
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (10): 1859-1872.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0476
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Chonghui1,3, YANG Guangsui1,3, ZHANG Zhiqun1,3, YIN Junmei2,3,*( )
)
Received:2021-07-19
Revised:2021-09-02
Online:2021-10-25
Published:2021-11-01
Contact:
YIN Junmei
E-mail:yinjunmei2004@163.com
CLC Number:
LI Chonghui, YANG Guangsui, ZHANG Zhiqun, YIN Junmei. A Novel R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor Gene AaMYB6 Involved in Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Anthurium andraeanum[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(10): 1859-1872.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0476

Fig. 1 Sequences alignment of AaMYB6 from anthurium with known R2R3-MYBs involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis A:The red box indicates the bHLH interacting motif;the green box indicates the different conserved“DNEI”motif for monocots R2R3-MYB;The blue box indicates the C-terminal-conserved motif KAX[K/R]C[S/T] for anthocyanin-regulating MYBs of monocots. Aa:Anthurium andraeanum;Zm:Zea mays;Pe:Phalaenopsis equestris;Fh:Freesia hybrid.
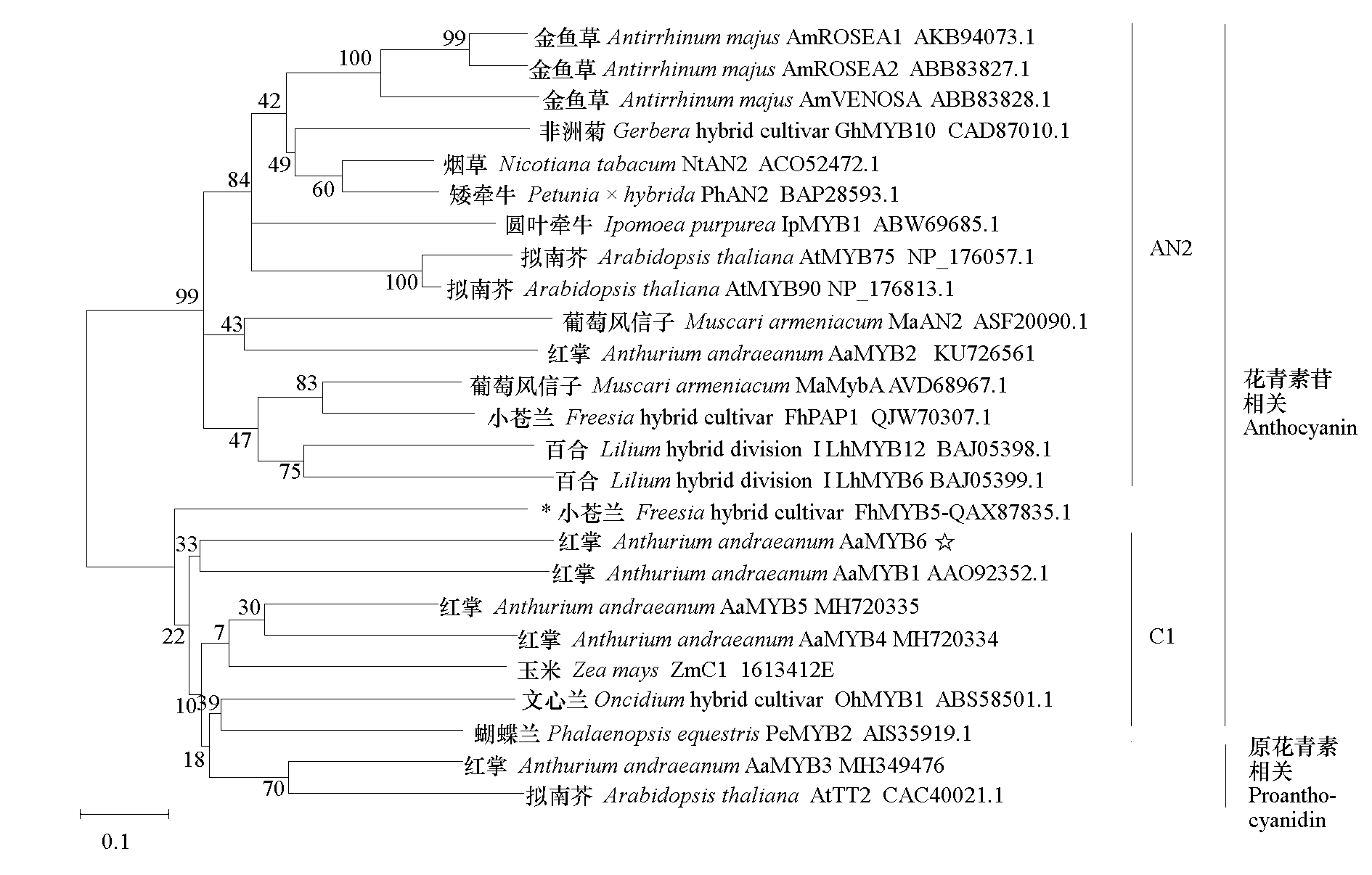
Fig. 2 Phylogenic tree of AaMYB6 from anthurium with known R2R3-MYBs involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis * Both correlated with anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin.
