
园艺学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (8): 1504-1516.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0216
齐振宇1, 王婷2, 桑康琪2, 刘玥2, 王明钦3, 喻景权2, 周艳虹2, 夏晓剑2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-04-15
修回日期:2021-07-06
出版日期:2021-08-25
发布日期:2021-09-06
通讯作者:
夏晓剑
E-mail:xiaojianxia@zju.edu.cn
基金资助:
QI Zhenyu1, WANG Ting2, SANG Kangqi2, LIU Yue2, WANG Mingqin3, YU Jingquan2, ZHOU Yanhong2, XIA Xiaojian2,*( )
)
Received:2021-04-15
Revised:2021-07-06
Online:2021-08-25
Published:2021-09-06
Contact:
XIA Xiaojian
E-mail:xiaojianxia@zju.edu.cn
摘要:
在设施弱光环境下对番茄植株采取顶部和植株间两个部位LED补光的方式,研究其对植株形态、光合效率和激素代谢的影响。结果发现顶部补光对不同位置叶片光合效率均有促进作用,并导致整体叶面积增大、植株变矮、叶夹角变小以及开花数增多,植株形态变化伴随生长素(IAA)含量降低、细胞分裂素(CK)含量升高以及油菜素内酯(BR)合成基因下调。植株间补光主要促进中部和下部叶片光合效率提高和叶面积增大,显著增加株高,能使上部叶片夹角略有增加,但对开花数没有影响,整体上对激素代谢的影响不如顶部补光。总体而言,顶部补光更有利于形成良好株形,整体上促进番茄光合作用和生长,有更高的推广应用价值。
中图分类号:
齐振宇, 王婷, 桑康琪, 刘玥, 王明钦, 喻景权, 周艳虹, 夏晓剑. 设施番茄不同叶位补光对植株形态、光合及激素合成的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(8): 1504-1516.
QI Zhenyu, WANG Ting, SANG Kangqi, LIU Yue, WANG Mingqin, YU Jingquan, ZHOU Yanhong, XIA Xiaojian. Effects of Supplemental Lighting at Different Positions on Tomato Plant Morphology,Photosynthesis and Endogenous Hormone Biosynthesis Under Low-light Environment[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(8): 1504-1516.
| 基因功能 Gene function | 基因 Gene name | 基因全称 Full gene name | 登录号 Accession number | 引物(5′-3′) Primer pair |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 生长素合成 | FZY1 | FLOOZY 1 | Solyc06g065630 | F:TGGTTGTGGGTTAATGGACCT |
| Auxin biosynthetic gene | R:TCAAACAACGGGAGTTGACA | |||
| 生长素极性运输 | PIN1 | PIN-FORMED 1 | Solyc03g118740 | F:GGCATGGCAATGTTCAGTCT |
| Auxin transport protein gene | R:ACAGCTGGACCTGTAAGGAA | |||
| PIN2 | PIN-FORMED 2 | Solyc07g006900 | F:CAGGACCAGCTGTTATTGCT | |
| R:GCAAAGCAGCCTGAACGATA | ||||
| PIN3 | PIN-FORMED 3 | Solyc04g007690 | F:GGCTGCCGCTTCTATTATCG | |
| R:AATCCCTTGTGGCAATGCAG | ||||
| PIN4 | PIN-FORMED 4 | Solyc05g008060 | F:TGCTGGTCTTGGAATGGCTA | |
| R:CTGCTGGGCCAGTTAGAAAC | ||||
| 细胞分裂素合成 | IPT2 | ISOPENTENYL-TRANSFERASE 2 | Solyc04g007240 | F:AGCAGCCATGGAGATAAAGG |
| Cytokinin biosynthetic gene | R:CGTTTCTGTTGCATCCACTC | |||
| IPT3 | ISOPENTENYL-TRANSFERASE 3 | Solyc01g080150 | F:ACGTGCAATTGGAGTACCAG | |
| R:GCAAGCCAATTTGCATGTAT | ||||
| 油菜素内酯(BR)合成 | DET2 | DE-ETIOLATED 2 | Solyc10g086500 | F:ATTTACCCTCTTCGCCTCCG R:ACAACATACCCGACCCGAAT |
| Brassinosteroid | ||||
| biosynthetic gene | DWF4 | DWARF 4 | Solyc02g085360 | F:GTCCTGCTGCTGTTCAACAA R:TCCTGTGCAGAAACCTCACT |
| CPD | CONSTITUTIVE PHOTOMORPHOGENIC DWARF | Solyc06g051750 | F:ATCCAATTAACGTCCAACAT R:ACCTTTCATACACCTCCCTC | |
