
园艺学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3): 482-492.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0244
相立1, 赵蕾1, 王玫1, 吕毅2, 王艳芳3, 沈向1, 陈学森1, 尹承苗1,**( ), 毛志泉1,**(
), 毛志泉1,**( )
)
收稿日期:2021-04-26
修回日期:2021-05-10
出版日期:2022-03-25
发布日期:2022-03-25
通讯作者:
尹承苗,毛志泉
E-mail:yinchengmiao@163.com;mzhiquan@sdau.edu.cn
基金资助:
XIANG Li1, ZHAO Lei1, WANG Mei1, LÜ Yi2, WANG Yanfang3, SHEN Xiang1, CHEN Xuesen1, YIN Chengmiao1,**( ), MAO Zhiquan1,**(
), MAO Zhiquan1,**( )
)
Received:2021-04-26
Revised:2021-05-10
Online:2022-03-25
Published:2022-03-25
Contact:
YIN Chengmiao,MAO Zhiquan
E-mail:yinchengmiao@163.com;mzhiquan@sdau.edu.cn
摘要:
以苹果砧木M9T337(Malling 9 NAKBT337)为试材,克隆了1个WRKY转录因子基因,命名为MdWRKY74(XM_029090147.1)。其开放阅读框为939 bp,编码312个氨基酸,含有1个典型的WRKY结构域。氨基酸序列比对和进化树分析发现MdWRKY74与梨PyWRKY74同源性最高。亚细胞定位结果显示MdWRKY74定位于细胞核。荧光定量PCR分析表明,MdWRKY74在苹果的不同组织中均有表达。在拟南芥中过表达MdWRKY74可提高植株的抗盐性,并能促进SOS1和NHX1的表达。结果表明MdWRKY74可被盐胁迫诱导,可能参与苹果抗盐调控。
中图分类号:
相立, 赵蕾, 王玫, 吕毅, 王艳芳, 沈向, 陈学森, 尹承苗, 毛志泉. 苹果MdWRKY74的克隆和功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(3): 482-492.
XIANG Li, ZHAO Lei, WANG Mei, LÜ Yi, WANG Yanfang, SHEN Xiang, CHEN Xuesen, YIN Chengmiao, MAO Zhiquan. Cloning and Functional Analysis of MdWRKY74 in Apple[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(3): 482-492.
| 用途 Use | 引物名称 Primer name | 序列(5′-3′) Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| CDs | MdWRKY74 | F:ATGGAGGAGGTTGAGGCAGC;R:CCAGGCCGATTGTGAATGC |
| qRT-PCR | MdWRKY74 | F:GGAAGAGGAAGAGTGAGA;R:GGAAAGTAGGAGGGAGTAA |
| qRT-PCR | MdActin | F:TGACCGAATGAGCAAGGAAATTACT;R:TACTCAGCTTTGGCAATCCACATC |
| qRT-PCR | AtSOS1 | F:GGAAGAGGAAGAGTGAGA;R:GGAAAGTAGGAGGGAGTAA |
| qRT-PCR | AtNHX1 | F:TCTTGCTATTGGTGCCATAT;R:AGGTGTCTCGTCTTGATTC |
| qRT-PCR | AtActin | F:CGCTCTTTCTTTCCAAGCTC;R:AACAGCCCTGGGAGCATC |
| 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization | MdWRKY74 | F:CAAGCTTGCATGCCTGCAGGTCGACATGGAGGAGGTTGAGGCAGC; R:CTCGCCCTTGCTCACCATGGATCCCCAGGCCGATTGTGAATGC |
表1 基因克隆和实时荧光定量所用引物序列
Table 1 Primers used for cloning and qRT-PCR analysis in this study
| 用途 Use | 引物名称 Primer name | 序列(5′-3′) Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| CDs | MdWRKY74 | F:ATGGAGGAGGTTGAGGCAGC;R:CCAGGCCGATTGTGAATGC |