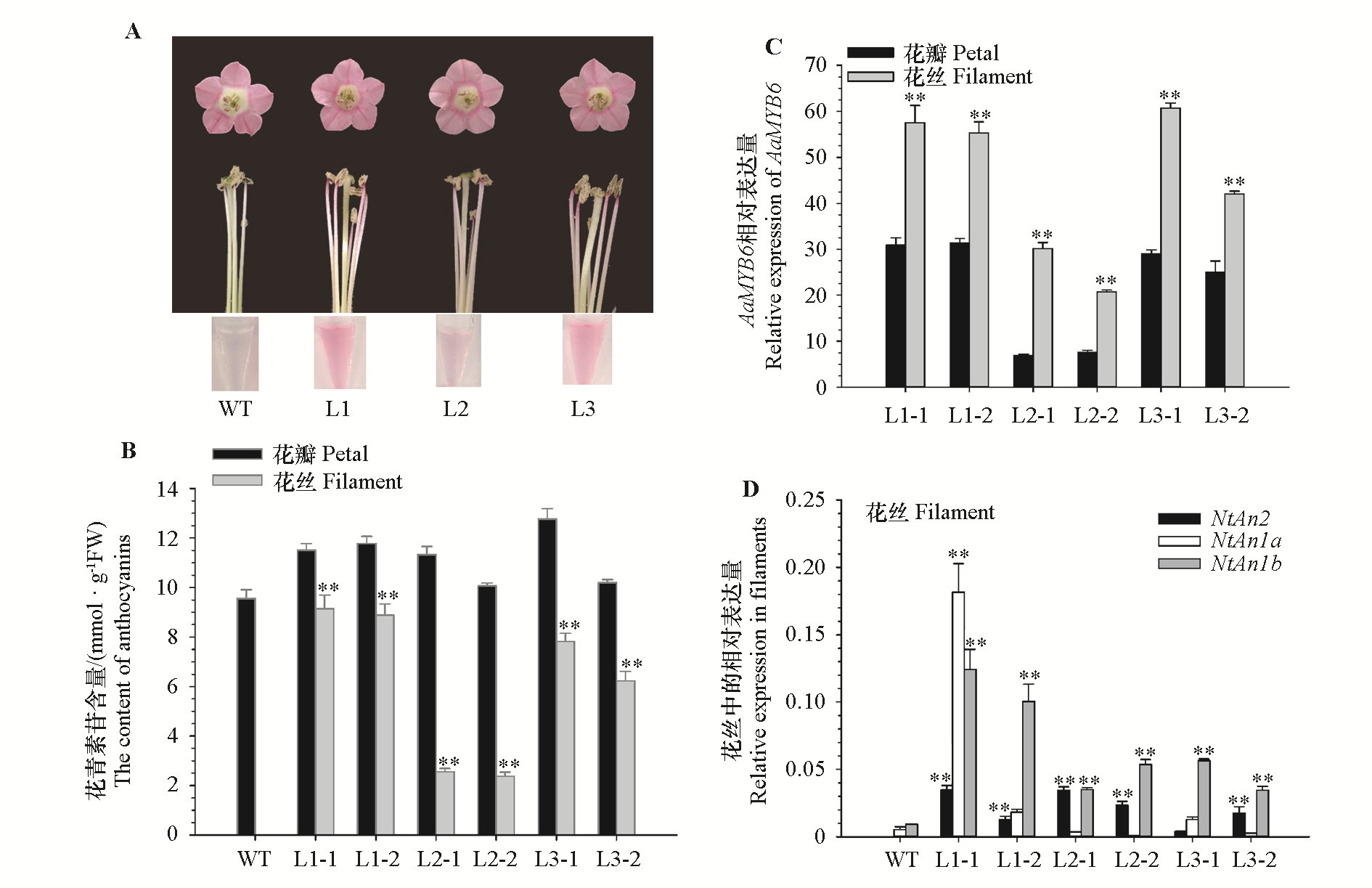
Fig. 5 The phenotypes and the content of anthocyanin of AaMYB6 transgenic tobacco(A)and detection of gene expression(B,C) WT:Wild type tobacco plants;L1-L3:Three AaMYB6 overexpression T1 tobacco lines,and there were two plants of each line(-1,-2).t-test [Comparison between transgenic lines and wild type plants(A,D)or between different tissue(B,C)],** α = 0.01.

Fig. 6 The relative expression of enzyme genes in petals and filaments of transgenic tobacco plants FC:Fold changes against the WT;L1-L3:Three AaMYB6 overexpression T1 tobacco lines,there were two plants of each line(-1,-2).

Fig. 7 Interactions between AaMYB6 and AabHLH1 detected using the Y2H and BiFC assays A:Y2H Gold yeast cells containing plasmids were grown on double- and quadruple-selection SD media. The X-α-gal assay was performed to confirm the positive interactions;BD:pGBKT7 empty plasmid;AD:pGADT7 empty plasmid;AD-AaMYB6:pGAD-AaMYB6 recombinant plasmid;BD-AabHLH1:pGBK-AabHLH1 recombinant plasmid;B:Bimolecular fluorescence complementation visualization of the AaMYB6 and AabHLH1 interaction in the in protoplasts of Arabidopsis.
| [1] |
Albert N W, Arathoon S, Collette V E, Schwinn K E, Jameson P E, Lewis D H, Zhang H, Davies K M. 2010. Activation of anthocyanin synthesis in Cymbidium orchids:variability between known regulators. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Culture, 100 (3):355-360.
doi: 10.1007/s11240-009-9649-0 URL |
| [2] |
Bai Y, Pattanaik S, Patra B, Werkman J R, Xie C H, Yuan L. 2011. Flavonoid-related basic helix-loop-helix regulators,NtAn1a and NtAn1b,of tobacco have originated from two ancestors and are functionally active. Planta, 234:363-375.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-011-1407-y URL |
| [3] |
Bariola P A, Green M I J. 1999. Regulation of S-like ribonuclease levels in Arabidopsis. Antisense inhibition of RNS 1 or RNS2 elevates anthocyanin accumulation. Plant Physiology, 119 (1):331.
pmid: 9880376 |
| [4] |
Bhargava A, Mansfield S D, Hall H C, Douglas C J, Ellis B E. 2010. MYB 75 functions in regulation of secondary cell wall formation in the Arabidopsis inflorescence stem. Plant Physiology, 154:1428-1438.
doi: 10.1104/pp.110.162735 pmid: 20807862 |
| [5] | Cao Yuwei, Xu Leifeng, Yang Panpan, Xu Hua, He Guoren, Tang Yuchao, Ren Junfang, Ming Jun. 2019. Differential expression of three R2R3-MYBs genes regulating anthocyanin pigmentation patterns in Lilium spp. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 46 (5):955-963.(in Chinese) |
| 曹雨薇, 徐雷锋, 杨盼盼, 徐华, 何国仁, 唐玉超, 任君芳, 明军. 2019. 百合花青素苷呈色类型中3种R2R3-MYBs基因的差异表达. 园艺学报, 46 (5):955-963. | |
| [6] |
Chen K L, Du L J, Liu H L, Liu Y L. 2019. A novel R2R3-MYB from grape hyacinth,MaMybA,which is different from MaAN2,confers intense and magenta anthocyanin pigmentation in tobacco. BMC Plant Biology, 19 (1):390.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-1999-0 URL |
| [7] |
Chen K L, Liu H L, Lou Q, Liu Y L. 2017. Ectopic expression of the grape hyacinth(Muscari armeniacum)R2R3-MYB transcription factor gene,MaAN2,induces anthocyanin accumulation in tobacco. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8:965.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00965 URL |
| [8] |
Clark B R, Bliss B J, Suzuki J Y, Borris R P. 2014. Chemotaxonomy of Hawaiian Anthurium cultivars based on multivariate analysis of phenolic metabolites. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 62:11323-11334.
doi: 10.1021/jf502187c URL |
| [9] |
Collette V E, Jameson P E, Schwinn K E, Umaharan P, Davies K M. 2004. Temporal and spatial expression of flavonoid biosynthetic genes in flowers of Anthurium andraeanum. Physiologia Plantarum, 122:297-304.
doi: 10.1111/ppl.2004.122.issue-3 URL |
| [10] | Dai Si-lan, Hong Yan. 2016. Molecular breeding for flower colors modification on ornamental plants based on the mechanism of anthocyanins biosynthesis and coloration. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 49 (3):529-542.(in Chinese) |
| 戴思兰, 洪艳. 2016. 基于花青素苷合成和呈色机理的观赏植物花色改良分子育种. 中国农业科学, 49 (3):529-542. | |
| [11] |
Dubos C, Stracke R, Grotewold E, Weisshaar B, Martin C, Lepiniec L. 2010. MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends in Plant Science, 15 (10):573-581.
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2010.06.005 URL |
| [12] |
Elibox W, Umaharan P. 2008. Inheritance of major spathe colors in Anthurium andraeanum Hort. is determined by three major genes. HortScience, 43:787-791.
doi: 10.21273/HORTSCI.43.3.787 URL |
| [13] |
Fu Z Z, Shang H Q, Jiang H, Gao J, Dong X Y, Wang H J, Li Y M, Wang L M, Zhang J, Shu Q Y, Chao Y C, Xu M L, Wang R, Wang L S, Zhang H C. 2020. Systematic identification of the light-quality responding anthocyanin synthesis-related transcripts in petunia petals. Horticultural Plant Journal, 6 (6):428-438.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2020.11.006 URL |
| [14] |
Gopaulchan D, Lennon A M, Umaharan P. 2015. Expression analysis of the anthocyanin genes in pink spathes of anthurium with different color intensities. Journal of the American Society For Horticultural Science, 140:480-489.
doi: 10.21273/JASHS.140.5.480 URL |
| [15] |
Gopaulchan D, Lennon A M, Umaharan P. 2013. Identification of reference genes for expression studies using quantitative RT-PCR in spathe tissue of Anthurium andraeanum(Hort.). Scientia Horticulturae, 153:1-7.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2013.01.024 URL |
| [16] |
Gopaulchan D, Umaharan P, Lennon A M. 2014. A molecular assessment of the genetic model of spathe color inheritance in Anthurium andraeanum(Hort.). Planta, 239:695-705.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-013-2007-9 pmid: 24363030 |
| [17] | Horsch R B, Fry J, Hoffmann N, Neidermeyer J, Rogers S G, Fraley R T. 1988. Leaf disc transformation//Gelvin S B,Schilperoort R A. Plant Molecular Biology Manual. Dordrecht:Kluwer Academic Publishers:1-9. |
| [18] |
Hsu C C, Chen Y Y, Tsai W C, Chen W H, Chen H H. 2015. Three R2R3-MYB transcription factors regulate distinct floral pigmentation patterning in Phalaenopsis spp. Plant Physiology, 168:175-191.
doi: 10.1104/pp.114.254599 URL |
| [19] |
Huang W, Khaldun A B M, Lv H, Du L, Zhang C, Wang Y. 2016. Isolation and functional characterization of a R2R3-MYB regulator of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway from Epimedium sagittatum. Plant Cell Reports, 35:883-894.
doi: 10.1007/s00299-015-1929-z URL |
| [20] |
Huang Y J, Song S, Allan A C, Liu X F, Yin X R, Xu C J, Chen K S. 2013. Differential activation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis and tobacco over-expressing an R2R3 MYB from Chinese bayberry. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Culture, 113:491-499.
doi: 10.1007/s11240-013-0291-5 URL |
| [21] |
Huang Z A, Zhao T, Fan H J, Wang N, Zheng S S, Ling H Q. 2012. The upregulation of NtAN2 expression at low temperature is required for anthocyanin accumulation in juvenile leaves of Lc-transgenic tobacco(Nicotiana tabacum L.). Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 39:149-156.
doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2012.01.007 URL |
| [22] |
Lai B, Li X J, Hu B, Qin Y H, Huang X M, Wang H C, Hu G B. 2014. LcMYB1is a key determinant of differential anthocyanin accumulation among genotypes,tissues,developmental phases and ABA and light stimuli in Litchi chinensi. PLoS ONE, 9 (1):e86293.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086293 URL |
| [23] | Li C H, Qiu J, Ding L, Huang M Z, Huang S R, Yang G S, Yin J M. 2017. Anthocyanin biosynthesis regulation of DhMYB2 and DhbHLH1 in Dendrobium hybrids petals. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 12:335-345. |
| [24] |
Li C H, Qiu J, Huang S R, Yang G S, Yin J M. 2019a. Ectopic expression of the Anthurium andraeanum(Hort.)R2R3-MYB genes AaMYB4 and AaMYB5 enhance the flower color in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Culture, 139:105-117.
doi: 10.1007/s11240-019-01667-7 URL |
| [25] |
Li C H, Qiu J, Huang S R, Yin J M, Yang G S. 2019b. AaMYB 3 interacts with AabHLH1 to regulate proanthocyanidin accumulation in Anthurium andraeanum(Hort.)-another strategy to modulate pigmentation. Horticulture Research, 6:14.
doi: 10.1038/s41438-018-0102-6 URL |
| [26] |
Li C H, Qiu J, Yang G S, Huang S R, Yin J M. 2016. Isolation and characterization of a R2R3-MYB transcription factor gene related to anthocyanin biosynthesis in the spathes of Anthurium andraeanum(Hort.). Plant Cell Reports, 35:2151-2165.
doi: 10.1007/s00299-016-2025-8 URL |
| [27] | Li Chong-hui, Yang Guang-sui. 2019. The expression pattern of AaMYB1 in anthurium and its overexpression in tobacco. Molecular Plant Breeding, 17 (6):1898-1905. (in Chiese) |
| 李崇晖, 杨光穗. 2019. 红掌AaMYB1的表达特征及其在烟草中的过表达. 分子植物育种, 17 (6):1898-1905. | |
| [28] | Li Y Q, Shan X T, Tong L N, Wei C, Lu K Y, Li S Y, Kimani S, Wang S C, Wang L, Gao X. 2020. The conserved and particular roles of the R2R3-MYB regulator FhPAP 1 from Freesia hybrida in flower anthocyanin biosynthesis. Plant and Cell Physiology,(7):7. |
| [29] |
Li Y Q, Shan X T, Zhou L D, Gao R F, Yang S, Wang S C, Wang L, Gao X. 2019c. The R2R3-MYB factor FhMYB 5 from Freesia hybrida contributes to the regulation of anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin biosynthesis. Frontiers in Plant Science, 9:1935.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01935 URL |
| [30] |
Li Z Y, Wang J B, Fu Y L, Gao Y, Lu H Z, Xu L. 2018. Transcriptome profiling in the spathe of Anthurium andraeanum‘Albama’and its anthocyanin-loss mutant‘Xueyu’. Scientific Data, 5:180247.
doi: 10.1038/sdata.2018.247 URL |
| [31] |
Li Z Y, Wang J B, Zhang X Q, Xu L. 2015. Comparative transcriptome analysis of Anthurium‘Albama’and its anthocyanin-loss mutant. PLoS ONE, 10 (3):e0119027.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119027 URL |
| [32] |
Meng J X, Gao Y, Han M L, Liu P Y, Yang C, Shen T, Li H H. 2020. In vitro anthocyanin induction and metabolite analysis in Malus spectabilis leaves under low nitrogen conditions. Horticultural Plant Journal, 6 (5):284-292.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2020.06.004 URL |
| [33] |
Pattanaik S, Kong Q, Zaitlin D, Werkman J R, Xie C H, Patra B, Yuan L. 2010. Isolation and functional characterization of a floral tissue-specific R2R3 MYB regulator from tobacco. Planta, 231:1061-1076.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-010-1108-y URL |
| [34] |
Petroni K, Tonelli C. 2011. Recent advances on the regulation of anthocyanin synthesis in reproductive organs. Plant Science, 181:219-229.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2011.05.009 pmid: 21763532 |
| [35] |
Pérez-Díaz J R, Pérez-Díaz J, Madrid-Espinoza J, Gonzúlez-Villanueva E, Moreno Y, Ruiz-Lara S. 2016. New member of the R2R3-MYB transcription factors family in grapevine suppresses the anthocyanin accumulation in the flowers of transgenic tobacco. Plant Molecular Biology, 90 (1-2):63-76.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-015-0394-y pmid: 26497001 |
| [36] |
Suzuki J Y, Amore T D, Calla B, Palmer N A, Scully E D, Sattler S E, Sarath G, Lichty J S, Myers R Y, Keith L M, Matsumot T K, Geib S M. 2017. Organ-specific transcriptome profiling of metabolic and pigment biosynthesis pathways in the floral ornamental progenitor species Anthurium amnicola Dressler. Scientific Reports, 7 (1):1596.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-00808-2 pmid: 28473720 |
| [37] |
Tanaka Y, Sasaki N, Ohmiya A. 2008. Biosynthesis of plant pigments:anthocyanins,betalains and carotenoids. Plant Journal, 54:733-749.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03447.x URL |
| [38] |
Xiang L L, Liu X F, Li X, Yin X R, Grierson D, Li F, Chen K S. 2015. A novel bHLH transcription factor involved in regulating anthocyanin biosynthesis in chrysanthemums(Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat.). PLoS ONE, 10 (11):e0143892.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143892 URL |
| [39] |
Xu W, Dubos C, Lepiniec L. 2015. Transcriptional control of flavonoid biosynthesis by MYB-bHLH-WDR complexes. Trends Plant Science, 20:176-185.
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2014.12.001 URL |
| [40] |
Yamagishi M. 2011. Oriental hybrid lily Sorbonne homologue of LhMYB12 regulates anthocyanin biosyntheses in flower tepals and tepal spots. Molecular Breeding, 28:381-389.
doi: 10.1007/s11032-010-9490-5 URL |
| [41] |
Yamagishi M. 2016. A novel R2R3-MYB transcription factor regulates light-mediated floral and vegetative anthocyanin pigmentation patterns in Lilium regale. Molecular Breeding, 36:1-14.
doi: 10.1007/s11032-015-0425-z URL |
| [42] |
Yamagishi M, Shimoyamada Y, Nakatsuka T, Masuda K. 2010. Two R2R3-MYB genes,homologs of petunia AN2,regulate anthocyanin biosyntheses in flower tepals,tepal spots and leaves of Asiatic hybrid lily. Plant Cell Physiology, 51:463-474.
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcq011 URL |
| [43] |
Yamagishi M, Toda S, Tasaki K. 2014. The novel allele of the LhMYB12,gene is involved in splatter-type spot formation on the flower tepals of Asiatic hybrid lilies(Lilium spp.). New Phytologist, 201:1009-1020.
doi: 10.1111/nph.12572 pmid: 24180488 |
| [44] | Yang Guanxian, Xu Haifeng, Zhang Jing, Wang Nan, Fang Hongcheng, Jiang Shenghui, Wang Yicheng, Su Mengyu, Chen Xuesen. 2019. Functional identification of apple anthocyanin regulatory gene MdMYB111. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 46 (5):832-840. (in Chiese) |
| 杨官显, 许海峰, 张静, 王楠, 房鸿成, 姜生辉, 王意程, 苏梦雨, 陈学森. 2019. 苹果花青苷调控基因MdMYB111的功能鉴定. 园艺学报, 46 (5):832-840. | |
| [45] | Yoo S D, Cho Y H, Sheen J. 2014. Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplasts:a versatile cell system for transient gene expression analysis. Nature Protocol, 2 (7):1565-1572. |
| [46] |
Yuan Y W, Sagawa J M, Frost L, Vela J P, Bradshaw H D. 2014. Transcriptional control of floral anthocyanin pigmentation in monkey flowers(Mimulus). New Phytologist, 204:1013-1027.
doi: 10.1111/nph.2014.204.issue-4 URL |
| [1] | YE Zimao, SHEN Wanxia, LIU Mengyu, WANG Tong, ZHANG Xiaonan, YU Xin, LIU Xiaofeng, and ZHAO Xiaochun, . Effect of R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor CitMYB21 on Flavonoids Biosynthesis in Citrus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 250-264. |
| [2] | ZOU Xue, DING Fan, LIU Lifang, YU Hankaizong, CHEN Nianwei, and RAO Liping. A New Purple Potato Cultivar‘Mianziyu 1’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S1): 93-94. |
| [3] | WANG Sha, ZHANG Xinhui, ZHAO Yujie, LI Bianbian, ZHAO Xueqing, SHEN Yu, DONG Jianmei, YUAN Zhaohe. Cloning and Functional Analysis of PgMYB111 Related to Anthocyanin Synthesis in Pomegranate [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(9): 1883-1894. |
| [4] | HUANG Ling, HU Xianmei, LIANG Zehui, WANG Yanping, CHAN Zhulong, XIANG Lin. Cloning and Function Identification of Anthocyanidin Synthase Gene TgANS in Tulipa gesneriana [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(9): 1935-1944. |
| [5] | LI Maofu, YANG Yuan, WANG Hua, FAN Youwei, SUN Pei, JIN Wanmei. Analysis the Function of R2R3 MYB Transcription Factor RhMYB113c on Regulating Anthocyanin Synthesis in Rosa hybrida [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(9): 1957-1966. |
| [6] | YANG Yuyan, DUAN Xinyuan, HE Zhilin, BING Qihao, CHEN Suoying, LIU Xiaoman, ZENG Ming, LIU Xiaogang. Cloning and Function Characterization of UDP-L-rhamnose Synthase from Fortunella crassifolia [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1663-1672. |
| [7] | XU Haifeng, WANG Zhongtang, CHEN Xin, LIU Zhiguo, WANG Lihu, LIU Ping, LIU Mengjun, ZHANG Qiong. The Analyses of Target Metabolomics in Flavonoid and Its Potential MYB Regulation Factors During Coloring Period of Winter Jujube [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1761-1771. |
| [8] | TAO Xin, ZHU Rongxiang, GONG Xin, WU Lei, ZHANG Shaoling, ZHAO Jianrong, ZHANG Huping. Fructokinase Gene PpyFRK5 Plays an Important Role in Sucrose Accumulation of Pear Fruit [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1429-1440. |
| [9] | QIAN Jieyu, JIANG Lingli, ZHENG Gang, CHEN Jiahong, LAI Wuhao, XU Menghan, FU Jianxin, ZHANG Chao. Identification and Expression Analysis of MYB Transcription Factors Regulating the Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Zinnia elegans and Function Research of ZeMYB9 [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1505-1518. |
| [10] | ZHANG Lugang, LU Qianqian, HE Qiong, XUE Yihua, MA Xiaomin, MA Shuai, NIE Shanshan, YANG Wenjing. Creation of Novel Germplasm of Purple-orange Heading Chinese Cabbage [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1582-1588. |
| [11] | MA Mingying, HAO Chenxing, ZHANG Kai, XIAO Guihua, SU Hanying, WEN Kang, DENG Ziniu, MA Xianfeng. CsSWEET2a Promotes the Infection of Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1247-1260. |
| [12] | CHEN Daozong, LIU Yi, SHEN Wenjie, ZHU Bo, TAN Chen. Identification and Analysis of PAP1/2 Homologous Genes in Brassica rapa,B. oleracea and B. napus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1301-1312. |
| [13] | WANG Yan, SUN Zheng, FENG Shan, YUAN Xinyi, ZHONG Linlin, ZENG Yunliu, FU Xiaopeng, CHENG Yunjiang, Bao Manzhu, ZHANG Fan. The Negative Regulation of DcERF-1 on Senescence of Cut Carnation [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1313-1326. |
| [14] | LI Xiaoming, YU Junchi, WANG Chunxia. Comparison of Growth and Secondary Metabolites of Purple and White Flower Dracocephalum moldavica Under Field,Greenhouse and Greenhouse Shading Conditions [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1363-1370. |
| [15] | LI Lixian, WANG Shuo, CHEN Ying, WU Yingtao, WANG Yaqian, FANG Yue, CHEN Xuesen, TIAN Changping, FENG Shouqian. PavMYB10.1 Promotes Anthocyanin Accumulation by Positively Regulating PavRiant in Sweet Cherry [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(5): 1023-1030. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd