
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (2): 365-379.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0970
• Genetic & Breeding·Germplasm Resources·Molecular Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
YAN Xu, LI Yue, FU Xiaopeng, NING Guogui, LIANG Mei*( )
)
Received:2024-09-15
Revised:2024-12-23
Online:2025-02-25
Published:2025-02-23
Contact:
LIANG Mei
YAN Xu, LI Yue, FU Xiaopeng, NING Guogui, LIANG Mei. Allele-specific Imbalance Analysis and Related Molecular Marker Development in Rosa chinensis‘Old Blush’[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(2): 365-379.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0970
| 引物 Primer | 正引物序列(5′-3′) Forward primer | 反引物序列(5′-3′) Reverse primer | 片段大小/bp Fragment size | 基因ID Gene ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP2 | TCATCTATGAAAGAATTTGGAG | GAAGGAATGCGACTGTTAGG | Hap1:962 Hap2:807 | Rc3g0243000 Rc3g0468481 |
| MYB4 | TAGGACTCAAGT TACCACAA | TCGTGAGGTACATTATCATCTA | Hap1:240 Hap2:430 | Rc7g0018900 Rc7g0178681 |
| DSC1 | CGTGAGGTACAT TATCATCTA | AAGATGACTGGACCAGAGCAA | Hap1:599 Hap2:1051 | Rc3g0384800 Rc3g0451671 |
Table 1 Primers sequence of molecular marker
| 引物 Primer | 正引物序列(5′-3′) Forward primer | 反引物序列(5′-3′) Reverse primer | 片段大小/bp Fragment size | 基因ID Gene ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP2 | TCATCTATGAAAGAATTTGGAG | GAAGGAATGCGACTGTTAGG | Hap1:962 Hap2:807 | Rc3g0243000 Rc3g0468481 |
| MYB4 | TAGGACTCAAGT TACCACAA | TCGTGAGGTACATTATCATCTA | Hap1:240 Hap2:430 | Rc7g0018900 Rc7g0178681 |
| DSC1 | CGTGAGGTACAT TATCATCTA | AAGATGACTGGACCAGAGCAA | Hap1:599 Hap2:1051 | Rc3g0384800 Rc3g0451671 |

Fig. 1 Comparative analysis of the RcOB_hap1 and RcOB_hap2 genomes in Rosa chinensis‘Old Blush’ A:Large segment alignment of RcOB_hap1 and RcOB_hap2;B:Distribution percentage of the gene and transposon on the specific chromosome regions for two genomes;C:Dot-plots of the whole-genomic gene alignment between RcOB_hap1 and RcOB_hap2;D:Distribution survey of the K-mer for‘Old Blush’re-sequence genome(K = 17)
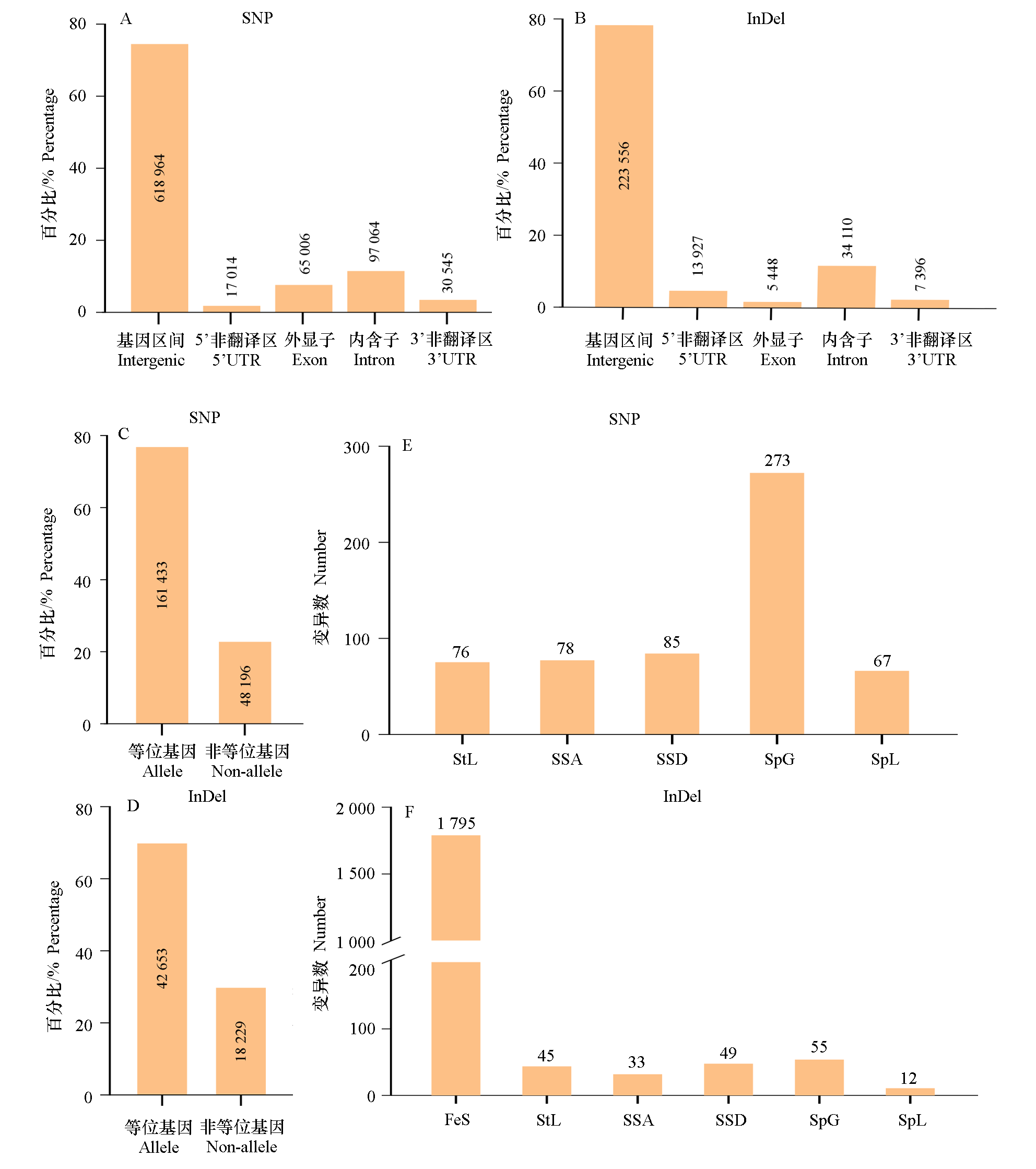
