
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (10): 1907-1920.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0406
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
YIN Hantai1,3,4, YIN Junmei2,4,*( ), LIAO Yi3,4, LU Shunjiao3,4, LI Chonghui3,4,*(
), LIAO Yi3,4, LU Shunjiao3,4, LI Chonghui3,4,*( )
)
Received:2021-07-19
Revised:2021-09-02
Online:2021-10-25
Published:2021-11-01
Contact:
YIN Junmei,LI Chonghui
E-mail:yinjunmei2004@163.com;blchh@sina.com
CLC Number:
YIN Hantai, YIN Junmei, LIAO Yi, LU Shunjiao, LI Chonghui. Phenotype Classification Based on Flower Color,Pigment Distribution and Epidermal Cell Shape of Dendrobium Hybrids[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(10): 1907-1920.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0406
| 色系 Color group | 颜色描述 Color description | 品种数 Number | % | CIELab表色系统 CIELab coordinate | 颜色指 数CIRG | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 明度L* | 红度a* | 黄度b* | 彩度C | 色相角h | |||||
| 白 White | 白、淡粉白、淡紫白色 White,pale pinkish white,pale purplish white | 16 | 15.0 | 71.68 ~ 87.08 | -13.05 ~ 2.65 | -2.88 ~ 24.64 | 1.41 ~ 27.50 | -47.38 ~ 143.71 | 0.40 ~ 2.67 |
| 粉 Pink | 浅粉色 Light pink | 4 | 3.7 | 65.55 ~ 74.60 | 6.52 ~ 26.54 | -0.60 ~ 3.42 | 6.54 ~ 26.63 | -5.23 ~ 9.38 | 1.86 ~ 2.43 |
| 黄绿 Yellow green | 黄、绿和黄绿色Yellow,green,yellowish green | 11 | 10.2 | 69.40 ~ 79.49 | -21.71 ~ -12.32 | 41.20 ~ 74.50 | 45.78 ~ 75.51 | 99.39 ~ 115.83 | 0.51 ~ 0.60 |
| 紫红 Purple red | 暗紫红、深棕红、 深蓝紫色 Dark purplish red, deep brownish red, deep bluish purple | 9 | 8.4 | 14.30 ~ 36.30 | 5.41 ~ 23.13 | -9.62 ~ 2.90 | 5.53 ~ 23.31 | -45.29 ~ 8.09 | 3.24 ~ 8.19 |
| 浅紫 Light purple | 浅紫色、浅红紫色 Light purple, light reddish purple | 17 | 15.9 | 42.00 ~ 66.25 | 20.23 ~ 39.16 | -27.54 ~-13.09 | 24.32 ~ 47.87 | -37.17 ~-28.28 | 2.13 ~ 3.10 |
| 紫 Purple | 紫、红紫色 Purple, reddish purple | 8 | 7.5 | 24.06 ~ 46.49 | 48.47 ~ 56.99 | -34.37 ~-23.83 | 58.47 ~ 65.45 | -34.14 ~-24.05 | 2.02 ~ 2.47 |
| 深紫 Deep purple | 深紫色、深红紫色 Deep purple, deep reddish purple | 26 | 24.3 | 14.01 ~ 39.70 | 21.12 ~ 47.21 | -27.97 ~-0.28 | 26.88 ~ 52.40 | -43.95 ~-0.48 | 2.46 ~ 4.17 |
