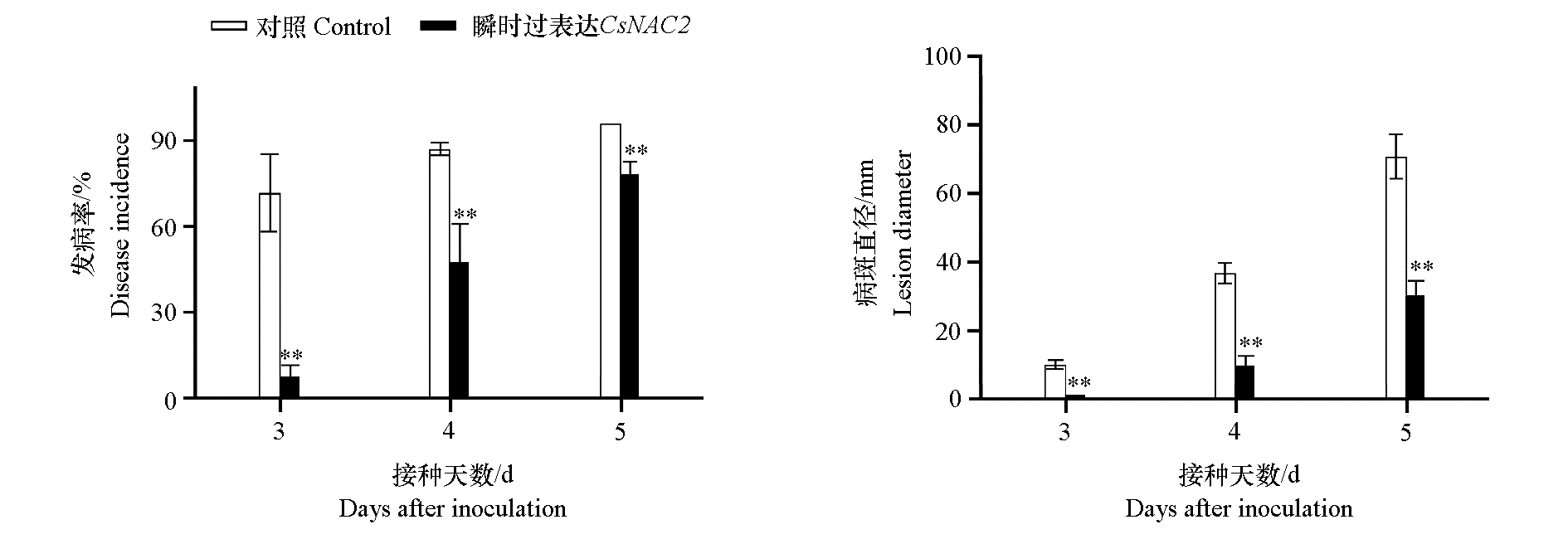
图4 CsNAC2 瞬时过表达对柑橘果实接种指状青霉引起的绿霉病发病率与病斑直径的影响 ** P < 0.01.
Fig. 4 Effect of transient overexpression of CsNAC2 on the disease incidence and lesion diameter of citrus green mold caused by inoculation of Penicillium digitalum in citrus fruits
| 途径Pathway | 基因 Gene symbol | log2(FC) | 功能注释 Description | 基因编号 Citrus sinensis ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 苯丙烷生物合成 Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis | COMT1 | 1.07 | 咖啡酸3甲基转移酶 Caffeic acid 3-O-Methyltransferase-like | Cs5g13580 |
| COMT | 1.29 | 咖啡酸3甲基转移酶 Caffeic acid 3-O-Methyltransferase-like | Cs5g18050 | |
| LAC7 | 1.18 | 漆酶 Laccase-7-like | Cs6g07400 | |
| 类胡萝卜素生物合成 Carotenoid biosynthesis | NCED1 | 1.18 | 9-顺式环氧类胡萝卜素双加氧酶 9-cis-Epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase | Cs2g03270 |
| NCED3 | 1.42 | 9-顺式环氧类胡萝卜素双加氧酶 9-cis-Epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase | Cs5g14370 | |
| 氨基酸和核苷酸糖代谢 Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism | EP3 | 1.38 | 几丁质酶 Chitinase | Cs5g21870 |
| 角质素、软木脂和蜡质生物合成 Cutin, suberine and wax biosynthesis | CER1 | 1.22 | 乙醛脱羧酶 Aldehyde decarbonylase | Cs1g02750 |
