
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 714-726.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0404
丛鑫1, 胡乾元2, 庞桂斌1, 徐立荣1, 徐征和1,*( ), 刘鸿飞1, 裴向丽1
), 刘鸿飞1, 裴向丽1
收稿日期:2024-07-17
修回日期:2025-01-22
出版日期:2025-03-25
发布日期:2025-03-25
通讯作者:
基金资助:
CONG Xin1, HU Qianyuan2, PANG Guibin1, XU Lirong1, XU Zhenghe1,*( ), LIU Hongfei1, PEI Xiangli1
), LIU Hongfei1, PEI Xiangli1
Received:2024-07-17
Revised:2025-01-22
Published:2025-03-25
Online:2025-03-25
摘要:
为明确不同矿化度微咸水灌溉对冬枣自然生产条件下的灌溉效果与适用性,2020—2022年在山东省滨州市沾化区开展为期3年的冬枣灌溉水矿化度田间试验,供试枣品种为‘沾冬2号’,设置5个矿化度(含盐量)水平:1(对照)、2、3、4和5 g · L-1,研究不同矿化度灌溉水处理对冬枣的生理特性、生长、产量和果实品质的影响。在生理方面,总体上叶片叶绿素相对含量(SPAD)、净光合速率(Pn)、蒸腾速率(Tr)、暗呼吸速率(Rd)和表观量子效率(α)峰值出现在3或4 g · L-1矿化度处理,且相比对照显著升高;5 g · L-1处理的SPAD、Pn、Tr、α、初始荧光(F0)、PSⅡ最大量子产率(Fv/Fm)与3或4 g · L-1相比显著下降,而最大荧光(Fm)显著上升。在生长和产量方面,随灌溉水矿化度升高枣吊长度和产量均呈现降低趋势,4和5 g · L-1处理的产量较1 g · L-1显著降低。在品质方面,随灌溉水矿化度的升高,可溶性糖、可溶性固形物(TSS)、可滴定酸与维生素C显著增加,综合评价4 g · L-1处理的品质最佳。相关性分析发现,枣吊长度和Fv/Fm是影响产量的主要因素;基于随机算法对影响果实品质的叶片生理指标的重要性排序,Tr、Pn,max、Rd、Fv/Fm与Fm是影响品质的主要因素。从3年灌溉周期后的土壤盐分平衡状况分析,4和5 g · L-1矿化度处理存在土壤盐分积累过度的潜在风险。结果表明,在山东省滨州地区对‘沾冬2号’果园进行2 ~ 3 g · L-1微咸水灌溉,植株可通过调节自身光合特性来抵抗盐胁迫,维持正常生长并可提高果实品质。
丛鑫, 胡乾元, 庞桂斌, 徐立荣, 徐征和, 刘鸿飞, 裴向丽. 灌溉水矿化度对冬枣生长及产量品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 714-726.
CONG Xin, HU Qianyuan, PANG Guibin, XU Lirong, XU Zhenghe, LIU Hongfei, PEI Xiangli. Effect of the Salinity of Irrigation Water on Growth,Yield,and Quality of Ziziphus jujuba‘Dongzao’[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(3): 714-726.
| 水质类型 Type of water quality | TDS/ (g · L-1) | EC/ (μS · cm-1) | pH | K+/ (mg · L-1) | Na+/ (mg · L-1) | Ca2+/ (mg · L-1) | Mg2+/ (mg · L-1) | Cl-/ (mg · L-1) | SO42-/ (mg · L-1) | HCO3-/ (mg · L-1) | CO32-/ (mg · L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 淡水 Fresh water | 0.70 | 1 400 | 7.2 | 6.99 | 127 | 61.4 | 24.5 | 150 | 193 | 20.8 | 117 |
| 咸水 Saline water | 4.60 | 9 500 | 8.4 | 30.3 | 1071 | 212 | 221 | 1 785 | 853 | 21.3 | 394 |
表1 两种水源的理化性质
Table 1 Water physicochemical properties content of two water sources
| 水质类型 Type of water quality | TDS/ (g · L-1) | EC/ (μS · cm-1) | pH | K+/ (mg · L-1) | Na+/ (mg · L-1) | Ca2+/ (mg · L-1) | Mg2+/ (mg · L-1) | Cl-/ (mg · L-1) | SO42-/ (mg · L-1) | HCO3-/ (mg · L-1) | CO32-/ (mg · L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 淡水 Fresh water | 0.70 | 1 400 | 7.2 | 6.99 | 127 | 61.4 | 24.5 | 150 | 193 | 20.8 | 117 |
| 咸水 Saline water | 4.60 | 9 500 | 8.4 | 30.3 | 1071 | 212 | 221 | 1 785 | 853 | 21.3 | 394 |
| 生育期 Growing period | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 降水量 Precipitation | 灌溉量 Irrigation amount | 降水量 Precipitation | 灌溉量 Irrigation amount | 降水量 Precipitation | 灌溉量 Irrigation amount | |
