
园艺学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 266-280.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0833
闫超凡, 孙雪梅, 钟启文, 邵登魁, 邓昌蓉, 文军琴*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-10-20
修回日期:2023-12-25
出版日期:2024-02-25
发布日期:2024-02-26
通讯作者:
基金资助:
YAN Chaofan, SUN Xuemei, ZHONG Qiwen, SHAO Dengkui, DENG Changrong, WEN Junqin*( )
)
Received:2023-10-20
Revised:2023-12-25
Published:2024-02-25
Online:2024-02-26
摘要:
20S蛋白酶体能够通过自身或泛素—蛋白酶体系统特异性降解细胞质和细胞核中的蛋白质,维持细胞蛋白质稳态。本研究中鉴定出21个番茄(Solanum lycopersicum L.)20S蛋白酶体基因家族成员,并对其进行生物信息分析。结果表明,番茄20S蛋白酶体大多数基因含有相似的启动子和内含子,其中,编码α亚基的基因保守性较好,而编码β亚基的基因保守性较差;亚细胞定位发现,绝大多数基因在细胞质中发挥功能;染色体定位和基因复制分析发现,21个20S蛋白酶体基因不均匀地分布在12条染色体上,存在2对片段复制基因对;进化分析表明,编码α亚基和编码β亚基的基因被划分在不同的类群或亚群;多物种共线性分析发现,番茄与辣椒(Capsicum annuum L.)和马铃薯(Solanum tuberosum L.)之间的同源基因对较多,而与拟南芥[Arabidopsis thaliana(L.)Heynh.]、水稻(Oryza sativa L.)和玉米(Zea mays L.)同源的基因对较少。SlPRA1-01、SlPRA10-04、SlPRA11-05和SlPRA16-09这4个基因在3个物种中均形成基因对;启动子和组织特异性表达分析结果显示,20S蛋白酶体基因家族在番茄逆境胁迫和生长发育中发挥着重要作用。
闫超凡, 孙雪梅, 钟启文, 邵登魁, 邓昌蓉, 文军琴. 番茄20S蛋白酶体基因家族鉴定及生物信息学分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 266-280.
YAN Chaofan, SUN Xuemei, ZHONG Qiwen, SHAO Dengkui, DENG Changrong, WEN Junqin. Identification and Bioinformatics Analysis of 20S Proteasome Gene Family in Tomato[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(2): 266-280.
| 基因 Gene | 基因ID Gene ID | 染色体定位 Chromosome location | 基因位置/ bp Gene location | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 起始Start | 终止End | |||
| SlPRA1-01 | Solyc01g111450.3.1 | Chr01:97599172..97602337(+) | 97 599 172 | 97 602 337 |
| SlPRA2-01 | Solyc01g111460.3.1 | Chr01:97605332..97606609(-) | 97 605 332 | 97 606 609 |
| SlPRA3-02 | Solyc02g070510.3.1 | Chr02:40805105..40810898(+) | 40 805 105 | 40 810 898 |
| SlPRA4-02 | Solyc02g081700.1.1 | Chr02:46112367..46113113(+) | 46 112 367 | 46 113 113 |
| SlPRA5-02 | Solyc02g084920.3.1 | Chr02:48607717..48616195(-) | 48 607 717 | 48 616 195 |
| SlPRA6-03 | Solyc03g033745.1.1 | Chr03:5362233..5373114(-) | 5 362 233 | 5 373 114 |
| SlPRA7-03 | Solyc03g063420.2.1 | Chr03:36767871..36777655(-) | 36 767 871 | 36 777 655 |
