
园艺学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (11): 2540-2554.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0395
王荣波1, 王海云2, 张前荣3, 蔡松龄1, 李本金1, 张美祥4, 刘裴清1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-05-28
修回日期:2024-09-08
出版日期:2024-12-12
发布日期:2024-11-25
通讯作者:
基金资助:
WANG Rongbo1, WANG Haiyun2, ZHANG Qianrong3, CAI Songling1, LI Benjin1, ZHANG Meixiang4, LIU Peiqing1,*( )
)
Received:2024-05-28
Revised:2024-09-08
Published:2024-12-12
Online:2024-11-25
摘要:
2021—2022年,从中国福建省5个主要番茄种植区分离得到62株青枯病菌株(Ralstonia solanacearum)。通过演化型特异性多重聚合酶链式反应(phylotype-specific multiplex polymerase chain reaction,Pmx-PCR)、生理小种和生化型的鉴定,发现所有菌株均属于演化型Ⅰ和生理小种1,其中61株为生化型Ⅲ,1株为非典型生化型。基于egl基因部分序列的系统发育分析进一步将演化型Ⅰ细分为序列变种14、15、16、17和34,其中序列变种15是主要优势变种。对13个番茄砧木品种进行了青枯菌抗性评估,结果显示,不同砧木品种对不同序列变种的青枯菌表现出明显的抗性差异,‘桂砧1号’和‘威尔神根’对福建省的优势菌系表现出广谱抗性。
王荣波, 王海云, 张前荣, 蔡松龄, 李本金, 张美祥, 刘裴清. 福建省番茄青枯病菌遗传多样性分析及其抗性砧木的筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(11): 2540-2554.
WANG Rongbo, WANG Haiyun, ZHANG Qianrong, CAI Songling, LI Benjin, ZHANG Meixiang, LIU Peiqing. Genetic Diversity of Ralstonia solanacearum Strains Isolated from Fujian Province and Evaluation of Tomato Rootstocks for Resistance to Bacterial Wilt[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(11): 2540-2554.
| 用途 Application | 材料 Material | 来源 Source |
|---|---|---|
| 番茄砧木 Tomato rootstock | 桂砧1号 Guizhen 1 | 广西南宁赛绿农业科技有限公司 Guangxi Nanning Sailü Agricultural Technology Co., Ltd. |
| 丽砧1号 Lizhen 1 | 大连市北蔬农业有限公司 Dalian Beishu Agriculture Co.,Ltd. | |
| 强力 Qiangli | 山东寿光市春秋种业总经销 Shandong Shouguang Spring and Autumn Seed Industry general distributor | |
| 朗达240 Langda 240 | 北京君川种业科技有限公司 Beijing Junchuan Seed Technology Co.,Ltd. | |
| 威尔神根 Weier Shengen | 山东威尔种子有限公司 Shandong Weier Seed Co.,Ltd. | |
| 番茄砧木6号 Tomato rootstock 6 | 以色列尼瑞特种业有限公司 Israel Nirait Seed Industry Co.,Ltd. | |
| 番茄砧木405 Tomato rootstock 405 | 上海惠和种业有限公司 Shanghai Huihe Seed Industry Co.,Ltd. | |
| 乾德番砧 Qiande tomato rootstock | 上海乾德种业有限公司 Shanghai Qiande Seed Industry Co.,Ltd. | |
| 浙砧1号 Zhezhen 1 | 浙江依农种业有限公司 Zhejiang Yinong Seed Industry Co.,Ltd. | |
| 番茄、茄子两用砧木 Tomato and eggplant rootstock | 西茄砧木Xiqie rootstock | 北京络芙特科贸有限公司 Beijing Luofute Science and Trade Co.,Ltd. |
| 亚拉 Yala | 贵州络芙特生物科技有限公司 Guizhou Lofute Biotechnology Co.,Ltd. | |
| 多用砧木Multipurpose rootstock | 大力神砧木F1 Dalishen rootstock F1 | 寿光市宏伟种业有限公司 Shouguang Hongwei Seed Industry Co.,Ltd. |
| 茄子砧木 Eggplant rootstock | 京丰808 Jingfeng 808 | 山东威尔种子有限公司 Shandong Weier Seed Co.,Ltd. |
表1 供试砧木
Table 1 Experimental rootstock
| 用途 Application | 材料 Material | 来源 Source |
|---|---|---|
| 番茄砧木 Tomato rootstock | 桂砧1号 Guizhen 1 | 广西南宁赛绿农业科技有限公司 Guangxi Nanning Sailü Agricultural Technology Co., Ltd. |
| 丽砧1号 Lizhen 1 | 大连市北蔬农业有限公司 Dalian Beishu Agriculture Co.,Ltd. | |
| 强力 Qiangli | 山东寿光市春秋种业总经销 Shandong Shouguang Spring and Autumn Seed Industry general distributor | |
| 朗达240 Langda 240 | 北京君川种业科技有限公司 Beijing Junchuan Seed Technology Co.,Ltd. | |
| 威尔神根 Weier Shengen | 山东威尔种子有限公司 Shandong Weier Seed Co.,Ltd. | |
| 番茄砧木6号 Tomato rootstock 6 | 以色列尼瑞特种业有限公司 Israel Nirait Seed Industry Co.,Ltd. | |
| 番茄砧木405 Tomato rootstock 405 | 上海惠和种业有限公司 Shanghai Huihe Seed Industry Co.,Ltd. | |
| 乾德番砧 Qiande tomato rootstock | 上海乾德种业有限公司 Shanghai Qiande Seed Industry Co.,Ltd. | |
