
园艺学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (8): 1446-1456.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0630
收稿日期:2020-12-10
修回日期:2021-04-26
出版日期:2021-08-25
发布日期:2021-09-06
通讯作者:
李明
E-mail:liming06@caas.cn
基金资助:
QI Xiliang, LIU Congli, SONG Lulu, LI Ming( )
)
Received:2020-12-10
Revised:2021-04-26
Online:2021-08-25
Published:2021-09-06
Contact:
LI Ming
E-mail:liming06@caas.cn
摘要:
从甜樱桃基因组中鉴定了4个磷酸蔗糖合酶(sucrose phosphate synthase,SPS)基因(PavSPSA1、PavSPSA2、PavSPSB和PavSPSC)。实时荧光定量PCR分析表明,PavSPSA1在甜果实发育和成熟过程中表达量最高,其次是PavSPSC,PavSPSA2和PavSPSB表达量较低;PavSPSA1和PavSPSA2在果实成熟软化过程中均上调表达,与甜樱桃果实的成熟软化过程吻合。通过利用病毒诱导的基因沉默(VIGS)技术沉默PavSPSA1,甜樱桃果实蔗糖含量降低,果实着色和果实成熟软化延迟;沉默PavSPSA2、PavSPSB和PavSPSC,甜樱桃果实蔗糖含量、果实着色和果实成熟软化与对照无差异,推测PavSPSA1或许是调控果实蔗糖合成与积累的关键基因,影响果实着色和成熟软化。
中图分类号:
齐希梁, 刘聪利, 宋露露, 李明. 甜樱桃磷酸蔗糖合酶基因PavSPS的功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(8): 1446-1456.
QI Xiliang, LIU Congli, SONG Lulu, LI Ming. Functional Analysis of Sucrose-phosphate Synthase Genes(SPS)in Sweet Cherry[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(8): 1446-1456.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 序列(5′-3′) Sequence | 引物名称 Primer name | 序列(5′-3′) Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| PavSPSA1-F | ATGGCGAGCAACGATTGGATAAAC | PavSPSA1-J-F | CAGGTTCATGCCCCGCATGGTGA |
| PavSPSA1-R | CTACGTCTTGACAACTCCGAGTT | PavSPSA1-J-R | ATTGTGGATGCCTTGGTTTGC |
| PavSPSA2-F | ATGGCGGGAAACGACTGGGTGAAC | PavSPSA2-J-F | GAGGCAGCAGCTTATGGTCTACCT |
| PavSPSA2-R | CTACCGCTTGAGAATCCCTAGT | PavSPSA2-J-R | CTTGTCCTTCCCTGCTGCCTCA |
| PavSPSB-F | ATTTGGCATCTTACCCGTAAGAAG | PavSPSB-J-F | ATGAAGGAGGTGGAAATAAGCTGCT |
| PavSPSB-R | TCACATTCGAGCAGCAGATTTAGAG | PavSPSB-J-R | AGTACATTGGATGGCAACGCAG |
| PavSPSC-F | ATGGCGGGAAACGACTGGTTAAACAG | PavSPSC-J-F | GAGATTCTGATACAGGTGGTCAGGT |
| PavSPSA1-q-F | GCAAACCAAGGCATCCACAAT | PavSPSC-J-R | AGCTCCTCAGCCTCGATCCTCTTC |
