
园艺学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 121-132.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-1116
收稿日期:2023-09-21
修回日期:2023-12-02
出版日期:2024-01-25
发布日期:2024-01-16
通讯作者:
基金资助:
JIN Tian1, XU Yuemei1, KUANG Guanling1, LIU Guidong1,2,*( )
)
Received:2023-09-21
Revised:2023-12-02
Published:2024-01-25
Online:2024-01-16
摘要:
为明确缺硼胁迫对枳[Poncirus trifoliata(L.)Raf.]幼苗根系损伤的机制,采用营养液培养法研究缺硼对枳幼苗根系生长发育、线粒体活性氧代谢、抗氧化酶活性变化、线粒体特性和线粒体超微结构的影响。结果表明:缺硼处理抑制了枳幼苗根系生长,根系总根长、总表面积、总体积、平均直径及根系生物量均明显降低,根系活力也显著下降。缺硼处理降低了根系线粒体超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化物酶(POD)和过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性,增加了过氧化氢(H2O2)和丙二醛(MDA)含量。缺硼处理还使线粒体膜吸光度变化值降低,说明增大了线粒体膜透性转换孔开放程度。缺硼处理降低了线粒体膜流动性、线粒体膜电位和细胞色素c/a值,线粒体功能受损导致ATP合成明显减少。透射电镜观察结果显示缺硼处理的根系线粒体结构被破坏,线粒体内嵴减少,出现空泡化现象。综上,缺硼会显著抑制枳幼苗的生长发育,其作用机制可能与线粒体结构与功能受损有关。
金天, 徐月美, 邝冠翎, 刘桂东. 缺硼胁迫对枳幼苗根系生长及线粒体功能的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(1): 121-132.
JIN Tian, XU Yuemei, KUANG Guanling, LIU Guidong. Effect of Boron Deficiency on the Root Growth and Mitochondrial Function of Trifoliate Orange Seedlings[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(1): 121-132.
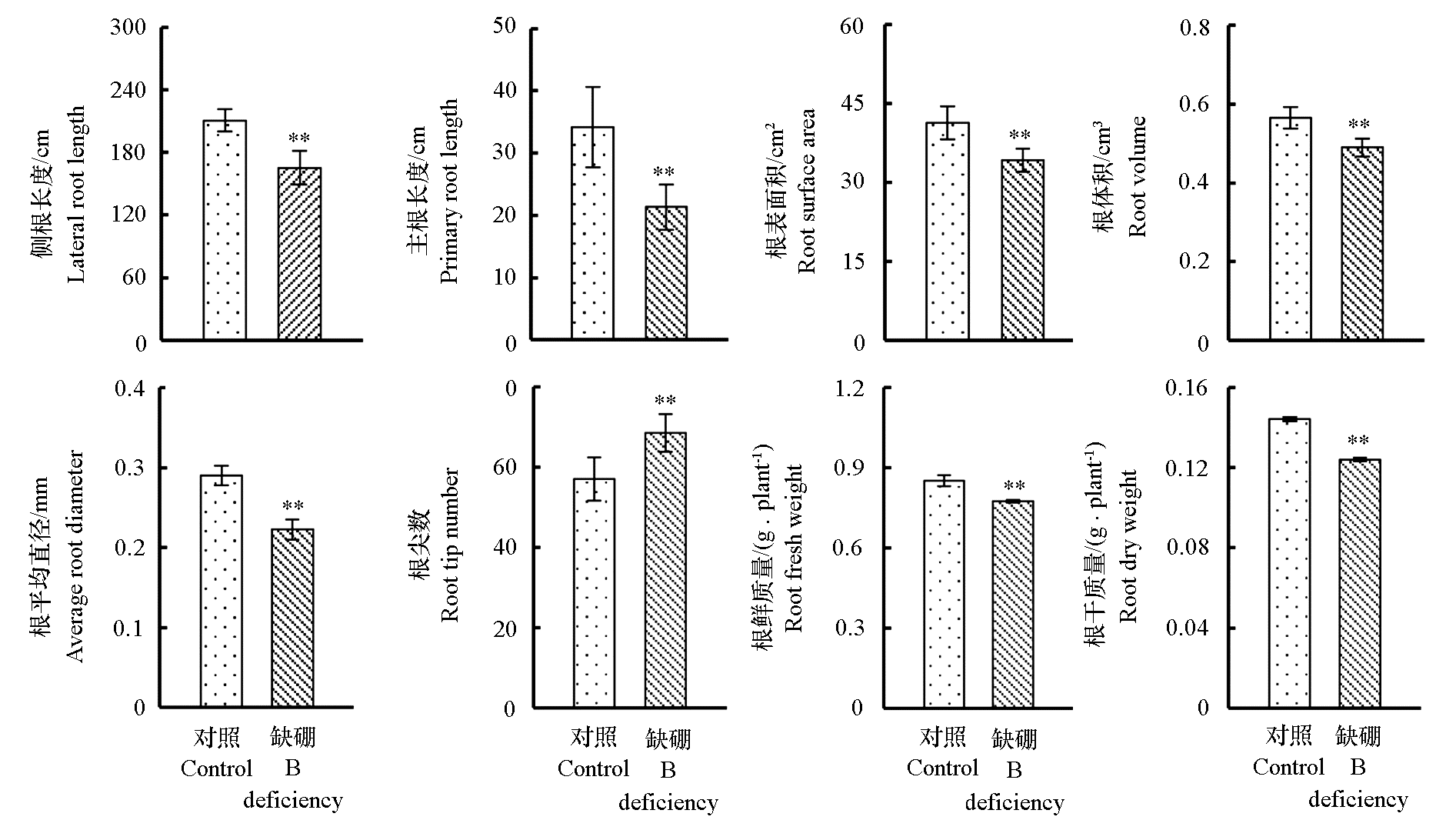
图2 缺硼对枳幼苗根系生长发育的影响 * 表示在0.05水平差异显著,** 表示在0.01水平差异显著,下同。
Fig. 2 Effects of boron deficiency on root growth and development of trifoliate orange seedlings * indicate significant difference at 0.05 level,and ** indicate significant difference at 0.01 level. The same below.
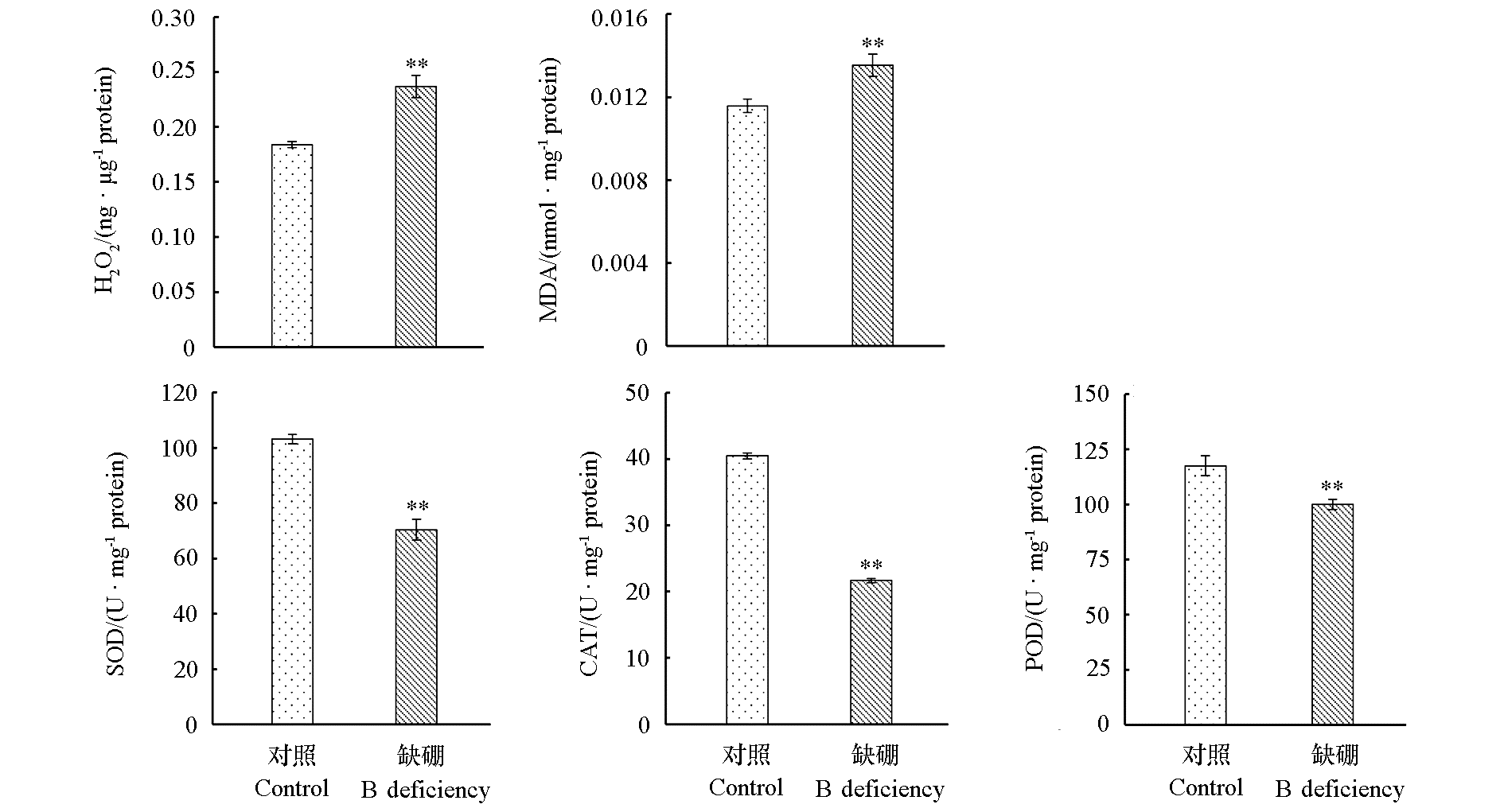
图4 缺硼对根系线粒体H2O2、丙二醛含量及抗氧化酶活性的影响
Fig. 4 Effects of boron deficiency on the concentrations of H2O2 and malondialdehyde and antioxidant enzyme activities in root mitochondria

图6 缺硼对根系细胞和线粒体超微结构的影响 CW:细胞壁;M:线粒体。
Fig. 6 Effect of boron deficiency on the ultrastructure of root cells and mitochondria CW:Cell wall;M:Mitochondria.

图7 缺硼对枳幼苗根系线粒体影响示意图 SOD:超氧化物歧化酶;POD:过氧化物酶;CAT:过氧化氢酶;ROS:活性氧;MDA:丙二醛;MPTP:线粒体膜透性转换孔;Cyt a:细胞色素a;Cyt c:细胞色素c;TCA:三羧酸循环;“+”:阳离子;mETC:线粒体电子传递链;ATP:腺苷三磷酸。 图中罗马数字代表电子传递复合体。实线表示已建立的关系,虚线表示可能的关系。
Fig. 7 Diagram showing the effect of boron deficiency on root mitochondria in trifoliate orange seedlings SOD:Superoxide dismutase;POD:Peroxidase;CAT:Catalase;ROS:Reactive oxygen species;MDA:Malondialdehyde;MPTP:Mitochondrial permeability transition pore;Cyt a:Cytochrome a;Cyt c:Cytochrome c;TCA:Tricarboxylic acid cycle;“+”:Cations;mETC:Mitochondrial respiratory electron transport chain. ATP:Adenosine triphosphate. The Roman numerals represent mitochondrial complex. Solid lines represent established interactions and dashed lines indicate proposed interactions.