| 复色 Multicolor | 存在明显两种或以上颜色 More than two distinct colors | 16 | 15.0 | 31.72 ~ 83.17 | -19.13 ~ 52.36 | -32.12 ~ 52.73 | 3.99 ~ 61.42 | -70.06 ~ 16.36 | 0.45 ~ 3.10 |
Table 1 Classification of flower color phenotype of 107 Dendrobium hybrid cultivars
| 色系 Color group | 颜色描述 Color description | 品种数 Number | % | CIELab表色系统 CIELab coordinate | 颜色指 数CIRG | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 明度L* | 红度a* | 黄度b* | 彩度C | 色相角h | |||||
| 白 White | 白、淡粉白、淡紫白色 White,pale pinkish white,pale purplish white | 16 | 15.0 | 71.68 ~ 87.08 | -13.05 ~ 2.65 | -2.88 ~ 24.64 | 1.41 ~ 27.50 | -47.38 ~ 143.71 | 0.40 ~ 2.67 |
| 粉 Pink | 浅粉色 Light pink | 4 | 3.7 | 65.55 ~ 74.60 | 6.52 ~ 26.54 | -0.60 ~ 3.42 | 6.54 ~ 26.63 | -5.23 ~ 9.38 | 1.86 ~ 2.43 |
| 黄绿 Yellow green | 黄、绿和黄绿色Yellow,green,yellowish green | 11 | 10.2 | 69.40 ~ 79.49 | -21.71 ~ -12.32 | 41.20 ~ 74.50 | 45.78 ~ 75.51 | 99.39 ~ 115.83 | 0.51 ~ 0.60 |
| 紫红 Purple red | 暗紫红、深棕红、 深蓝紫色 Dark purplish red, deep brownish red, deep bluish purple | 9 | 8.4 | 14.30 ~ 36.30 | 5.41 ~ 23.13 | -9.62 ~ 2.90 | 5.53 ~ 23.31 | -45.29 ~ 8.09 | 3.24 ~ 8.19 |
| 浅紫 Light purple | 浅紫色、浅红紫色 Light purple, light reddish purple | 17 | 15.9 | 42.00 ~ 66.25 | 20.23 ~ 39.16 | -27.54 ~-13.09 | 24.32 ~ 47.87 | -37.17 ~-28.28 | 2.13 ~ 3.10 |
| 紫 Purple | 紫、红紫色 Purple, reddish purple | 8 | 7.5 | 24.06 ~ 46.49 | 48.47 ~ 56.99 | -34.37 ~-23.83 | 58.47 ~ 65.45 | -34.14 ~-24.05 | 2.02 ~ 2.47 |
| 深紫 Deep purple | 深紫色、深红紫色 Deep purple, deep reddish purple | 26 | 24.3 | 14.01 ~ 39.70 | 21.12 ~ 47.21 | -27.97 ~-0.28 | 26.88 ~ 52.40 | -43.95 ~-0.48 | 2.46 ~ 4.17 |
| 复色 Multicolor | 存在明显两种或以上颜色 More than two distinct colors | 16 | 15.0 | 31.72 ~ 83.17 | -19.13 ~ 52.36 | -32.12 ~ 52.73 | 3.99 ~ 61.42 | -70.06 ~ 16.36 | 0.45 ~ 3.10 |
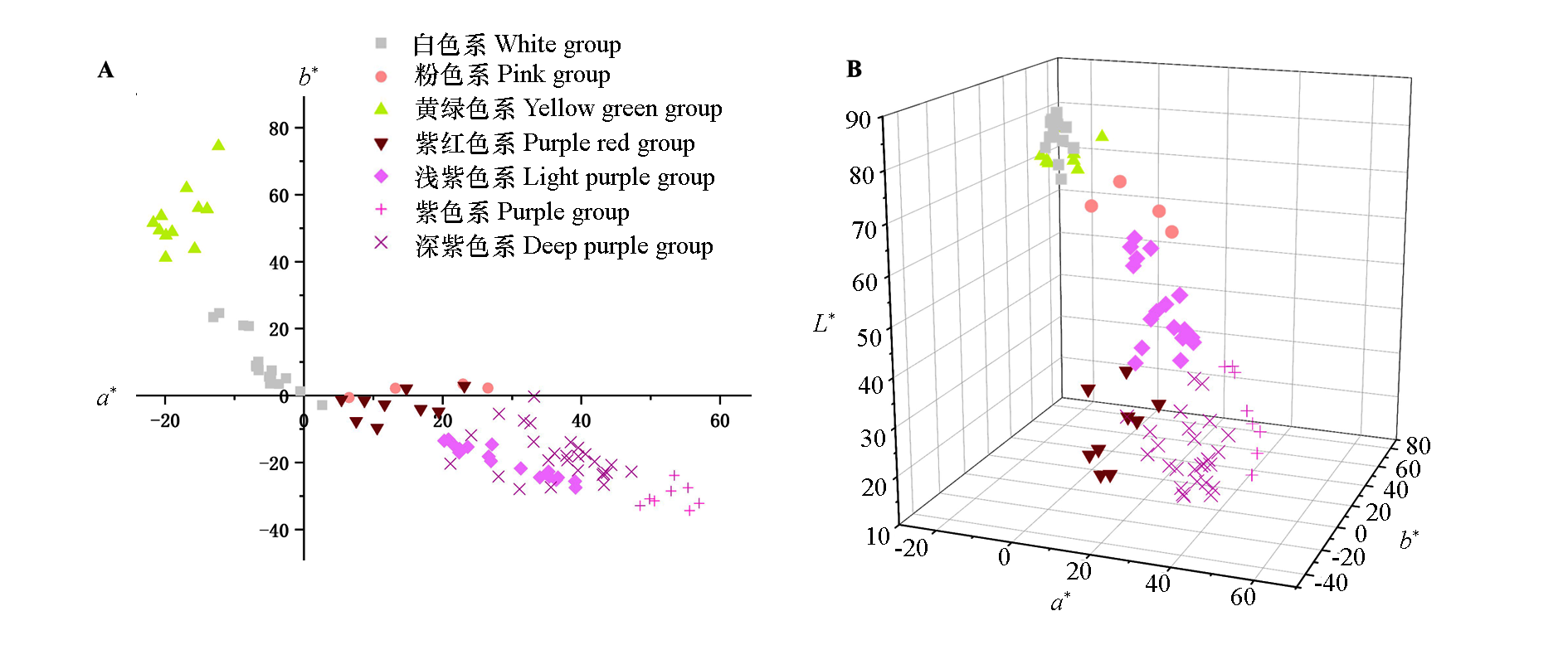
Fig. 2 Flower color distribution of Dendrobium hybrid cultivars A:Two-dimensional distribution diagram of a* and b* value;B:Three-dimensional distribution diagram of L*,a*and b* value.
| 器官 Organ | 明度 L* | 红度 a* | 黄度 b* | 彩度 C | 色相角 h | 颜色指数 CIRG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 花瓣 Petal | 49.47** | 19.47 | -3.61 | 34.80 | 15.54 | 2.36 |
| 唇瓣 Labellum | 44.28 | 20.31 | -4.95 | 32.62 | 10.31 | 2.69** |
Table 2 Flower color difference of Dendrobium hybrids between petal and labellum
| 器官 Organ | 明度 L* | 红度 a* | 黄度 b* | 彩度 C | 色相角 h | 颜色指数 CIRG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 花瓣 Petal | 49.47** | 19.47 | -3.61 | 34.80 | 15.54 | 2.36 |
| 唇瓣 Labellum | 44.28 | 20.31 | -4.95 | 32.62 | 10.31 | 2.69** |

Fig. 3 Distribution pattern of pigments in flowers of dendrobium In figures N,a:Upper epidermis;e:Lower epidermis;b:Upper palisade tissue;d:Lower palisade tissue;c:Spongy tissue.
| 序号 Code | 分布模式 Patterns | 品种数(%) Number(%) | 明度 L* | 红度 a* | 黄度 b* | 彩度 C* | 色相角 h | 颜色指数 CIRG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | abcde,abcd,abde,bcde | 18(25.0) | 24.54 ± 7.02cC | 26.34 ± 14.29aA | -10.18 ± 9.77bB | 29.04 ± 15.84aA | -19.49 ± 15.8bB | 4.27 ± 1.80aA |
| Ⅱ | abc,abd, abe,bcd | 14(19.4) | 46.67 ± 17.89bB | 27.33 ± 20.42aA | -14.52±18.48bB | 37.93 ± 15.51aA | -10.50 ± 53.9bB | 2.37 ± 0.86bAB |
| Ⅲ | ab,bc, be,b | 19(26.4) | 61.20 ± 13.19bAB | 19.48 ± 14.36aA | -7.71±14.12bB | 25.73 ± 13.04aA | 3.47 ± 57.53bB | 2.09 ± 0.76bB |
| Ⅳ | 21(29.2) | 78.18 ± 6.13aA | -11.92 ± 6.84bB | 29.11 ± 22.27aA | 31.69 ± 22.96aA | 118.05 ± 10.11aA | 0.57 ± 0.07cC |
Table 3 Patterns of anthocyanins in petals and effect on flower color phenotype of 72 Dendrobium hybrid cultivars
| 序号 Code | 分布模式 Patterns | 品种数(%) Number(%) | 明度 L* | 红度 a* | 黄度 b* | 彩度 C* | 色相角 h | 颜色指数 CIRG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | abcde,abcd,abde,bcde | 18(25.0) | 24.54 ± 7.02cC | 26.34 ± 14.29aA | -10.18 ± 9.77bB | 29.04 ± 15.84aA | -19.49 ± 15.8bB | 4.27 ± 1.80aA |
| Ⅱ | abc,abd, abe,bcd | 14(19.4) | 46.67 ± 17.89bB | 27.33 ± 20.42aA | -14.52±18.48bB | 37.93 ± 15.51aA | -10.50 ± 53.9bB | 2.37 ± 0.86bAB |
| Ⅲ | ab,bc, be,b | 19(26.4) | 61.20 ± 13.19bAB | 19.48 ± 14.36aA | -7.71±14.12bB | 25.73 ± 13.04aA | 3.47 ± 57.53bB | 2.09 ± 0.76bB |
| Ⅳ | 21(29.2) | 78.18 ± 6.13aA | -11.92 ± 6.84bB | 29.11 ± 22.27aA | 31.69 ± 22.96aA | 118.05 ± 10.11aA | 0.57 ± 0.07cC |

Fig. 4 Different epidermal cell types in flowers of Dendrobium hybrids a:Flat cells;b:Domed epidermal cells;c:Elongated dome cells;d:Papillate cells;e:Epidermal hair cells.