| 萌芽—展叶期Sprout leaves period | 57.6 | 48 | 60.3 | 48 | 203.8 | 24 |
| 开花—幼果期Blossom-young fruit period | 70.5 | 48 | 124.8 | 24 | 76.1 | 48 |
| 果实膨大期Developing fruit period | 244.9 | 48 | 268.4 | 24 | 384.9 | 24 |
| 着色—成熟期Fruit ripe period | 55.3 | 24 | 120.1 | 0 | 103.7 | 24 |
| 全生育期Whole growth period | 428.3 | 168 | 573.6 | 96 | 768.5 | 120 |
表2 冬枣各生育阶段的降水量与灌溉量
Table 2 Precipitation and irrigation amount of winter jujube at different growth stages mm
| 生育期 Growing period | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 降水量 Precipitation | 灌溉量 Irrigation amount | 降水量 Precipitation | 灌溉量 Irrigation amount | 降水量 Precipitation | 灌溉量 Irrigation amount | |
| 萌芽—展叶期Sprout leaves period | 57.6 | 48 | 60.3 | 48 | 203.8 | 24 |
| 开花—幼果期Blossom-young fruit period | 70.5 | 48 | 124.8 | 24 | 76.1 | 48 |
| 果实膨大期Developing fruit period | 244.9 | 48 | 268.4 | 24 | 384.9 | 24 |
| 着色—成熟期Fruit ripe period | 55.3 | 24 | 120.1 | 0 | 103.7 | 24 |
| 全生育期Whole growth period | 428.3 | 168 | 573.6 | 96 | 768.5 | 120 |
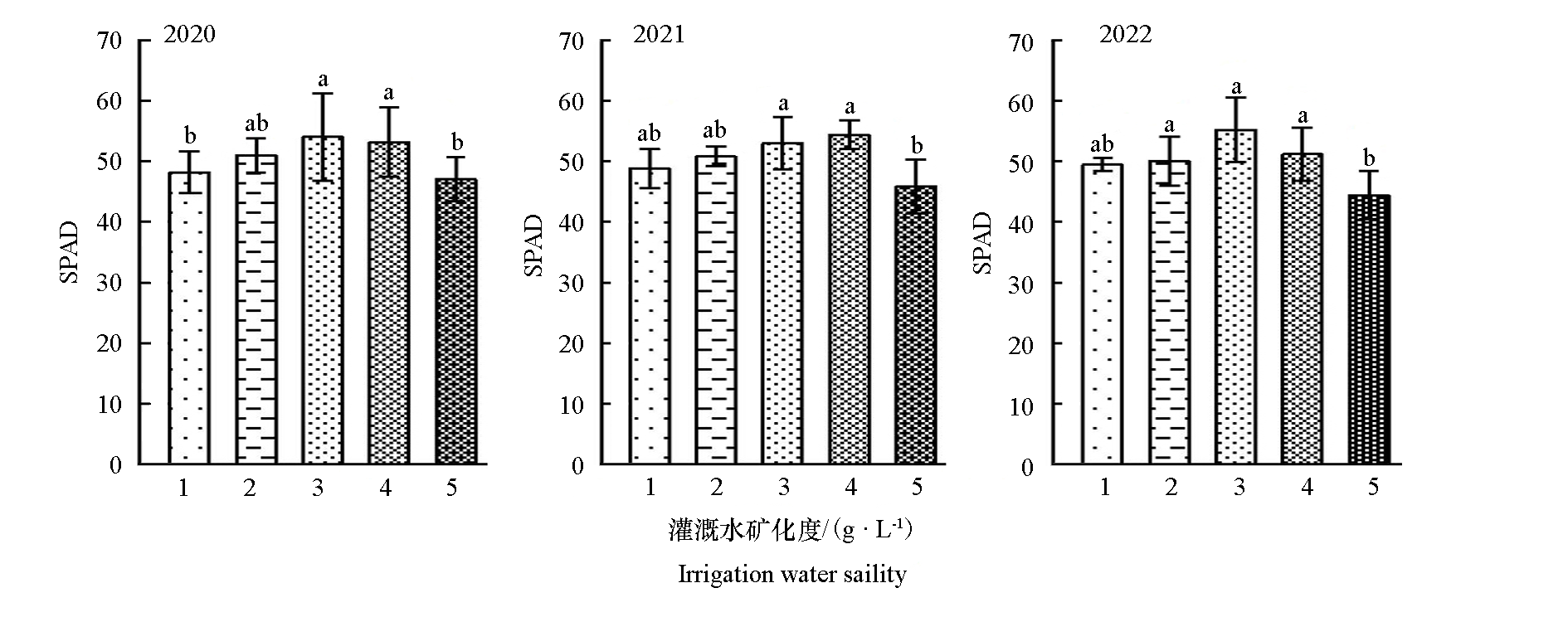
图2 不同矿化度灌溉水处理的冬枣叶片叶绿素相对含量(SPAD) 小写字母表示年内处理间差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同
Fig. 2 Chlorophyll SPAD of winter jujube leaves treated with different irrigation water salinity Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in processing time within the year at 0.05 level. The same below
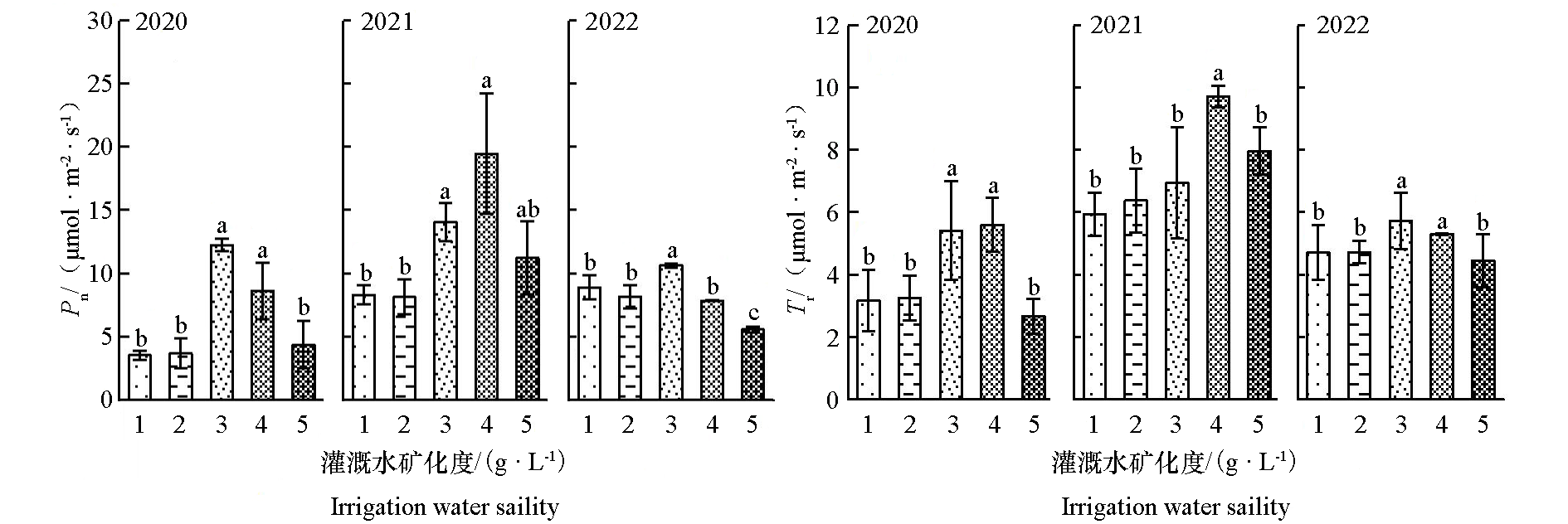
图3 不同矿化度灌溉水处理的冬枣叶片净光合速率与蒸腾速率
Fig. 3 Net photosynthetic rate and transpiration rate of winter jujube leaves treated with different irrigation water salinity
| 年 Year | 矿化度/(g · L-1)Salinity | Pn,max/(μmoL · m-2 · s-1) | Isat/(μmoL · m-2 · s-1) | Ic/(μmoL · m-2 · s-1) | Rd/(μmoL · m-2 · s-1) | α |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 1(对照control) | 19.90 ± 0.85 c | 1 242.89 ± 102.62 a | 61.14 ± 5.48 c | 4.41 ± 0.06 b | 0.0806 ± 0.0057 bc |
| 2 | 20.19 ± 0.91 c | 1 073.15 ± 49.41 b | 63.98 ± 6.14 c | 4.18 ± 0.06 b | 0.0710 ± 0.0035 c | |
| 3 | 28.65 ± 0.84 a | 950.19 ± 87.71 bc | 112.38 ± 2.57 b | 13.85 ± 0.91 a | 0.1474 ± 0.0124 a | |
| 4 | 29.02 ± 0.74 a | 915.48 ± 20.36 c | 115.37 ± 4.98 b | 15.85 ± 1.65 a | 0.1684 ± 0.0098 a | |
| 5 | 25.11 ± 0.45 b | 1 494.97 ± 150.41 a | 155.79 ± 2.64 a | 12.89 ± 1.34 a | 0.1031 ± 0.0192 bc | |
| 2021 | 1(对照control) | 8.99 ± 1.12 c | 1 859.22 ± 86.52 a | 108.43 ± 7.47 b | 2.59 ± 0.08 c | 0.0276 ± 0.0001 d |
| 2 | 15.68 ± 0.34 b | 1 930.57 ± 62.88 a | 100.19 ± 8.96 b | 3.44 ± 0.04 c | 0.0381 ± 0.0004 c | |
