
园艺学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (11): 2523-2539.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0469
收稿日期:2024-06-27
修回日期:2024-08-20
出版日期:2024-12-12
发布日期:2024-11-25
通讯作者:
基金资助:
TANG Zheng*( ), CHEN Sique, XU Qian, ZHONG Weijie, LIU Qing, ZHU Shiyang
), CHEN Sique, XU Qian, ZHONG Weijie, LIU Qing, ZHU Shiyang
Received:2024-06-27
Revised:2024-08-20
Published:2024-12-12
Online:2024-11-25
摘要:
通过对黑腐病病原菌侵染后的青花菜(Brassica oleracea L. var. italica)叶片进行转录组测序分析,探究青花菜对黑腐病的响应机制,挖掘并鉴定其中的抗病相关基因。Gene Ontology(GO)分析显示,与未接种相比,接种病原菌3、5和7 d后上调的差异表达基因均显著富集在胁迫应答和植物激素信号途径;3个比较组共有的差异表达基因中,上调表达的基因编码32个AP2/ERF转录因子;AP2/ERF编码的蛋白质序列长度在132 ~ 344 aa,且启动子中含有大量应答脱落酸、生长素、茉莉酸、赤霉素和水杨酸的顺式作用元件。水杨酸(SA)处理能够显著增强青花菜对黑腐病的抗性,强烈诱导AP2/ERF以及防御相关基因的表达。此外,BolC1t04894H编码的EAR型转录抑制子ERF4定位于细胞核中。瞬时表达青花菜ERF4导致烟草叶片对黑腐病病原菌处理敏感。EMSA结果显示,青花菜ERF4可以结合WRKY33启动子中的GCC-box序列,双荧光素酶报告系统试验表明ERF4抑制WRKY33的表达。综上,黑腐病病原菌侵染后,激活了青花菜激素信号转导途径,SA强烈诱导AP2/ERF的表达,进而调控一系列抗病相关基因的转录,启动防御反应。
唐征, 陈思雀, 徐谦, 钟伟杰, 刘庆, 朱世杨. AP2/ERF在青花菜苗期响应黑腐病的功能研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(11): 2523-2539.
TANG Zheng, CHEN Sique, XU Qian, ZHONG Weijie, LIU Qing, ZHU Shiyang. Functional Study of AP2/ERF in Response to Black Rot at Broccoli Seedling Stage[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(11): 2523-2539.
| 目的 | 引物名称 | 引物序列(5′-3′) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Primer name | Primer sequence | ||
| 转录水平检测 | BolC9t55823H | F:GGCGAAGGGGAAGCATTAC;R:TCTCCACGGAAAGTTCAGCA | ||
| Transcriptional level detection | BolC8t48739H | F:ACGCAACACTTAATTTTCCGGA;R:CTTCAGCCATCCCTTCCTCT | ||
| BolC7t43635H | F:GCCGTCAAAGGGAAAGCATT;R:CACGCATCCTAAAAGCAGCT | |||
| BolC7t42203H | F:GCAGCACCGTCGAATCATC;R:ACTACGATCCATCACCACAGA | |||
| BolC6t38421H | F:AGTGTCCGGGGAGAAGAATC;R:TCGGAGAAGTCATCAAACCCT | |||
| BolC5t33888H | F:GGCGACTGATGGGATTGTTC;R:TCGTAGAGACCTGCATCACC | |||
| BolC3t17033H | F:CACCCTTGACTGCGATTCTC;R:GGCGACCTAAAAGCTGACG | |||
| BolC2t10891H | F:GGGAAGCATTACAGAGGGGT;R:CACGCATCCTAAAAGCAGCT | |||
| BolC1t04894H | F:CTTGAGCTTAGTCTTGGCGG;R:CTCCCACAAGCCATCTTCGT | |||
| BolC1t04025H | F:CGGTATTAGGGTTTGGCTCG;R:GAACACCCATCCTCGTAGCT | |||
| BolC1t01080H | F:TAGAGTTTGGTTGGGGACGT;R:ACCGTTCTCCTCCGCTTC | |||
| BolC1t00081H | F:CCACACATGAGGCACGAGTA;R:TCTTGATACTCCTCTGCTTTTGG | |||
| PAL2 | F:TAACAATCGGACAAGTCGC;R:AGAGGTCGCTCCAAACCC | |||
| CHS | F:ACTACTACTTCCGCATCACC;R:GGGACTTCAACCACCACTA | |||
| CHI | F:GCTAACGCCTATCCGAGCTT;R:TGTACACATGGGAACTCTGGT | |||
| WRKY33 | F:CTGTGTTCAATGCCAGCCTT;R:TTGCTTCAGGTTCACTCCCA | |||
| Actin | F:CCAGAGGTCTTGTTCCAGCCATC;R:GTTCCACCACTGAGCACAATGTTAC | |||
| 亚细胞定位和凝胶迁移 Subcellar location and EMSA | ERF4-pENTR | F:GCAGGCTCCGCGGCCATGGTTAAGATGGGTTTGAA; R:AGCTGGGTCGGCGCGGGCCTGTTCCAACGGAGGAG | ||
| 双荧光素酶报告系统试验 Dual-luciferase reporter | ERF4-62SK | F:TAGAACTAGTGGATCCCCCATGGTTAAGATGGGTTTGAA; R:TATCGAATTCCTGCAGCCCTCAGGCCTGTTCCAACGGAGGAG | ||
| system | WRKY33pro-LUC | F:AGCTGGGTCGGCGCGGGCCTGTTCCAACGGAGGAG; R:TAGAACTAGTGGATCCCCCACATAAAAAAATTGAAGCTT | ||
表1 本研究中所用引物序列信息
Table 1 Primers sequence information used in this study
