
园艺学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1): 177-187.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0822
赵雪艳1, 王琪2, 王莉1, 王方圆1, 王庆1, 李艳1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-11-08
修回日期:2022-06-03
出版日期:2023-01-25
发布日期:2023-01-18
通讯作者:
*(E-mail:基金资助:
ZHAO Xueyan1, WANG Qi2, WANG Li1, WANG Fangyuan1, WANG Qing1, LI Yan1,*( )
)
Received:2021-11-08
Revised:2022-06-03
Online:2023-01-25
Published:2023-01-18
Contact:
*(E-mail:摘要:
延胡索(Corydalis yanhusuo)干燥块茎为传统中药,异喹啉生物碱类化合物是其主要的活性成分。采用Illumina高通量测序技术对延胡索块茎、根茎和叶片组织进行转录组测序,鉴定异喹啉生物碱生物合成的相关酶基因,并分析3种组织间的差异表达基因。在块茎vs.根茎、块茎vs.叶、根茎vs.叶比对中分别鉴别到6 161、8 852和5 772个差异表达基因。差异表达基因的KEGG富集分析表明,核糖体、淀粉和蔗糖代谢途径,苯丙素生物合成途径,植物激素信号转导途径以及异喹啉生物碱生物合成途径是主要的富集途径。其中47个转录本与延胡索异喹啉生物碱生物合成相关,其在块茎中的表达量最高,根茎次之,叶中的表达量最低。
中图分类号:
赵雪艳, 王琪, 王莉, 王方圆, 王庆, 李艳. 基于比较转录组的延胡索组织差异性表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 177-187.
ZHAO Xueyan, WANG Qi, WANG Li, WANG Fangyuan, WANG Qing, LI Yan. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Differential Expression in Different Tissues of Corydalis yanhusuo [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(1): 177-187.
| 基因名称(编号) Gene name(ID) | 正向引物序列(5′-3′) Forward primer sequence | 反向引物序列(5′-3′) Reverse primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Actin (AT1G49240) | GGTAACATTGTGCTCAGTGGTGG | AACGACCTTAATCTTCATGCTGC |
| NCS(transcript_36281) | TAGCAAGCATGGCAGCAGTCATC | TAGCCACCTCCACCTCTGTTGTC |
| 6OMT(transcript_4831) | AGGGACTGGTCACTTGGGATCG | AAAAGGCGTCGGTGCATCGG |
| CNMT(transcript_29289) | AGTGGGAAGCATTTCTCACGTACC | TTCCTCCATGATTGCCATCACTGC |
| NMCH(transcript_4028) | GCCAAAGCCCAATCAAGGAATCAG | TGGGGTTGGAGGGTGAAGTCTTAG |
| 4’OMT(transcript_4823) | CGTAGCACTGGAGGAGGGATCTG | CCTTTCTCTCCCACCTGTGTTCAC |
| SOMT(transcript_19389) | TTGCTGGGAAGGAGCCAAAAGTG | ACCACCACCAACATCAACCAACTC |
表1 实时荧光PCR引物
Table 1 The primers of real-time PCR
| 基因名称(编号) Gene name(ID) | 正向引物序列(5′-3′) Forward primer sequence | 反向引物序列(5′-3′) Reverse primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Actin (AT1G49240) | GGTAACATTGTGCTCAGTGGTGG | AACGACCTTAATCTTCATGCTGC |
| NCS(transcript_36281) | TAGCAAGCATGGCAGCAGTCATC | TAGCCACCTCCACCTCTGTTGTC |
| 6OMT(transcript_4831) | AGGGACTGGTCACTTGGGATCG | AAAAGGCGTCGGTGCATCGG |
| CNMT(transcript_29289) | AGTGGGAAGCATTTCTCACGTACC | TTCCTCCATGATTGCCATCACTGC |
| NMCH(transcript_4028) | GCCAAAGCCCAATCAAGGAATCAG | TGGGGTTGGAGGGTGAAGTCTTAG |
| 4’OMT(transcript_4823) | CGTAGCACTGGAGGAGGGATCTG | CCTTTCTCTCCCACCTGTGTTCAC |
| SOMT(transcript_19389) | TTGCTGGGAAGGAGCCAAAAGTG | ACCACCACCAACATCAACCAACTC |
| 样品 Sample | Clean read 数量 Clean read number | 碱基数 Base number | GC/% | % ≥ Q30 | 比对率/% Mapped ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 块茎 Tuber | 20 214 211 | 6 055 395 267 | 43.43 | 93.21 | 86.72 |
| 根茎 Rhizome | 21 439 743 | 6 422 326 271 | 43.24 | 93.17 | 72.78 |
| 叶 Leaf | 24 116 972 | 7 222 883 792 | 43.40 | 93.40 | 71.96 |
表2 延胡索测序数据结果
Table 2 Corydalis yanhusuo sequencing data
| 样品 Sample | Clean read 数量 Clean read number | 碱基数 Base number | GC/% | % ≥ Q30 | 比对率/% Mapped ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 块茎 Tuber | 20 214 211 | 6 055 395 267 | 43.43 | 93.21 | 86.72 |
| 根茎 Rhizome | 21 439 743 | 6 422 326 271 | 43.24 | 93.17 | 72.78 |
| 叶 Leaf | 24 116 972 | 7 222 883 792 | 43.40 | 93.40 | 71.96 |
| 样品对比 Sample pair | 总数 All | COG | GO | KEGG | KOG | Pfam | Swiss-Prot | eggNOG | Nr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 块茎 vs. 根茎 Tuber vs. Rhizome | 5 869 | 2 735 | 4 201 | 2 420 | 3 341 | 4 995 | 4.667 | 5 723 | 5 846 |
| 块茎 vs. 叶 Tuber vs. Leaf | 8 487 | 3 989 | 6 126 | 3 937 | 5 234 | 7 270 | 6.629 | 8 261 | 8 458 |
| 根茎 vs. 叶 Rhizome vs. Leaf | 5 529 | 2 674 | 3 989 | 2 557 | 3 465 | 4 741 | 4.340 | 5 361 | 5 508 |
表3 延胡索3种组织间差异表达基因的功能注释
Table 3 Functional annotation of differentially expressed genes among the three tissues of Corydalis yanhusuo
| 样品对比 Sample pair | 总数 All | COG | GO | KEGG | KOG | Pfam | Swiss-Prot | eggNOG | Nr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 块茎 vs. 根茎 Tuber vs. Rhizome | 5 869 | 2 735 | 4 201 | 2 420 | 3 341 | 4 995 | 4.667 | 5 723 | 5 846 |
| 块茎 vs. 叶 Tuber vs. Leaf | 8 487 | 3 989 | 6 126 | 3 937 | 5 234 | 7 270 | 6.629 | 8 261 | 8 458 |
| 根茎 vs. 叶 Rhizome vs. Leaf | 5 529 | 2 674 | 3 989 | 2 557 | 3 465 | 4 741 | 4.340 | 5 361 | 5 508 |
| 块茎 vs. 根茎 Tuber vs. Rhizome | 块茎 vs. 叶 Tuber vs. Leaf | 根茎 vs. 叶 Rhizome vs. Leaf | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 注释 Annotation | 数量 Number | Ks | 注释 Annotation | 数量 Number | Ks | 注释 Annotation | 数量 Number | Ks |
| 多糖分解 Polysaccharide catabolic | 242 | 1.0E-30 | 翻译 Translation | 521 | 4.7E-25 | 氧化还原 Oxidation-reduction | 481 | 2.3E-17 |
| 淀粉生物合成 Starch biosynthetic | 29 | 6.2E-10 | 多糖分解Polysaccharide catabolic | 240 | 1.1E-19 | 翻译Translation | 365 | 4.9E-14 |
| 糖原生物合成Glycogen biosynthetic | 24 | 8.9E-8 | 细胞质翻译Cytoplasmic translation | 39 | 2.1E-9 | 核糖体小亚基组装Ribosomal small subunit assembly | 24 | 2.3E-6 |
| 亚精胺生物合成Spermidine biosynthetic | 11 | 4.9E-7 | 核糖体小亚基组装Ribosomal small subunit assembly | 28 | 4.3E-9 | 次生代谢产物合成Secondary metabolite biosynthetic | 41 | 9.5E-6 |
| 异喹啉生物碱生物合成Isoquinoline alkaloid biosynthetic | 24 | 5.3E-7 | 次生代谢产物合成Secondary metabolite biosynthetic | 54 | 8.1E-7 | 谷胱甘肽代谢Glutathione metabolic | 18 | 1.9E-5 |
| 蛋白磷酸化 Protein phosphorylation | 290 | 7.2E-7 | 氧化还原 Oxidation-reduction | 634 | 2.0E-6 | 寡肽运输 Oligopeptide transport | 11 | 4.0E-5 |
| 次生代谢产物合成Secondary metabolite biosynthetic | 44 | 9.3E-7 | 氨基酸跨膜转运 Amino acid transmembrane transport | 24 | 3.7E-6 | 芥子油苷分解Glucosinolate catabolic | 8 | 0.00012 |
| 药物跨膜运输Drug transmembrane transport | 26 | 9.3E-7 | 亚精胺生物合成Spermidine biosynthetic | 11 | 1.8E-5 | (S)-心果碱代谢 (S)-reticuline metabolic | 10 | 0.00014 |
| 淀粉分解 Starch catabolic | 25 | 7.3E-6 | 精氨酸分解 Arginine catabolic | 8 | 2.5E-5 | 细胞质翻译 Cytoplasmic translation | 28 | 0.00014 |
| 块茎 vs. 根茎 Tuber vs. Rhizome | 块茎 vs. 叶 Tuber vs. Leaf | 根茎 vs. 叶 Rhizome vs. Leaf | ||||||
| 注释 Annotation | 数量 Number | Ks | 注释 Annotation | 数量 Number | Ks | 注释 Annotation | 数量 Number | Ks |
| (S)-心果碱代谢 (S)-reticuline metabolic | 17 | 1.4E-5 | 对真菌的响应 Response to molecule of fungal origin | 21 | 3.8E-5 | L-苯丙氨酸分解 L-phenylalanine catabolic | 8 | 0.00015 |
| 膜整体部分 Integral component of membrane | 1 116 | 1.2E-12 | 胞质大核糖体亚基Cytosolic large ribosomal subunit | 146 | 7.6E-26 | 胞质小核糖体亚基Cytosolic small ribosomal subunit | 78 | 3.2E-17 |
| 细胞壁 Cell wall | 125 | 3.4E-9 | 胞质小核糖体亚基Cytosolic small ribosomal subunit | 88 | 6.3E-24 | 胞质大核糖体亚基Cytosolic large ribosomal subunit | 104 | 1.4E-15 |
| 胞外区 Extracellular region | 129 | 4.5E-9 | 核糖体 Ribosome | 398 | 1.6E-11 | 核糖体 Ribosome | 297 | 3.7E-8 |
| 质膜部分 Integral component of plasma membrane | 63 | 3.7E-8 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast | 536 | 1.1E-10 | 叶绿体基质 Chloroplast stroma | 126 | 5.2E-8 |
| β-淀粉酶活性 Beta-amylase activity | 180 | 1.0E-30 | 核糖体结构Structural constituent of ribosome | 379 | 1.0E-30 | 核糖体结构 Structural constituent of ribosome | 289 | 1.0E-30 |
| 水解酶活性 Hydrolase activity,hydrolyzing O-glycosyl compounds | 338 | 6.5E-9 | β-淀粉酶活性 β-amylase activity | 179 | 6.3E-23 | 铁离子结合Iron ion binding | 81 | 1.2E-8 |
| 药物跨膜运输 Drug transmembrane transporter | 26 | 1.1E-6 | rRNA结合 rRNA binding | 81 | 1.6E-12 | 血红素结合 Heme binding | 81 | 4.8E-8 |
| 催化活性 Catalytic activity | 2 450 | 1.9E-6 | 大核糖体亚基rRNA结合 Large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding | 16 | 6.9E-7 | 单加氧酶活性Monooxygenase activity | 82 | 2.0E-7 |
| 葡萄糖-1-磷酸-腺苷转移酶活性Glucose-1-phosphate adenylyltransferase activity | 11 | 2.6E-6 | 氨基酸跨膜运输活性 Amino acid transmembrane transporter activity | 26 | 5.2E-6 | rRNA结合 rRNA binding | 57 | 4.1E-6 |
| 半胱氨酸肽链内切酶 Cysteine-type endopeptidase activity | 19 | 2.9E-6 | 氧化还原酶活性Oxidoreductase activity | 55 | 6.1E-6 | 过氧化物酶活性 Peroxidase activity | 40 | 3.6E-5 |
| 氧化还原酶活性Oxidoreductase activity | 47 | 6.2E-6 | 2-链烯还原酶活性 2-Alkenal reductase [NAD(P)]activity | 54 | 3.0E-5 | 氧化还原酶活性Oxidoreductase activity | 82 | 4.9E-5 |
| 精氨酸脱羧酶活性 Arginine decarboxylase activity | 6 | 2.2E-5 | 磷酸转移激酶活性 Phosphorelay sensor kinase activity | 14 | 4.7E-5 | β-葡糖苷酶活性β-glucosidase activity | 22 | 6.0E-5 |
表4 差异表达基因GO富集分类
