
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 671-692.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0355
程小改, 万源, 林琭*( ), 谢鹏, 李志强, 李谧, 王鹏鹏, 牛自勉
), 谢鹏, 李志强, 李谧, 王鹏鹏, 牛自勉
收稿日期:2024-10-14
修回日期:2025-01-17
出版日期:2025-03-25
发布日期:2025-03-25
通讯作者:
基金资助:
CHENG Xiaogai, WAN Yuan, LIN Lu*( ), XIE Peng, LI Zhiqiang, LI Mi, WANG Pengpeng, NIU Zimian
), XIE Peng, LI Zhiqiang, LI Mi, WANG Pengpeng, NIU Zimian
Received:2024-10-14
Revised:2025-01-17
Published:2025-03-25
Online:2025-03-25
摘要:
以36年生、不同树干高度(对照0.8 ~ 1.0 m、低干1.2 ~ 1.5 m、中干1.5 ~ 1.8 m、高干1.8 ~ 2.1 m)的开心树形‘长富2号’苹果树为试材,研究树干高度对不同冠层部位叶片光合特性及果实品质的影响。结果表明:(1)冠层不同部位(1.5 m高处的东侧、西侧、内膛和2.5 m高处的内膛)均为高干的光合有效辐射(PAR)最高,分别比对照提高132.47%、178.29%、113.7%和32.37%。(2)与中干、低干和对照相比,高干叶片Pn-PAR响应的最大净光合速率以及光响应特征参数光饱和点、可利用光强范围和表观量子效率等均显著提高;与对照相比,高干和中干叶片的最大电子传递速率和磷酸丙糖利用速率显著提高。(3)光能捕获效率、光系统Ⅱ的实际光化学效率和光化学淬灭系数在各处理的外围(东侧)和内膛间均有显著差异且高干最高,非光化学淬灭在外围(东侧)各处理之间表现为高干、中干、低干均显著低于对照,内膛差异不显著。(4)1.5 m和2.5 m两个高度处,高干冠层各部位的单果质量和色度值a均显著高于对照;在2.5 m高度的东侧和西侧,高干可溶性固形物和固酸比显著高于对照,而果实酸度则显著低于对照;果皮叶绿素含量在不同部位间均表现为高干显著低于对照;果皮花色苷、总酚和总黄酮含量以及自由基清除能力总体上表现为东侧>西侧>内膛,其中高干东侧显著高于对照东侧。综上,苹果开心树形不同树干高度的叶片光合特性及果实品质在在冠层内呈现明显的空间异质性;高干叶片的光合速率、光合能力及光能利用效率均较强,因而果实综合品质(尤其是东侧)得到显著提升。
程小改, 万源, 林琭, 谢鹏, 李志强, 李谧, 王鹏鹏, 牛自勉. 苹果开心树形树干高度对不同冠层部位叶片光合特性及果实品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 671-692.
CHENG Xiaogai, WAN Yuan, LIN Lu, XIE Peng, LI Zhiqiang, LI Mi, WANG Pengpeng, NIU Zimian. Influences of Trunk Heights on Leaf Photosynthesis and Fruit Qualities at Different Canopy Locations in Open-Central Canopy of Apple[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(3): 671-692.
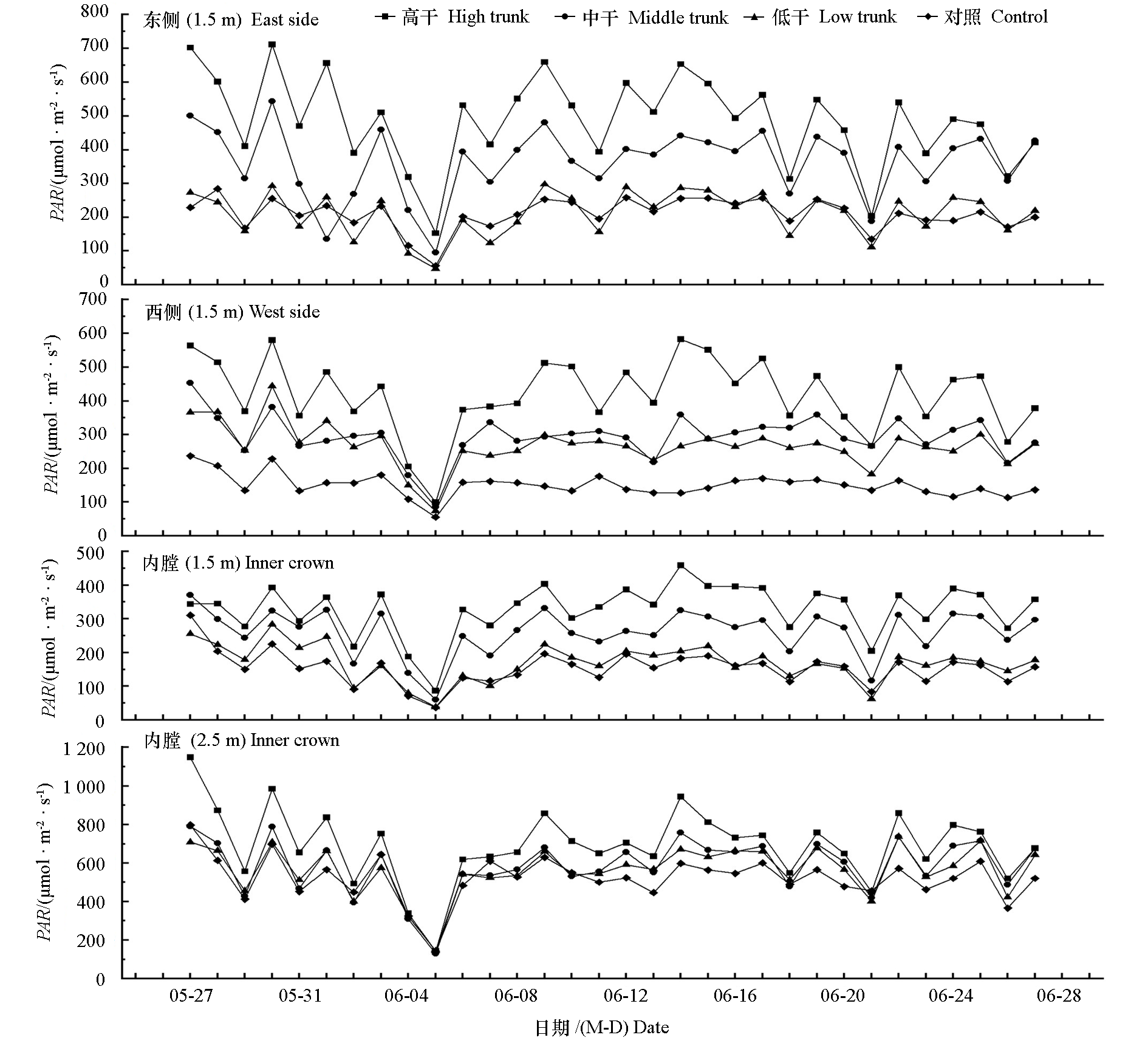
图1 开心树形不同树干高度的冠层部位光合有效辐射(PAR)日均值变化
Fig. 1 Changes in daily means of photosynthetically active radiation(PAR)at different canopy locations in open-central canopy with different trunk heights
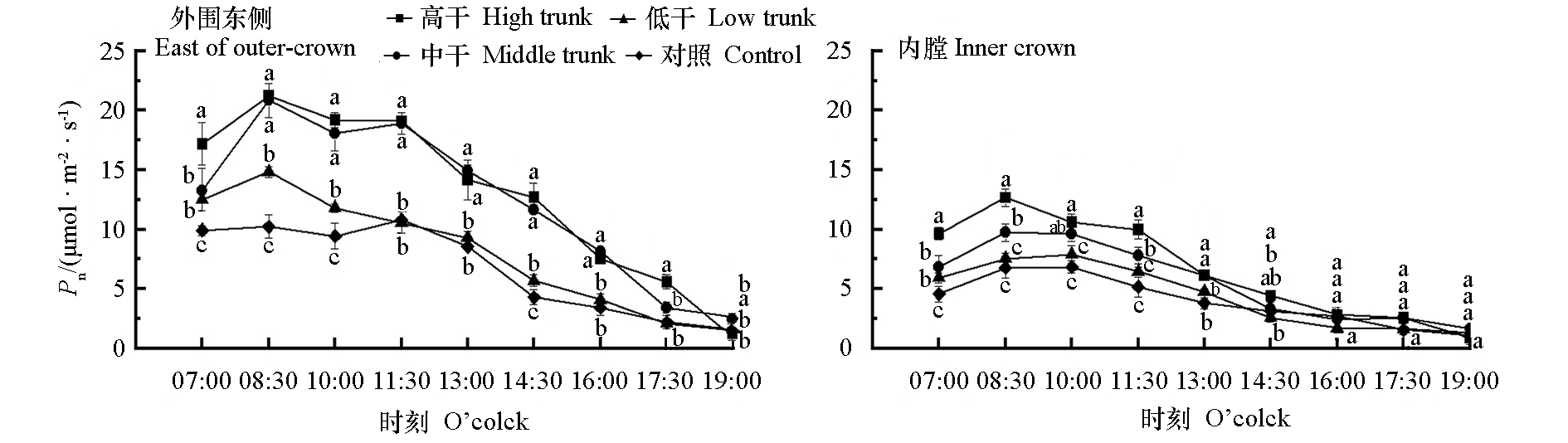
图2 开心树形不同树干高度的冠层部位叶片净光合速率(Pn)日变化 不同小写字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同
Fig. 2 Diurnal changes of leaf net photosynthetic rate(Pn)at different canopy locations in open-central canopy with different trunk heights The different lowercase letters indicate significant differences(P < 0.05). The same below

图3 开心树形不同树干高度及冠层部位叶片净光合速率(Pn)、气孔导度(Gs)、胞间CO2浓度(Ci)和瞬时蒸腾速率(Tr)的光响应曲线
Fig. 3 Light response curves of leaf net photosynthetic rate(Pn),stomatal conductance(Gs),intercellular CO2 concentration(Ci)and instantaneous transpiration rate(Tr)at different canopy locations in open-central canopy with different trunk heights

图4 开心树形不同树干高度及冠层部位叶片Pn-PAR响应曲线的特征参数差异 Amax:最大净光合速率;AQE:表观量子效率;LSP:光饱和点;LCP:光补偿点;LUR:可利用光强范围;Rd:暗呼吸速率
Fig. 4 Differences of characteristic parameters derived from Pn-PAR response curves at different canopy locations in open-central canopy with different trunk heights Amax:Maximum net photosynthetic rate;AQE:Apparent quantum efficiency;LSP:Light saturation point;LCP:Light compensation point;LUR:Light utilization range;Rd:Dark respiration rate

图5 开心树形不同树干高度及冠层部位的叶片净光合速率(Pn)对胞间CO2浓度(Ci)的响应曲线
Fig. 5 Response curves of leaf net photosynthetic rate(Pn)to intercellular CO2 concentration(Ci)at different canopy locations in open-central canopy with different trunk heights
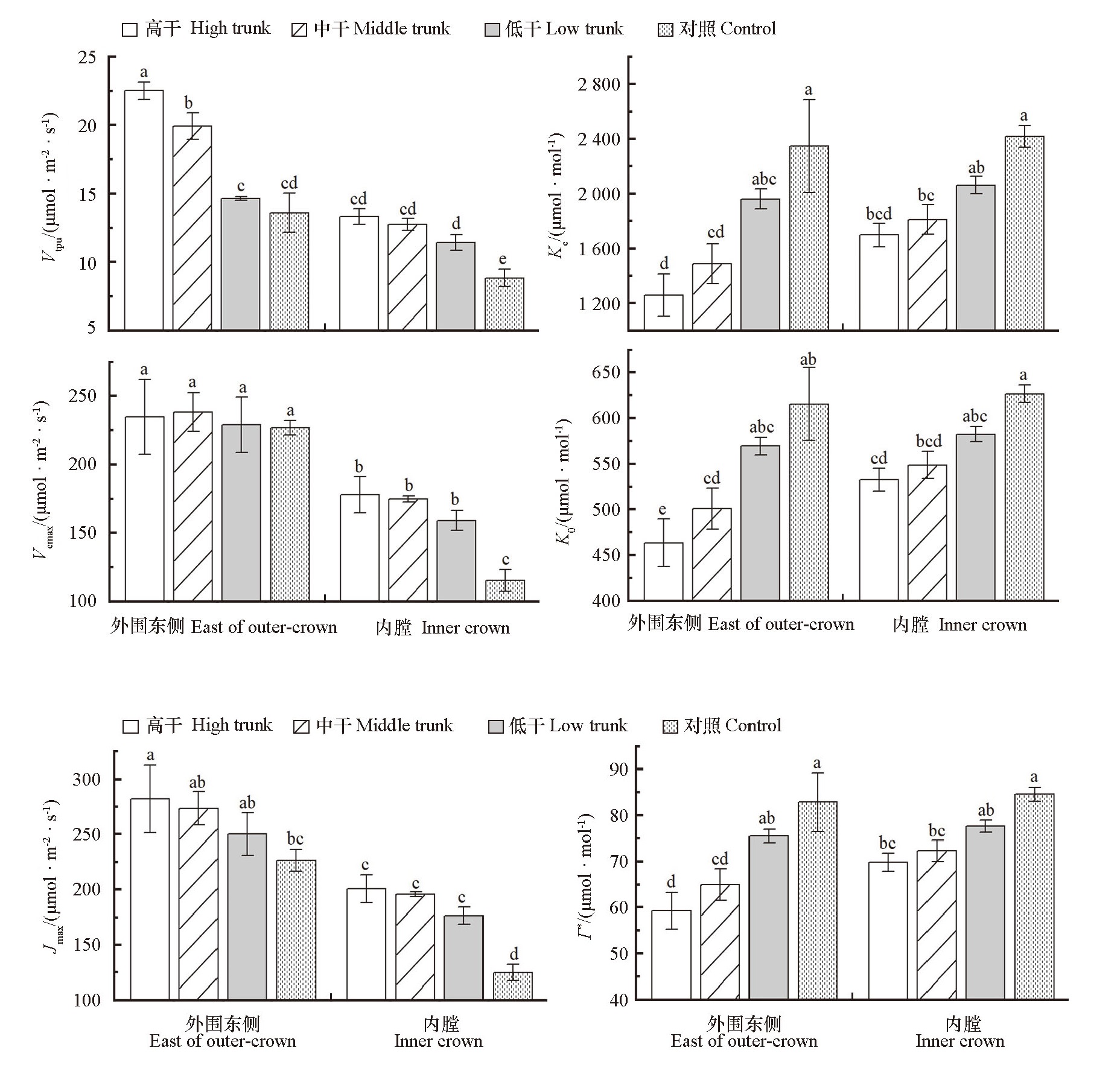
图6 开心树形不同树干高度及冠层部位的叶片Pn-Ci响应曲线特征参数差异 Vcmax-Rubisco酶活性限制下的最大羧化速率,Jmax-饱和光强下的最大电子传递速率,Vtpu-磷酸丙糖利用速率,Kc-Rubisco对CO2的米氏常数,Ko-Rubisco对O2的米氏常数,Γ*-光下暗呼吸的CO2补偿点
Fig.6 Differences of characteristic parameters derived from Pn-Ci response curves at different canopy locations in open-central canopy with different trunk heights Vcmax-maximum carboxylation rate under the restriction of Rubisco,Jmax-maximum rate of electron transfer under light saturation,Vtpu-supplying rate of triose phosphate,Kc-Michaelis constant of Rubisco to CO2,Ko-Michaelis constant of Rubisco to O2,Γ*-CO2 compensation point of dark respiration under light

图7 开心树形不同树干高度及冠层部位的叶片荧光淬灭动力学曲线
Fig. 7 Kinetics curves of Fv′/Fm′,qP,NPQ and ΦPSII during the process of fluorescence quenching at different canopy locations in open-central canopy with different trunk heights

图8 开心树形不同树干高度及冠层部位的果实外观品质差异
Fig. 8 Differences in appearance qualities of fruits at different canopy locations in open-central canopy with different trunk heights

图9 开心树形不同树干高度及冠层不同部位的果皮色度值差异
Fig. 9 Differences in chromatic value of peels at different canopy locations in open-central canopy with different trunk heights
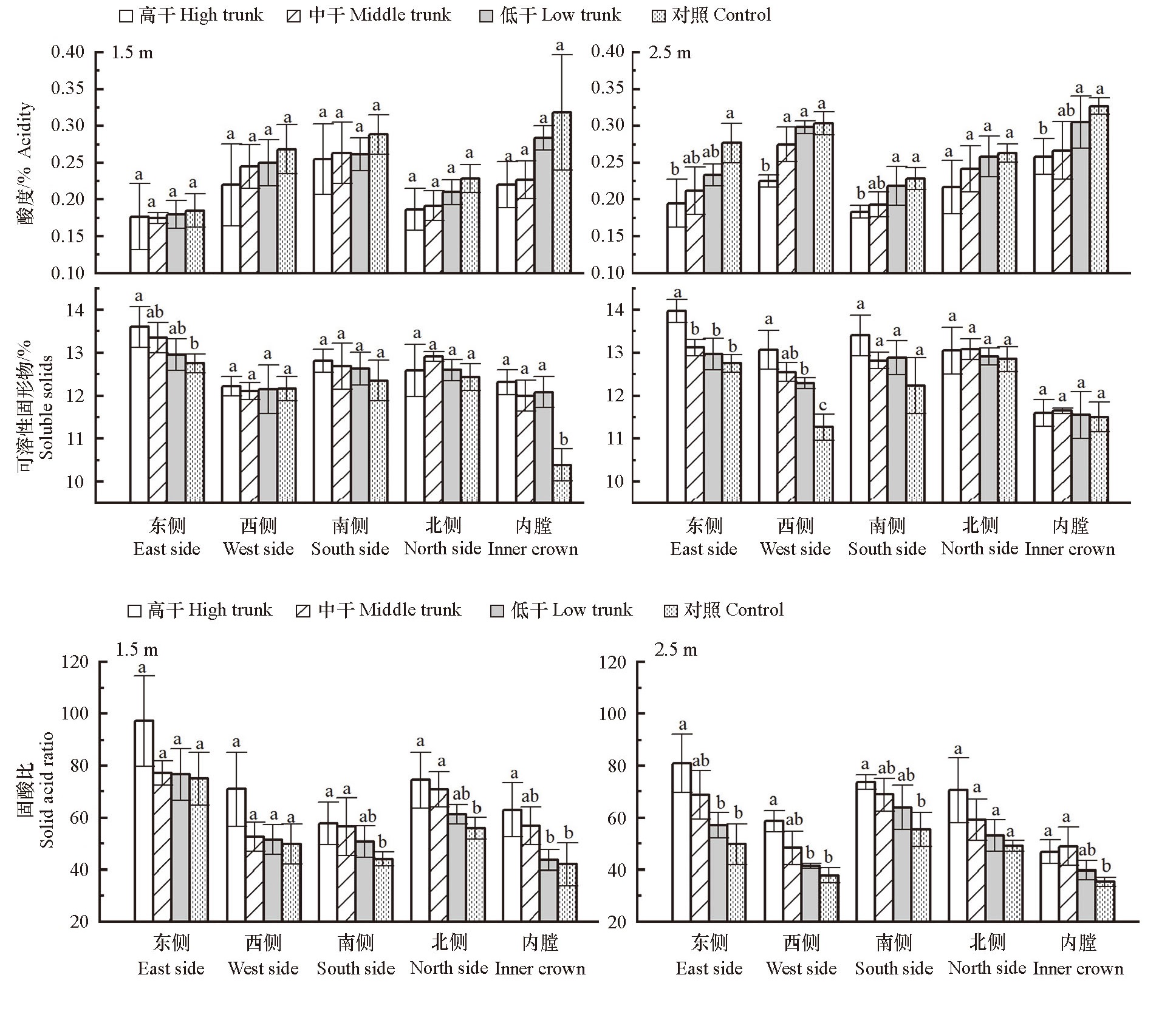
图11 开心树形不同树干高度及冠层不同部位果实内在品质差异
Fig. 11 Differences in internal qualities of fruits at different canopy locations in open-central canopy with different trunk heights.

图12 开心树形不同树干高度及冠层不同部位的果皮色素含量差异
Fig. 12 Differences of pigment content in peel at different canopy locations in open-central canopy with different trunk heights

图13 开心树形不同树干高度及冠层不同部位果皮和果肉的总酚和总黄酮含量差异 GAE:没食子酸当量;RE:芦丁当量
Fig. 13 Differences in contents of total phenols and total flavonoids in peel and flesh at different canopy locations in open-central canopy with different trunk heights. GAE:Gallic acid equivalent;RE:Rutin equivalent

图14 开心树形不同树干高度及冠层不同部位的果皮和果肉的抗氧化能力差异 TE:水溶性维生素E当量
Fig. 14 Differences in antioxidant capacity of peel and flesh at different canopy locations in open-central canopy with different trunk heights TE:Trolox E quivalent
| [1] |
|
|
安佰义, 谷娜, 刘晓嘉, 张艳波, 宋宏伟, 李锋. 2019. 不同树形对李树冠层结构和光合特性的影响. 北方园艺,(3):29-35.
|
|
| [2] |
|
|
白岗栓, 杜社妮, 王建平. 2021. 陕北山地苹果树形改造研究. 中国农业大学学报, 26 (12):54-66.
|
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.17.00904 pmid: 29018097 |
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
|
高方胜, 王明友, 潘恩敬, 苏荣存. 2011. 红富士苹果不同树形冠层光照参数与果实品质产量关系的研究. 中国果树,(1):14-17.
|
|
| [10] |
|
|
高照全, 赵晨霞, 李志强, 张显川. 2013. 我国4种主要苹果树形光合能力差异研究. 中国生态农业学报, 21 (7):853-859.
|
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2017.09.019 |
|
胡德玉, 刘雪峰, 何绍兰, 谢让金, 钱春, 吕强, 易时来, 郑永强, 邓烈. 2017. 郁闭柑橘园整形改造对植株冠层生理特性、产量和果实品质的影响. 中国农业科学, 50 (9):1734-1746.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2017.09.019 |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
|
贾浩, 郝建博, 曹洪波, 韩艳, 李丹, 陈海江. 2015. 遮荫对‘保佳红’桃树叶片快速叶绿素荧光诱导动力学曲线的影响. 西北植物学报, 35 (9):1861-1867.
|
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
|
林琭, 李志强, 蔚露, 王红宁, 牛自勉. 2020a. 苹果两种树形叶片对光强和CO2浓度互作的光合响应及光抑制特性. 园艺学报, 47 (11):2073-2085.
|
|
| [20] |
pmid: 26710629 |
|
林琭, 汤昀, 张纪涛, 闫万丽, 肖建红, 丁超, 董川, 籍增顺. 2015. 不同水势对黄瓜花后叶片气体交换及叶绿素荧光参数的影响. 应用生态学报, 26 (7):2030-2040.
pmid: 26710629 |
|
| [21] |
|
|
林琭, 蔚露, 王红宁, 牛自勉, 谢鹏. 2020b. 冠层结构对梨叶片光合特性及果实品质的影响. 西北植物学报, 40 (7):1180-1191.
|
|
| [22] |
pmid: 14759845 |
| [23] |
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202011.030 |
|
牛军强, 孙文泰, 董铁, 尹晓宁, 刘兴禄, 马明. 2020. 间伐改形对陇东高原密闭富士苹果园冠层微域环境及叶片生理特性的影响. 应用生态学报, 31 (11):3681-3690.
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202011.030 |
|
| [24] |
|
|
牛自勉, 孙俊宝, 蔚露, 郭爱珍, 王建新. 2011. 树干高度对苹果开心形树产量及品质的影响. 山西农业科学, 39 (10):1067-1069,1091.
|
|
| [25] |
|
|
牛自勉, 蔚露, 谢鹏, 韩苹苹, 李全. 2015. 干高对梨树开心树形产量与品质的影响. 山西农业科学, 43 (10):1272-1275.
|
|
| [26] |
|
|
牛自勉, 蔚露, 张文和. 2012. 开心树形叶幕结构对苹果园地面太阳辐射的影响. 山西农业科学, 40 (11):1164-1168.
|
|
| [27] |
pmid: 26915197 |
|
屈振江, 尚小宁, 王景红, 梁轶, 高峰, 杨芳. 2015. 黄土高原两种树形苹果园花期温度垂直变化特征及预测. 应用生态学报,(11):3405-3412.
pmid: 26915197 |
|
| [28] |
doi: 10.1093/treephys/tps020 pmid: 22491489 |
| [29] |
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2011.18.011 |
|
阮班录, 刘建海, 李雪薇, 李丙智, 韩明玉, 张林森, 周永博. 2011. 乔砧苹果郁闭园不同改造方法对冠层光照和叶片状况及产量品质的影响. 中国农业科学, 44 (18):3805-3811.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2011.18.011 |
|
| [30] |
|
|
苏渤海, 范崇辉, 李国栋, 张军科, 韩明玉. 2008. 红富士苹果改形过程中不同树形光照分布及其对产量品质的影响. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 36 (1):158-162.
|
|
| [31] |
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.201809.026 |
|
孙文泰, 牛军强, 董铁, 刘兴禄, 尹晓宁, 马明. 2018. 间伐改形对陇东旱塬密闭苹果园树体冠层结构和发育后期叶片质量的影响. 应用生态学报, 29 (9):3008-3016.
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.201809.026 |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
|
王建新, 牛自勉, 李志强, 郭爱萍, 高慧卿. 2011. 乔砧富士苹果不同冠形相对光照强度的差异及对果实品质的影响. 果树学报, 28 (1):8-14.
|
|
| [35] |
|
|
王文军, 陈奇凌, 郑强卿, 王晶晶, 王振东. 2021. 不同树形对灰枣叶片光合及叶绿素荧光特性的影响. 新疆农业科学, 58 (4):616-624.
doi: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2021.04.004 |
|
| [36] |
|
|
王琰, 范崇辉, 江道伟, 李丙智, 杜荣. 2011. 苹果不同树形树冠特性和果实品质的比较. 西北农业学报, 20 (12):93-97.
|
|
| [37] |
|
|
魏钦平, 鲁韧强, 张显川, 王小伟, 高照全, 刘军. 2004. 富士苹果高干开心形光照分布与产量品质的关系研究. 园艺学报, 31 (3):291-296.
|
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
|
闫小莉, 王德炉. 2014. 遮荫对苦丁茶树叶片特征及光合特性的影响. 生态学报, 34 (13):3538-3547.
|
|
| [41] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2019-0146 URL |
|
蔚露, 牛自勉, 林琭, 姜闯道, 王红宁, 谢鹏, 李志强, 郭晋鸣. 2020. 小冠开心形和细型主干形‘玉露香’梨光能截获与光合作用差异. 园艺学报, 47 (1):11-22.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2019-0146 URL |
|
| [42] |
|
|
蔚露, 牛自勉, 林琭, 谢鹏, 李小平. 2017. 树干高度对苹果开心形叶幕PPFD与UV的影响. 山西农业科学, 45 (11):1755-1759.
|
|
| [43] |
|
|
张显川, 高照全, 付占方, 方建辉, 李天红. 2007. 苹果树形改造对树冠结构和冠层光合能力的影响. 园艺学报, 34 (3):537-542.
|
|
| [44] |
|
|
张显川, 高照全, 舒先迂, 魏钦平. 2005. 苹果开心形树冠不同部位光合与蒸腾能力的研究. 园艺学报, 42 (6):975-979.
|
|
| [45] |
|
| [1] | 李敖, 郑旭, 吴承勖, 聂瑞宁, 姬新颖, 唐佳莉, 张俊佩. 丛枝菌根真菌对盐胁迫下核桃幼苗生长及生理的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 423-438. |
| [2] | 史兴秀, 冯贝贝, 闫鹏, 耿文娟, 朱玛孜拉·沙尔山木汗. ‘王林’苹果早期水心病发生过程中的相关生理变化[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 171-184. |
| [3] | 张松彦, 迭鹏翔, 宋梦婷, 李志坚, 周建. 烟草过表达刺槐RpACBP3对光合生理的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2155-2167. |
| [4] | 邱辉, 朱德娟, 张永乐, 高玉洁, 李柳, 王国平, 洪霓. ACLSV外壳蛋白与梨两种E3泛素连接酶互作及亚细胞定位[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1715-1727. |
| [5] | 刘英浩, 李允, 吕伟静, 陈冉, 姜伟涛, 尹承苗, 毛志泉, 王艳芳. 不同温度烧制的生物炭对苹果连作土壤真菌群落结构的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1853-1867. |
| [6] | 李旭娇, 吕齐, 姚东东, 赵丰云, 王小非, 于坤. ‘烟富3’苹果不同砧木嫁接对其15N–尿素吸收利用的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1868-1880. |
| [7] | 田雯, 李子琛, 王霖, 王大江, 王昆, 孙思邈, 王广艺, 刘昭, 路翔, 冯建荣, 高源. 苹果重要性状全基因组关联分析研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1565-1579. |
| [8] | 刘成龙, 范旭东, 任芳, 张尊平, 胡国君, 董雅凤. 苹果病毒检测技术[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1580-1594. |
| [9] | 覃艮红, 袁洪波, 王卓妮, 史冰柯, 范洋洋, 王丽, 张猛, 涂洪涛, 徐超, 侯珲. 蜡样芽孢杆菌挥发物对苹果轮纹病菌的拮抗活性[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1403-1412. |
| [10] | 史冰柯, 王卓妮, 覃艮红, 黄天祥, 王丽, 涂洪涛, 袁洪波, 侯珲. 苹果轮纹病拮抗真菌Pa2的分离与鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1113-1125. |
| [11] | 夏宏义, 刘巧, 彭家清, 吴伟, 龚林忠. ‘阳光玫瑰’葡萄避雨栽培f式树形对光合及果实品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 560-570. |
| [12] | 高永臣, 苏新建, 余城, 刘铸, 毛柯, 邹养军, 龚小庆. 苹果树盘地布和药渣覆盖对土壤理化性质和细菌群落的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 587-600. |
| [13] | 孙权, 何政辰, 叶俊丽, 魏冉冉, 尹映紫, 柴利军, 谢宗周, 徐强, 徐娟, 郭文武, 程运江, 邓秀新. 与呼吸跃变型果实共贮藏改善柑橘果实色泽和品质[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 601-615. |
| [14] | 杨江山, 陈亚娟, 戴子博, 李斗, 邵璋, 金鑫, 王宇航, 王春恒. 黄腐酸钾对‘蛇龙珠’葡萄光合特性及果实品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(12): 2843-2856. |
| [15] | 林琭, 蔚露, 谢鹏, 李志强, 王红宁, 赵国平, 牛自勉. 矮化中间砧SC1对苹果光合特性及果实品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(12): 2871-2885. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司