| 3 | 21.93 ± 0.78 a | 874.33 ± 20.16 c | 175.89 ± 8.25 a | 20.05 ± 0.18 a | 0.1489 ± 0.0018 a | |
| 4 | 21.18 ± 1.24 a | 937.60 ± 114.48 c | 99.80 ± 13.98 b | 11.49 ± 1.49 b | 0.1455 ± 0.0016 a | |
| 5 | 19.39 ± 1.59 a | 1 302.94 ± 31.80 b | 126.90 ± 14.54 b | 8.99 ± 1.18 b | 0.0866 ± 0.0002 b | |
| 2022 | 1(对照control) | 15.56 ± 0.28 a | 1 219.47 ± 48.92 c | 17.29 ± 6.67 c | 0.68 ± 0.01 c | 0.0401 ± 0.0001 a |
| 2 | 7.93 ± 1.98 b | 1 148.68 ± 90.20 c | 30.90 ± 6.64 bc | 0.64 ± 0.02 c | 0.0212 ± 0.0009 c | |
| 3 | 12.17 ± 2.47 b | 1 713.03 ± 78.16 a | 37.38 ± 5.98 b | 1.49 ± 0.05 b | 0.0429 ± 0.0001 a | |
| 4 | 8.74 ± 0.98 b | 1 474.51 ± 62.2 b | 64.12 ± 3.45 a | 1.91 ± 0.04 a | 0.0335 ± 0.0003 b | |
| 5 | 8.59 ± 1.21 b | 994.32 ± 81.27 c | 43.91 ± 3.55 b | 1.44 ± 0.04 b | 0.0353 ± 0.0004 b |
表3 不同矿化度灌溉水处理的冬枣叶片光响应曲线参数
Table 3 Parameters of light response curve of winter jujube leaves treated with different irrigation water salinity
| 年 Year | 矿化度/(g · L-1)Salinity | Pn,max/(μmoL · m-2 · s-1) | Isat/(μmoL · m-2 · s-1) | Ic/(μmoL · m-2 · s-1) | Rd/(μmoL · m-2 · s-1) | α |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 1(对照control) | 19.90 ± 0.85 c | 1 242.89 ± 102.62 a | 61.14 ± 5.48 c | 4.41 ± 0.06 b | 0.0806 ± 0.0057 bc |
| 2 | 20.19 ± 0.91 c | 1 073.15 ± 49.41 b | 63.98 ± 6.14 c | 4.18 ± 0.06 b | 0.0710 ± 0.0035 c | |
| 3 | 28.65 ± 0.84 a | 950.19 ± 87.71 bc | 112.38 ± 2.57 b | 13.85 ± 0.91 a | 0.1474 ± 0.0124 a | |
| 4 | 29.02 ± 0.74 a | 915.48 ± 20.36 c | 115.37 ± 4.98 b | 15.85 ± 1.65 a | 0.1684 ± 0.0098 a | |
| 5 | 25.11 ± 0.45 b | 1 494.97 ± 150.41 a | 155.79 ± 2.64 a | 12.89 ± 1.34 a | 0.1031 ± 0.0192 bc | |
| 2021 | 1(对照control) | 8.99 ± 1.12 c | 1 859.22 ± 86.52 a | 108.43 ± 7.47 b | 2.59 ± 0.08 c | 0.0276 ± 0.0001 d |
| 2 | 15.68 ± 0.34 b | 1 930.57 ± 62.88 a | 100.19 ± 8.96 b | 3.44 ± 0.04 c | 0.0381 ± 0.0004 c | |
| 3 | 21.93 ± 0.78 a | 874.33 ± 20.16 c | 175.89 ± 8.25 a | 20.05 ± 0.18 a | 0.1489 ± 0.0018 a | |
| 4 | 21.18 ± 1.24 a | 937.60 ± 114.48 c | 99.80 ± 13.98 b | 11.49 ± 1.49 b | 0.1455 ± 0.0016 a | |
| 5 | 19.39 ± 1.59 a | 1 302.94 ± 31.80 b | 126.90 ± 14.54 b | 8.99 ± 1.18 b | 0.0866 ± 0.0002 b | |
| 2022 | 1(对照control) | 15.56 ± 0.28 a | 1 219.47 ± 48.92 c | 17.29 ± 6.67 c | 0.68 ± 0.01 c | 0.0401 ± 0.0001 a |
| 2 | 7.93 ± 1.98 b | 1 148.68 ± 90.20 c | 30.90 ± 6.64 bc | 0.64 ± 0.02 c | 0.0212 ± 0.0009 c | |
| 3 | 12.17 ± 2.47 b | 1 713.03 ± 78.16 a | 37.38 ± 5.98 b | 1.49 ± 0.05 b | 0.0429 ± 0.0001 a | |
| 4 | 8.74 ± 0.98 b | 1 474.51 ± 62.2 b | 64.12 ± 3.45 a | 1.91 ± 0.04 a | 0.0335 ± 0.0003 b | |
| 5 | 8.59 ± 1.21 b | 994.32 ± 81.27 c | 43.91 ± 3.55 b | 1.44 ± 0.04 b | 0.0353 ± 0.0004 b |