Table 4 The enriched gene ontology of differentially expressed genes
| 块茎 vs. 根茎 Tuber vs. Rhizome | 块茎 vs. 叶 Tuber vs. Leaf | 根茎 vs. 叶 Rhizome vs. Leaf | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 注释 Annotation | 数量 Number | Ks | 注释 Annotation | 数量 Number | Ks | 注释 Annotation | 数量 Number | Ks |
| 多糖分解 Polysaccharide catabolic | 242 | 1.0E-30 | 翻译 Translation | 521 | 4.7E-25 | 氧化还原 Oxidation-reduction | 481 | 2.3E-17 |
| 淀粉生物合成 Starch biosynthetic | 29 | 6.2E-10 | 多糖分解Polysaccharide catabolic | 240 | 1.1E-19 | 翻译Translation | 365 | 4.9E-14 |
| 糖原生物合成Glycogen biosynthetic | 24 | 8.9E-8 | 细胞质翻译Cytoplasmic translation | 39 | 2.1E-9 | 核糖体小亚基组装Ribosomal small subunit assembly | 24 | 2.3E-6 |
| 亚精胺生物合成Spermidine biosynthetic | 11 | 4.9E-7 | 核糖体小亚基组装Ribosomal small subunit assembly | 28 | 4.3E-9 | 次生代谢产物合成Secondary metabolite biosynthetic | 41 | 9.5E-6 |
| 异喹啉生物碱生物合成Isoquinoline alkaloid biosynthetic | 24 | 5.3E-7 | 次生代谢产物合成Secondary metabolite biosynthetic | 54 | 8.1E-7 | 谷胱甘肽代谢Glutathione metabolic | 18 | 1.9E-5 |
| 蛋白磷酸化 Protein phosphorylation | 290 | 7.2E-7 | 氧化还原 Oxidation-reduction | 634 | 2.0E-6 | 寡肽运输 Oligopeptide transport | 11 | 4.0E-5 |
| 次生代谢产物合成Secondary metabolite biosynthetic | 44 | 9.3E-7 | 氨基酸跨膜转运 Amino acid transmembrane transport | 24 | 3.7E-6 | 芥子油苷分解Glucosinolate catabolic | 8 | 0.00012 |
| 药物跨膜运输Drug transmembrane transport | 26 | 9.3E-7 | 亚精胺生物合成Spermidine biosynthetic | 11 | 1.8E-5 | (S)-心果碱代谢 (S)-reticuline metabolic | 10 | 0.00014 |
| 淀粉分解 Starch catabolic | 25 | 7.3E-6 | 精氨酸分解 Arginine catabolic | 8 | 2.5E-5 | 细胞质翻译 Cytoplasmic translation | 28 | 0.00014 |
| 块茎 vs. 根茎 Tuber vs. Rhizome | 块茎 vs. 叶 Tuber vs. Leaf | 根茎 vs. 叶 Rhizome vs. Leaf | ||||||
| 注释 Annotation | 数量 Number | Ks | 注释 Annotation | 数量 Number | Ks | 注释 Annotation | 数量 Number | Ks |
| (S)-心果碱代谢 (S)-reticuline metabolic | 17 | 1.4E-5 | 对真菌的响应 Response to molecule of fungal origin | 21 | 3.8E-5 | L-苯丙氨酸分解 L-phenylalanine catabolic | 8 | 0.00015 |
| 膜整体部分 Integral component of membrane | 1 116 | 1.2E-12 | 胞质大核糖体亚基Cytosolic large ribosomal subunit | 146 | 7.6E-26 | 胞质小核糖体亚基Cytosolic small ribosomal subunit | 78 | 3.2E-17 |
| 细胞壁 Cell wall | 125 | 3.4E-9 | 胞质小核糖体亚基Cytosolic small ribosomal subunit | 88 | 6.3E-24 | 胞质大核糖体亚基Cytosolic large ribosomal subunit | 104 | 1.4E-15 |
| 胞外区 Extracellular region | 129 | 4.5E-9 | 核糖体 Ribosome | 398 | 1.6E-11 | 核糖体 Ribosome | 297 | 3.7E-8 |
| 质膜部分 Integral component of plasma membrane | 63 | 3.7E-8 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast | 536 | 1.1E-10 | 叶绿体基质 Chloroplast stroma | 126 | 5.2E-8 |
| β-淀粉酶活性 Beta-amylase activity | 180 | 1.0E-30 | 核糖体结构Structural constituent of ribosome | 379 | 1.0E-30 | 核糖体结构 Structural constituent of ribosome | 289 | 1.0E-30 |
| 水解酶活性 Hydrolase activity,hydrolyzing O-glycosyl compounds | 338 | 6.5E-9 | β-淀粉酶活性 β-amylase activity | 179 | 6.3E-23 | 铁离子结合Iron ion binding | 81 | 1.2E-8 |
| 药物跨膜运输 Drug transmembrane transporter | 26 | 1.1E-6 | rRNA结合 rRNA binding | 81 | 1.6E-12 | 血红素结合 Heme binding | 81 | 4.8E-8 |
| 催化活性 Catalytic activity | 2 450 | 1.9E-6 | 大核糖体亚基rRNA结合 Large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding | 16 | 6.9E-7 | 单加氧酶活性Monooxygenase activity | 82 | 2.0E-7 |
| 葡萄糖-1-磷酸-腺苷转移酶活性Glucose-1-phosphate adenylyltransferase activity | 11 | 2.6E-6 | 氨基酸跨膜运输活性 Amino acid transmembrane transporter activity | 26 | 5.2E-6 | rRNA结合 rRNA binding | 57 | 4.1E-6 |
| 半胱氨酸肽链内切酶 Cysteine-type endopeptidase activity | 19 | 2.9E-6 | 氧化还原酶活性Oxidoreductase activity | 55 | 6.1E-6 | 过氧化物酶活性 Peroxidase activity | 40 | 3.6E-5 |
| 氧化还原酶活性Oxidoreductase activity | 47 | 6.2E-6 | 2-链烯还原酶活性 2-Alkenal reductase [NAD(P)]activity | 54 | 3.0E-5 | 氧化还原酶活性Oxidoreductase activity | 82 | 4.9E-5 |
| 精氨酸脱羧酶活性 Arginine decarboxylase activity | 6 | 2.2E-5 | 磷酸转移激酶活性 Phosphorelay sensor kinase activity | 14 | 4.7E-5 | β-葡糖苷酶活性β-glucosidase activity | 22 | 6.0E-5 |
| 块茎 vs. 根茎 Tuber vs. Rhizome | 块茎 vs. 叶 Tuber vs. Leaf | 根茎 vs. 叶 Rhizome vs. Leaf | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 代谢通路 Pathway | 数量 Number | P | 代谢通路 Pathway | 数量Number | P | 代谢通路 Pathway | 数量Number | P |
| 淀粉和蔗糖代谢 Starch and sucrose metabolism | 152 | 1.0E-19 | 核糖体 Ribosome | 379 | 2.9E-61 | 核糖体 Ribosome | 291 | 8.67E-46 |
| 植物激素信号转导 Plant hormone signal transduction | 85 | 1.8E-6 | 淀粉和蔗糖代谢 Starch and sucrose metabolism | 179 | 6.9E-8 | 苯丙素生物合成Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis | 70 | 1.83E-08 |
| 半乳糖代谢 Galactose metabolism | 44 | 2.7E-6 | 苯丙素生物合成Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis | 76 | 0.0012 | 氰基氨基酸代谢Cyanoamino acid metabolism | 39 | 5.13E-06 |
| 块茎 vs. 根茎 Tuber vs. Rhizome | 块茎 vs. 叶 Tuber vs. Leaf | 根茎 vs. 叶 Rhizome vs. Leaf | ||||||
| 代谢通路 Pathway | 数量 Number | P | 代谢通路 Pathway | 数量Number | P | 代谢通路 Pathway | 数量Number | P |
| 植物与病原菌互作 Plant-pathogen interaction | 67 | 4.0E-5 | 植物激素信号转导 Plant hormone signal transduction | 109 | 0.0071 | 光合作用有机体碳固定 Carbon fixation in photosynthetic organisms | 51 | 0.0147 |
| 苯丙素生物合成 Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis | 59 | 7.1E-6 | 氰基氨基酸代谢Cyanoamino acid metabolism | 42 | 0.0054 | 生理节律—植物 Circadian rhythm - plant | 29 | 0.0041 |
| 亚油酸代谢 Linoleic acid metabolism | 16 | 0.0001 | 亚油酸代谢 Linoleic acid metabolism | 17 | 0.0254 | 谷胱甘肽代谢 Glutathione metabolism | 41 | 0.0236 |
| 醚脂类代谢 Ether lipid metabolism | 19 | 0.0202 | α-亚麻酸代谢α-Linolenic acid metabolism | 34 | 0.0682 | 半胱氨酸和蛋氨酸代谢 Cysteine and methionine metabolism | 63 | 0.0364 |
| 异喹啉生物碱生物合成Isoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis | 26 | 0.0674 | 乙醛酸和二羧酸的代谢Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism | 58 | 0.1629 | 苯丙氨酸,酪氨酸和色氨酸合成Phenylalanine,tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis | 33 | 0.0974 |
| 核糖体 Ribosome | 156 | 0.0919 | 光合作用有机体碳固定Carbon fixation in photosynthetic organisms | 61 | 0.4460 | 淀粉和蔗糖代谢 Starch and sucrose metabolism | 114 | 0.1132 |
| 氨基糖和核苷酸糖的代谢 Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism | 54 | 0.0997 | 生理节律-植物 Circadian rhythm-plant | 31 | 0.6627 | 抗坏血酸和醛糖酸代谢Ascorbate and aldarate metabolism | 28 | 0.1157 |
| α-亚麻酸代谢 α-Linolenic acid metabolism | 24 | 0.1153 | 抗坏血酸和醛糖酸代谢Ascorbate and aldarate metabolism | 31 | 1.0000 | 异喹啉生物碱生物合成Isoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis | 28 | 0.1157 |
| 丙氨酸、天冬氨酸、谷氨酸代谢Alanine,aspartate and glutamate metabolism | 34 | 0.4667 | 氨基酸生物合成Biosynthesis of amino acids | 190 | 1.0000 | 酪氨酸代谢 Tyrosine metabolism | 31 | 0.2676 |
| ABC转运体 ABC transporters | 14 | 0.5534 | 类胡萝卜素生物合成Carotenoid biosynthesis | 18 | 1.0000 | 甘油脂类代谢 Glycerolipid metabolism | 36 | 0.4619 |
| 精氨酸和脯氨酸代谢 Arginine and proline metabolism | 23 | 0.7312 | 果糖和甘露糖代谢 Fructose and mannose metabolism | 36 | 1.0000 | 油菜素内脂生物合成Brassinosteroid biosynthesis | 13 | 0.6647 |
| 戊糖、葡萄糖醛酸转换 Pentose and glucuronate interconversions | 23 | 0.7312 | 糖酵解/糖异生Glycolysis/ Gluconeogenesis | 90 | 1.0000 | 卟啉和叶绿素代谢Porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism | 23 | 0.8207 |
| 氮代谢 Nitrogen metabolism | 12 | 0.9688 | 氮代谢 Nitrogen metabolism | 15 | 1.0000 | 丙氨酸、天冬氨酸、谷氨酸代谢 Alanine,aspartate and glutamate metabolism | 35 | 1.0000 |
| 花生四烯酸代谢 Arachidonic acid metabolism | 7 | 1.0000 | 戊糖、葡萄糖醛酸转换Pentose and glucuronate interconversions | 32 | 1.0000 | 戊糖、葡萄糖醛酸转换Pentose and glucuronate interconversions | 24 | 1.0000 |
| 半胱氨酸和蛋氨酸代谢 Cysteine and methionine metabolism | 50 | 1.0000 | 磷酸戊糖途径Pentose phosphate pathway | 46 | 1.0000 | 有机含硒化合物代谢Selenocompound metabolism | 20 | 1.0000 |
| 类固醇生物合成 Steroid biosynthesis | 20 | 1.0000 | 类固醇生物合成 Steroid biosynthesis | 28 | 1.0000 | 类固醇生物合成 Steroid biosynthesis | 22 | 1.0000 |
| 维生素B6代谢 Vitamin B6 metabolism | 7 | 1.0000 | 缬氨酸、亮氨酸和异亮氨酸的降解 Valine,leucine and isoleucine degradation | 41 | 1.00000 | 芪类、二芳基庚烷和姜酚生物合成 Stilbenoid,diarylheptanoid and gingerol biosynthesis | 9 | 1.0000 |
表5 差异表达基因富集的KEGG代谢通路
Table 5 The enriched KEGG pathways of differentially expressed genes
| 块茎 vs. 根茎 Tuber vs. Rhizome | 块茎 vs. 叶 Tuber vs. Leaf | 根茎 vs. 叶 Rhizome vs. Leaf | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 代谢通路 Pathway | 数量 Number | P | 代谢通路 Pathway | 数量Number | P | 代谢通路 Pathway | 数量Number | P |
| 淀粉和蔗糖代谢 Starch and sucrose metabolism | 152 | 1.0E-19 | 核糖体 Ribosome | 379 | 2.9E-61 | 核糖体 Ribosome | 291 | 8.67E-46 |
| 植物激素信号转导 Plant hormone signal transduction | 85 | 1.8E-6 | 淀粉和蔗糖代谢 Starch and sucrose metabolism | 179 | 6.9E-8 | 苯丙素生物合成Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis | 70 | 1.83E-08 |
| 半乳糖代谢 Galactose metabolism | 44 | 2.7E-6 | 苯丙素生物合成Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis | 76 | 0.0012 | 氰基氨基酸代谢Cyanoamino acid metabolism | 39 | 5.13E-06 |
| 块茎 vs. 根茎 Tuber vs. Rhizome | 块茎 vs. 叶 Tuber vs. Leaf | 根茎 vs. 叶 Rhizome vs. Leaf | ||||||
| 代谢通路 Pathway | 数量 Number | P | 代谢通路 Pathway | 数量Number | P | 代谢通路 Pathway | 数量Number | P |
| 植物与病原菌互作 Plant-pathogen interaction | 67 | 4.0E-5 | 植物激素信号转导 Plant hormone signal transduction | 109 | 0.0071 | 光合作用有机体碳固定 Carbon fixation in photosynthetic organisms | 51 | 0.0147 |
| 苯丙素生物合成 Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis | 59 | 7.1E-6 | 氰基氨基酸代谢Cyanoamino acid metabolism | 42 | 0.0054 | 生理节律—植物 Circadian rhythm - plant | 29 | 0.0041 |
| 亚油酸代谢 Linoleic acid metabolism | 16 | 0.0001 | 亚油酸代谢 Linoleic acid metabolism | 17 | 0.0254 | 谷胱甘肽代谢 Glutathione metabolism | 41 | 0.0236 |
| 醚脂类代谢 Ether lipid metabolism | 19 | 0.0202 | α-亚麻酸代谢α-Linolenic acid metabolism | 34 | 0.0682 | 半胱氨酸和蛋氨酸代谢 Cysteine and methionine metabolism | 63 | 0.0364 |
| 异喹啉生物碱生物合成Isoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis | 26 | 0.0674 | 乙醛酸和二羧酸的代谢Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism | 58 | 0.1629 | 苯丙氨酸,酪氨酸和色氨酸合成Phenylalanine,tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis | 33 | 0.0974 |
| 核糖体 Ribosome | 156 | 0.0919 | 光合作用有机体碳固定Carbon fixation in photosynthetic organisms | 61 | 0.4460 | 淀粉和蔗糖代谢 Starch and sucrose metabolism | 114 | 0.1132 |
| 氨基糖和核苷酸糖的代谢 Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism | 54 | 0.0997 | 生理节律-植物 Circadian rhythm-plant | 31 | 0.6627 | 抗坏血酸和醛糖酸代谢Ascorbate and aldarate metabolism | 28 | 0.1157 |
| α-亚麻酸代谢 α-Linolenic acid metabolism | 24 | 0.1153 | 抗坏血酸和醛糖酸代谢Ascorbate and aldarate metabolism | 31 | 1.0000 | 异喹啉生物碱生物合成Isoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis | 28 | 0.1157 |
| 丙氨酸、天冬氨酸、谷氨酸代谢Alanine,aspartate and glutamate metabolism | 34 | 0.4667 | 氨基酸生物合成Biosynthesis of amino acids | 190 | 1.0000 | 酪氨酸代谢 Tyrosine metabolism | 31 | 0.2676 |
| ABC转运体 ABC transporters | 14 | 0.5534 | 类胡萝卜素生物合成Carotenoid biosynthesis | 18 | 1.0000 | 甘油脂类代谢 Glycerolipid metabolism | 36 | 0.4619 |
| 精氨酸和脯氨酸代谢 Arginine and proline metabolism | 23 | 0.7312 | 果糖和甘露糖代谢 Fructose and mannose metabolism | 36 | 1.0000 | 油菜素内脂生物合成Brassinosteroid biosynthesis | 13 | 0.6647 |
| 戊糖、葡萄糖醛酸转换 Pentose and glucuronate interconversions | 23 | 0.7312 | 糖酵解/糖异生Glycolysis/ Gluconeogenesis | 90 | 1.0000 | 卟啉和叶绿素代谢Porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism | 23 | 0.8207 |
| 氮代谢 Nitrogen metabolism | 12 | 0.9688 | 氮代谢 Nitrogen metabolism | 15 | 1.0000 | 丙氨酸、天冬氨酸、谷氨酸代谢 Alanine,aspartate and glutamate metabolism | 35 | 1.0000 |
| 花生四烯酸代谢 Arachidonic acid metabolism | 7 | 1.0000 | 戊糖、葡萄糖醛酸转换Pentose and glucuronate interconversions | 32 | 1.0000 | 戊糖、葡萄糖醛酸转换Pentose and glucuronate interconversions | 24 | 1.0000 |
| 半胱氨酸和蛋氨酸代谢 Cysteine and methionine metabolism | 50 | 1.0000 | 磷酸戊糖途径Pentose phosphate pathway | 46 | 1.0000 | 有机含硒化合物代谢Selenocompound metabolism | 20 | 1.0000 |
| 类固醇生物合成 Steroid biosynthesis | 20 | 1.0000 | 类固醇生物合成 Steroid biosynthesis | 28 | 1.0000 | 类固醇生物合成 Steroid biosynthesis | 22 | 1.0000 |
| 维生素B6代谢 Vitamin B6 metabolism | 7 | 1.0000 | 缬氨酸、亮氨酸和异亮氨酸的降解 Valine,leucine and isoleucine degradation | 41 | 1.00000 | 芪类、二芳基庚烷和姜酚生物合成 Stilbenoid,diarylheptanoid and gingerol biosynthesis | 9 | 1.0000 |
| 简称 Abbreviation | 全称 Full name | 基因编号 Gene ID |
|---|---|---|
| NCS | (S)-去甲基乌药碱合酶 (S)-norcoclaurine synthase | transcript_17057,transcript_19226,transcript_543,transcript_5764,transcript_34030,transcript_13099,transcript_21615,transcript_9018,transcript_5209,transcript_36281,transcript_527,transcript_8823 |
| 6OMT | (S)-去甲基乌药碱-6-氧甲基转移酶 (S)-norcoclaurine 6-O-methyltransferase | transcript_33869,transcript_4831,transcript_19521,transcript_21316,transcript_26993,transcript_21935,transcript_27053,transcript_32190,transcript_4822,transcript_4816,transcript_31617,transcript_6804,transcript_4484,transcript_32370,transcript_22232,transcript_4266 |
| CNMT | (S)-乌药碱-N-甲基转移酶 (S)-coclaurine-N-methyltransferase | transcript_29289,transcript_16285,transcript_15928,transcript_21025,transcript_24962,transcript_4897,transcript_23886,transcript_20924,transcript_3652 |
| NMCH | (S)-羟基-N-甲基乌药碱羟化酶 (S)-N-methylcoclaurine hydroxylase | transcript_33528,transcript_4028 |
| 4’OMT | (S)-羟基-N-甲基乌药碱-4’-O-甲基转移酶 (S)-3’-hydroxy-N-methylcoclaurine-4’-O-methyltransferase | transcript_4823,transcript_33789 |
| SOMT | (S)-金黄紫堇碱-9-O-甲基转移酶 (S)-scoulerine-9-O-methyltransferasese | transcript_19389,transcript_27465,transcript_5219,transcript_26864,transcript_8610,transcript_4164 |
表6 鉴别到的参与延胡索异喹啉生物碱生物合成的基因
Table 6 Identified genes involved in isoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis of Corydalis yanhusuo
| 简称 Abbreviation | 全称 Full name | 基因编号 Gene ID |
|---|---|---|
| NCS | (S)-去甲基乌药碱合酶 (S)-norcoclaurine synthase | transcript_17057,transcript_19226,transcript_543,transcript_5764,transcript_34030,transcript_13099,transcript_21615,transcript_9018,transcript_5209,transcript_36281,transcript_527,transcript_8823 |
| 6OMT | (S)-去甲基乌药碱-6-氧甲基转移酶 (S)-norcoclaurine 6-O-methyltransferase | transcript_33869,transcript_4831,transcript_19521,transcript_21316,transcript_26993,transcript_21935,transcript_27053,transcript_32190,transcript_4822,transcript_4816,transcript_31617,transcript_6804,transcript_4484,transcript_32370,transcript_22232,transcript_4266 |
| CNMT | (S)-乌药碱-N-甲基转移酶 (S)-coclaurine-N-methyltransferase | transcript_29289,transcript_16285,transcript_15928,transcript_21025,transcript_24962,transcript_4897,transcript_23886,transcript_20924,transcript_3652 |
| NMCH | (S)-羟基-N-甲基乌药碱羟化酶 (S)-N-methylcoclaurine hydroxylase | transcript_33528,transcript_4028 |
| 4’OMT | (S)-羟基-N-甲基乌药碱-4’-O-甲基转移酶 (S)-3’-hydroxy-N-methylcoclaurine-4’-O-methyltransferase | transcript_4823,transcript_33789 |
| SOMT | (S)-金黄紫堇碱-9-O-甲基转移酶 (S)-scoulerine-9-O-methyltransferasese | transcript_19389,transcript_27465,transcript_5219,transcript_26864,transcript_8610,transcript_4164 |
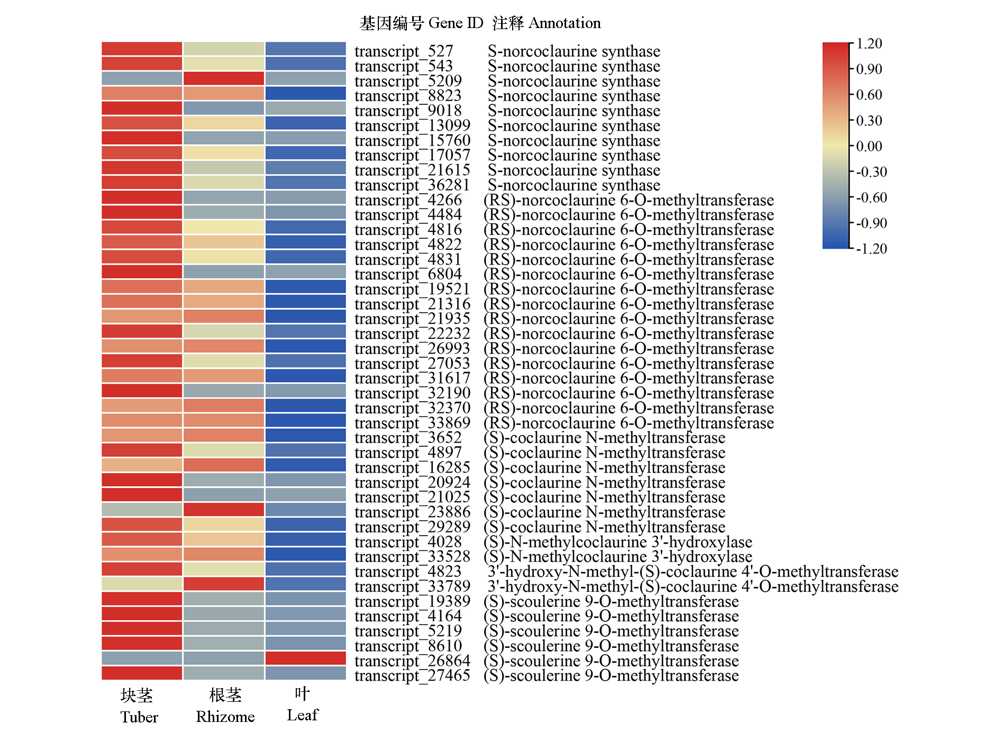
图1 延胡索异喹啉生物碱合成相关基因的表达模式 红色和蓝色分别表示上调和下调转录本。
Fig. 1 Expression patterns of isoquinoline alkaloid synthesis related genes in Corydalis yanhusuo Red and blue colors indicated up-regulated and down-regulated transcripts,respectively.
| [1] |
Beaudoin G A, Facchini P J. 2014. Benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis in Opium poppy. Planta, 240:19-32.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-014-2056-8 URL |
| [2] | Bennett M R, Thompson M L, Shepherd S A, Dunstan M S, Herbert A J, Smith D R M, Cronin V A, Menon B R K, Levy C, Micklefield J. 2018. Structure and biocatalytic scope of coclaurine N-methyltransferase. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 7 (33):10600-10604. |
| [3] | Chen Keyu. 2011. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of genes involved in berberine alkaloids biosynthesis in Corydalis saxicola Bunt. and microbial transformation of steroidal alkaloids in Veratrum nigrum Linn [Ph. D. Dissertation]. Shanghai: Second Military Medical University. (in Chinese) |
| 陈柯羽. 2011. 岩黄连中小檗碱型生物碱生物合成途径相关基因的研究及藜芦中甾体生物碱的微生物转化[博士论文]. 上海: 第二军医大学. | |
| [4] | Chinese Pharmacopeia Committee. 2020. Phamacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. Beijing: Chinese Medical Science Press:145. (in Chinese) |
| 国家药典委员会. 2020. 中华人民共和国药典. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社:145. | |
| [5] | Cong Kun. 2017. Transcriptome analysis for SSR and discovering genes involved in isoquinoline alkaloids biosynthesis in Coptis[M. D. Dissertation]. Kunming: Yunnan Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 丛琨. 2017. 转录组分析发现黄连异喹啉生物碱合成相关基因及SSR标记[硕士论文]. 昆明: 云南农业大学. | |
| [6] |
Dang T T T, Facchini P J. 2012. Characterization of three O-methyltransferases involved in noscapine biosynthesis in Opium poppy. Plant Physiology, 159:618-631.