| 浙砧1号 Zhezhen 1 | 浙江依农种业有限公司 Zhejiang Yinong Seed Industry Co.,Ltd. | |
| 番茄、茄子两用砧木 Tomato and eggplant rootstock | 西茄砧木Xiqie rootstock | 北京络芙特科贸有限公司 Beijing Luofute Science and Trade Co.,Ltd. |
| 亚拉 Yala | 贵州络芙特生物科技有限公司 Guizhou Lofute Biotechnology Co.,Ltd. | |
| 多用砧木Multipurpose rootstock | 大力神砧木F1 Dalishen rootstock F1 | 寿光市宏伟种业有限公司 Shouguang Hongwei Seed Industry Co.,Ltd. |
| 茄子砧木 Eggplant rootstock | 京丰808 Jingfeng 808 | 山东威尔种子有限公司 Shandong Weier Seed Co.,Ltd. |
| 鉴定用途 Application | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence | 大小/bp Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| 青枯菌 Ralstonia solanacearum | AU759 | GTCGCCGTCAACTCACTTTCC | 281 |
| AU760 | GTCGCCGTCAGCAATGCGGAATCG | ||
| 演化型Ⅰ上游 Phylotype I-F | Nmult21:1F | CGTTGATGAGGCGCGCAATTT | 144 |
| 演化型Ⅱ上游 Phylotype Ⅱ-F | Nmult21:2F | AAGTTATGGACGGTGGAAGTC | 372 |
| 演化型Ⅲ上游 Phylotype Ⅲ-F | Nmult23:AF | ATTACAGAGCAATCGAAAGATT | 91 |
| 演化型Ⅳ上游 Phylotype Ⅳ-F | Nmult22:InF | ATTGCCAAGACGAGAGAAGTA | 213 |
| 演化型下游 Phylotype-R | Nmult22:RR | TCGCTTGACCCTATAACGAGTA | |
| 生理小种1 Race 1 | PS-IS | F:CGCAACGCTGGATGAACCC;R:CAGACGATGCGAAGCCTGAC | 1 070 |
| 生理小种2 Race 2 | ISRso19 | F:TGGGAGAGGATGGCGGCTTT;R:TGACCCGCCTTTCGGTGTTT | 1 884 |
| 生理小种4 Race 4 | 21 | F:CGACGCTGACGAAGGGACTC;R:CTGACACGGCAAGCGCTCA | 125 |
| egl | Endo | F:ATGCATGCCGCTGGTCGCCGC;R:GCGTTGCCCGGCACGAACACC | 698 |
表2 本试验中的PCR扩增引物
Table 2 List of primers used in this study
| 鉴定用途 Application | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence | 大小/bp Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| 青枯菌 Ralstonia solanacearum | AU759 | GTCGCCGTCAACTCACTTTCC | 281 |
| AU760 | GTCGCCGTCAGCAATGCGGAATCG | ||
| 演化型Ⅰ上游 Phylotype I-F | Nmult21:1F | CGTTGATGAGGCGCGCAATTT | 144 |
| 演化型Ⅱ上游 Phylotype Ⅱ-F | Nmult21:2F | AAGTTATGGACGGTGGAAGTC | 372 |
| 演化型Ⅲ上游 Phylotype Ⅲ-F | Nmult23:AF | ATTACAGAGCAATCGAAAGATT | 91 |
| 演化型Ⅳ上游 Phylotype Ⅳ-F | Nmult22:InF | ATTGCCAAGACGAGAGAAGTA | 213 |
| 演化型下游 Phylotype-R | Nmult22:RR | TCGCTTGACCCTATAACGAGTA | |
| 生理小种1 Race 1 | PS-IS | F:CGCAACGCTGGATGAACCC;R:CAGACGATGCGAAGCCTGAC | 1 070 |
| 生理小种2 Race 2 | ISRso19 | F:TGGGAGAGGATGGCGGCTTT;R:TGACCCGCCTTTCGGTGTTT | 1 884 |
| 生理小种4 Race 4 | 21 | F:CGACGCTGACGAAGGGACTC;R:CTGACACGGCAAGCGCTCA | 125 |
| egl | Endo | F:ATGCATGCCGCTGGTCGCCGC;R:GCGTTGCCCGGCACGAACACC | 698 |
| 生化型 Biovar | 乳糖 Lactose | 麦芽糖 Maltose | 纤维二糖 Cellobiose | 甘露醇 Mannitol | 山梨醇 Sorbitol | 甜醇 Dulcitol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Ⅱ | + | + | + | - | - | - |
| Ⅲ | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Ⅲ-1 | + | + | + | + | + | - |
| Ⅲ-2 | + | - | + | + | + | - |
| Ⅳ | - | - | - | + | + | + |
| Ⅴ | + | + | + | + | - | - |
表3 青枯菌生化型的划分标准
Table 3 Criteria for the classification of biovar of Ralstonia solanacearum
| 生化型 Biovar | 乳糖 Lactose | 麦芽糖 Maltose | 纤维二糖 Cellobiose | 甘露醇 Mannitol | 山梨醇 Sorbitol | 甜醇 Dulcitol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Ⅱ | + | + | + | - | - | - |
| Ⅲ | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Ⅲ-1 | + | + | + | + | + | - |
| Ⅲ-2 | + | - | + | + | + | - |
| Ⅳ | - | - | - | + | + | + |
| Ⅴ | + | + | + | + | - | - |
| 参考菌株 Reference strain | 寄主 Host | 来源 Origin | 演化型 Phylotype | 序列变种 Sequevar | egl登录号 Accession number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R288 | 桑树Morus alba L. | 中国 China | Ⅰ | 12 | GQ907153 |