| 矿化度/(g · L-1)Salinity | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1(对照control) | 29.5 ± 1.05 a | 30.4 ± 1.08 a | 28.6 ± 2.14 a |
| 2 | 27.4 ± 2.09 a | 29.8 ± 2.08 a | 29.2 ± 1.54 a |
| 3 | 25.1 ± 2.52 a | 28.9 ± 1.87 a | 27.9 ± 1.57 a |
| 4 | 24.1 ± 2.90 b | 28.1 ± 3.88 b | 25.8 ± 1.90 b |
| 5 | 23.2 ± 2.07 c | 27.1 ± 1.29 b | 23.1 ± 2.20 c |
表4 不同矿化度灌溉水对冬枣枣吊长度的影响
Table 4 Effects of the salinity of irrigation water on jujube hanging length of winter jujube cm
| 矿化度/(g · L-1)Salinity | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1(对照control) | 29.5 ± 1.05 a | 30.4 ± 1.08 a | 28.6 ± 2.14 a |
| 2 | 27.4 ± 2.09 a | 29.8 ± 2.08 a | 29.2 ± 1.54 a |
| 3 | 25.1 ± 2.52 a | 28.9 ± 1.87 a | 27.9 ± 1.57 a |
| 4 | 24.1 ± 2.90 b | 28.1 ± 3.88 b | 25.8 ± 1.90 b |
| 5 | 23.2 ± 2.07 c | 27.1 ± 1.29 b | 23.1 ± 2.20 c |
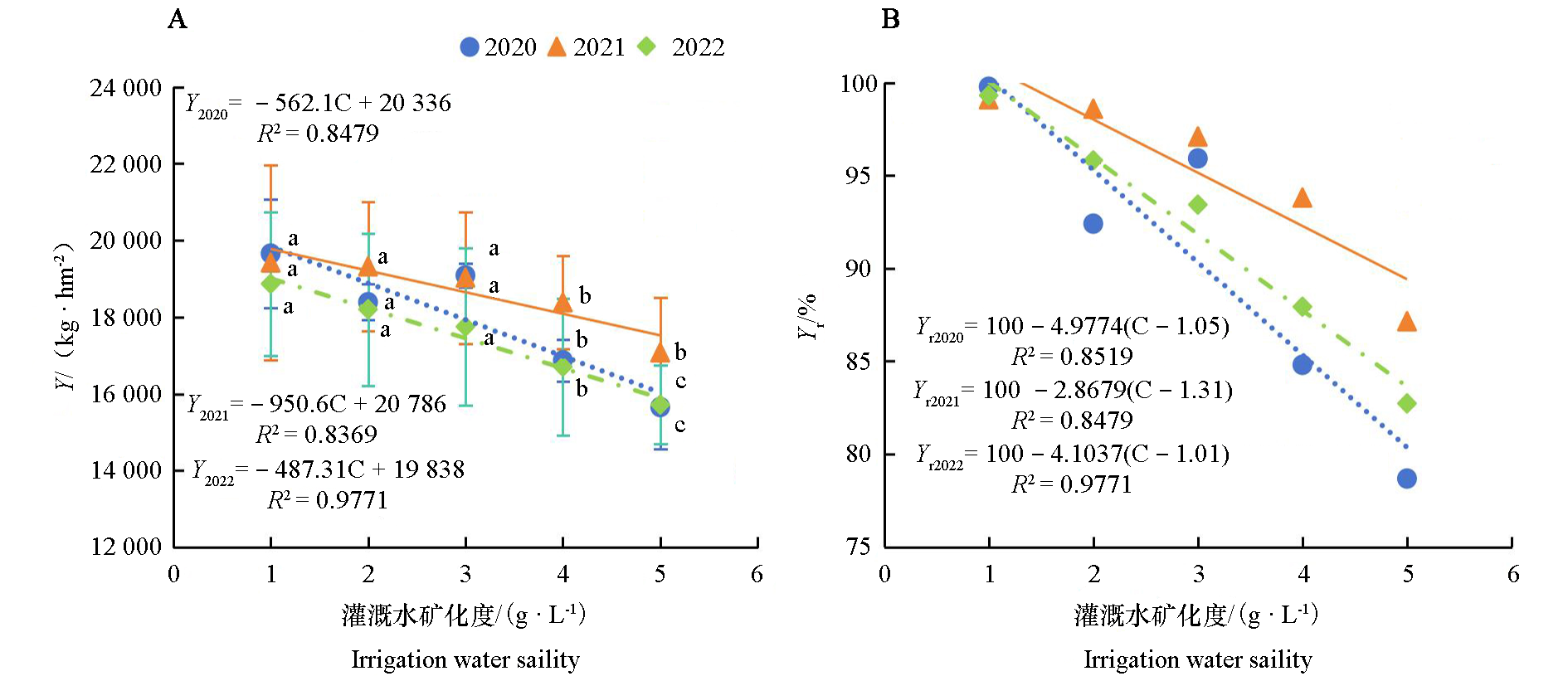
图5 冬枣产量(Y)、相对产量(Yr)和灌溉水矿化度(C)的拟合关系
Fig. 5 The fitting relationship between irrigation water salinity(C)and winter jujube yield(Y)and relative yield(Yr)
| 年份 | 矿化度/(g · L-1)Salinity | 果形指数 Fruit shape index | 单果质量/g Single fruit weight | 可溶性糖/% Soluble sugar | 总可溶性固形物/% Total soluble solids | 可滴定酸/% Titratable acid | 维生素C/(mg · g-1) Vitamin C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 1(对照control) | 0.95 ± 0.04 a | 24.57 ± 1.77 a | 19.78 ± 0.20 c | 21.10 ± 0.75 b | 0.12 ± 0.01 b | 2.82 ± 0.16 c |
| 2 | 1.01 ± 0.01 a | 22.99 ± 0.59 a | 20.26 ± 0.20 b | 22.27 ± 0.68 a | 0.12 ± 0.01 b | 2.93 ± 0.14 b | |
| 3 | 1.01 ± 0.02 a | 23.99 ± 0.40 a | 21.68 ± 0.20 b | 23.70 ± 1.73 a | 0.16 ± 0.01 a | 3.12 ± 0.08 b | |
| 4 | 1.01 ± 0.01 a | 21.90 ± 0.68 b | 22.34 ± 0.20 a | 24.23 ± 0.30 a | 0.16 ± 0.01 a | 3.65 ± 0.06 a | |
| 5 | 0.98 ± 0.02 a | 19.57 ± 2.12 b | 20.72 ± 0.20 b | 22.13 ± 0.80 a | 0.14 ± 0.01 ab | 3.07 ± 0.13 b | |
| 2021 | 1(对照control) | 0.97 ± 0.01 a | 23.78 ± 1.89 a | 17.06 ± 0.50 a | 20.07 ± 1.36 b | 0.29 ± 0.01 b | 2.41 ± 0.04 b |
| 2 | 0.98 ± 0.01 a | 24.16 ± 2.77 a | 16.59 ± 0.57 a | 21.42 ± 0.89 b | 0.27 ± 0.02 b | 2.53 ± 0.16 a | |
| 3 | 0.96 ± 0.07 a | 23.79 ± 2.45 a | 17.47 ± 0.98 a | 21.27 ± 0.92 b | 0.32 ± 0.01 a | 2.60 ± 0.20 a | |
| 4 | 0.99 ± 0.05 a | 21.73 ± 1.91 b | 19.18 ± 1.24 a | 22.89 ± 0.59 b | 0.32 ± 0.02 a | 2.62 ± 0.18 a | |
| 5 | 0.98 ± 0.05 a | 20.10 ± 3.07 b | 18.05 ± 0.3 a | 24.18 ± 1.03 a | 0.34 ± 0.03 a | 2.51 ± 0.05 a | |
| 2022 | 1(对照control) | 0.96 ± 0.11 a | 15.44 ± 1.44 a | 17.06 ± 0.50 a | 20.07 ± 1.36 b | 0.22 ± 0.02 b | 2.41 ± 0.04 b |
| 2 | 0.92 ± 0.06 a | 17.56 ± 1.52 a | 16.59 ± 0.57 a | 21.42 ± 0.89 b | 0.26 ± 0.02 b | 2.53 ± 0.16 a | |