| CYP85A1 | Cytochrome P450 85A1 | Solyc02g089160 | F:ATGAAGCGAAAGGACTGGTC R:TGCACCCCTCATGTACTTGT | |
| Rubisco活化酶 | RCA | Rubisco activase | Solyc09g011080 | F:AGCCAAGGTCTTCGCCAATA |
| Rubisco activating enzyme gene | R:TGGGCAACGTTAAGAAGTTC | |||
| Rubisco大亚基 | RbcL | Rubisco large subunit | Solyc01g111020 | F:GCGAATTCTGGTCAGGTTGA |
| Rubisco large subunit gene | R:ACCTCTGGTGTTCCCTTGAT | |||
| 内参基因 | Actin | / | Solyc03g078400 | F:TGGTCGGAATGGGACAGAAG |
| Reference gene | R:CTCAGTCAGGAGAACAGGGT |
表1 实时荧光定量PCR引物列表
Table 1 Primers used for qRT-PCR assays
| 基因功能 Gene function | 基因 Gene name | 基因全称 Full gene name | 登录号 Accession number | 引物(5′-3′) Primer pair |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 生长素合成 | FZY1 | FLOOZY 1 | Solyc06g065630 | F:TGGTTGTGGGTTAATGGACCT |
| Auxin biosynthetic gene | R:TCAAACAACGGGAGTTGACA | |||
| 生长素极性运输 | PIN1 | PIN-FORMED 1 | Solyc03g118740 | F:GGCATGGCAATGTTCAGTCT |
| Auxin transport protein gene | R:ACAGCTGGACCTGTAAGGAA | |||
| PIN2 | PIN-FORMED 2 | Solyc07g006900 | F:CAGGACCAGCTGTTATTGCT | |
| R:GCAAAGCAGCCTGAACGATA | ||||
| PIN3 | PIN-FORMED 3 | Solyc04g007690 | F:GGCTGCCGCTTCTATTATCG | |
| R:AATCCCTTGTGGCAATGCAG | ||||
| PIN4 | PIN-FORMED 4 | Solyc05g008060 | F:TGCTGGTCTTGGAATGGCTA | |
| R:CTGCTGGGCCAGTTAGAAAC | ||||
| 细胞分裂素合成 | IPT2 | ISOPENTENYL-TRANSFERASE 2 | Solyc04g007240 | F:AGCAGCCATGGAGATAAAGG |
| Cytokinin biosynthetic gene | R:CGTTTCTGTTGCATCCACTC | |||
| IPT3 | ISOPENTENYL-TRANSFERASE 3 | Solyc01g080150 | F:ACGTGCAATTGGAGTACCAG | |
| R:GCAAGCCAATTTGCATGTAT | ||||
| 油菜素内酯(BR)合成 | DET2 | DE-ETIOLATED 2 | Solyc10g086500 | F:ATTTACCCTCTTCGCCTCCG R:ACAACATACCCGACCCGAAT |
| Brassinosteroid | ||||
| biosynthetic gene | DWF4 | DWARF 4 | Solyc02g085360 | F:GTCCTGCTGCTGTTCAACAA R:TCCTGTGCAGAAACCTCACT |
| CPD | CONSTITUTIVE PHOTOMORPHOGENIC DWARF | Solyc06g051750 | F:ATCCAATTAACGTCCAACAT R:ACCTTTCATACACCTCCCTC | |
| CYP85A1 | Cytochrome P450 85A1 | Solyc02g089160 | F:ATGAAGCGAAAGGACTGGTC R:TGCACCCCTCATGTACTTGT | |
| Rubisco活化酶 | RCA | Rubisco activase | Solyc09g011080 | F:AGCCAAGGTCTTCGCCAATA |
| Rubisco activating enzyme gene | R:TGGGCAACGTTAAGAAGTTC | |||
| Rubisco大亚基 | RbcL | Rubisco large subunit | Solyc01g111020 | F:GCGAATTCTGGTCAGGTTGA |
| Rubisco large subunit gene | R:ACCTCTGGTGTTCCCTTGAT | |||
| 内参基因 | Actin | / | Solyc03g078400 | F:TGGTCGGAATGGGACAGAAG |
| Reference gene | R:CTCAGTCAGGAGAACAGGGT |
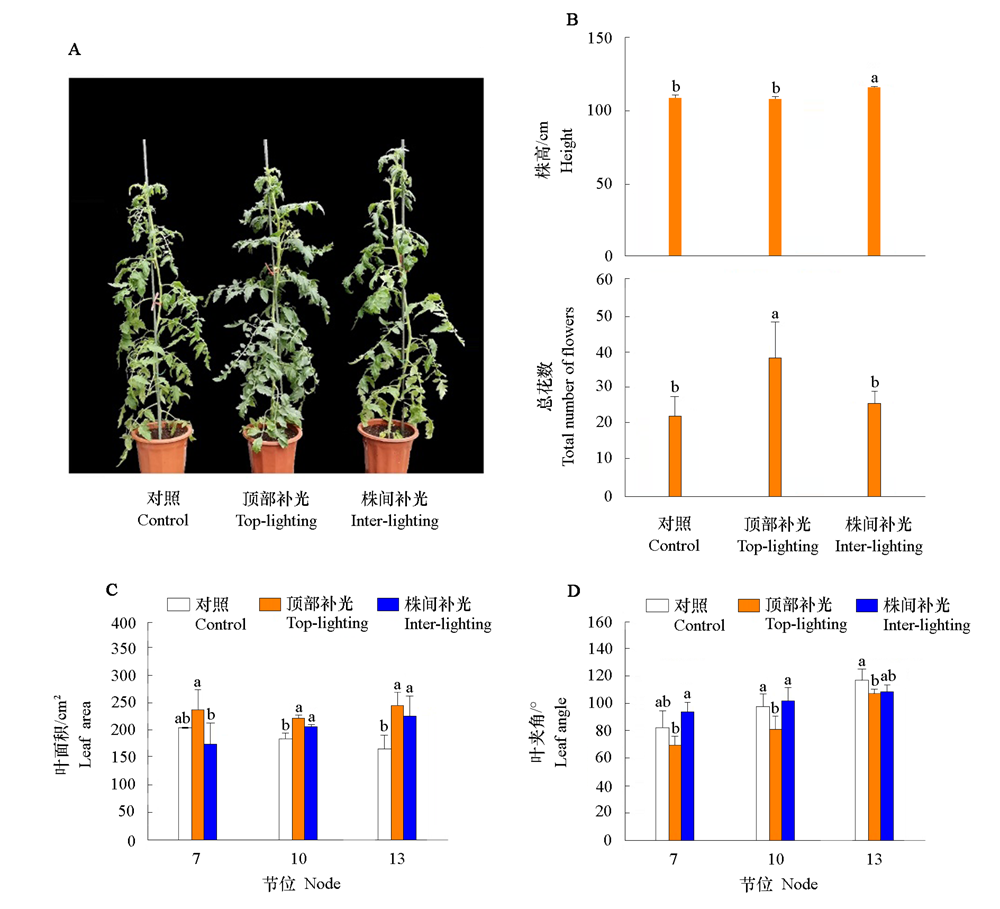
图2 番茄不同位置补光对株高、叶面积、花数和叶夹角的影响 不同小写字母表示差异显著。下同。
Fig. 2 Effects of supplemental lighting at different positions on tomato plant height,leaf area,total number of flowers and leaf angle Different lowercase letters indicate significant different at level of 0.05. The same below.