| qRT-PCR | MdWRKY74 | F:GGAAGAGGAAGAGTGAGA;R:GGAAAGTAGGAGGGAGTAA |
| qRT-PCR | MdActin | F:TGACCGAATGAGCAAGGAAATTACT;R:TACTCAGCTTTGGCAATCCACATC |
| qRT-PCR | AtSOS1 | F:GGAAGAGGAAGAGTGAGA;R:GGAAAGTAGGAGGGAGTAA |
| qRT-PCR | AtNHX1 | F:TCTTGCTATTGGTGCCATAT;R:AGGTGTCTCGTCTTGATTC |
| qRT-PCR | AtActin | F:CGCTCTTTCTTTCCAAGCTC;R:AACAGCCCTGGGAGCATC |
| 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization | MdWRKY74 | F:CAAGCTTGCATGCCTGCAGGTCGACATGGAGGAGGTTGAGGCAGC; R:CTCGCCCTTGCTCACCATGGATCCCCAGGCCGATTGTGAATGC |

图3 苹果MdWRKY74与其他物种WRKY74蛋白系统进化树分析 节点处数字代表亲缘关系的远近。
Fig. 3 Phylogenetic tree analysis of apple MdWRKY74 and other species WRKY74 proteins The numbers at node represent the distance of the kinship.
| 作用元件 Functional element | 序列 Sequence | 位点功能 Function of site | 位置 Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABRE | ACGTG | 参与ABA响应 cis-acting element involved in the abscisic acid responsiveness | + 1 530 |
| CGTCA-motif | CGTCA | 参与MeJA响应 cis-acting regulatory element involved in the MeJA-responsiveness | -215 |
| LTR | CCGAAA | 低温响应 cis-acting element involved in low-temperature responsiveness | + 485 |
| MBS | CAACTG | 与干旱诱导相关的MYB绑定位点 MYB binding site involved in drought-inducibility | -175 |
| TC-rich repeats | ATTTTCTTCA | 参与防御反应和胁迫响应 cis-acting element involved in defense and stress responsiveness | + 927 |
表2 MdWRKY74基因上游调控序列顺式作用元件分析
Table 2 Analysis of cis-acting regulatory elements in the upstream regulatory sequences of MdWRKY74 gene
| 作用元件 Functional element | 序列 Sequence | 位点功能 Function of site | 位置 Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABRE | ACGTG | 参与ABA响应 cis-acting element involved in the abscisic acid responsiveness | + 1 530 |
| CGTCA-motif | CGTCA | 参与MeJA响应 cis-acting regulatory element involved in the MeJA-responsiveness | -215 |
| LTR | CCGAAA | 低温响应 cis-acting element involved in low-temperature responsiveness | + 485 |
| MBS | CAACTG | 与干旱诱导相关的MYB绑定位点 MYB binding site involved in drought-inducibility | -175 |
| TC-rich repeats | ATTTTCTTCA | 参与防御反应和胁迫响应 cis-acting element involved in defense and stress responsiveness | + 927 |
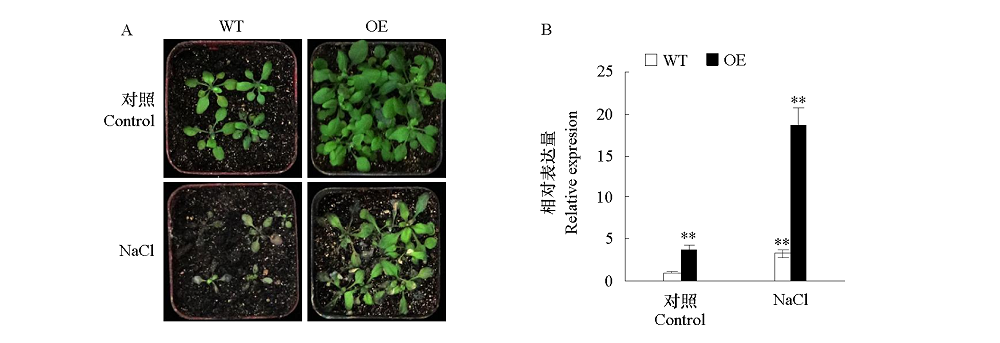
图6 NaCl处理条件下野生型(WT)和过表达MdWRKY74(OE)拟南芥形态(A)和qRT-PCR检测基因的表达量(B) **α = 0.01.