doi: 10.1104/pp.112.194886 URL |
| [7] |
Facchini P J, de Luca V. 2008. Opium poppy and Madagascar periwinkle:model non-model systems to investigate alkaloid biosynthesis in plants. Plant Journal, 54:763-784.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03438.x URL |
| [8] |
Farrow S C, Hagel J M, Facchini P J. 2012. Transcript and metabolite profiling in cell cultures of 18 plant species that produce benzylisoquinoline alkaloids. Phytochemistry, 77:79-88.
doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2012.02.014 pmid: 22424601 |
| [9] | Gao Puzhu, Jin Xiaojun, Zhang Ximin, Ren Yijie, Lü Duo, Wu Xiuqin. 2018. Effect of applying diammonium phosphate on yield and quality of Corydalis yanhusuo. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 49:3687-3691. (in Chinese) |
| 高普珠, 晋小军, 张喜民, 任一杰, 吕铎, 吴秀琴. 2018. 施用磷酸二铵对延胡索产量品质的影响. 中草药, 49:3687-3691. | |
| [10] |
Grabherr M G, Haas B J, Yassour M, Levin J Z, Thompson D A, Amit I, Adiconis X, Fan L, Raychowdhury R, Zeng Q, Chen Z, Mauceli E, Hacohen N, Gnirke A, Rhind N, Palma F, Birren B W, Nusbaum C, Lindblad-Toh K, Friedman N, Regev A. 2011. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nature Biotechnology, 29 (7):644-652.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.1883 pmid: 21572440 |
| [11] |
Han Y, Zhang W, Tang Y, Bai W L, Yang F, Xie L P, Li X Z, Zhou S M, Pan S Y, Chen Q, Ferro A, Ji Y. 2012. l-Tetrahydropalmatine,an active component of Corydalis yanhusuo W. T. Wang,protects against myocardial ischaemia reperfusion injury in rats. PLoS ONE, 7:e38627.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038627 URL |
| [12] | He Kai, Gao Jianli, Zhao Guangshu. 2007. Advances in studies on chemistry,pharmacology,and quality control of Corydalis yanhusuo. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 38 (12):1909-1912. (in Chinese) |
| 贺凯, 高建莉, 赵光树. 2007. 延胡索化学成分、药理作用及质量控制研究进展. 中草药, 38 (12):1909-1912. | |
| [13] | He Xiaofeng, Zhang Jing, Zhang Mei. 2017. Research progress on chemical constituents,pharmacological activities and toxic side effects of rhizoma Corydalis. Shanghai Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 51 (11):97-100. (in Chinese) |
| 何晓凤, 张晶, 张梅. 2017. 延胡索化学成分、药理活性及毒副作用研究进展. 上海中医药杂志, 51 (11):97-100. | |
| [14] | Hu Ke, Wei Jiayu. 2018. Observation of growth process of Corydalis yanhusuo. Journal of Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, 33 (4):78-80. (in Chinese) |
| 胡珂, 韦佳玉. 2018. 延胡索块茎生长发育过程观察. 安徽中医药大学学报, 33 (4):78-80. | |
| [15] |
Li Q, Bu J, Ma Y, Yang J, Hu Z, Lai C, Xu Y, Tang J, Cui G, Wang Y, Zhao Y, Jin B, Shen Y, Guo J, Huang L. 2020. Characterization of O-methyltransferases involved in the biosynthesis of tetrandrine in Stephania tetrandra. Journal Plant Physiology, 250:153181.
doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2020.153181 URL |
| [16] |
Liao D Q, Wang P F, Jia C, Sun P, Qi J J, Zhou L L, Li X E. 2016. Identification and developmental expression profiling of putative alkaloid biosynthetic genes in Corydalis yanhusuo bulbs. Scientific Reports, 6:19460.
doi: 10.1038/srep19460 URL |
| [17] | Liu Manyu, Zhao Wanli, Liu Jiahua. 2021. Prokaryotic expression and bioinformatic analysis of three O-methyltransferases in Stephania intermedia Lo. Chinese Wild Plant Resources, 40 (4):38-52. (in Chinese) |
| 刘曼玉, 赵万里, 刘吉华. 2021. 河谷地不容3个O-甲基转移酶原核表达及生物信息学相关分析. 中国野生植物资源, 40 (4):38-52. | |
| [18] |
Menéndez-Perdomo I M, Facchini P J. 2020. Isolation and characterization of two O-methyltransferases involved in benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis in sacred lotus (Nelumbo nucifera). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 295 (6):1598-1612.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.011547 pmid: 31914404 |
| [19] |
Samanani N, Park S U, Facchini P J. 2005. Cell type-specific localization of transcripts encoding nine consecutive enzymes involved in protoberberine alkaloid biosynthesis. Plant Cell, 17:915-926.
pmid: 15722473 |
| [20] | Sohrabi S M, Ismaili A, Firouzabadi F N. 2018. Simultaneous over-expression and silencing of some benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthetic genes in Opium poppy. Industrial Crops & Products, 123:581-590. |
| [21] |
Tan C N, Zhang Q, Li C H, Fan J J, Yang F Q, Hu Y J, Hu G. 2019. Potential target-related proteins in rabbit platelets treated with active monomers dehydrocorydaline and canadine from rhizoma Corydalis. Phytomedicine, 54:231-239.
doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.09.200 URL |
| [22] |
Wang D, Zhao L, Wang D, Yu X, Wei Y, Ouyang Z. 2018. Transcriptome analysis and identification of key genes involved in 1-deoxynojirimycin biosynthesis of mulberry(Morus alba L.). Peer J, 6 (6000):e5443.
doi: 10.7717/peerj.5443 URL |
| [23] |
Wang X, Li S T, Li J, Li C F, Zhang Y S. 2015. De novo transcriptome sequencing in Pueraria lobata to identify putative genes involved in isoflavones biosynthesis. Plant Cell Reports, 34:733-743.
