
园艺学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3): 548-560.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0423
夏铭1,2, 李经纬1,2, 罗章瑞2, 祖贵东3, 王娅4, 张万萍1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-05-06
修回日期:2021-09-09
出版日期:2022-03-25
发布日期:2022-03-25
通讯作者:
张万萍
E-mail:1226190368@qq.com
基金资助:
XIA Ming1,2, LI Jingwei1,2, LUO Zhangrui2, ZU Guidong3, WANG Ya4, ZHANG Wanping1,2,*( )
)
Received:2021-05-06
Revised:2021-09-09
Online:2022-03-25
Published:2022-03-25
Contact:
ZHANG Wanping
E-mail:1226190368@qq.com
摘要:
以‘江南圆白’萝卜(Raphanus sativus)幼苗为材料,叶片喷施等量0、50、100、500、1 000和1 500 μmol · L-1褪黑素,测定各处理幼苗生物量、总叶绿素含量、APX酶活性、H2O2含量,内源褪黑素含量以及亚细胞结构,同时对各处理幼苗接种芸薹链格孢菌(Alternaria)后的发病情况进行统计。结果表明,在50、500 μmol · L-1褪黑素浓度范围内,幼苗生长和抗性随喷施浓度升高而增加,其中500 μmol · L-1处理各项指标最佳,而1 000、1 500 μmol · L-1褪黑素处理降低各项指标,说明褪黑素可通过剂量依赖模式调节萝卜生长及抗性。此外对0、500和1 500 μmol · L-1褪黑素处理的样品进行RNA-Seq转录组分析,筛选出8个与光合调控(Ubr)和逆境抗性(Aos1、Prp1、Zat-like、Jub1-like、Edr1、Usp和Eda)相关的差异表达基因,且其表达量亦呈明显的剂量依赖效应。
中图分类号:
夏铭, 李经纬, 罗章瑞, 祖贵东, 王娅, 张万萍. 外源褪黑素影响萝卜生长及对链格孢菌抗性的机理研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(3): 548-560.
XIA Ming, LI Jingwei, LUO Zhangrui, ZU Guidong, WANG Ya, ZHANG Wanping. Research on Mechanism of Exogenous Melatonin Effects on Radish Growth and Resistence to Alternaria brassicae[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(3): 548-560.
| 基因名 Gene ID | 基因名 Gene name | 描述 Description | KEGG通路ID KEGG pathway ID | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 108828933 | Aos1 | 丙二烯氧化物合酶,叶绿体 Allene oxide synthase,chloroplastic | Ko00592:α-亚麻酸代谢 α-Linolenic acid metabolism | F:ACCTACATGCCCTCGACGGATC R:TTGGCGTGTTTCGGCTCTGATG |
| 108859130 | Prp1 | 致病相关类蛋白1 Pathogenesis-related protein 1-like | Ko04626: 植物—病菌互作 Plant-pathogen interaction | F:AACCAAGCACGACAGGCAGTAAG R:ACTCTTAGTCGGTCGGCGTAGC |
| 108818819 | At-like | 锌指类蛋白ZAT10 Zinc finger protein ZAT10-like | 无Naught | F:TCCACCACCAGAAGAACCTCACC R:GCACTTGTAGGACGACTTCTCAGC |
| 108834050 | Jub1-like | JUNGBRUNNEN类转录因子1 Transcription factor JUNGBRUNNEN 1-like | Ko04141:内质网中的蛋白质加工Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum | F:CACAAGCCACACGAGCCACAG R:AATCTCCACCGTCGAGGTTCCC |
| 108862765 | Edr1 | 丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶EDR1 Serine/threonine-protein kinase EDR1 | 无Naught | F:TTCGCAGACCTTAACCCGTTTCAG R:TGCAGGAGACTTACCAACCAGAGG |
| 108848467 | Ubr | 紫外线B受体UVR8亚型X1 Ultraviolet-B receptor UVR8 isoform X1 | Ko04120:泛素介导的蛋白质水解 Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | F:AGTCACCGTTCTCCTCCTTCTCG R:TTGTTGCGTGGACTGCTCGATTAG |