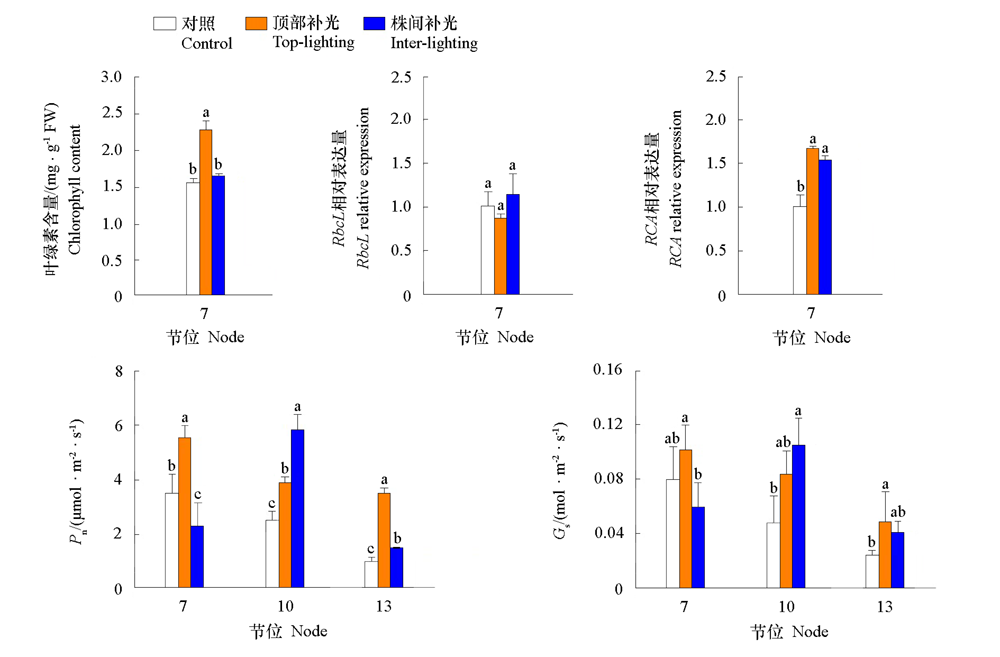
图3 不同位置补光对番茄叶绿素含量、净光合速率(Pn)、气孔导度(Gs)以及Rubisco活化酶(RCA)和Rubisco大亚基(RbcL)mRNA相对表达量的影响
Fig. 3 Effects of supplemental lighting at different positions on chlorophyll content,net photosynthetic rate(Pn),stomatal conductance (Gs),and relative expression of Rubisco activase(RCA)and Rubisco large subunit(RbcL)of tomato

图4 不同位置补光对番茄Rubisco活化酶(RCA)和Rubisco大亚基(RbcL)蛋白含量的影响
Fig. 4 Effects of supplemental lighting at different positions on protein content of Rubisco activase(RCA)and Rubisco large subunit(RbcL)of tomato
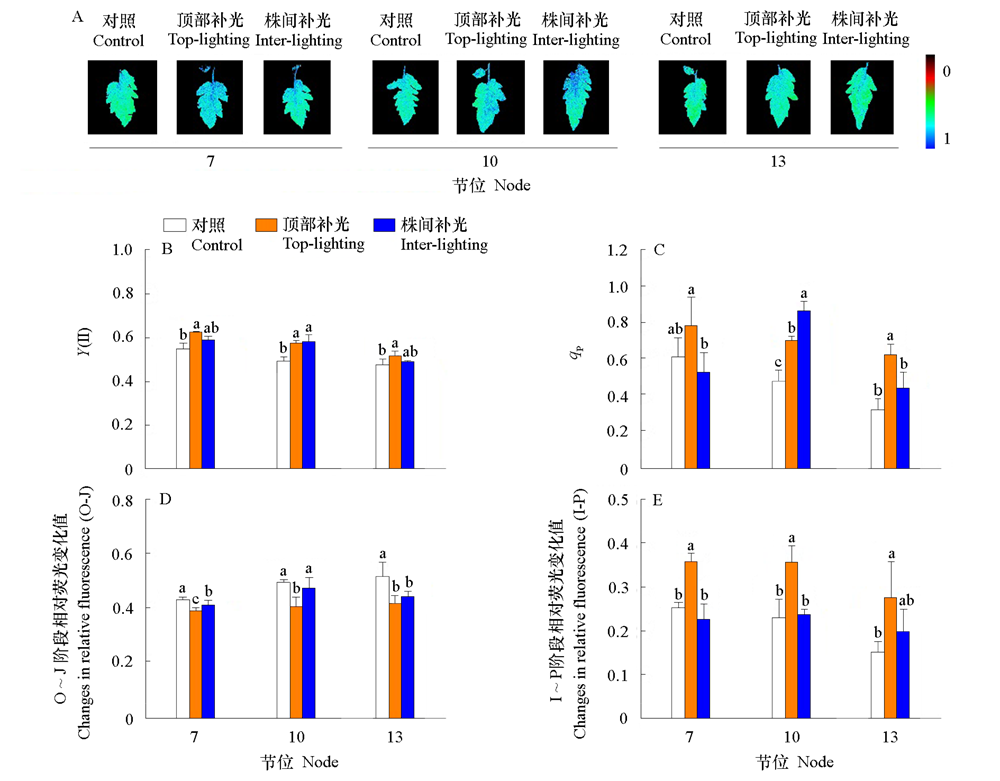
图5 不同位置补光对番茄光系统Ⅱ光化学效率Y(Ⅱ)、光化学猝灭系数(qP)和OJIP曲线参数的影响
Fig. 5 Effects of supplemental lighting at different positions on photosystem II photochemical efficiency,photochemical quenching coefficient(qP)and parameters of OJIP curve of tomato
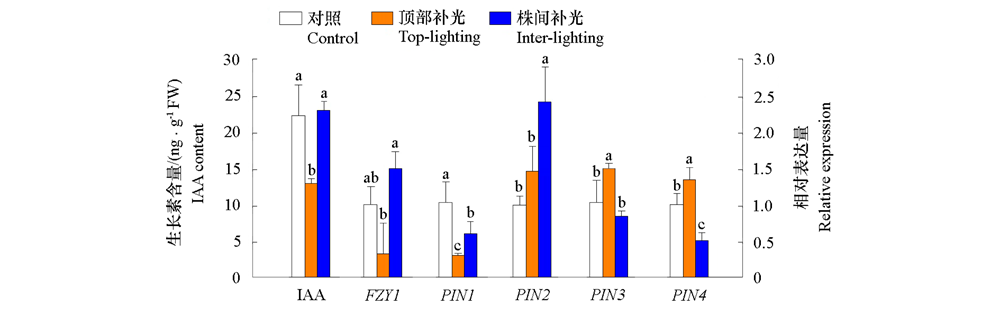
图6 不同位置补光对番茄内源生长素(IAA)含量及其合成与运输相关基因表达的影响
Fig. 6 Effects of supplemental lighting at different positions on the content of endogenous auxin(IAA)and the expression of genes related to IAA synthesis and transport in tomato
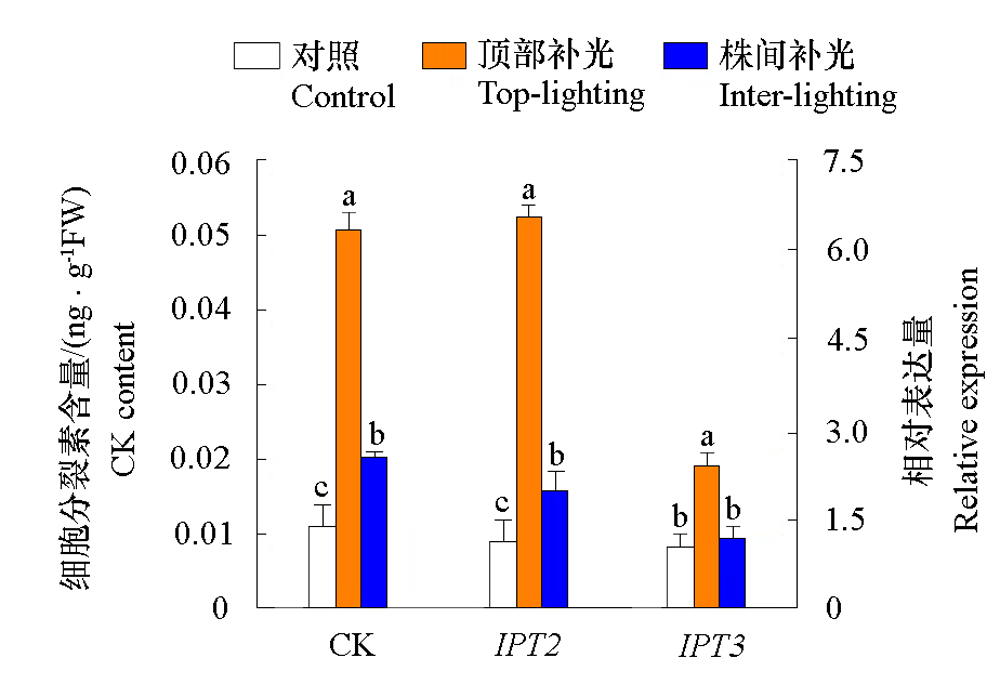