| SlPRA8-04 | Solyc04g009410.3.1 | Chr04:2830248..2840325(+) | 2 830 248 | 2 840 325 |
| SlPRA9-04 | Solyc04g024420.3.1 | Chr04:31500067..31505977(+) | 31 500 067 | 31 505 977 |
| SlPRA10-04 | Solyc04g080590.3.1 | Chr04:64787899..64791729(-) | 64 787 899 | 64 791 729 |
| SlPRA11-05 | Solyc05g013820.3.1 | Chr05:7123832..7132561(-) | 7 123 832 | 7 132 561 |
| SlPRA12-05 | Solyc05g056160.3.1 | Chr05:66400334..66404473(-) | 66 400 334 | 66 404 473 |
| SlPRA13-07 | Solyc07g016200.3.1 | Chr07:6438876..6447830(-) | 6 438 876 | 6 447 830 |
| SlPRA14-07 | Solyc07g055080.3.1 | Chr07:63355928..63361757(+) | 63 355 928 | 63 361 757 |
| SlPRA15-08 | Solyc08g016510.3.1 | Chr08:7711628..7717929(-) | 7 711 628 | 7 717 929 |
| SlPRA16-09 | Solyc09g082320.3.1 | Chr09:68500118..68505978(-) | 68 500 118 | 68 505 978 |
| SlPRA17-10 | Solyc10g008010.3.1 | Chr10:2165246..2178357(+) | 2 165 246 | 2 178 357 |
| SlPRA18-10 | Solyc10g077030.2.1 | Chr10:60039871..60049610(-) | 60 039 871 | 60 049 610 |
| SlPRA19-10 | Solyc10g081130.2.1 | Chr10:62399725..62404172(+) | 62 399 725 | 62 404 172 |
| SlPRA20-11 | Solyc11g069150.2.1 | Chr11:54042842..54049437(-) | 54 042 842 | 54 049 437 |
| SlPRA21-12 | Solyc12g009140.2.1 | Chr12:2452941..2457449(-) | 2 452 941 | 2 457 449 |
表1 番茄20S蛋白酶体基因家族
Table 1 20S proteasome gene family of tomato
| 基因 Gene | 基因ID Gene ID | 染色体定位 Chromosome location | 基因位置/ bp Gene location | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 起始Start | 终止End | |||
| SlPRA1-01 | Solyc01g111450.3.1 | Chr01:97599172..97602337(+) | 97 599 172 | 97 602 337 |
| SlPRA2-01 | Solyc01g111460.3.1 | Chr01:97605332..97606609(-) | 97 605 332 | 97 606 609 |
| SlPRA3-02 | Solyc02g070510.3.1 | Chr02:40805105..40810898(+) | 40 805 105 | 40 810 898 |
| SlPRA4-02 | Solyc02g081700.1.1 | Chr02:46112367..46113113(+) | 46 112 367 | 46 113 113 |
| SlPRA5-02 | Solyc02g084920.3.1 | Chr02:48607717..48616195(-) | 48 607 717 | 48 616 195 |
| SlPRA6-03 | Solyc03g033745.1.1 | Chr03:5362233..5373114(-) | 5 362 233 | 5 373 114 |
| SlPRA7-03 | Solyc03g063420.2.1 | Chr03:36767871..36777655(-) | 36 767 871 | 36 777 655 |
| SlPRA8-04 | Solyc04g009410.3.1 | Chr04:2830248..2840325(+) | 2 830 248 | 2 840 325 |
| SlPRA9-04 | Solyc04g024420.3.1 | Chr04:31500067..31505977(+) | 31 500 067 | 31 505 977 |
| SlPRA10-04 | Solyc04g080590.3.1 | Chr04:64787899..64791729(-) | 64 787 899 | 64 791 729 |
| SlPRA11-05 | Solyc05g013820.3.1 | Chr05:7123832..7132561(-) | 7 123 832 | 7 132 561 |
| SlPRA12-05 | Solyc05g056160.3.1 | Chr05:66400334..66404473(-) | 66 400 334 | 66 404 473 |
| SlPRA13-07 | Solyc07g016200.3.1 | Chr07:6438876..6447830(-) | 6 438 876 | 6 447 830 |
| SlPRA14-07 | Solyc07g055080.3.1 | Chr07:63355928..63361757(+) | 63 355 928 | 63 361 757 |
| SlPRA15-08 | Solyc08g016510.3.1 | Chr08:7711628..7717929(-) | 7 711 628 | 7 717 929 |
| SlPRA16-09 | Solyc09g082320.3.1 | Chr09:68500118..68505978(-) | 68 500 118 | 68 505 978 |
| SlPRA17-10 | Solyc10g008010.3.1 | Chr10:2165246..2178357(+) | 2 165 246 | 2 178 357 |
| SlPRA18-10 | Solyc10g077030.2.1 | Chr10:60039871..60049610(-) | 60 039 871 | 60 049 610 |
| SlPRA19-10 | Solyc10g081130.2.1 | Chr10:62399725..62404172(+) | 62 399 725 | 62 404 172 |
| SlPRA20-11 | Solyc11g069150.2.1 | Chr11:54042842..54049437(-) | 54 042 842 | 54 049 437 |
| SlPRA21-12 | Solyc12g009140.2.1 | Chr12:2452941..2457449(-) | 2 452 941 | 2 457 449 |

图2 20S蛋白酶体基因家族的染色体定位及复制关系 外侧方框代表染色体骨架,中间和内侧方框表示基因密度,每个基因在染色体骨架上的大致分布用短黑线标出。红色、绿色和浅灰色线分别代表相似性为0.98 ~ 0.99、0.97 ~ 0.98和不足0.95及其他基因的连锁群。
Fig. 2 Chromosomal localization and replication relationships of the 20S proteasome gene family The outer box represents the chromosome skeleton,the middle and inner boxes indicate gene density,and the approximate distribution of each tomato 20S proteasome gene is marked on the chromosome skeleton by a short black line. Coloured lines refer to the linkage groups with more than 0.95 similarity,red lines 0.98-0.99,green lines 0.97-0.98,and light grey lines refer to the linkage groups with less than 0.95 similarity and the linkage groups of other genes.

图5 6个物种20S蛋白酶体基因家族序列的系统进化树 α、β分别代表不同α亚基、β亚基。
Fig. 5 Phylogenetic tree of 20S proteasome gene family sequences from six species α and β represent different α-subunits and β-subunits.

图6 不同物种20S蛋白酶体基因的共线性分析 灰色线条表示番茄与其他物种之间的共线性区块,红色线条突出了20S蛋白酶体基因对。
Fig. 6 Covariance analysis of 20S proteasome genes in different species Gray lines indicate blocks of covariance between tomato and other species,and red lines highlight 20S proteasome gene pairs.
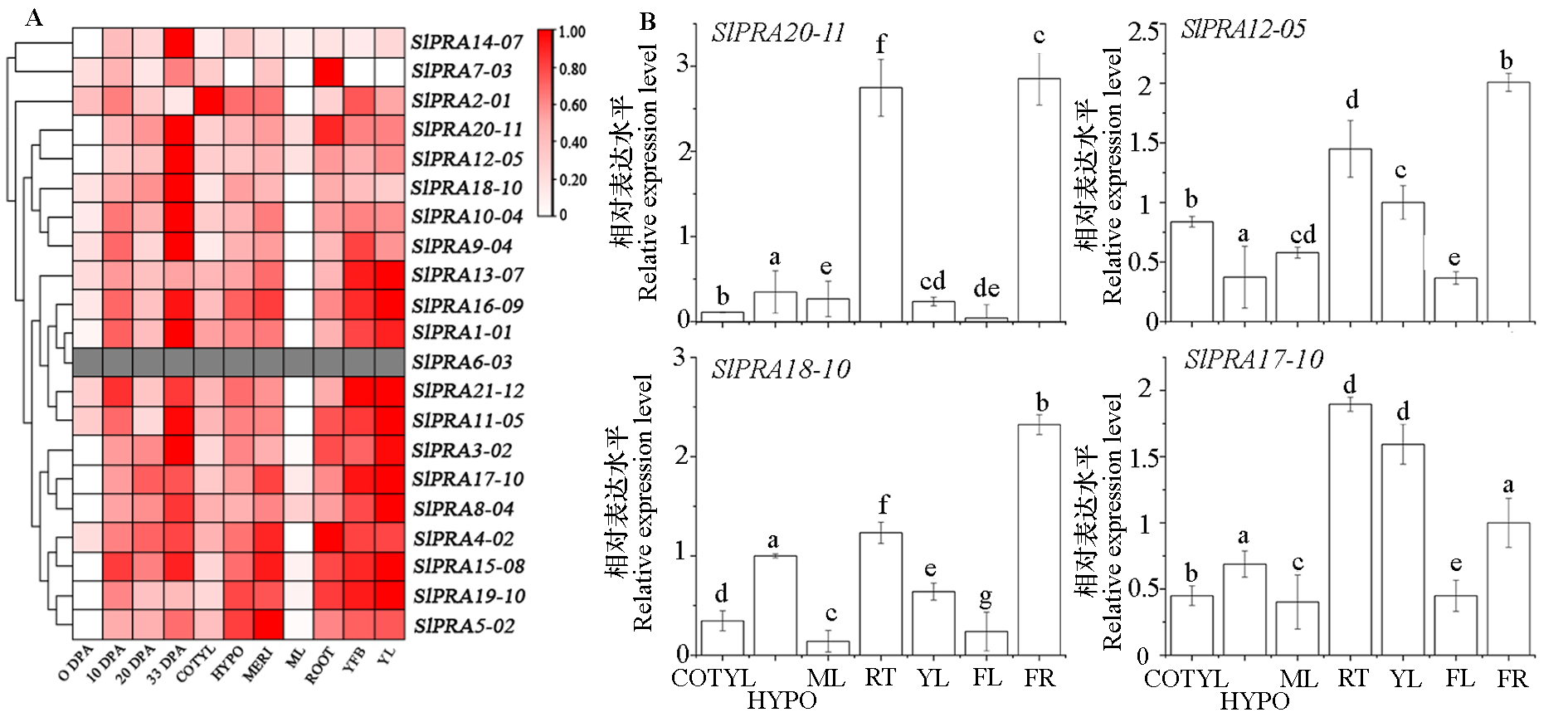
图8 番茄20S蛋白酶体基因组织特异性表达 A:不同组织和不同发育阶段的相对表达量(TFGD),B:部分基因表达水平的qPCR分析。0 DPA:花期的花,10 DPA:开花后10 d的果实,20 DPA:开花后20 d的果实,33 DPA:成熟果实。COTYL:子叶;HYPO:下胚轴;MERI:植物分生组织;ML:成熟叶片;RT:根;YFB:嫩花蕾;YL:嫩叶;FL:花;FR:果实。
Fig. 8 Tissue-specific expression of 20S proteasome gene in tomato A shows the relative expression of tomato 20S proteasome genes in different tissues and different developmental stages(TFGD),and figure B shows qPCR analysis of the expression levels of some genes. 0 DPA:Anthesis flowers;10 DPA:10 days post anthesis fruit;20 DPA:20 days post anthesis fruit;33 DPA:Rippening fruit. COTYL:Cotyledons;HYPO:Hypocotyl;MERI:Vegitative meristems;ML:Mature leaves;RT:Root;YFB:Young flower buds,YL:Young flower buds;FL:Flower;FR:Fruit.
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
doi: 10.3390/biom4030862 pmid: 25250704 |
| [3] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.021345 pmid: 15208399 |
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
doi: S0022-2836(17)30270-X pmid: 28583440 |
| [6] |
|
|
陈文奕, 陈惠萍. 2023. 水稻糊粉层蛋白酶体参与种子萌发的研究. 热带作物学报, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1019.S.20230403.0936.002.html.
|
|
| [7] |
|
|
杜国华, 张立军, 樊金娟, 阮燕晔, 刘淳, 许红梅. 2010. 高等植物蛋白质的特异性降解系统. 分子植物育种, 8 (3):567-576.
|
|
| [8] |
doi: 10.1093/genetics/149.2.677 pmid: 9611183 |
| [9] |
|
|
韩晔, 种康. 2004. 泛素降解途径与生长素的调节. 植物生理学通讯,(6):653-658.
|
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
doi: 10.1016/j.str.2014.11.017 pmid: 25599644 |
| [12] |
|
|
何浩, 王志明, 张立强, 唐艺真, 夏琪, 李忠源, 张怀渝. 2023. 小麦PDR基因家族的鉴定与表达分析. 农业生物技术学报,(3):445-459.
|
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1038/s41477-020-0721-4 pmid: 32690892 |
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-2218 pmid: 18347166 |
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
|
孙鹏, 刘淼, 冯利兴, 刘璇. 2015. 蛋白酶体结构和活性调节机制的研究进展. 生物化学与生物物理进展, 42 (12):1084-1093.