| JT523 | 马铃薯 Solanum tuberosum L. | 留尼汪岛 Reunion Island | Ⅰ | 13 | AF295252 |
| PSS81 | 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum L. | 中国 China | Ⅰ | 14 | FJ561066 |
| PSS358 | 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum L. | 中国 China | Ⅰ | 15 | EU407298 |
| UW151 | 姜 Zingiber officinale Roscoe | 澳大利亚 Australia | Ⅰ | 16 | AF295254 |
| P11 | 花生 Arachis hypogaea L. | 中国 China | Ⅰ | 17 | FJ561068 |
| GMI1000 | 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum L. | 法国 France | Ⅰ | 18 | AF295251 |
| JT519 | 天竺葵 Pelargonium hortorum Bailey | 留尼汪岛 Reunion Island | Ⅰ | 31 | GU295032 |
| PSS219 | 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum L. | 中国 China | Ⅰ | 34 | FJ561167 |
| O3 | 橄榄树 Canarium album Rauesch | 中国 China | Ⅰ | 44 | FJ561069 |
| Tb28 | 烟草 Nicotiana tabacum L. | 中国 China | Ⅰ | 44 | FJ561127 |
| Tb43 | 烟草 Nicotiana tabacum L. | 中国 China | Ⅰ | 44 | FJ561129 |
| Bd11 | 木槿 Hibiscus syriacus L. | 中国 China | Ⅰ | 44 | FJ561098 |
| CIP365 | 马铃薯 Solanum tuberosum L. | 菲律宾 Philippines | Ⅰ | 45 | GQ907151 |
| MAD17 | 辣椒 Capsicum annuum L. | 马达加斯加 Madagascar | Ⅰ | 46 | GU295040 |
| GMI8254 | 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum L. | 印度尼西亚 Indonesia | Ⅰ | 47 | GU295014 |
| M2 | 桑树 Morus alba L. | 中国 China | Ⅰ | 48 | FJ561067 |
| CMR87 | 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum L. | 喀麦隆 Cameroon | Ⅱ | 35 | EF439727 |
| CMR121 | 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum L. | 喀麦隆 Cameroon | Ⅱ | 52 | EF439725 |
| CMR39 | 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum L. | 喀麦隆 Cameroon | Ⅱ | 41 | EF439726 |
| CFBP2972 | 马铃薯 Solanum tuberosum L. | 马提尼克 Martinique | Ⅱ | 35 | EF371809 |
| UW551 | 天竺葵 Pelargonium hortorum Bailey | 肯尼亚 Kenya | Ⅱ | 1 | DQ657596 |
| ICMP7963 | 马铃薯 Solanum tuberosum L. | 肯尼亚 Kenya | Ⅱ | 7 | AF295263 |
| UW162 | 香蕉 Musa nana Lour. | 秘鲁 Peru | Ⅱ | 4 | AF295256 |
| MOLK2 | 香蕉 Musa nana Lour. | 菲律宾Philippines | Ⅱ | 3 | EF371841 |
| CMR66 | 木龙葵 Solanum scabrum Mill. | 喀麦隆Cameroon | Ⅲ | 49 | EF439729 |
| JT525 | 天竺葵 Pelargonium hortorum Bailey | 留尼汪岛 Reunion Island | Ⅲ | 19 | AF295272 |
| CFBP3059 | 茄子 Solanum melongena L. | 布基纳法索The Burkina Faso | Ⅲ | 23 | AF295270 |
| NCPPB332 | 马铃薯 Solanum tuberosum L. | 津巴布韦 Zimbabwe | Ⅲ | 22 | DQ657649 |
| MAFF301558 | 马铃薯 Solanum tuberosum L. | 日本 Japan | Ⅳ | 8 | AY465002 |
| Psi7 | 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum L. | 印度尼西亚 Indonesia | Ⅳ | 10 | EF371804 |
| ACH732 | 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum L. | 澳大利亚 Australia | Ⅳ | 11 | GQ907150 |
表4 基于部分egl序列的系统发育分析中使用的青枯菌参考菌株
Table 4 Reference strains of R. solanacearum used in the phylogenetic study based on sequence variations of partial endoglucanase(egl)gene
| 参考菌株 Reference strain | 寄主 Host | 来源 Origin | 演化型 Phylotype | 序列变种 Sequevar | egl登录号 Accession number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R288 | 桑树Morus alba L. | 中国 China | Ⅰ | 12 | GQ907153 |
| JT523 | 马铃薯 Solanum tuberosum L. | 留尼汪岛 Reunion Island | Ⅰ | 13 | AF295252 |
| PSS81 | 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum L. | 中国 China | Ⅰ | 14 | FJ561066 |