Fig. 6 The Arabidopsis thaliana that overexpressing MdWRKY74 treated with NaCl(A),and qRT-PCR detection of MdWRKY74 expression in transgenic Arabidopsis(B)
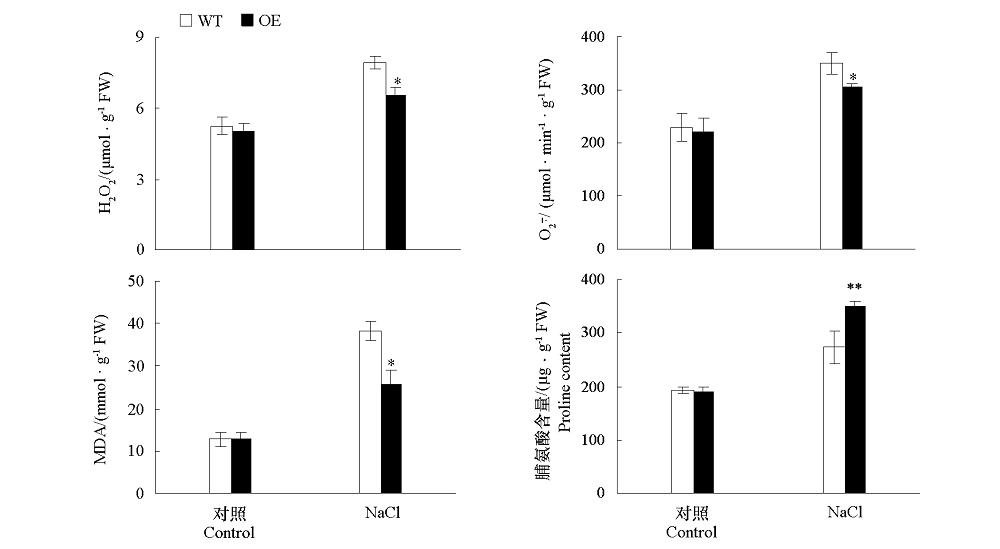
图7 NaCl处理条件下野生型(WT)和过表达MdWRKY74(OE)拟南芥相关生理指标 *α = 0.05;**α = 0.01.
Fig. 7 Related physiological indexes of overexpressing MdWRKY74(OE)Arabidopsis and wile type(WT)treated with NaCl
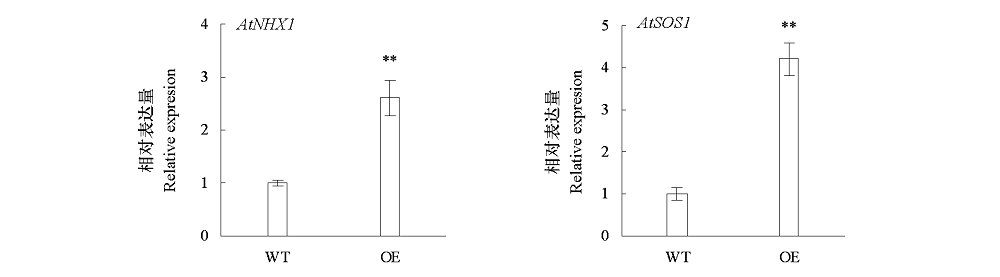
图8 野生型(WT)和过表达MdWRKY74(OE)拟南芥相关基因表达水平分析 **α = 0.01.