Fig. 2 The DNA sequence variation between RcOB_hap1 and RcOB_hap2 genomes in Rosa chinensis‘Old Blush’ SNP:Single nucleotide polymorphism;InDel:Insertion or deletion;FeS:Frame shift;SpL:Stop codon lost;SSA:Splice site acceptor;SSD:Splice site donor;SpG:Stop codon gained or premature stop;StL:Start codon lost
| 基因 Gene | SNP编号 SNP ID | Hap1型读长数 Hap1-type read number | Hap2型读长数 Hap2-type read number | 变化倍数的log2值 log2 fold change | ASE基因 (是/否) ASE gene (yes/no) | P值 P-value | 基因注释 Annotation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rc1g0350201 | Chr01_43344427 | 0 | 131 | -10.17 | 是 Yes | 8.28e-108 | 未知蛋白 Unknown protein |
| Chr01_43344491 | 0 | 149 | |||||
| Chr01_43344521 | 0 | 136 | |||||
| Chr01_43344550 | 0 | 158 | |||||
| 小计Subtotal | 0 | 574 | |||||
| Rc2g0129651 | Chr02_45318393 | 31 | 53 | -0.83 | 否 No | 1.15e-4 | 未知蛋白 Unknown protein |
| Chr02_45318518 | 30 | 53 | |||||
| Chr02_45318530 | 30 | 56 | |||||
| Chr02_45318549 | 30 | 53 | |||||
| 小计Subtotal | 121 | 215 | |||||
| Rc3g0468121 | Chr03_14202662 | 86 | 13 | 2.83 | 是 Yes | 1.70e-47 | 磷酸酶 Protein phosphatase |
| Chr03_14202709 | 81 | 13 | |||||
| Chr03_14202963 | 69 | 10 | |||||
| Chr03_14203072 | 75 | 8 | |||||
| Chr03_14204073 | 84 | 11 | |||||
| 小计Subtotal | 395 | 55 | |||||
| Rc5g0077891 | Chr05_83740197 | 173 | 133 | 0.35 | 否 No | 2.74e-4 | 未知蛋白 Unknown protein |
| Chr05_83740290 | 132 | 107 | |||||
| 小计Subtotal | 305 | 240 |
Table 3 ASE analysis result of gene examples in petal
| 基因 Gene | SNP编号 SNP ID | Hap1型读长数 Hap1-type read number | Hap2型读长数 Hap2-type read number | 变化倍数的log2值 log2 fold change | ASE基因 (是/否) ASE gene (yes/no) | P值 P-value | 基因注释 Annotation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rc1g0350201 | Chr01_43344427 | 0 | 131 | -10.17 | 是 Yes | 8.28e-108 | 未知蛋白 Unknown protein |
| Chr01_43344491 | 0 | 149 | |||||
| Chr01_43344521 | 0 | 136 | |||||
| Chr01_43344550 | 0 | 158 | |||||
| 小计Subtotal | 0 | 574 | |||||
| Rc2g0129651 | Chr02_45318393 | 31 | 53 | -0.83 | 否 No | 1.15e-4 | 未知蛋白 Unknown protein |
| Chr02_45318518 | 30 | 53 | |||||
| Chr02_45318530 | 30 | 56 | |||||
| Chr02_45318549 | 30 | 53 | |||||
| 小计Subtotal | 121 | 215 | |||||