|
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
doi: 10.1039/c1mb05283g pmid: 22027891 |
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
|
王丰, 施一公. 2014. 26S蛋白酶体的结构生物学研究进展. 中国科学:生命科学, 44 (10):965-974.
|
|
| [30] |
|
|
许传俊, 李玲. 2007. 泛素/26S蛋白酶体途径与植物的生长发育. 西北植物学报,(3):635-643.
|
|
| [31] |
|
|
余婷, 关洪鑫, 欧阳松应. 2021. 蛋白酶体调节颗粒的结构生物学特征及其功能. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 37 (3):270-288.
doi: 10.13865/j.cnki.cjbmb.2021.01.1523 |
|
| [32] |
|
|
张亚飞, 曹丽娜, 樊昊驹, 严海川, 刘关君. 2021. 毛果杨20S蛋白酶体基因家族成员预测及生物信息学分析. 分子植物育种,
|
| [1] | 韩荧, 段颖, 牛一杰, 李衍素, 贺超兴, 孙敏涛, 王君, 李强, 陈双臣, 闫妍. 腐殖酸生物降解地膜提高番茄品质的转录代谢机制研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1758-1772. |
| [2] | 龚小雅, 李贤, 周新刚, 吴凤芝. 分蘖洋葱伴生番茄诱导的根际微生物对根结线虫病的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1913-1926. |
| [3] | 孟思达, 韩磊磊, 相恒佐, 朱美玉, 冯 珍, 叶云珠, 孙美华, 李艳冰, 赵利萍, 谭昌华, 齐明芳, 李天来. 番茄心室数的调控机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1649-1664. |
| [4] | 马星云, 范冰丽, 唐光彩, 贾芝琪, 李营, 薛东齐, 张世文. DXR调控番茄叶绿体发育、花色与果实着色机制初探[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1241-1255. |
| [5] | 张文静, 徐大勇, 吴倩琳, 杨佛, 信丙越, 曾昕, 李峰. 拮抗番茄灰霉病的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌XDY66基因组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1413-1425. |
| [6] | 王永珍, 张剑国, 刘彩虹, 李思蓓, 吕甜甜. 番茄新品种‘圆红212’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1435-1436. |
| [7] | 刘泽营, 孙帅, 刘志强, 崔霞, 李仁. 番茄尖果脐突变体的生理特性及其候选基因分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 982-992. |
| [8] | 李品, 甘宁, 陈家伟, 项思翔, 沈静漪, 欧阳波, 卢永恩. 番茄自然群体磷利用效率分析及耐低磷种质筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 993-1004. |
| [9] | 杨婷, 席德慧, 夏明, 李佳楠. α-苦瓜素基因提高番茄对烟草花叶病毒抗性的机理研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1126-1136. |
| [10] | 胡志峰, 邵景成, 张莉. 番茄新品种‘陇番15号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 917-918. |
| [11] | 刘根忠, 李方曼, 葛平飞, 陶金宝, 张星雨, 叶志彪, 张余洋. 番茄抗坏血酸含量相关QTL定位及候选基因鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 219-228. |
| [12] | 董舒超, 洪骏, 凌嘉怡, 谢紫欣, 张胜军, 赵丽萍, 宋刘霞, 王银磊, 赵统敏. 番茄抗旱性的全基因组关联分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 229-238. |
| [13] | 徐琴, 王嘉颖, 张曼楠, 萧志浩, 郑涵楷, 卢永恩, 王涛涛, 张余洋, 张俊红, 叶志彪, 叶杰. 番茄苗期耐盐相关遗传位点鉴定及分子标记开发[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 239-252. |
| [14] | 杨亮, 刘欢, 马燕勤, 李菊, 王海娥, 周玉洁, 龙海成, 苗明军, 李志, 常伟. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术创制高番茄红素番茄新材料[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 253-265. |
| [15] | 张文昊, 张辉, 刘雨婷, 王艳, 张迎迎, 王馨曼, 王全华, 朱为民, 杨学东. 番茄含糖量不同的两个材料果实转录组初步分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 281-294. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司