| 半胱氨酸和蛋氨酸代谢 Cysteine and methionine metabolism | CAS2 | 1.29 | 半胱胺酸合成酶 Cysteine synthase | orange1.1t00386 |
| 谷胱甘肽代谢 Glutathione metabolism | HSP26-A | 1.06 | 谷胱甘肽S转移酶 Glutathione S-transferase | Cs7g15760 |
| 植物激素信号转导 Plant hormone signal transduction | IAA29 | 1.25 | 植物激素响应蛋白IAA Auxin-responsive protein IAA | Cs4g18240 |
表2 CsNAC2可能与抗病相关的下游靶基因
Table 2 Possible downstream target genes of CsNAC2 associated with disease resistance
| 途径Pathway | 基因 Gene symbol | log2(FC) | 功能注释 Description | 基因编号 Citrus sinensis ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 苯丙烷生物合成 Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis | COMT1 | 1.07 | 咖啡酸3甲基转移酶 Caffeic acid 3-O-Methyltransferase-like | Cs5g13580 |
| COMT | 1.29 | 咖啡酸3甲基转移酶 Caffeic acid 3-O-Methyltransferase-like | Cs5g18050 | |
| LAC7 | 1.18 | 漆酶 Laccase-7-like | Cs6g07400 | |
| 类胡萝卜素生物合成 Carotenoid biosynthesis | NCED1 | 1.18 | 9-顺式环氧类胡萝卜素双加氧酶 9-cis-Epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase | Cs2g03270 |
| NCED3 | 1.42 | 9-顺式环氧类胡萝卜素双加氧酶 9-cis-Epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase | Cs5g14370 | |
| 氨基酸和核苷酸糖代谢 Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism | EP3 | 1.38 | 几丁质酶 Chitinase | Cs5g21870 |