| 108860024 | Usp | 普遍应激蛋白A样蛋白 Universal stress protein A-like protein | 无Naught | F:ACGAAAGCGAAGAGAGCATGGAAG R:CCCTGCGGTGTCAATGGAAGAG |
| 108807199 | Ech-like | 类内源几丁质酶At2g43590 Endochitinase At2g43590-like | Ko00520:氨基糖和核苷酸糖代谢 Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism | F:CCTCGGGCGTATGTTGTAGTCAG R:GCAAGGACCTGATCGGCAACC |
| 108847559 | Actin-1 Actin-2 | actin-7-like actin-7-like | 无Naught 无Naught | F:GCATCACACTTTCTACAAC R:CCTGGATAGCAACATACAT F:GCAAGAGCTGGATACCGCAAAG R:CGATGAGCGATGGCTGGAAC |
表1 差异表达基因 RT-qPCR引物及其序列
Table 1 The RT-qPCR Primers and their sequences for DEGs
| 基因名 Gene ID | 基因名 Gene name | 描述 Description | KEGG通路ID KEGG pathway ID | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 108828933 | Aos1 | 丙二烯氧化物合酶,叶绿体 Allene oxide synthase,chloroplastic | Ko00592:α-亚麻酸代谢 α-Linolenic acid metabolism | F:ACCTACATGCCCTCGACGGATC R:TTGGCGTGTTTCGGCTCTGATG |
| 108859130 | Prp1 | 致病相关类蛋白1 Pathogenesis-related protein 1-like | Ko04626: 植物—病菌互作 Plant-pathogen interaction | F:AACCAAGCACGACAGGCAGTAAG R:ACTCTTAGTCGGTCGGCGTAGC |
| 108818819 | At-like | 锌指类蛋白ZAT10 Zinc finger protein ZAT10-like | 无Naught | F:TCCACCACCAGAAGAACCTCACC R:GCACTTGTAGGACGACTTCTCAGC |
| 108834050 | Jub1-like | JUNGBRUNNEN类转录因子1 Transcription factor JUNGBRUNNEN 1-like | Ko04141:内质网中的蛋白质加工Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum | F:CACAAGCCACACGAGCCACAG R:AATCTCCACCGTCGAGGTTCCC |
| 108862765 | Edr1 | 丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶EDR1 Serine/threonine-protein kinase EDR1 | 无Naught | F:TTCGCAGACCTTAACCCGTTTCAG R:TGCAGGAGACTTACCAACCAGAGG |
| 108848467 | Ubr | 紫外线B受体UVR8亚型X1 Ultraviolet-B receptor UVR8 isoform X1 | Ko04120:泛素介导的蛋白质水解 Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | F:AGTCACCGTTCTCCTCCTTCTCG R:TTGTTGCGTGGACTGCTCGATTAG |
| 108860024 | Usp | 普遍应激蛋白A样蛋白 Universal stress protein A-like protein | 无Naught | F:ACGAAAGCGAAGAGAGCATGGAAG R:CCCTGCGGTGTCAATGGAAGAG |
| 108807199 | Ech-like | 类内源几丁质酶At2g43590 Endochitinase At2g43590-like | Ko00520:氨基糖和核苷酸糖代谢 Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism | F:CCTCGGGCGTATGTTGTAGTCAG R:GCAAGGACCTGATCGGCAACC |
| 108847559 | Actin-1 Actin-2 | actin-7-like actin-7-like | 无Naught 无Naught | F:GCATCACACTTTCTACAAC R:CCTGGATAGCAACATACAT F:GCAAGAGCTGGATACCGCAAAG R:CGATGAGCGATGGCTGGAAC |
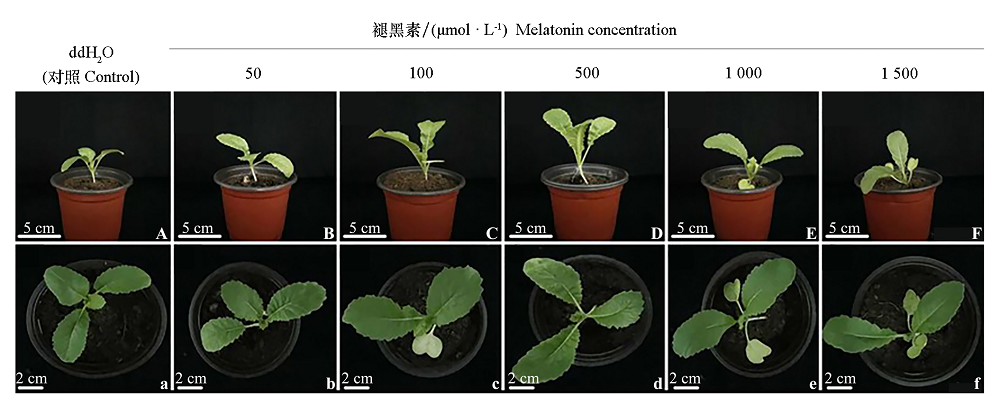
图1 梯度浓度外源褪黑素处理对‘江南圆白’萝卜幼苗生长的影响 A ~ F为正拍;a ~ f为俯拍。
Fig. 1 Effect of exogenous melatonin on vegetative growth of‘Jiangnan Yuanbai’rabish seedlings A-F is the forward shot;a-f is the overhead shot.
| 褪黑素/(μmol · L-1) Melatonin | 株高/cm Plant height | 茎粗/mm Stem diameter | 鲜质量/g Fresh weight | 干质量/g Dry weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ddH2O(对照Control) | 13.57 ± 0.19 d | 3.37 ± 0.04 cd | 126.33 ± 0.93 d | 10.75 ± 0.05 d |
| 50 | 14.47 ± 0.18 c | 3.73 ± 0.03 b | 130.07 ± 0.87 c | 11.81 ± 0.08 c |
| 100 | 15.33 ± 0.22 b | 3.90 ± 0.03 ab | 139.17 ± 0.83 b | 12.34 ± 0.06 b |
| 500 | 16.11 ± 0.10 a | 4.05 ± 0.07 a | 156.27 ± 0.83 a | 12.76 ± 0.04 a |
| 1 000 | 14.79 ± 0.14 c | 3.52 ± 0.05 c | 126.53 ± 0.45 d | 10.78 ± 0.16 d |
| 1 500 | 12.91 ± 0.08 e | 3.29 ± 0.03 d | 123.61 ± 0.66 e | 10.41 ± 0.10 e |
表2 外源褪黑素对‘江南圆白’萝卜幼苗生长指标的影响
Table 2 Effects of exogenous melatonin on growth indexes of‘Jiangnan Yuanbai’radish seedlings
| 褪黑素/(μmol · L-1) Melatonin | 株高/cm Plant height | 茎粗/mm Stem diameter | 鲜质量/g Fresh weight | 干质量/g Dry weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ddH2O(对照Control) | 13.57 ± 0.19 d | 3.37 ± 0.04 cd | 126.33 ± 0.93 d | 10.75 ± 0.05 d |
| 50 | 14.47 ± 0.18 c | 3.73 ± 0.03 b | 130.07 ± 0.87 c | 11.81 ± 0.08 c |
| 100 | 15.33 ± 0.22 b | 3.90 ± 0.03 ab | 139.17 ± 0.83 b | 12.34 ± 0.06 b |
| 500 | 16.11 ± 0.10 a | 4.05 ± 0.07 a | 156.27 ± 0.83 a | 12.76 ± 0.04 a |
| 1 000 | 14.79 ± 0.14 c | 3.52 ± 0.05 c | 126.53 ± 0.45 d | 10.78 ± 0.16 d |
| 1 500 | 12.91 ± 0.08 e | 3.29 ± 0.03 d | 123.61 ± 0.66 e | 10.41 ± 0.10 e |
| 褪黑素/(μmol · L-1) Melatonin | 叶片褪黑素含量/(ng · mL-1) Melatonin content of leaf | SPAD | H2O2含量/(mmol · g-1 FW) H2O2 content | APX活性/(μmol · g-1 FW) APX activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ddH2O(对照Control) | 14.36 ± 1.12 c | 32.66 ± 0.54 d | 7.35 ± 0.12 a | 0.372 ± 0.009 e |
| 50 | — | 34.98 ± 0.24 c | 6.37 ± 0.08 b | 0.551 ± 0.037 d |
| 100 | — | 36.94 ± 0.23 b | 5.64 ± 0.08 c | 0.752 ± 0.017 c |
| 500 | 19.23 ± 0.60 b | 38.49 ± 0.27 a | 4.69 ± 0.17 d | 1.070 ± 0.023 a |
| 1 000 | — | 35.58 ± 0.06 c | 5.73 ± 0.06 c | 0.863 ± 0.034 b |
| 1 500 | 25.04 ± 0.82 a | 32.79 ± 0.63 d | 6.51 ± 0.14 b | 0.422 ± 0.005 e |
表3 外源褪黑素处理对‘江南圆白’萝卜幼苗叶片内源褪黑素、叶绿素、H2O2含量和APX酶活性的影响
Table 3 Effects of exogenous melatonin treatment on melatonin,chlorophyll,H2O2 content and APX activity in leaves of ‘Jiangnan Yuanbai’radish seedlings
| 褪黑素/(μmol · L-1) Melatonin | 叶片褪黑素含量/(ng · mL-1) Melatonin content of leaf | SPAD | H2O2含量/(mmol · g-1 FW) H2O2 content | APX活性/(μmol · g-1 FW) APX activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ddH2O(对照Control) | 14.36 ± 1.12 c | 32.66 ± 0.54 d | 7.35 ± 0.12 a | 0.372 ± 0.009 e |
| 50 | — | 34.98 ± 0.24 c | 6.37 ± 0.08 b | 0.551 ± 0.037 d |
| 100 | — | 36.94 ± 0.23 b | 5.64 ± 0.08 c | 0.752 ± 0.017 c |
| 500 | 19.23 ± 0.60 b | 38.49 ± 0.27 a | 4.69 ± 0.17 d | 1.070 ± 0.023 a |
| 1 000 | — | 35.58 ± 0.06 c | 5.73 ± 0.06 c | 0.863 ± 0.034 b |
| 1 500 | 25.04 ± 0.82 a | 32.79 ± 0.63 d | 6.51 ± 0.14 b | 0.422 ± 0.005 e |

图2 不同浓度褪黑素处理对萝卜叶肉细胞亚细胞结构的影响 V:液泡;CW:细胞壁;C:叶绿体;S:淀粉粒。
Fig. 2 Effects of melatonin treatment of different concentration on subcellular structure of radish mesophyll cell V:Vacuole;CW:Cell wall;C:Chloroplast;S:Starch grain.