doi: 10.1007/s00299-014-1733-1 pmid: 25547742 |
| [24] | Wang Xiaoling, Zheng Zhen, Hong Zhanying, Fan Guorong. 2011. Advancements on chemical components and quality control of rhizoma Corydalis. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research,(1):227-229. (in Chinese) |
| 王晓玲, 郑振, 洪战英, 范国荣. 2011. 中药延胡索的化学成分与质量控制研究进展. 时珍国医国药,(1):227-229. | |
| [25] |
Wu W H, Wang P, Liu M T, Tang L Y, Fang J. 2015. A 1HNMR-based metabonomic study on the anti-depressive effect of the total alkaloid of Corydalis rhizoma. Molecules, 20:10047-10064.
doi: 10.3390/molecules200610047 URL |
| [26] |
Xu D, Lin H, Tang Y, Huang L, Xu J, Nian S, Zhao Y. 2021. Integration of full-length transcriptomics and targeted metabolomics to identify benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthetic genes in Corydalis yanhusuo. Horticulture Research, 8:16.
doi: 10.1038/s41438-020-00450-6 URL |
| [27] | Xu X H, Wang Z T, Yu G D, Ruan B F, Li J. 2002. Alkaloids from rhizoma Corydalis. Journal of China Pharmaceutical University, 33:483-486. |
| [28] |
Zhao W, Shen C, Zhu J, Ou C, Liu M, Dai W, Liu X, Liu J. 2020. Identification and characterization of methyltransferases involved in benzylisoquinoline alkaloids biosynthesis from Stephania intermedia. Biotechnology Letters, 42 (3):461-469.
doi: 10.1007/s10529-019-02785-0 URL |
| [29] | Zhang Tianlong, Zhao Jirong, Chen Qiqing, Zhao Ning, Zhu Bao, Ma Tong, Xue Xu, Cai Yi. 2021. Research progress on chemical components and analgesic mechanism of Corydalis rhizome. Chinese Journal of Information on TCM, 28 (5):141-144. (in Chinese) |
| 张天龙, 赵继荣, 陈祁青, 赵宁, 朱宝, 马同, 薛旭, 蔡毅. 2021. 延胡索化学成分及镇痛作用机制研究进展. 中国中医药信息杂志, 28 (5):141-144. | |
| [30] | Zhang Tiejun, Xu Jun, Han Yanqi, Zhang Hongbing, Gong Suxiao, Liu Chuangxiao. 2016. Quality markers research on Chinese materia medica:quality evaluation and quality standards of Corydalis rhizome. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 47 (9):1458-1467. (in Chinese) |
| 张铁军, 许浚, 韩彦琪, 张洪兵, 龚苏晓, 刘昌孝. 2016. 中药质量标志物(Q-marker)研究: 延胡索质量评价和质量标准研究. 中草药, 47 (9):1458-1467. | |
| [31] |
Zhong F, Huang L, Qi L, Ma Y, Yan Z. 2020. Full-length transcriptome analysis of Coptis deltoidea and identification of putative genes involved in benzylisoquinoline alkaloids biosynthesis based on combined sequencing platforms. Plant Molecular Biology, 102:477-499.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-019-00959-y URL |
| [32] | Zhu Yunhao, Zhang Mengjia, Li Lu, Zhao Le, Dong Chengming. 2020. Comparative transcriptome analysis of differential expression in different tissues of Prunella vulgaris. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 51 (13):3523-3529. (in Chinese) |
| 朱畇昊, 张梦佳, 李璐, 赵乐, 董诚明. 2020. 基于比较转录组的夏枯草组织差异表达分析. 中草药, 51 (13):3523-3529. |
| [1] | 蒋 彧, 涂勋良, 何俊蓉. 国兰叶色突变体叶片差异表达基因分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 371-381. |
| [2] | 蔺海娇, 梁雨晨, 李玲, 马军, 张璐, 兰振颖, 苑泽宁. 薰衣草CBF途径相关耐寒基因挖掘与调控网络分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 131-144. |
| [3] | 高彦龙, 吴玉霞, 张仲兴, 王双成, 张瑞, 张德, 王延秀. 苹果ELO家族基因鉴定及其在低温胁迫下的表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(8): 1621-1636. |
| [4] | 邱子文, 刘林敏, 林永盛, 林晓洁, 李永裕, 吴少华, 杨超. 千层金MbEGS基因的克隆与功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(8): 1747-1760. |
| [5] | 郑林, 王帅, 刘语诺, 杜美霞, 彭爱红, 何永睿, 陈善春, 邹修平. 柑橘响应黄龙病菌侵染的NAC基因的克隆及表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(7): 1441-1457. |
| [6] | 马维峰, 李艳梅, 马宗桓, 陈佰鸿, 毛娟. 苹果POD家族基因的鉴定与MdPOD15的功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(6): 1181-1199. |
| [7] | 张凯, 麻明英, 王萍, 李益, 金燕, 盛玲, 邓子牛, 马先锋. 柑橘HSP20家族基因鉴定及其响应溃疡病菌侵染表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(6): 1213-1232. |
| [8] | 梁晨, 孙如意, 向锐, 孙艺萌, 师校欣, 杜国强, 王莉. 葡萄生长调控因子GRF家族基因的鉴定及表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(5): 995-1007. |
| [9] | 肖学宸, 刘梦雨, 蒋梦琦, 陈燕, 薛晓东, 周承哲, 吴兴健, 吴君楠, 郭寅生, 叶开温, 赖钟雄, 林玉玲. 龙眼褪黑素合成途径SNAT、ASMT和COMT家族基因鉴定及表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(5): 1031-1046. |
| [10] | 周徐子鑫, 杨威, 毛美琴, 薛彦斌, 马均. 金边红苞凤梨叶色突变体色素鉴定及类胡萝卜素合成限速基因筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(5): 1081-1091. |
| [11] | 高玮林, 张力曼, 薛超玲, 张垚, 刘孟军, 赵锦. 枣E类MADS基因在花和果中的表达及其蛋白互作研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(4): 739-748. |
| [12] | 沈楠, 张荆城, 王成晨, 边银丙, 肖扬. 香菇子实体发育过程中的转录组研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(4): 801-815. |
| [13] | 夏铭, 李经纬, 罗章瑞, 祖贵东, 王娅, 张万萍. 外源褪黑素影响萝卜生长及对链格孢菌抗性的机理研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(3): 548-560. |
| [14] | 刘梦雨, 蒋梦琦, 陈燕, 张舒婷, 薛晓东, 肖学宸, 赖钟雄, 林玉玲. 龙眼GDSL酯酶/脂肪酶基因的全基因组鉴定及表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(3): 597-612. |
| [15] | 张瑞, 张夏燚, 赵婷, 王双成, 张仲兴, 刘博, 张德, 王延秀. 基于转录组分析垂丝海棠响应盐碱胁迫的分子机制[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(2): 237-251. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司