| 角质素、软木脂和蜡质生物合成 Cutin, suberine and wax biosynthesis | CER1 | 1.22 | 乙醛脱羧酶 Aldehyde decarbonylase | Cs1g02750 |
| 半胱氨酸和蛋氨酸代谢 Cysteine and methionine metabolism | CAS2 | 1.29 | 半胱胺酸合成酶 Cysteine synthase | orange1.1t00386 |
| 谷胱甘肽代谢 Glutathione metabolism | HSP26-A | 1.06 | 谷胱甘肽S转移酶 Glutathione S-transferase | Cs7g15760 |
| 植物激素信号转导 Plant hormone signal transduction | IAA29 | 1.25 | 植物激素响应蛋白IAA Auxin-responsive protein IAA | Cs4g18240 |
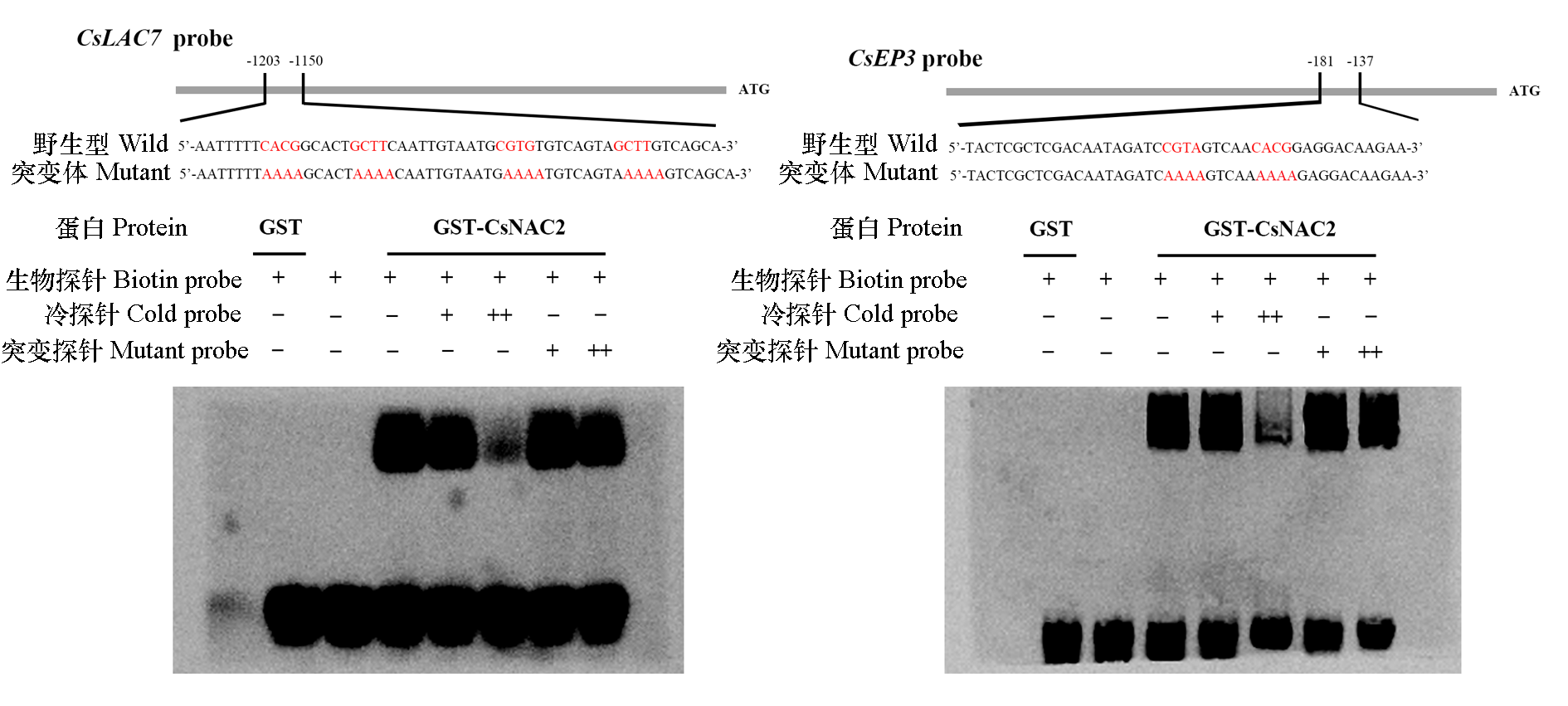
图5 CsNAC2对下游靶基因CsLAC7和CsEP3启动子的结合能力 分别以只添加GST蛋白和不添加任何蛋白作为阴性对照,试验组均添加GST-CsNAC2蛋白。标红部分表示NAC下游靶基因启动子区的顺式作用元件NACRS,突变探针是将NACRS的核心基序全部替换成“AAAA”碱基序列。“+”表示添加探针,“−”表示不添加探针,“++”表示加入高浓度的探针。
Fig. 5 The binding ability of CsNAC2 to promoters of downstream target genes CsLAC7 and CsEP3 GST protein and no protein were used as negative controls,respectively,and all experimental groups were added with GST-CsNAC2 protein. The marked red part represents the cis-acting elements NACRS in the promoter of downstream target genes of NAC,and the mutant probe replaced the core motif of NACRS with the“AAAA”base sequence. The symbols“+”and“−”represent presence or absence of the probe and the symbol“++”represent high concentration probe.