Fig. 8 The expression level analysis of related gene of overexpressing MdWRKY74(OE)Arabidopsis and wile type(WT)
| [1] |
Ali M A, Azeem F, Nawaz M A, Acet T, Abbas A, Imran Q M, Snah K H, Rehman H M, Chung G, Yang S H, Bohlman H. 2018. Transcription factors WRKY11 and WRKY17 are involved in abiotic stress responses in Arabidopsis. Journal of Plant Physiology, 226(7):12-21.
doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2018.04.007 URL |
| [2] |
Castañares J L, Bouzo C A. 2019. Effect of exogenous melatonin on seed germination and seedling growth in melon(Cucumis melo L.)under salt stress. Horticultural Plant Journal, 5(2):79-87.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2019.01.002 URL |
| [3] |
Chen H, Lai Z, Shi J, Xiao Y, Chen Z, Xu X. 2010. Roles of Arabidopsis WRKY18, WRKY40 and WRKY60 transcription factors in plant responses to abscisic acid and abiotic stress. BMC Plant Biology, 10(1):281.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-281 URL |
| [4] | Chu X Q, Wang C, Chen X B, Lu W J, Li H, Wang X L, Hao L L, Guo X Q. 2015. The cotton WRKY gene GhWRKY41 positively regulates salt and drought stress tolerance in transgenic Nicotiana benthamiana. PLoS ONE, 11(6):e0157026. |
| [5] |
Cui X, Yan Q, Gan S, Xue D, Wang H, Xing H, Zhao J, Guo N. 2019. GmWRKY40,a member of the WRKY transcription factor genes identified from Glycine max L. enhanced the resistance to Phytophthora sojae. BMC Plant Biology, 19(1):1-15.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1600-2 URL |
| [6] |
Dong J, Chen C, Chen Z. 2003. Expression profile of the Arabidopsis WRKY gene superfamily during plant defense response. Plant Molecular Biology, 51(1):21-37.
doi: 10.1023/A:1020780022549 URL |
| [7] |
Gao Y, Liu J, Yang F, Zhang G, Wang D, Zhang L, Ou Y, Yao Y. 2020. The WRKY transcription factor WRKY8 promotes resistance to pathogen infection and mediates drought and salt stress tolerance in Solanum lycopersicum. Physiologia Plantarum, 168(1):98-117.
doi: 10.1111/ppl.v168.1 URL |
| [8] |
Gong D, Guo Y, Schumaker K, Zhu J. 2004. The SOS3 family of calcium sensors and SOS2 family of protein kinases in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology, 134(3):919-926.
doi: 10.1104/pp.103.037440 URL |
| [9] | Gu Yan-bing. 2016. Cloning and expression analysis of two WRKY transcription factors in apple(Malus domestica Borkh.)[M. D. Dissertation]. Xincheng: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences. (in Chinese) |
| 谷彦冰. 2016. 苹果两个WRKY转录因子的克隆和表达分析[硕士论文]. 兴城: 中国农业科学院. | |
| [10] | Guo Yu-min, Zhang Yun-hua, Jing Tao, Zang Xiao-ping. 2020. Overexpression of a maize transcription factor ZmWRKY101 improving salt tolerance of Arabidopsis plants. Plant Physiology Journal, 56(9):1921-1932. (in Chinese) |
| 郭玉敏, 张云华, 井涛, 臧小平. 2020. 过表达玉米转录因子ZmWRKY101基因提高拟南芥植株的耐盐力. 植物生理学报, 56(9):1921-1932. | |
| [11] | Jiang Ming-yue, Su Xiao-shuai, Zhang Bao-hua, Li Xiao-juan, Xiao Kai. 2020. Function analysis of wheat(Triticum aestivum)TaWRKY46 gene in mediating salt stress tolerance in transgenic tobacco(Nicotiana tabacum). Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 28(10):1733-1746. (in Chinese) |
| 蒋明月, 苏晓帅, 张宝华, 李小娟, 肖凯. 2020. 小麦TaWRKY46介导转基因烟草耐盐性的功能分析. 农业生物技术学报, 28(10):1733-1746. | |
| [12] |
Jiang Y, Deyholos M K. 2009. Functional characterization of Arabidopsis NaCl-inducible WRKY25 and WRKY33 transcription factors in abiotic stresses. Plant Molecular Biology, 69(1):91-105.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-008-9408-3 URL |
| [13] |
Jiang Y, Liang G, Yu D. 2012. Activated expression of WRKY57 confers drought tolerance in Arabidopsis. Molecular Plant, 5(6):1375-1388.
doi: 10.1093/mp/sss080 URL |
| [14] | Lan Liming, Luo Changguo, Wang Sanhong. 2021. Analysis of resistance mechanism to powdery mildew based on transcriptome sequencing in Malus hupehensis. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 48(5):860-872. (in Chinese) |
| 兰黎明, 罗昌国, 王三红. 2021. 基于转录组测序的湖北海棠抗白粉病机制分析. 园艺学报, 48(5):860-872. | |
| [15] |
Li C, Wei Z, Liang D, Zhou S, Li Y, Liu C, Ma F W. 2013. Enhanced salt resistance in apple plants overexpressing a Malus vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene is associated with differences in stomatal behavior and photosynthesis. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 70(9):164-173.
doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2013.05.005 URL |
| [16] |
Li S, Fu Q, Chen L, Huang W, Yu D. 2011. Arabidopsis thaliana WRKY25,WRKY26,and WRKY33 coordinate induction of plant thermotolerance. Planta, 233(6):1237-1252.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-011-1375-2 URL |
| [17] |
Li Y, Qin R, Li H, Xu R, Qiu C, Sun Y, Ma H, Yang Y, Ni D, Li L, Wei P, Yang J. 2015. Identification and analysis of the mechanism underlying heat-inducible expression of rice aconitase 1. Plant Science, 233(4):22-31.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.01.003 URL |
| [18] | Liu Yong, Wang Zeqiong, Gong Linzhong, Wang Furong, Wang Huiliang, Ai Xiaoyan, He Huaping. 2020. Cloning and functional analysis of ERF transcription factor gene PpERF1a in peach. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47(6):1165-1171. (in Chinese) |
| 刘勇, 王泽琼, 龚林忠, 王富荣, 王会良, 艾小艳, 何华平. 2020. 桃乙烯应答因子PpERF1a的克隆与功能分析. 园艺学报, 47(6):1165-1171. | |
| [19] |
Livak K, Schmittgen. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-∆∆CT method. Methods, 25(4):402-408.
doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262 pmid: 11846609 |
| [20] | Luo Guo-wei. 2020. Screening of salt-tolerant mutants in maize and molecular characterization of ZmWRKY74[M. D. Dissertation]. Heifei: Anhui Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 罗国伟. 2020. 玉米耐盐突变体的筛选及ZmWRKY74的分子特征研究[硕士论文]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学. | |
| [21] | Lü B B, Wu Q, Wang A H, Li Q, Dong Q, Yang J J, Zhao H X, Wang X, Chen H, Li C L. 2020. A WRKY transcription factor,FtWRKY46,from Tartary buckwheat improves salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiolgy and Biochemistry, 147(2):43-53. |
| [22] |
Merz P R, Moser T, Höll J, Kortekamp A, Buchholz G, Zyprian E, Bogs J. 2015. The transcription factor VvWRKY33 is involved in the regulation of grapevine(Vitis vinifera)defense against the oomycete pathogen Plasmopara viticola. Physiologia Plantarum, 153(3):365-380.