图3 不同浓度外源褪黑素处理萝卜幼苗后接种链格孢菌的发病情况(A)及病情指数(B)
Fig. 3 Disease incidence(A)and disease index(B)of Alternaria alternata inoculated radish seedlings treated with different concentrations of melatonin
| 基因ID Gene ID | 基因名 Gene name | 褪黑素处理(μmol · L-1) Melatonin treatment | Log2比值 Log2 Ratio | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ddH2O | 500 | 1 500 | 500 vs ddH2O | 1 500 vs ddH2O | 500 vs 1 500 | ||
| 108828933 | Aos1 | 6.04 | 37.51 | 4.12 | 6.21 | 0.68 | 9.10 |
| 108859130 | Prp1 | 12.48 | 65.54 | 29.11 | 5.25 | 2.33 | 2.25 |
| 108818819 | Zat-like | 17.79 | 41.10 | 18.44 | 2.30 | 1.04 | 2.23 |
| 108834050 | Jub1-like | 0.05 | 0.65 | 0.44 | 13.00 | 8.80 | 1.47 |
| 108862765 | Edr1 | 6.34 | 6.70 | 4.18 | 1.06 | 0.65 | 1.60 |
| 108848467 | Ubr | 2.65 | 3.88 | 2.13 | 1.46 | 0.80 | 1.82 |
| 108860024 | Usp | 180.23 | 268.96 | 9.09 | 1.49 | 0.05 | 29.58 |
| 108807199 | Ech-like | 251.88 | 670.56 | 5.13 | 2.66 | 0.02 | 130.71 |
表4 DEG的RNA-seq FPKM值
Table 4 RNA-seq FPKM value of DEGs
| 基因ID Gene ID | 基因名 Gene name | 褪黑素处理(μmol · L-1) Melatonin treatment | Log2比值 Log2 Ratio | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ddH2O | 500 | 1 500 | 500 vs ddH2O | 1 500 vs ddH2O | 500 vs 1 500 | ||
| 108828933 | Aos1 | 6.04 | 37.51 | 4.12 | 6.21 | 0.68 | 9.10 |
| 108859130 | Prp1 | 12.48 | 65.54 | 29.11 | 5.25 | 2.33 | 2.25 |
| 108818819 | Zat-like | 17.79 | 41.10 | 18.44 | 2.30 | 1.04 | 2.23 |
| 108834050 | Jub1-like | 0.05 | 0.65 | 0.44 | 13.00 | 8.80 | 1.47 |
| 108862765 | Edr1 | 6.34 | 6.70 | 4.18 | 1.06 | 0.65 | 1.60 |
| 108848467 | Ubr | 2.65 | 3.88 | 2.13 | 1.46 | 0.80 | 1.82 |
| 108860024 | Usp | 180.23 | 268.96 | 9.09 | 1.49 | 0.05 | 29.58 |
| 108807199 | Ech-like | 251.88 | 670.56 | 5.13 | 2.66 | 0.02 | 130.71 |
| 基因ID Gene ID | 基因名 Gene name | 褪黑素处理(μmol · L-1) Melatonin treatment | Log2比值 Log2 Ratio | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ddH2O | 500 | 1 500 | 500 vs ddH2O | 1 500 vs ddH2O | 500 vs 1 500 | ||
| 108828933 | Aos1 | 0.95 ± 0.14 a | 1.19 ± 0.13 a | 0.21 ± 0.01 b | 1.25 | 0.22 | 5.66 |
| 108859130 | Prp1 | 0.12 ± 0.14 c | 1.26 ± 0.03 a | 0.65 ± 0.00 b | 10.50 | 5.41 | 1.93 |
| 108818819 | Zat-like | 1.02 ± 0.15 b | 1.92 ± 0.11 a | 1.11 ± 0.01 b | 1.88 | 1.08 | 1.79 |
| 108834050 | Jub1-like | 2.30 ± 0.10 b | 3.24 ± 0.29 a | 2.55 ± 0.07 b | 1.41 | 1.11 | 1.27 |
| 108862765 | Edr1 | 1.36 ± 0.01 b | 2.33 ± 0.18 a | 1.14 ± 0.06 b | 1.71 | 0.84 | 2.04 |
| 108848467 | Ubr | 0.10 ± 0.003 b | 0.21 ± 0.01 a | 0.07 ± 0.002 c | 2.10 | 0.70 | 3.00 |
| 108860024 | Usp | 16.21 ± 0.65 b | 23.48 ± 1.13 a | 12.66 ± 0.12 c | 1.45 | 0.78 | 1.85 |
| 108807199 | Ech-like | 1.16 ± 0.04 a | 1.31 ± 0.08 a | 1.14 ± 0.11 a | 1.12 | 0.98 | 1.14 |
表5 DEGs的RT-qPCR的验证
Table 5 RT-qPCR verification of DEGs
| 基因ID Gene ID | 基因名 Gene name | 褪黑素处理(μmol · L-1) Melatonin treatment | Log2比值 Log2 Ratio | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ddH2O | 500 | 1 500 | 500 vs ddH2O | 1 500 vs ddH2O | 500 vs 1 500 | ||
| 108828933 | Aos1 | 0.95 ± 0.14 a | 1.19 ± 0.13 a | 0.21 ± 0.01 b | 1.25 | 0.22 | 5.66 |
| 108859130 | Prp1 | 0.12 ± 0.14 c | 1.26 ± 0.03 a | 0.65 ± 0.00 b | 10.50 | 5.41 | 1.93 |
| 108818819 | Zat-like | 1.02 ± 0.15 b | 1.92 ± 0.11 a | 1.11 ± 0.01 b | 1.88 | 1.08 | 1.79 |
| 108834050 | Jub1-like | 2.30 ± 0.10 b | 3.24 ± 0.29 a | 2.55 ± 0.07 b | 1.41 | 1.11 | 1.27 |
| 108862765 | Edr1 | 1.36 ± 0.01 b | 2.33 ± 0.18 a | 1.14 ± 0.06 b | 1.71 | 0.84 | 2.04 |
| 108848467 | Ubr | 0.10 ± 0.003 b | 0.21 ± 0.01 a | 0.07 ± 0.002 c | 2.10 | 0.70 | 3.00 |
| 108860024 | Usp | 16.21 ± 0.65 b | 23.48 ± 1.13 a | 12.66 ± 0.12 c | 1.45 | 0.78 | 1.85 |
| 108807199 | Ech-like | 1.16 ± 0.04 a | 1.31 ± 0.08 a | 1.14 ± 0.11 a | 1.12 | 0.98 | 1.14 |
| [1] | Acuna-Castroviejo D, Escames G, Rodriguez M I, Lopez L C. 2007. Melatonin role in the mitochondrial function. Frontiers in Bioscience A Journal & Virtual Library, 12(4):947-963. |
| [2] | Allorent G, Lefebvre-Legendre L, Chappuis R, Kuntz M, Truong T B, Niyogi K K, Ulm R, Michel G C. 2017. Uv-b photoreceptor-mediated protection of the photosynthetic machinery in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 113(51):14864-14869. |
| [3] |
Alshareef N O, Wang J Y, Ali S, Babili S A, Tester M, Schmockel S M. 2019. Overexpression of the NAC transcription factor JUNGBRUNNEN1(JUB1)increases salinity tolerance in tomato. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 140:113-121.