| 器官 Organ | 部位 Position | 细胞形态Cells shape | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高/μm Height | 宽/μm Width | 高宽比Height/width | 夹角/°Included angle | ||
| 花瓣 Petal | 上表皮 Upper epidermis | 28.19**(5.91 ~ 59.57) | 56.47(37.21 ~ 78.50) | 0.49**(0.13 ~ 0.93) | 74.81(30.12 ~ 140.38) |
| 下表皮 Lower epidermis | 15.97(5.27 ~ 31.18) | 58.80*(31.08 ~ 90.01) | 0.27(0.09 ~ 0.48) | 110.66**(62.97 ~ 148.41) | |
| 唇瓣 Labellum | 上表皮 Upper epidermis | 30.35**(9.57 ~ 52.05) | 50.65(31.40 ~ 71.94) | 0.60**(0.20 ~ 1.05) | 64.82(20.05 ~ 122.69) |
| 下表皮 Lower epidermis | 14.34(7.20 ~ 30.86) | 53.05(36.24 ~ 80.54) | 0.27(0.12 ~ 0.67) | 112.49**(64.07 ~ 151.52) | |
Table 4 Difference of upper and lower epidermal cells shape between petal and labellum of 72 Dendrobium hybrid cultivars
| 器官 Organ | 部位 Position | 细胞形态Cells shape | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高/μm Height | 宽/μm Width | 高宽比Height/width | 夹角/°Included angle | ||
| 花瓣 Petal | 上表皮 Upper epidermis | 28.19**(5.91 ~ 59.57) | 56.47(37.21 ~ 78.50) | 0.49**(0.13 ~ 0.93) | 74.81(30.12 ~ 140.38) |
| 下表皮 Lower epidermis | 15.97(5.27 ~ 31.18) | 58.80*(31.08 ~ 90.01) | 0.27(0.09 ~ 0.48) | 110.66**(62.97 ~ 148.41) | |
| 唇瓣 Labellum | 上表皮 Upper epidermis | 30.35**(9.57 ~ 52.05) | 50.65(31.40 ~ 71.94) | 0.60**(0.20 ~ 1.05) | 64.82(20.05 ~ 122.69) |
| 下表皮 Lower epidermis | 14.34(7.20 ~ 30.86) | 53.05(36.24 ~ 80.54) | 0.27(0.12 ~ 0.67) | 112.49**(64.07 ~ 151.52) | |

Fig. 5 Correlation between petal epidermal cells and color phenotype of Dendrobium hybrids in different patterns of anthocyanins * indicate the significant difference,P < 0.05;** indicate the extremely significant difference,P < 0.01.