| 目的 | 引物名称 | 引物序列(5′-3′) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Primer name | Primer sequence | ||
| 转录水平检测 | BolC9t55823H | F:GGCGAAGGGGAAGCATTAC;R:TCTCCACGGAAAGTTCAGCA | ||
| Transcriptional level detection | BolC8t48739H | F:ACGCAACACTTAATTTTCCGGA;R:CTTCAGCCATCCCTTCCTCT | ||
| BolC7t43635H | F:GCCGTCAAAGGGAAAGCATT;R:CACGCATCCTAAAAGCAGCT | |||
| BolC7t42203H | F:GCAGCACCGTCGAATCATC;R:ACTACGATCCATCACCACAGA | |||
| BolC6t38421H | F:AGTGTCCGGGGAGAAGAATC;R:TCGGAGAAGTCATCAAACCCT | |||
| BolC5t33888H | F:GGCGACTGATGGGATTGTTC;R:TCGTAGAGACCTGCATCACC | |||
| BolC3t17033H | F:CACCCTTGACTGCGATTCTC;R:GGCGACCTAAAAGCTGACG | |||
| BolC2t10891H | F:GGGAAGCATTACAGAGGGGT;R:CACGCATCCTAAAAGCAGCT | |||
| BolC1t04894H | F:CTTGAGCTTAGTCTTGGCGG;R:CTCCCACAAGCCATCTTCGT | |||
| BolC1t04025H | F:CGGTATTAGGGTTTGGCTCG;R:GAACACCCATCCTCGTAGCT | |||
| BolC1t01080H | F:TAGAGTTTGGTTGGGGACGT;R:ACCGTTCTCCTCCGCTTC | |||
| BolC1t00081H | F:CCACACATGAGGCACGAGTA;R:TCTTGATACTCCTCTGCTTTTGG | |||
| PAL2 | F:TAACAATCGGACAAGTCGC;R:AGAGGTCGCTCCAAACCC | |||
| CHS | F:ACTACTACTTCCGCATCACC;R:GGGACTTCAACCACCACTA | |||
| CHI | F:GCTAACGCCTATCCGAGCTT;R:TGTACACATGGGAACTCTGGT | |||
| WRKY33 | F:CTGTGTTCAATGCCAGCCTT;R:TTGCTTCAGGTTCACTCCCA | |||
| Actin | F:CCAGAGGTCTTGTTCCAGCCATC;R:GTTCCACCACTGAGCACAATGTTAC | |||
| 亚细胞定位和凝胶迁移 Subcellar location and EMSA | ERF4-pENTR | F:GCAGGCTCCGCGGCCATGGTTAAGATGGGTTTGAA; R:AGCTGGGTCGGCGCGGGCCTGTTCCAACGGAGGAG | ||
| 双荧光素酶报告系统试验 Dual-luciferase reporter | ERF4-62SK | F:TAGAACTAGTGGATCCCCCATGGTTAAGATGGGTTTGAA; R:TATCGAATTCCTGCAGCCCTCAGGCCTGTTCCAACGGAGGAG | ||
| system | WRKY33pro-LUC | F:AGCTGGGTCGGCGCGGGCCTGTTCCAACGGAGGAG; R:TAGAACTAGTGGATCCCCCACATAAAAAAATTGAAGCTT | ||
| 比较组 | 上调 | 下调 |
|---|---|---|
| Comparison group | Up regulated | Down regulated |
| 0 d vs. 1 d | 蛋白泛素化 Protein ubiquitination | DNA复制起始 DNA replication initiation |
| 光呼吸 Photorespiration | 蛋白折叠 Protein refolding | |
| 昼夜节律 Circadian rhythm | 叶绿体 Chloroplast | |
| 还原戊糖磷酸循环 Reductive pentose phosphate cycle | ||
| 0 d vs. 3 d | 伤害应答 Response to wounding | 翻译 Translation |
| 盐胁迫应答 Response to salt stress | 光合作用 Photosynthesis | |
| 高温应答 Response to heat | 叶绿体 Chloroplast | |
| 氧化胁迫应答 Response to oxidative stress | 钙离子结合 Calcium ion binding | |
| 几丁质酶应答 Response to chitin | 核糖体结构成分 Structural constituent of ribosome | |
| Karrikin应答 Response to karrikin | rRNA结合 rRNA binding | |
| 茉莉酸应答 Response to jasmonic acid | ||
| 脱落酸应答 Response to abscisic acid | ||
| 乙烯激活信号通路 Ethylene-activated signaling pathway | ||
| 0 d vs. 5 d | 伤害应答 Response to wounding | 光合作用 Photosynthesis |
| 盐胁迫应答 Response to salt stress | 生长调节 Regulation of growth | |
| 钙离子应答 Response to calcium ion | 生长素激活信号通路 Auxin-activated signaling pathway | |
| 氧化胁迫应答 Response to oxidative stress | 叶绿体 Chloroplast | |
| 几丁质酶应答 Response to chitin | 叶绿素结合 Chlorophyll binding | |
| Karrikin应答 Response to karrikin | ||
| 茉莉酸应答 Response to jasmonic acid | ||
| 乙烯激活信号通路 Ethylene-activated signaling pathway | ||
| 防御应答 Defense response | ||
| 0 d vs. 7 d | 伤害应答 Response to wounding | 光和作用 Photosynthesis |
| 盐胁迫应答 Response to salt stress | 细胞壁组织 Cell wall organization | |
| 氧化胁迫应答 Response to oxidative stress | 碳水化合物代谢 Carbohydrate metabolic process | |
| 茉莉酸应答 Response to jasmonic acid | 叶绿体 Chloroplast | |
| 几丁质酶应答 Response to chitin | ||
| Karrikin应答 Response to karrikin | ||
| 水杨酸应答 Response to salicylic acid | ||
| 脱落酸应答 Response to abscisic acid | ||
| 乙烯激活信号通路 Ethylene-activated signaling pathway | ||
| 防御应答 Defense response |
表2 黑腐病病原菌侵染青花菜叶片后差异表达基因的GO富集分析
Table 2 GO enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes after broccoli leaf infected by black rot pathogen
| 比较组 | 上调 | 下调 |
|---|---|---|
| Comparison group | Up regulated | Down regulated |
| 0 d vs. 1 d | 蛋白泛素化 Protein ubiquitination | DNA复制起始 DNA replication initiation |
| 光呼吸 Photorespiration | 蛋白折叠 Protein refolding | |
| 昼夜节律 Circadian rhythm | 叶绿体 Chloroplast | |
| 还原戊糖磷酸循环 Reductive pentose phosphate cycle | ||
| 0 d vs. 3 d | 伤害应答 Response to wounding | 翻译 Translation |
| 盐胁迫应答 Response to salt stress | 光合作用 Photosynthesis | |
| 高温应答 Response to heat | 叶绿体 Chloroplast | |
| 氧化胁迫应答 Response to oxidative stress | 钙离子结合 Calcium ion binding | |
| 几丁质酶应答 Response to chitin | 核糖体结构成分 Structural constituent of ribosome | |
| Karrikin应答 Response to karrikin | rRNA结合 rRNA binding | |
| 茉莉酸应答 Response to jasmonic acid | ||
| 脱落酸应答 Response to abscisic acid | ||
| 乙烯激活信号通路 Ethylene-activated signaling pathway | ||
| 0 d vs. 5 d | 伤害应答 Response to wounding | 光合作用 Photosynthesis |
| 盐胁迫应答 Response to salt stress | 生长调节 Regulation of growth | |
| 钙离子应答 Response to calcium ion | 生长素激活信号通路 Auxin-activated signaling pathway | |
| 氧化胁迫应答 Response to oxidative stress | 叶绿体 Chloroplast | |
| 几丁质酶应答 Response to chitin | 叶绿素结合 Chlorophyll binding | |
| Karrikin应答 Response to karrikin | ||
| 茉莉酸应答 Response to jasmonic acid | ||
| 乙烯激活信号通路 Ethylene-activated signaling pathway | ||
| 防御应答 Defense response | ||
| 0 d vs. 7 d | 伤害应答 Response to wounding | 光和作用 Photosynthesis |
| 盐胁迫应答 Response to salt stress | 细胞壁组织 Cell wall organization | |
| 氧化胁迫应答 Response to oxidative stress | 碳水化合物代谢 Carbohydrate metabolic process | |
| 茉莉酸应答 Response to jasmonic acid | 叶绿体 Chloroplast | |
| 几丁质酶应答 Response to chitin | ||
| Karrikin应答 Response to karrikin | ||
| 水杨酸应答 Response to salicylic acid | ||
| 脱落酸应答 Response to abscisic acid | ||
| 乙烯激活信号通路 Ethylene-activated signaling pathway | ||
| 防御应答 Defense response |

图2 青花菜接种黑腐病病原菌3个比较组(0 d vs. 3 d,0 d vs. 5 d,0 d vs. 7 d)共有的860个上调差异基因表达热图
Fig. 2 Heat map of 860 common upregulated differentially expressed genes in three comparison groups (0 d vs. 3 d,0 d vs. 5 d,0 d vs. 7 d)inoculated with black rot pathogen in broccoli
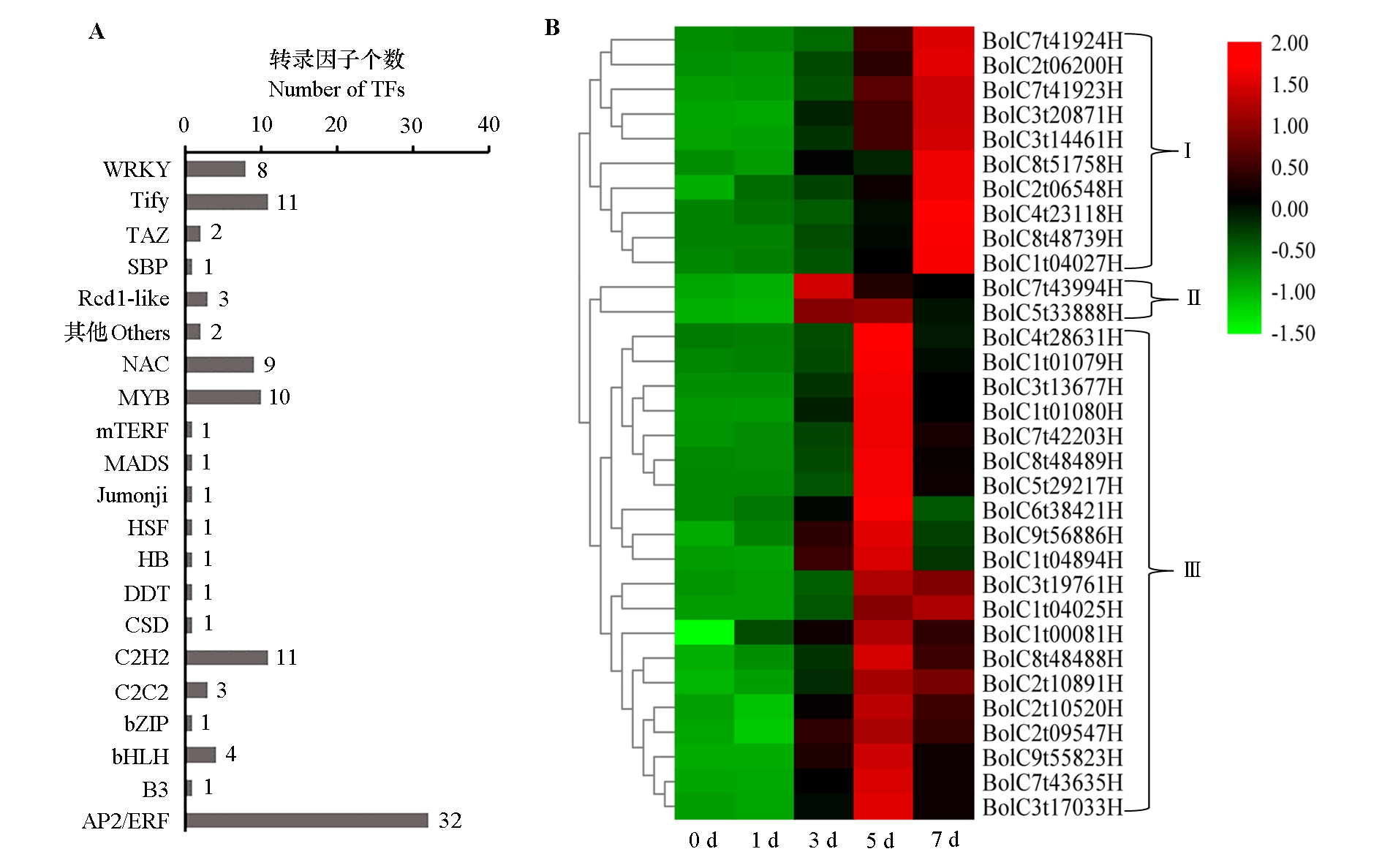
图3 青花菜叶片接种黑腐病病原菌(Xcc)后的响应转录因子分析 A:响应Xcc的转录因子种类;B:32个编码AP2/ERF转录因子的基因热图。
Fig. 3 Analysis of responsive transcription factors after inoculated with black rot pathogen(Xcc)in broccoli leaf A:Types of transcription factors that respond to Xcc;B:Heat map of 32 genes coding AP2/ERF transcription factor.