doi: S0981-9428(19)30172-X pmid: 31100704 |
| [4] |
Arnao M B, Hernandez-Ruiz J. 2015. Functions of melatonin in plants:a review. Journal of Pineal Research, 59(2):133-150.
doi: 10.1111/jpi.12253 URL |
| [5] |
Arnao M B, Hernández-Ruiz J. 2018. Melatonin:A new plant hormone and/or a plant master regulator? Trends in Plant Science, 24(1):38-49.
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2018.10.010 URL |
| [6] | Bian Fenge, Tang Cuihua, Xing Hao, Xu Yuhan, Huang Lipeng, Zhang Xue, Lu Wenli, Du Yuanpeng, Zhai Heng, Sun Yongjiang. 2018. Effect of exogenous melatonin on endogenous melatonin and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics in grapevine under drought stress. Plant Physiology Communications, 54(10):1615-1623. (in Chinese) |
| 卞凤娥, 唐翠花, 邢浩, 徐玉涵, 黄丽鹏, 张雪, 陆文利, 杜远鹏, 翟衡, 孙永江. 2018. 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下葡萄内源褪黑素及叶绿素荧光特性的影响. 植物生理学报, 54(10):1615-1623. | |
| [7] |
Botelho R V, Roberti R, Tessarin P, Garcia-Mina J M, Rombolà A D. 2016. Physiological responses of grapevines to biodynamic management. Renewable Agriculture and Food Systems, 31:402-413.
doi: 10.1017/S1742170515000320 URL |
| [8] | Browse J. 2009. Jasmonate passes muster:a receptor and targets for the defense hormone. Annual Review of Plant Molecular Biology, 60:183-205. |
| [9] |
Butsanets P A, Baik A S, Shugaev A G, Kuznetsov V V. 2019. Melatonin inhibits peroxide production in plant mitochondria. Doklady Biochemistry and Biophysics, 489(1):367-369.
doi: 10.1134/S1607672919060036 pmid: 32130601 |
| [10] |
Chen K, Sun X, Amombo E, Zhu Q, Zhao Z, Chen L, Xu Q, Fu J. 2014. High correlation between thermotolerance and photosystem II activity in tall fescue. Photosynthesis Research, 122:305-314.
doi: 10.1007/s11120-014-0035-3 pmid: 25145554 |
| [11] | Chen L, Fan J B, Hu Z, Huang X, Erick A, Liu A, Bi A Y, Chen K, Xie Y, Fu J M. 2017. Melatonin is involved in regulation of bermudagrass growth and development and response to low K+ stress. Frontiers in Plan Science, 8:2038-2047. |
| [12] |
Davey M P, Susanti N I, Wargent J J, Findlay J E, Quick W P, Paul N D, Jenkins G I. 2012. The UV-B photoreceptor uvr8 promotes photosynthetic efficiency in Arabidopsis thaliana exposed to elevated levels of UV-B. Photosynthesis Research, 114(2):121-131.
doi: 10.1007/s11120-012-9785-y URL |
| [13] | Ding W, Zhao Y T, Xu J W, Zhao P, Li T, Ma H X, Russel J, Yu X Y. 2018. Melatonin:a multifunctional molecule that triggers defense responses against high light and nitrogen starvation stress in Haematococcus pluvialis. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 66:7701-7711. |
| [14] | Fan J B, Hu Z R, Xie Y, Chan Z L, Chen K, Amombo E, Chen L, Fu J M. 2015. Alleviation of cold damage to photosystem II and metabolisms by melatonin in Bermudagrass. Frontiers in Plant Science, 6:925-939. |
| [15] | Fonseca S, Chico J M, Solano R. 2009. The jasmonate pathway:the ligand,the receptor and the core signalling module. Current Opinion of Plant Molecular Biology, 12:539-547. |
| [16] |
Fu J J, Wu Y, Miao Y J, Xu Y M, Zhao E H, Wang J, Sun H E, Liu Q, Xue Y W, Xu Y F, Hu T M. 2017. Improved cold tolerance in Elymus nutans by exogenous application of melatonin may involve ABA dependent and ABA-independent pathways. Scientific Reports, 7:39865-39876.
doi: 10.1038/srep39865 URL |
| [17] |
Gu Q, Chen Z P, Yu X L, Cui W T, Pan J C, Zhao G, Xu S, Wang R, Shen W B. 2017. Melatonin confers plant tolerance against cadmium stress via the decrease of cadmium accumulation and reestablishment of microrna-mediated redox homeostasis. Plant Science, 261(17):28-37.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2017.05.001 URL |
| [18] |
Hu Z R, Fan J B, Chen K, Amombo E, Chen L, Fu J M. 2016. Effects of ethylene on photosystem II and antioxidant enzyme activity in Bermuda grass under low temperature. Photosynthesis Research, 128:59-72.
doi: 10.1007/s11120-015-0199-5 URL |
| [19] |
Jarolim K, Favero D G, Pahlke G, Dostal V, Zimmermann K, Heiss E, Ellmer D, Stark T D, Hofmann T, Marko D. 2017. Activation of the Nrf2-ARE pathway by the Alternaria alternata mycotoxins altertoxin I and II. Archives of Toxicology, 91:203-216.
doi: 10.1007/s00204-016-1726-7 URL |
| [20] |
Jopcik M, Moravcikova J, Matusikova I, Bauer M, Libantova J. 2016. Structural and functional characterisation of a classⅠendochitinase of the carnivorous sundew(Drosera rotundifolia L.). Planta, 245(2):1-15.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-016-2607-2 URL |
| [21] | Jung Y J, Melencion S M B, Lee E S, Park J H, Alinapon C V, Oh H T, Yun D J, Chi Y H, Lee S Y. 2015. Universal stress protein exhibits a redox-dependent Chaperone function in Arabidopsis and enhances plant tolerance to heat shock and oxidative stress. Frontiers in Plant Science, 6:1141-1152. |
| [22] | King S R. 1994. Screening,selection,and genetics of resistance to Alternaria diseases in Brassica oleracea[Ph. D. Dissertation]. New York:Cornell University. |
| [23] |
Lee H Y, Back K. 2016. Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways are required for melatonin-mediated defense responses in plants. Journal of Pineal Research, 60:327-335.
doi: 10.1111/jpi.12314 URL |
| [24] |
Lee H Y, Back K. 2017. Melatonin is required for H2O2 and NO-mediated defense signaling through MAPKKK3 and OXI1 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Journal of Pineal Research, 62:e12379-12421.
doi: 10.1111/jpi.2017.62.issue-2 URL |
| [25] | Lee H Y, Byeon Y, Back K. 2014. Melatonin as a signal molecule triggering defense responses against pathogen attack in Arabidopsis and tobacco. Journal of Pineal Reserch, 57:262-268. |
| [26] |
Lee H Y, Byeon Y, Tan D X, Reiter R J, Back K. 2015. Arabidopsis serotonin N-acetyltransferase knockout mutant plants exhibit decreased melatonin and salicylic acid levels resulting in susceptibility to an avirulent pathogen. Journal of Pineal Research, 58:291-299.
doi: 10.1111/jpi.12214 URL |
| [27] | Li Cheng. 2019. Mechanism of melatonin enhancing the resistance of upland cotton to Verticillium wilt[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University. (in Chinese) |
| 李诚. 2019. 褪黑素增强陆地棉黄萎病抗性的机理研究[博士论文]. 杭州: 浙江大学. | |
| [28] |
Li H R, Li Y X, Deng H, Sun X C, Wang A Q, Tang X F, Gao Y F, Zhang N, Wang L, Yang S Z, Liu Y S, Wang S H. 2018. Tomato UV-B receptor SIUVR8 mediates plant acclimation to UV-B radiation and enhances fruit chloroplast development via regulating SLGLK2. Scientific Reports, 8(1):6097-6109.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24309-y URL |
| [29] |
Lin Z F, Alexander L, Hackett R, Grierson D. 2008. Lectr2,a CTR1-like protein kinase from tomato,plays a role in ethylene signalling,development and defence. The Plant Journal, 54:1083-1093.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03481.x URL |
| [30] |
Liu C X, Chen L L, Zhao R R, Li R, Zhang S J, Yu W Q, Sheng J P, Shen L. 2019. Melatonin induces disease resistance to Botrytis cinerea in tomato fruit by activating jasmonic acid signaling pathway. Journal of Agricultural And Food Chemistry, 67(22):6116-6124.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b00058 URL |
| [31] | Liu Jianlong. 2019. Regulatory function of exogenous melatonin on fruit development,postharvest fruit quality and ring rot disease resistance in pears[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University. (in Chinese) |
| 刘建龙. 2019. 外源褪黑素对梨果实发育、采后品质和抗轮纹病的影响及其调控机制研究[博士论文]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学. | |
| [32] | Mehterov N, Balazadeh S, Hille J, Toneva V, Mueller-Roeber B, Gechev T. 2012. Oxidative stress provokes distinct transcriptional responses in the stress-tolerant atr7 and stress-sensitive loh2 arabidopsis thaliana mutants as revealed by multi-parallel quantitative real-time pcr analysis of ros marker and antioxidant genes. Plant Physiology & Biochemistry, 59(2):20-29. |
| [33] |
Nawaz M A, Jiao Y Y, Chen C, Shireen F, Zheng Z H, Imtiaz M, Bie Z L, Huang Y. 2018. Melatonin pretreatment improves vanadium stress tolerance of watermelon seedlings by reducing vanadium concentration in the leaves and regulating melatonin biosynthesis and antioxidant-related gene expression. Journal of Plant Physiology, 220:115-127.
doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2017.11.003 URL |
| [34] | Niu J S, Zhang L N, Hong D F, Wang Y H. 2005. Cloning,characterization and expression of wheat EDR1(enhanced disease resistance)gene. Journal of Plant Physiology and Molecular Biology, 31(5):477-484. |
| [35] | Norman-Setterblad C, Vidal S, Palva E T. 2000. Interacting signal pathways control defense gene expression in arabidopsis in response to cell wall-degrading enzymes from Erwinia carotovora. Molecular Plant Pathology, 13:430-438. |
| [36] |
Pajerowska-Mukhtar K M, Mukhtar M S, Guex N, Halim V A, Rosahl S, Gebhardt S C. 2008. Natural variation of potato allene oxide synthase 2 causes differential levels of jasmonates and pathogen resistance in Arabidopsis. Planta, 228(2):293-306.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-008-0737-x pmid: 18431595 |
| [37] | Pinto V E, Patriarca A. 2017. Alternaria species and their associated mycotoxins. Methods in Molecular Biology, 1542:13-32. |
| [38] | Ren S X, Rutto L, Katuuramu D. 2019. Melatonin acts synergistically with auxin to promote lateral root development through fine tuning auxin transport in arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS ONE, 14(8):e0221687-221706. |
| [39] |
Reymond P, Farmer E E. 1998. Jasmonate and salicylate as global signals for defense gene expression. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 1:404-411.
pmid: 10066616 |
| [40] |
Rychlik M, Zappa G, Anorga L, Belc N, Isabel C, Olivier F X D, Lenka K, Ogrinc N, Marga C O, Presser K, Zoani C. 2018. Ensuring food integrity by metrology and FAIR data principles. Frontiers in Chemistry, 6:49-56.
doi: 10.3389/fchem.2018.00049 URL |
| [41] | Sinha P, Pazhamala L T, Singh V K, Saxena R K, Krishnamurthy L, Azam S, Khan A W, Varshney R K. 2014. Identification and validation of selected universal stress protein domain containing drought-responsive genes in pigeonpea(Cajanus cajan L.). Frontiers in Plant science, 6:1065-1075. |
| [42] | Szafránska K, Reiter R J, Posmyk M M. 2016. Melatonin application to Pisum sativum L. seeds positively influences the function of the photosynthetic apparatus in growing seedlings during paraquat-induced oxidative stress. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7(575):1663-1675. |
| [43] |
Turk H, Genisel M. 2020. Melatonin-related mitochondrial respiration responses are associated with growth promotion and cold tolerance in plants-sciencedirect. Cryobiology, 92:76-85.
doi: 10.1016/j.cryobiol.2019.11.006 URL |
| [44] | Wang Tan. 2012. Studies on Identification and control of the causal organism of black spot,a new Ligustrum × vicaryi Disease[M. D. Dissertation]. Nanning: Guangxi University. (in Chinese) |
| 王坦. 2012. 金叶女贞新病害—黑斑病的病原鉴定及其防治研究[硕士论文]. 南宁: 广西大学. | |
| [45] | Wang X, Li F, Chen Z Y, Yang B X, Zhou S L. 2020. Proteomic analysis reveals the effects of melatonin on soybean root tips under flooding stress. Journal of Proteomics, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2020.104064. |
| [46] | Wei Y X, Hu W, Wang Q N, Zeng H Q, Li X L, Yan Y, Reiter R J, He C Z, Shi H T. 2017. Identification,transcriptional and functional analysis of heat-shock protein 90s in banana(Musa acuminata L.)highlight their novel role in melatonin-mediated plant response to Fusarium wilt. Journal of Pineal Research, 62:e12367-e12404. |
| [47] | Wei Y X, Zeng H Q, Hu W, Chen L Z, He C Z, Shi H T. 2016. Comparative transcriptional profiling of melatonin synthesis and catabolic genes indicates the possible role of melatonin in developmental and stress responses in rice. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7:676-691. |
| [48] |
Wu A H, Allu A D, Garapati P, Siddiqui H, Dortay H, Zanor M I, Asensi-Fabado M A, Munne-Bosch S, Antonio C, Tohge T, Fernie A R, Kaufmann K, Xue G P, Mueller-Roeber B, Balazadeh S. 2012. JUNGBRUNNEN1,a reactive oxygen species-responsive NAC transcription factor,regulates longevity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 24(2):482-506.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.090894 URL |
| [49] | Xie Y J, Mao Y, Lai D W, Zhang W, Shen W B. 2012. H2 enhances Arabidopsis salt tolerance by manipulating ZAT10/12-mediated antioxidant defence and controlling sodium exclusion. PLoS ONE, 7(11):e49800-e49812. |
| [50] |
Xu L L, Xiang G Q, Sun Q H, Ni Y, Jin Z X, Gao S W, Yao Y X. 2019. Melatonin enhances salt tolerance by promoting MYB108A-mediated ethylene biosynthesis in grapevines. Horticulture Research, 6:114-128.
doi: 10.1038/s41438-019-0197-4 URL |
| [51] | Yin L H, Wang P, Li M J, Ke X W, Li C Y, Liang D, Wu S, Ma X L, Li C, Zou Y J, Ma F W. 2013. Exogenous melatonin improves Malus resistance to Marssonina apple blotch. Journal of Pineal Reserch, 54:426-434. |
| [52] |
Yoeun S, Cho K, Han O. 2018. Structural evidence for the substrate channeling of rice allene oxide cyclase in biologically analogous nazarov reaction. Frontiers in Chemistry, 6:500-511.
doi: 10.3389/fchem.2018.00500 URL |
| [53] |
Zhang S M, Zheng X Z, Reiter R J, Feng S, Wang Y, Liu S, Jin L, Li Z G, Datla R, Ren M Z. 2017. Melatonin attenuates potato late blight by disrupting cell growth,stress tolerance,fungicide susceptibility and homeostasis of gene expression in Phytophthora infestans. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8:1993-2012.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01993 URL |
| [54] | Zhao D K, Wang H P, Chen S Y, Yu D Q, Reiter R J. 2020. Phytomelatonin:an emerging regulator of plant biotic stress resistance. Trends in Plant Science, 13:2027-2040. |
| [55] | Zhao Shen. 2010. Cloning and expression analysis of VpUSP gen in chinese wild Vitis pseudoreticulata[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University. (in Chinese) |
| 赵莘. 2010. 中国野生华东葡萄抗白粉病基因(VpUSP)克隆及表达分析[博士论文]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学. |
| [1] | 蒋 彧, 涂勋良, 何俊蓉. 国兰叶色突变体叶片差异表达基因分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 371-381. |
| [2] | 蔺海娇, 梁雨晨, 李玲, 马军, 张璐, 兰振颖, 苑泽宁. 薰衣草CBF途径相关耐寒基因挖掘与调控网络分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 131-144. |
| [3] | 赵雪艳, 王琪, 王莉, 王方圆, 王庆, 李艳. 基于比较转录组的延胡索组织差异性表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 177-187. |
| [4] | 余阳俊, 汪维红, 苏同兵, 张凤兰, 张德双, 赵岫云, 于拴仓, 李佩荣, 辛晓云, 王 姣. 抗根肿病耐抽薹大白菜新品种‘京春CR3’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 87-88. |
| [5] | 王丽丽, 王 鑫, 吴海东, 温 蔷, 杨晓飞. 抗根肿病大白菜新品种‘辽白28’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 89-90. |
| [6] | 张鲁刚, 卢倩倩, 何琼, 薛一花, 马晓敏, 马帅, 聂姗姗, 杨文静. 紫橙色大白菜新种质的创制[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(7): 1582-1588. |
| [7] | 刘众杰, 郑婷, 赵方贵, 傅伟红, 诸葛雅贤, 张志昌, 房经贵. 葡萄砧木对渗透胁迫的抗性差异及生理响应机理[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(5): 984-994. |
| [8] | 肖学宸, 刘梦雨, 蒋梦琦, 陈燕, 薛晓东, 周承哲, 吴兴健, 吴君楠, 郭寅生, 叶开温, 赖钟雄, 林玉玲. 龙眼褪黑素合成途径SNAT、ASMT和COMT家族基因鉴定及表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(5): 1031-1046. |
| [9] | 周徐子鑫, 杨威, 毛美琴, 薛彦斌, 马均. 金边红苞凤梨叶色突变体色素鉴定及类胡萝卜素合成限速基因筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(5): 1081-1091. |
| [10] | 向妙莲, 吴帆, 李树成, 马巧利, 王印宝, 肖刘华, 陈金印, 陈明. 外源褪黑素调控活性氧代谢诱导梨果实抗采后黑斑病[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(5): 1102-1110. |
| [11] | 何静娟, 范燕萍. 观赏植物花色相关的类胡萝卜素组成及代谢调控研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(5): 1162-1172. |
| [12] | 沈楠, 张荆城, 王成晨, 边银丙, 肖扬. 香菇子实体发育过程中的转录组研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(4): 801-815. |
| [13] | 张世才, 李怡斐, 王春萍, 杨小苗, 黄启中, 黄任中. 辣椒种质尖孢炭疽菌抗性鉴定与评价[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(4): 885-892. |
| [14] | 白二俊, 刘莉铭, 郝小苑, 彭斌, 吴会杰, 古勤生, 康保珊. 抗小西葫芦黄花叶病毒的西瓜自交系抗性遗传特征研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(3): 633-640. |
| [15] | 张瑞, 张夏燚, 赵婷, 王双成, 张仲兴, 刘博, 张德, 王延秀. 基于转录组分析垂丝海棠响应盐碱胁迫的分子机制[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(2): 237-251. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司