| 器官 Organ | 部位 Position | 类胡萝卜素 Carotenoids | 细胞形态Cells shape | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高/μm Height | 宽/μm Width | 高宽比 Height/width | 夹角/° Included angle | |||
| 花瓣Petal | 上表皮Upper epidermis | 有 Yes | 16.65 | 49.78 | 0.33 | 98.21** |
| 无 No | 32.03** | 58.70** | 0.55** | 67.01 | ||
| 下表皮Lower epidermis | 有 Yes | 10.16 | 52.13 | 0.20 | 123.16** | |
| 无 No | 17.91** | 61.03** | 0.29** | 106.49 | ||
| 唇瓣Labellum | 上表皮Upper epidermis | 有 Yes | 23.42 | 45.59 | 0.51 | 75.83* |
| 无 No | 32.66** | 52.00** | 0.64** | 61.15 | ||
| 下表皮Lower epidermis | 有 Yes | 11.87 | 52.14 | 0.23 | 118.70 | |
| 无 No | 15.16** | 53.35 | 0.29* | 110.42 | ||
Table 5 Differences of epidermal cells shape between two groups containing carotenoids in petal and labellum
| 器官 Organ | 部位 Position | 类胡萝卜素 Carotenoids | 细胞形态Cells shape | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高/μm Height | 宽/μm Width | 高宽比 Height/width | 夹角/° Included angle | |||
| 花瓣Petal | 上表皮Upper epidermis | 有 Yes | 16.65 | 49.78 | 0.33 | 98.21** |
| 无 No | 32.03** | 58.70** | 0.55** | 67.01 | ||
| 下表皮Lower epidermis | 有 Yes | 10.16 | 52.13 | 0.20 | 123.16** | |
| 无 No | 17.91** | 61.03** | 0.29** | 106.49 | ||
| 唇瓣Labellum | 上表皮Upper epidermis | 有 Yes | 23.42 | 45.59 | 0.51 | 75.83* |
| 无 No | 32.66** | 52.00** | 0.64** | 61.15 | ||
| 下表皮Lower epidermis | 有 Yes | 11.87 | 52.14 | 0.23 | 118.70 | |
| 无 No | 15.16** | 53.35 | 0.29* | 110.42 | ||
| [1] | Bai Xin-xiang. 2007. Phenotype analysis of flower coloration of Chrysanthemum × morifolium Ramat[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Beijing:Beijing Forestry University.(in Chinese) |
| 白新祥. 2007. 菊花花色形成的表型分析[博士论文]. 北京: 北京林业大学. | |
| [2] | Christensen K I, Hansen H V. 1998. Sem-studies of epidermal patterns of petals in the angiosperms. Opera Botanica,(135):5-87. |
| [3] | Fu Jing, Liu Lin-zi, Dai Si-lan. 2016. The anatomic observation on Ray flowers of different color Chrysanthemum varieties//Advances in Ornamental Horticulture of China. Beijing: China Foestry Publishing House:110-117.(in Chinese) |
| 伏静, 刘琳子, 戴思兰. 2016. 不同花色菊花品种舌状花解剖结构观察//中国观赏园艺研究进展. 北京: 中国林业出版社:110-117. | |
| [4] |
Gorton H L, Vogelmann T C. 1996. Effects of epidermal cell shape and pigmentation on optical properties of Antirrhinum petals at visible and ultraviolet wavelengths. Plant Physiology, 112 (3):879-888.
pmid: 12226425 |
| [5] |
Hong Y, Yang L W, Li M L, Dai S L. 2016. Comparative analyses of light-induced anthocyanin accumulation and gene expression between the ray florets and leaves in chrysanthemum. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 103:120-132.
doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.03.006 pmid: 26990403 |
| [6] | Hong Yan, Bai Xin-xiang, Sun Wei, Jia Feng-wei, Dai Si-lan. 2012. The numerical classification of chrysanthemum flower color phenotype. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 39 (7):1330-1340.(in Chinese) |
| 洪艳, 白新祥, 孙卫, 贾锋炜, 戴思兰. 2012. 菊花品种花色表型数量分类研究. 园艺学报, 39 (7):1330-1340. | |
| [7] | Jia Ni. 2008. Studies on petal coloration mechanism and chemotaxonomy of herbaceous peony[M. D. Dissertation]. Beijing: the Chinese Academy of Sciences.(in Chinese) |
| 贾妮. 2008. 芍药花色形成的化学机制及其化学分类研究[硕士论文]. 北京: 中国科学院. | |
| [8] |
Kallam K, Appelhagen I, Luo J, Albert N, Zhang H B, Deroles S, Hill L, Findlay K, Andersen M, Davies K, Martin C. 2017. Aromatic decoration determines the formation of anthocyanic vacuolar inclusions. Current Biology, 27 (7):945.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2017.02.027 URL |
| [9] | Kanchit T. 1984. Flower pigments in yellow Dendrobium species and hybrids[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Honolulu:University of Hawaii,HI,USA. |
| [10] |
Kuehnle A R, Lewis D H, Markham K R, Mitchell K A, Davies K M, Jordan B R. 1997. Floral flavonoids and pH in Dendrobium orchid species and hybrids. Euphytica, 95 (2):187-194.
doi: 10.1023/A:1002945632713 URL |
| [11] |
Lei T, Song Y, Jin X H, Su T Y, Pu Y W. 2017. Effects of pigment constituents and their distribution on spathe coloration of Zantedeschia hybrida. HortScience, 52 (12):1840-1848.
doi: 10.21273/HORTSCI12229-17 URL |
| [12] | Li Chong-hui, Ren Yu, Huang Su-rong, Huang Shao-hua, Yang Guang-sui. 2013. Floral colors of Phalaenopsis type dendrobium and their flavonoid composition. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 40 (1):107-116.(in Chinese) |
| 李崇晖, 任羽, 黄素荣, 黄少华, 杨光穗. 2013. 蝴蝶石斛兰花色表型及类黄酮成分分析. 园艺学报, 40 (1):107-116. | |
| [13] |
Li Chong-hui, Yin Jun-mei. 2019. Genetic engineering progress and breeding tactics on blue flowers. Biotechnology Bulletin, 35 (11):160-168.(in Chinese)
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2019-0450 |
|
李崇晖, 尹俊梅. 2019. 蓝色花形成的基因工程进展与育种策略. 生物技术通报, 35 (11):160-168.
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2019-0450 |
|
| [14] | Liao Yi. 2018. Cultivation and maintenance of Dendrobium. China Flowers & Horticulture,(24):28-30. |
| 廖易. 2018. 秋石斛栽培与养护. 中国花卉园艺,(24):28-30. | |
| [15] | Lin Deng-gui, Zeng Li, Pei Feng, Peng Yong-zheng, Wang Peng, Wang Ge, Liu Xiao-cong, Dili Da-er. 2015. Anatomical structures of vegetative organs and ray floret in Tagetes erecta L. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University(Agricultural Science), 33 (4):59-64.(in Chinese) |
| 林登贵, 曾丽, 裴峰, 彭勇政, 王鹏, 王戈, 刘晓丛, 迪力达尔. 2015. 万寿菊营养器官及舌状花解剖结构的研究. 上海交通大学学报(农业科学版), 33 (4):59-64. | |
| [16] | Liu Yi-ping, Wu Fang-fang, He Dan, Zhuang Yuan, Kong De-zheng. 2020. Numerical classification of lotus cultivars based on flower color phenotype. Journal of Zhejiang University(Agric & Life Sci), 46 (3):319-326.(in Chinese) |
| 刘艺平, 吴芳芳, 贺丹, 庄苑, 孔德政. 2020. 基于花色表型的荷花品种数量分类. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 46 (3):319-326. | |
| [17] | Lü Xiao-fan, Zhou Xin-hong, Wang Ying, Wu Ya-ni. 2021. Component analysis of Dendrobium phalaenopsis anthocyanin extract and its antioxidant activity and irritation in vitro. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 29 (4):374-381.(in Chinese) |
| 吕晓帆, 周新红, 王莹, 吴亚妮. 2021. 秋石斛花青素提取液成分分析及其体外抗氧化活性和刺激性研究. 热带亚热带植物学报, 29 (4):374-381. | |
| [18] |
Markham K R, Gould K S, Winefield C S, Mitchell K A, Bloor S J, Boase M R. 2000. Anthocyanic vacuolar inclusions - their nature and significance in flower colouration. Phytochemistry, 55 (4):327-336.
pmid: 11117881 |
| [19] |
Martin C, Glover B J. 2007. Functional aspects of cell patterning in aerial epidermis. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 10 (1):70-82.
doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2006.11.004 URL |
| [20] |
Mudalige R G, Kuehnle A R, Amore T D. 2003. Pigment distribution and epidermal cell shape in Dendrobium species and hybrids. HortScience, 38 (4):573-577.
doi: 10.21273/HORTSCI.38.4.573 URL |
| [21] |
Noda K I, Glover B J, Linstead P, Martin C. 1994. Flower colour intensity depends on specialized cell shape controlled by a MYB-related transcription factor. Nature, 369 (6482):661.
doi: 10.1038/369661a0 URL |
| [22] | Pan Li-jing, Cao You-pei, Xiao Yang, Fan Gan-qun, Chen Wei-ting. 2009. Review of research on breeding technology of Dendrobium. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences,(9):71-73.(in Chinese) |
| 潘丽晶, 曹友培, 肖杨, 范干群, 陈伟庭. 2009. 观赏石斛育种技术研究综述. 广东农业科学,(9):71-73. | |
| [23] |
Robert C P, Catherine J S. 1980. Occurrence,location and development of anthocyanoplasts. Phytochemistry, 19 (12):2571-2576.
doi: 10.1016/S0031-9422(00)83921-7 URL |
| [24] | Rolle L, Guidoni S. 2007. Color and anthocyanin evaluation of red winegrapes by CIE L*,a*,b* parameters. Journal International Des Sciences De La Vigne Et Du Vin, 41 (4):193-201. |
| [25] |
Wang L S, Shiraishi A, Hashimoto F, Aoki N, Shimizu K, Sakata Y. 2001. Analysis of petal anthocyanins to investigate flower coloration of Zhongyuan(Chinese)and Daikon Island(Japanese)tree peony cultivars. Journal of Plant Research, 114 (1):33-43.
doi: 10.1007/PL00013966 URL |
| [26] | Wang Sa, Zhang Yang, Li Yu-hua. 2012. Research progress on the mechanism of petal conical epidermal cells formation and attraction to pollinating insects. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 39 (9):1781-1792.(in Chinese) |
| 王卅, 张旸, 李玉花. 2012. 花瓣锥形表皮细胞形成及对授粉昆虫吸引作用机制研究进展. 园艺学报, 39 (9):1781-1792. | |
| [27] | Wang Yu-jiao, Gao Lan, Yang Yong, Yu Xiao-nan. 2018. Numerical classification of peony cultivars based on flower color phenotype. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 40 (7):96-103.(in Chinese) |
| 王玉蛟, 高岚, 杨勇, 于晓南. 2018. 基于花色表型的芍药品种数量分类研究. 北京林业大学学报, 40 (7):96-103. | |
| [28] |
Whitney H M, Bennett K M V, Dorling M, Sandbach L, Prince D, Chittka L, Glover B J. 2011. Why do so many petals have conical epidermal cells? Annals of Botany, 108 (4):609.
doi: 10.1093/aob/mcr065 URL |
| [29] |
Whitney H M, Chittka L, Bruce T J A, Glover B J. 2009. Conical epidermal cells allow bees to grip flowers and increase foraging efficiency. Current Biology, 19 (11):948-953.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2009.04.051 URL |
| [30] | Wu Fang-fang, Miao Run-tian, Wang An-yin, Li Xiao-kang, He Dan, Zhang Man. 2021. Numerical classification of tree peony and herbaceous peony cultivars based on flower color phenotype. Northern Horticulture,(3):66-75.(in Chinese) |
| 吴芳芳, 苗润田, 汪安印, 李小康, 贺丹, 张曼. 2021. 基于花色表型的牡丹和芍药品种数量分类研究. 北方园艺,(3):66-75. | |
| [31] | Wu Jing, Cheng Fang-yun, Zhong Yuan. 2016. The numerical classification of flower color phenotype in flare tree peony. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 43 (5):947-956.(in Chinese) |
| 吴静, 成仿云, 钟原. 2016. 紫斑牡丹花色表型数量分类研究. 园艺学报, 43 (5):947-956. | |
| [32] | Wu Yan-mei, Wu Yi-ping, Jin Xue-hua, Meng-han . 2020. Effects of anthocyanin composition and distribution on flower color of Rieger Begonia. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 40 (1):58-68.(in Chinese) |
| 吴艳梅, 吴艺萍, 金雪花, 孟晗. 2020. 丽格海棠花青素苷成分及分布对花色的影响. 西北植物学报, 40 (1):58-68. | |
| [33] |
Yang R Z, Wei X L, Gao F F, Wang L S, Zhang H J, Xu Y J, Li C H, Ge Y X, Zhang J J, Jie Z. 2009. Simultaneous analysis of anthocyanins and flavonols in petals of lotus(Nelumbo)cultivars by high-performance liquid chromatography-photodiode array detection/electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 1216 (1):106-112.
doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2008.11.046 URL |
| [34] | Yi Shuang-shuang, Li Chong-hui, Yang Guang-sui, Nui Jun-hai. 2018. Classification study on the flower color phenotype in anthurium. Northern Horticulture,(16):105-111.(in Chinese) |
| 易双双, 李崇晖, 杨光穗, 牛俊海. 2018. 红掌花色表型分类研究. 北方园艺,(16):105-111. | |
| [35] | Yue Juan. 2013. Phenotype observation and anatomic structure resrarch of petals from the monocotyledons blue flower[M. D. Dissertation]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University.(in Chinese) |
| 岳娟. 2013. 单子叶植物蓝色花花瓣表型观察与解剖结构研究[硕士论文]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学. | |
| [36] |
Zhang Y, Sun T X, Xie L N, Hayashi T, Kawabata S, Li Y H. 2015. Relationship between the velvet-like texture of flower petals and light reflection from epidermal cell surfaces. Journal of Plant Research, 128 (4):623-632.
doi: 10.1007/s10265-015-0725-8 pmid: 25912473 |
| [37] | Zhao Chang-ling, Zhang Li-mei, Liu Fu-cui. 2008. Existent states of anthocyanins in vacuole and their coloration effects in higher plants. Guihaia,(3):395-401.(in Chinese) |
| 赵昶灵, 张丽梅, 刘福翠. 2008. 高等植物花色苷在液泡中的存在状态及其着色效应. 广西植物,(3):395-401. |
| [1] | ZOU Xue, DING Fan, LIU Lifang, YU Hankaizong, CHEN Nianwei, and RAO Liping. A New Purple Potato Cultivar‘Mianziyu 1’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S1): 93-94. |
| [2] | WANG Sha, ZHANG Xinhui, ZHAO Yujie, LI Bianbian, ZHAO Xueqing, SHEN Yu, DONG Jianmei, YUAN Zhaohe. Cloning and Functional Analysis of PgMYB111 Related to Anthocyanin Synthesis in Pomegranate [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(9): 1883-1894. |
| [3] | HUANG Ling, HU Xianmei, LIANG Zehui, WANG Yanping, CHAN Zhulong, XIANG Lin. Cloning and Function Identification of Anthocyanidin Synthase Gene TgANS in Tulipa gesneriana [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(9): 1935-1944. |
| [4] | LI Maofu, YANG Yuan, WANG Hua, FAN Youwei, SUN Pei, JIN Wanmei. Analysis the Function of R2R3 MYB Transcription Factor RhMYB113c on Regulating Anthocyanin Synthesis in Rosa hybrida [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(9): 1957-1966. |
| [5] | YANG Xiuwei, SU Jiangshuo, ZHANG Fei, GUAN Zhiyong, FANG Weimin, CHEN Fadi. Quantitative Evaluation and Genetic Variation of Flower Opening Angles in Spray Cut Chrysanthemums [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1723-1734. |
| [6] | QIAN Jieyu, JIANG Lingli, ZHENG Gang, CHEN Jiahong, LAI Wuhao, XU Menghan, FU Jianxin, ZHANG Chao. Identification and Expression Analysis of MYB Transcription Factors Regulating the Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Zinnia elegans and Function Research of ZeMYB9 [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1505-1518. |
| [7] | ZHANG Lugang, LU Qianqian, HE Qiong, XUE Yihua, MA Xiaomin, MA Shuai, NIE Shanshan, YANG Wenjing. Creation of Novel Germplasm of Purple-orange Heading Chinese Cabbage [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1582-1588. |
| [8] | CHEN Daozong, LIU Yi, SHEN Wenjie, ZHU Bo, TAN Chen. Identification and Analysis of PAP1/2 Homologous Genes in Brassica rapa,B. oleracea and B. napus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1301-1312. |
| [9] | ZHANG Meng, SHAN Yuying, YANG Yebo, ZHAI Feifei, WANG Zhaoshan, JU Guansheng, SUN Zhenyuan, LI Zhenjian. AFLP Analysis of Genetic Resources of Dendrobium from China [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1339-1350. |
| [10] | LI Xiaoming, YU Junchi, WANG Chunxia. Comparison of Growth and Secondary Metabolites of Purple and White Flower Dracocephalum moldavica Under Field,Greenhouse and Greenhouse Shading Conditions [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1363-1370. |
| [11] | LI Lixian, WANG Shuo, CHEN Ying, WU Yingtao, WANG Yaqian, FANG Yue, CHEN Xuesen, TIAN Changping, FENG Shouqian. PavMYB10.1 Promotes Anthocyanin Accumulation by Positively Regulating PavRiant in Sweet Cherry [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(5): 1023-1030. |
| [12] | ZHOU Xuzixin, YANG Wei, MAO Meiqin, XUE Yanbin, MA Jun. Identification of Pigment Components and Key Genes in Carotenoid Pathway in Mutants of Chimeric Ananas comosus var. bracteatus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(5): 1081-1091. |
| [13] | HE Jingjuan, FAN Yanping. Progress in Composition and Metabolic Regulation of Carotenoids Related to Floral Color [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(5): 1162-1172. |
| [14] | SHEN Zhiguo, ZHANG Lin, YUAN Deyi, CHENG Jianming. Research Progress on Flower Color and New Red Flower Resource of Wintersweets(Chimonanthus praecox) [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(4): 924-934. |
| [15] | WANG Jing, XU Leifeng, WANG Ling, QI Xianyu, SONG Meng, CAO Yuwei, HE Guoren, TANG Yuchao, YANG Panpan, MING Jun. The Numerical Classification of Flower Color Phenotype in Lily [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(3): 571-580. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd