
园艺学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (2): 250-264.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-1188
叶子茂1, 申晚霞1,2,*( ), 刘梦雨1, 王彤1, 张晓楠1, 余歆1,2, 刘小丰1,2, 赵晓春1,2,*(
), 刘梦雨1, 王彤1, 张晓楠1, 余歆1,2, 刘小丰1,2, 赵晓春1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-08-08
修回日期:2022-10-19
出版日期:2023-02-25
发布日期:2023-03-06
通讯作者:
*(E-mail:基金资助:
YE Zimao1, SHEN Wanxia1,2,*( ), LIU Mengyu1, WANG Tong1, ZHANG Xiaonan1, YU Xin1,2, LIU Xiaofeng1,2, ZHAO Xiaochun1,2,*(
), LIU Mengyu1, WANG Tong1, ZHANG Xiaonan1, YU Xin1,2, LIU Xiaofeng1,2, ZHAO Xiaochun1,2,*( )
)
Received:2022-08-08
Revised:2022-10-19
Online:2023-02-25
Published:2023-03-06
Contact:
*(E-mail:摘要:
以‘巴西酸橙’(Citrus aurantium L.)、‘本地早橘’(C. reticulata Blanco)、‘桂花蒂南丰蜜橘’(C. reticulata Blanco)、‘北碚447锦橙’[C. sinensis(L.)Osbeck]等30份柑橘种质为试材,挖掘与柑橘类黄酮生物合成相关的R2R3-MYB转录因子。通过比较转录组分析发现ERF、MYB以及Dof转录因子家族与果实发育过程中类黄酮的代谢密切相关,其中两个R2R3-MYB转录因子基因CitMYB21(Ciclev10021699m)和CitMYB33(Ciclev10012152m)的表达水平与类黄酮生物合成途径中的关键结构基因CitCHS2的表达量明显负相关。系统发育分析显示,这两个基因分别属于R2R3-MYB中的第2和第1亚族。从‘北碚447锦橙’中克隆得到了CitMYB21编码区的全长序列,共804 bp,编码267个氨基酸。CitMYB21的表达有显著的组织特异性及明显的种质特异性,并与类黄酮的含量呈显著负相关。CitMYB21沉默的柑橘植株叶片中类黄酮含量显著增加,而瞬时过表达的果皮中类黄酮的含量明显降低。研究结果表明CitMYB21显著负影响柑橘类黄酮的含量,可能是负调控类黄酮生物合成的重要转录因子。
中图分类号:
叶子茂, 申晚霞, 刘梦雨, 王彤, 张晓楠, 余歆, 刘小丰, 赵晓春. R2R3-MYB转录因子CitMYB21对柑橘类黄酮生物合成的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 250-264.
YE Zimao, SHEN Wanxia, LIU Mengyu, WANG Tong, ZHANG Xiaonan, YU Xin, LIU Xiaofeng, ZHAO Xiaochun. Effect of R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor CitMYB21 on Flavonoids Biosynthesis in Citrus[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 250-264.
| 种类 Specific name | 种质编号 Code | 名称 Name | 种类 Specific name | 种质编号 Code | 名称 Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 宽皮橘 Citrus reticulate Blanco | ZY004 | 桂花蒂南丰蜜橘 Guihuadinanfeng Mandarin | 宽皮橘 C. reticulate Blanco | ZY198 | 半野生橘杂种No.3 Hybrid of Semi-wild No.3 |
| ZY013 | 槾橘 Manju | ZY208 | 无核早橘 Seedless Zaoju | ||
| ZY014 | 野橘 2 Yeju 2 | ZY215 | 丙中洛橘 Bingzhongluoju | ||
| ZY026 | 酸橘 Suanju | ZY222 | 红橘 Hongju | ||
| ZY035 | 鹅蛋香柑 E Dan Xianggan | ZY007 | 津优 Jinyou | ||
| ZY036 | 汉源黄果柑 Hanyuan Huangguogan | ZY008 | 扁柑 Biangan | ||
| ZY037 | 德昌金钱橘 Dechang Jinqianju | ZY011 | 久贺早生温州 Kuga Wase | ||
| ZY049 | 冰糖香柑 Bingtang Xianggan | ZY012 | 北口温州 Kitaguchi Wase | ||
| ZY084 | 青红橘 Qinghongju | 温州蜜柑 C. unshiu Macf. | ZY067 | 久能温州 Kunou Wase | |
| ZY085 | 红橙 Hongcheng | ZY070 | 繁田温州 Shigeta Wase | ||
| ZY090 | 元阳酸橘 Yuanyang Suanju | ZY124 | 大分1号温州 Dafen No.1 Wase | ||
| ZY108 | 沅江南橘 Yuanjiang Nanju | ZY145 | 湘慈43号 Xiangci No.43 | ||
| ZY119 | 马塔里橘 Matari Tangerine | ZY168 | 谷口系日南1号温州 | ||
| ZY151 | 新生系3号椪柑 No.3 Ponkan | Taniguchi Line Nichinan No.1 Wase | |||
| ZY174 | 春见 Harumi | ZY231 | 桥本温州 Hashimoto Wase | ||
| ZY002 | 平阳橘 Duong Mandarin |
表1 种质名单
Table 1 List of citrus germplasms
| 种类 Specific name | 种质编号 Code | 名称 Name | 种类 Specific name | 种质编号 Code | 名称 Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 宽皮橘 Citrus reticulate Blanco | ZY004 | 桂花蒂南丰蜜橘 Guihuadinanfeng Mandarin | 宽皮橘 C. reticulate Blanco | ZY198 | 半野生橘杂种No.3 Hybrid of Semi-wild No.3 |
| ZY013 | 槾橘 Manju | ZY208 | 无核早橘 Seedless Zaoju | ||
| ZY014 | 野橘 2 Yeju 2 | ZY215 | 丙中洛橘 Bingzhongluoju | ||
| ZY026 | 酸橘 Suanju | ZY222 | 红橘 Hongju | ||
| ZY035 | 鹅蛋香柑 E Dan Xianggan | ZY007 | 津优 Jinyou | ||
| ZY036 | 汉源黄果柑 Hanyuan Huangguogan | ZY008 | 扁柑 Biangan | ||
| ZY037 | 德昌金钱橘 Dechang Jinqianju | ZY011 | 久贺早生温州 Kuga Wase | ||
| ZY049 | 冰糖香柑 Bingtang Xianggan | ZY012 | 北口温州 Kitaguchi Wase | ||
| ZY084 | 青红橘 Qinghongju | 温州蜜柑 C. unshiu Macf. | ZY067 | 久能温州 Kunou Wase | |
| ZY085 | 红橙 Hongcheng | ZY070 | 繁田温州 Shigeta Wase | ||
| ZY090 | 元阳酸橘 Yuanyang Suanju | ZY124 | 大分1号温州 Dafen No.1 Wase | ||
| ZY108 | 沅江南橘 Yuanjiang Nanju | ZY145 | 湘慈43号 Xiangci No.43 | ||
| ZY119 | 马塔里橘 Matari Tangerine | ZY168 | 谷口系日南1号温州 | ||
| ZY151 | 新生系3号椪柑 No.3 Ponkan | Taniguchi Line Nichinan No.1 Wase | |||
| ZY174 | 春见 Harumi | ZY231 | 桥本温州 Hashimoto Wase | ||
| ZY002 | 平阳橘 Duong Mandarin |
| 引物名称 Primers name | 序列(5′-3′) Sequence | 酶切位点 Restriction site |
|---|---|---|
| OE-CitMYB21F | CCATTTAAATATGGTGAGAGCTCCATGCTG | SwaⅠ |
| OE-CitMYB21R | CGGGATCCCGACTTCTCATCAAAAAGGAAGGA | BamHⅠ |
| VIGS-CitMYB21F | TCCCCCGGGACAACAAGAGCCCGTGATTA | SmaⅠ |
| VIGS-CitMYB21R | CGGGATCCAACTATAGACAGTGGGTCGGC | BamHⅠ |
| q-CitMYB21F | CATGCTGCGAGAAGATGGGA | |
| q-CitMYB21R | CTGCTTGTTTGGGAAGTGCC | |
| Actin-F | CATCCCTCAGCACCTTCC | |
| Actin-R | CCAACCTTAGCACTTCTCC | |
| pTRV1-F | TTGGGTTGCTACTGATTCGACT | |
| pTRV1-R | CTGTAAGGACCATCATACTTCGC | |
| pTRV2_GFP-F | CTGCCCGACAACCACTACCT | |
| pTRV2_GFP-R | CTTGTACAGCTCGTCCATGCC |
表2 所用引物
Table 2 Sequences of primers
| 引物名称 Primers name | 序列(5′-3′) Sequence | 酶切位点 Restriction site |
|---|---|---|
| OE-CitMYB21F | CCATTTAAATATGGTGAGAGCTCCATGCTG | SwaⅠ |
| OE-CitMYB21R | CGGGATCCCGACTTCTCATCAAAAAGGAAGGA | BamHⅠ |
| VIGS-CitMYB21F | TCCCCCGGGACAACAAGAGCCCGTGATTA | SmaⅠ |
| VIGS-CitMYB21R | CGGGATCCAACTATAGACAGTGGGTCGGC | BamHⅠ |
| q-CitMYB21F | CATGCTGCGAGAAGATGGGA | |
| q-CitMYB21R | CTGCTTGTTTGGGAAGTGCC | |
| Actin-F | CATCCCTCAGCACCTTCC | |
| Actin-R | CCAACCTTAGCACTTCTCC | |
| pTRV1-F | TTGGGTTGCTACTGATTCGACT | |
| pTRV1-R | CTGTAAGGACCATCATACTTCGC | |
| pTRV2_GFP-F | CTGCCCGACAACCACTACCT | |
| pTRV2_GFP-R | CTTGTACAGCTCGTCCATGCC |
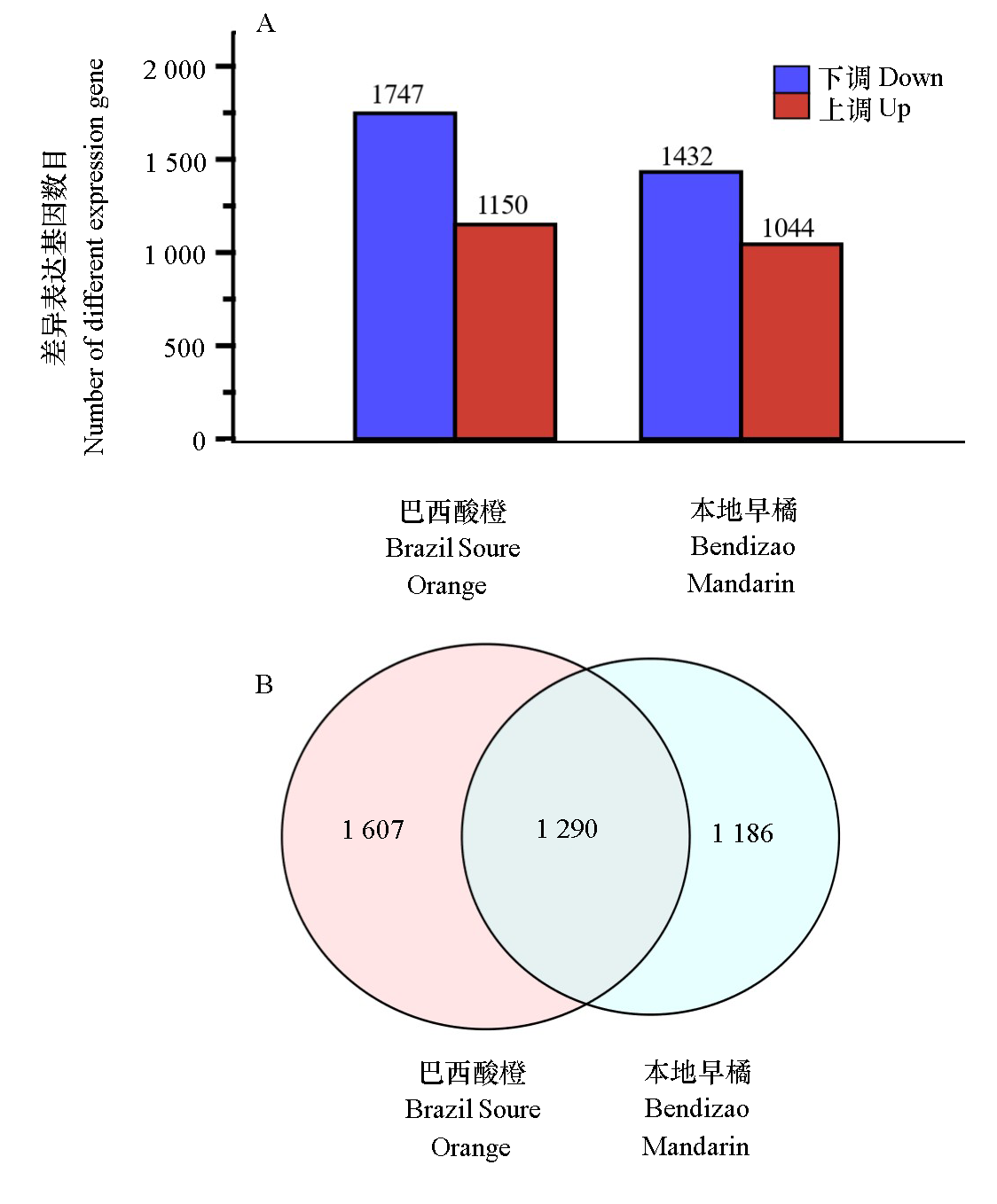
图1 ‘巴西酸橙’和‘本地早橘’花后160 d vs. 100 d果实间差异表达基因数量(A)及维恩图(B)
Fig. 1 The number of differentially expressed genes(A)and Venn diagram(B)between the fruits of Brazil Sour Orange and Bendizao Mandarin at 160 d vs. 100 d after flowering
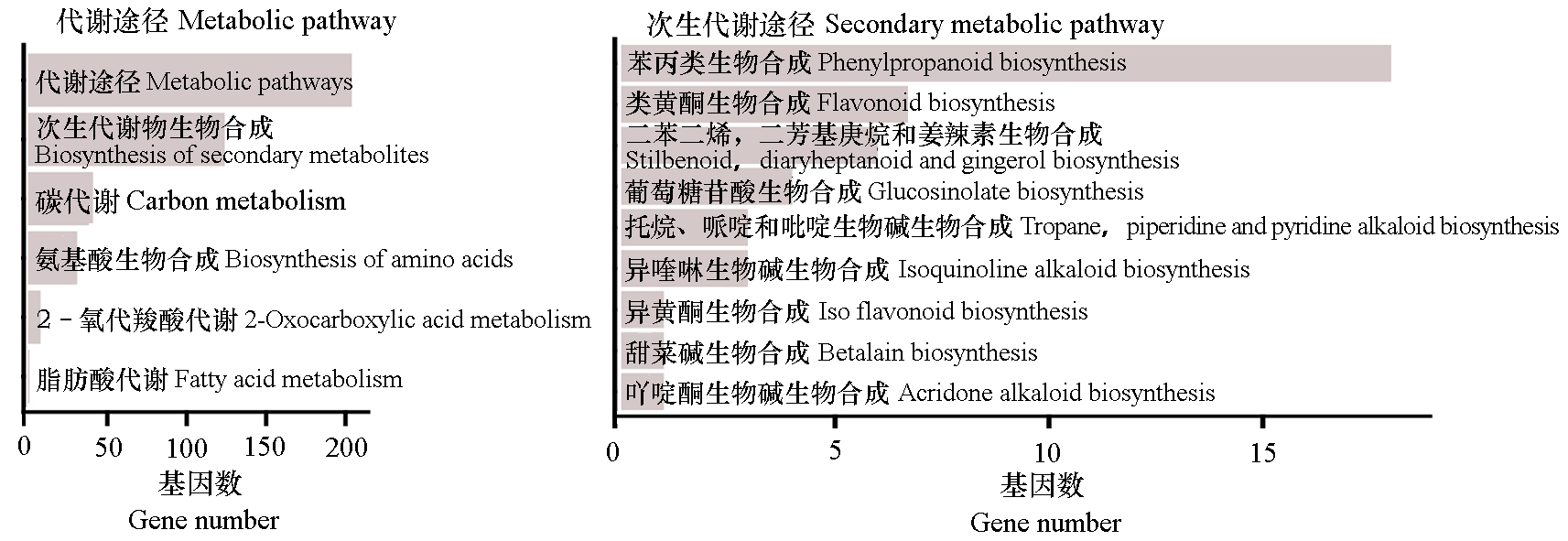
图2 ‘巴西酸橙’和‘本地早橘’花后160 d vs. 100 d果实共有的差异表达基因KEGG功能注释
Fig. 2 KEGG functional annotation of co-shared differently expression genes between Brazil Sour Orange and Bendizao Mandarin at 160 d vs. 100 d after flowering
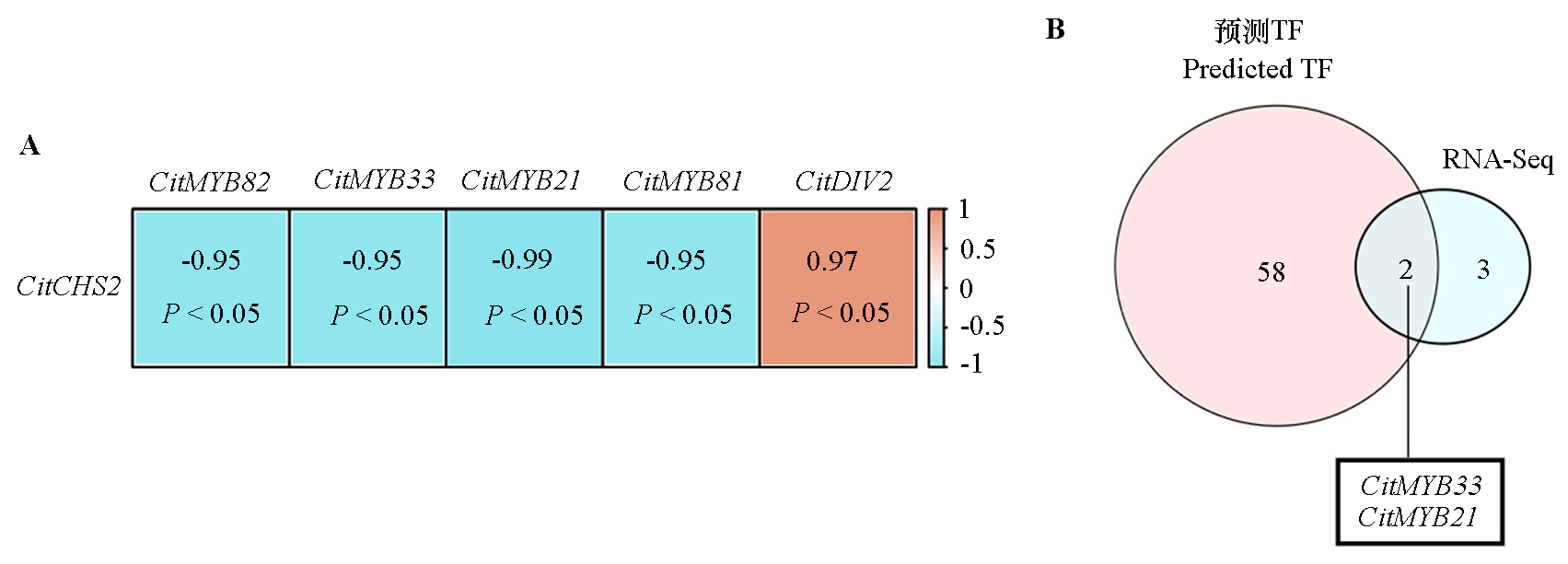
图5 与类黄酮生物合成相关的R2R3-MYB的鉴定 A:与结构基因CitCHS2相关的R2R3-MYB转录因子;B:预测的R2R3-MYB与差异表达基因中筛选的R2R3-MYB的交集。
Fig. 5 Identification of candidate R2R3-MYB transcription factors related to flavonoids biosynthesis A:Correlation analysis of R2R3-MYB transcription factors with flavonoids biosynthesis related structural genes CitCHS2. B:The Venn diagram of predicted R2R3-MYB and identified R2R3-MYB from DEGs.
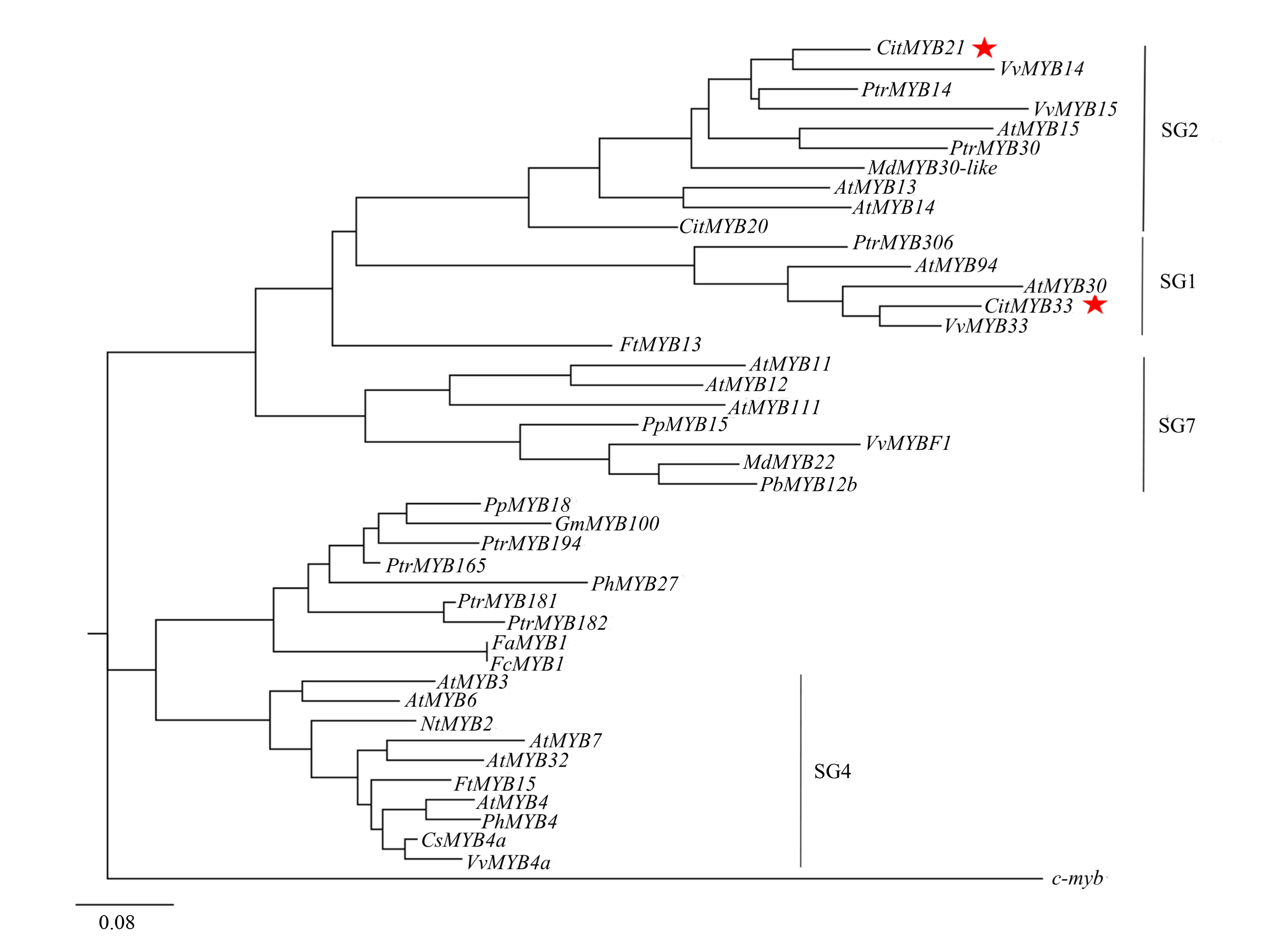
图6 候选R2R3-MYB成员的系统发育分析 Cit:柑橘;At:拟南芥;Ptr:杨树;Vv:葡萄;Md:苹果;Pp:桃;Pb:梨;Ft:荞麦;Gm:大豆;Fa:草莓;Fc:智利草莓;Ph:矮牵牛;Cs:茶树;Nt:水仙。
Fig. 5 Phylogenetic analysis of candidate R2R3-MYB members Cit:Citrus clementina;At:Arabidopsis thaliana;Ptr:Populus trichocarpa;Vv:Vitis vinifera;Md:Malus × domestica;Pp:Prunus persica;Pb:Pyrus bretschneideri;Ft:Fagopyrum tataricum;Gm:Glycine max;Fa:Fragaria × ananassa;Fc:Fragaria chiloensis;Ph:Petunia × hybrida;Cs:Camellia sinensis;Nt:Narcissus tazetta.
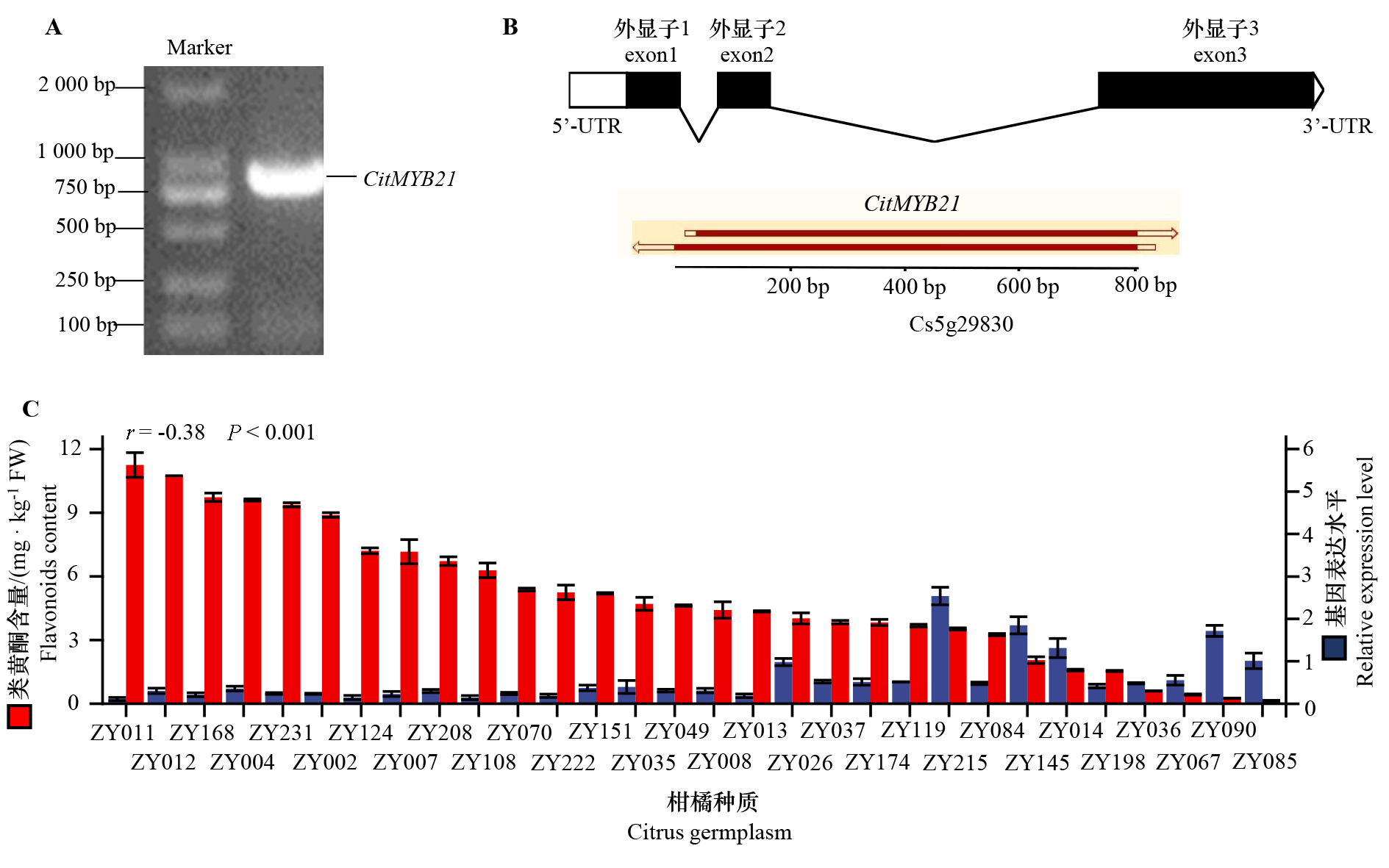
图7 CitMYB21克隆及其表达量与类黄酮含量的相关性分析 A:CitMYB21克隆产物电泳图;B:CitMYB21基因结构图及与Cs5g29830序列相似性比对;C:30份种质(详见表1)中CitMYB21表达量与类黄酮含量。
Fig. 7 CitMYB21 gene cloning and correlation analysis of its expression and flavonoid content A:Gel electrophoresis of cloned production of CitMYB21. B:The structure and sequence similarity of CitMYB21 and Cs5g29830. C:Relative expression level of CitMYB21 and flavonoids content in 30 citrus germplasms(See Table 1).

图9 ‘桂花蒂南丰蜜橘’叶片发育过程中CitMYB21表达水平和类黄酮含量的变化
Fig. 9 The change pattern of CitMYB21 expression and flavonoids content during leaf developing of Guihuadi Nanfeng Mandarin
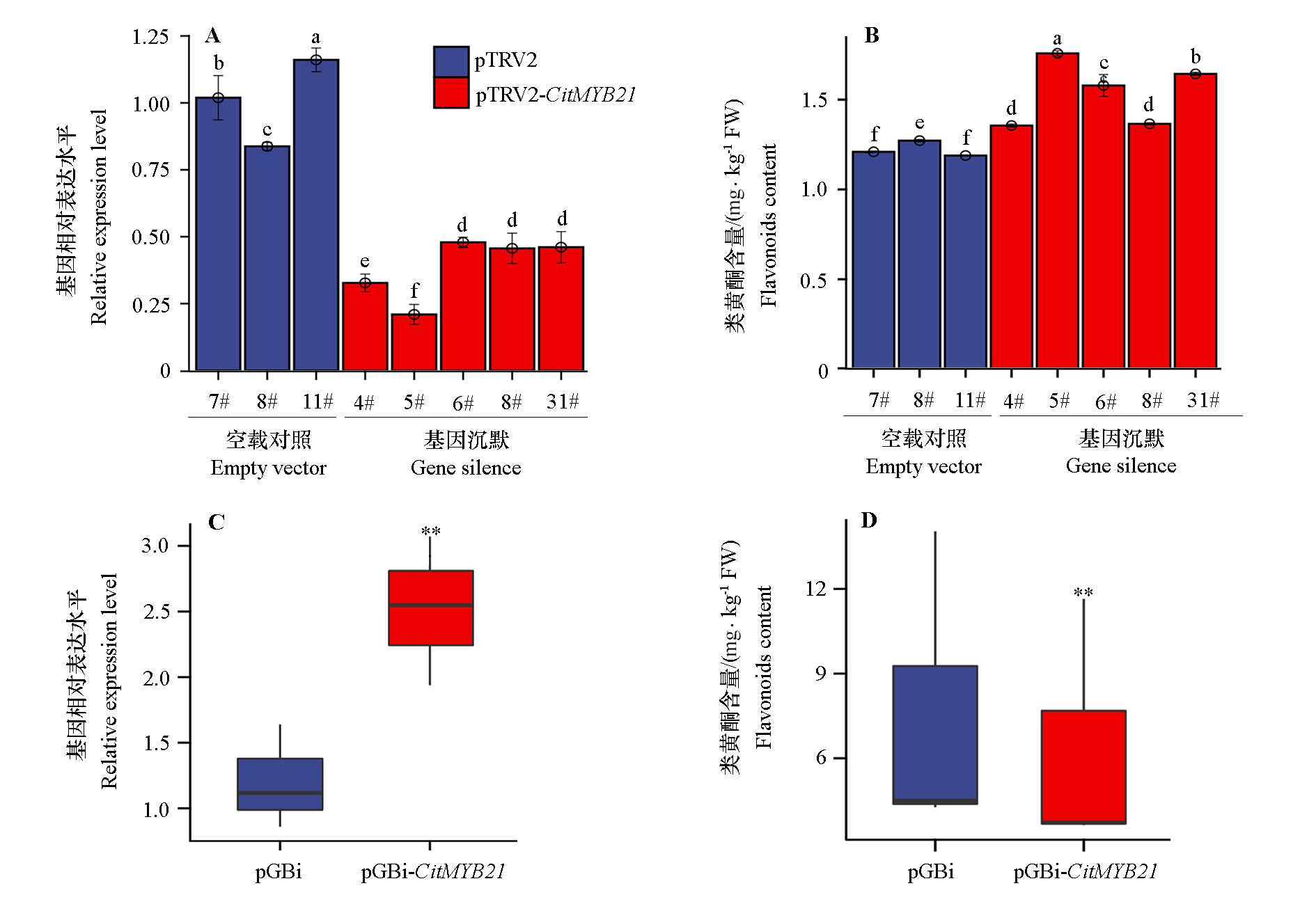
图10 ‘北碚447锦橙’基因沉默植株(A、B)和过表达果皮(C、D)中CitMYB21表达水平和类黄酮含量 ** 表示处理间差异极显著(P < 0.01)。
Fig. 10 CitMYB21 expression level and flavonoid content in Beibei 447 Jincheng gene-silenced plants(A,B)and overexpressed peels(C,D) ** indicate extremely significant differences between different treatments at 0.01 level.
| 转化方式 Transformation method | r 相关性Correlation | P 显著性Significance |
|---|---|---|
| 病毒诱导的基因沉默Virus induced gene slicing | -0.8 | < 0.01 |
| 瞬时表达Transient expression | -0.8 | > 0.05 |
表3 ‘北碚447锦橙’转基因植株中CitMYB21表达与类黄酮含量的相关性
Table 3 The correlation of CitMYB21 expression and flavonoids content in transgenic lines of Beibei 447 Jincheng
| 转化方式 Transformation method | r 相关性Correlation | P 显著性Significance |
|---|---|---|
| 病毒诱导的基因沉默Virus induced gene slicing | -0.8 | < 0.01 |
| 瞬时表达Transient expression | -0.8 | > 0.05 |
| 基因 Gene | CitPAL | CitC4H | Cit4CL1 | Cit4CL2 | CitCHS2 | CitCHI | 条件 Condition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CitMYB21 | -0.7** | 0.3 | -0.5* | 0.3 | -0.4 | -0.5 | 叶片发育早期Leaf early developmental stage |
| CitMYB21 | 0.1 | -0.4 | 0.5* | -0.5 | 0.6* | 0.4 | 叶片发育后期Leaf late developmental stage |
| CitMYB21 | 0.1 | 0.9** | -0.6 | 0.7 | -0.6 | 0.8** | 组织部位Tissue |
| CitMYB21 | 0.3 | 0.6* | -0.4 | -0.5 | -0.7** | -0.6** | 基因沉默Gene silencing |
| CitMYB21 | 0.2 | 0.8 | -0.3** | 0.7 | -0.9** | -0.9** | 瞬时表达Transient expression |
表4 CitMYB21表达与类黄酮合成相关基因表达水平的相关性
Table 4 The correlation analysis of expression level of CitMYB21 and structural genes related to flavonoids biosynthesis
| 基因 Gene | CitPAL | CitC4H | Cit4CL1 | Cit4CL2 | CitCHS2 | CitCHI | 条件 Condition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CitMYB21 | -0.7** | 0.3 | -0.5* | 0.3 | -0.4 | -0.5 | 叶片发育早期Leaf early developmental stage |
| CitMYB21 | 0.1 | -0.4 | 0.5* | -0.5 | 0.6* | 0.4 | 叶片发育后期Leaf late developmental stage |
| CitMYB21 | 0.1 | 0.9** | -0.6 | 0.7 | -0.6 | 0.8** | 组织部位Tissue |
| CitMYB21 | 0.3 | 0.6* | -0.4 | -0.5 | -0.7** | -0.6** | 基因沉默Gene silencing |
| CitMYB21 | 0.2 | 0.8 | -0.3** | 0.7 | -0.9** | -0.9** | 瞬时表达Transient expression |
| [1] |
Abad-García B, Berrueta L A, Garmón-Lobato S, Gallo B, Vicente F. 2009. A general analytical strategy for the characterization of phenolic compounds in fruit juices by high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection coupled to electrospray ionization and triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 1216 (28):5398-5415.
doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2009.05.039 pmid: 19500791 |
| [2] |
Albert N W, Davies K M, Lewis D H, Zhang H, Montefiori M, Brendolise C, Boase M R, Ngo H, Jameson P E, Schwinn K E. 2014. A conserved network of transcriptional activators and repressors regulates anthocyanin pigmentation in eudicots. The Plant Cell, 26 (3):962-980.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.122069 pmid: 24642943 |
| [3] |
Bondonno N P, Dalgaard F, Kyrø C, Murray K, Bondonno C P, Lewis J R, Croft K D, Gislason G, Scalbert A, Cassidy A, Tjønneland A, Overvad K, Hodgson J M. 2019. Flavonoid intake is associated with lower mortality in the Danish dietcancer and health cohort. Nature Communication, 10 (1):3651.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11622-x |
| [4] |
Borevitz J O, Xia Y, Blount J, Dixon R A, Lamb C. 2000. Activation tagging identifies a conserved MYB regulator of phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. The Plant Cell, 12 (12):2383-2394.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.12.12.2383 URL |
| [5] |
Butelli E, Licciardello C, Zhang Y, Liu J, Mackay S, Bailey P, Reforgiato-Recupero G, Martin C. 2012. Retrotransposons control fruit-specific,cold-dependent accumulation of anthocyanins in blood oranges. The Plant Cell, 24 (3):1242.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.095232 URL |
| [6] |
Chezem W R, Memon A, Li F S, Weng J K, Clay N K. 2017. SG2-type R2R3-MYB transcription factor MYB 15 controls defense-induced lignification and basal immunity in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 29 (8):1907-1926.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.16.00954 URL |
| [7] |
Dubos C, Stracke R, Grotewold E, Weisshaar B, Martin C, Lepiniec L. 2010. MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends in Plant Science, 15 (10):573-581.
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2010.06.005 URL |
| [8] |
Durand-Hulak M, Dugrand A, Duval T, Bidel L P R, Jay-Allemand C, Froelicher Y, Bourgaud F, Fanciullino A L. 2015. Mapping the genetic and tissular diversity of 64 phenolic compounds in Citrus species using a UPLC-MS approach. Annals of Botany, 115 (5):861-877.
doi: 10.1093/aob/mcv012 pmid: 25757470 |
| [9] |
Grant C E, Bailey T L, Noble W S. 2011. FIMO:scanning for occurrences of a given motif. Bioinformatics, 27 (7):1017-1018.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr064 URL |
| [10] | Hamamouch N, Winkel B S J, Li C, Davis E L. 2020. Modulation of flavonol biosynthesis genes by cyst and root-knot nematodes. Plants(Basel,Switzerland), 9 (2):253. |
| [11] |
Höll J, Vannozzi A, Czemmel S, D'Onofrio C, Walker A R, Rausch T, Lucchin M, Boss P K, Dry I B, Bogs J. 2013. The R2R3-MYB transcription factors MYB14 and MYB 15 regulate stilbene biosynthesis in Vitis vinifera. The Plant Cell, 25 (10):4135-4149.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.117127 URL |
| [12] |
Huang D, Tang Z, Fu J, Yuan Y, Deng X, Xu Q. 2020. CsMYB3 and CsRuby 1 form an‘activator-and-repressor’loop for the regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in citrus. Plant and Cell Physiology, 61 (2):318-330.
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcz198 pmid: 31642503 |
| [13] | Huang D, Yuan Y, Tang Z, Huang Y, Kang C, Deng X, Xu Q. 2019. Retrotransposon promoter of Ruby 1 controls both light- and cold-induced accumulation of anthocyanins in blood orange. Plant,Cell & Environment, 42 (11):3092-3104. |
| [14] |
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K. 2016. MEGA7:molecular evolutionary genetics analysis Version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 33 (7):1870-1874.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw054 URL |
| [15] |
Lewinsohn E, Britsch L, Mazur Y, Gressel J. 1989. Flavanone glycoside biosynthesis in citrus:chalcone synthase,udp-glucose:flavanone-7- O-glucosyl-transferase and -rhamnosyl-transferase activities in cell-free extracts. Plant Physiology, 91 (4):1323-1328.
doi: 10.1104/pp.91.4.1323 pmid: 16667183 |
| [16] |
Liu C, Long J, Zhu K, Liu L, Yang W, Zhang H, Li L, Xu Q, Deng X. 2016. Characterization of a citrus R2R3-MYB transcription factor that regulates the flavonol and hydroxycinnamic acid biosynthesis. Scientific Reports, 6 (1):25352.
doi: 10.1038/srep25352 |
| [17] |
Liu C, Wang X, Xu Y, Deng X, Xu Q. 2014. Genome-wide analysis of the R2R3-MYB transcription factor gene family in sweet orange(Citrus sinensis). Molecular Biology Reports, 41 (10):6769-6785.
doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3563-1 URL |
| [18] |
Lo Piero A R. 2015. The state of the art in biosynthesis of anthocyanins and its regulation in pigmented sweet oranges[Citrus sinensis L. Osbeck]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 63 (16):4031-4041.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b01123 URL |
| [19] |
Ma D, Constabel C P. 2019. MYB repressors as regulators of phenylpropanoid metabolism in plants. Trends in Plant Science, 24 (3):275-289.
doi: S1360-1385(18)30290-5 pmid: 30704824 |
| [20] |
Masumi Y. 2022. High temperature enhances anthocyanin coloration in Asiatic hybrid lily flowers via upregulation of the MYB 12 positive regulator. Horticultural Plant Journal, 8 (6):769-776.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2022.05.003 URL |
| [21] | Mierziak J, Kostyn K, Kulma A. 2014. Flavonoids as important molecules of plant interactions with the environment. Molecules(Basel,Switzerland), 19 (10):16240-16265. |
| [22] |
Moriguchi T, Kita M, Tomono Y, Endo-Inagaki T, Omura M. 1999. One type of chalcone synthase gene expressed during embryogenesis regulates the flavonoid accumulation in citrus cell cultures. Plant and Cell Physiology, 40 (6):651-655.
pmid: 10483126 |
| [23] |
Pang Y, Shen G, Wu W, Liu X, Lin J, Tan F, Sun X, Tang K. 2005. Characterization and expression of chalcone synthase gene from Ginkgo biloba. Plant Science, 168 (6):1525-1531.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2005.02.003 URL |
| [24] |
Peters D J, Constabel C P. 2002. Molecular analysis of herbivore-induced condensed tannin synthesis:cloning and expression of dihydroflavonol reductase from trembling aspen(Populus tremuloides). Plant Journal, 32 (5):701-712.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2002.01458.x URL |
| [25] |
Petrussa E, Braidot E, Zancani M, Peresson C, Bertolini A, Patui S, Vianello A. 2013. Plant flavonoids-biosynthesis,transport and involvement in stress responses. International Journal of Molecular Science, 14 (7):14950-14973.
doi: 10.3390/ijms140714950 URL |
| [26] |
Robinson M D, McCarthy D J, Smyth G K. 2009. edgeR:a Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics, 26 (1):139-140.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp616 URL |
| [27] |
Shan X, Li Y, Yang S, Yang Z, Qiu M, Gao R, Han T, Meng X, Xu Z, Wang L, Gao X. 2020. The spatio-temporal biosynthesis of floral flavonols is controlled by differential phylogenetic MYB regulators in Freesia hybrida. New Phytologist, 228 (6):1864-1879.
doi: 10.1111/nph.v228.6 URL |
| [28] |
Shen Y, Sun T, Pan Q, Anupol N, Chen H, Shi J, Liu F, Deqiang D, Wang C, Zhao J, Yang S, Wang C, Liu J, Bao M, Ning G. 2019. RrMYB5- and RrMYB10-regulated flavonoid biosynthesis plays a pivotal role in feedback loop responding to wounding and oxidation in Rosa rugosa. Plant Biotechnol Journal, 17 (11):2078-2095.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.v17.11 URL |
| [29] |
Sun L, Subar A F, Bosire C, Dawsey S M, Kahle L L, Zimmerman T P, Abnet C C, Heller R, Graubard B I, Cook M B, Petrick J L. 2017. Dietary flavonoid intake reduces the risk of head and neck but not esophageal or gastric cancer in US men and women. The Journal of Nutrition, 147 (9):1729-1738.
doi: 10.3945/jn.117.251579 URL |
| [30] |
Sun W, Meng X, Liang L, Jiang W, Huang Y, He J, Hu H, Almqvist J, Gao X, Wang L. 2015. Molecular and biochemical analysis of chalcone synthase from Freesia hybrid in flavonoid biosynthetic pathway. PLoS ONE, 10 (3):e0119054.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119054 URL |
| [31] |
Tang N, Cao Z, Yang C, Ran D, Wu P, Gao H, He N, Liu G, Chen Z. 2021. A R2R3-MYB transcriptional activator LmMYB 15 regulates chlorogenic acid biosynthesis and phenylpropanoid metabolism in Lonicera macranthoides. Plant Science, 308:110924.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2021.110924 URL |
| [32] |
Torregrosa C, Cluzet S, Fournier J, Huguet T, Gamas P, Prospéri J-M, Esquerré-Tugayé M-T, Dumas B, Jacquet C. 2004. Cytological,genetic,and molecular analysis to characterize compatible and incompatible interactions between Medicago truncatula and Colletotrichum trifolii. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interaction, 17 (8):909-920.
doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2004.17.8.909 URL |
| [33] |
Wang F, Wang M, Liu X, Xu Y, Zhu S, Shen W, Zhao X. 2017a. Identification of putative genes involved in limonoids biosynthesis in citrus by comparative transcriptomic analysis. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8 (782):Doi:10.3389/fpls.2017.00782.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00782 |
| [34] |
Wang N, Xu H, Jiang S, Zhang Z, Lu N, Qiu H, Qu C, Wang Y, Wu S, Chen X. 2017b. MYB12 and MYB 22 play essential roles in proanthocyanidin and flavonol synthesis in red-fleshed apple(Malus sieversii f. niedzwetzkyana). The Plant Journal, 90 (2):276-292.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.2017.90.issue-2 URL |
| [35] |
Wang S, Yang C, Tu H, Zhou J, Liu X, Cheng Y, Luo J, Deng X, Zhang H, Xu J. 2017c. Characterization and metabolic diversity of flavonoids in citrus species. Scientific Reports, 7 (1):10549.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10970-2 |
| [36] | Wang Zhi-bin. 2019. Gene diversity and functional study of CHS gene in citrus[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Chongqing: Southwest University. |
| 王志彬. 2019. 柑橘查尔酮合成酶基因遗传多样性及其功能研究[博士论文]. 重庆: 西南大学. | |
| [37] |
Wang Zhi-bin, Shen Wan-xia, Zhu Shi-ping, Xue Yang, Zhao Xiao-chun. 2015. Polymorphism and expression of chalcone synthase gene in citrus related to the flavonoids content. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 42 (3):435-444. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2014-1036 |
| 王志彬, 申晚霞, 朱世平, 薛杨, 赵晓春. 2015. 柑橘CHS基因序列多态性及表达水平对类黄酮生物合成的影响. 园艺学报, 42 (3):435-444. | |
| [38] |
Xie R, Li Y, He S, Zheng Y, Yi S, Lv Q, Deng L. 2014. Genome-wide analysis of citrus R2R3MYB genes and their spatiotemporal expression under stresses and hormone treatments. PLoS ONE, 9 (12):e113971.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113971 URL |
| [39] |
Xie S, Lei Y, Chen H, Li J, Chen H, Zhang Z. 2020. R2R3-MYB transcription factors regulate anthocyanin biosynthesis in grapevine vegetative tissues. Frontiers in Plant Science, 11:527.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00527 pmid: 32457776 |
| [40] |
Zhai R, Zhao Y, Wu M, Yang J, Li X, Liu H, Wu T, Liang F, Yang C, Wang Z, Ma F, Xu L. 2019. The MYB transcription factor PbMYB12b positively regulates flavonol biosynthesis in pear fruit. BMC Plant Biology, 19 (1):85.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-1687-0 pmid: 30791875 |
| [41] | Zhang D, Jiang C, Huang C, Wen D, Lu J, Chen S, Zhang T, Shi Y, Xue J, Ma W, Xiang L, Sun W, Chen S. 2019. The light-induced transcription factor FtMYB 116 promotes accumulation of rutin in Fagopyrum tataricum. Plant,Cell & Environment, 42 (4):1340-1351. |
| [42] |
Zhao C, Liu X, Gong Q, Cao J, Shen W, Yin X, Grierson D, Zhang B, Xu C, Li X, Chen K, Sun C. 2021. Three AP2/ERF family members modulate flavonoid synthesis by regulating type IV chalcone isomerase in citrus. Plant Biotechnol Journal, 19 (4):671-688.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.v19.4 URL |
| [43] |
Zhao J. 2015. Flavonoid transport mechanisms:how to go,and with whom. Trends in Plant Science, 20 (9):576-585.
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2015.06.007 URL |
| [44] |
Zheng Jie, Zhao Qi-yang, Zhang Yao-hai, Jiao Bi-ning. 2014. Simultaneous determination of main flavonoids and phenolic acids in citrus fruit by Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 47 (23):4706-4717. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2014.23.015 |
|
郑洁, 赵其阳, 张耀海, 焦必宁. 2014. 超高效液相色谱法同时测定柑橘中主要酚酸和类黄酮物质. 中国农业科学, 47 (23):4706-4717.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2014.23.015 |
|
| [45] |
Zhong R, Richardson E A, Ye Z-H. 2007. The MYB 46 transcription factor is a direct target of SND1 and regulates secondary wall biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 19 (9):2776.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.053678 URL |
| [1] | 赖恒鑫, 李文广, 彭良志, 何义仲, 朱攀攀, 杨万云, 凌丽俐, 付行政, 淳长品, 曹立. 沃柑果实春夏季留树保鲜品质变化研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(3): 485-494. |
| [2] | 刘语诺, 曹亚, 王帅, 杜美霞, 郑林, 陈善春, 邹修平. 柑橘CsMYB41和CsMYB63响应溃疡病菌侵染的表达[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(3): 495-507. |
| [3] | 蒋靖东, 韦壮敏, 王楠, 朱晨桥, 叶俊丽, 谢宗周, 邓秀新, 柴利军. 山金柑四倍体资源的发掘与鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 27-35. |
| [4] | 杜玉玲, 杨凡, 赵娟, 刘书琪, 龙超安. 新鱼腥草素钠对柑橘指状青霉的抑菌作用[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 145-152. |
| [5] | 李镇希, 潘睿翾, 许美容, 郑正, 邓晓玲. 柑橘黄龙病菌双重实时荧光PCR检测方法的建立[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 188-196. |
| [6] | 葛诗蓓, 张学宁, 韩文炎, 李青云, 李鑫. 植物类黄酮的生物合成及其抗逆作用机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 209-224. |
| [7] | 朱凯杰, 张哲惠, 曹立新, 向舜德, 叶俊丽, 谢宗周, 柴利军, 邓秀新, . 棕色晚熟脐橙新品种‘宗橙’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 41-42. |
| [8] | 朱世平, 文荣中, 王媛媛, 曾 杨. 特晚熟柑橘新品种‘金乐柑’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 43-44. |
| [9] | 许海峰, 王中堂, 陈新, 刘志国, 王利虎, 刘平, 刘孟军, 张琼. 冬枣果皮着色相关类黄酮靶向代谢组学及潜在MYB转录因子分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(8): 1761-1771. |
| [10] | 郑林, 王帅, 刘语诺, 杜美霞, 彭爱红, 何永睿, 陈善春, 邹修平. 柑橘响应黄龙病菌侵染的NAC基因的克隆及表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(7): 1441-1457. |
| [11] | 杨海健, 张云贵, 周心智. 柑橘新品种‘云贵脆橙’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(7): 1611-1612. |
| [12] | 张凯, 麻明英, 王萍, 李益, 金燕, 盛玲, 邓子牛, 马先锋. 柑橘HSP20家族基因鉴定及其响应溃疡病菌侵染表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(6): 1213-1232. |
| [13] | 李文婷, 李翠晓, 林小清, 郑永钦, 郑正, 邓晓玲. 基于STR位点对广东省柑橘溃疡病菌种群遗传结构的分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(6): 1233-1246. |
| [14] | 麻明英, 郝晨星, 张凯, 肖桂华, 苏翰英, 文康, 邓子牛, 马先锋. 甜橙SWEET2a促进柑橘溃疡病菌侵染[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(6): 1247-1260. |
| [15] | 陈道宗, 刘镒, 沈文杰, 朱博, 谭晨. 白菜、甘蓝和甘蓝型油菜PAP1/2同源基因的鉴定及分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(6): 1301-1312. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司