| 基因号 Gene ID | 位置 Position | 氨基酸数 Amino acid | 定位预测 Predicted location | 拟南芥同源基因(ID) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arabidopsis thaliana homologous gene | ||||
| BolC9t56886H | Chr9:37 383 176 ~ 37 383 838 | 220 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF105(AT5G51190) |
| BolC9t55823H | Chr9:23 228 516 ~ 23 229 238 | 240 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF2(AT5G47220) |
| BolC8t51758H | Chr8:44 860 010 ~ 44 860 951 | 313 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF053(AT2G20880) |
| BolC8t48739H | Chr8:24 675 340 ~ 24 676 173 | 277 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF054(AT4G28140) |
| BolC8t48489H | Chr8:22 668 610 ~ 22 669 377 | 255 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF1A(AT4G17500) |
| BolC8t48488H | Chr8:22 653 145 ~ 22 654 017 | 290 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF6(AT4G17490) |
| BolC7t43994H | Chr7:41 081 592 ~ 41 082 626 | 344 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ARF14(AT3G25730) |
| BolC7t43635H | Chr7:38 015 941 ~ 38 016 609 | 222 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF2(AT5G47220) |
| BolC7t42203H | Chr7:24 871 566 ~ 24 872 072 | 168 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF11(AT1G28370) |
| BolC7t41924H | Chr7:21 967 071 ~ 21 967 469 | 132 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF095(AT3G23220) |
| BolC7t41923H | Chr7:21 965 156 ~ 21 965 572 | 138 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF098(AT3G23230) |
| BolC6t38421H | Chr6:32 042 058 ~ 32 042 651 | 197 | 细胞质,细胞核Cytoplasm,nucleus | ERF018(AT1G74930) |
| BolC5t33888H | Chr5:46 627 650 ~ 46 628 303 | 217 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF4(AT3G15210) |
| BolC5t29217H | Chr5: 2 216 228 ~ 2 216 962 | 244 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF094(AT1G06160) |
| BolC4t28631H | Chr4:64 415 607 ~ 64 416 320 | 237 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF13(AT2G44840) |
| BolC4t23118H | Chr4:11 617 647 ~ 11 618 985 | 216 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF112(AT2G33710) |
| BolC3t20871H | Chr3:67 338 370 ~ 67 339 152 | 260 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF109(AT4G34410) |
| BolC3t19761H | Chr3:57 780 467 ~ 57 780 985 | 172 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF11(AT1G28370) |
| BolC3t17033H | Chr3:28 276 839 ~ 28 277 453 | 204 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF4(AT3G15210) |
| BolC3t14461H | Chr3:10 357 105 ~ 10 357 806 | 233 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF15(AT2G31230) |
| BolC3t13677H | Chr3: 5 792 930 ~ 5 793 562 | 210 | 细胞质,细胞核Cytoplasm,nucleus | ERF016(AT5G21960) |
| BolC2t10891H | Chr2:48 942 393 ~ 48 943 094 | 233 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF2(AT5G47220) |
| BolC2t10520H | Chr2:44 830 922 ~ 44 831 503 | 193 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF9(AT5G44210) |
| BolC2t09547H | Chr2:30 078 233 ~ 30 079 165 | 310 | 细胞核 Nucleus | RAP2-4(AT1G78080) |
| BolC2t06548H | Chr2: 3 356 340 ~ 3 358 302 | 254 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF113(AT5G13330) |
| BolC2t06200H | Chr2: 1 544 843 ~ 1 545 811 | 322 | 细胞核 Nucleus | DREB2A(AT5G05410) |
| BolC1t04894H | Chr1:44 469 287 ~ 44 469 943 | 218 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF4(AT3G15210) |
| BolC1t04027H | Chr1:36 457 782 ~ 36 459 026 | 212 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF098(AT3G23230) |
| BolC1t04025H | Chr1:36 421 156 ~ 36 421 788 | 210 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF1B(AT3G23240) |
| BolC1t01080H | Chr1: 6 205 090 ~ 6 205 785 | 231 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF1A(AT4G17500) |
| BolC1t01079H | Chr1: 6 195 373 ~ 6 196 152 | 259 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF6(AT4G17490) |
| BolC1t00081H | Chr1: 423 978 ~ 424 808 | 276 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF060(AT4G39780) |
表3 青花菜AP2/ERF基因的基本信息、定位预测以及拟南芥同源基因
Table 3 The broccoli AP2/ERF genes basic information,localization prediction,and Arabidopsis thaliana homologous genes
| 基因号 Gene ID | 位置 Position | 氨基酸数 Amino acid | 定位预测 Predicted location | 拟南芥同源基因(ID) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arabidopsis thaliana homologous gene | ||||
| BolC9t56886H | Chr9:37 383 176 ~ 37 383 838 | 220 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF105(AT5G51190) |
| BolC9t55823H | Chr9:23 228 516 ~ 23 229 238 | 240 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF2(AT5G47220) |
| BolC8t51758H | Chr8:44 860 010 ~ 44 860 951 | 313 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF053(AT2G20880) |
| BolC8t48739H | Chr8:24 675 340 ~ 24 676 173 | 277 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF054(AT4G28140) |
| BolC8t48489H | Chr8:22 668 610 ~ 22 669 377 | 255 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF1A(AT4G17500) |
| BolC8t48488H | Chr8:22 653 145 ~ 22 654 017 | 290 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF6(AT4G17490) |
| BolC7t43994H | Chr7:41 081 592 ~ 41 082 626 | 344 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ARF14(AT3G25730) |
| BolC7t43635H | Chr7:38 015 941 ~ 38 016 609 | 222 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF2(AT5G47220) |
| BolC7t42203H | Chr7:24 871 566 ~ 24 872 072 | 168 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF11(AT1G28370) |
| BolC7t41924H | Chr7:21 967 071 ~ 21 967 469 | 132 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF095(AT3G23220) |
| BolC7t41923H | Chr7:21 965 156 ~ 21 965 572 | 138 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF098(AT3G23230) |
| BolC6t38421H | Chr6:32 042 058 ~ 32 042 651 | 197 | 细胞质,细胞核Cytoplasm,nucleus | ERF018(AT1G74930) |
| BolC5t33888H | Chr5:46 627 650 ~ 46 628 303 | 217 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF4(AT3G15210) |
| BolC5t29217H | Chr5: 2 216 228 ~ 2 216 962 | 244 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF094(AT1G06160) |
| BolC4t28631H | Chr4:64 415 607 ~ 64 416 320 | 237 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF13(AT2G44840) |
| BolC4t23118H | Chr4:11 617 647 ~ 11 618 985 | 216 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF112(AT2G33710) |
| BolC3t20871H | Chr3:67 338 370 ~ 67 339 152 | 260 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF109(AT4G34410) |
| BolC3t19761H | Chr3:57 780 467 ~ 57 780 985 | 172 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF11(AT1G28370) |
| BolC3t17033H | Chr3:28 276 839 ~ 28 277 453 | 204 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF4(AT3G15210) |
| BolC3t14461H | Chr3:10 357 105 ~ 10 357 806 | 233 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF15(AT2G31230) |
| BolC3t13677H | Chr3: 5 792 930 ~ 5 793 562 | 210 | 细胞质,细胞核Cytoplasm,nucleus | ERF016(AT5G21960) |
| BolC2t10891H | Chr2:48 942 393 ~ 48 943 094 | 233 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF2(AT5G47220) |
| BolC2t10520H | Chr2:44 830 922 ~ 44 831 503 | 193 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF9(AT5G44210) |
| BolC2t09547H | Chr2:30 078 233 ~ 30 079 165 | 310 | 细胞核 Nucleus | RAP2-4(AT1G78080) |
| BolC2t06548H | Chr2: 3 356 340 ~ 3 358 302 | 254 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF113(AT5G13330) |
| BolC2t06200H | Chr2: 1 544 843 ~ 1 545 811 | 322 | 细胞核 Nucleus | DREB2A(AT5G05410) |
| BolC1t04894H | Chr1:44 469 287 ~ 44 469 943 | 218 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF4(AT3G15210) |
| BolC1t04027H | Chr1:36 457 782 ~ 36 459 026 | 212 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF098(AT3G23230) |
| BolC1t04025H | Chr1:36 421 156 ~ 36 421 788 | 210 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF1B(AT3G23240) |
| BolC1t01080H | Chr1: 6 205 090 ~ 6 205 785 | 231 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF1A(AT4G17500) |
| BolC1t01079H | Chr1: 6 195 373 ~ 6 196 152 | 259 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF6(AT4G17490) |
| BolC1t00081H | Chr1: 423 978 ~ 424 808 | 276 | 细胞核 Nucleus | ERF060(AT4G39780) |

图4 AP2/ERF的系统进化树(A)、保守基序(B)、基因结构(C)和启动子顺势作用元件(D)分析
Fig. 4 Phylogenetic tree(A),conserved motif(B),gene structure(C)and promoter cis-elements(D)analyses of AP2/ERF
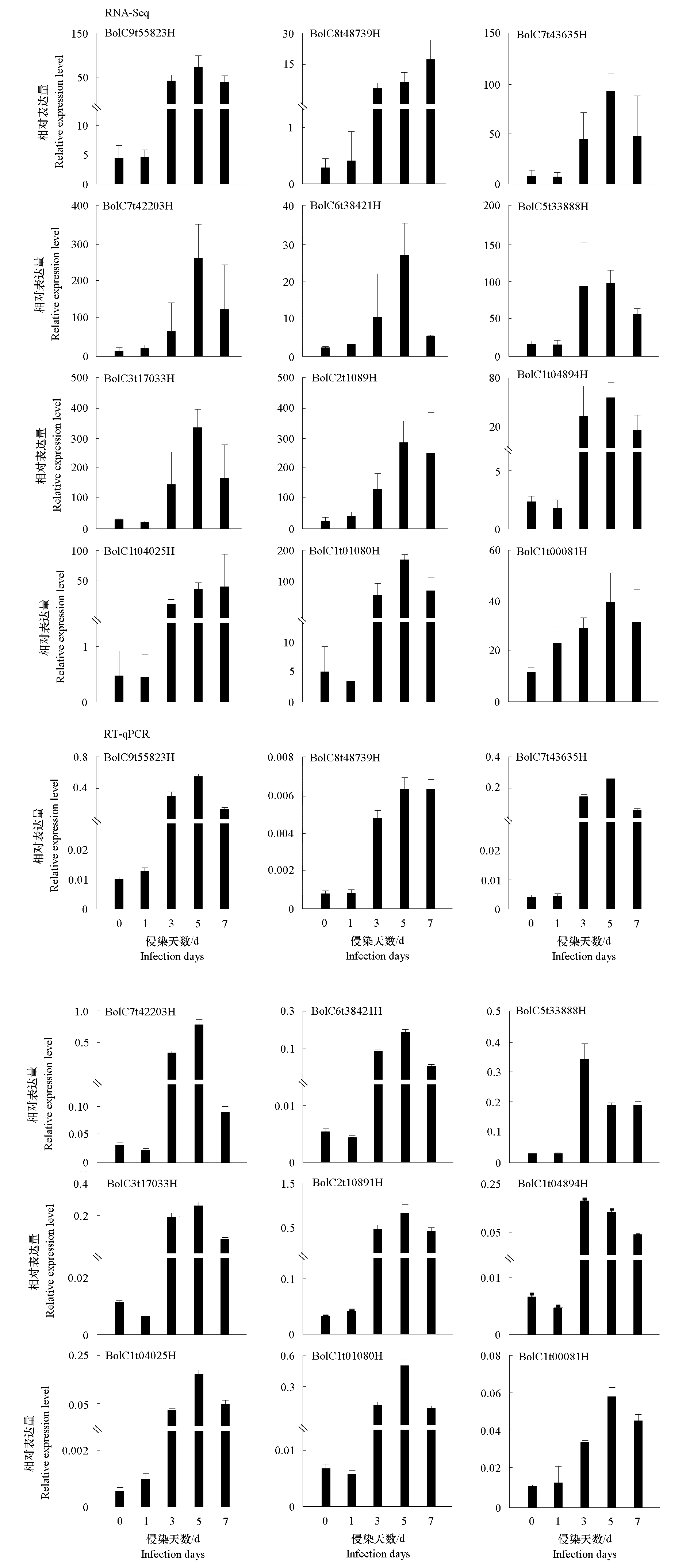
图5 防御反应相关的12个AP2/ERF差异表达基因的RNA-Seq及RT-qPCR验证
Fig. 5 RNA-Seq and the validation of 12 defense-related AP2/ERF differentially expressed genes by RT-qPCR

图6 水杨酸(SA,100 μmol · L-1)预处理的青花菜接种Xcc后的抗病反应 A:SA预处理增强了青花菜的抗病性;B:SA处理后AP2/ERF基因的表达;C:防御相关基因的表达热图;D:防御相关基因表达的RT-qPCR检测。不同小写字母代表P < 0.05差异显著(单因素方差分析的Tukey’s检验)。
Fig. 6 Disease resistance response to Xcc of broccoli pretreated with salicylic acid(SA,100 μmol · L-1) A:SA pretreatment enhanced the disease resistance of broccoli. B:The expression of AP2/ERF genes was detected after SA treatment. C:Heat map analysis of defense-related genes expression. D:The expression of defense-related genes was detected by RT-qPCR. Different lowercase letters represent a significant difference at P < 0.05(one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test).
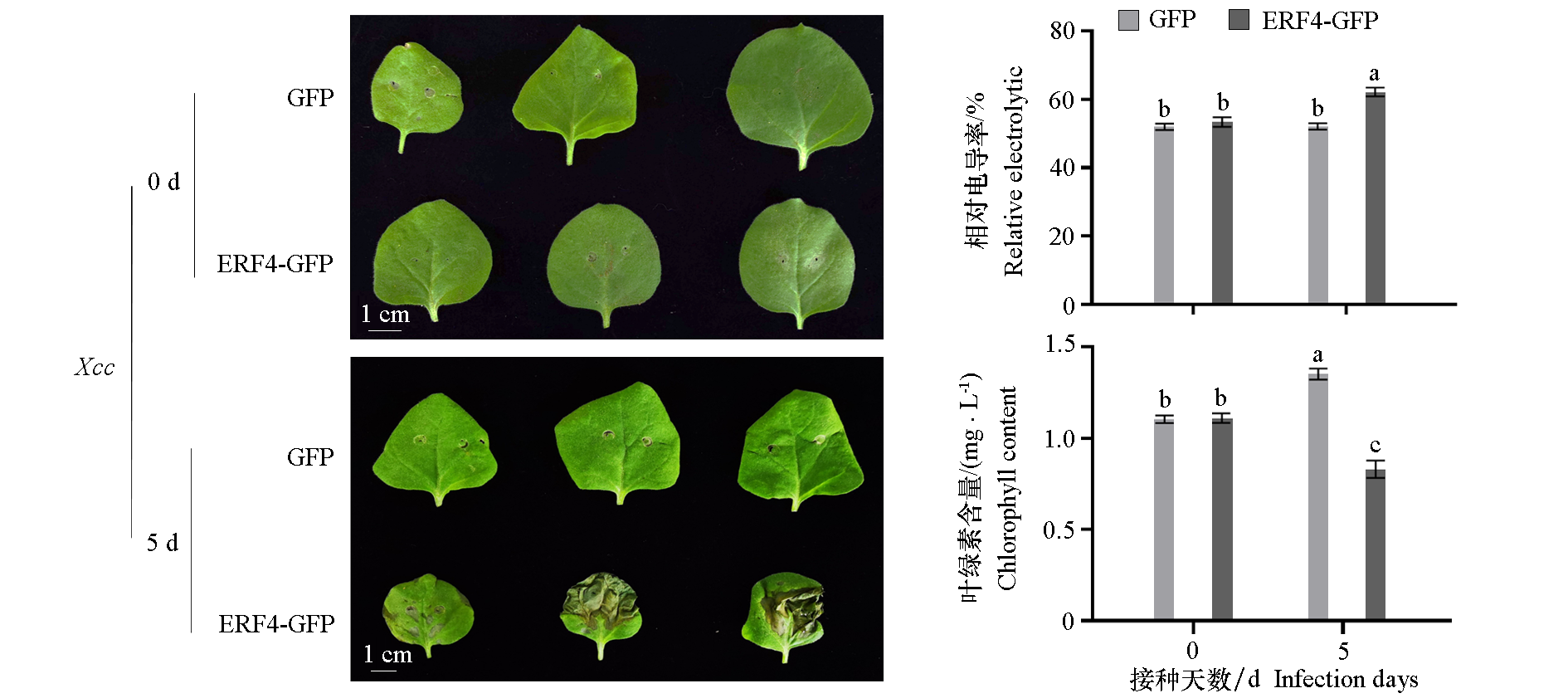

图8 瞬时表达青花菜ERF4的烟草叶片接种Xcc的敏感表型及相对电导率和叶绿素含量变化 不同小写字母代表P < 0.05的显著性差异(单因素方差分析的Tukey’s检验)。
Fig. 8 Transiently expressing broccoli ERF4 tobacco leaves sensitive performance and its relative electrolytic leakage and chlorophyll content change after inoculated with Xcc Different lowercase letters represent a significant difference at P < 0.05(one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test).
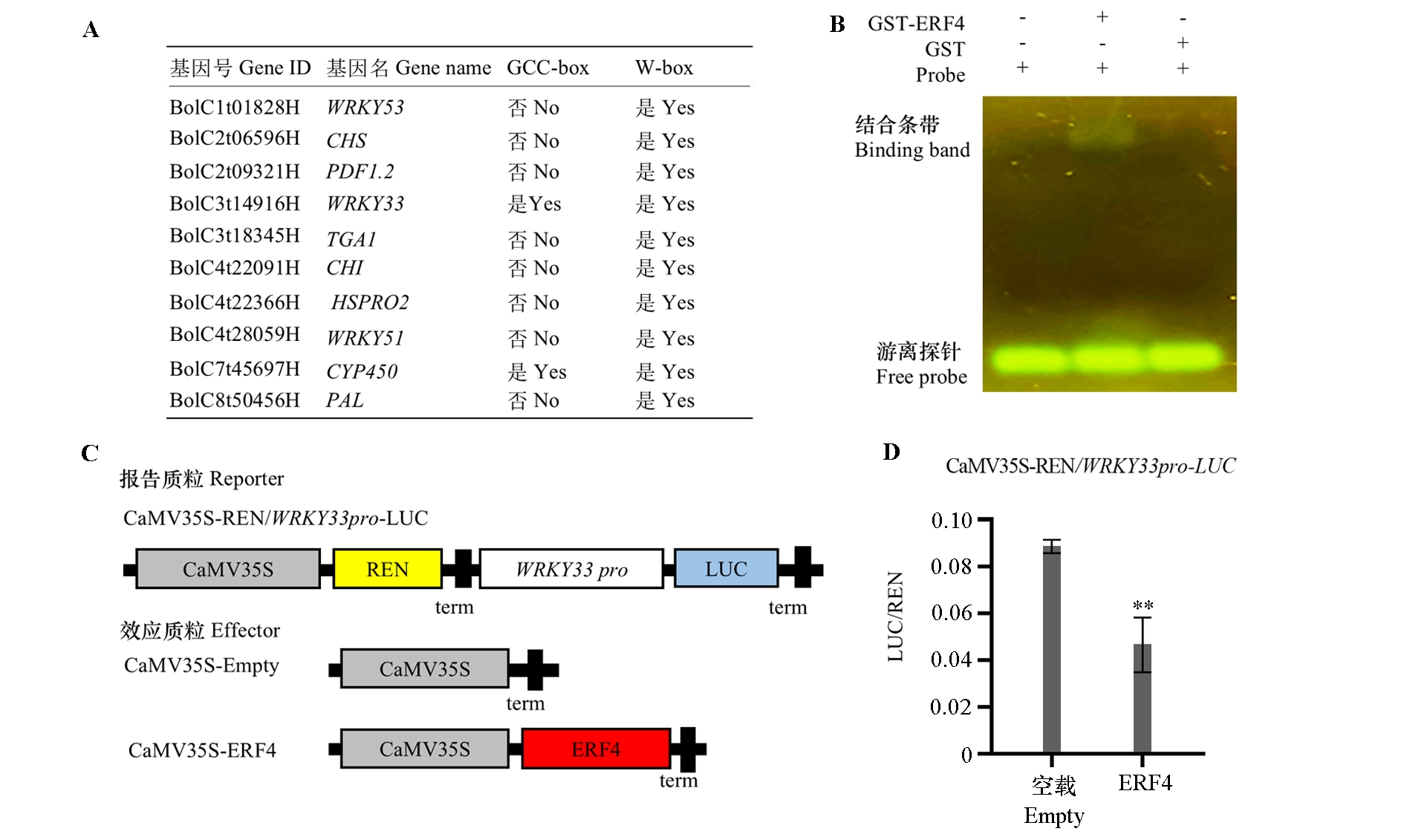
图9 ERF4通过结合WRKY33的启动子区抑制其表达 A:防御相关基因的启动子(-2 kb)分析;B:EMSA检测ERF4与GCC-box的结合活性;C:双荧光素酶系统试验载体;D:ERF4在烟草叶片中对WRKY33的转录调控,LUC/REN表示最终的转录活性。** P < 0.01,统计学差异检测使用Student’s t-test。
Fig. 9 ERF4 inhibited WRKY33 expression by binding to its promoter A:Analysis of promoters(-2 kb)of defense-related genes. B:The binding activity of ERF4 to GCC-box was detected by EMSA;C:Double luciferase system experimental vector. D:Transcriptional regulation of ERF4 to WRKY33 in tobacco leaves. The LUC/REN was calculated as the final transcriptional activity. The statistically significant differences were determined by Students’ t-test. ** P < 0.01.
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
|
崔波, 郝平安, 梁芳, 张燕, 王喜蒙, 李俊霖, 蒋素华, 许申平. 2020. 蝴蝶兰AP2/ERF家族基因的克隆及在低温下表达特性分析. 园艺学报, 47 (1):85-97.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2019-0091 |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
|
韩风庆, 李占省, 刘玉梅, 方智远, 杨丽梅, 庄木, 张扬勇, 吕红豪, 王勇. 2019. 青花菜黑腐病发病规律及综合防治措施. 中国蔬菜,(11):98-101.
|
|
| [7] |
|
|
韩睿, 钟雄辉, 陈登辉, 崔建, 乐祥庆, 颉建明, 康俊根. 2023. 黑腐病菌效应因子XopR的甘蓝靶标基因BobHLH34的克隆及功能分析. 园艺学报, 50 (2):319-330.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-1274 |
|
| [8] |
pmid: 16937017 |
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
|
赖丹妮, 蔡翔, 陈东红, 韩之刚, 吴令上, 斯金平, 李聪. 2022. 铁皮石斛白绢病响应miR171b及miR171b靶标DcGRAS基因家族的鉴定及表达分析. 农业生物技术学报, 30 (10):1869-1883.
|
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
|
李继东, 倪静, 叶霞, 陈鹏, 谭彬, 张梦洋, 郑先波, 张玉, 冯建灿. 2020. 枣AP2/ERF转录因子鉴定及其响应枣疯病植原体表达分析. 园艺学报, 47 (8):1463-1474.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2019-0965 |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.105.068544 pmid: 16183832 |
| [16] |
|
|
徐志璇, 任仲海. 2020. 番茄AP2/ERF 超家族重鉴定及过表达SlERF.D.3株系表型分析. 园艺学报, 47 (4):653-664.
|
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
|
姚星伟, 牛国保, 单晓政, 刘莉莉, 文正华, 江汉民, 张小丽. 2018. 花椰菜苗期黑腐病抗病性鉴定. 黑龙江农业科学,(8):39-41.
|
|
| [20] |
|
|
姚玉荣, 霍建飞, 郝永娟, 贲海燕, 王万立. 2020. 花椰菜苗期黑腐病抗、感品种转录组差异表达分析. 山东农业科学, 52 (2):1-6.
|
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [1] | 刘宇香, 韩风庆, 赵鑫雨, 刘玉梅, 李占省, 方智远, . 青花菜侧枝调控基因BoBRC1的克隆及功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 1997-2007. |
| [2] | 马存发, 武婷, 赵辉, 张天培, 赵立坚, 余永辉, 肖建成, 李军, 巫水钦. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术敲除青花菜BoSP11创制自交亲和系[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 509-519. |
| [3] | 王荣波, 王海云, 张前荣, 蔡松龄, 李本金, 张美祥, 刘裴清. 福建省番茄青枯病菌遗传多样性分析及其抗性砧木的筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(11): 2540-2554. |
| [4] | 王勇, 杨丽梅, $\boxed{\hbox{方智远}}$, 张扬勇, 季家磊, 吕红豪, 庄木, 刘玉梅, 李占省, 韩风庆. 秋甘蓝新品种‘中甘596’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(1): 217-218. |
| [5] | 陈琪, 李婷, 陈佳琳, 陈鸥, 王文军, 姚世响, 曾凯芳. 柑橘CsNAC2在果实绿霉病抗病性中的功能和机制研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(12): 2701-2712. |
| [6] | 王 飞, 李 宁, 尹延旭, 高升华, 徐 凯, 姚明华. 辣椒新品种‘鄂椒红元帅’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 119-120. |
| [7] | 魏晓羽, 王跃进. 中国野生葡萄果皮解剖结构与白粉病抗性的相关性研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(6): 1200-1212. |
| [8] | 黄静静, 刘伟, 刘玉梅, 韩风庆, 方智远, 杨丽梅, 庄木, 张扬勇, 吕红豪, 王勇, 季家磊, 李占省. Ogura CMS青花菜育性恢复材料创制及其遗传背景研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(3): 533-547. |
| [9] | 唐 征, 徐 谦, 张小玲, 刘 庆, 朱世杨, 钟伟杰. 青花菜新品种‘瓯绿75’[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(S2): 2835-2836. |
| [10] | 王 飞, 李 宁, 尹延旭, 高升华, 姚明华. 辣椒新品种‘鄂玉兰椒’[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(S2): 2843-2844. |
| [11] | 张双双, 苏维, 刘阳, 王海平, 宋江萍, 阳文龙, 贾会霞, 张晓辉, 李锡香. 白菜与埃塞俄比亚芥远缘杂交种质创制及黑腐病抗性转育[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(7): 1304-1316. |
| [12] | 荐红举, 万梦圆, 付毅, 丁艺, 琚熙三, 尚丽娜, 李辉, 王季春, 胡柏耿, 吕典秋. 马铃薯CHI家族基因鉴定及其对外源水杨酸和茉莉酸的响应分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(1): 83-95. |
| [13] | 李继东*,倪 静*,叶 霞,陈 鹏,谭 彬,张梦洋,郑先波,张 玉,冯建灿**. 枣AP2/ERF转录因子鉴定及其响应枣疯病植原体表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2020, 47(8): 1463-1474. |
| [14] | 吴元立1,黄秉智1,*,张智胜2,杨兴玉1. 香蕉枯萎病抗性离体接种鉴定方法的优化[J]. 园艺学报, 2020, 47(8): 1577-1584. |
| [15] | 赵凯茜,丁 茜,王跃进*. 中国野生毛葡萄芪合酶基因VqSTS11和VqSTS23调控抗白粉病的研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2020, 47(7): 1264-1276. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司