| PSS358 | 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum L. | 中国 China | Ⅰ | 15 | EU407298 |
| UW151 | 姜 Zingiber officinale Roscoe | 澳大利亚 Australia | Ⅰ | 16 | AF295254 |
| P11 | 花生 Arachis hypogaea L. | 中国 China | Ⅰ | 17 | FJ561068 |
| GMI1000 | 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum L. | 法国 France | Ⅰ | 18 | AF295251 |
| JT519 | 天竺葵 Pelargonium hortorum Bailey | 留尼汪岛 Reunion Island | Ⅰ | 31 | GU295032 |
| PSS219 | 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum L. | 中国 China | Ⅰ | 34 | FJ561167 |
| O3 | 橄榄树 Canarium album Rauesch | 中国 China | Ⅰ | 44 | FJ561069 |
| Tb28 | 烟草 Nicotiana tabacum L. | 中国 China | Ⅰ | 44 | FJ561127 |
| Tb43 | 烟草 Nicotiana tabacum L. | 中国 China | Ⅰ | 44 | FJ561129 |
| Bd11 | 木槿 Hibiscus syriacus L. | 中国 China | Ⅰ | 44 | FJ561098 |
| CIP365 | 马铃薯 Solanum tuberosum L. | 菲律宾 Philippines | Ⅰ | 45 | GQ907151 |
| MAD17 | 辣椒 Capsicum annuum L. | 马达加斯加 Madagascar | Ⅰ | 46 | GU295040 |
| GMI8254 | 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum L. | 印度尼西亚 Indonesia | Ⅰ | 47 | GU295014 |
| M2 | 桑树 Morus alba L. | 中国 China | Ⅰ | 48 | FJ561067 |
| CMR87 | 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum L. | 喀麦隆 Cameroon | Ⅱ | 35 | EF439727 |
| CMR121 | 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum L. | 喀麦隆 Cameroon | Ⅱ | 52 | EF439725 |
| CMR39 | 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum L. | 喀麦隆 Cameroon | Ⅱ | 41 | EF439726 |
| CFBP2972 | 马铃薯 Solanum tuberosum L. | 马提尼克 Martinique | Ⅱ | 35 | EF371809 |
| UW551 | 天竺葵 Pelargonium hortorum Bailey | 肯尼亚 Kenya | Ⅱ | 1 | DQ657596 |
| ICMP7963 | 马铃薯 Solanum tuberosum L. | 肯尼亚 Kenya | Ⅱ | 7 | AF295263 |
| UW162 | 香蕉 Musa nana Lour. | 秘鲁 Peru | Ⅱ | 4 | AF295256 |
| MOLK2 | 香蕉 Musa nana Lour. | 菲律宾Philippines | Ⅱ | 3 | EF371841 |
| CMR66 | 木龙葵 Solanum scabrum Mill. | 喀麦隆Cameroon | Ⅲ | 49 | EF439729 |
| JT525 | 天竺葵 Pelargonium hortorum Bailey | 留尼汪岛 Reunion Island | Ⅲ | 19 | AF295272 |
| CFBP3059 | 茄子 Solanum melongena L. | 布基纳法索The Burkina Faso | Ⅲ | 23 | AF295270 |
| NCPPB332 | 马铃薯 Solanum tuberosum L. | 津巴布韦 Zimbabwe | Ⅲ | 22 | DQ657649 |
| MAFF301558 | 马铃薯 Solanum tuberosum L. | 日本 Japan | Ⅳ | 8 | AY465002 |
| Psi7 | 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum L. | 印度尼西亚 Indonesia | Ⅳ | 10 | EF371804 |
| ACH732 | 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum L. | 澳大利亚 Australia | Ⅳ | 11 | GQ907150 |

图1 番茄青枯病发病植株和维管束症状(A、B)、菌落形态(C)
Fig. 1 Disease symptoms of tomato plant and vascular infected with Ralstonia solanacearum(A,B),colony morphology of R. solanacearum isolates(C)
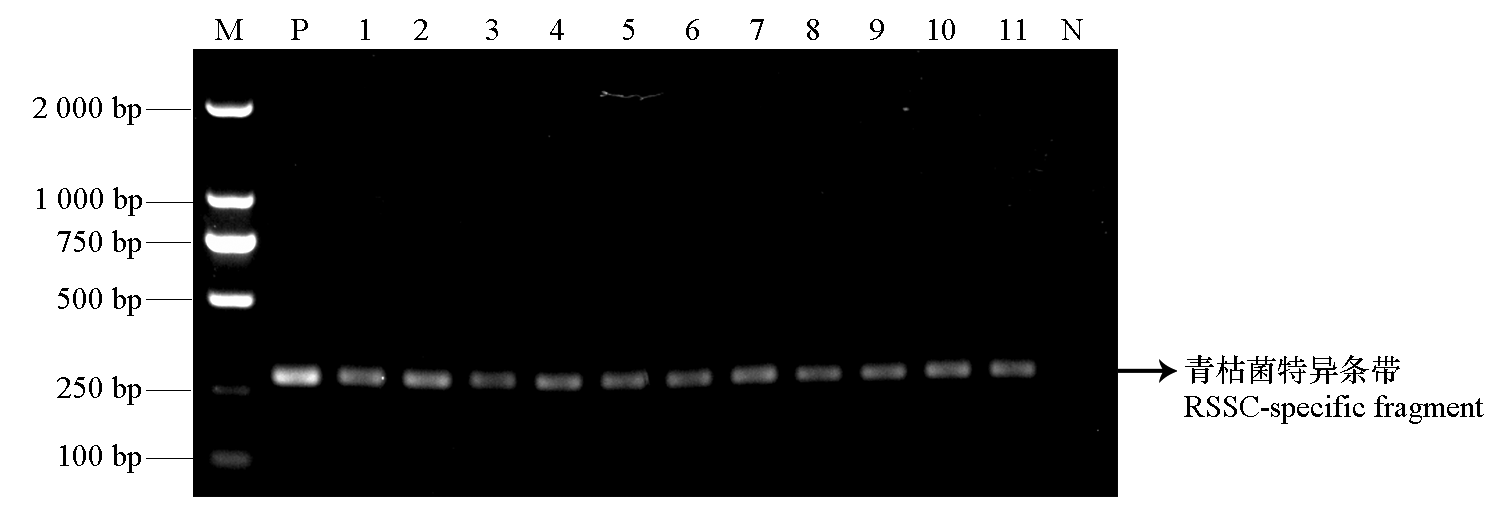
图2 病原菌特异性引物鉴定 M:DL2000 marker;1 ~ 11:福建番茄青枯菌代表菌株;P:阳性对照(GMI1000菌株);N:阴性对照。
Fig. 2 Identification of isolates with RSSC-specific primer M:DL2000 marker;1-11:Partial representative R. solanacearum isolates from Fujian;P:Positive control GMI1000 strain;N:Negative control.

图3 福建番茄青枯菌代表菌株(1 ~ 10)生理小种1、2、4特异性引物(A、B、C)PCR鉴定 M:DL2000 marker;P:阳性对照(生理小种1、3、4、5菌株GMI1000、Po41、Z-Aq-1和M6混合DNA);N:阴性对照。
Fig. 3 PCR detection of representative Ralstonia solanacearum strains(1-10)from Fujian by various race-specific primers of race 1,2 and 4 M:DL2000 marker;P:Positive control,a mixed sample consisting of strains GMI1000(race 1),Po41(race 3), Z-Aq-1(race 4)and M6(race 5);N:Negative control.
| 地点 Origin | 菌株 Strain | 生理小种 Race | 演化型 Phylotype | 序列变种 Sequevar | 生化型 Biovar | GenBank序列号 GenBank accession number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 福州市 | RS210523F | 1 | Ⅰ | 14 | Ⅲ | PP639179 |
| Fuzhou | RS210527F | 1 | Ⅰ | 14 | Ⅲ | PP639177 |
| RS210531F | 1 | Ⅰ | 14 | Ⅲ | PP639178 | |
| RS20220502F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639152 | |
| RS20220503F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639153 | |
| RS20220504F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639154 | |
| RS20220505FT | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639155 | |
| RS20220501F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639151 | |
| RS210507F | 1 | Ⅰ | 34 | Ⅲ | PP639142 | |
| RS210553FT | 1 | Ⅰ | 34 | Ⅲ | PP639143 | |
| RS210557F | 1 | Ⅰ | 34 | Ⅲ | PP639144 | |
| RS210561FT | 1 | Ⅰ | 34 | Ⅲ | PP639171 | |
| 宁德市 | RS202107129F | 1 | Ⅰ | 14 | Ⅲ | PP639182 |
| Ningde | RS202107131F | 1 | Ⅰ | 14 | Ⅲ | PP639183 |
| RS202107132F | 1 | Ⅰ | 14 | Ⅲ | PP639184 | |
| RS2107128F | 1 | Ⅰ | 14 | Ⅲ | PP639167 | |
| RS2107130F | 1 | Ⅰ | 14 | Ⅲ | PP639168 | |
| RS2107133F | 1 | Ⅰ | 14 | Ⅲ | PP639169 | |
| RS2107139F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639166 | |
| RS202107134F | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639185 | |
| RS202107137F | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639186 | |
| RS2107135F | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639170 | |
| RS2107136F | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639164 | |
| RS2107138F | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639165 | |
| 莆田市 | RS210599FT | 1 | Ⅰ | 14 | Ⅲ | PP639173 |
| Putian | RS2105107FT | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639149 |
| RS2105115FT | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639150 | |
| RS210564F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639145 | |
| RS210566F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639187 | |
| RS210571F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639188 | |
| RS210584F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639147 | |
| RS210586F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639189 | |
| RS210592F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639148 | |
| RS210597F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639190 | |
| RS210576F | 1 | Ⅰ | 16 | Ⅳ | PP639146 | |
| RS2105108FT | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639176 | |
| RS210568F | 1 | Ⅰ | 34 | Ⅲ | PP639172 | |
| 三明市 | RS210422F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639180 |
| Sanming | RS210437F | 1 | Ⅰ | 16 | Ⅲ | PP639198 |
| RS210438F | 1 | Ⅰ | 16 | Ⅲ | PP639175 | |
| RS210439F | 1 | Ⅰ | 16 | Ⅲ | PP639199 | |
| RS210417F | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639191 | |
| RS210418F | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639192 | |
| RS210420F | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639193 | |
| RS210424F | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639194 | |
| RS210426F | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639181 | |
| RS210428F | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639174 | |
| RS210431F | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639195 | |
| RS210433F | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639196 | |
| RS210435F | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639197 | |
| 漳州市 | RS211205F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639158 |
| Zhangzhou | RS2112115FT | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639159 |
| RS2112124FT | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639160 | |
| RS211215F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639161 | |
| RS211235F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639162 | |
| RS211242F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639163 | |
| RS211101F | 1 | Ⅰ | 16 | Ⅲ | PP639156 | |
| RS211103F | 1 | Ⅰ | 16 | Ⅲ | PP639157 | |
| RS202112112FT | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639202 | |
| RS202112121FT | 1 | Ⅰ | 34 | Ⅲ | PP639203 | |
| RS20211219F | 1 | Ⅰ | 34 | Ⅲ | PP639200 | |
| RS20211229F | 1 | Ⅰ | 34 | Ⅲ | PP639201 |
表5 福建省番茄青枯菌遗传多样性及地域分布
Table 5 Distribution and host sources of Ralstonia solanacearum strains isolated from Fujian Province
| 地点 Origin | 菌株 Strain | 生理小种 Race | 演化型 Phylotype | 序列变种 Sequevar | 生化型 Biovar | GenBank序列号 GenBank accession number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 福州市 | RS210523F | 1 | Ⅰ | 14 | Ⅲ | PP639179 |
| Fuzhou | RS210527F | 1 | Ⅰ | 14 | Ⅲ | PP639177 |
| RS210531F | 1 | Ⅰ | 14 | Ⅲ | PP639178 | |
| RS20220502F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639152 | |
| RS20220503F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639153 | |
| RS20220504F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639154 | |
| RS20220505FT | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639155 | |
| RS20220501F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639151 | |
| RS210507F | 1 | Ⅰ | 34 | Ⅲ | PP639142 | |
| RS210553FT | 1 | Ⅰ | 34 | Ⅲ | PP639143 | |
| RS210557F | 1 | Ⅰ | 34 | Ⅲ | PP639144 | |
| RS210561FT | 1 | Ⅰ | 34 | Ⅲ | PP639171 | |
| 宁德市 | RS202107129F | 1 | Ⅰ | 14 | Ⅲ | PP639182 |
| Ningde | RS202107131F | 1 | Ⅰ | 14 | Ⅲ | PP639183 |
| RS202107132F | 1 | Ⅰ | 14 | Ⅲ | PP639184 | |
| RS2107128F | 1 | Ⅰ | 14 | Ⅲ | PP639167 | |
| RS2107130F | 1 | Ⅰ | 14 | Ⅲ | PP639168 | |
| RS2107133F | 1 | Ⅰ | 14 | Ⅲ | PP639169 | |
| RS2107139F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639166 | |
| RS202107134F | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639185 | |
| RS202107137F | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639186 | |
| RS2107135F | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639170 | |
| RS2107136F | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639164 | |
| RS2107138F | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639165 | |
| 莆田市 | RS210599FT | 1 | Ⅰ | 14 | Ⅲ | PP639173 |
| Putian | RS2105107FT | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639149 |
| RS2105115FT | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639150 | |
| RS210564F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639145 | |
| RS210566F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639187 | |
| RS210571F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639188 | |
| RS210584F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639147 | |
| RS210586F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639189 | |
| RS210592F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639148 | |
| RS210597F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639190 | |
| RS210576F | 1 | Ⅰ | 16 | Ⅳ | PP639146 | |
| RS2105108FT | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639176 | |
| RS210568F | 1 | Ⅰ | 34 | Ⅲ | PP639172 | |
| 三明市 | RS210422F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639180 |
| Sanming | RS210437F | 1 | Ⅰ | 16 | Ⅲ | PP639198 |
| RS210438F | 1 | Ⅰ | 16 | Ⅲ | PP639175 | |
| RS210439F | 1 | Ⅰ | 16 | Ⅲ | PP639199 | |
| RS210417F | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639191 | |
| RS210418F | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639192 | |
| RS210420F | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639193 | |
| RS210424F | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639194 | |
| RS210426F | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639181 | |
| RS210428F | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639174 | |
| RS210431F | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639195 | |
| RS210433F | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639196 | |
| RS210435F | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639197 | |
| 漳州市 | RS211205F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639158 |
| Zhangzhou | RS2112115FT | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639159 |
| RS2112124FT | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639160 | |
| RS211215F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639161 | |
| RS211235F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639162 | |
| RS211242F | 1 | Ⅰ | 15 | Ⅲ | PP639163 | |
| RS211101F | 1 | Ⅰ | 16 | Ⅲ | PP639156 | |
| RS211103F | 1 | Ⅰ | 16 | Ⅲ | PP639157 | |
| RS202112112FT | 1 | Ⅰ | 17 | Ⅲ | PP639202 | |
| RS202112121FT | 1 | Ⅰ | 34 | Ⅲ | PP639203 | |
| RS20211219F | 1 | Ⅰ | 34 | Ⅲ | PP639200 | |
| RS20211229F | 1 | Ⅰ | 34 | Ⅲ | PP639201 |

图4 番茄青枯菌代表菌株(1 ~ 10)对3种双糖和3种己醇的利用 N:阴性对照;P:阳性对照(GMI1000菌株)。
Fig. 4 Biovar detection of Ralstonia solanacearum strains by carbohydrate utilization test N:Negative control;P:Positive control(GMI1000 strain).
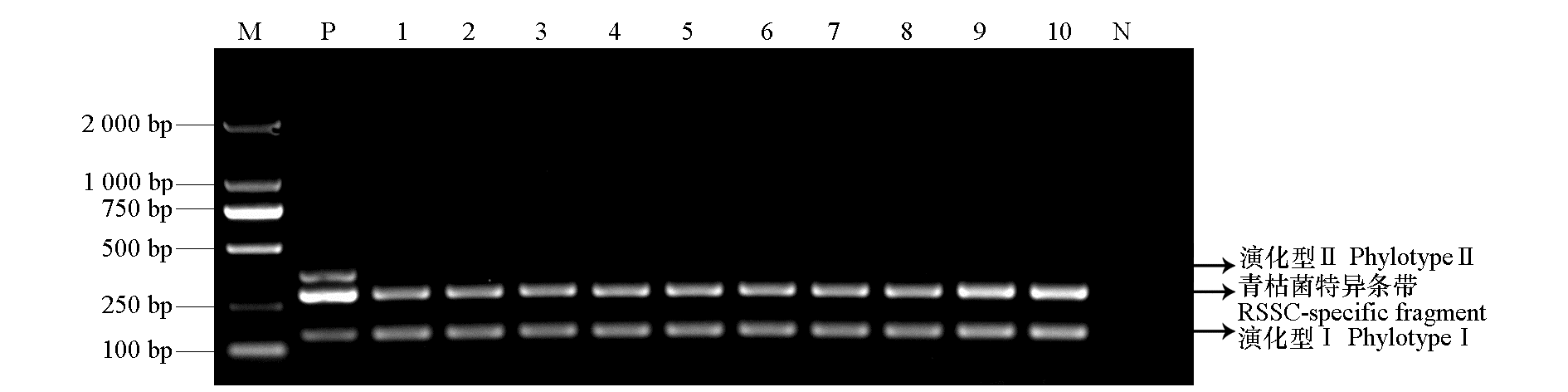
图5 福建番茄青枯菌代表菌株(1 ~ 10)演化型多重PCR鉴定 M:DL2000 marker;P:阳性对照(演化型Ⅰ菌株GMI1000与演化型Ⅱ菌株Po41混合模板);N:阴性对照。
Fig. 5 Phylotype identification of partial isolates Ralstonia solanacearum via Pmx-PCR analysis M:DL2000 marker;P:Positive control[a mixed sample consisting of strains GMI1000(Phylotype I)and Po41(PhylotypeⅡ)];N:Negative control.
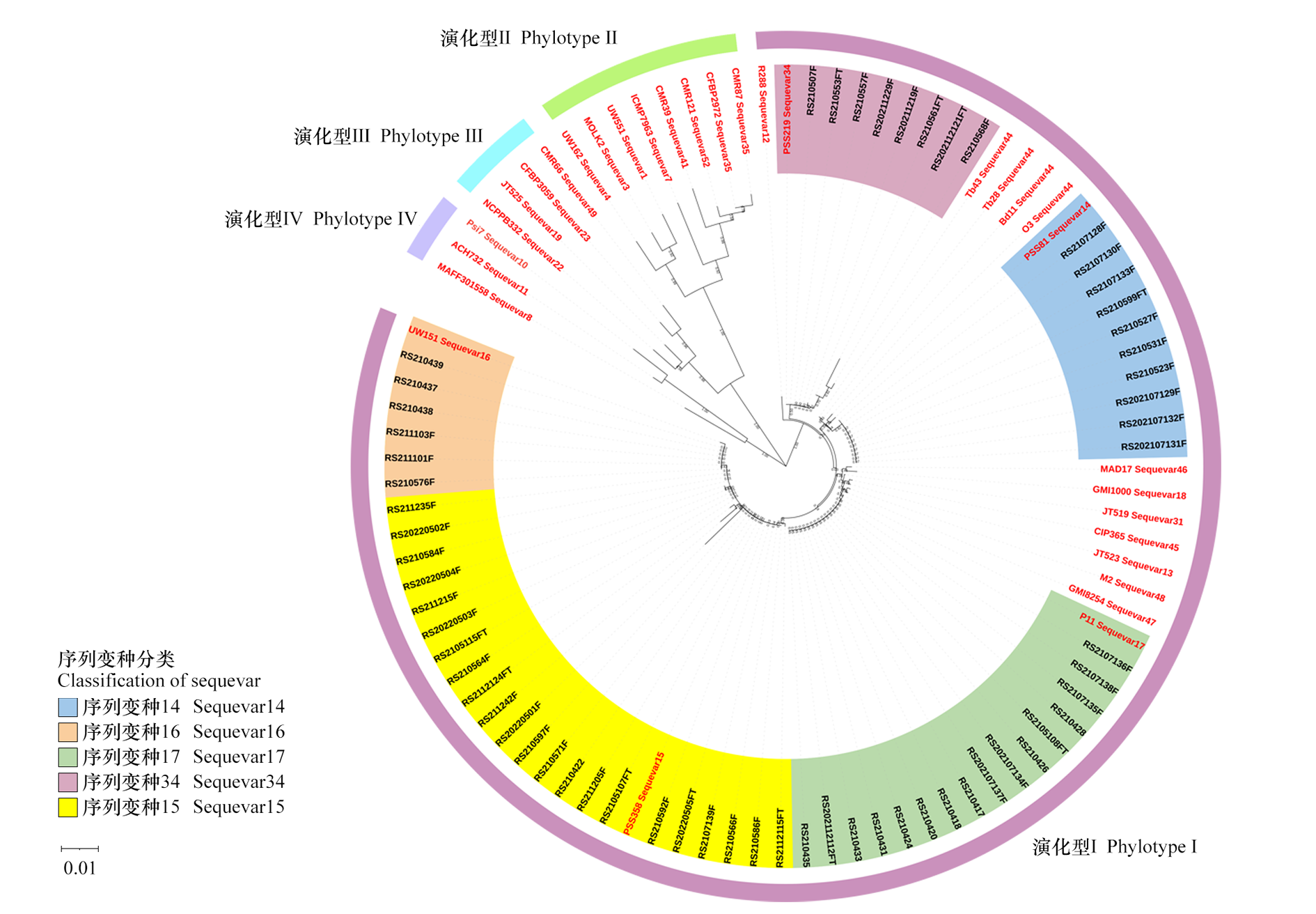
图6 基于egl基因部分序列的番茄青枯菌系统发育分析 红色字体为参考菌株。
Fig. 6 Phylogenetic analysis of Ralstonia solanacearum strains based on partial egl gene sequences The red fonts indicates the reference strains.