图7 不同位置补光对番茄内源细胞分裂素(CK)的含量及其合成相关基因表达的影响
Fig. 7 Effects of supplemental lighting at different positions on the content of endogenous cytokinin(CK)and the expression of genes related to CK synthesis in tomato
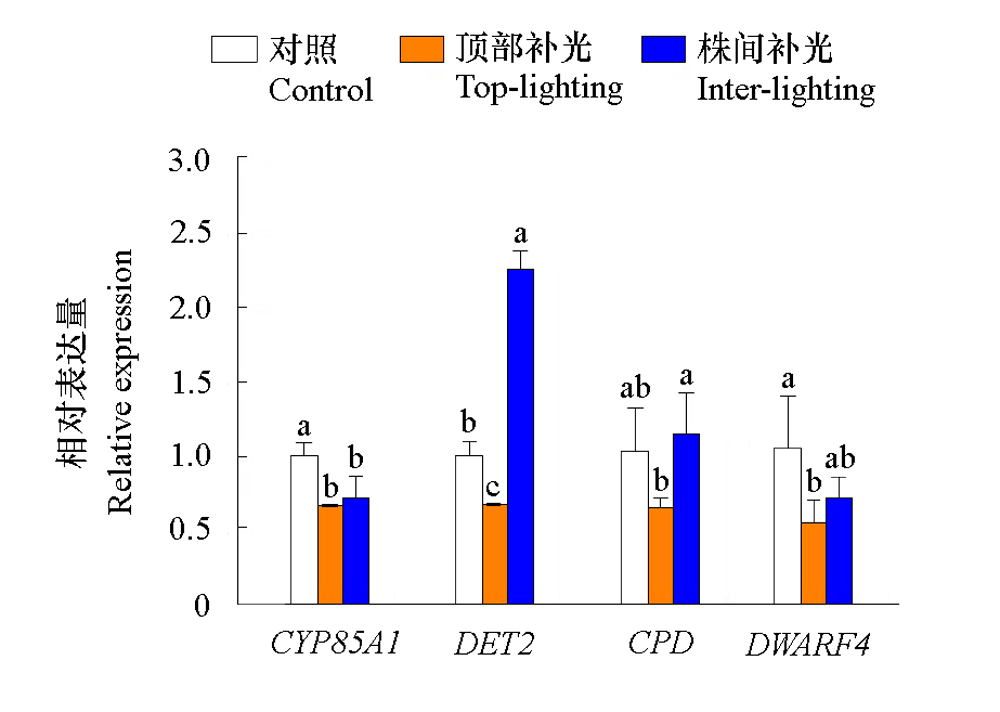
图8 不同位置补光对番茄内源油菜素内酯(BR)合成基因表达的影响
Fig. 8 Effects of supplemental lighting at different positions on the expression of genes related to endogenous brassinosteroid(BR)synthesis in tomato
| [1] |
Arnon D I. 1949. Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiology, 24:1-15.
pmid: 16654194 |
| [2] |
Baker N R. 2008. Chlorophyll fluorescence:a probe of photosynthesis in vivo. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 59:89-113.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092759 pmid: 18444897 |
| [3] |
Boonman A, Prinsen E, Gilmer F, Schurr U, Peeters A J M, Voesenek L A C J, Pons T L. 2007. Cytokinin import rate as a signal for photosynthetic acclimation to canopy light gradients. Plant Physiology, 143 (4):1841-1852.
pmid: 17277095 |
| [4] |
Carmo-Silva E, Scales J C, Madgwick P J, Parry M A J. 2015. Optimizing Rubisco and its regulation for greater resource use efficiency. Plant Cell and Environment, 38 (9):1817-1832.
doi: 10.1111/pce.2015.38.issue-9 URL |
| [5] |
Casal J J. 2013. Photoreceptor signaling networks in plant responses to shade. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 64:403-427.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-050312-120221 URL |
| [6] |
Chaves I, Pokorny R, Byrdin M, Hoang N, Ritz T, Brettel K, Essen L O, van der Horst G T J, Batschauer A, Ahmad M. 2011. The cryptochromes:blue light photoreceptors in plants and animals. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 62:335-364.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-042110-103759 URL pmid: 21526969 |
| [7] |
Christie J M. 2007. Phototropin blue-light receptors. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 58:21-45.
pmid: 17067285 |
| [8] |
Demotes-Mainard S, Peron T, Corot A, Bertheloot J, Le Gourrierec J, Pelleschi-Travier S, Crespel L, Morel P, Huche-Thelier L, Boumaza R, Vian A, Guerin V, Leduc N, Sakr S. 2016. Plant responses to red and far-red lights,applications in horticulture. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 121:4-21.
doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2015.05.010 URL |
| [9] | Ding Xiao-tao, Jiang Yu-ping, Wang Hong, Zhou Qiang, He Li-zhong, Yu Ji-zhu. 2016. Effects of LED supplementary lighting among plants on tomato growth and fruit quality. Acta Agriculturae Shanghai, 32 (6):48-51. (in Chinese) |
| 丁小涛, 姜玉萍, 王虹, 周强, 何立中, 余纪柱. 2016. LED株间补光对番茄生长和果实品质的影响. 上海农业学报, 32 (6):48-51. | |
| [10] | FAOSTAT. Food and agriculture organization corporate statistical database. Available online:http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC . |
| [11] | Guo Rui, Hua Ming-yan, Tong Ya-na, Yang Xiao-ling. 2018. Study on the supplemental lighting in tomato based on characteristics of photosynthetic physiological in different position of leaves and time. Northern Horticulture, 24:70-74. (in Chinese) |
| 郭锐, 华明艳, 仝雅娜, 杨小玲. 2018. 基于叶位和时段光合特性的番茄补光技术研究. 北方园艺, 24:70-74. | |
| [12] | Guo Z X, Wang F, Xiang X, Ahammed G J, Wang M M, Onac E, Zhou J, Xia X J, Shi K, Yin X R, Chen K S, Yu J Q, Foyer C H, Zhou Y H. 2016. Systemic induction of photosynthesis via illumination of the shoot apex is mediated sequentially by phytochrome B,auxin and hydrogen peroxide in tomato. Plant Physiology, 172 (2):1259-1272. |
| [13] | He Wei, Chen Dan-yan, Hu Xiao-ting, Wang Xiao-xu, Chen Le-han, Zhang Hai-chun, Yang Zhen-chao. 2018. Effects of different photoperiods and photon flux ratios of red and blue LEDs on growth and development of tomato plants. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 27 (4):562-570. (in Chinese) |
| 何蔚, 陈丹艳, 胡晓婷, 王晓旭, 陈乐涵, 张海春, 杨振超. 2018. 不同光周期与光质配比对番茄植株生长发育的影响. 西北农业学报, 27 (4):562-570. | |
| [14] | Hu Wen-hai, Yan Xiao-hong, Li Xiao-hong, Cao Zao-gui. 2021. Effects of 24-epibrassinolide on the chlorophyll fluorescence transient in leaves of pepper under drought stress. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 41 (1):53-59. (in Chinese) |
| 胡文海, 闫小红, 李晓红, 曹灶桂. 2021. 24-表油菜素内酯对干旱胁迫下辣椒叶片快速叶绿素荧光诱导动力学曲线的影响. 植物研究, 41 (1):53-59. | |
| [15] |
Jiao Y L, Lau O S, Deng X W. 2007. Light-regulated transcriptional networks in higher plants. Nature Reviews Genetics, 8 (3):217-230.
doi: 10.1038/nrg2049 URL |
| [16] |
Kim S Y, Stessman D J, Wright D A, Spalding M H, Ort D R. 2020. Arabidopsis plants expressing only the redox-regulated Rca-α isoform have constrained photosynthesis and plant growth. Plant Journal, 103 (6):2250-2262.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.v103.6 URL |
| [17] |
Li Peng-min, Gao Hui-yuan, Strasser R J. 2005. Application of the fast chlorophyll fluorescence induction dynamics analysis in photosynthesis study. Journal of Plant Physiology and Molecular Biology, 31 (6):559-566. (in Chinese)
pmid: 16361781 |
|
李鹏民, 高辉远, Strasser R J. 2005. 快速叶绿素荧光诱导动力学分析在光合作用研究中的应用. 植物生理与分子生物学学报, 31 (6):559-566.
pmid: 16361781 |
|
| [18] |
Li X J, Chen X J, Guo X, Yin L L, Ahammed G J, Xu C J, Chen K S, Liu C C, Xia X J, Shi K, Zhou J, Zhou Y H, Yu J Q. 2016b. DWARF overexpression induces alteration in phytohormone homeostasis,development,architecture and carotenoid accumulation in tomato. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 14 (3):1021-1033.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.2016.14.issue-3 URL |
| [19] |
Li X J, Guo X, Zhou Y H, Shi K, Zhou J, Yu J Q, Xia X J. 2016a. Overexpression of a brassinosteroid biosynthetic gene DWARF enhances photosynthetic capacity through activation of Calvin cycle enzymes in tomato. BMC Plant Biology, 16:33.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-016-0715-6 URL |
| [20] |
Li X N, Cai J, Liu F L, Dai T B, Cao W X, Jiang D. 2014. Cold priming drives the sub-cellular antioxidant systems to protect photosynthetic electron transport against subsequent low temperature stress in winter wheat. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 82:34-43.
doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2014.05.005 URL |
| [21] | Liu Xin, Chen Yunzhu, Kim Pyol, Kim Min-Jun, Song Hyondok, Li Yuhua, Wang Yu. 2020. Progress on molecular mechanism and regulation of tomato fruit color formation. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47 (9):1689-1704. |
| 刘昕, 陈韵竹, Kim Pyol, Kim Min-Jun, Song Hyondok, 李玉花, 王宇. 2020. 番茄果实颜色形成的分子机制及调控研究进展. 园艺学报, 47 (9):1689-1704. | |
| [22] | Liu Zai-liang, Ma Cheng-wei, Yang Qi-chang. 2004. Review on controlling the ratio of red light to far-red light in protected environment. Transactions of the CSAE, 20 (1):270-273. (in Chinese) |
| 刘再亮, 马承伟, 杨其长. 2004. 设施环境中红光与远红光比值调控的研究进展. 农业工程学报, 20 (1):270-273. | |
| [23] |
Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative pcr and the 2-DDCt method. Methods, 25 (4):402-408.
pmid: 11846609 |
| [24] |
Lu J Y, Nawaz M A, Wei N N, Cheng F, Bie Z L. 2020. Suboptimal temperature acclimation enhances chilling tolerance by improving photosynthetic adaptability and osmoregulation ability in watermelon. Horticultural Plant Journal, 6 (1):49-60.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2020.01.001 URL |
| [25] | Ma Chao-feng, Dai Si-lan. 2019. Advances in photoreceptor-mediated signaling transduction in flowering time regulation. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 54 (1):9-22. (in Chinese) |
| 马朝峰, 戴思兰. 2019. 光受体介导信号转导调控植物开花研究进展. 植物学报, 54 (1):9-22. | |
| [26] |
Pfeiffer A, Janocha D, Dong Y H, Medzihradszky A, Schone S, Daum G, Suzaki T, Forner J, Longenecker T, Rempel E, Schmid M, Wirtz M, Hell R, Lohmann J U. 2016. Integration of light and metabolic signals for stem cell activation at the shoot apical meristem. eLife, 5:e17023.
doi: 10.7554/eLife.17023 URL |
| [27] |
Rizzini L, Favory J J, Cloix C, Faggionato D, O'Hara A, Kaiserli E, Baumeister R, Schäfer E, Nagy F, Jenkins G I, Ulm R. 2011. Perception of UV-B by the Arabidopsis UVR8 protein. Science, 332 (6025):103-106.
doi: 10.1126/science.1200660 URL pmid: 21454788 |
| [28] | Strasser R J, Tsimilli-Michael M, Srivastava A. 2004. Analysis of the chlorophyll a fluorescence transient//Papageorgiou G C,Govindjee,Chlorophyll a fluorescence. Advances in Photosynthesis and Respiration. Springer:321-282. |
| [29] | Tang Wei, Li Tian-lai, Zhang Xiu-mei, Zhao Bo. 2007. Effects of low light stress on growth and chlorophyll content of seedling tomato and recovery effectiveness. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 38 (3):278-282. (in Chinese) |
| 唐韡, 李天来, 张秀美, 赵博. 2007. 苗期弱光胁迫对番茄生长和叶绿素含量的影响及其恢复效应. 沈阳农业大学学报, 38 (3):278-282. | |
| [30] |
Waldie T, Leyser O. 2018. Cytokinin targets auxin transport to promote shoot branching. Plant Physiology, 177 (2):803-818.
doi: 10.1104/pp.17.01691 pmid: 29717021 |
| [31] | Wang Feng, Yan Jiarong, Chen Xueyu, Jiang Chenghao, Meng Sida, Liu Yufeng, Xu Tao, Qi Mingfang, Li Tianlai. 2019. Light regulation of chlorophyll biosynthesis in plants. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 46 (5):975-994. (in Chinese) |
| 王峰, 闫家榕, 陈雪玉, 姜程浩, 孟思达, 刘玉凤, 许涛, 齐明芳, 李天来. 2019. 光调控植物叶绿素生物合成的研究进展. 园艺学报, 46 (5):975-994. | |
| [32] | Xie Jing, Liu Hou-cheng, Song Shi-wei, Sun Guang-wen, Chen Ri-yuan. 2012. Research progresses in application of artificial supplement light source in greenhouse vegetable production. China Vegetables,(2):1-7. (in Chinese) |
| 谢景, 刘厚诚, 宋世威, 孙光闻, 陈日远. 2012. 光源及光质调控在温室蔬菜生产中的应用研究进展. 中国蔬菜,(2):1-7. | |
| [33] |
Xu C, Liberatore K L, MacAlister C A, Huang Z J, Chu Y H, Jiang K, Brooks C, Ogawa-Ohnishi M, Xiong G Y, Pauly M, van Eck J, Matsubayashi Y, van der Knaap E, Lippman Z B. 2015. A cascade of arabinosyltransferases controls shoot meristem size in tomato. Nature Genetics, 47 (7):784-792.
doi: 10.1038/ng.3309 |
| [34] |
Xu H L, Xu Q C, Li F L, Feng Y Z, Qin F F, Fang W. 2012. Applications of xerophytophysiology in plant production-led blue light as a stimulus improved the tomato crop. Scientia Horticulturae, 148:190-196.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2012.06.044 URL |
| [35] | Xu Li, Liu Shi-qi, Qi Lian-dong, Liang Qing-ling, Yu Wen-yan. 2007. Effect of light quality on leaf lettuce photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 23 (1):96-100. (in Chinese) |
| 许莉, 刘世琦, 齐连东, 梁庆玲, 于文艳. 2007. 不同光质对叶用莴苣光合作用及叶绿素荧光的影响. 中国农学通报, 23 (1):96-100. | |
| [36] | Xuan Shou-li, Shi Chun-lin, Jin Zhi-qing, Cao Hong-xin, Wei Xiu-fang, Wang Jing-jing. 2012. Variation of solar radiation over the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River and its influence on photosynthetically active radiation. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 28 (6):1444-1450. (in Chinese) |
| 宣守丽, 石春林, 金之庆, 曹宏鑫, 魏秀芳, 王晶晶. 2012. 长江中下游地区太阳辐射变化及其对光合有效辐射的影响. 江苏农业学报, 28 (6):1444-1450. | |
| [37] | Yan Wen-kai, Zhang Ya-ting, Zhang Yu-qi, Yang Qi-chang, Li Tao. 2018. Effects of LED interlighting on yield and photosynthesis of tomato in solar greenhouse. Journal of Northwest A & F University(Nat Sci Ed), 46 (7):132-138,146. (in Chinese) |
| 闫文凯, 张雅婷, 张玉琪, 杨其长, 李涛. 2018. LED株间补光对日光温室番茄产量及光合作用的影响. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 46 (7):132-138,146. | |
| [38] | Yang Wan-ji, Yu Xi-hong, Jiang Xin-mei, Gao Huan, Cheng Yao, Zhang Fu, Li Yang-dan, Sun Dong-xue. 2017. Effects of low light stress on photosynthetic characteristics and root growth of tomato seedlings. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 45 (17):112-114. (in Chinese) |
| 杨万基, 于锡宏, 蒋欣梅, 高欢, 程瑶, 张福, 李扬丹, 孙冬雪. 2017. 弱光胁迫对番茄幼苗光合特性和根系生长的影响. 江苏农业科学, 45 (17):112-114. | |
| [39] | You Jie, Zhang Yu-yang, Pu Min, Xu Zhi-gang. 2020. Effects of supplemental-lighting ways on growth, development of overwintering tomatoes in facilities. Zhaoming Gongcheng Xuebao, 31 (5):39-45. (in Chinese) |
| 尤杰, 张宇阳, 浦敏, 徐志刚. 2020. 补光方式对设施越冬番茄生长发育的影响. 照明工程学报, 31 (5):39-45. | |
| [40] |
Yu J Q, Huang L F, Hu W H, Zhou Y H, Mao W H, Ye S F, Nogues S. 2004. A role for brassinosteroids in the regulation of photosynthesis in Cucumis sativus. Journal of Experimental Botany, 55 (399):1135-1143.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erh124 URL |
| [41] | Zhang Xin-ping, Dong Jie, Zhang Fang-fang, Wang De-xiang. 2016. Comparison of leaf area measurement method for several commonly planted tree species. Journal of Chinese Urban Forestry, 14 (2):38-42. (in Chinese) |
| 张新平, 董洁, 张芳芳, 王得祥. 2016. 几种常用的树木叶面积测量方法比较. 中国城市林业, 14 (2):38-42. | |
| [42] |
Zhang Y Q, Liu Z J, Wang J F, Chen Y D, Bi Y R, He J X. 2015. Brassinosteroid is required for sugar promotion of hypocotyl elongation in Arabidopsis in darkness. Planta, 242 (4):881-893.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-015-2328-y URL |
| [43] |
Zhu X C, Liu S Q, Sun L Y, Song F B, Liu F L, Li X N. 2018. Cold tolerance of photosynthetic electron transport system is enhanced in wheat plants grown under elevated CO2. Frontiers in Plant Science, 9:933.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00933 URL |
| [44] |
Zushi K, Matsuzoe N. 2017. Using of chlorophyll a fluorescence OJIP transients for sensing salt stress in the leaves and fruits of tomato. Scientia Horticulturae, 219:216-221.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2017.03.016 URL |
| [1] | 史洪丽, 李腊, 郭翠梅, 余婷婷, 简伟, 杨星勇. 番茄灰霉病生防菌株TL1的分离、鉴定及其生防能力分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 79-90. |
| [2] | 忽靖宇, 阙开娟, 缪田丽, 吴少政, 王田田, 张磊, 董鲜, 季鹏章, 董家红. 侵染鸢尾的番茄斑萎病毒鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 170-176. |
| [3] | 郑积荣, 王同林, 胡松申. 高品质番茄新品种‘杭杂603’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 103-104. |
| [4] | 郑积荣, 王同林. 番茄新品种‘杭杂601’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 105-106. |
| [5] | 郑积荣, 王同林. 樱桃番茄新品种‘杭杂503’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 107-108. |
| [6] | 黄婷婷, 刘淑芹, 张永志, 李 平, 张志焕, 宋立波. 樱桃番茄新品种‘樱莎红4号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 109-110. |
| [7] | 张前荣, 李大忠, 裘波音, 林 珲, 马慧斐, 叶新如, 刘建汀, 朱海生, 温庆放. 设施番茄新品种‘闽农科2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 73-74. |
| [8] | 韩帅, 吴婕, 张河庆, 席亚东. 四川莴笋上番茄斑萎病毒的电镜观察与小RNA测序鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(9): 2007-2016. |
| [9] | 董桑婕, 葛诗蓓, 李岚, 贺丽群, 范飞军, 齐振宇, 喻景权, 周艳虹. 不同光质补光对辣椒幼苗生长、丛枝菌根共生和磷吸收的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(8): 1699-1712. |
| [10] | 陈礼浪, 杨天章, 蔡儒平, 林小漫, 邓南康, 车海彦, 林雅婷, 孔祥义. 海南西番莲主要病毒种类的分子检测与鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(8): 1785-1794. |
| [11] | 路涛, 余宏军, 李强, 蒋卫杰. 叶果量调控对番茄生长发育、果实品质和产量的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(6): 1261-1274. |
| [12] | 孟宪敏, 崔青青, 段韫丹, 庄团结, 濮丹, 董春娟, 杨文才, 尚庆茂. 烯效唑对番茄幼苗嫁接愈合的促进作用及其机理研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(6): 1275-1289. |
| [13] | 刘尚佳, 吕尧, 曹逼力, 陈子敬, 高松, 徐坤. 高温渍涝胁迫对姜叶片光合作用和氮代谢的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(5): 1073-1080. |
| [14] | 王莹, 秦阳阳, 曾婷, 廖平, 张伟, 周彦, 周常勇. 柑橘黄脉病毒侵染对柠檬光合特性和叶绿体超微结构的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(4): 861-867. |
| [15] | 崔东禹, 李长青, 孙焱鑫, 王激清, 邹国元, 杨俊刚. 温室番茄东西向栽培条件下矮化密植对其生长和产量的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(4): 875-884. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司