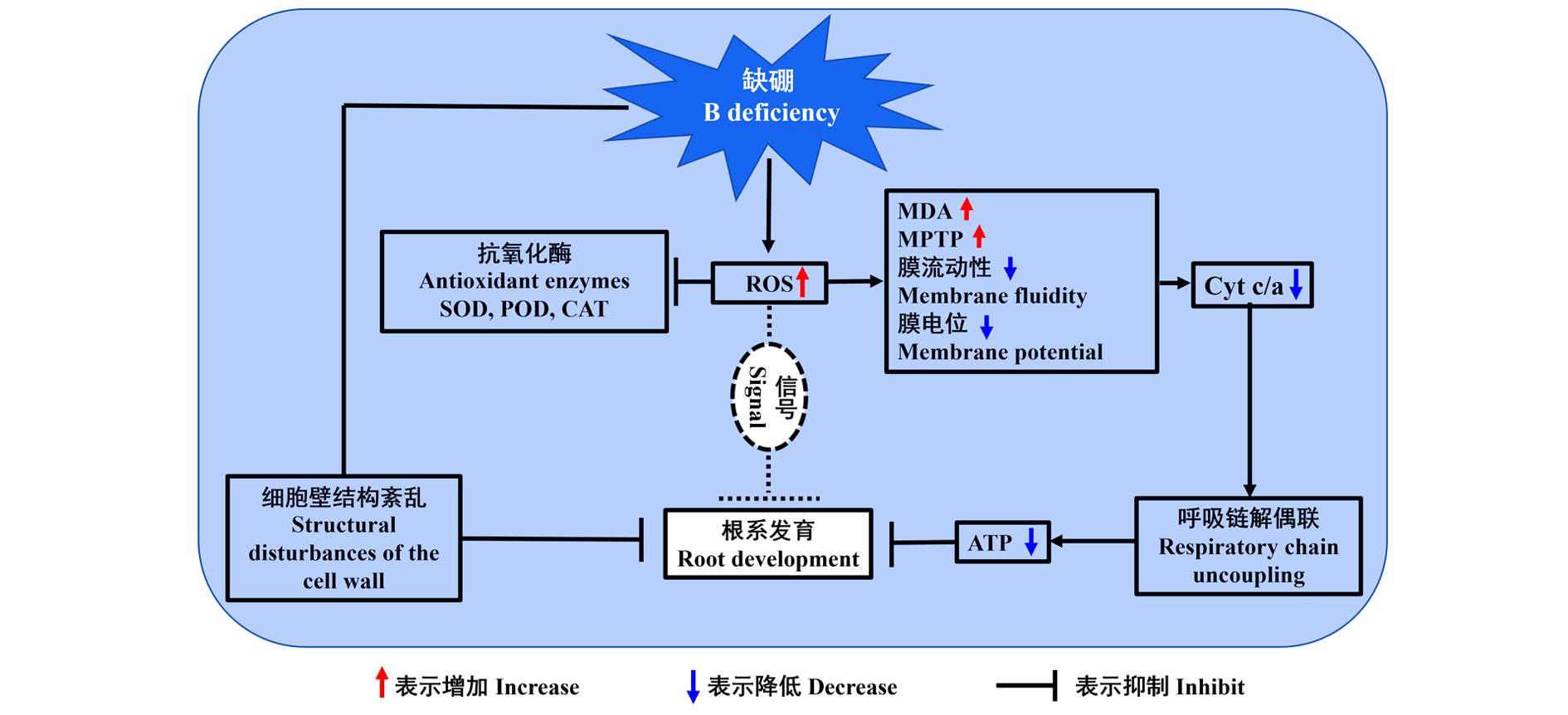
图8 缺硼影响枳幼苗根系发育的可能机制 SOD:超氧化物歧化酶;POD:过氧化物酶;CAT:过氧化氢酶;ROS:活性氧;MDA:丙二醛; MPTP:线粒体膜透性转换孔;Cyt c/a:细胞色素c/a;ATP:腺苷三磷酸。实线表示已建立的关系,虚线表示可能的关系。
Fig. 8 Possible mechanism of boron deficiency affecting root development of trifoliate orange seedlings SOD:Superoxide dismutase;POD:Peroxidase;CAT:Catalase;ROS:Reactive oxygen species;MDA:Malondialdehyde;MPTP:Mitochondrial permeability transition pore;Cyt c/a:Cytochrome c/a;ATP:Adenosine triphosphate. Solid lines represent established interactions and dashed lines indicate proposed interactions.
| [1] |
|
|
鲍士旦. 2008. 土壤农化分析. 北京: 中国农业出版社.
|
|
| [2] |
doi: 10.1023/A:1001898027218 URL |
| [3] |
doi: 10.3390/ijms21041424 URL |
| [4] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv186 pmid: 25922480 |
| [5] |
|
|
曹逼力, 刘灿玉, 徐坤. 2014. 硅对干旱胁迫下番茄根系细胞超微结构及线粒体活性氧代谢的影响. 园艺学报, 41 (12):2419-2426.
|
|
| [6] |
|
|
曹慧, 潘利, 姜倩倩, 邹岩梅, 束怀瑞. 2018. 外源钙和硫化氢对镉胁迫下平邑甜茶幼苗根系活性氧代谢和线粒体特性的影响. 华北农学报, 33 (2):163-168.
doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.2018.02.023 |
|
| [7] |
|
|
曹先梅, 刘立云, 李佳. 2020. 缺硼槟榔幼苗的生理反应和根系发育特征. 植物营养与肥料学报, 26 (2):386-392.
|
|
| [8] |
|
|
从心黎, 江行玉, 黄绵佳, 钟曼茜, 李新国. 2015. 免疫化学法探讨缺硼导致樱桃萝卜细胞壁松弛的机理. 南方农业学报, 46 (3):397-400.
|
|
| [9] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0701 URL |
|
邓秀新. 2022. 中国柑橘育种60年回顾与展望. 园艺学报, 49 (10):2063-2074.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0701 URL |
|
| [10] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0050 URL |
|
杜晨晴, 吴秀文, 闫磊, 刘亚林, 姜存仓. 2018. 缺硼和低pH对枳苗根系细胞壁组分及细胞中硼分布的影响. 园艺学报, 45 (7):1272-1282.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0050 URL |
|
| [11] |
pmid: 12231978 |
| [12] |
doi: 10.1111/nph.12997 pmid: 25187269 |
| [13] |
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00800 pmid: 31293607 |
| [14] |
pmid: 9714722 |
| [15] |
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057654 URL |
| [16] |
doi: 10.1016/S0176-1617(11)81928-0 URL |
| [17] |
|
|
李合生. 2000. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术. 北京: 高等教育出版社.
|
|
| [18] |
doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2022.09.033 pmid: 36219993 |
| [19] |
doi: 10.1007/s11104-013-1659-3 URL |
| [20] |
doi: 10.1093/treephys/tpu047 URL |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1007/s00344-021-10524-x |
| [22] |
doi: 10.1111/ppl.2013.147.issue-2 URL |
| [23] |
doi: 10.3390/ijms21061905 URL |
| [24] |
doi: 10.1111/jac.2009.195.issue-3 URL |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1126/science.1062319 URL |
| [26] |
doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.37.22923 URL |
| [27] |
pmid: 27396122 |
|
潘雄波, 向丽霞, 胡晓辉, 任文奇, 张丽, 倪新欣. 2016. 外源亚精胺对盐碱胁迫下番茄幼苗根系线粒体功能的影响. 应用生态学报, 27 (2):491-498.
pmid: 27396122 |
|
| [28] |
doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2014.02.007 URL |
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.10.020 pmid: 21074051 |
| [31] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2009.12.006 pmid: 20116882 |
| [32] |
doi: 10.1111/tpj.2014.79.issue-1 URL |
| [33] |
|
|
王瑞东, 姜存仓, 刘桂东, 王运华, 彭抒昂, 曾庆銮. 2011. 赣南脐橙产区果园土壤有效硼含量的现状与分析. 中国南方果树, 40 (4):1-3,7.
|
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
doi: 10.32615/bp.2019.026 URL |
| [36] |
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202004.030 |
|
魏国芹, 陶吉寒, 付全娟, 侯森, 杨兴华, 隋曙光, 余贤美, 孙玉刚. 2020. 硫化氢对低温胁迫下甜樱桃柱头和子房线粒体功能的影响. 应用生态学报, 31 (4):1121-1129.
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202004.030 |
|
| [37] |
|
|
魏文学, 王运华, 孙香芝, 瞿波. 1989. 缺硼条件下向日葵叶片叶绿体及线粒体解剖结构的观察. 华中农业大学学报, 8 (4):361-363,409.
|
|
| [38] |
doi: 10.1007/s11104-018-3684-8 |
| [39] |
doi: S0981-9428(20)30178-9 pmid: 32335386 |
| [40] |
|
|
吴妤, 禹文雅, 李奕松. 2013. 缺铁胁迫对草莓幼苗光合特性及细胞器铁含量的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 19 (4):918-925.
|
|
| [41] |
|
|
许长成, 赵世杰. 1992. 植物组织内丙二醛的分离与鉴定. 植物生理学通讯, 28 (4):288-290.
|
|
| [42] |
|
|
徐建兴. 2003. 细胞色素c在线粒体中的抗氧化功能. 中国科学院院刊, 18 (4):277-278.