| 砧木 Rootstock | RS210507F (序列变种34 Sequevar 34) | RS2107128F (序列变种14 Sequevar 14) | RS210564F (序列变种15 Sequevar 15) | RS210426F (序列变种17 Sequevar 17) | RS211101F (序列变种16 Sequevar 16) | GMI1000 (对照,序列变种18 Control,sequevar 18) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 小汤姆 MicroTom | S | S | MS | S | S | S | |||||||
| 桂砧1号 Guizhen 1 | R | R | MR | MR | R | MR | |||||||
| 丽砧1号 Lizhen 1 | MS | S | MS | MR | MR | MR | |||||||
| 强力 Qiangli | S | S | MS | MS | MS | MR | |||||||
| 朗达240 Langda 240 | S | MS | S | S | S | S | |||||||
| 威尔神根 Weier Shengen | R | MS | R | R | R | R | |||||||
| 番茄砧木6号 Tomato rootstock 6 | MS | MS | MR | MS | MS | MR | |||||||
| 番茄砧木405 Tomato rootstock 405 | S | S | MR | MR | R | MR | |||||||
| 乾德番砧 Qiande tomato rootstock | MR | MS | MS | MS | MS | MS | |||||||
| 浙砧1号 Zhezhen 1 | MS | MR | MR | MS | MS | S | |||||||
| 西茄砧木 Xiqie rootstock | MS | MS | MR | MR | R | MS | |||||||
| 亚拉 Yala | MS | MS | MR | MR | S | MS | |||||||
| 大力神砧木F1 Dalishen rootstock F1 | MS | S | S | MS | S | S | |||||||
| 京丰808 Jingfeng 808 | HS | HS | S | S | S | HS |
表6 供试番茄砧木对不同青枯菌株的抗病性
Table 6 Resistance of tested tomato rootstocks to different strains of Ralstonia solanacearum
| 砧木 Rootstock | RS210507F (序列变种34 Sequevar 34) | RS2107128F (序列变种14 Sequevar 14) | RS210564F (序列变种15 Sequevar 15) | RS210426F (序列变种17 Sequevar 17) | RS211101F (序列变种16 Sequevar 16) | GMI1000 (对照,序列变种18 Control,sequevar 18) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 小汤姆 MicroTom | S | S | MS | S | S | S | |||||||
| 桂砧1号 Guizhen 1 | R | R | MR | MR | R | MR | |||||||
| 丽砧1号 Lizhen 1 | MS | S | MS | MR | MR | MR | |||||||
| 强力 Qiangli | S | S | MS | MS | MS | MR | |||||||
| 朗达240 Langda 240 | S | MS | S | S | S | S | |||||||
| 威尔神根 Weier Shengen | R | MS | R | R | R | R | |||||||
| 番茄砧木6号 Tomato rootstock 6 | MS | MS | MR | MS | MS | MR | |||||||
| 番茄砧木405 Tomato rootstock 405 | S | S | MR | MR | R | MR | |||||||
| 乾德番砧 Qiande tomato rootstock | MR | MS | MS | MS | MS | MS | |||||||
| 浙砧1号 Zhezhen 1 | MS | MR | MR | MS | MS | S | |||||||
| 西茄砧木 Xiqie rootstock | MS | MS | MR | MR | R | MS | |||||||
| 亚拉 Yala | MS | MS | MR | MR | S | MS | |||||||
| 大力神砧木F1 Dalishen rootstock F1 | MS | S | S | MS | S | S | |||||||
| 京丰808 Jingfeng 808 | HS | HS | S | S | S | HS |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
|
蔡佳欣, 黃淑苓, 李佳蓉, 林静宜, 吕昀升. 2020. 青枯病菌(Ralstonia solanacearum Race1/Biovar1/PhylotypeII/Sequevar7)引起之番茄青枯病. 台湾产业研究, 69 (4):274-285.
|
|
| [3] |
|
|
陈雪, 代园风, 余祥文, 杨振智, 喻会平, 游兴琳, 徐同伟, 陈德鑫. 2016. 烟草青枯病生物防治研究进展. 农业灾害研究, 6 (5):10-12.
|
|
| [4] |
|
|
褚新培, 吕桂云, 鹿秀云, 贾邱颖, 梁垚, 高洪波. 2020. 番茄枯萎病菌分离鉴定及嫁接砧木抗病性评价. 中国蔬菜,(6):64-68.
|
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
|
范梅, 谢莉, 蔡鹏, 房超. 2015. 番茄嫁接抗青枯病栽培技术. 四川农业科技,(7):37-38.
|
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
|
郭堂勋, 莫贱友. 2009. 番茄砧木品种材料抗青枯病接种鉴定试验. 广西农业科学, 40 (3):250-252.
|
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
|
何自福, 虞皓. 2001. 广东省主要番茄品种对青枯病的抗性研究初报. 广东农业科学,(3):42-44.
|
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
|
黄天云, 赵兴爱, 蒋雪荣. 2009. 不同砧木嫁接番茄抗青枯病效果比较. 长江蔬菜,(10):55-56.
|
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00076 pmid: 28197157 |
| [18] |
|
|
黄益鸿, 雷东阳. 2013. 不同砧木嫁接番茄抗青枯病效果研究. 江西农业学报, 25 (1):73-75.
|
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.1094/PHYTO.1999.89.4.320 pmid: 18944778 |
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
|
黎妍妍, 刘海龙, 郑露, 黄俊斌, 李锡宏. 2015. 我国植物青枯菌遗传多样性研究进展. 安徽农业科学, 43 (14):107-110,112.
|
|
| [27] |
|
|
李玉洪, 李业勇, 李刚, 滕献有, 刘春惠, 赵小兰. 2017. 抗青枯病番茄砧木品种—宝砧6号. 蔬菜,(1):74-75.
|
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2012.00804.x pmid: 22672649 |
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
pmid: 11249017 |
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
|
史艳玮, 吴宏昱, 李蝶, 李文嘉, 蒋雅琴, 王益奎, 王先裕, 甘桂云. 2024. 抗青枯病番茄砧木新品种勇士3号的选育. 中国蔬菜,(2):119-122,139.
|
|
| [35] |
|
|
王杰, 龙世芳, 王正文, 谌金吾, 姜发洋, 李星. 2020. 番茄青枯病防治研究进展. 中国蔬菜,(1):22-30.
|
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0569 |
|
韦建明, 李云洲, 梁燕. 2023. 嫁接技术提高番茄抗病抗逆性的研究进展. 园艺学报, 50 (9):1997-2014.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0569 |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
|
袁远国, 黄露, 段正凤, 白明松, 李慧娟, 吴石平, 佘小漫. 2021. 番茄青枯菌遗传多样性及砧木品种抗性评价. 种子, 40 (4):27-33,38.
|
|
| [41] |
|
|
张元国, 杨晓东, 魏家鹏, 王林武, 刘树森, 周峰. 2016. 国内番茄嫁接育苗现状与发展趋势. 园艺与种苗,(9):5-9.
|
|
| [42] |
|
|
赵绕芬. 2012. 番茄青枯病的症状识别与防治方法. 中国农技推广, 28 (5):52-53.
|
|
| [43] |
doi: 10.16409/j.cnki.2095-039x.2022.06.002 |
|
郑雪芳, 陈燕萍, 肖荣凤, 陈梅春, 陈峥, 刘欣, 王阶平, 刘波. 2022. 福建青枯雷尔氏菌的遗传多样性及其生防放线菌的筛选. 中国生物防治学报, 38 (5):1269-1279.
doi: 10.16409/j.cnki.2095-039x.2022.06.002 |
|
| [44] |
|
|
周杰, 师恺, 夏晓剑, 周艳虹, 喻景权. 2022. 中国蔬菜栽培科技60年回顾与展望. 园艺学报, 49 (10):2131-2142.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0858 |
| [1] | 韩荧, 段颖, 牛一杰, 李衍素, 贺超兴, 孙敏涛, 王君, 李强, 陈双臣, 闫妍. 腐殖酸生物降解地膜提高番茄品质的转录代谢机制研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1758-1772. |
| [2] | 秦子璐, 徐正康, 戴晓港, 陈赢男. 望春玉兰种质资源遗传多样性分析与核心种质构建[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1823-1832. |
| [3] | 李旭娇, 吕齐, 姚东东, 赵丰云, 王小非, 于坤. ‘烟富3’苹果不同砧木嫁接对其15N–尿素吸收利用的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1868-1880. |
| [4] | 龚小雅, 李贤, 周新刚, 吴凤芝. 分蘖洋葱伴生番茄诱导的根际微生物对根结线虫病的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1913-1926. |
| [5] | 孟思达, 韩磊磊, 相恒佐, 朱美玉, 冯 珍, 叶云珠, 孙美华, 李艳冰, 赵利萍, 谭昌华, 齐明芳, 李天来. 番茄心室数的调控机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1649-1664. |
| [6] | 马星云, 范冰丽, 唐光彩, 贾芝琪, 李营, 薛东齐, 张世文. DXR调控番茄叶绿体发育、花色与果实着色机制初探[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1241-1255. |
| [7] | 张文静, 徐大勇, 吴倩琳, 杨佛, 信丙越, 曾昕, 李峰. 拮抗番茄灰霉病的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌XDY66基因组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1413-1425. |
| [8] | 王永珍, 张剑国, 刘彩虹, 李思蓓, 吕甜甜. 番茄新品种‘圆红212’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1435-1436. |
| [9] | 刘泽营, 孙帅, 刘志强, 崔霞, 李仁. 番茄尖果脐突变体的生理特性及其候选基因分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 982-992. |
| [10] | 李品, 甘宁, 陈家伟, 项思翔, 沈静漪, 欧阳波, 卢永恩. 番茄自然群体磷利用效率分析及耐低磷种质筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 993-1004. |
| [11] | 袁娜, 徐勤圆, 徐照龙, 周玲, 刘晓庆, 陈新, 杜建厂. 基于靶向测序技术的菜豆SNP液相芯片开发及验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1017-1032. |
| [12] | 杨婷, 席德慧, 夏明, 李佳楠. α-苦瓜素基因提高番茄对烟草花叶病毒抗性的机理研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1126-1136. |
| [13] | 游 平, 杨 进, 周 俊, 黄爱军, 鲍敏丽, 易 龙, . 柑橘黄龙病菌原噬菌体的遗传多样性分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 727-736. |
| [14] | 胡志峰, 邵景成, 张 莉. 番茄新品种‘陇番15号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 917-918. |
| [15] | 尤园园, 王帅, 方莹莹, 齐诚, 李淑培, 张映, 陈钰辉, 刘伟, 刘富中, 舒金帅. 茄子全基因组InDel变异特征及分子标记开发和应用[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 520-532. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司