| PavSPSA1-q-R | GAACCCTACAGAGCCTTCAGT | PaNCED1-F | CATGTCGGAGGACGACTTGCCGT |
| PavSPSA2-q-F | TGAGGCAGCAGGGAAGGACAAG | PaNCED1-R | GCGCCGTCTGGAGAGACGTGGA |
| PavSPSA2-q-R | AGCCCCAACGGACATACAGATACC | PaPG1-F | ATCACCTTCCGCATTGCTG |
| PavSPSB-q-F | GGCTTGCTTGTGGACCCTCAT | PaPG1-R | TCACCTTAATGTTGTTGGAG |
| PavSPSB-q-R | AGCAGCTTATTTCCACCTCCTTC | PaXYL1-F | ACAACTGGAACGGTGTCGAT |
| PavSPSC-q-F | ACCCCACCACCCGCTTTCA | PaXYL1-R | TCCTGGTGTAATGTTGCTCG |
| PavSPSC-q-R | GACCCTCGCCATTGCCTACG | PaPL-1-F | GATGGTCGCTTCTATGTTGTCA |
| PavSPSA2-RNAi-F | AGTAAGGTTACCGAATTCTGAGGCAGCAGGGAAGGACAAG | PaPL-1-R | TGAGATGGAGAGCTCCTCACC |
| PavSPSA2-RNAi-R | GAGCTCGGTACCGGTACCAGCCCCAACGGACATACAGATACC | PaPAL-F | GCCTCACCAGGCAACAAGAGCA |
| PavSPSB-RNAi-F | AGTAAGGTTACCGAATTCGGCTTGCTTGTGGACCCTCAT | PaPAL-R | TCTGGCCATCTGGTCCAACAGC |
| PavSPSB-RNAi-R | GAGCTCGGTACCGGTACCAGCAGCTTATTTCCACCTCCTTCAT | PaCHS-F | GTATGTGCGAGTACATGGCA |
| PavSPSC-RNAi-F | AGTAAGGTTACCGAATTCACCCCACCACCCGCTTTCA | PaCHS-R | GCTTAGTGAGCTGATAGTC |
| PavSPSC-RNAi-R | GAGCTCGGTACCGGTACCGACCCTCGCCATTGCCTACG | PaDFR-F | CTGCACCGGAGTGTTCCATGT |
| Histone2-F | GGTGTGCTTCCGCAGATAA | PaDFR-R | CTGGTGCTCTTCGACGTTCAC |
| Histone2-R | TCCTCCTTGGGTGGTGAAT | PaANS-F | ATCTCCGATGAGCTCATGG |
| PaANS-R | CTCAATGTAATCAGCAGGTG |
表1 本研究中所用的引物信息
Table 1 Primers used in this study
| 引物名称 Primer name | 序列(5′-3′) Sequence | 引物名称 Primer name | 序列(5′-3′) Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| PavSPSA1-F | ATGGCGAGCAACGATTGGATAAAC | PavSPSA1-J-F | CAGGTTCATGCCCCGCATGGTGA |
| PavSPSA1-R | CTACGTCTTGACAACTCCGAGTT | PavSPSA1-J-R | ATTGTGGATGCCTTGGTTTGC |
| PavSPSA2-F | ATGGCGGGAAACGACTGGGTGAAC | PavSPSA2-J-F | GAGGCAGCAGCTTATGGTCTACCT |
| PavSPSA2-R | CTACCGCTTGAGAATCCCTAGT | PavSPSA2-J-R | CTTGTCCTTCCCTGCTGCCTCA |
| PavSPSB-F | ATTTGGCATCTTACCCGTAAGAAG | PavSPSB-J-F | ATGAAGGAGGTGGAAATAAGCTGCT |
| PavSPSB-R | TCACATTCGAGCAGCAGATTTAGAG | PavSPSB-J-R | AGTACATTGGATGGCAACGCAG |
| PavSPSC-F | ATGGCGGGAAACGACTGGTTAAACAG | PavSPSC-J-F | GAGATTCTGATACAGGTGGTCAGGT |
| PavSPSA1-q-F | GCAAACCAAGGCATCCACAAT | PavSPSC-J-R | AGCTCCTCAGCCTCGATCCTCTTC |
| PavSPSA1-q-R | GAACCCTACAGAGCCTTCAGT | PaNCED1-F | CATGTCGGAGGACGACTTGCCGT |
| PavSPSA2-q-F | TGAGGCAGCAGGGAAGGACAAG | PaNCED1-R | GCGCCGTCTGGAGAGACGTGGA |
| PavSPSA2-q-R | AGCCCCAACGGACATACAGATACC | PaPG1-F | ATCACCTTCCGCATTGCTG |
| PavSPSB-q-F | GGCTTGCTTGTGGACCCTCAT | PaPG1-R | TCACCTTAATGTTGTTGGAG |
| PavSPSB-q-R | AGCAGCTTATTTCCACCTCCTTC | PaXYL1-F | ACAACTGGAACGGTGTCGAT |
| PavSPSC-q-F | ACCCCACCACCCGCTTTCA | PaXYL1-R | TCCTGGTGTAATGTTGCTCG |
| PavSPSC-q-R | GACCCTCGCCATTGCCTACG | PaPL-1-F | GATGGTCGCTTCTATGTTGTCA |
| PavSPSA2-RNAi-F | AGTAAGGTTACCGAATTCTGAGGCAGCAGGGAAGGACAAG | PaPL-1-R | TGAGATGGAGAGCTCCTCACC |
| PavSPSA2-RNAi-R | GAGCTCGGTACCGGTACCAGCCCCAACGGACATACAGATACC | PaPAL-F | GCCTCACCAGGCAACAAGAGCA |
| PavSPSB-RNAi-F | AGTAAGGTTACCGAATTCGGCTTGCTTGTGGACCCTCAT | PaPAL-R | TCTGGCCATCTGGTCCAACAGC |
| PavSPSB-RNAi-R | GAGCTCGGTACCGGTACCAGCAGCTTATTTCCACCTCCTTCAT | PaCHS-F | GTATGTGCGAGTACATGGCA |
| PavSPSC-RNAi-F | AGTAAGGTTACCGAATTCACCCCACCACCCGCTTTCA | PaCHS-R | GCTTAGTGAGCTGATAGTC |
| PavSPSC-RNAi-R | GAGCTCGGTACCGGTACCGACCCTCGCCATTGCCTACG | PaDFR-F | CTGCACCGGAGTGTTCCATGT |
| Histone2-F | GGTGTGCTTCCGCAGATAA | PaDFR-R | CTGGTGCTCTTCGACGTTCAC |
| Histone2-R | TCCTCCTTGGGTGGTGAAT | PaANS-F | ATCTCCGATGAGCTCATGG |
| PaANS-R | CTCAATGTAATCAGCAGGTG |
| 基因名称 Gene name | cDNA/ bp | 氨基酸 Amino acid | GenBank登录号 ID in GenBank | 染色体位置 Chromosome location | 拟南芥同源基因 Homologous gene in Arabidopsis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAIR位置 Locus in TAIR | 氨基酸相似度/% Similarity of amino acid | |||||
| PavSPSA1 | 3 174 | 1 057 | XM_021953379.1 | Chr7:18 650 177 ~ 18 655 575 | AtSPS1F(At5g20280) | 77.69 |
| PavSPSA2 | 3 180 | 1 059 | XM_021966658.1 | Chr1:35 009 999 ~ 35 016 230 | AtSPS2F(At5g11110) | 71.36 |
| PavSPSB | 2 844 | 947 | XM_021946233.1 | chrUn:91 085 245 ~ 91 090 791 | AtSPS3F(At1g04920) | 67.35 |
| PavSPSC | 3 072 | 1 023 | XM_021957268.1 | Chr8:324 800 ~ 330 670 | AtSPS4F(At4g10120) | 72.10 |
表2 甜樱桃基因组中SPS基因的相关信息
Table 2 Information of sucrose-phosphate synthase(SPS)genes identified in sweet cherry
| 基因名称 Gene name | cDNA/ bp | 氨基酸 Amino acid | GenBank登录号 ID in GenBank | 染色体位置 Chromosome location | 拟南芥同源基因 Homologous gene in Arabidopsis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAIR位置 Locus in TAIR | 氨基酸相似度/% Similarity of amino acid | |||||
| PavSPSA1 | 3 174 | 1 057 | XM_021953379.1 | Chr7:18 650 177 ~ 18 655 575 | AtSPS1F(At5g20280) | 77.69 |
| PavSPSA2 | 3 180 | 1 059 | XM_021966658.1 | Chr1:35 009 999 ~ 35 016 230 | AtSPS2F(At5g11110) | 71.36 |
| PavSPSB | 2 844 | 947 | XM_021946233.1 | chrUn:91 085 245 ~ 91 090 791 | AtSPS3F(At1g04920) | 67.35 |
| PavSPSC | 3 072 | 1 023 | XM_021957268.1 | Chr8:324 800 ~ 330 670 | AtSPS4F(At4g10120) | 72.10 |
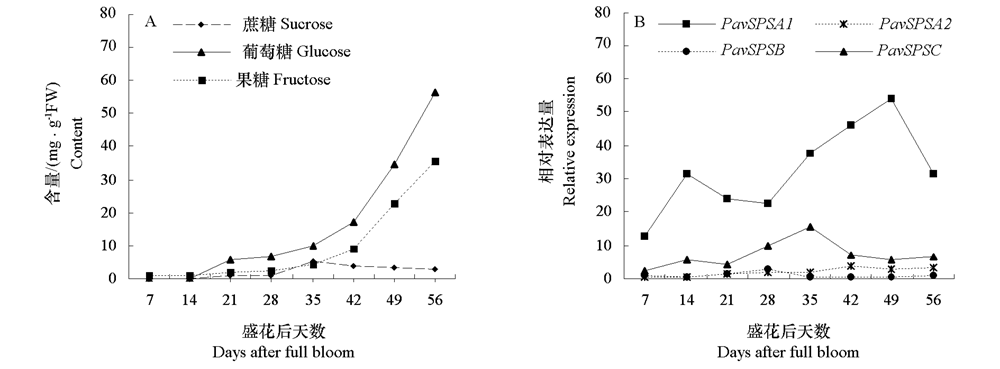
图2 甜樱桃各发育时期果糖、葡萄糖和蔗糖的含量变化(A)及PavSPS的表达(B)
Fig. 2 Changes in fructose,glucose and sucrose contents(A)and expression profile of PavSPS(B)during fruit growth and development of sweet cherry
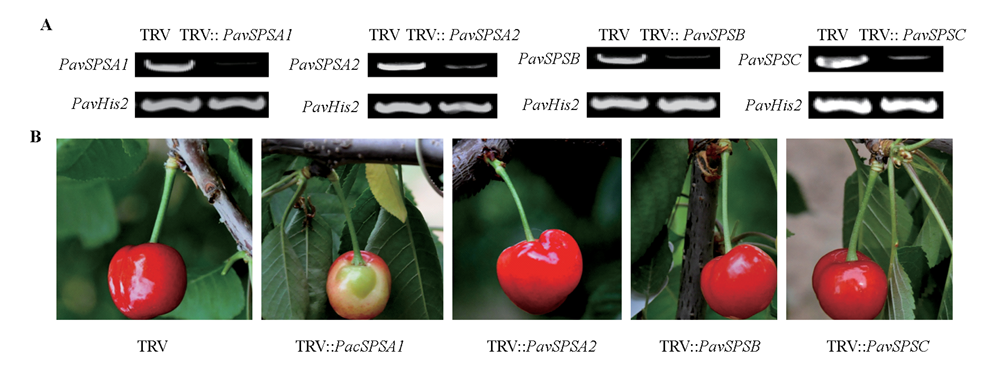
图3 PavSPS沉默后甜樱桃果实PavSPSA1、PavSPSA2、PavSPSB和PavSPSC基因相对表达量变化(A)及果实表型(B)
Fig. 3 Quantify of PavSPSA1,PavSPSA2,PavSPSB,and PavSPSC genes(A)in gene silenced sweet cherry fruit and phenotype(B)
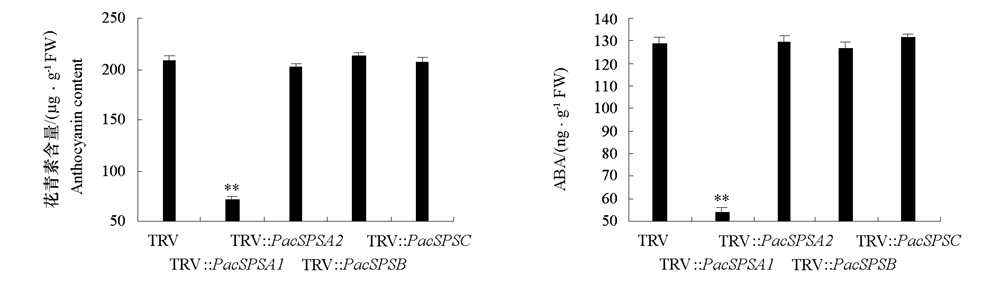
图4 沉默PavSPSA1、PavSPSA2、PavSPSB和PavSPSC的甜樱桃果实中花青素和ABA含量 显著性差异分析采用One-way ANOVA方法对每个变量进行邓肯氏检验,** 表示达到显著性差异水平P < 0.01。下同。
Fig. 4 Effect of silencing of PavSPSA1,PavSPSA2,PavSPSB,and PavSPSC in sweet cherry fruits on anthocyanin and ABA Statistically significant differences between means were determined using one-way analysis of variance(ANOVA)at the 1% significance level. ?? indicates significant differences P-value < 0.01. The same below.