|
|
| [43] |
doi: 10.3390/plants11010040 URL |
| [44] |
|
|
姚婷婷, 朱丽琴, 杨双, 周杰, 朱树华. 2010. 一氧化氮对采后李果实线粒体膜氧化损伤的影响. 中国农业科学, 43 (13):2767-2774.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2010.13.017 |
|
| [45] |
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2016.05.016 |
|
尹承苗, 胡艳丽, 王功帅, 张先富, 周慧, 沈向, 陈学森, 毛志泉. 2016. 苹果连作土壤中主要酚酸类物质对平邑甜茶幼苗根系的影响. 中国农业科学, 49 (5):961-969.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2016.05.016 |
|
| [46] |
doi: 10.1186/s12284-020-00383-7 pmid: 32274603 |
| [47] |
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2021.04206 |
|
曾紫君, 曾钰, 闫磊, 程锦, 姜存仓. 2021. 低硼及高硼胁迫对棉花幼苗生长与脯氨酸代谢的影响. 作物学报, 47 (8):1616-1623.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2021.04206 |
|
| [48] |
doi: 10.1111/tpj.v107.2 URL |
| [49] |
doi: 10.1007/s11738-018-2785-6 |
| [50] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0709 URL |
|
赵永, 朱红菊, 杨东东, 龚成胜, 刘文革. 2022. 果实柠檬酸代谢研究进展. 园艺学报, 49 (12):2579-2596.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0709 URL |
|
| [51] |
doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2009.05.002 URL |
| [1] | 胡亚伟, 马金龙, 钟八莲, 姚锋先, 刘桂东. 脐橙幼树夏施15N-尿素的利用与土壤残留初探[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 705-713. |
| [2] | 张书凝, 郑舒琪, 王新胜, 柯甫志, 张岚岚, 孙学鹏, 宫金礼. 柑橘果皮生理性病害与细胞壁代谢的关系研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 513-525. |
| [3] | 杨金磊, 吕壁纹, 陈岳文, 金燕, 杨俊枫, 周铁, 唐俊, 常媛媛, 杨长耀, 卢晓鹏. 湖南柑橘产区镉污染状况及镉对柑橘发育影响分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 200-212. |
| [4] | 董丽婷, 屈荣荣, 庞淑炜, 莫凯琴, 陈爽, 商兰月, 邹修平. 柑橘CsMEKK1-1响应黄龙病菌侵染的表达特征与功能探究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2168-2182. |
| [5] | 张文龙, 万润楚, 郑妮, 陈焱, 赖恒鑫, 余歆, 钱春, 曹立. 柑橘不育系新品种‘阳光1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2221-2222. |
| [6] | 李欣, 柴应芳, 田真, 王鹏蔚, 程运江. 线粒体分离纯化及其在果实成熟衰老研究中的应用进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1516-1528. |
| [7] | 杜美霞, 庞淑玮, 董丽婷, 莫凯琴, 候梦圆, 王帅, 邹修平. 柑橘黄龙病菌与寄主互作的分子机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1623-1638. |
| [8] | 曹惠祥, 罗鑫, 刘婉荣, 管书萍, 王婷婷, 伍小萌, 郭文武, 解凯东. 柑橘2个三倍体果实囊衣发育与化渣性评价[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1179-1188. |
| [9] | 周慧珍, 张嘉, 胡军华, 李白雪, 曹立, 余歆, 王福生, 邹修平, 周彦. 柑橘感染褐斑病过程中BAG1的作用[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 956-970. |
| [10] | 彭爱红, 张婧芸, 陈志毅, 苏娟, 何永睿, 姚利晓. CsEXPA8过表达对‘晚锦橙’生长及溃疡病抗性的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 971-981. |
| [11] | 游平, 杨进, 周俊, 黄爱军, 鲍敏丽, 易龙. 柑橘黄龙病菌原噬菌体的遗传多样性分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 727-736. |
| [12] | 熊志伟, 李智龙, 尹晖, 高玉霞. 柑橘黄龙病菌亚洲种的泛基因组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 737-747. |
| [13] | 易倩, 张曼曼, 汪小利, 冯继鹏, 朱世平, 王福生, 赵晓春. CclSAUR49对柑橘生长及类柠檬苦素代谢的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 479-494. |
| [14] | 孙权, 何政辰, 叶俊丽, 魏冉冉, 尹映紫, 柴利军, 谢宗周, 徐强, 徐娟, 郭文武, 程运江, 邓秀新. 与呼吸跃变型果实共贮藏改善柑橘果实色泽和品质[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 601-615. |
| [15] | 吴卓群, 陈鹏旭, 陈思怡, 张福琼, 方红, 祝建, 谢宗周, 李春龙, 刘继红. 温州蜜柑与椪柑果实日灼发生差异及机制[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(12): 2743-2757. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司