| 3 | 1.01 ± 0.10 a | 18.31 ± 1.56 a | 17.47 ± 0.98 a | 21.27 ± 0.92 b | 0.29 ± 0.03 a | 2.60 ± 0.20 a | |
| 4 | 1.04 ± 0.08 a | 14.55 ± 1.56 b | 19.18 ± 1.24 a | 22.89 ± 0.59 b | 0.36 ± 0.02 a | 2.62 ± 0.18 a | |
| 5 | 0.98 ± 0.09 a | 10.41 ± 2.81 c | 18.05 ± 0.3 a | 24.18 ± 1.03 a | 0.33 ± 0.03 a | 2.51 ± 0.05 a |
表5 不同灌溉水矿化度对冬枣品质指标的影响
Table 5 Effects of the salinity of irrigation water on quality indexes of winter jujube
| 年份 | 矿化度/(g · L-1)Salinity | 果形指数 Fruit shape index | 单果质量/g Single fruit weight | 可溶性糖/% Soluble sugar | 总可溶性固形物/% Total soluble solids | 可滴定酸/% Titratable acid | 维生素C/(mg · g-1) Vitamin C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 1(对照control) | 0.95 ± 0.04 a | 24.57 ± 1.77 a | 19.78 ± 0.20 c | 21.10 ± 0.75 b | 0.12 ± 0.01 b | 2.82 ± 0.16 c |
| 2 | 1.01 ± 0.01 a | 22.99 ± 0.59 a | 20.26 ± 0.20 b | 22.27 ± 0.68 a | 0.12 ± 0.01 b | 2.93 ± 0.14 b | |
| 3 | 1.01 ± 0.02 a | 23.99 ± 0.40 a | 21.68 ± 0.20 b | 23.70 ± 1.73 a | 0.16 ± 0.01 a | 3.12 ± 0.08 b | |
| 4 | 1.01 ± 0.01 a | 21.90 ± 0.68 b | 22.34 ± 0.20 a | 24.23 ± 0.30 a | 0.16 ± 0.01 a | 3.65 ± 0.06 a | |
| 5 | 0.98 ± 0.02 a | 19.57 ± 2.12 b | 20.72 ± 0.20 b | 22.13 ± 0.80 a | 0.14 ± 0.01 ab | 3.07 ± 0.13 b | |
| 2021 | 1(对照control) | 0.97 ± 0.01 a | 23.78 ± 1.89 a | 17.06 ± 0.50 a | 20.07 ± 1.36 b | 0.29 ± 0.01 b | 2.41 ± 0.04 b |
| 2 | 0.98 ± 0.01 a | 24.16 ± 2.77 a | 16.59 ± 0.57 a | 21.42 ± 0.89 b | 0.27 ± 0.02 b | 2.53 ± 0.16 a | |
| 3 | 0.96 ± 0.07 a | 23.79 ± 2.45 a | 17.47 ± 0.98 a | 21.27 ± 0.92 b | 0.32 ± 0.01 a | 2.60 ± 0.20 a | |
| 4 | 0.99 ± 0.05 a | 21.73 ± 1.91 b | 19.18 ± 1.24 a | 22.89 ± 0.59 b | 0.32 ± 0.02 a | 2.62 ± 0.18 a | |
| 5 | 0.98 ± 0.05 a | 20.10 ± 3.07 b | 18.05 ± 0.3 a | 24.18 ± 1.03 a | 0.34 ± 0.03 a | 2.51 ± 0.05 a | |
| 2022 | 1(对照control) | 0.96 ± 0.11 a | 15.44 ± 1.44 a | 17.06 ± 0.50 a | 20.07 ± 1.36 b | 0.22 ± 0.02 b | 2.41 ± 0.04 b |
| 2 | 0.92 ± 0.06 a | 17.56 ± 1.52 a | 16.59 ± 0.57 a | 21.42 ± 0.89 b | 0.26 ± 0.02 b | 2.53 ± 0.16 a | |
| 3 | 1.01 ± 0.10 a | 18.31 ± 1.56 a | 17.47 ± 0.98 a | 21.27 ± 0.92 b | 0.29 ± 0.03 a | 2.60 ± 0.20 a | |
| 4 | 1.04 ± 0.08 a | 14.55 ± 1.56 b | 19.18 ± 1.24 a | 22.89 ± 0.59 b | 0.36 ± 0.02 a | 2.62 ± 0.18 a | |
| 5 | 0.98 ± 0.09 a | 10.41 ± 2.81 c | 18.05 ± 0.3 a | 24.18 ± 1.03 a | 0.33 ± 0.03 a | 2.51 ± 0.05 a |

图6 冬枣生长生理指标与产量的相关性分析 Y:产量;JHL:枣吊长度
Fig. 6 Correlation analysis between growth physiological indicators and yield of winter jujube Y:Yield;JHL:Jujube hanging length
| 指标 Indicator | 单果质量 Single fruit weight | 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar | 总可溶性固形物 Total soluble solids | 可滴定酸 Titratable acid | 维生素C Vitamin C | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 重要度 Importance | 排序 Ranking | 重要度 Importance | 排序 Ranking | 重要度 Importance | 排序 Ranking | 重要度 Importance | 排序 Ranking | 重要度 Importance | 排序 Ranking | |
| SPAD | -0.100 | 11 | -0.019 | 7 | 0.080 | 4 | -0.122 | 11 | 0.011 | 3 |
| Pn | -0.093 | 10 | -0.086 | 10 | -0.022 | 7 | 0.090 | 3 | -0.089 | 9 |
| Tr | 0.014 | 6 | 0.243 | 1 | -0.092 | 9 | 0.458 | 1 | 0.338 | 1 |
| α | 0.014 | 5 | 0.129 | 3 | 0.038 | 6 | -0.036 | 6 | -0.033 | 4 |
| Pn,max | 0.159 | 2 | 0.220 | 2 | 0.047 | 5 | 0.021 | 4 | 0.017 | 2 |
| Isat | -0.048 | 8 | 0.012 | 5 | -0.095 | 10 | -0.093 | 8 | -0.090 | 10 |
| Ic | 0.103 | 4 | -0.085 | 9 | -0.063 | 8 | -0.007 | 5 | -0.049 | 6 |
| Rd | 0.132 | 3 | 0.087 | 4 | 0.141 | 3 | -0.096 | 9 | -0.061 | 7 |
| F0 | -0.091 | 9 | -0.099 | 11 | -0.129 | 11 | 0.121 | 2 | -0.119 | 11 |
| Fm | 0.255 | 1 | -0.009 | 6 | 0.154 | 2 | -0.082 | 7 | -0.046 | 5 |
| Fv/Fm | -0.011 | 7 | -0.026 | 8 | 0.174 | 1 | -0.100 | 10 | -0.068 | 8 |
表6 冬枣叶片生理指标对冬枣果实品质影响程度的重要性排序
Table 6 The order of importance of the influence of physiological indicators of winter jujube leaves on quality
| 指标 Indicator | 单果质量 Single fruit weight | 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar | 总可溶性固形物 Total soluble solids | 可滴定酸 Titratable acid | 维生素C Vitamin C | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 重要度 Importance | 排序 Ranking | 重要度 Importance | 排序 Ranking | 重要度 Importance | 排序 Ranking | 重要度 Importance | 排序 Ranking | 重要度 Importance | 排序 Ranking | |
| SPAD | -0.100 | 11 | -0.019 | 7 | 0.080 | 4 | -0.122 | 11 | 0.011 | 3 |
| Pn | -0.093 | 10 | -0.086 | 10 | -0.022 | 7 | 0.090 | 3 | -0.089 | 9 |
| Tr | 0.014 | 6 | 0.243 | 1 | -0.092 | 9 | 0.458 | 1 | 0.338 | 1 |
| α | 0.014 | 5 | 0.129 | 3 | 0.038 | 6 | -0.036 | 6 | -0.033 | 4 |
| Pn,max | 0.159 | 2 | 0.220 | 2 | 0.047 | 5 | 0.021 | 4 | 0.017 | 2 |
| Isat | -0.048 | 8 | 0.012 | 5 | -0.095 | 10 | -0.093 | 8 | -0.090 | 10 |
| Ic | 0.103 | 4 | -0.085 | 9 | -0.063 | 8 | -0.007 | 5 | -0.049 | 6 |
| Rd | 0.132 | 3 | 0.087 | 4 | 0.141 | 3 | -0.096 | 9 | -0.061 | 7 |
| F0 | -0.091 | 9 | -0.099 | 11 | -0.129 | 11 | 0.121 | 2 | -0.119 | 11 |
| Fm | 0.255 | 1 | -0.009 | 6 | 0.154 | 2 | -0.082 | 7 | -0.046 | 5 |
| Fv/Fm | -0.011 | 7 | -0.026 | 8 | 0.174 | 1 | -0.100 | 10 | -0.068 | 8 |
| 年Year | 矿化度/(g · L-1)Salinity | 背景值 Background | 萌芽—展叶期 Sprout leaves period | 开花—幼果期 Blossom-young fruit period | 果实膨大期 Developing fruit period | 着色—成熟期 Fruit ripe period | 积盐量 Salt accumulation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 1(对照control) | 1.25 | 1.20 | 1.32 | 1.17 | 1.24 | -0.01 |
| 2 | 1.24 | 1.36 | 1.52 | 1.37 | 1.40 | 0.16 | |
| 3 | 1.17 | 1.46 | 1.73 | 1.50 | 1.60 | 0.43 | |
| 4 | 1.24 | 1.62 | 1.91 | 1.74 | 1.89 | 0.65 | |
| 5 | 1.27 | 1.94 | 2.02 | 1.82 | 1.98 | 0.71 | |
| 2021 | 1(对照control) | 1.19 | 1.04 | 1.17 | 1.07 | 0.89 | -0.30 |
| 2 | 1.03 | 0.94 | 1.10 | 1.05 | 0.86 | -0.16 | |
| 3 | 1.27 | 1.29 | 1.56 | 1.41 | 0.78 | -0.50 | |
| 4 | 1.57 | 1.69 | 1.93 | 1.69 | 0.97 | -0.60 | |
| 5 | 1.69 | 1.87 | 2.09 | 1.65 | 1.02 | -0.67 | |
| 2022 | 1(对照control) | 0.97 | 0.82 | 0.52 | 0.59 | 0.52 | -0.45 |
| 2 | 0.98 | 1.22 | 0.88 | 1.00 | 0.92 | -0.06 | |
| 3 | 0.99 | 1.40 | 1.01 | 1.40 | 1.03 | 0.04 | |
| 4 | 1.09 | 1.59 | 1.24 | 1.77 | 1.17 | 0.08 | |
| 5 | 1.23 | 1.87 | 1.18 | 1.75 | 1.26 | 0.03 |
表7 不同矿化度灌溉水处理下0 ~ 100 cm土层盐分变化
Table 7 The variation of soil salinity in the 0-100 cm soil layer treated with different irrigation water salinity treatments g · kg-1
| 年Year | 矿化度/(g · L-1)Salinity | 背景值 Background | 萌芽—展叶期 Sprout leaves period | 开花—幼果期 Blossom-young fruit period | 果实膨大期 Developing fruit period | 着色—成熟期 Fruit ripe period | 积盐量 Salt accumulation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 1(对照control) | 1.25 | 1.20 | 1.32 | 1.17 | 1.24 | -0.01 |
| 2 | 1.24 | 1.36 | 1.52 | 1.37 | 1.40 | 0.16 | |
| 3 | 1.17 | 1.46 | 1.73 | 1.50 | 1.60 | 0.43 | |
| 4 | 1.24 | 1.62 | 1.91 | 1.74 | 1.89 | 0.65 | |
| 5 | 1.27 | 1.94 | 2.02 | 1.82 | 1.98 | 0.71 | |
| 2021 | 1(对照control) | 1.19 | 1.04 | 1.17 | 1.07 | 0.89 | -0.30 |
| 2 | 1.03 | 0.94 | 1.10 | 1.05 | 0.86 | -0.16 | |
| 3 | 1.27 | 1.29 | 1.56 | 1.41 | 0.78 | -0.50 | |
| 4 | 1.57 | 1.69 | 1.93 | 1.69 | 0.97 | -0.60 | |
| 5 | 1.69 | 1.87 | 2.09 | 1.65 | 1.02 | -0.67 | |
| 2022 | 1(对照control) | 0.97 | 0.82 | 0.52 | 0.59 | 0.52 | -0.45 |
| 2 | 0.98 | 1.22 | 0.88 | 1.00 | 0.92 | -0.06 | |
| 3 | 0.99 | 1.40 | 1.01 | 1.40 | 1.03 | 0.04 | |
| 4 | 1.09 | 1.59 | 1.24 | 1.77 | 1.17 | 0.08 | |
| 5 | 1.23 | 1.87 | 1.18 | 1.75 | 1.26 | 0.03 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
|
高会, 赵亮, 刘斌, 付同刚, 刘金铜. 2023. 河北滨海盐碱地浅层轻度咸水资源冬小麦灌溉安全利用研究. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 31 (7):1102-1109.
|
|
| [6] |
doi: S0308-8146(18)30104-3 pmid: 29478523 |
| [7] |
|
|
李少雄, 刘淑慧, 赵春龙, 段志文. 2024. 微咸水滴灌对温室黄瓜土壤酶活性和产量的影响. 灌溉排水学报, 43 (6):26-33.
|
|
| [8] |
|
|
李学孚, 倪智敏, 吴月燕, 李美芹, 刘蓉, 饶慧云. 2015. 盐胁迫对‘鄞红’葡萄光合特性及叶片细胞结构的影响. 生态学报, 35 (13):4436-4444.
|
|
| [9] |
|
|
李占俊, 王立仙, 李占辉, 王仲霞, 郭俊华, 李文杰. 2023. 山东沾化冬枣产业现状及发展对策. 中国果菜, 43 (7):71-74,84.
|
|
| [10] |
|
|
梁文斌, 聂东伶, 吴思政, 柏文富, 沈素贞. 2015. 遮荫对短梗大参苗木光合作用及生长的影响. 生态学杂志, 34 (2):413-419.
|
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
|
马嘉莹, 王兴鹏, 王洪博, 王海瑞, 王学成, 李朝阳. 2022. 咸水灌溉对土壤水盐分布及设施番茄产量和品质的影响. 干旱地区农业研究, 40 (3):104-112.
|
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
|
裴书瑶, 曹红霞, 张泽宇, 赵方洋, 李志军. 2024. 盆栽番茄对NaCl和Na2SO4微咸水灌溉的生理响应. 中国农业科学, 57 (3):570-583.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2024.03.011 |
|
| [15] |
|
|
彭玲, 冯璐, 宋爱云, 董林水, 李庆军, 刘京涛. 2023. 不同浓度盐和氮处理对冬枣果实品质形成的交互作用. 园艺学报, 50 (10):2192-2206.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0740 URL |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
|
王天宇, 王金童, 徐征和, 庞桂斌, 刘精凯. 2017. 微咸水灌溉对冬枣根区土壤水盐动态及效益的影响. 节水灌溉,(6):46-49,54.
|
|
| [18] |
|
|
王智华, 侯红燕, 徐德芳, 娄金华, 李亚玲, 魏立兴. 2022. 微咸水灌溉对黄河三角洲地区水稻产量和品质的影响. 北方水稻, 52 (6):24-28,41.
|
|
| [19] |
|
|
吴奇峰, 郑国玉, 辛朗, 梁亚康, 王之风. 2024. 咸水灌溉下设施番茄水盐生产函数构建及产量预测. 东北农业大学学报, 55 (2):57-68.
|
|
| [20] |
|
|
徐呈祥, 马艳萍, 徐锡增. 2011. 15个枣树品种耐盐性研究. 广东农业科学, 38 (16):31-32.
|
|
| [21] |
|
|
姚岭柏, 韩海霞. 2016. 盐胁迫对樱桃萝卜生长及生理生化指标的影响. 北方园艺,(13):5-8.
|
|
| [22] |
|
|
张世卿. 2016. 微咸水滴灌对枣园土壤、枣树生长和红枣果实品质的影响[硕士论文]. 阿拉尔: 塔里木大学.
|
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.11686/cyxb2022041 |
|
周晓瑾, 黄海霞, 张君霞, 马步东, 陆刚, 齐建伟, 张婷, 朱珠. 2023. 盐胁迫对裸果木幼苗光合特性的影响. 草业学报, 32 (2):75-83.
doi: 10.11686/cyxb2022041 |
|
| [24] |
|
|
邹琦. 2000. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 中国农业出版社.
|
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2023.07.028 |
|
左强, 吴训, 石建初, 王全九, 刘兆辉, 朱安宁, 尹冬勤, 冯权泷, 纪文君, 康绍忠. 2023. 黄河三角洲滨海盐碱地可持续利用的水土资源约束与均衡配置策略. 中国工程科学, 25 (4):169-179.
doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2023.07.028 |
| [1] | 程小改, 万源, 林琭, 谢鹏, 李志强, 李谧, 王鹏鹏, 牛自勉. 苹果开心树形树干高度对不同冠层部位叶片光合特性及果实品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 671-692. |
| [2] | 任艺, 张益兴, 侯赛赛, 乜兰春, 李青云, 王鑫鑫. 生物炭的制备方法及其在设施蔬菜中的应用研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 792-812. |
| [3] | 许桐, 王越, 吴丽娜, 张航, 尹立来, 徐柯宇, 郑小林. 褪黑素处理对‘桃形李’采后果实品质及花色苷代谢的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 395-405. |
| [4] | 陈亚娟, 金鑫, 杨江山, 戴子博, 李斗, 邵璋. 黄腐酸钾对‘蛇龙珠’葡萄果实糖酸代谢及香味物质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 406-422. |
| [5] | 毛欣, 元文飞, 郭雨润, 徐欣欣, 李艺, 张毅, 苗妍秀, 白龙强, 李衍素. 日光温室黄瓜有机物料种植板栽培中有机物料腐解及根区和叶片养分含量的变化[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 439-452. |
| [6] | 王珊珊, 郭瑞, 何棱, 吴春红, 陈禅友, 万何平, 赵慧霞. 长豇豆Lhc家族基因鉴定及其在盐胁迫下的表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 111-122. |
| [7] | 张诗琦, 黄璐, 程茜, 张晓燕, 袁宇婷, 侯轶晨, 戴冬青, 夏秀东, 袁星星, 陈新, 朱月林, 薛晨晨. 不同播期对鲜食大豆品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 213-228. |
| [8] | 邹学校, 杨莎, 戴雄泽, 胡博文, 徐昊, 朱凡, 裴宋雨, 远方. 中国辣椒产业快速发展40年回顾与展望[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 247-258. |
| [9] | 李国亮, 章时蕃, 李菲, 张慧, 孙日飞, 张淑江. 薹用芥菜新品种‘玉芽702’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 261-262. |
| [10] | 刘新月, 翟昭慈, 陶佳淋, 冯坤, 蔡晓腾, 刘志国, 刘孟军. 不同落叶剂对冬枣落叶效果及养分回流的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2120-2130. |
| [11] | 李洁, 武超, 贾祥堑, 王娟. ‘壶瓶枣’果皮着色物质及其相关基因筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1728-1742. |
| [12] | 马宗桓, 李玉梅, 韦霞霞, 李文芳, 陈佰鸿, 毛娟. 河西走廊不同产地‘美乐’葡萄品质及香气物质的差异分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1083-1098. |
| [13] | 李斗, 王宇航, 王春恒, 金鑫, 杨江山, 陈亚娟, 戴子博, 冯丽丹. GABA对葡萄叶片光合色素及糖含量和果实风味的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 815-831. |
| [14] | 王文军, 王晶晶, 陈奇凌, 郑强卿. 灰枣优质高产主干树形参数的确立及建模[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 832-846. |
| [15] | 郝金倩, 王宝驹, 佟静, 刘明池, 武占会, 王素娜, 刘宁. 外源褪黑素对水培韭菜生长和品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 847-858. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司