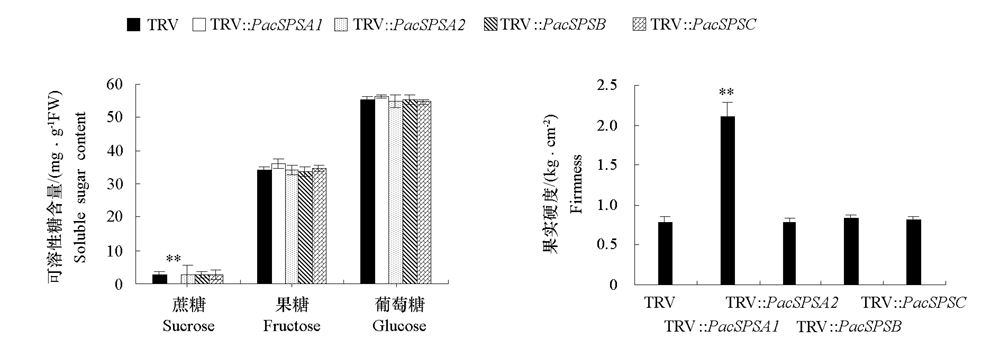
图5 沉默PavSPSA1、PavSPSA2、PavSPSB和PavSPSC的甜樱桃果实中可溶性糖(蔗糖、葡萄糖和果糖)含量和果实硬度的变化
Fig. 5 Effect of silencing of PavSPSA1,PavSPSA2,PavSPSB and PavSPSC in sweet cherry fruits on soluble sugar content (sucrose,fructose and glucose)and fruit firmness
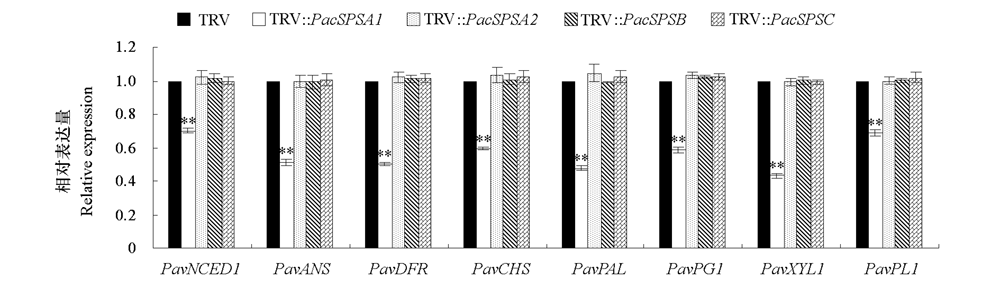
图6 沉默PavSPSA1、PavSPSA2、PavSPSB和PavSPSC后的甜樱桃果实成熟相关基因PavNCED1、PavANS、PavDFR、PavCHS、PavPAL、PavPG1、PavXYL1和PavPL1表达量的变化
Fig. 6 Changes of expression levels of PavNCED1,PavANS,PavDFR,PavCHS,PavPAL,PavPG1,PavXYL1 and PavPL1 in PavSPSA1-,PavSPSA2-,PavSPSB- and PavSPSC-silencing sweet cherry fruit PaNCED1(9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase,Pav_sc0003135.1_g490.1.mk),PavANS(anthocyanidin synthase,Pav_sc0000107.1_g100.1.mk),PavDFR(dihydro flavonol 4-reductase,Pav_sc0002208.1_g840.1.mk),PavCHS(Chalcone synthase,Pav_sc0000045.1_g280.1.mk),PavPAL(phenylalanine ammonia-lyase,Pav_co4071347.1_g010.1.mk),PavPG1(polygalacturonase,Pav_sc0000557.1_g320.1.br),PavXYL1(β-D-xylosidase,Pav_sc0001014.1_g030.1.mk),PavPL1(Pectate lyase 1,Pav_sc0000207.1_g1250.1.mk).
| [1] |
Castleden C K, Aoki N, Gillespie V J, MacRae E A, Quick W P, Buchner P, Foyer C H, Furban R T, Lunn J E. 2004. Evolution and function of the sucrose-phosphate synthase gene families in wheat and other grasses. Plant Physiology, 135 (3):1753-1764.
pmid: 15247374 |
| [2] |
Cheng G W, Breen P J. 1991. Activity of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase(Pal)and concentrations of anthocyanins and phenolics in developing strawberry fruit. Journal of the American Society for Horticultural Science, 116 (5):865-869.
doi: 10.21273/JASHS.116.5.865 URL |
| [3] |
Fu D Q, Zhu B Z, Zhu H L, Jiang W B, Luo Y B. 2005. Virus-induced gene silencing in tomato fruit. The Plant Journal, 43 (2):299-308.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.2005.43.issue-2 URL |
| [4] |
Hirose T, Hashida Y, Aoki N, Okamura M, Yonekura M, Ohto C, Terao T, Ohsugi R. 2014. Analysis of gene-disruption mutants of a sucrose phosphate synthase gene in rice,OsSPS1,shows the importance of sucrose synthesis in pollen germination. Plant Science, 225:102-106.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2014.05.018 URL |
| [5] |
Huang D L, Qin C X, Gui Y Y, Zhao L H, Chen Z L, Wang M, Sun Y, Liao Q, Li Y R, Lakshmanan P. 2017. Role of the SPS gene families in the regulation of sucrose accumulation in sugarcane. Sugar Tech, 19 (2):117-124.
doi: 10.1007/s12355-016-0454-x URL |
| [6] |
Jia H, Jiu S, Zhang C, Wang C, Tariq P, Liu Z, Wang B, Cui L, Fang J. 2016. Abscisic acid and sucrose regulate tomato and strawberry fruit ripening through the abscisic acid-stress-ripening transcription factor. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 14 (10):2045-2065.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.2016.14.issue-10 URL |
| [7] |
Jia H, Wang Y, Sun M, Li B, Han Y, Zhao Y, Li X, Ding N, Li C, Ji W, Jia W. 2013. Sucrose functions as a signal involved in the regulation of strawberry fruit development and ripening. New Phytologist, 198 (2):453-465.
doi: 10.1111/nph.2013.198.issue-2 URL |
| [8] |
Jiang Y, Guo W, Zhu H, Ruan Y L, Zhang T. 2012. Overexpression of GhSusA1 increases plant biomass and improves cotton fiber yield and quality. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 10 (3):301-312.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.2012.10.issue-3 URL |
| [9] |
Langenkämper G, Fung R W, Newcomb R D, Atkinson R G, Gardner R C, Macrae E A. 2002. Sucrose phosphate synthase genes in plants belong to three different families. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 54 (3):322-332.
URL pmid: 11847558 |
| [10] |
Kelley D S, Adkins Y, Laugero K D. 2018. A review of the health benefits of cherries. Nutrients, 10 (3):368.
doi: 10.3390/nu10030368 URL |
| [11] |
Komatsu A, Takanokura Y, Akihama T, Omura M. 1996. Cloning and molecular analysis of cDNAs encoding three sucrose phosphate synthase isoforms from a citrus fruit(Citrus unshiu Marc.). Molecular and General Genetics, 252 (3):346-351.
pmid: 8842155 |
| [12] |
Li B, Xie Z, Zhang A, Xu W, Zhang C, Liu Q, Liu C, Wang S. 2010. Tree growth characteristics and flower bud differentiation of sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.)under different climate conditions in China. Horticultural Science, 37 (1):6-13.
doi: 10.17221/HORTSCI URL |
| [13] | Li Fu-peng, Qin Xao-wei, Wu Bao-duo, Zhao Xi-zhu, Wang Hua, Zhu Zi-hui, Lai Jian-xiong. 2015. Phylogeny and expression profile of the sucrose phosphate synthase gene family in cacao(Theobroma cacao L.). Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 36 (9):1608-1613. (in Chinese) |
| 李付鹏, 秦晓威, 伍宝朵, 赵溪竹, 王华, 朱自慧, 赖剑雄. 2015. 可可蔗糖磷酸合成酶基因家族进化及组织表达分析. 热带作物学报, 36 (9):1608-1613. | |
| [14] | Li Hui-xia, Zhu Ling-cheng, Zhang Zhao, Ma Feng-wang, Li Ming-jun. 2017. Expression analysis of apple sucrose synthase gene families and their relationship with sucrose accumulation in apple. Journal of Northwest Botanical Sciences, 37 (5):872-878. (in Chinese) |
| 李会霞, 祝令成, 张钊, 马锋旺, 李明军. 2017. 苹果中磷酸蔗糖合酶家族基因的表达特性及其与蔗糖含量的关系. 西北植物学报, 37 (5):872-878. | |
| [15] | Lü Jia-hong, Wang Ying-zhen, Cheng Rui, Wang Guo-ming, Zhang Shao-ling, Wu Jun, Zhang Hu-ping. 2018. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of sucrose synthase(SUS)and sucrose phosphate synthase(SPS)gene families in pear. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 45 (3):421-435. (in Chinese) |
| 吕佳红, 王英珍, 程瑞, 王国明, 张绍铃, 吴俊, 张虎平. 2018. 梨蔗糖合成相关酶SUS和SPS基因家族的鉴定与表达分析. 园艺学报, 45 (3):421-435. | |
| [16] |
Lunn J E, MacRae E. 2003. New complexities in the synthesis of sucrose. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 6 (3):208-214.
doi: 10.1016/S1369-5266(03)00033-5 URL |
| [17] |
Lutfiyya L L, Xu N, Robert L D, Morrell J A, Miller P W, Duff S M. 2007. Phylogenetic and expression analysis of sucrose phosphate synthase isozymes in plants. Journal of Plant Physiology, 164 (7):923-933.
pmid: 16876912 |
| [18] |
McCune L M, Kubota C, Stendell-Hollis N R, Thomson C A. 2010. Cherries and health:a review. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 51 (1):1-12.
doi: 10.1080/10408390903001719 URL |
| [19] |
Nemati F, Ghanati F, Gavlighi H A, Sharifi M. 2018. Comparison of sucrose metabolism in wheat seedlings during drought stress and subsequent recovery. Biologia Plantarum, 62 (3):595-599.
doi: 10.1007/s10535-018-0792-5 URL |
| [20] | Qi Xi-liang, Li Ming, Liu Cong-li, Song Lu-lu. 2018. Construction of TRV-mediated Virus Induced Gene Silencing(VIGS)system in sweet cherry Fruit. Journal of Fruit Science, 35 (11):1309-1315.. (in Chinese) |
| 齐希梁, 李明, 刘聪利, 宋露露. 2018. TRV介导欧洲甜樱桃果实VIGS体系的建立. 果树学报, 35 (11):1309-1315. | |
| [21] | Solís-Guzmán M G, Argüello-Astorga G, López-Bucio J, Ruiz-Herrera L F, López-Meza J E, Sánchez-Calderón L, Carreón-Abud Y, Martínez-Trujillo M. 2017. Arabidopsis thaliana sucrose phosphate synthase(SPS)genes are expressed differentially in organs and tissues,and their transcription is regulated by osmotic stress. Gene Expression Patterns, 25:92-101. |
| [22] |
Verma A K, Upadhyay S K, Verma P C, Solomon S, Singh S B. 2011. Functional analysis of sucrose phosphate synthase(SPS)and sucrose synthase (SS)in sugarcane(Saccharum)cultivars. Plant Biology, 13 (2):325-332.
doi: 10.1111/j.1438-8677.2010.00379.x URL pmid: 21309979 |
| [23] |
Vimolmangkang S, Zheng H, Peng Q, Jiang Q, Wang H, Fang T, Liao L, Lu W, He H P, Han Y P. 2016. Assessment of sugar components and genes involved in the regulation of sucrose accumulation in peach fruit. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 64 (35):6723-6729.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b02159 pmid: 27537219 |
| [24] |
Wang D, Zhao J T, Hu B, Li J Q, Qin Y Q, Chen L H, Qin Y H, Hu G B. 2018. Identification and expression profile analysis of the sucrose phosphate synthase gene family in Litchi chinensis Sonn. Peer J, 6:e4379.
doi: 10.7717/peerj.4379 URL |
| [25] |
Wang J, Du J, Mu X, Wang P. 2017. Cloning and characterization of the Cerasus humilis sucrose phosphate synthase gene(ChSPS1). PLoS ONE, 12 (10):e0186650.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186650 URL |
| [26] | Wei Qingjiang, Ma Zhangzheng, Le Si, Lei Changyu, Ma Qiaoli, Gu Qingqing. 2020. Identification and expression analysis of sucrose-phosphate synthase(SPS)genes in citrus. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47 (2):334-344. (in Chinese) |
| 魏清江, 马张正, 勒思, 雷常玉, 马巧利, 辜青青. 2020. 柑橘磷酸蔗糖合酶基因CsSPS的鉴定和表达. 园艺学报, 47 (2):334-344. | |
| [27] |
Wind J, Smeekens S, Hanson J. 2010. Sucrose:metabolite and signaling molecule. Phytochemistry, 71 (14-15):1610-1614.
doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2010.07.007 URL |
| [28] | Zhang Kai-chun, Yan Guo-hua, Zhang Xiao-ming, Wang Jing, Duan Xu-wei. 2017. The cultivation history,production situation and development proposals of sweet cherry in China. Deciduous Fruits, 49 (6):1-5. (in Chinese) |
| 张开春, 闫国华, 张晓明, 王晶, 段续伟. 2017. 中国甜樱桃的栽培历史、生产现状及发展建议. 落叶果树, 49 (6):1-5 | |
| [29] |
Zhang X M, Wang W, Du L Q, Xie J H, Yao Y L, Sun G M. 2012. Expression patterns,activities and carbohydrate-metabolizing regulation of sucrose phosphate synthase,sucrose synthase and neutral invertase in pineapple fruit during development and ripening. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13 (8):9460-9477.
doi: 10.3390/ijms13089460 URL |
| [1] | 王晓晨, 聂子页, 刘先菊, 段 伟, 范培格, 梁振昌, . 脱落酸对‘京香玉’葡萄果实单萜物质合成的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 237-249. |
| [2] | 翟含含, 翟宇杰, 田义, 张叶, 杨丽, 温陟良, 陈海江. 桃SAUR家族基因分析及PpSAUR5功能鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 1-14. |
| [3] | 吴延军, 刘庆忠, 陈鸿才, 戚行江, 朱东姿, 郑家祥, 曹学敏, 方丹燕. 甜樱桃新品种‘江南锦’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 29-30. |
| [4] | 张晓明, 闫国华, 周 宇, 王 晶, 段续伟, 吴传宝, 张开春. 甜樱桃砧木新品种‘京春2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 31-32. |
| [5] | 张秋悦, 刘昌来, 于晓晶, 杨甲定, 封超年. 盐胁迫条件下杜梨叶片差异表达基因qRT-PCR内参基因筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(7): 1557-1570. |
| [6] | 邱可立, 王玉民, 何金铃, 俞红, 潘海发, 盛玉, 谢庆梅, 陈红莉, 周晖, 张金云. 桃漆酶家族基因鉴定及PpLAC21功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(6): 1351-1362. |
| [7] | 李丽仙, 王烁, 陈莹, 邬滢涛, 王雅倩, 房月, 陈学森, 田长平, 冯守千. 甜樱桃PavMYB10.1促进PavRiant表达和花青苷积累[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(5): 1023-1030. |
| [8] | 李亚梅, 马福利, 张山奇, 黄锦秋, 陈梦婷, 周军永, 孙其宝, 孙俊. 酸枣愈伤组织转化体系构建及在ZjBRC1调控ZjYUCCA表达中的应用[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(4): 749-757. |
| [9] | 张瑞, 张夏燚, 赵婷, 王双成, 张仲兴, 刘博, 张德, 王延秀. 基于转录组分析垂丝海棠响应盐碱胁迫的分子机制[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(2): 237-251. |
| [10] | 周至铭, 杨佳宝, 张程, 曾令露, 孟晚秋, 孙黎. 向日葵LACS家族鉴定及响应非生物胁迫表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(2): 352-364. |
| [11] | 戴文珊, 吴玥, 王敏. 金柑FcRGA1抗溃疡病机制初探[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(11): 2325-233. |
| [12] | 乔军, 王利英, 刘婧, 李素文. 基于转录组测序的茄子萼下果色光敏相关基因表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(11): 2347-2356. |
| [13] | 叶广继, 郑贞贞, 纳添仓, 王舰. 马铃薯资源糖苷生物碱含量评价及合成相关基因表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(11): 2357-2366. |
| [14] | 侯天泽, 易双双, 张志群, 王健, 李崇晖. 秋石斛RT-qPCR内参基因的筛选与验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(11): 2489-2501. |
| [15] | 周铁, 潘斌, 李菲菲, 马小川, 汤孟婧, 廉雪菲, 常媛媛, 陈岳文, 卢晓鹏. 膨大期干旱对温州蜜柑品质形成的影响及复水后树体水分吸收转运规律[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(1): 11-22. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司