
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (7): 1901-1914.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0515
李红1,2,4, 牛新湘3,5, 吴凤康2,6, 杨红梅2,4,5, 楚敏2,4,5, 包慧芳2,4, 王宁2,4,5, 詹发强2,4, 杨蓉2,4, 娄恺2,4, 史应武1,2,4,5,*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-04-14
修回日期:2025-05-09
出版日期:2025-07-23
发布日期:2025-07-23
通讯作者:
基金资助:
LI Hong1,2,4, NIU Xinxiang3,5, WU Fengkang2,6, YANG Hongmei2,4,5, CHU Min2,4,5, BAO Huifang2,4, WANG Ning2,4,5, ZHAN Faqiang2,4, YANG Rong2,4, LOU Kai2,4, and SHI Yingwu1,2,4,5,*( )
)
Received:2025-04-14
Revised:2025-05-09
Published:2025-07-23
Online:2025-07-23
摘要: 为了鉴定萎缩芽孢杆菌(Bacillus atrophicus)SHZ-24产生的脂类抑菌物质,采用硅胶柱层析和液质联用(LC-MS)法对其进行鉴定;同时,在厚皮甜瓜‘西州蜜25号’上施用该菌提取的脂类抑菌物质,测定贮藏期间香气成分,以及乙醇脱氢酶(ADH)和脂氧合酶(LOX)的酶活性,探究脂类抑菌物质对厚皮甜瓜贮藏期风味品质的影响。结果表明,萎缩芽孢杆菌SHZ-24的脂类提取物对甜瓜腐烂病病原菌CH-3(Fusarium oxysporum)的抑菌活性为66.54%,有明显的抑菌作用,且起主要作用的是羟基脂肪酸类物质。将该物质作用于厚皮甜瓜‘西州蜜25号’25 d后,相较于正常贮藏的,其挥发性风味物质从25种增加到35种,其中乙酸乙酯、乙酸己脂、乙酸-2-甲基丁酯等主要风味物质相对含量明显提高;相较于病原菌处理后贮藏的,醇类、醛类、烃类物质种类和相对含量均有所降低。对厚皮甜瓜酯类代谢关键酶测定发现,相较于被病原菌侵染的厚皮甜瓜,用脂类抑菌物质处理后的乙醇脱氢酶的活性提高了4.53倍,脂氧合酶的活性提高了1.18倍,说明该菌脂类提取物能抑制病原菌侵染厚皮甜瓜,调节脂类代谢关键酶,延缓厚皮甜瓜的腐败,同时可有效维持甜瓜的香气。菌株SHZ-24脂类抑菌物质在厚皮甜瓜贮藏期间表现出较好的生物防治效果,可应用于甜瓜的贮藏保鲜。
李红, 牛新湘, 吴凤康, 杨红梅, 楚敏, 包慧芳, 王宁, 詹发强, 杨蓉, 娄恺, 史应武. 萎缩芽孢杆菌抑菌物质的鉴定及其对厚皮甜瓜贮藏期风味品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(7): 1901-1914.
LI Hong, NIU Xinxiang, WU Fengkang, YANG Hongmei, CHU Min, BAO Huifang, WANG Ning, ZHAN Faqiang, YANG Rong, LOU Kai, and SHI Yingwu. Identification of Antifungal Substances of Bacillus atrophicus and Their Effects on Flavor Quality of Thick-skinned Melons During the Storage Period[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(7): 1901-1914.

图1 抑菌脂类对厚皮甜瓜病原菌的抑制效果(A)和抑菌脂类柱层析各组分抑菌活性(B)
Fig. 1 Inhibitory effect of antibacterial lipids on pathogenic bacteria of muskmelon(A)and antibacterial activity of each component of antibacterial lipid column chromatography(B)

图2 抑菌脂类对厚皮甜瓜病原菌的抑制作用 CK:对照;T1:乙酸乙酯;T2:抑菌物质
Fig. 2 Inhibitory effect of inhibitory lipids on pathogenic bacteria of thick-skinned melons CK:Control;T1:Ethyl acetate;T2:Antifungal substances
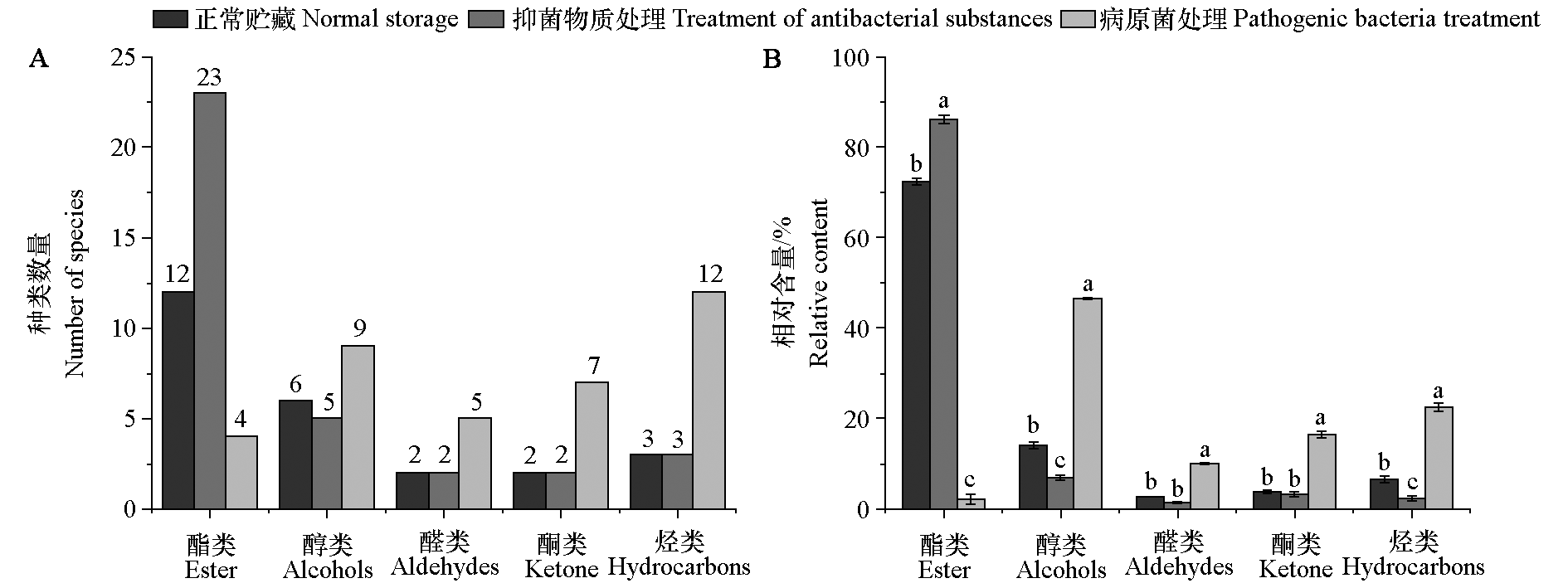
图4 抑菌物质处理和病原菌处理后甜瓜中香气物质种类(A)和相对含量(B)差异 不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P < 0.05)
Fig. 4 Differences in the types(A)and relative content(B)of aroma substances in Cucumis melo after treatment with antifungal substances and pathogen treatment Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between treatments(P < 0.05)
| 类别 Category | 组分名称 Component name | 正常贮藏 Normal storage | 病原菌处理 Pathogenic bacteria treatment | SHZ-24处理 SHZ-24 processing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 酯类 Ester | 2-己烯-1-醇乙酸酯 2-Hexen-1-ol acetate | 4.82 ± 0.27 a | - | 2.79 ± 0.03 b |
| 乙酸正己酯 Hexyl acetate | 11.66 ± 0.16 a | - | 3.97 ± 0.02 b | |
| 3-壬烯-1-醇乙酸酯 3-Nonen-1-ol acetate | 4.52 ± 0.06 a | - | 3.29 ± 0.01 b | |
| 乙酸异丙酯 Isopropyl acetate | 2.34 ± 0.01 | - | - | |
| 2-甲基丙酸甲酯 Methyl 2-methylpropionate | 1.57 ± 0.01 | - | - | |
| 乙酸乙酯 Ethyl acetate | 3.66 ± 0.23 b | - | 28.45 ± 0.31 a | |
| 2-甲基丁酸甲酯 Methyl 2-methylbutyrate | 6.54 ± 0.19 a | - | 4.28 ± 0.02 b | |
| 乙酸仲丁酯 Sec-butyl acetate | 0.78 ± 0.01 | - | - | |
| 乙酸异丁酯 Isobutyl acetate | 26.86 ± 0.06 a | - | 7.37 ± 0.04 b | |
| 乙酸正丁酯 Butyl acetate | 5.22 ± 0.12 | - | 1.28 ± 0.17 | |
| 2-甲基丁酸乙酯 Ethyl 2-methylbutyrate | 3.45 ± 0.01 a | - | 1.87 ± 0.01 b | |
| 乙酸正戊酯 Pentyl acetate | 0.88 ± 0.06 | - | - | |
| 壹亚油酸甘油酯 Glycerol monooleate | - | 1.03 ± 0.04 | - | |
| 9-十六碳烯酸乙酯 Ethyl 9-hexadecenoate | - | 0.55 ± 0.02 | - | |
| 2,2,4-三甲基-1,3-戊二醇二异丁酸酯 2,2,4-Trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol diisobutyrate | - | 0.26 ± 0.01 | - | |
| 十八烯酸乙酯 Ethyl octadecenoate | - | 0.19 ± 0.01 | - | |
| 异丁酸乙酯 Ethyl isobutyrate | - | - | 1.96 ± 0.01 | |
| 乙酸丁酯 Butyl acetate | - | - | 3.05 ± 0.14 | |
| 乙酸-2-甲基丁酯 2-Methylbutyl acetate | - | - | 5.97 ± 0.21 | |
| 乙酸已酯 Hexyl acetate | - | - | 8.25 ± 1.56 | |
| 乙酸苯甲酯 Phenylmethyl acetate | - | - | 2.35 ± 0.02 | |
| 丙酸苯甲酯 Phenylmethyl propionate | - | - | 0.86 ± 0.04 | |
| 4-甲基-3-己醇乙酸酯 4-Methyl-3-hexanol acetate | - | - | 0.17 ± 0.01 | |
| 丙酸-2-甲基3-苯乙酯 Propionic acid-2-methyl-3-phenylethyl ester | - | - | 3.78 ± 0.37 | |
| 氯乙酸-2-苯乙酯 2-Phenylethyl chloroacetate | - | - | 1.43 ± 0.33 | |
| 1,5-戊二醇二乙酸酯1,5-Pentanediol diacetate | - | - | 0.18 ± 0.56 | |
| 丙酸-2-甲基丙酯Propionate-2-methylpropyl ester | - | - | 0.68 ± 0.01 | |
| 乙酸辛酯 Octylacetate | - | - | 0.54 ± 0.11 | |
| (Z)-乙酸-3-己烯-1-醇酯 (Z)-3-Hexen-1-ol acetate | - | - | 0.75 ± 0.10 | |
| 2-甲基-1-丁醇乙酸酯 2-Methyl-1-butanol acetate | - | - | 1.45 ± 0.01 | |
| 正丙酸异丁酯 Isobutyl propionate | - | - | 1.42 ± 0.38 | |
| 醇类 Alcohols | 1-壬醇 1-nonanol | 2.87 ± 0.25 | - | - |
| 2,4-壬二烯-1-醇 2,4-Nonadien-1-ol | - | - | 1.27 ± 0.01 | |
| 3-壬烯-1-醇 3-Nonen-1-ol | 3.96 ± 0.43 | - | - | |
| 异辛醇 Isooctanol | 1.76 ± 0.46 a | 0.60 ± 0.01 b | 2.59 ± 0.50 a | |
| 1-正己醇 1-Hexanol | 0.67 ± 0.11 | - | - | |
| 3-辛醇 3-octanol | - | 0.78 ± 0.01 | - | |
| 反式-3-己烯-1-醇 trans-3-Hexen-1-ol | - | 0.59 ± 0.19 | - | |
| 无水乙醇 Absolute alcohol | - | 3.13 ± 0.37 | - | |
| 苯乙醇 Phenylethyl alcohol | 2.72 ± 1.7 b | 25.53 ± 0.79 a | 1.12 ± 0.66 b | |
| (2R,3R)-(-)-2,3-丁二醇(2R,3R)-(-)-2,3-Butanediol | - | 8.17 ± 2.09 | - | |
| 2,3-丁二醇 2,3-Butanediol | - | 1.17 ± 0.82 | - | |
| 1-烯-3-辛醇 1-ene-3-Octanol | - | 1.90 ± 0.73 | - | |
| 甲基苯甲醇 Methyl benzyl alcohol | - | 4.70 ± 0.66 | - | |
| 3,6-壬二烯-1-醇 3,6-Nonadien-1-ol | 2.15 ± 0.01 a | - | 1.52 ± 0.01 a | |
| 4-壬烯-1-醇 4-Nonen-1-ol | - | - | 0.27 ± 0.01 | |
| 醛类 Aldehydes | 2,5-二羟基苯甲醛 2,5-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde | 0.95 ± 0.38 b | 5.59 ± 0.42 a | - |
| 反-2-壬烯醛 trans-2-Nonenal | 1.76 ± 0.14 a | 0.57 ± 0.57 b | - | |
| 2-苯基巴豆醛 2-Phenylcrotonaldehyde | - | 1.15 ± 0.43 | - | |
| 苄甲醛 Benzaldehyde | - | 0.59 ± 0.55 | - | |
| (E)-壬烯醛(E)-Nonenal | - | 2.05 ± 0.17 a | 0.13 ± 0.09 b | |
| (E)-2-壬烯醛(E)-2-Nonenal | - | - | 1.28 ± 0.01 a | |
| 酮类 Ketone | 异佛尔酮 Isophorone | 0.33 ± 0.05 b | - | 2.21 ± 0.07 a |
| 香叶基丙酮 Geranyl acetone | 3.41 ± 1.03 a | 0.58 ± 0.62 c | 1.01 ± 0.56 b | |
| 苯乙酮 Acetophenone | - | 6.63 ± 1.28 | - | |
| 乙偶姻 Acetoin | - | 2.91 ± 0.01 | - | |
| 3-辛酮 3-Octanone | - | 2.77 ± 0.26 | - | |
| 3-辛烯-2-酮 3-Octen-one | - | 0.54 ± 0.07 | - | |
| 2-(1-盐酸环戊醇乙胺酯-1-烯基-1-甲基乙基甲酮)环戊酮 2-(1-Cyclopentyl ethylamine hydrochloride-1-alkenyl- 1-methylethyl ketone)cyclopentanone | - | 2.71 ± 0.86 | - | |
| 1-(1,4-二甲基-3-环己烯-1-基)乙酮 1-(1,4-dimethyl-3-cyclohexen-1-yl)ethanone | - | 0.29 ± 0.77 | - | |
| 烃类 Hydrocarbons | 正十四烷 N-tetradecane | 1.20 ± 0.01 a | 2.21 ± 0.51 a | 0.40 ± 0.04 b |
| 长叶烯 Longifolene | 2.69 ± 0.33 a | 0.36 ± 0.12 c | 1.36 ± 0.69 b | |
| 正十九烷 N-nonadecane | - | - | 0.66 ± 0.01 a | |
| 姜黄烯 Curcumene | - | 0.76 ± 0.24 | - | |
| 3,5-二甲氧基甲苯 3,5-Dimethoxytoluene | - | 1.94 ± 0.47 | - | |
| 2,6,10-三甲基十三烷 2,6,10-Trimethyltridecane | - | 0.49 ± 0.25 | - | |
| 卡地那-1,4-二烯 Cardina-1,4-diene | - | 2.17 ± 0.17 | - | |
| 正二十一烷 N-heneicosane | - | 1.92 ± 0.36 | - | |
| 4-烯丙基-1,2-二甲氧基苯 4-Allyl-1,2-dimethoxybenzene | - | 0.30 ± 0.01 | - | |
| (+)-花侧柏烯(+)-Platycladiene | - | 0.24 ± 0.05 | - | |
| 荜澄茄油宁烯 Cubenene | - | 2.01 ± 0.07 | - | |
| 十八甲基环蜀氧烷 Octadecylmethylcyclosiloxane | - | 9.53 ± 0.58 | - | |
| 2,6,10-三甲基十三烷 2,6,10-Trimethyltridecane | 2.53 ± 0.43 a | 0.49 ± 0.01 b | - |
表1 不同处理组甜瓜香气成分与相对含量比较
Table 1 Comparison of aroma components and relative contents of melon in different treatment groups %
| 类别 Category | 组分名称 Component name | 正常贮藏 Normal storage | 病原菌处理 Pathogenic bacteria treatment | SHZ-24处理 SHZ-24 processing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 酯类 Ester | 2-己烯-1-醇乙酸酯 2-Hexen-1-ol acetate | 4.82 ± 0.27 a | - | 2.79 ± 0.03 b |
| 乙酸正己酯 Hexyl acetate | 11.66 ± 0.16 a | - | 3.97 ± 0.02 b | |
| 3-壬烯-1-醇乙酸酯 3-Nonen-1-ol acetate | 4.52 ± 0.06 a | - | 3.29 ± 0.01 b | |
| 乙酸异丙酯 Isopropyl acetate | 2.34 ± 0.01 | - | - | |
| 2-甲基丙酸甲酯 Methyl 2-methylpropionate | 1.57 ± 0.01 | - | - | |
| 乙酸乙酯 Ethyl acetate | 3.66 ± 0.23 b | - | 28.45 ± 0.31 a | |
| 2-甲基丁酸甲酯 Methyl 2-methylbutyrate | 6.54 ± 0.19 a | - | 4.28 ± 0.02 b | |
| 乙酸仲丁酯 Sec-butyl acetate | 0.78 ± 0.01 | - | - | |
| 乙酸异丁酯 Isobutyl acetate | 26.86 ± 0.06 a | - | 7.37 ± 0.04 b | |
| 乙酸正丁酯 Butyl acetate | 5.22 ± 0.12 | - | 1.28 ± 0.17 | |
| 2-甲基丁酸乙酯 Ethyl 2-methylbutyrate | 3.45 ± 0.01 a | - | 1.87 ± 0.01 b | |
| 乙酸正戊酯 Pentyl acetate | 0.88 ± 0.06 | - | - | |
| 壹亚油酸甘油酯 Glycerol monooleate | - | 1.03 ± 0.04 | - | |
| 9-十六碳烯酸乙酯 Ethyl 9-hexadecenoate | - | 0.55 ± 0.02 | - | |
| 2,2,4-三甲基-1,3-戊二醇二异丁酸酯 2,2,4-Trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol diisobutyrate | - | 0.26 ± 0.01 | - | |
| 十八烯酸乙酯 Ethyl octadecenoate | - | 0.19 ± 0.01 | - | |
| 异丁酸乙酯 Ethyl isobutyrate | - | - | 1.96 ± 0.01 | |
| 乙酸丁酯 Butyl acetate | - | - | 3.05 ± 0.14 | |
| 乙酸-2-甲基丁酯 2-Methylbutyl acetate | - | - | 5.97 ± 0.21 | |
| 乙酸已酯 Hexyl acetate | - | - | 8.25 ± 1.56 | |
| 乙酸苯甲酯 Phenylmethyl acetate | - | - | 2.35 ± 0.02 | |
| 丙酸苯甲酯 Phenylmethyl propionate | - | - | 0.86 ± 0.04 | |
| 4-甲基-3-己醇乙酸酯 4-Methyl-3-hexanol acetate | - | - | 0.17 ± 0.01 | |
| 丙酸-2-甲基3-苯乙酯 Propionic acid-2-methyl-3-phenylethyl ester | - | - | 3.78 ± 0.37 | |
| 氯乙酸-2-苯乙酯 2-Phenylethyl chloroacetate | - | - | 1.43 ± 0.33 | |
| 1,5-戊二醇二乙酸酯1,5-Pentanediol diacetate | - | - | 0.18 ± 0.56 | |
| 丙酸-2-甲基丙酯Propionate-2-methylpropyl ester | - | - | 0.68 ± 0.01 | |
| 乙酸辛酯 Octylacetate | - | - | 0.54 ± 0.11 | |
| (Z)-乙酸-3-己烯-1-醇酯 (Z)-3-Hexen-1-ol acetate | - | - | 0.75 ± 0.10 | |
| 2-甲基-1-丁醇乙酸酯 2-Methyl-1-butanol acetate | - | - | 1.45 ± 0.01 | |
| 正丙酸异丁酯 Isobutyl propionate | - | - | 1.42 ± 0.38 | |
| 醇类 Alcohols | 1-壬醇 1-nonanol | 2.87 ± 0.25 | - | - |
| 2,4-壬二烯-1-醇 2,4-Nonadien-1-ol | - | - | 1.27 ± 0.01 | |
| 3-壬烯-1-醇 3-Nonen-1-ol | 3.96 ± 0.43 | - | - | |
| 异辛醇 Isooctanol | 1.76 ± 0.46 a | 0.60 ± 0.01 b | 2.59 ± 0.50 a | |
| 1-正己醇 1-Hexanol | 0.67 ± 0.11 | - | - | |
| 3-辛醇 3-octanol | - | 0.78 ± 0.01 | - | |
| 反式-3-己烯-1-醇 trans-3-Hexen-1-ol | - | 0.59 ± 0.19 | - | |
| 无水乙醇 Absolute alcohol | - | 3.13 ± 0.37 | - | |
| 苯乙醇 Phenylethyl alcohol | 2.72 ± 1.7 b | 25.53 ± 0.79 a | 1.12 ± 0.66 b | |
| (2R,3R)-(-)-2,3-丁二醇(2R,3R)-(-)-2,3-Butanediol | - | 8.17 ± 2.09 | - | |
| 2,3-丁二醇 2,3-Butanediol | - | 1.17 ± 0.82 | - | |
| 1-烯-3-辛醇 1-ene-3-Octanol | - | 1.90 ± 0.73 | - | |
| 甲基苯甲醇 Methyl benzyl alcohol | - | 4.70 ± 0.66 | - | |
| 3,6-壬二烯-1-醇 3,6-Nonadien-1-ol | 2.15 ± 0.01 a | - | 1.52 ± 0.01 a | |
| 4-壬烯-1-醇 4-Nonen-1-ol | - | - | 0.27 ± 0.01 | |
| 醛类 Aldehydes | 2,5-二羟基苯甲醛 2,5-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde | 0.95 ± 0.38 b | 5.59 ± 0.42 a | - |
| 反-2-壬烯醛 trans-2-Nonenal | 1.76 ± 0.14 a | 0.57 ± 0.57 b | - | |
| 2-苯基巴豆醛 2-Phenylcrotonaldehyde | - | 1.15 ± 0.43 | - | |
| 苄甲醛 Benzaldehyde | - | 0.59 ± 0.55 | - | |
| (E)-壬烯醛(E)-Nonenal | - | 2.05 ± 0.17 a | 0.13 ± 0.09 b | |
| (E)-2-壬烯醛(E)-2-Nonenal | - | - | 1.28 ± 0.01 a | |
| 酮类 Ketone | 异佛尔酮 Isophorone | 0.33 ± 0.05 b | - | 2.21 ± 0.07 a |
| 香叶基丙酮 Geranyl acetone | 3.41 ± 1.03 a | 0.58 ± 0.62 c | 1.01 ± 0.56 b | |
| 苯乙酮 Acetophenone | - | 6.63 ± 1.28 | - | |
| 乙偶姻 Acetoin | - | 2.91 ± 0.01 | - | |
| 3-辛酮 3-Octanone | - | 2.77 ± 0.26 | - | |
| 3-辛烯-2-酮 3-Octen-one | - | 0.54 ± 0.07 | - | |
| 2-(1-盐酸环戊醇乙胺酯-1-烯基-1-甲基乙基甲酮)环戊酮 2-(1-Cyclopentyl ethylamine hydrochloride-1-alkenyl- 1-methylethyl ketone)cyclopentanone | - | 2.71 ± 0.86 | - | |
| 1-(1,4-二甲基-3-环己烯-1-基)乙酮 1-(1,4-dimethyl-3-cyclohexen-1-yl)ethanone | - | 0.29 ± 0.77 | - | |
| 烃类 Hydrocarbons | 正十四烷 N-tetradecane | 1.20 ± 0.01 a | 2.21 ± 0.51 a | 0.40 ± 0.04 b |
| 长叶烯 Longifolene | 2.69 ± 0.33 a | 0.36 ± 0.12 c | 1.36 ± 0.69 b | |
| 正十九烷 N-nonadecane | - | - | 0.66 ± 0.01 a | |
| 姜黄烯 Curcumene | - | 0.76 ± 0.24 | - | |
| 3,5-二甲氧基甲苯 3,5-Dimethoxytoluene | - | 1.94 ± 0.47 | - | |
| 2,6,10-三甲基十三烷 2,6,10-Trimethyltridecane | - | 0.49 ± 0.25 | - | |
| 卡地那-1,4-二烯 Cardina-1,4-diene | - | 2.17 ± 0.17 | - | |
| 正二十一烷 N-heneicosane | - | 1.92 ± 0.36 | - | |
| 4-烯丙基-1,2-二甲氧基苯 4-Allyl-1,2-dimethoxybenzene | - | 0.30 ± 0.01 | - | |
| (+)-花侧柏烯(+)-Platycladiene | - | 0.24 ± 0.05 | - | |
| 荜澄茄油宁烯 Cubenene | - | 2.01 ± 0.07 | - | |
| 十八甲基环蜀氧烷 Octadecylmethylcyclosiloxane | - | 9.53 ± 0.58 | - | |
| 2,6,10-三甲基十三烷 2,6,10-Trimethyltridecane | 2.53 ± 0.43 a | 0.49 ± 0.01 b | - |
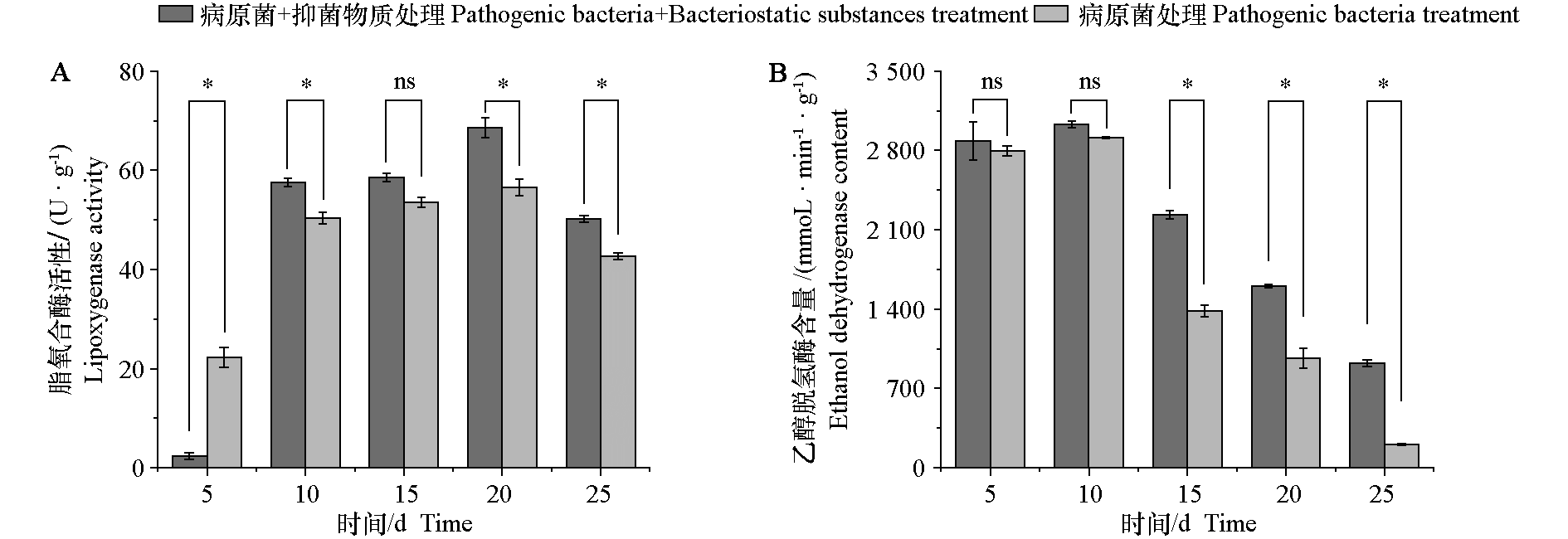
图5 抑菌脂类物质对厚皮甜瓜酯类代谢关键酶脂氧合酶(A)和乙醇脱氢酶(B)的影响 * 表示不同处理间差异显著(P < 0.05);ns表示不同处理间没有显著差异
Fig. 5 Effects of antimicrobial lipids on the key enzymes lipoxygenase(A)and alcohol dehydrogenase(B)in ester metabolism of Cucumis melo * indicates significant difference between treatments(P < 0.05);ns indicates no significant difference between treatments
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
|
陈莉. 2016. Bacillus atrophaeus B44产生iturin A及其对棉苗立枯病的防病促生作用[博士论文]. 石河子: 石河子大学.
|
|
| [3] |
|
|
程小梅. 2022. 肉桂酸对白地霉的抑菌机制研究[博士论文]. 长沙: 湖南大学. (in Chinese)
|
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
|
代文婷, 刘战霞, 陈伟君, 张强. 2024. 脂氧合酶对甜瓜果实后熟软化生理及相关基因表达的影响. 江苏农业科学, 52 (1):128-133.
|
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
|
韩洁. 2023. 棕榈酸对溶藻弧菌的抑菌机理及毒力调控机制研究[硕士论文]. 西安: 陕西科技大学.
|
|
| [8] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0741 |
|
何亚芳, 包慧芳, 王宁, 詹发强, 张学军, 史应武, 杨蓉, 侯新强, 龙宣杞. 2023. 甜瓜镰刀菌果腐病菌拮抗菌筛选及其拮抗性研究. 园艺学报, 50 (10):2257-2270.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0741 |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
|
黄东梅, 马伏宁, 吴斌, 许奕, 徐兵强, 邢文婷, 宋顺. 2022. 紫果西番莲果实发育过程中挥发性香气物质及相关酶活性的变化. 热带作物学报, 43 (9):1935-1944.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2022.09.022 |
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.1007/s13197-020-04333-5 pmid: 32624603 |
| [13] |
|
|
李娟, 魏珊珊, 刘贵珊, 康宁波, 鲁玲, 贾莉莉. 2022. 果实采后贮藏过程乙醇代谢的研究进展. 中国果树,(9):1-6.
|
|
| [14] |
|
|
李亚男, 蒋芬, 张杰, 范永义, 陈敬, 彭友林, 胡运高. 2017. 高原土壤中稻瘟病拮抗细菌的抑菌效果及抗菌机理. 应用与环境生物学报, 23 (1):33-40. (in Chinese)
|
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
doi: 10.16606/j.cnki.issn0253-4320.2019.12.011 |
|
刘思靖. 2019. 萎缩芽孢杆菌次级代谢产物的研究进展. 现代化工, 39 (12):48-51.
doi: 10.16606/j.cnki.issn0253-4320.2019.12.011 |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0053 |
|
刘文欢, 邱芳颖, 王娅, 陈朗, 马岩岩, 吕强, 易时来, 谢让金, 郑永强. 2022. 枯草芽孢杆菌液态肥对柑橘养分吸收和果实品质的影响. 园艺学报, 49 (3):509-518.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0053 |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
|
马荣, 王敏, 蔡桂芳, 翟亚伟, 贾海英, 鲁海龙. 2020. 萎缩芽孢杆菌XW2对苹果树腐烂病的室内防效评价. 新疆农业大学学报, 43 (2):108-112. (in Chinese)
|
|
| [21] |
|
|
马伟超, 康艳丽, 李一婧. 2021. 不同保鲜剂对秦安蜜桃贮藏期香气成分的影响. 中国果菜, 41 (6):67-73,111.
|
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.1094/PDIS-04-19-0741-RE pmid: 32223640 |
| [24] |
|
|
穆晓清, 鲁耀雄, 戴良英, 黄国林, 陈薇, 张榉邺, 韦晨曦. 2024. 贝莱斯芽胞杆菌YFB3-1对辣椒疫霉的抑菌效果及其抑菌物质. 农业生物技术学报, 32 (4):859-872.
|
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
|
冉林, 焦阳, 凌键, 杨宇红, 茆振川, 谢丙炎, 李彦. 2024. 苇状木霉3199菌株对黄瓜枯萎病的生物防治研究. 植物病理学报, 54 (2):429-435.
doi: 10.13926/j.cnki.apps.001608 |
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-04-10-0125 pmid: 20879844 |
| [30] |
Rodrigues Magalhães H C,
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
|
苏慧, 曾瑶英, 张家铭, 熊玉帛, 郭航宇, 熊雯, 龚林, 周文化. 2025. 葡萄采后表皮蜡质与果实贮藏品质的研究. 食品工业科技, 46 (5):318-328.
|
|
| [33] |
doi: 10.1007/s00122-021-03843-w pmid: 33950283 |
| [34] |
|
|
王璐. 2019. 萎缩芽孢杆菌CP 297和解淀粉芽孢杆菌CP 2014对毛桃致腐霉菌的抑菌机理及保鲜应用[硕士论文]. 太谷: 山西农业大学.
|
|
| [35] |
|
|
王静怡, 佐长赓, 牛新湘, 管力慧, 杨红梅, 楚敏, 王宁, 林青, 娄恺, 史应武. 2022. 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌处理对厚皮甜瓜保鲜效果及保护酶活性的影响. 食品工业科技, 43 (17):355-362.
|
|
| [36] |
|
|
王亚男, 史雅坤, 唐晓琳. 2020. 脂类物质抗菌的研究进展. 中国微生态学杂志, 32 (10):1210-1214.
|
|
| [37] |
|
|
吴琼, 张甜甜, 李茂营, 吴慧玲, 郭绍贵, 张洁, 任毅, 张海英, 宫国义. 2024. 解淀粉芽孢杆菌5号防控西瓜CGMMV机制初探. 园艺学报, 51 (10):2427-2438.
|
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
|
宰清勇, 陈华国, 谢文, 周欣. 2023. 不同提取方法对宁夏枸杞多糖化学组成及生物活性的影响研究. 中国中药杂志, 48 (1):60-70.
|
|
| [41] |
|
|
张容鹄, 邓浩, 梁振深, 李远颂, 冯建成, 方宗壮. 2017. HS-SPME-GC-MS法分析西州蜜25号甜瓜贮藏中的香气成分. 保鲜与加工, 17 (6):98-105.
|
|
| [42] |
|
|
郑贺云, 耿新丽, 姚军, 张翠环, 廖新福. 2020. 新疆厚皮甜瓜采后病害真菌的鉴定及多样性分析. 西南农业学报, 33 (4):788-796.
|
|
| [43] |
|
|
郑鄢燕, 赵力卉, 王宇滨, 马越, 赵晓燕. 2020. 链格孢、粉红单端孢通过降解果皮细胞壁导致哈密瓜病害. 食品与发酵工业, 46 (10):124-131.
doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.023148 |
|
| [44] |
|
|
郑怡, 江红霞, 林雄平. 2004. 厚网藻脂类化合物的化学分析及抑菌作用. 海洋科学,(10):42-44.
|
| [1] | 余小林, 平 凡, 黄 鹂, 曹家树, 宋建伟, 卢 钢. 早中熟不结球白菜新品种‘钱塘青’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 91-92. |
| [2] | 张古文, 沈 立, 刘 娜, 冯志娟, 卜远鹏, 王 斌, 龚亚明. 菜用大豆新品种‘浙农15号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 129-130. |
| [3] | 吴丹丹, 林梦桦, 李亚辉, 梁颖, 张志勇. ‘玉露香’梨不同采摘期及贮藏期果实品质变化分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(6): 1553-1574. |
| [4] | 陈学森, 王楠, 张宗营, 张淑辉, 刘文军, 邹琦, 于蕾, 张静, 姜远茂, 胡大刚, 李媛媛, 毛志泉. 富营养强风味轻简化宜机化苹果育种研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(6): 1661-1676. |
| [5] | 褚文龙, 张晓莉, 徐良, 王燕, 柳李旺. 萝卜基因组学与分子育种研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(5): 1251-1270. |
| [6] | 许秀秀, 叶鑫雨, 师博, 张淑江, 章时蕃, 李菲, 李国亮, 孙日飞, 王顺利, 孙华刚, 张慧. 大白菜玉田包尖的风味品质分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(5): 1364-1374. |
| [7] | 杜豪, 赵世龙, 肖元松, 罗静静, 彭福田. 蛋氨酸对桃树新梢生长和果实品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(4): 973-983. |
| [8] | 孔佳涛, 付彩霞, 吴雅诺, 刘园, 胡哲辉, 徐娟, 黄皓, 赵曌, 陈磊, 陈嘉景. 冰糖橙风味组学解析及风味品质差异分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(4): 984-996. |
| [9] | 林茜, 邓振鹏, 阳新月, 周克友, 易小平, 王季春. 减施化肥配施有机肥对马铃薯产量及养分利用的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(4): 1007-1019. |
| [10] | 程小改, 万源, 林琭, 谢鹏, 李志强, 李谧, 王鹏鹏, 牛自勉. 苹果开心树形树干高度对不同冠层部位叶片光合特性及果实品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 671-692. |
| [11] | 丛鑫, 胡乾元, 庞桂斌, 徐立荣, 徐征和, 刘鸿飞, 裴向丽. 灌溉水矿化度对冬枣生长及产量品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 714-726. |
| [12] | 任艺, 张益兴, 侯赛赛, 乜兰春, 李青云, 王鑫鑫. 生物炭的制备方法及其在设施蔬菜中的应用研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 792-812. |
| [13] | 许桐, 王越, 吴丽娜, 张航, 尹立来, 徐柯宇, 郑小林. 褪黑素处理对‘桃形李’采后果实品质及花色苷代谢的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 395-405. |
| [14] | 陈亚娟, 金鑫, 杨江山, 戴子博, 李斗, 邵璋. 黄腐酸钾对‘蛇龙珠’葡萄果实糖酸代谢及香味物质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 406-422. |
| [15] | 张诗琦, 黄璐, 程茜, 张晓燕, 袁宇婷, 侯轶晨, 戴冬青, 夏秀东, 袁星星, 陈新, 朱月林, 薛晨晨. 不同播期对鲜食大豆品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 213-228. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司