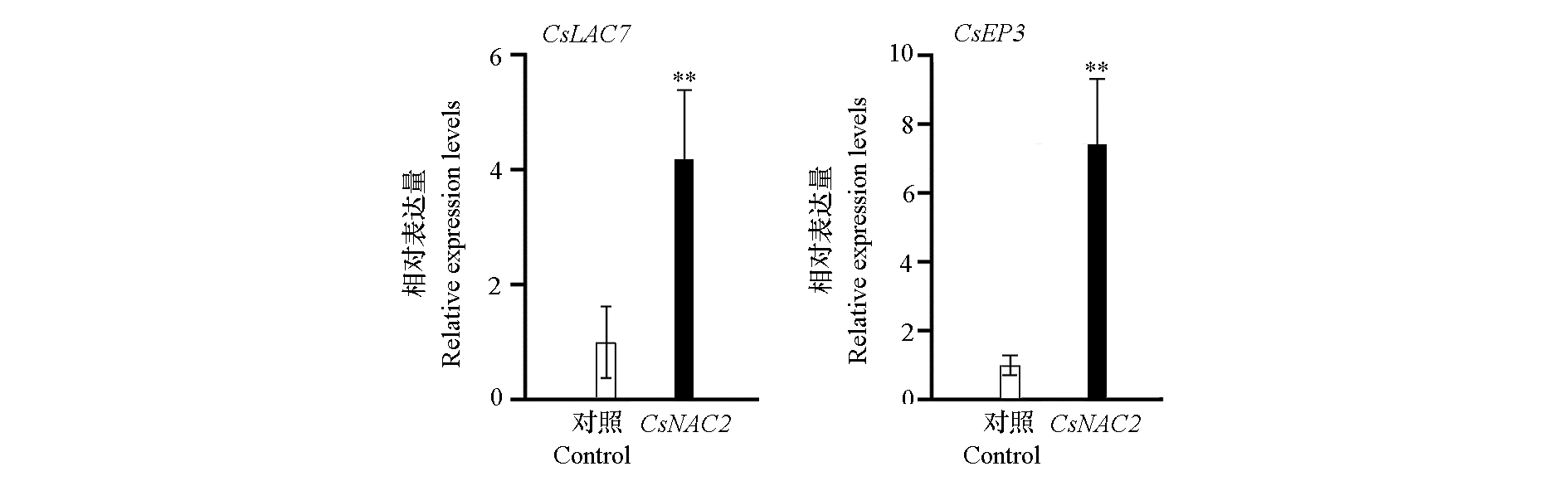
图6 CsNAC2瞬时过表达对下游靶基因CsLAC7和CsEP3表达量的影响 ** P < 0.01.
Fig. 6 Effects of transient overexpression of CsNAC2 on the expression levels of downstream target genes CsLAC7 and CsEP3
| [1] |
doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiab383 pmid: 34618056 |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.1111/tpj.v106.3 URL |
| [4] |
doi: 10.1071/FP19331 pmid: 32454004 |
| [5] |
|
|
陈江华, 崔雪婧, 程家森, 林杨, 谢甲涛, 付艳苹. 2019. 我国主要产区柑橘采后病害发生动态. 华中农业大学学报, 38 (6):92-97.
|
|
| [6] |
|
|
陈娜, 蒋晶, 曹必好, 雷建军, 陈长明. 2015. 植物NAC转录因子功能研究新进展. 分子植物育种, 13 (6):1407-1414.
|
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2018.08.012 URL |
| [8] |
doi: 10.1111/nph.v232.1 URL |
| [9] |
|
|
韩立涛. 2022. 玉米NAC类转录因子ZmNAC19的功能研究[硕士论文]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学.
|
|
| [10] |
|
|
胡嘉祺. 2020. 融合基因4CL1-CCR对烟草细胞壁影响的研究[博士论文]. 北京: 北京林业大学.
|
|
| [11] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2019.03.018 URL |
| [12] |
doi: 10.1007/s11105-017-1043-1 URL |
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2018.05.008 URL |
| [15] |
|
|
梁珂豪. 2020. 青杄NAC转录因子PwNAC30/PwNAC31的功能研究与验证[硕士论文]. 北京: 北京林业大学.
|
|
| [16] |
|
|
梁攀, 李悦妍, 黄少云, 陈良哲, 易庆平. 2021. 柑橘类水果贮藏保鲜技术研究进展. 包装工程, 42 (13):57-66.
|
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1007/s11103-018-0768-z pmid: 30387038 |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1007/s11103-018-0710-4 |
| [19] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.10.057 URL |
| [20] |
doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2021.06.1273 |
|
秦娟, 余凡, 刘璐, 朱婷婷, 陈伟, 曹士锋, 杨震峰, 施丽愉. 2021. 桃PpNAC19的克隆及其对PpCCD4启动子活性的调节分析. 核农学报, 35 (6):1273-1280.
doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2021.06.1273 |
|
| [21] |
doi: 10.1111/mpp.12281 pmid: 26033522 |
| [22] |
doi: 10.3390/ijms21031120 URL |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1111/mpp.v20.12 URL |
| [24] |
|
|
王芳, 孙立娇, 赵晓宇, 王婕婉, 宋兴舜. 2019. 植物NAC转录因子的研究进展. 生物技术通报, 35 (4):88-93.
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2018-0905 |
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2015.02.002 URL |
| [26] |
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2022.10.009 URL |
| [27] |
|
|
张晓孟. 2017. 黄瓜番茄NAC转录因子鉴定及在逆境应答和果实发育中的功能初步分析[博士论文]. 北京: 中国农业科学院.
|
|
| [28] |
|
|
郑林, 王帅, 刘语诺, 杜美霞, 彭爱红, 何永睿, 陈善春, 邹修平. 2022. 柑橘响应黄龙病菌侵染的NAC基因的克隆及表达分析. 园艺学报, 49 (7):1441-1457.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0553 URL |
|
| [29] |
|
|
周雅涵. 2017. 水杨酸、膜醭毕赤酵母、壳寡糖诱导柑橘果实抗病性及其生物学机制研究[博士论文]. 重庆: 西南大学.
|
|
| [30] |
|
|
周杨开. 2019. 转录因子NbNAC1调控植物系统性抗性防御病毒入侵的机制及其蛋白抗体制备[硕士论文]. 扬州: 扬州大学.
|
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
|
朱自果, 阴启忠, 张庆田, 韩真, 张倩, 李勃. 2020. 欧洲葡萄‘粉红亚都蜜'NAC基因DRL1负向调节植物抗旱性. 园艺学报, 47 (12):2290-2300.
|
|
| [33] |
|
|
朱凤鹃. 2005. 谈谈植物中的几丁质酶. 中国野生植物资源,(5):46-47,61.
|
| [1] | 金 天, 徐月美, 邝冠翎, 刘桂东, . 缺硼胁迫对枳幼苗根系生长及线粒体功能的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(1): 121-132. |
| [2] | 李素平, 李 微, 韩 冷, 黄建国, . 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌HY19挥发物对采后柑橘的防腐效果[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(1): 162-174. |
| [3] | 陈敏, 吴天利, 吕远达, 姜波, 闫化学, 李娟, 钟云. 不同砧木红江橙容器栽培生长和果实品质分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(7): 1547-1562. |
| [4] | 邓成凤, 李素平, 张瑞轩, 韩冷, 李勇. 产酶溶杆菌LE16对采后柑橘青霉绿霉病的防治作用[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(7): 1574-1586. |
| [5] | 张乐欢, 邹昌玉, 王兆昊, 杨雯, 邹修平, 何永睿, 陈善春, 龙琴. 柑橘AOS1-2的克隆及其响应溃疡病菌侵染的表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(6): 1355-1367. |
| [6] | 郭静, 廖满余, 金燕, 马小川, 张芬, 卢晓鹏, 邓子牛, 盛玲. 柑橘转录因子CsbHLH3调控柠檬酸代谢的功能解析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(5): 947-958. |
| [7] | 周平, 郭瑞, 颜少宾, 金光. 外源山梨醇影响桃叶片和果实糖代谢的分子机制研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(5): 959-971. |
| [8] | 吕若亚, 李云, 郑永钦, 邓晓玲, 郑正. 黄龙病菌在柑橘果实橘络中的分布[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(5): 1110-1117. |
| [9] | 王萍, 盛玲, 杨锦鹏, 周凌磊, 金燕, 罗旭钊, 马先锋, 邓子牛. 红心柚和美国枸橼杂种后代对柑橘溃疡病的抗性评价[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(4): 765-777. |
| [10] | 邹运乾, 罗曲娟, 张金, 许让伟, 程运江. 虫胶松香涂膜对柑橘货架期品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(4): 853-863. |
| [11] | 赖恒鑫, 李文广, 彭良志, 何义仲, 朱攀攀, 杨万云, 凌丽俐, 付行政, 淳长品, 曹立. 沃柑果实春夏季留树保鲜品质变化研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(3): 485-494. |
| [12] | 刘语诺, 曹亚, 王帅, 杜美霞, 郑林, 陈善春, 邹修平. 柑橘CsMYB41和CsMYB63响应溃疡病菌侵染的表达[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(3): 495-507. |
| [13] | 叶子茂, 申晚霞, 刘梦雨, 王彤, 张晓楠, 余歆, 刘小丰, 赵晓春. R2R3-MYB转录因子CitMYB21对柑橘类黄酮生物合成的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 250-264. |
| [14] | 梁圣敏, 张菲, 吴强盛. 丛枝菌根真菌通过调节枳根系多胺提高抗旱性[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(12): 2680-2688. |
| [15] | 张少然, 宗琪, 刘阳, 姜玲. 柑橘黄龙病病原菌nrdB基因的原位杂交分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(12): 2689-2700. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司