doi: 10.1111/ppl.2015.153.issue-3 URL |
| [23] | Niu C, Wei W, Zhou Q, Tian A, Hao Y, Zhang W, Ma B, Lin Q, Zhang Z, Zhang J. 2012. Wheat WRKY genes TaWRKY2 and TaWRKY19 regulate abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Plant Cell & Environment, 35(6):1156-1170. |
| [24] |
Qi Chen-hui, Zhao Xian-yan, Jiang Han, Zheng Peng-fei, Liu Hai-tao, Li Yuan-yuan, Hao Yu-jin. 2019. Cloning and functional identification of MdWRKY53 gene in apple. Plant Physiology Journal, 55(4):511-520. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.1104/pp.55.3.511 URL |
| 齐晨辉, 赵先炎, 姜翰, 郑朋飞, 刘海涛, 李媛媛, 郝玉金. 2019. 苹果MdWRKY53基因克隆和功能鉴定. 植物生理学报, 55(4):511-520. | |
| [25] | Qiao Yonggang, Wang Yongfei, Cao Yaping, He Jiaxin, Jia Mengjun, Li Zheng, Zhang Xinrui, Song Yun. 2020. Reference genes selection and related genes expression analysis under low and high temperature stress in Taraxacum officinale. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47(6):1153-1164. (in Chinese) |
| 乔永刚, 王勇飞, 曹亚萍, 贺嘉欣, 贾孟君, 李政, 张鑫瑞, 宋芸. 2020. 药用蒲公英低温和高温胁迫下内参基因筛选与相关基因表达分析. 园艺学报, 47(6):1153-1164. | |
| [26] | Qiu Hua-rong. 2017. The molecular mechanism of ethylene suppressed MAPK-WRKY33 immune signaling pathway induced by the apple ring rot pathogenenic fungi Botryosphaeria dothidea[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 邱化荣. 2017. 乙烯抑制苹果轮纹病菌诱导的MAPK-WRKY33免疫信号途径的分子机制[博士论文]. 泰安: 山东农业大学. | |
| [27] | Şahin-Çevik M, Çevik B, Coşkan A. 2020. Identification and expression analysis of salinity-induced genes in rangpur lime(Citrus limonia)Horticultural Plant Journal, 6(5):267-276. |
| [28] | Sanoubar R, Cellini A, Gianfranco G, Spinelli F. 2020. Osmoprotectants and antioxidative enzymes as screening tools for salinity tolerance in radish (Raphanus sativus). Horticultural Plant Journal, 6(1):11-24. |
| [29] |
Sarris P, Duxbury Z, Huh S, Ma Y, Segonzac C, Sklenar J, Derbyshire P, Cevik V, Rallapalli G, Saucet S, Wirthmueller L, Menke F, Sohn K, Jones J. 2015. A plant immune receptor detects pathogen effectors that target WRKY transcription factors. Cell, 161(5):1089-1100.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.04.024 URL |
| [30] |
Shi H, Ishitani M, Kim C, Zhu J. 2000. The Arabidopsis thaliana salt tolerance gene SOS1 encodes a putative Na+/H+ antiporter. PNAS, 97(12):6896-6901.
pmid: 10823923 |
| [31] |
Shi W N, Liu D, Hao L, Wu C A, Guo X Q, Li H. 2014. GhWRKY39,a member of the WRKY transcription factor family in cotton,has a positive role in disease resistance and salt stress tolerance. Plant Cell Tissue and Organ Culture, 118(5):17-32.
doi: 10.1007/s11240-014-0458-8 URL |
| [32] |
Singh N, Bhatla S C. 2016. Nitric oxide and iron modulate heme oxygenase activity as a long distance signaling response to salt stress in sunflower seedling cotyledons. Nitric Oxide, 53(2):54-64.
doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2016.01.003 URL |
| [33] |
Suzuki N, Rivero RM, Shulaev V, Blumwald E, Mittler R. 2014. Abiotic and biotic stress combinations. New Phytologist, 203(1):32-43.
doi: 10.1111/nph.2014.203.issue-1 URL |
| [34] | Wang N, Qu C, Wang Y, Xu H, Jiang S, Fang H, Liu J, Zhang Z, Chen X. 2017. MdMYB4 enhances apple callus salt tolerance by increasing MdNHX1 expression levels. Plant Cell Tissue & Organ Culture, 131(9):183-293. |
| [35] | Wang Quan-zhen, Liu Qian, Gao Ya-ni, Liu Xu. 2017. Review on the mechanisms of the response to salinity-alkalinity stress in plants. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37(16):5565-5577. (in Chinese) |
| 王佺珍, 刘倩, 高娅妮, 柳旭. 2017. 植物对盐碱胁迫的响应机制研究进展. 生态学报, 37(16):5565-5577. | |
| [36] | Wang X H, Guo R R, Tu M X, Wang D J, Guo C L, Wan R, Li Z, Wang X P. 2017. Ectopic expression of the wild grape WRKY transcription factor VqWRKY52 in Arabidopsis thaliana enhances resistance to the biotrophic pathogen powdery mildew but not to the necrotrophic pathogen Botrytis cinerea. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8:97. |
| [37] |
Wei W, Cui M H, Hu Y, Gao K, Xie Y G, Jiang Y, Feng J Y. 2018. Ectopic expression of FvWRKY42,a WRKY transcription factor from the diploid woodland strawberry(Fragaria vesca),enhances resistance to powdery mildew,improves osmotic stress resistance,and increases abscisic acid sensitivity in Arabidopsis. Plant Science, 275:60-74.
doi: S0168-9452(18)30191-2 pmid: 30107882 |
| [38] | Xiang L, Wang M, Pan F B, Wang G S, Jiang W T, Wang Y F, Chen X S, Yin C M, Mao Z Q. 2021. Transcriptome analysis Malus domestica ‘M9T337’root molecular responses to Fusarium solani infection. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 113(1):101567. |
| [39] | Xu Hai-feng, Yang Guan-xian, Zhang-jing, Zou Qi, Wang Yi-cheng, Qu Chang-zhi, Jiang Sheng-hui, Wang Nan, Chen Xue-sen. 2018. Molecular mechanism of apple MdWRKY18 and MdWRKY40 participating in salt stress. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 51(23):4514-4521. (in Chinese) |
| 许海峰, 杨官显, 张静, 邹琦, 王意程, 曲常志, 姜生辉, 王楠, 陈学森. 2018. 苹果MdWRKY18和MdWRKY40参与盐胁迫途径分子机理研究. 中国农业科学, 51(23):4514-4521. | |
| [40] | Yu Yan-chong, Qiao Meng, Liu Zhen-hua, Xiang Feng-ning. 2010. Diversification function of WRKY transcription factor. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 22(4):345-351. (in Chinese) |
| 于延冲, 乔孟, 刘振华, 向凤宁. 2010. WRKY转录因子功能的多样化. 生命科学, 22(4):345-351. | |
| [41] | Yue Maolan, Jiang Leiyu, Liu Yi, Li Yue, Liu Yongqiang, Chen Qing, Lin Yuanxiu, Tang Haoru. 2019. Cloning,subcellular location and expression analysis of FaWRKY31 in Fragaria × ananassa. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 46(10):1947-1959. (in Chinese) |
| 岳茂兰, 江雷雨, 刘怡, 李栎, 刘勇强, 陈清, 林源秀, 汤浩茹. 2019. 草莓FaWRKY31的克隆、亚细胞定位及表达特性分析. 园艺学报, 46(10):1947-1959. | |
| [42] |
Zhang J, Xu H, Wang N, Jiang S, Fang H, Zhang Z, Yang G, Wang Y, Su M, Xu L, Chen X. 2018. The ethylene response factor MdERF1B regulates anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin biosynthesis in apple. Plant Molecular Biology, 98(9):205-218.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-018-0770-5 URL |
| [43] |
Zhang X, Henriques R, Lin S, Niu Q, Chua N. 2006. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana using the floral dip method. Nature Protocols, 1(2):641-646.
doi: 10.1038/nprot.2006.97 URL |
| [44] |
Zhang Y, Wang L. 2005. The WRKY transcription factor superfamily: its origin in eukaryotes and expansion in plants. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 5(1):1-12.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-5-1 URL |
| [45] |
Zhou L, Wang N, Gong S, Lu R, Li Y, Li X. 2015. Overexpression of a cotton(Gossypium hirsutum)WRKY gene,GhWRKY34,in Arabidopsis enhances salt-tolerance of the transgenic plants. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 96(11):311-320.
doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2015.08.016 URL |
| [46] | Zhou Tao, Wang Juan, Wang Lulu, Wang Baike, Hu Jiahui, Lan Haiyan, Yu Qinghui. 2020. Cloning and prokaryotic expression analysis of a transcription factor gene SlWRKY16 in tomato. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47(7):1312-1322. (in Chinese) |
| 周涛, 王娟, 王露露, 王柏柯, 胡佳蕙, 兰海燕, 余庆辉. 2020. 番茄转录因子基因SlWRKY16的克隆及原核表达分析. 园艺学报, 47(7):1312-1322. | |
| [47] |
Zhu D, Che Y, Xiao P, Hou L, Guo Y, Liu X. 2018. Functional analysis of a grape WRKY30 gene in drought resistance. Plant Cell Tissue and Organ Culture, 132(11):449-459.
doi: 10.1007/s11240-017-1341-1 URL |
| [1] | 于婷婷, 李 欢, 宁源生, 宋建飞, 彭璐琳, 贾竣淇, 张玮玮, 杨洪强. 苹果GRAS全基因组鉴定及其对生长素的响应分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 397-409. |
| [2] | 韩晓蕾, 张彩霞, 刘 锴, 杨 安, 严家帝, 李武兴, 康立群, 丛佩华. 中熟苹果新品种‘中苹优蕾’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 1-2. |
| [3] | 韩晓蕾, 张彩霞, 刘 锴, 严家帝, 李武兴, 康立群, 丛佩华. 中熟苹果新品种‘苹优2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 1-2. |
| [4] | 王 强, 丛佩华, 刘肖烽. 晚熟苹果新品种‘华优甜娃’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 3-4. |
| [5] | 王 强, 丛佩华, 刘肖烽. 中熟苹果新品种‘华优宝蜜’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 5-6. |
| [6] | 杨 玲, 丛佩华, 王 强, 李武兴, 康立群. 中熟鲜食苹果新品种‘华丰’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 7-8. |
| [7] | 王沙, 张心慧, 赵玉洁, 李变变, 招雪晴, 沈雨, 董建梅, 苑兆和. 石榴花青苷合成相关基因PgMYB111的克隆与功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(9): 1883-1894. |
| [8] | 丁志杰, 包金波, 柔鲜古丽, 朱甜甜, 李雪丽, 苗浩宇, 田新民. 新疆野苹果与‘元帅’‘金冠’的叶绿体基因组比对研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(9): 1977-1990. |
| [9] | 高彦龙, 吴玉霞, 张仲兴, 王双成, 张瑞, 张德, 王延秀. 苹果ELO家族基因鉴定及其在低温胁迫下的表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(8): 1621-1636. |
| [10] | 林元秘, 朱文姣, 陈敏, 薛春梅, 晋芳宇, 朱羽平, 蒋欣玥, 叶凌峰, 倪姝南伶, 杨清. miR396b负调控茄子对黄萎病的防御反应[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(8): 1713-1722. |
| [11] | 郑晓东, 袭祥利, 李玉琪, 孙志娟, 马长青, 韩明三, 李少旋, 田义轲, 王彩虹. 油菜素内酯对盐碱胁迫下平邑甜茶幼苗生长的影响及调控机理研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(7): 1401-1414. |
| [12] | 夏炎, 黄松, 武雪莉, 刘一琪, 王苗苗, 宋春晖, 白团辉, 宋尚伟, 庞宏光, 焦健, 郑先波. 基于宏病毒组测序技术的苹果病毒病鉴定与分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(7): 1415-1428. |
| [13] | 刘照霞, 张鑫, 王璐, 马玉婷, 陈倩, 朱占玲, 葛顺峰, 姜远茂. 肥料穴施位点对苹果细根生长、15N吸收利用及产量品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(7): 1545-1556. |
| [14] | 马维峰, 李艳梅, 马宗桓, 陈佰鸿, 毛娟. 苹果POD家族基因的鉴定与MdPOD15的功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(6): 1181-1199. |
| [15] | 冯琛, 黄学旺, 李兴亮, 周佳, 李天红. 不同苹果矮化砧穗组合的抗旱性比较研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(5): 945-957. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司