| Rc3g0468121 | Chr03_14202662 | 86 | 13 | 2.83 | 是 Yes | 1.70e-47 | 磷酸酶 Protein phosphatase |
| Chr03_14202709 | 81 | 13 | |||||
| Chr03_14202963 | 69 | 10 | |||||
| Chr03_14203072 | 75 | 8 | |||||
| Chr03_14204073 | 84 | 11 | |||||
| 小计Subtotal | 395 | 55 | |||||
| Rc5g0077891 | Chr05_83740197 | 173 | 133 | 0.35 | 否 No | 2.74e-4 | 未知蛋白 Unknown protein |
| Chr05_83740290 | 132 | 107 | |||||
| 小计Subtotal | 305 | 240 |
| 基因 Gene | 等位基因比较 Allele comparison | 基因型频率 Frequency of different genotypes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基因表达(有/无差异) Gene expression(DIF./No DIF.) | 蛋白功能(有/无差异) Protein function(DIF./No DIF.) | 36份野生种 36 wild species | 147份栽培种 147 cultivated varieties | ||
| AP2 | 有差异(茎和刺:Hap1 < Hap2) DIF.(Hap1 < Hap2 in stem & prickle) | 有差异(Hap2型:提前终止) DIF.(Hap2-type:Premature) | Hap2: 8 Hap1&2: 6 Hap2&3: 6 Hap3: 9 No band: 7 | Hap2: 45 Hap1&2: 18 Hap2&3: 70 Hap3: 5 Hap1&3: 6 No band: 3 | |
| MYB4 | 有差异(茎和雌蕊:Hap1 < Hap2) DIF.(Hap1 < Hap2 in stem & pistil) | 无差异 No DIF. | Hap1: 17 Hap2: 1 Hap1&2: 11 No band: 7 | Hap1: 94 Hap2: 5 Hap1&2: 47 No band: 1 | |
| DSC1 | 有差异(所有组织:Hap1 < Hap2) DIF.(Hap1 < Hap2 in all tissues) | 有差异(Hap1型:移码) (Hap1-type:Frame shift) | Hap1: 3 Hap2: 3 Hap1&2: 6 No band: 24 | Hap1: 83 Hap2: 5 Hap1&2: 30 No band: 29 | |
Table 4 Comparison of two alleles of AP2,MYB4 and DSC1 and their frequency in 183 materials
| 基因 Gene | 等位基因比较 Allele comparison | 基因型频率 Frequency of different genotypes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基因表达(有/无差异) Gene expression(DIF./No DIF.) | 蛋白功能(有/无差异) Protein function(DIF./No DIF.) | 36份野生种 36 wild species | 147份栽培种 147 cultivated varieties | ||
| AP2 | 有差异(茎和刺:Hap1 < Hap2) DIF.(Hap1 < Hap2 in stem & prickle) | 有差异(Hap2型:提前终止) DIF.(Hap2-type:Premature) | Hap2: 8 Hap1&2: 6 Hap2&3: 6 Hap3: 9 No band: 7 | Hap2: 45 Hap1&2: 18 Hap2&3: 70 Hap3: 5 Hap1&3: 6 No band: 3 | |
| MYB4 | 有差异(茎和雌蕊:Hap1 < Hap2) DIF.(Hap1 < Hap2 in stem & pistil) | 无差异 No DIF. | Hap1: 17 Hap2: 1 Hap1&2: 11 No band: 7 | Hap1: 94 Hap2: 5 Hap1&2: 47 No band: 1 | |
| DSC1 | 有差异(所有组织:Hap1 < Hap2) DIF.(Hap1 < Hap2 in all tissues) | 有差异(Hap1型:移码) (Hap1-type:Frame shift) | Hap1: 3 Hap2: 3 Hap1&2: 6 No band: 24 | Hap1: 83 Hap2: 5 Hap1&2: 30 No band: 29 | |
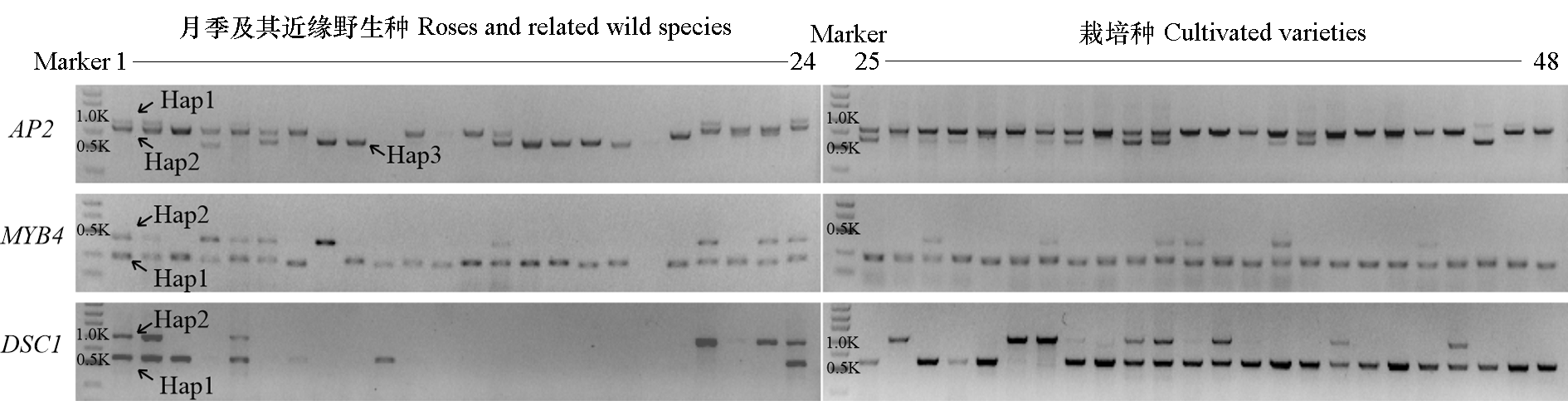

Fig. 6 Amplification results of molecular markers among roses and related wild species(line 1 to 24) and cultivated varieties(line 25 to 48) Line 1 is Rosa chinensis‘Old Blush’;Line 46 is Rosa hybrida var.‘Sweet Pretty’with simple flower
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msab293 pmid: 34597405 |
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erq342 pmid: 21068208 |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-30918-4 pmid: 30150746 |
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.022087 pmid: 15194819 |
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1038/s41588-021-00971-3 pmid: 34980919 |
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
|
焦文标. 2013. 基于二代测序技术的甜橙基因组杂合度与起源研究[硕士论文]. 武汉: 华中农业大学.
|
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.6.9.1211 pmid: 7919989 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.177246 pmid: 27765809 |
| [22] |
pmid: 15049300 |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1038/s41597-020-0428-4 pmid: 32161269 |
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
|
李淑斌, 周宁宁, 周青, 晏慧君, 蹇洪英, 王其刚, 陈敏, 邱显钦, 张颢, 王书芳, 李树发, 唐开学. 2015. ‘月月粉’连续开花习性遗传规律分析. 园艺学报, 42 (11):2223-2228.
|
|
| [27] |
|
|
李叶飞. 2020. 迷人的英国玫瑰. 天津: 天津人民出版社.
|
|
| [28] |
doi: 10.1038/s41477-020-0597-3 pmid: 32055045 |
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa115 pmid: 32096823 |
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
doi: 10.1038/nrg2815 pmid: 20567245 |
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv074 pmid: 25819081 |
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
doi: 10.1126/science.1153917 pmid: 18436778 |
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
doi: 10.1111/pbi.13806 pmid: 35258172 |
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
doi: 10.1038/s41477-021-00941-x pmid: 34140668 |
| [48] |
doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-2285-x pmid: 32054439 |
| [49] |
|
|
文晓鹏, 邓秀新. 2002. 五种蔷薇属植物基因组DNA的提取及鉴定. 种子,(6):18-21.
|
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
doi: 10.1534/genetics.109.103499 pmid: 19474198 |
| [53] |
|
|
张佐双, 朱秀珍. 2006. 中国月季. 北京: 中国林业出版社.
|
| [1] | LIU Gangyun, DUAN Shixiang, XU Nana, GUO Yaomiao, DOU Junling, YANG Sen, NIU Huanhuan, LIU Dongming, YANG Luming, HU Jianbin, ZHU Huayu. Molecular Markers Assisted Construction of Cmerecta Near-Isogenic Line of Melon Dwarfing Gene [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(9): 2048-2062. |
| [2] | YANG Binan, LI Bowen, YANG Zhenyu, XU Yipeng, YAN Yunqing, LOU Yuxia, FENG Shucheng, MING Feng. The Mechanism of Heat Stress Response and the Exploration of Functional Genes in Rosa chinensis‘Angela’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1284-1296. |
| [3] | WANG Wen, ZHANG Peng, WANG Zhimin, LIU Genzhong, BAO Zhilong, MA Fangfang. Analysis of Differential Genes in Response to Sucrose Feeding in Disc Florets of Chrysanthemum nankingense [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1297-1310. |
| [4] | WANG Wenyu, WANG Jiayin, DU Tingting, ZHANG Jingjing, ZHANG Chao, XIN Cuihua, GUO Jiangbo, PEI Haixia. Cloning of RhRNF185-like Gene from Rose and Its Effect on Petal Senescence [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(5): 1047-1055. |
| [5] | LAN Wei, MENG Yanqiong, XUAN Yun, ZHU Kangning, DING Xiaohao, FAN Dexin, KANG Liyun. A New Rose Cultivar‘Yinghe’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(4): 925-926. |
| [6] | XU Qin, WANG Jiaying, ZHANG Mannan, XIAO Zhihao, ZHENG Hankai, LU Yong'en, WANG Taotao, ZHANG Yuyang, ZHANG Junhong, YE Zhibiao, YE Jie. Identification of Genetic Loci and Molecular Marker Development of Salt Tolerance in Tomato Seedlings [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(2): 239-252. |
| [7] | LIANG Yuqing, SUN Chunhui, DENG Congliang, SHI Xiju, ZHONG Yan, LI Yongqiang. Identification and Analysis of Complete Genomic Sequence of Broad Bean Wilt Virus 2 Beijing Rose Isolate [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(10): 2320-2328. |
| [8] | LI Chunniu, SU Qun, LI Xianmin, HUANG Zhanwen, SUN Mingyan, LU Jiashi, WANG Hongyan, BU Zhaoyang. SSR Molecular Markers Development and Parentage Relationship Identification Based on Whole Genomic Sequences of Jasminum sambac [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(10): 2343-2357. |
| [9] | ZHANG Lilan, YANG Jun, WANG Rangjian. Mining of Genetic Locus of Phenylethyl Alcohol Primrose Glycoside Abundance in Tea Plants [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(1): 77-90. |
| [10] | LÜ Honghao, ZHANG Yangyong, $\boxed{\hbox{FANG Zhiyuan}}$, YANG Limei, ZHUANG Mu, LIU Yumei, WANG Yong, JI Jialei, LI Zhansheng, HAN Fengqing. A New Spring Cabbage Cultivar‘Zhonggan D22’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(1): 213-214. |
| [11] | ZHOU Yan, GAO Shumin , CUI Rongfeng , SUN Liping , and FU Zihao, . Breeding of New Rose Cultivar of‘Yanjinghuang’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(S1): 149-150. |
| [12] | GAO Junping, MA Nan, ZHOU Hougao, WANG Jiaxi, ZHANG Changqing, LI Yonghong, ZHOU Xiaofeng, SUN Xiaoming. A New Cut Rose Cultivar‘Feiyun’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(4): 915-916. |
| [13] | CUI Jian, ZHONG Xionghui, LIU Zeci, CHEN Denghui, LI Hailong, HAN Rui, YUE Xiangqing, KANG Jungen, WANG Chao. Construction of Cabbage Chromosome Segment Substitution Lines [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(1): 65-78. |
| [14] | LIU Yiping, NI Menghui, WU Fangfang, LIU Hongli, HE Dan, KONG Dezheng. Association Analysis of Organ Traits with SSR Markers in Lotus(Nelumbo nucifera) [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(1): 103-115. |
| [15] | OUYANG Liying, HUANG Yanfei, CHEN Junmei, YANG Shu, and LIAN Huashan. A New Miniature Rose Cultivar‘Jiuer’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 223-224. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd